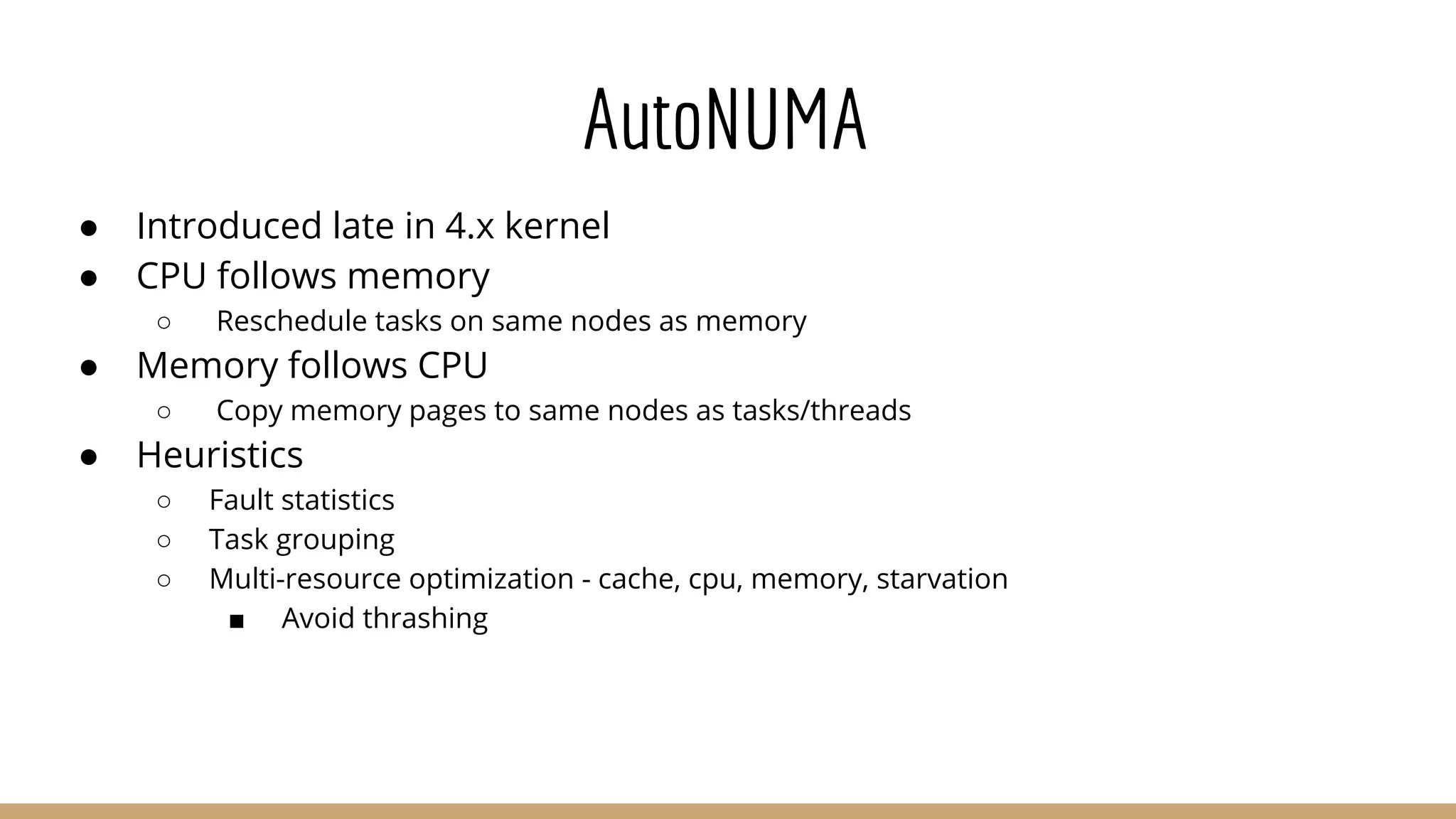
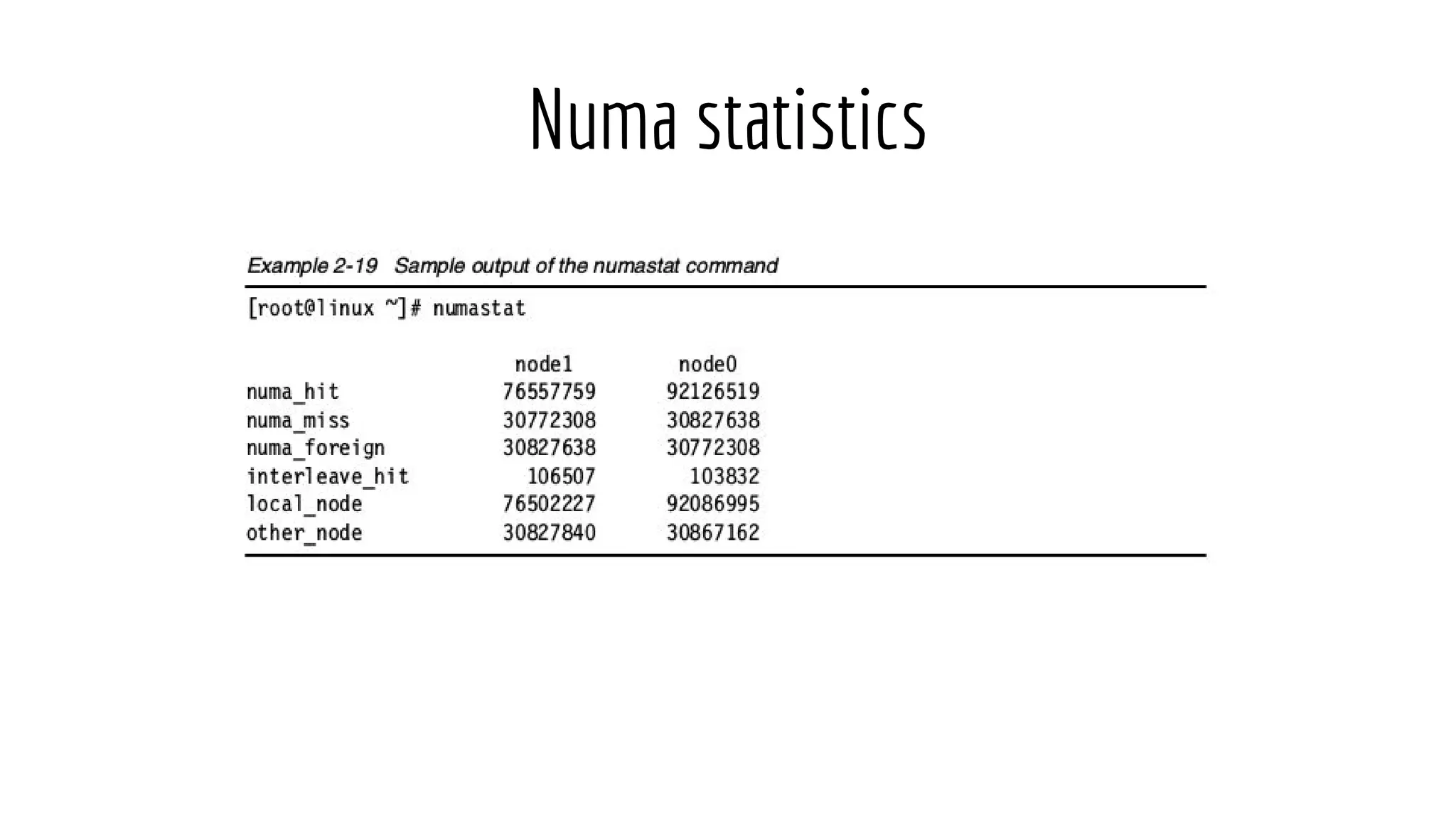
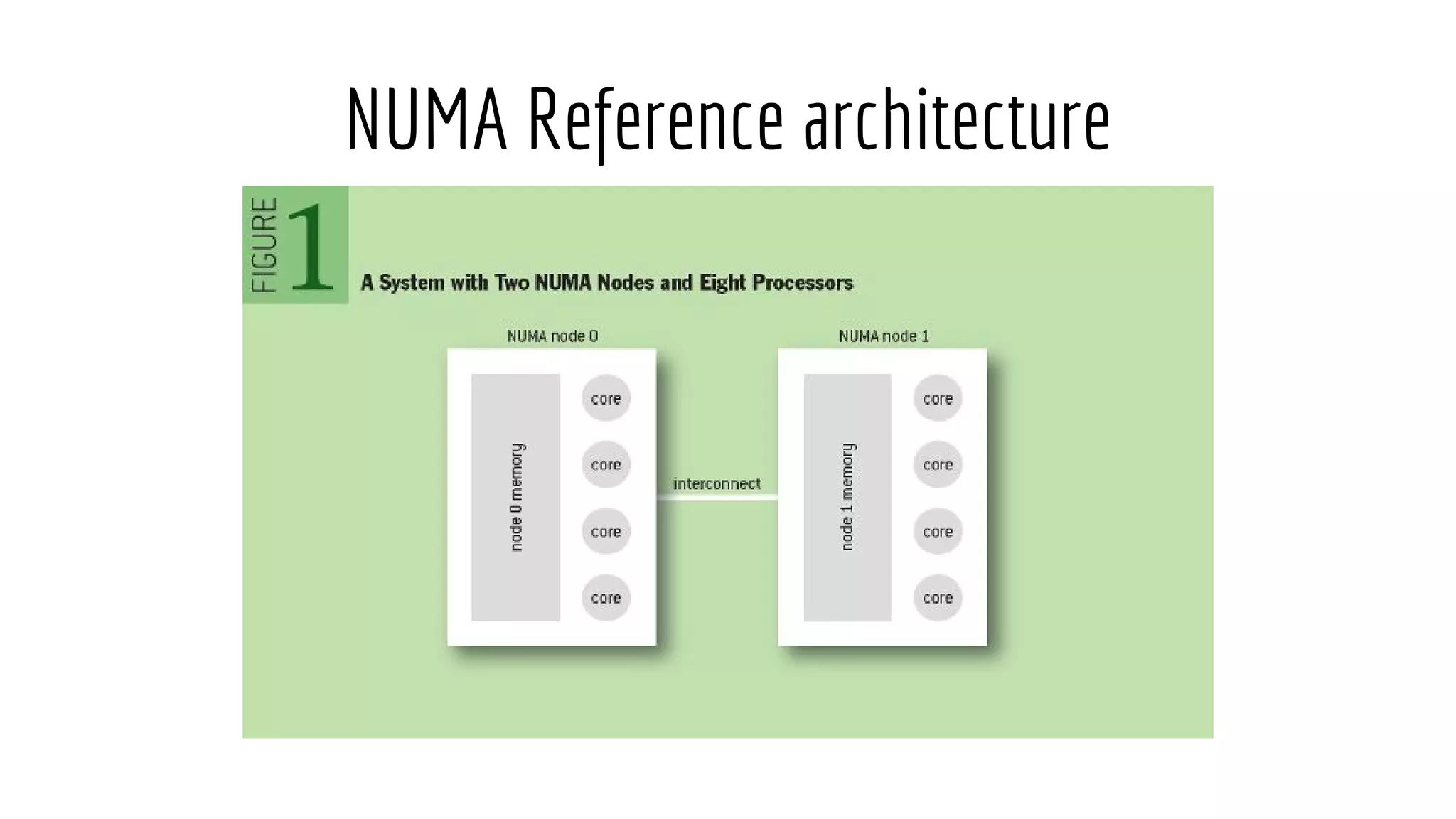
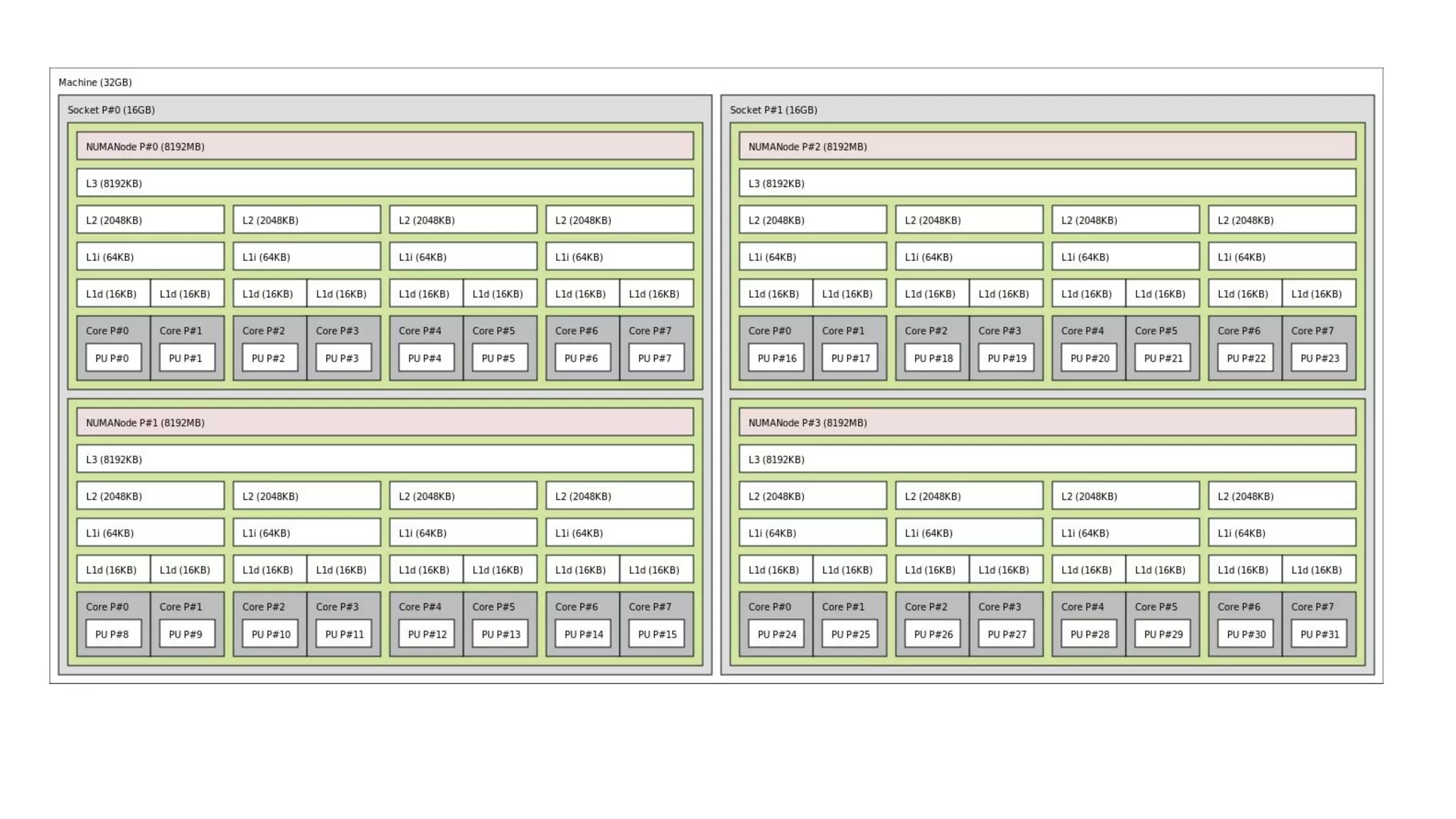
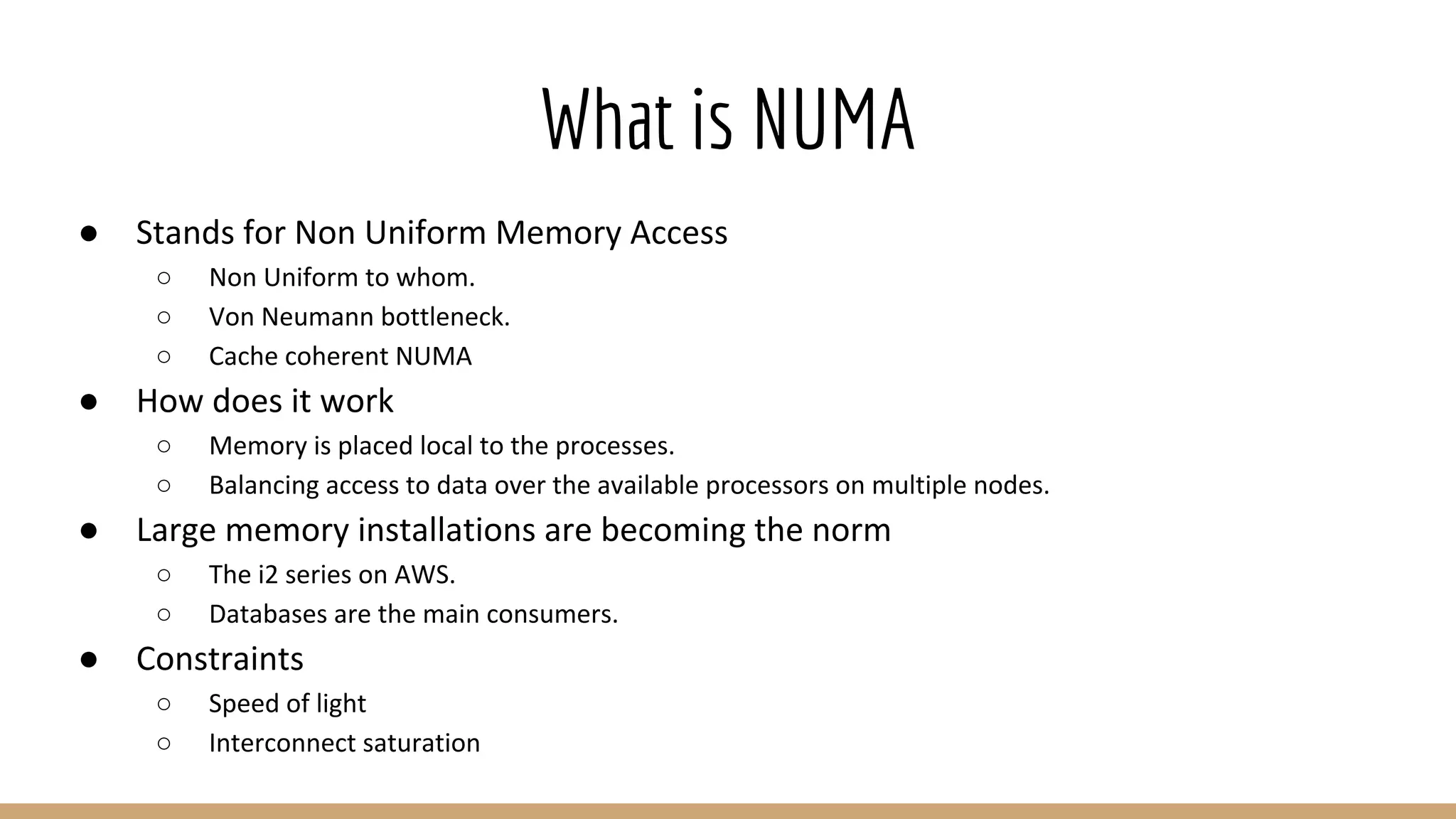
