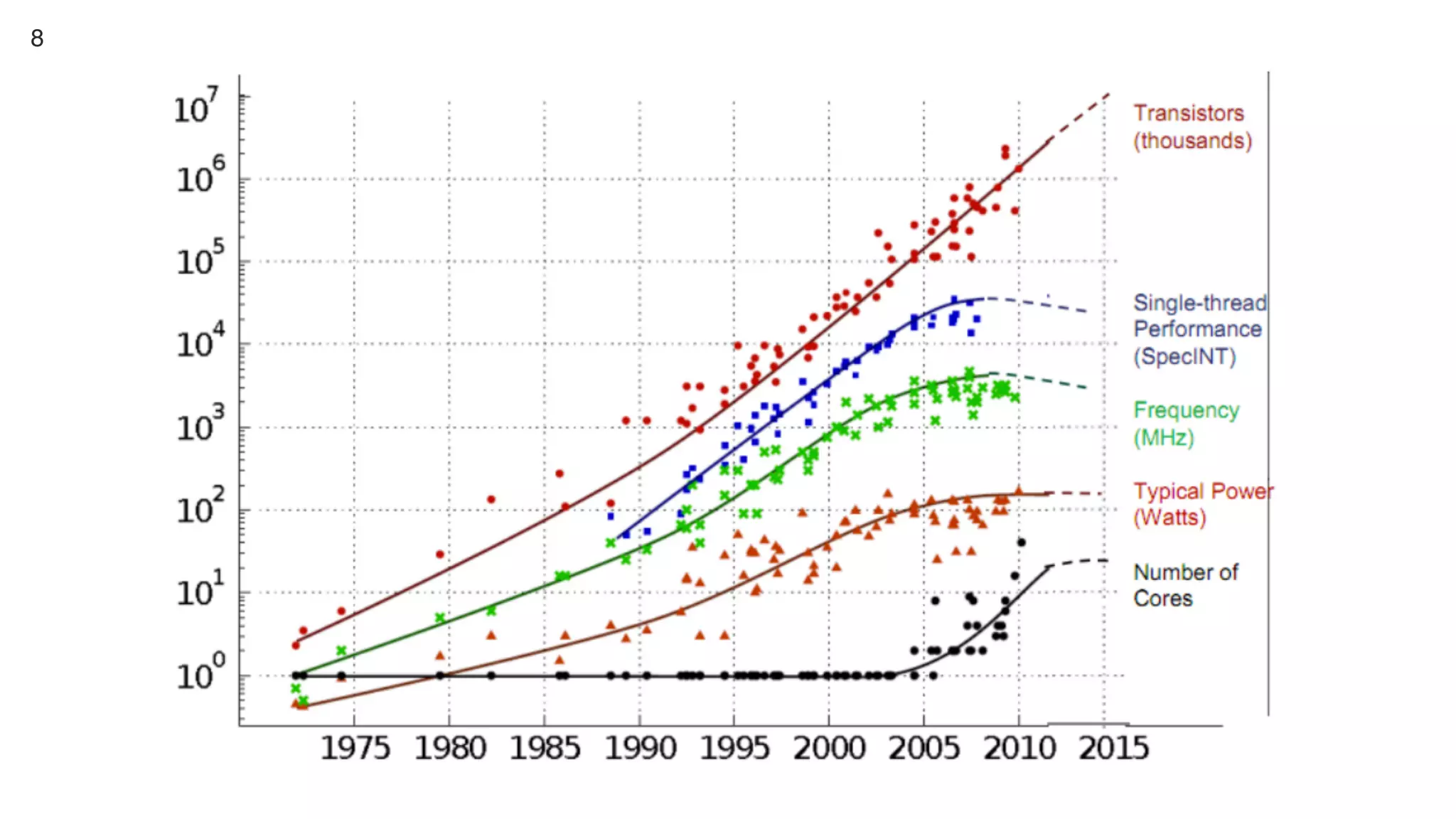
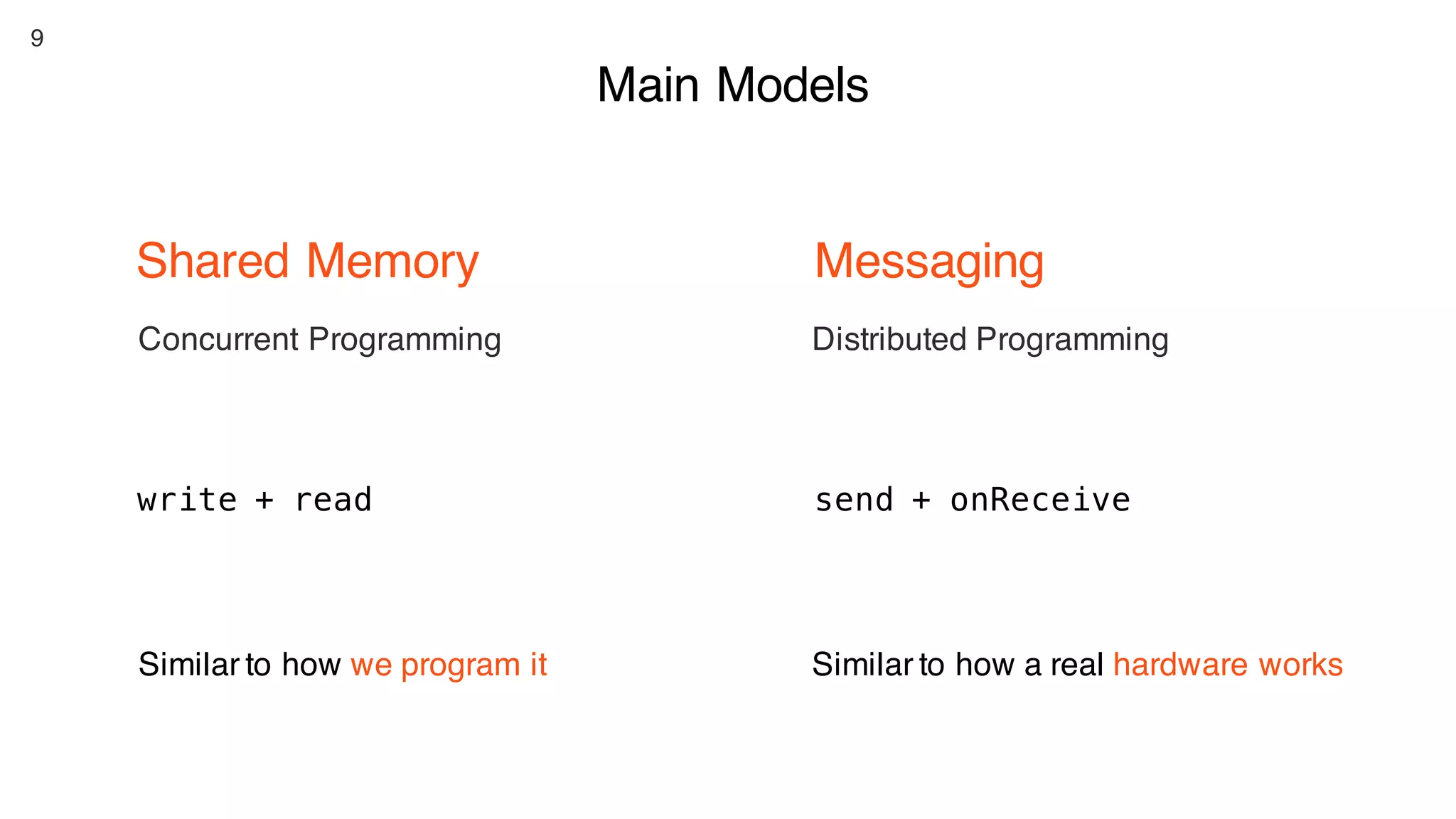
