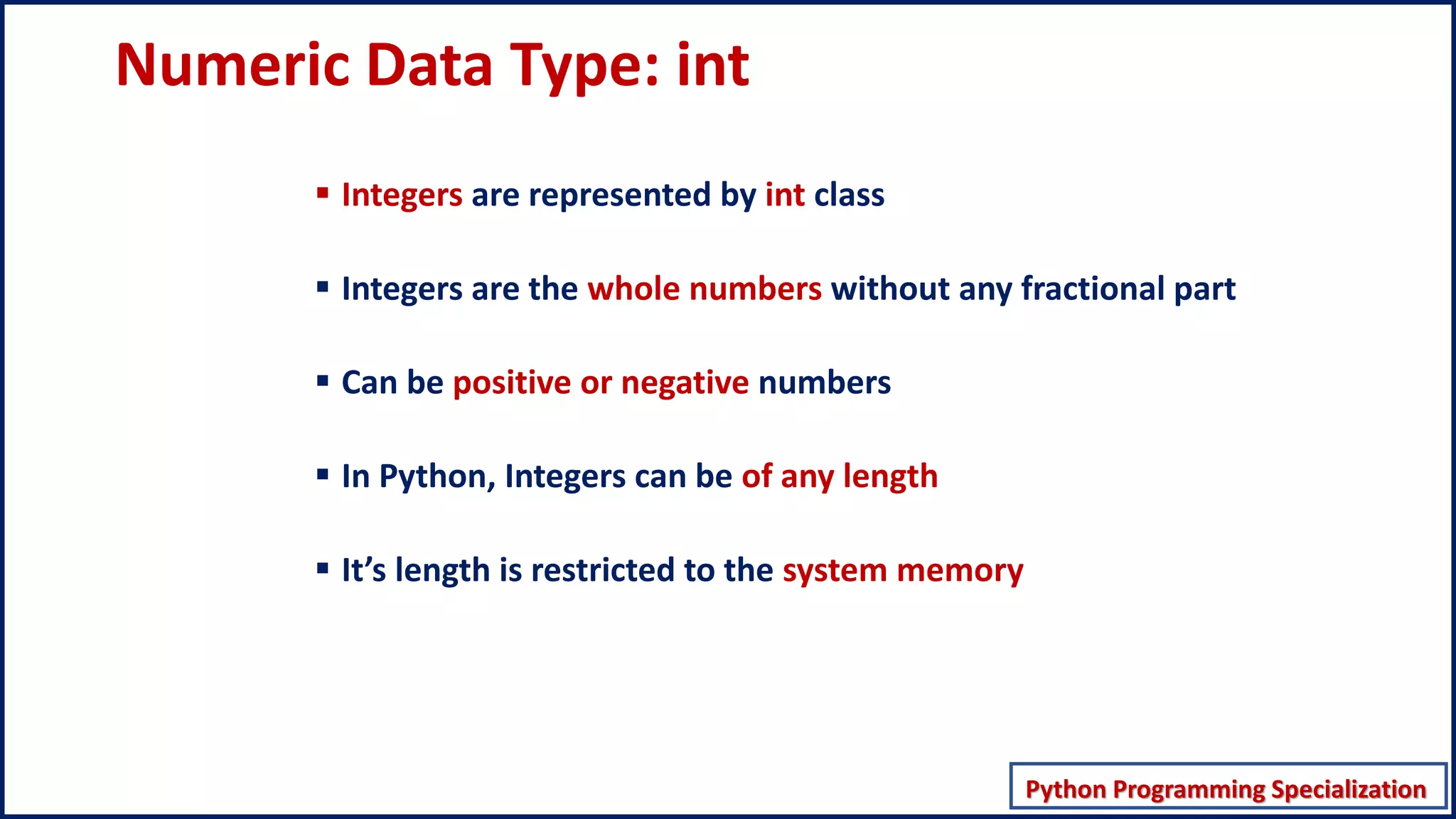
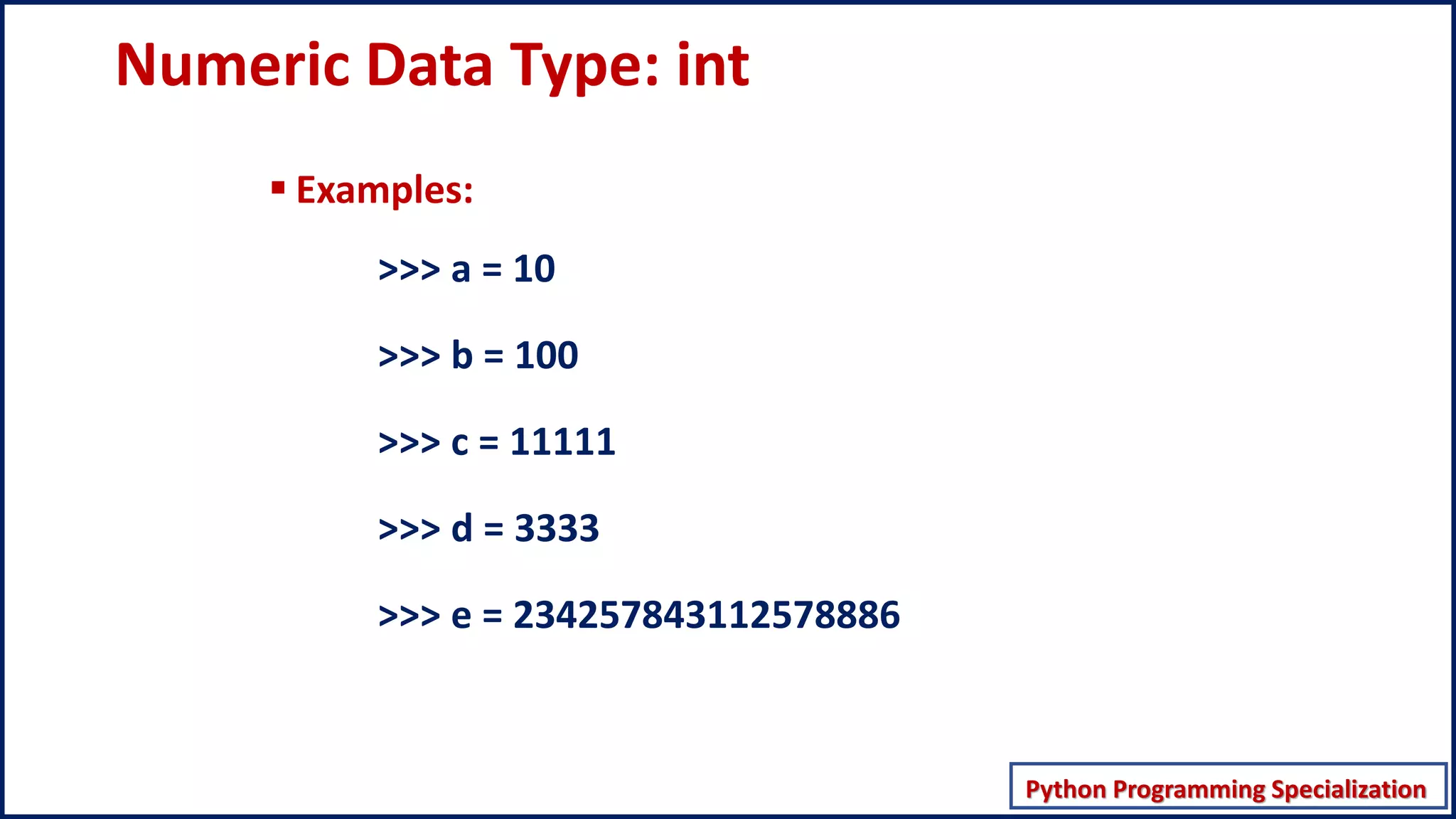
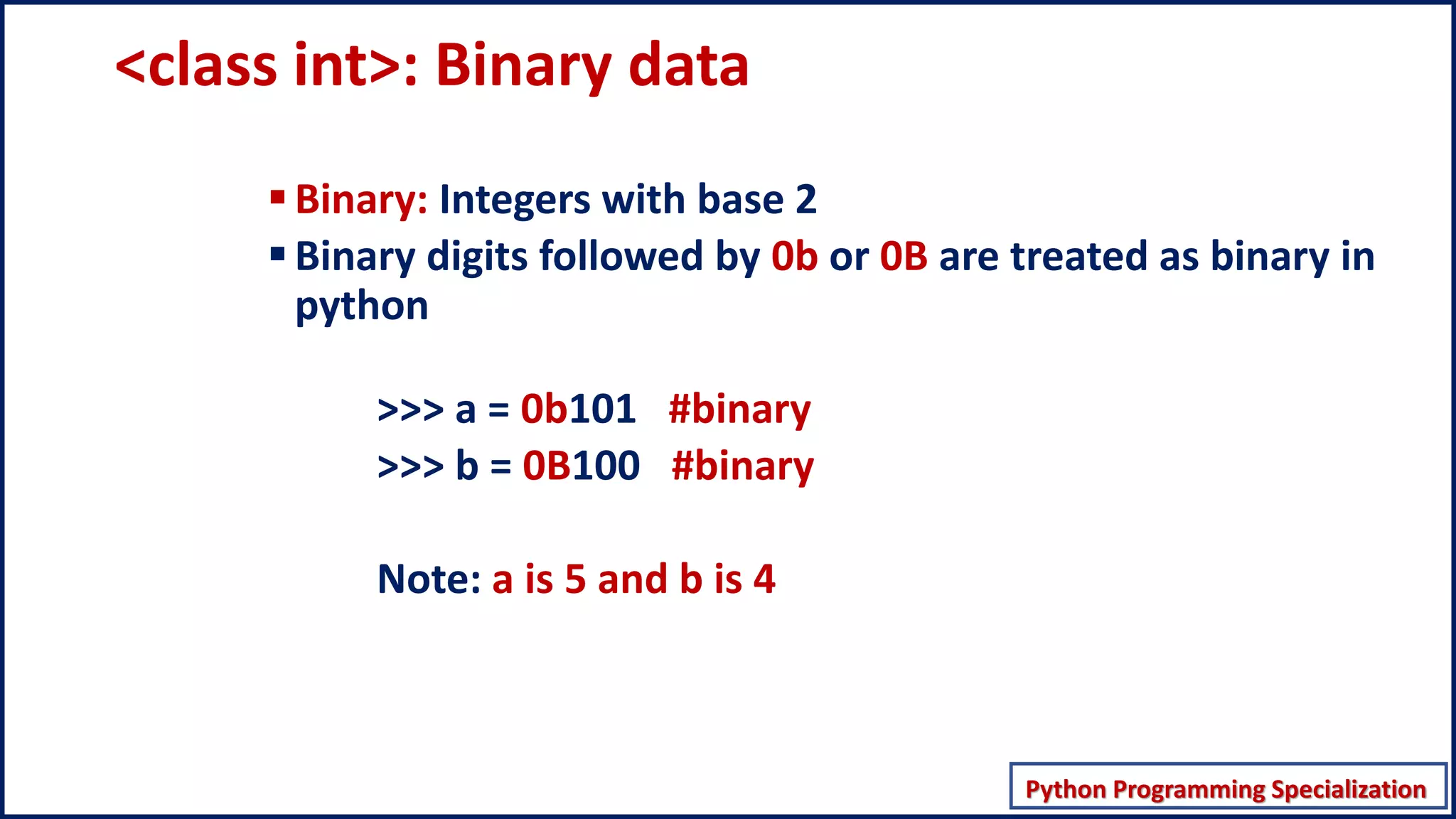