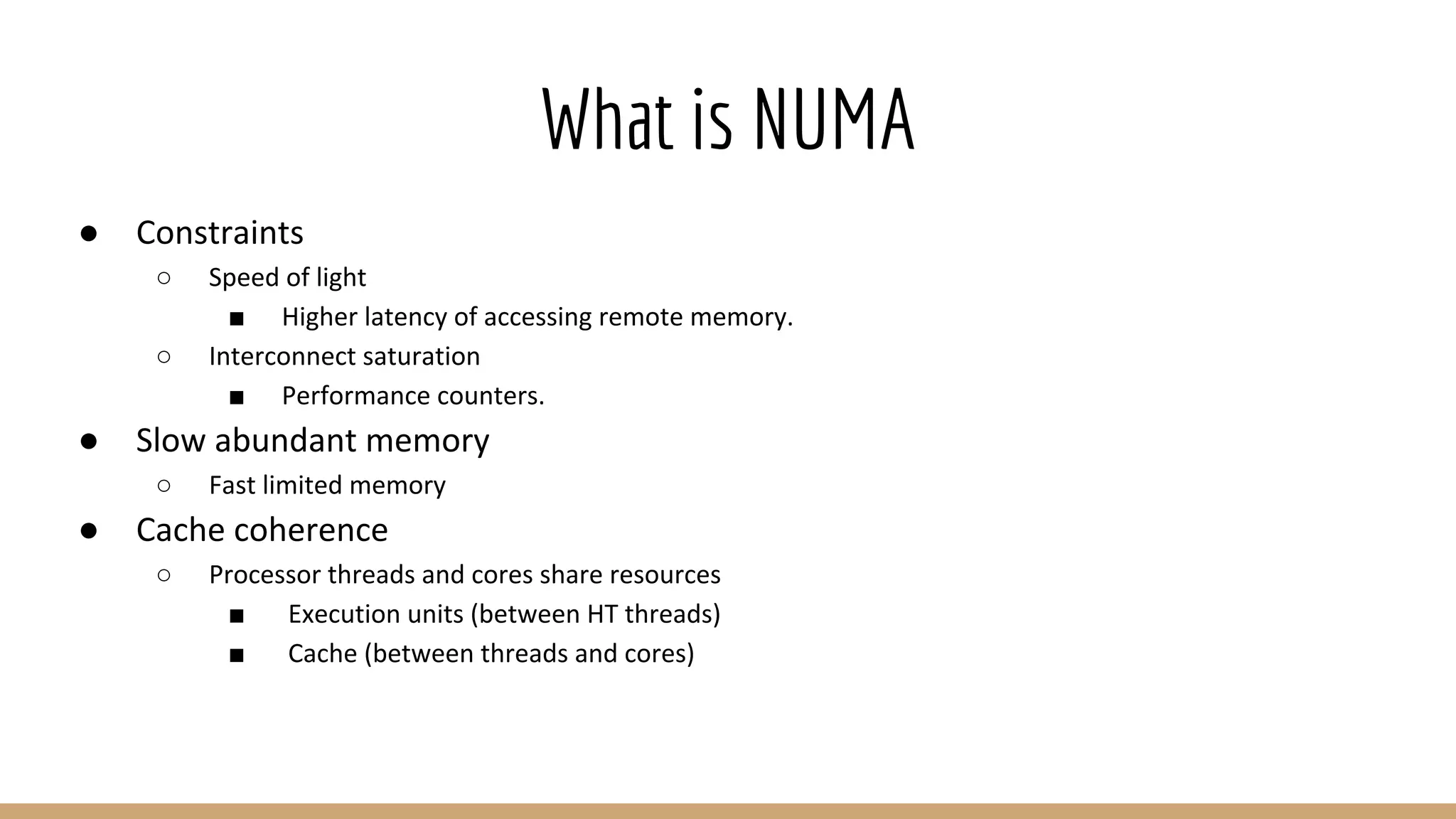
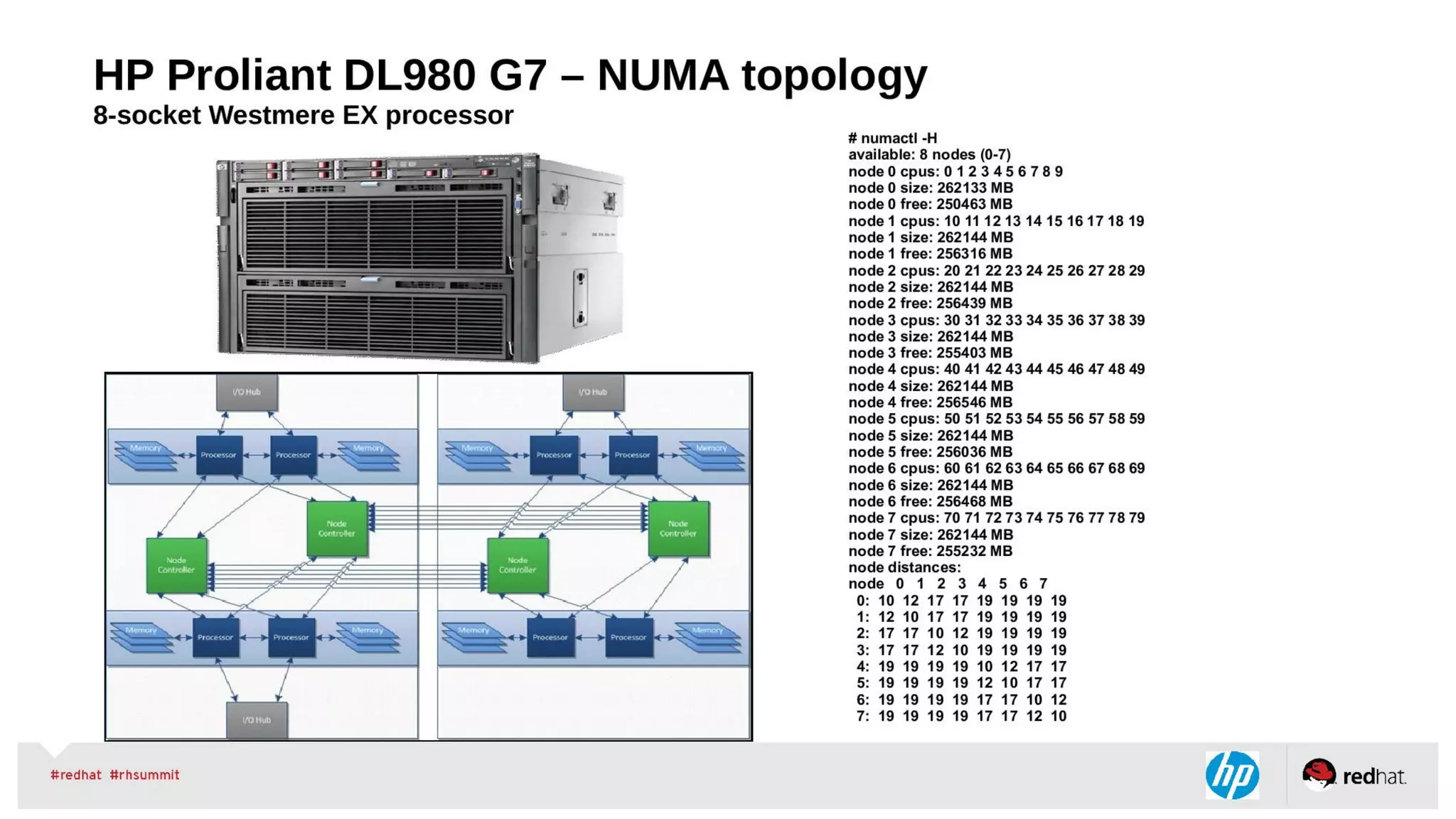
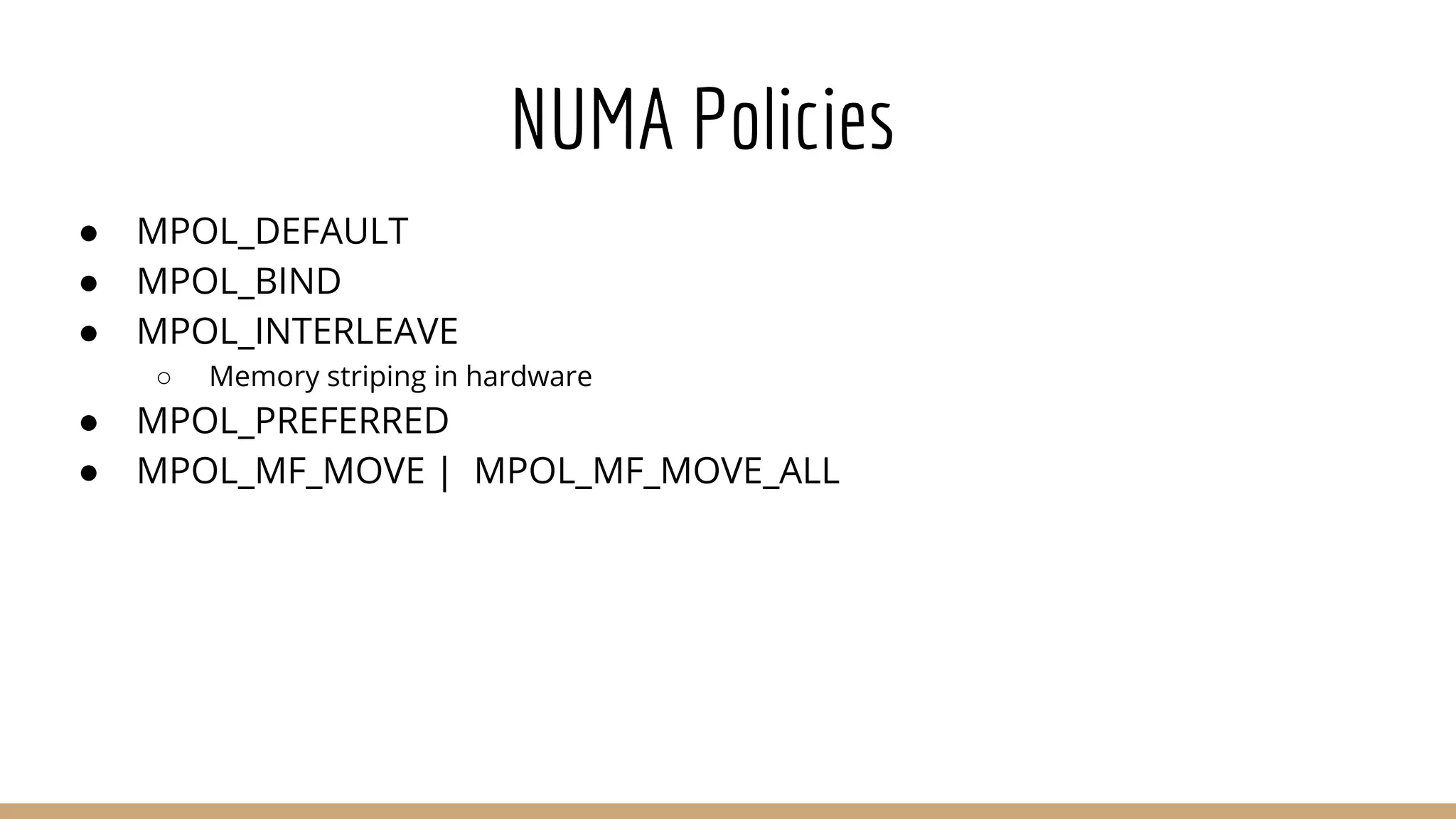
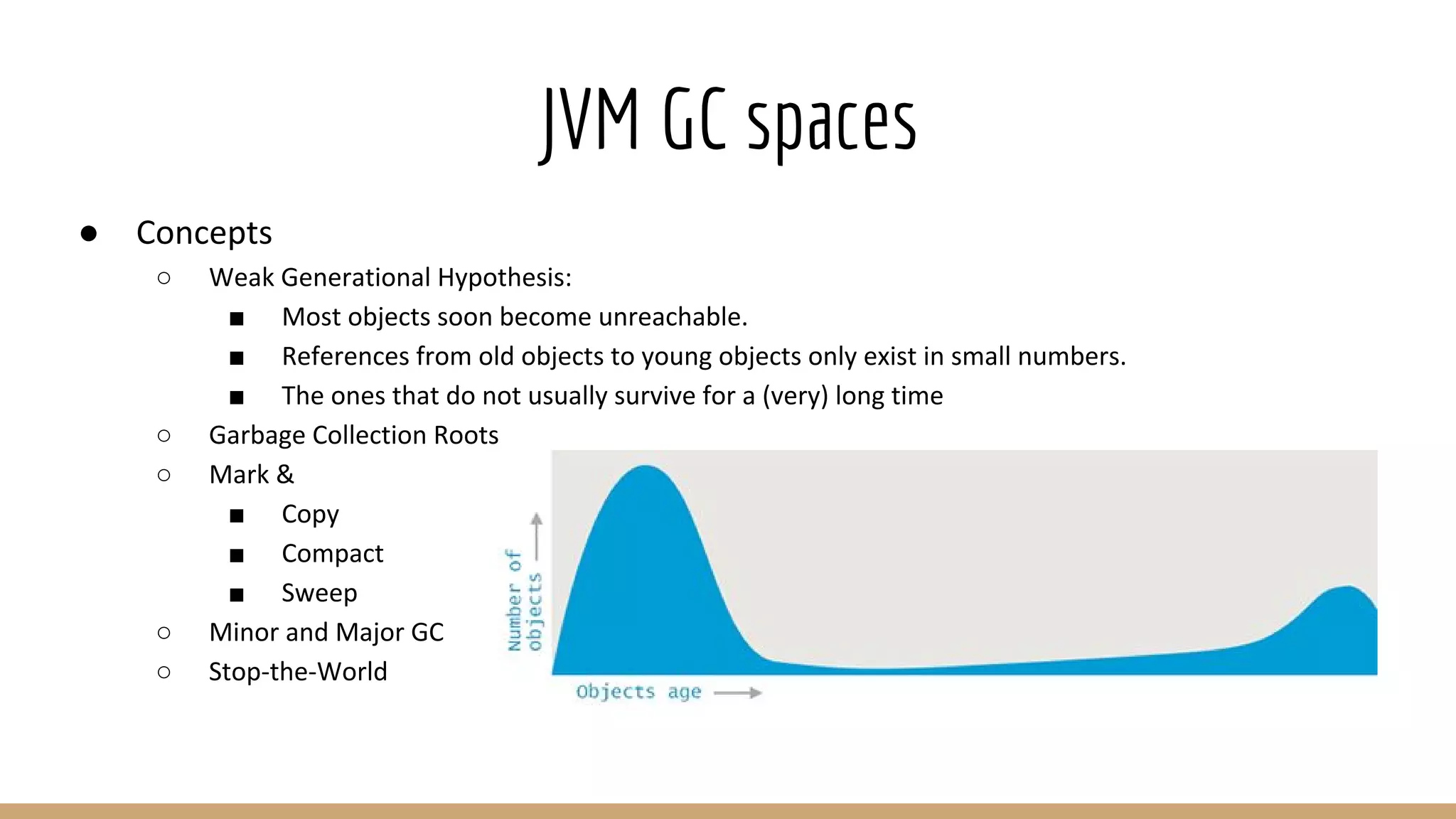
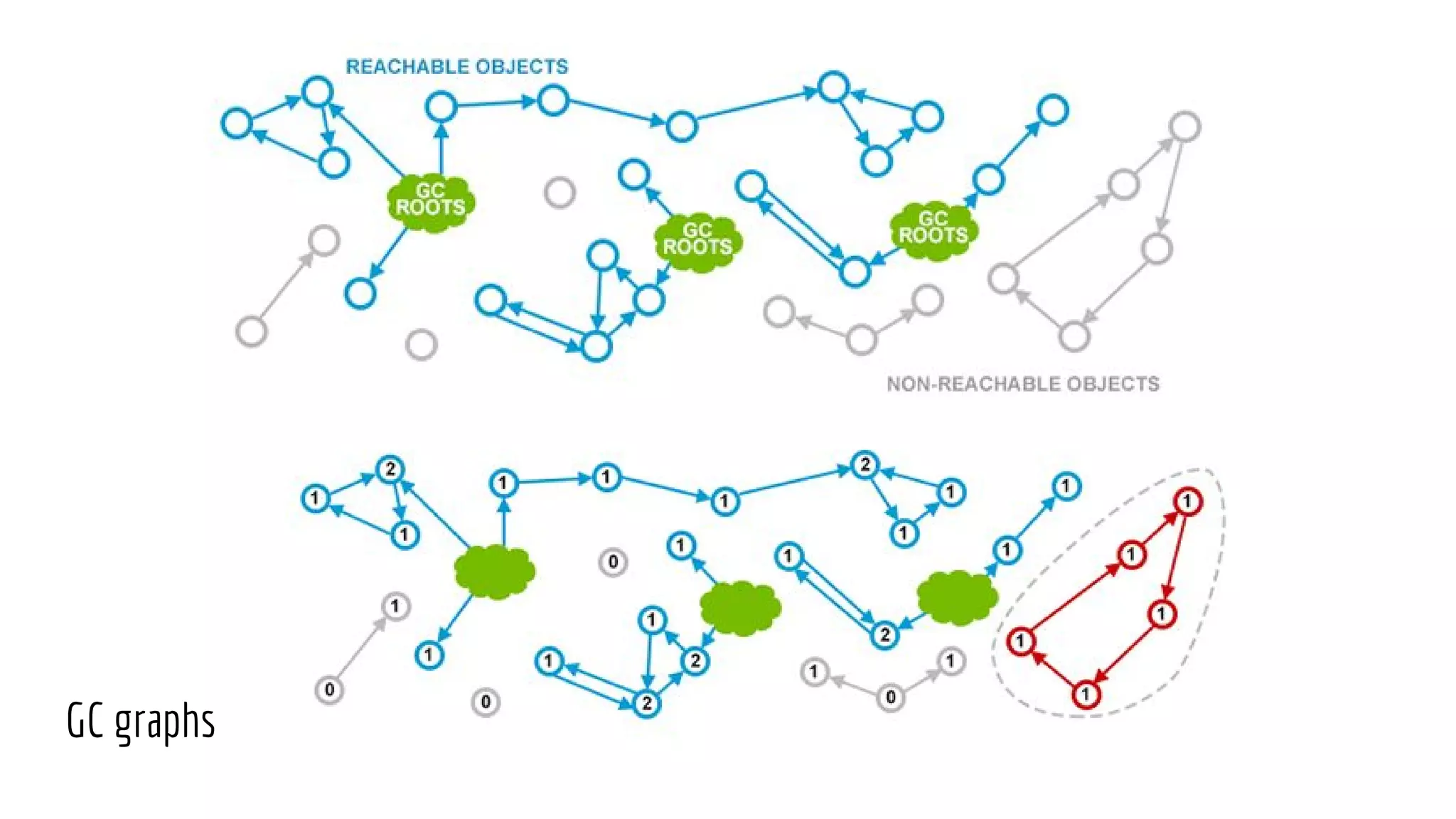
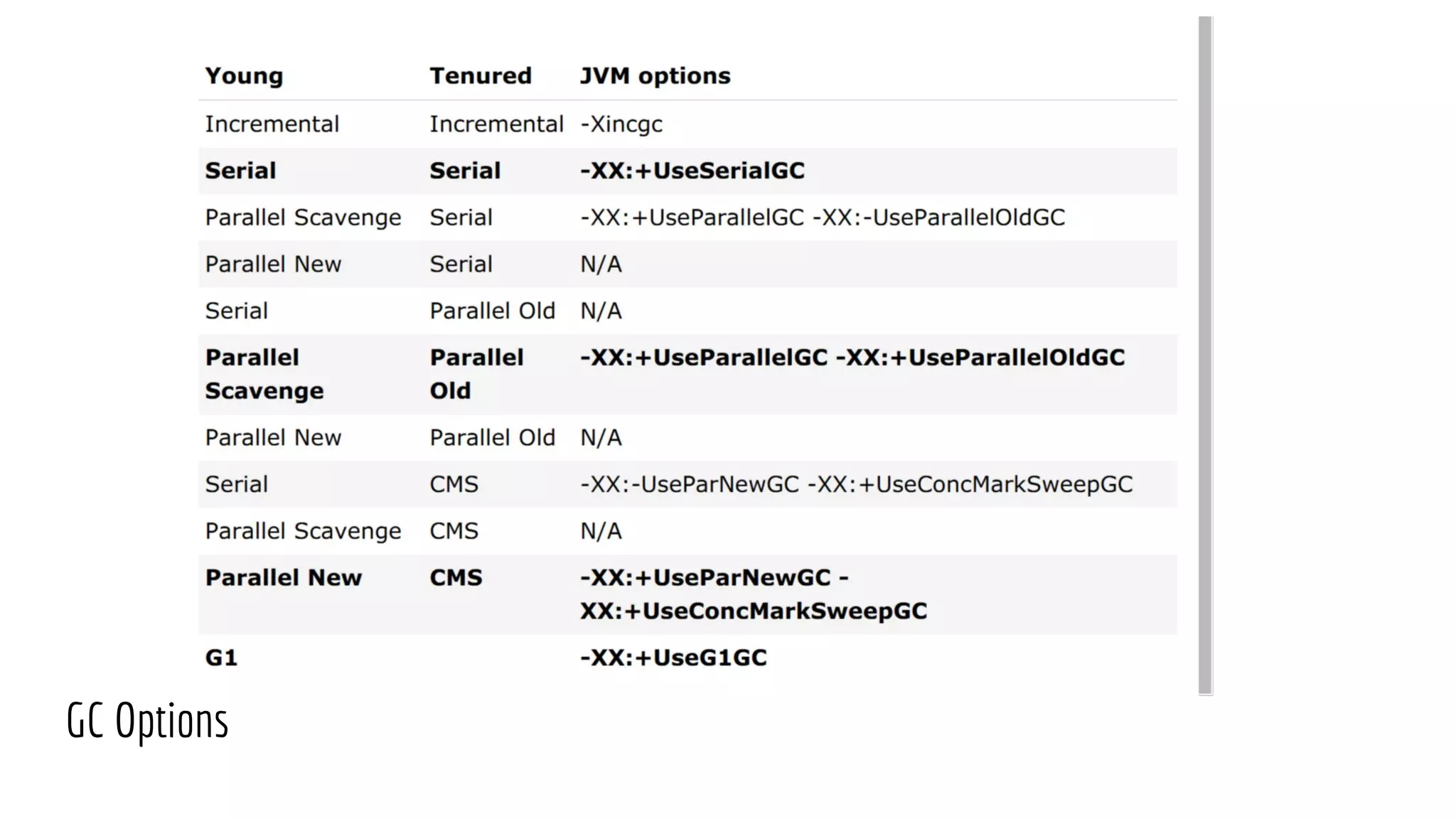