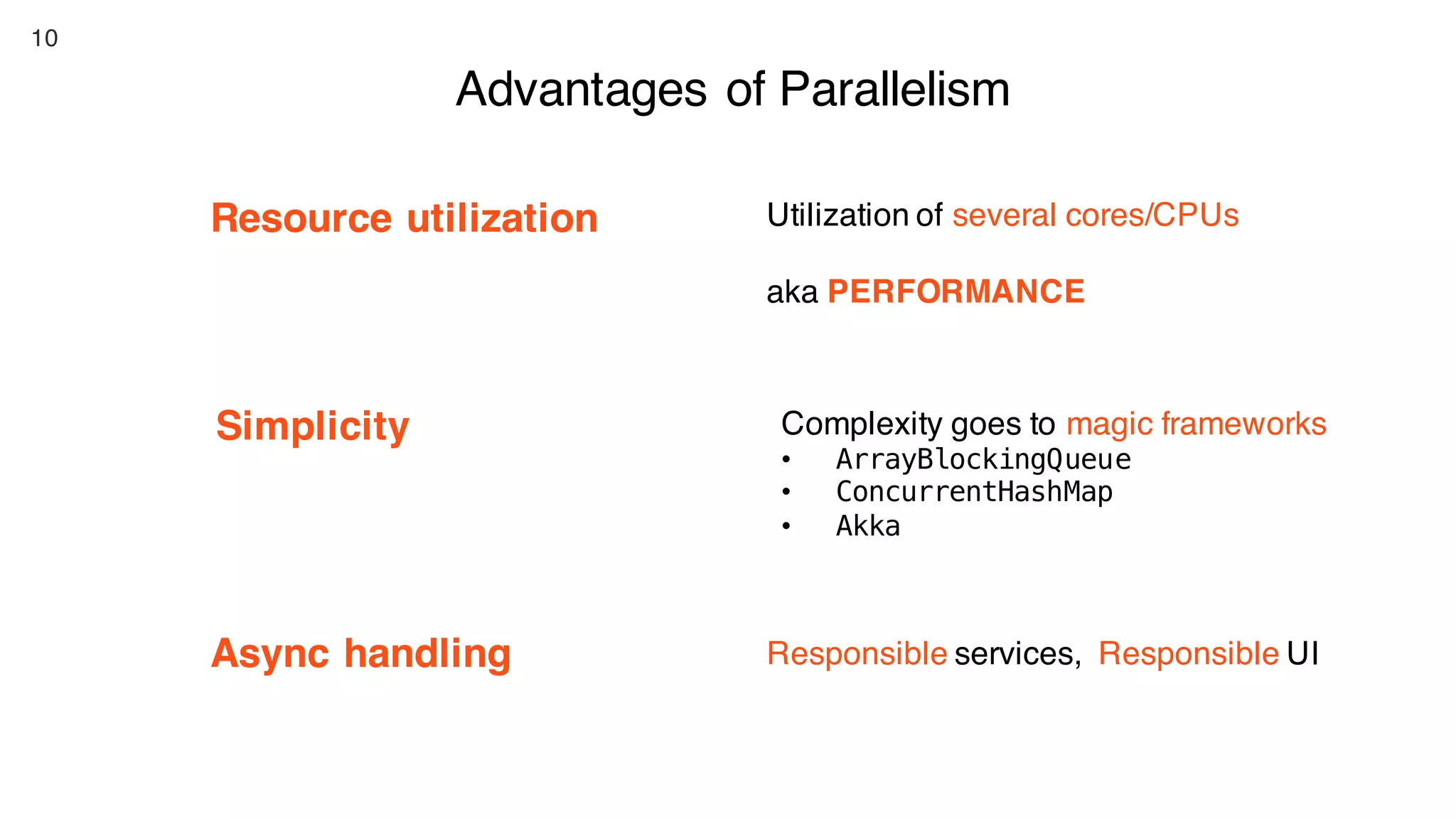