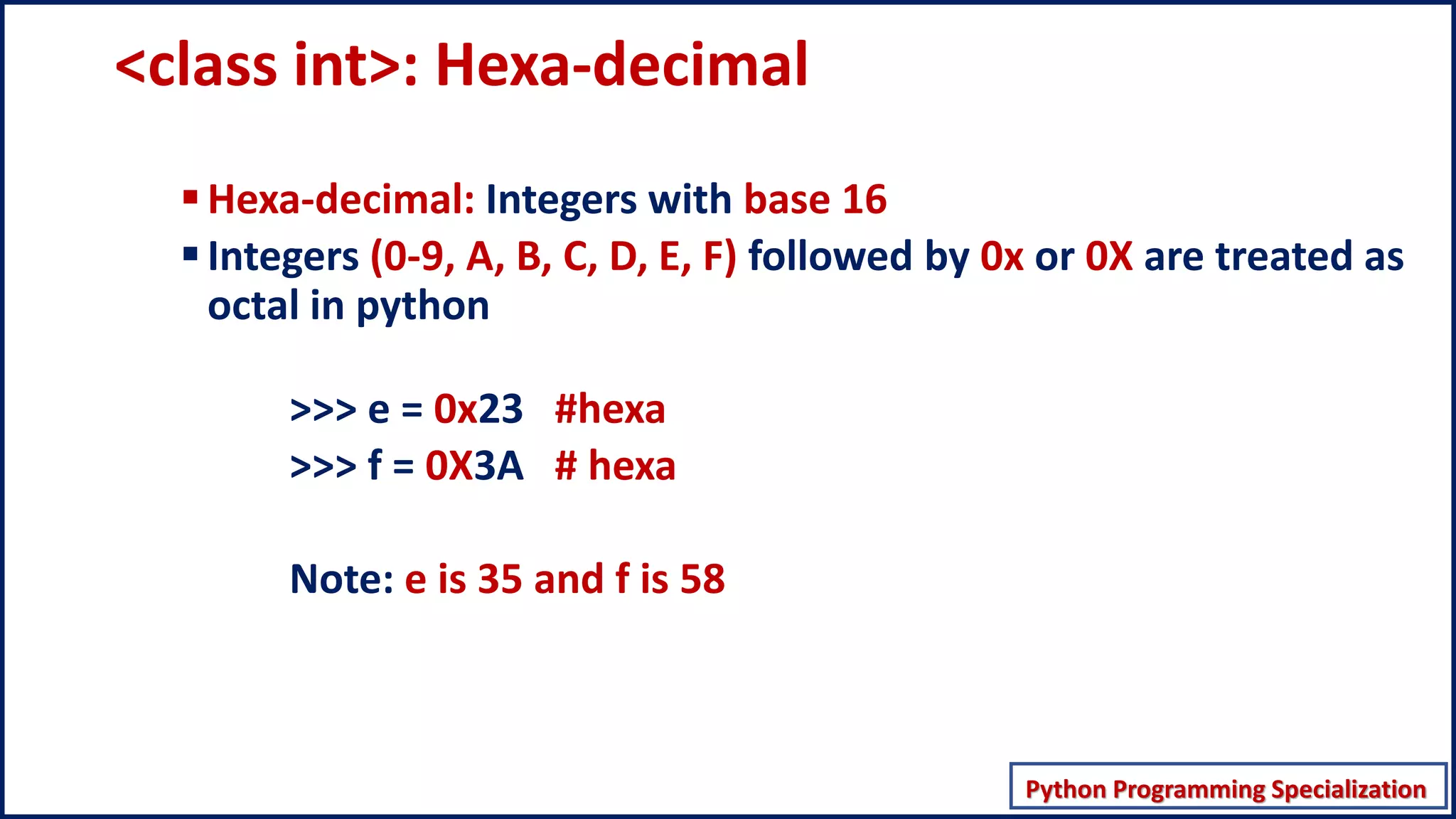
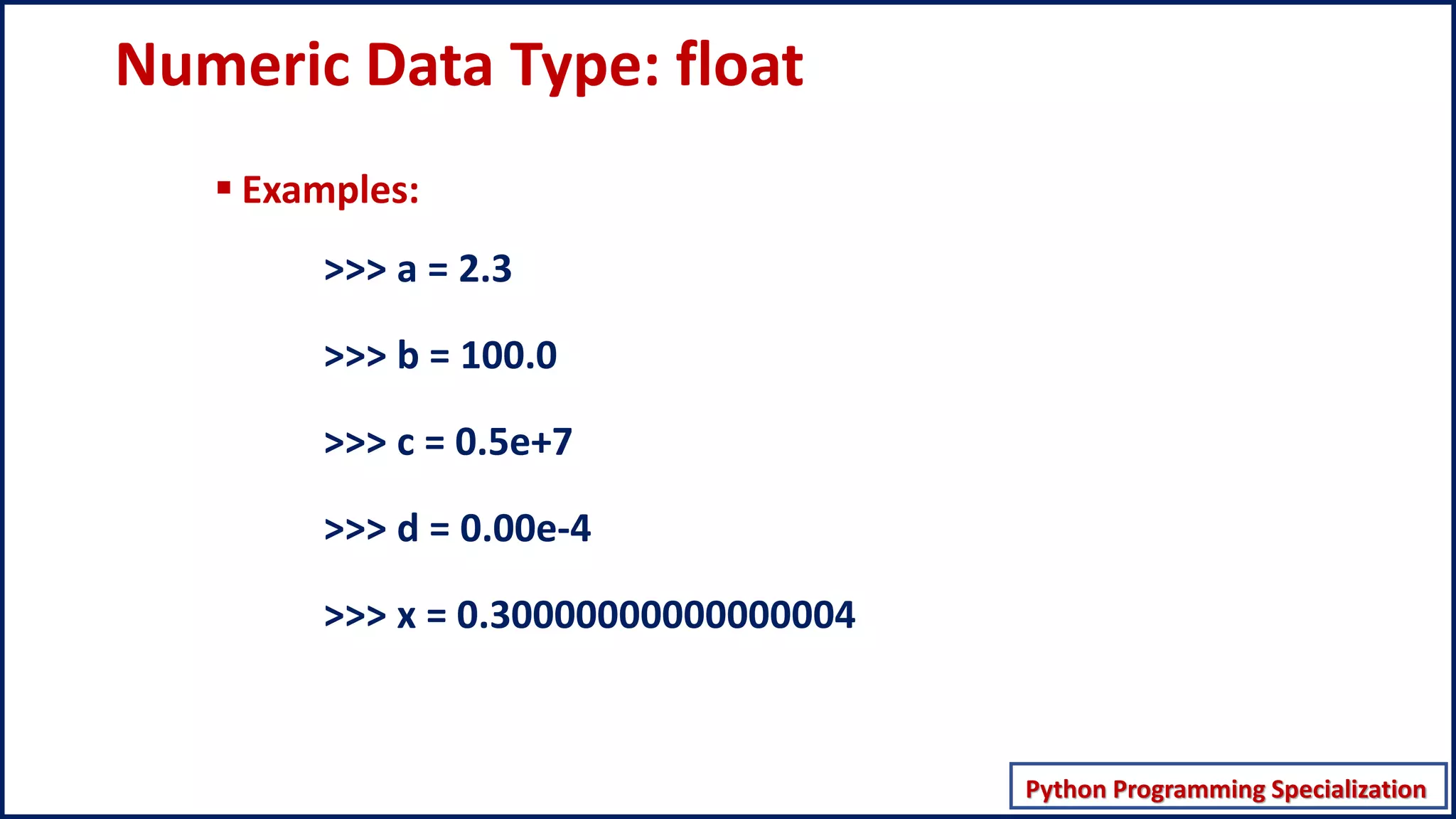