The document discusses Non-Uniform Memory Access (NUMA) architecture and its implications for databases, highlighting its performance constraints and how memory distribution impacts data access. It examines various tools for managing NUMA in Linux, including the use of Java Virtual Machine (JVM) garbage collection options, and specific JVM settings that optimize performance for applications like Cassandra. The author provides insights on off-heap memory usage in Cassandra and suggests best practices for leveraging NUMA for better performance while cautioning against inappropriate allocation strategies.


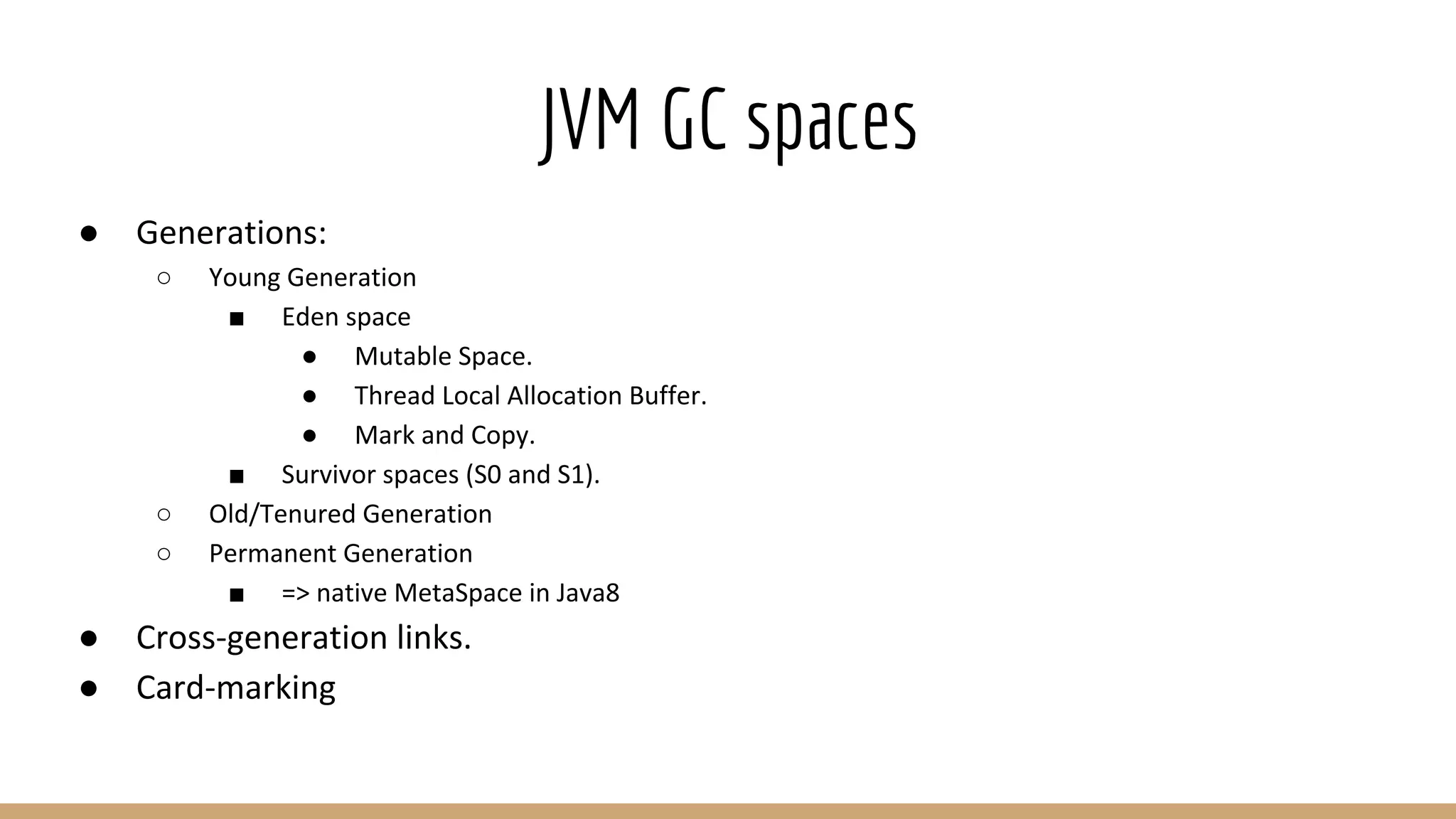