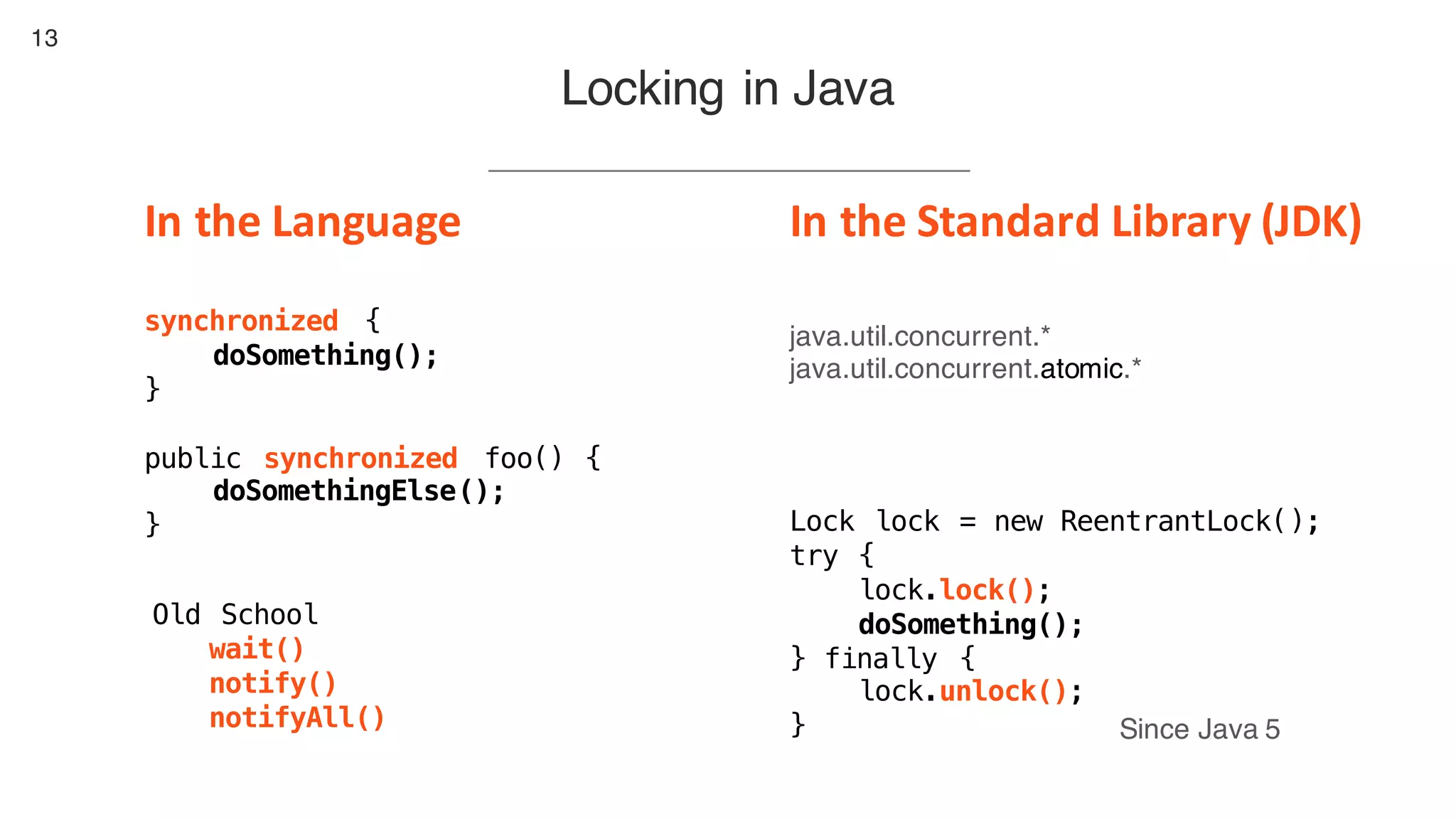