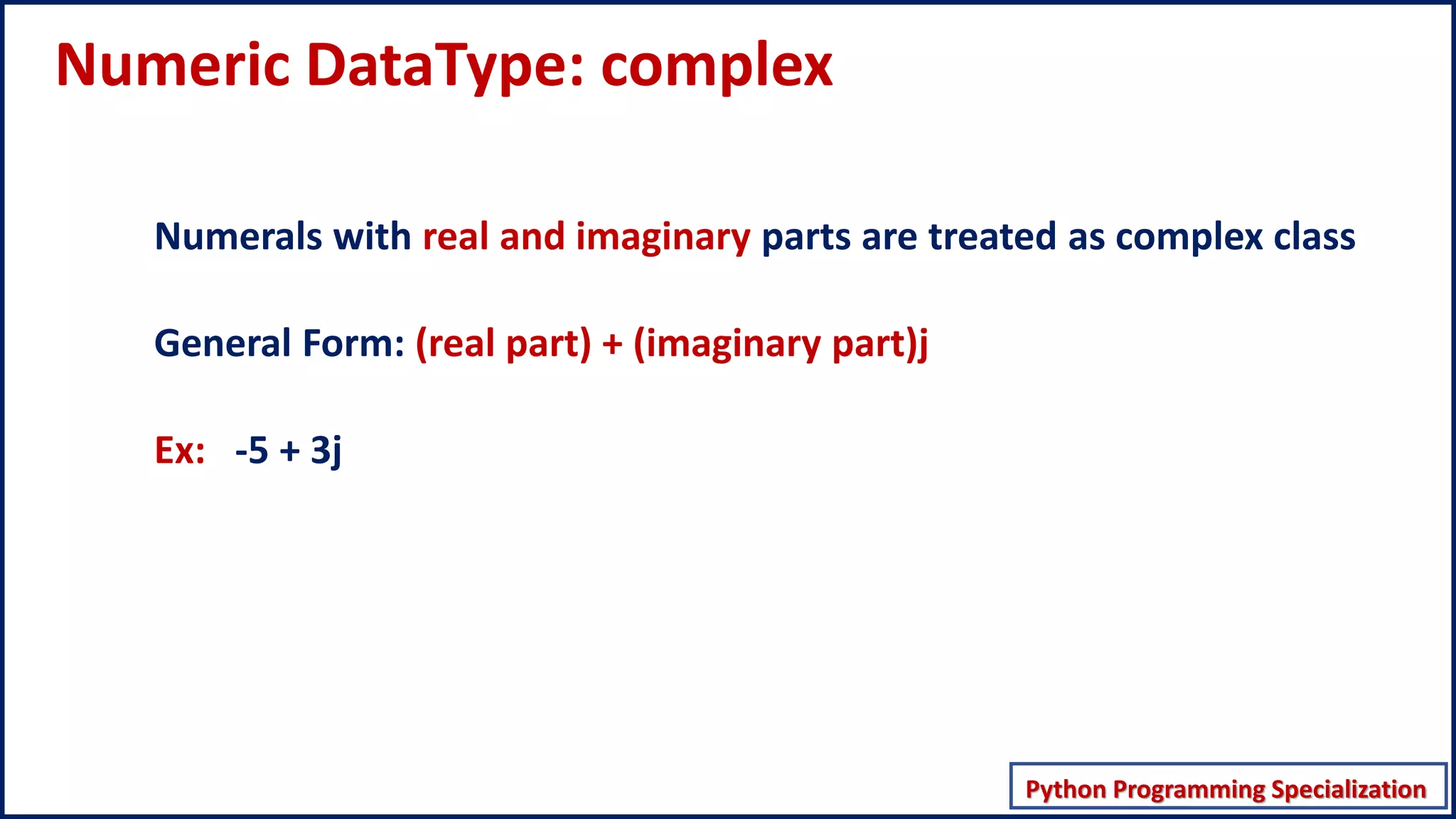
This document discusses numeric data types in Python, including integers (int), floating point numbers (float), and complex numbers. Integers can be any whole number without a fractional component and can be positive or negative. Floats contain both integer and fractional parts and are accurate to 15 decimal places. Complex numbers contain real and imaginary parts in the form (real) + (imaginary)j.