![Numa issues
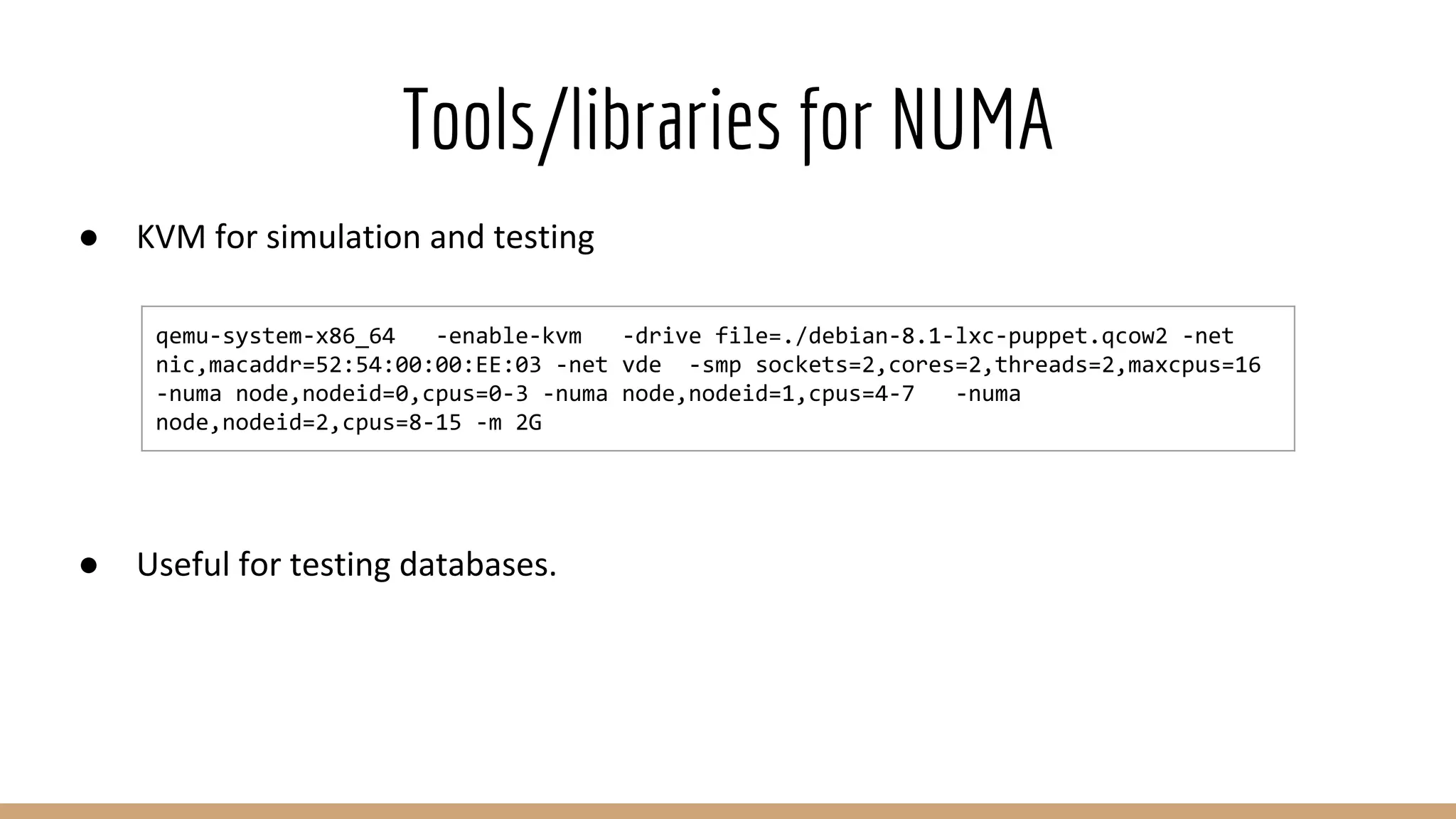
● Numactl --interleave:
○ Thread-local native allocations - Bad [X]
■ Tons of them throughout code which bypass JVM.
○ JVM’s Eden space will also be interleaved - Bad [X]
● JVM’s options only:
○ Native allocations will be local.
○ Large off-heap allocations can suffer.
● Numactl + JVM
■ JVM-aware GC (Parallel)
● Best possible combination (without invasive code changes in cassandra).
● JVM’s memory options will override numactl.
● But, ParallelGC is not comparable to new ones (G1).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/numaandjavadatabases-161110220821/75/NUMA-and-Java-Databases-21-2048.jpg)