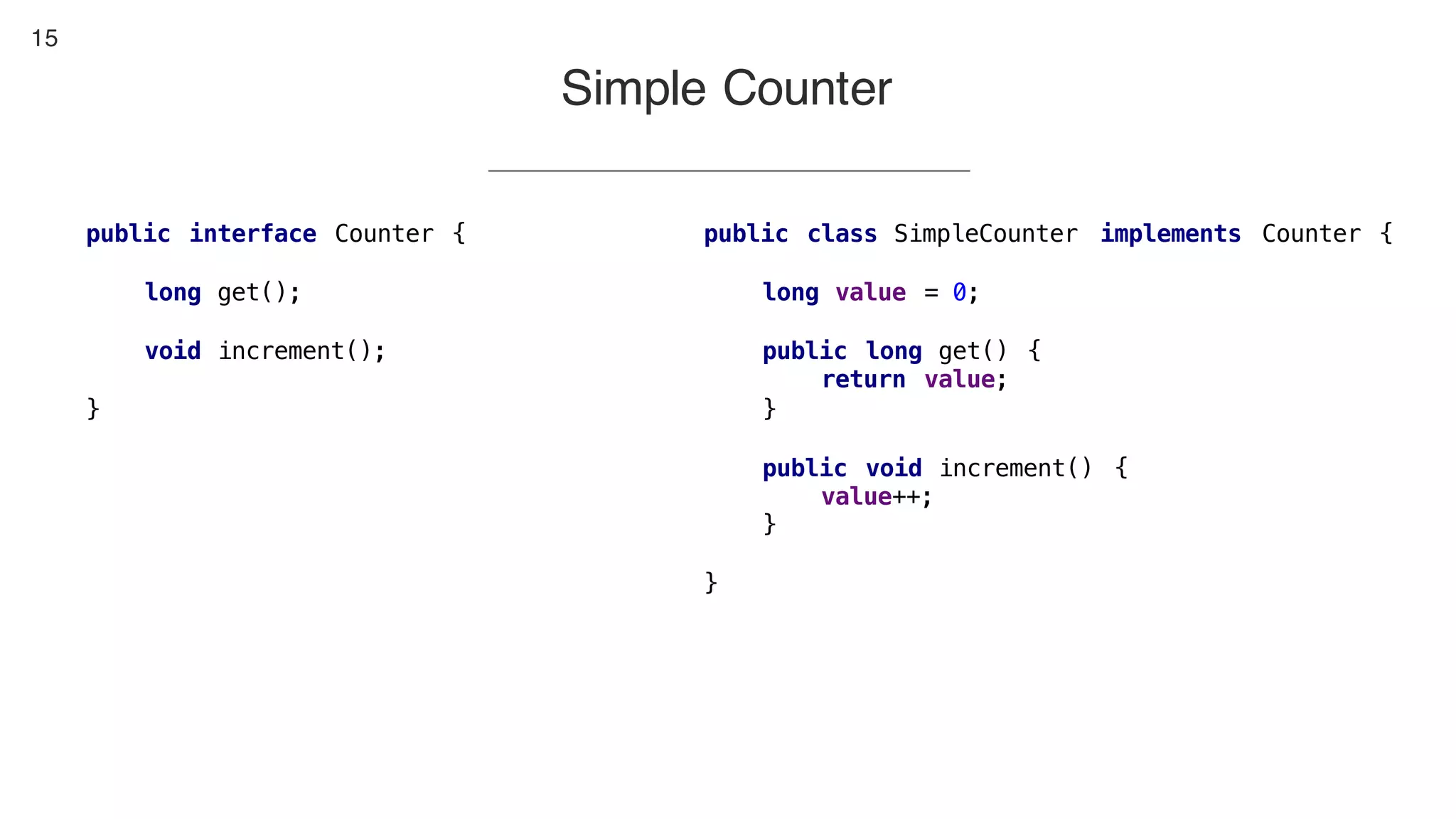
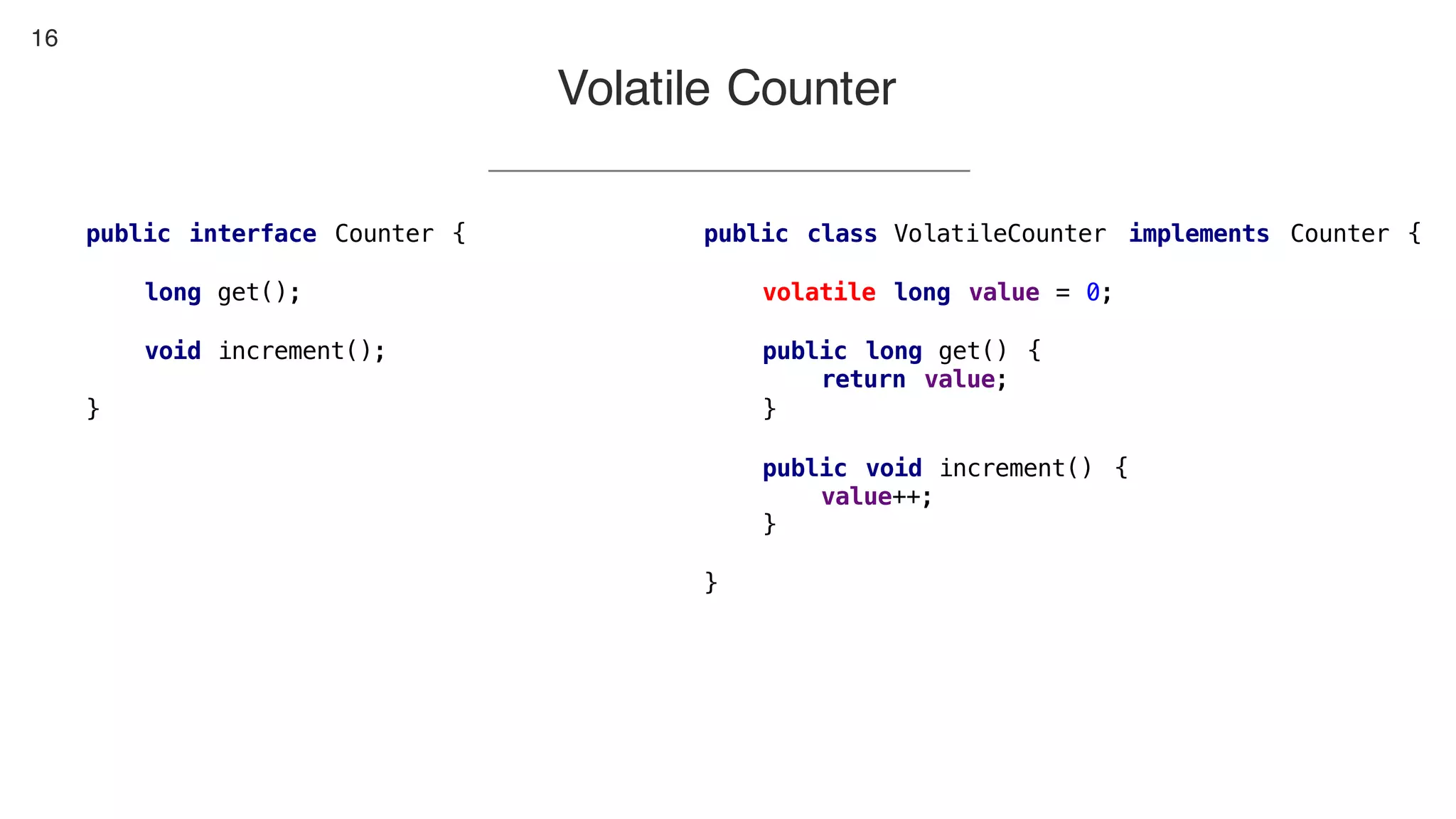
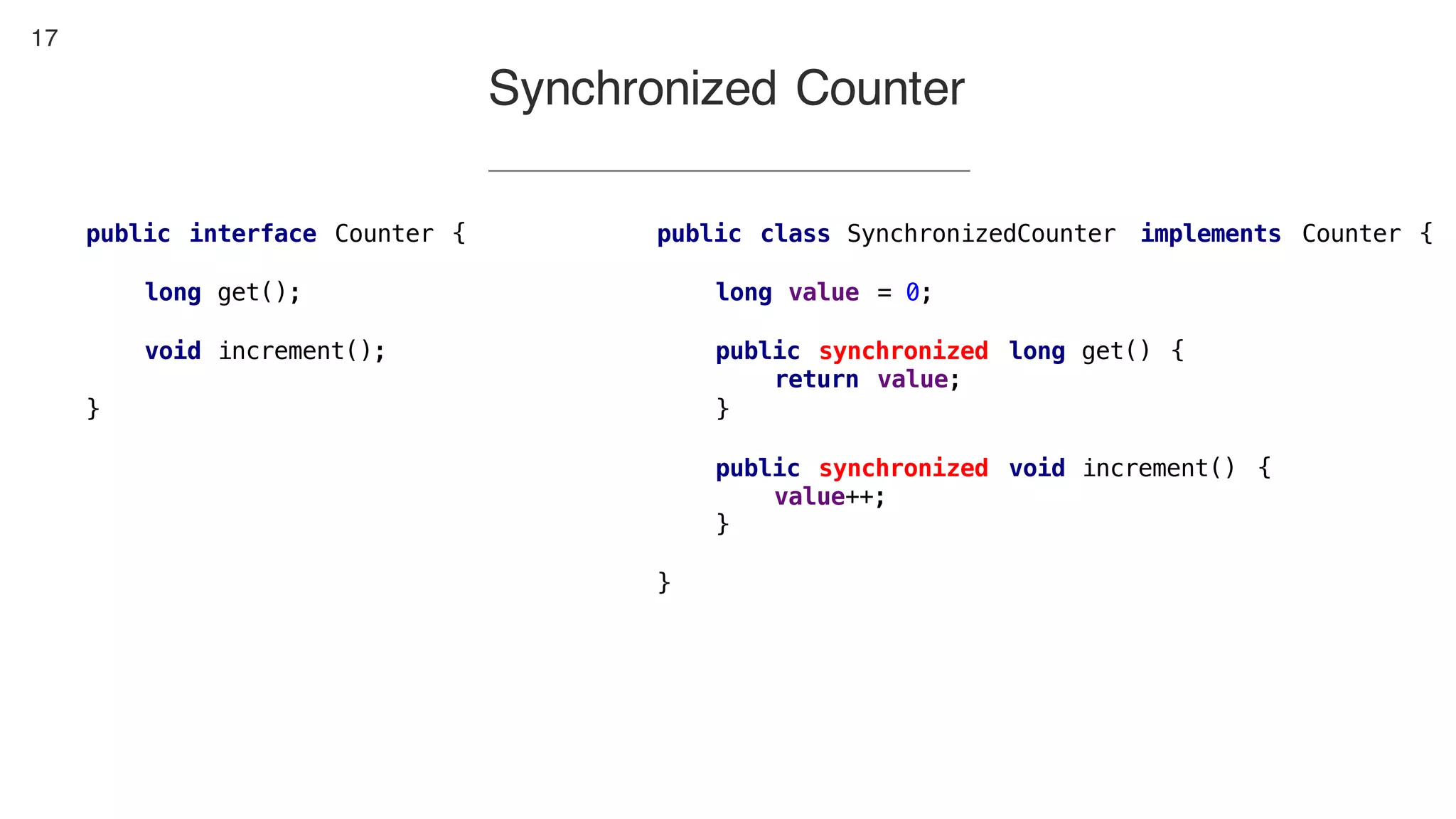
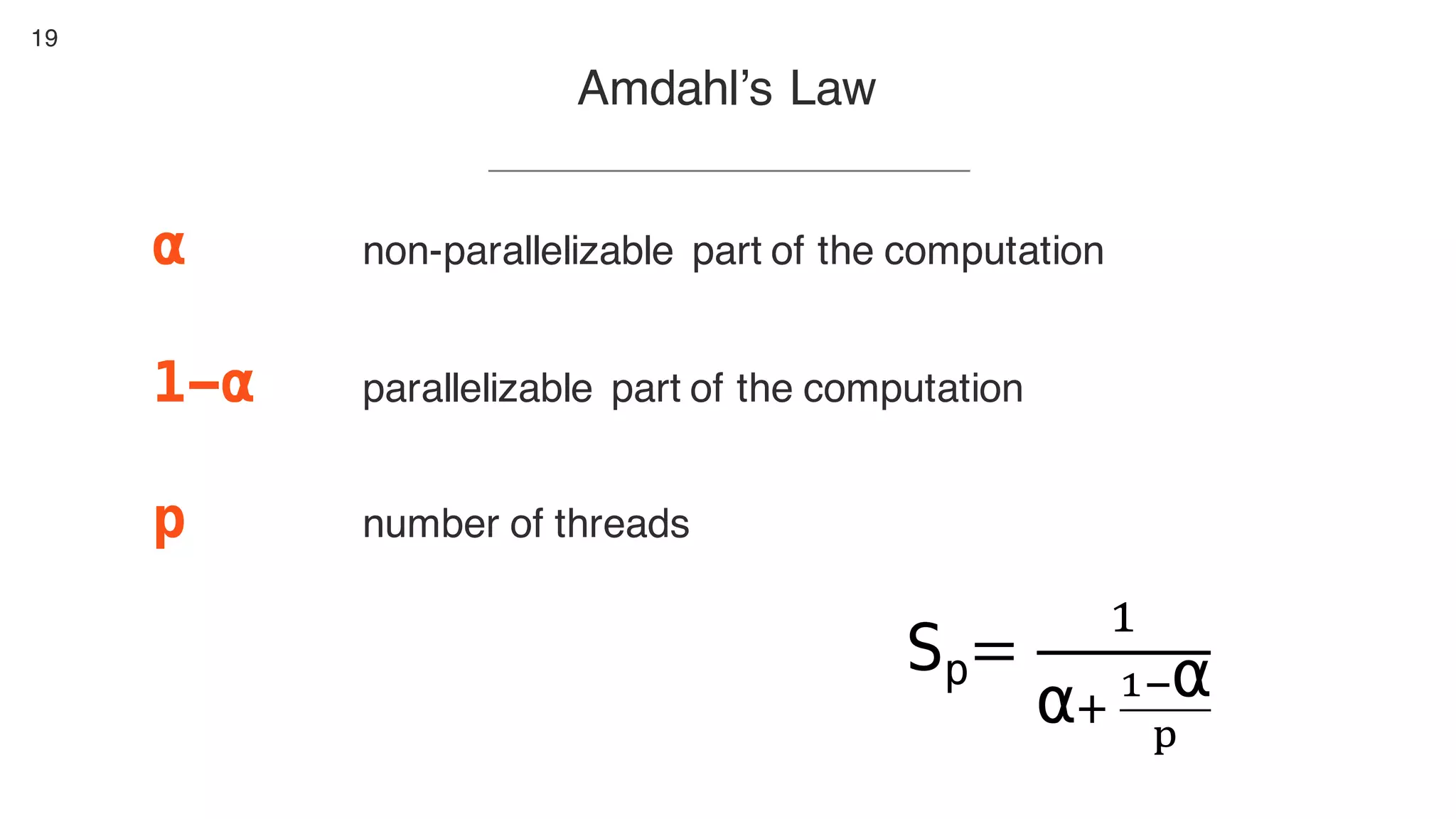
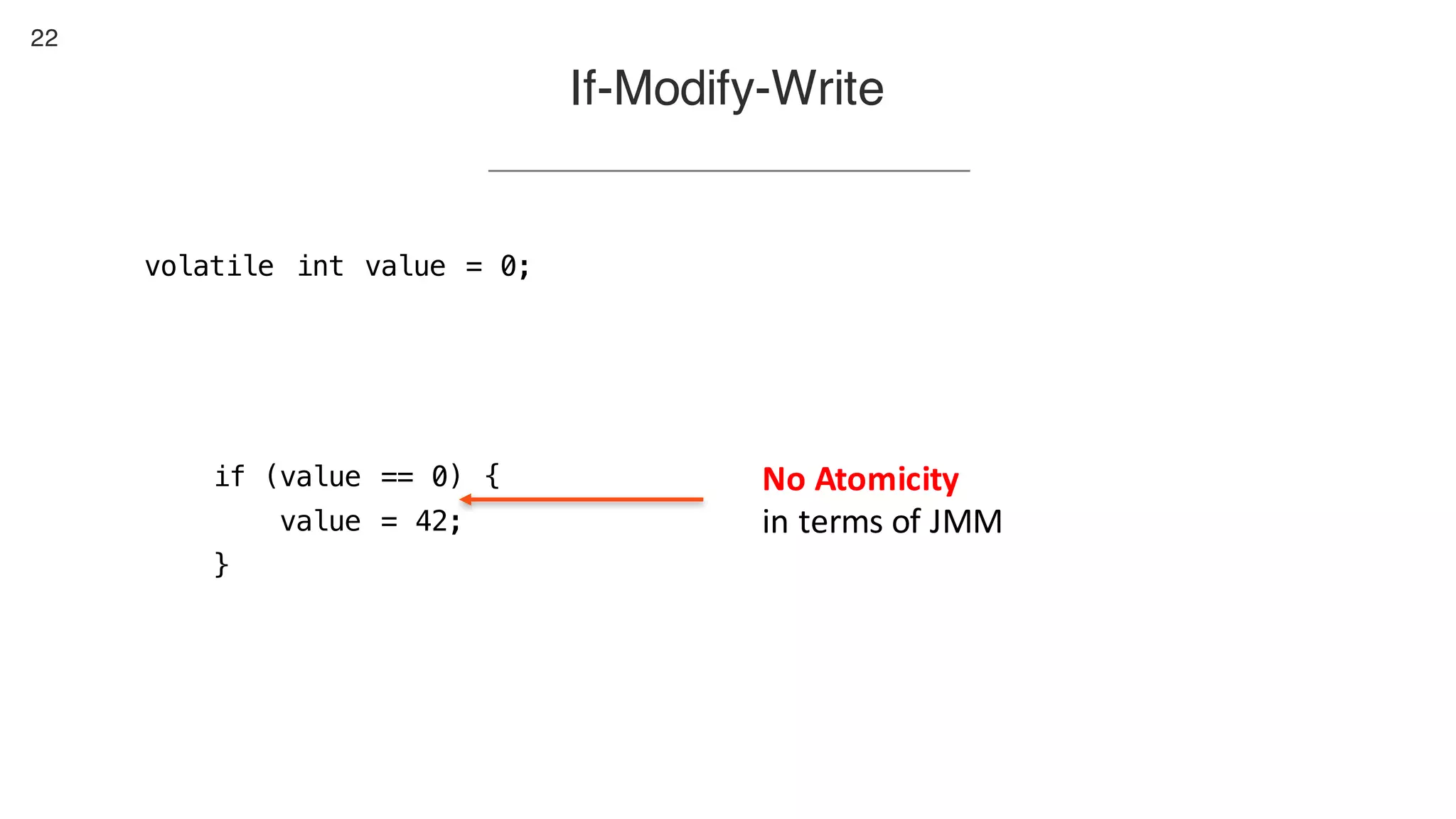
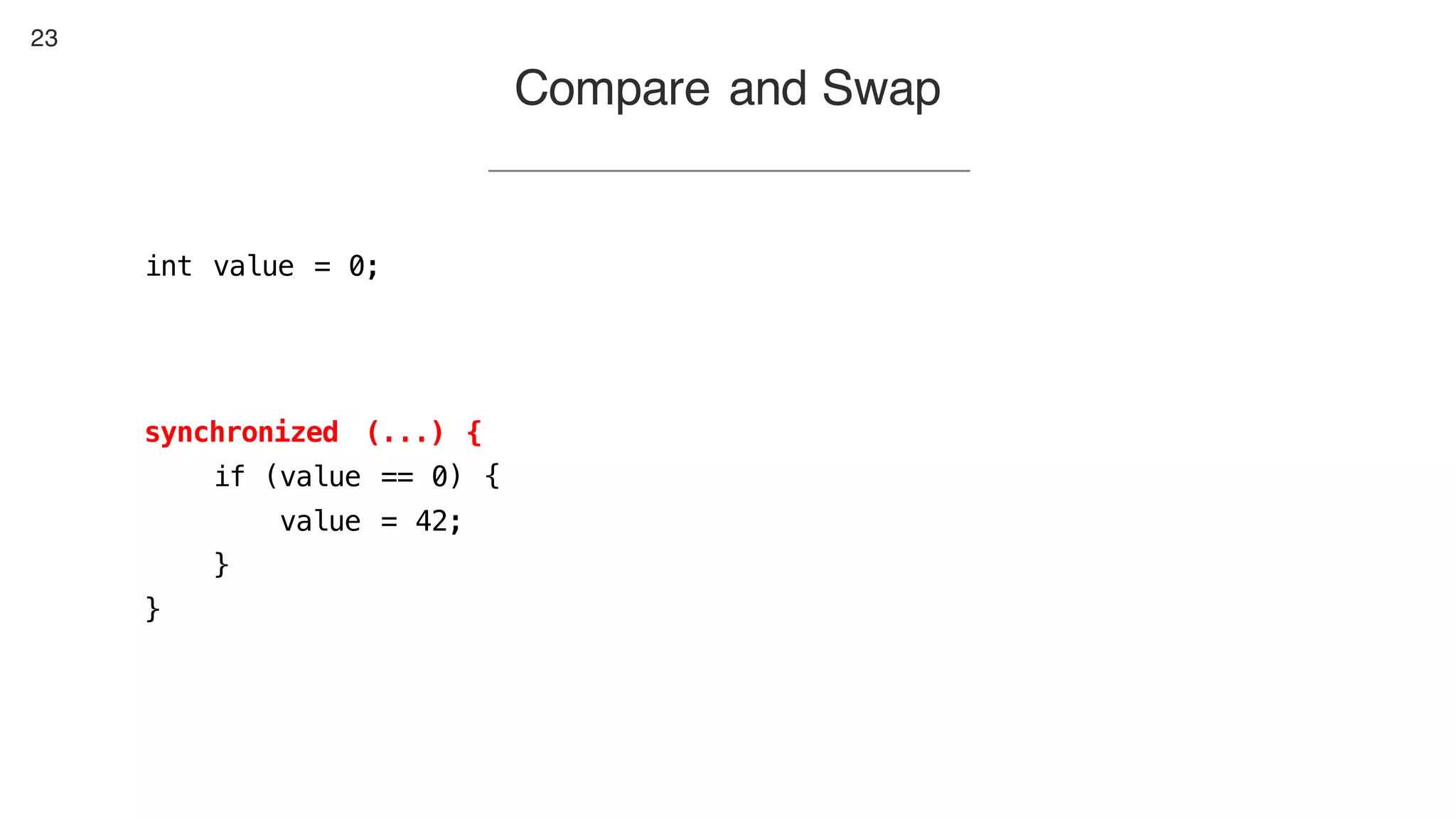
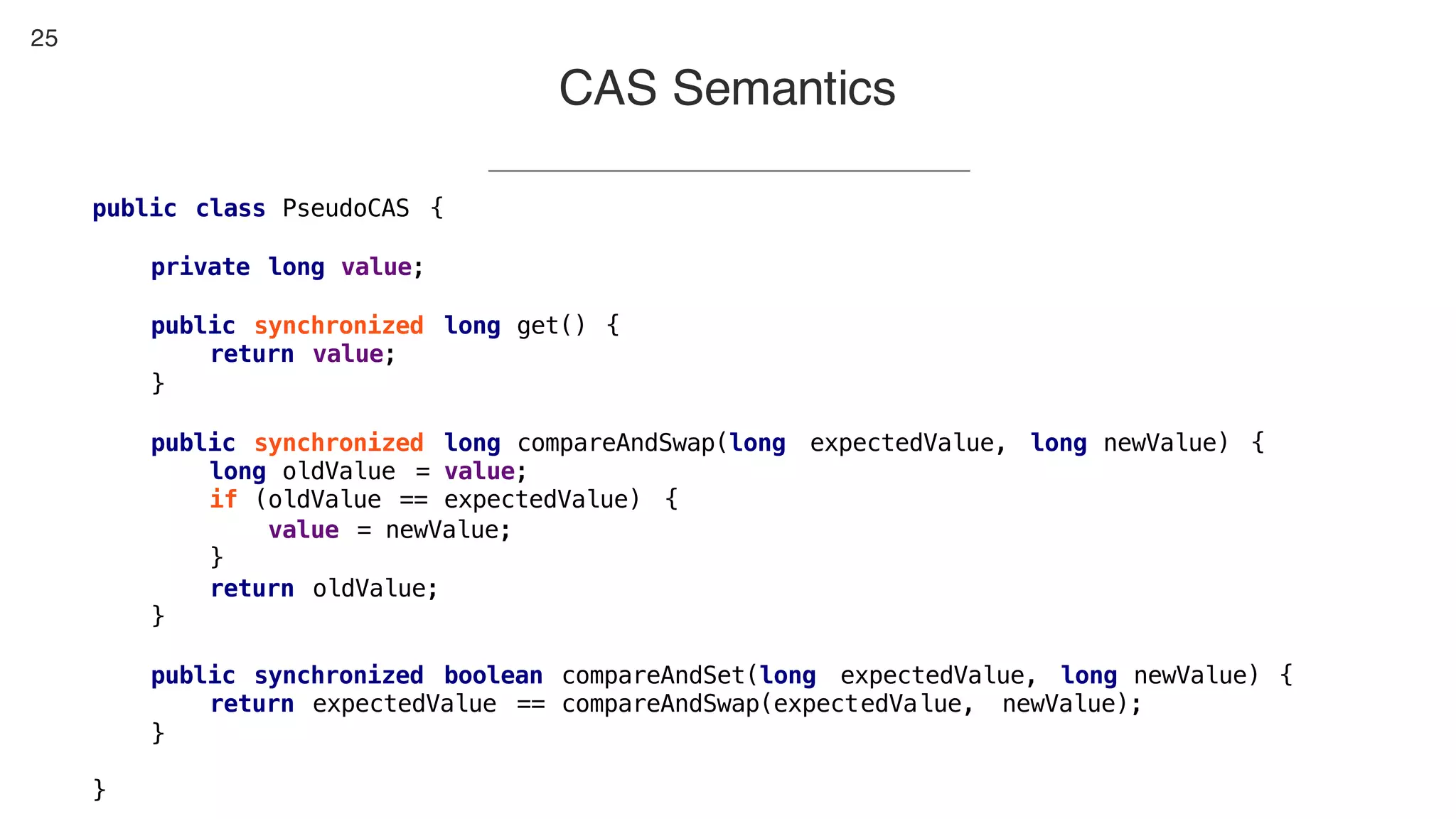
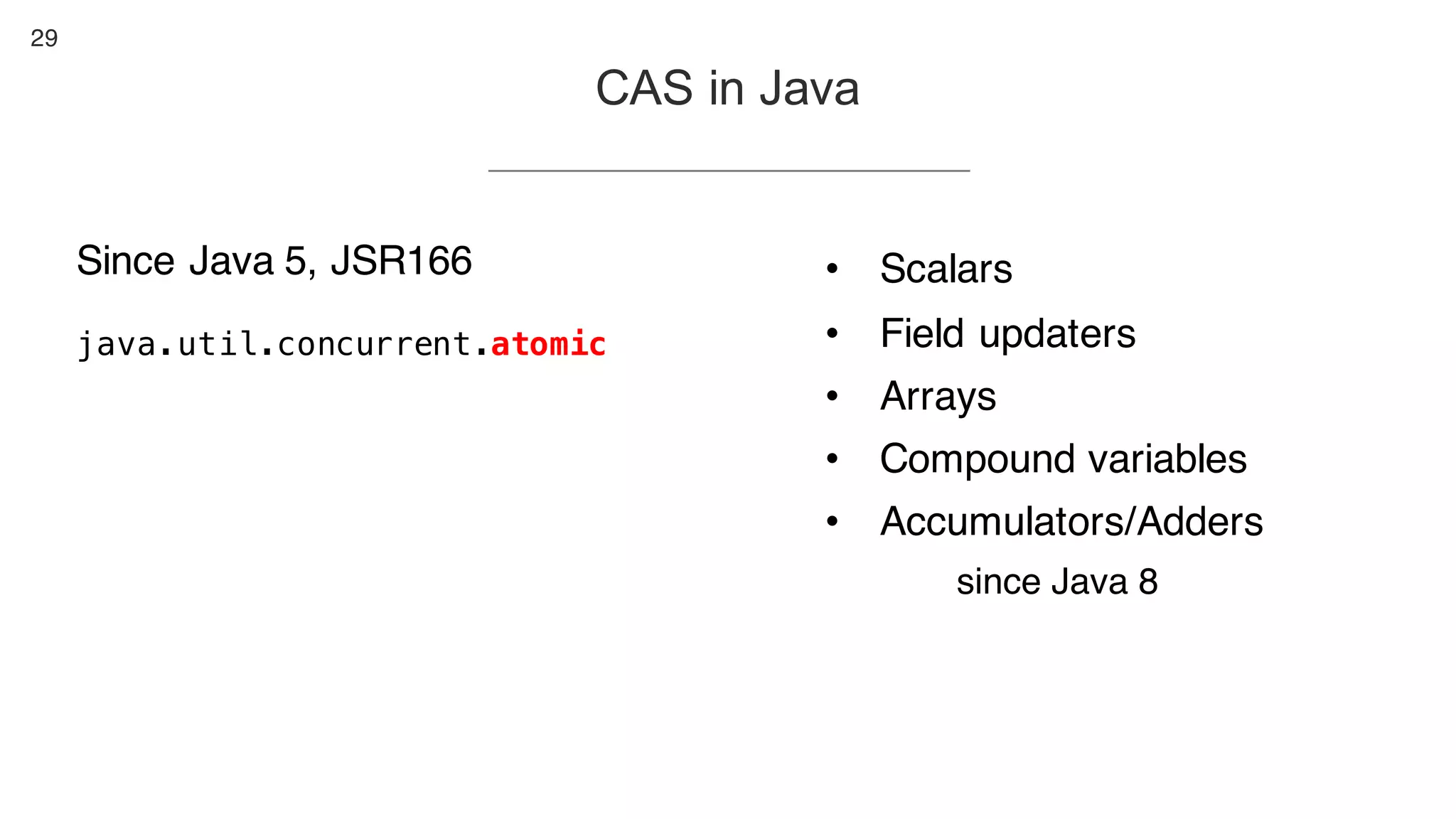
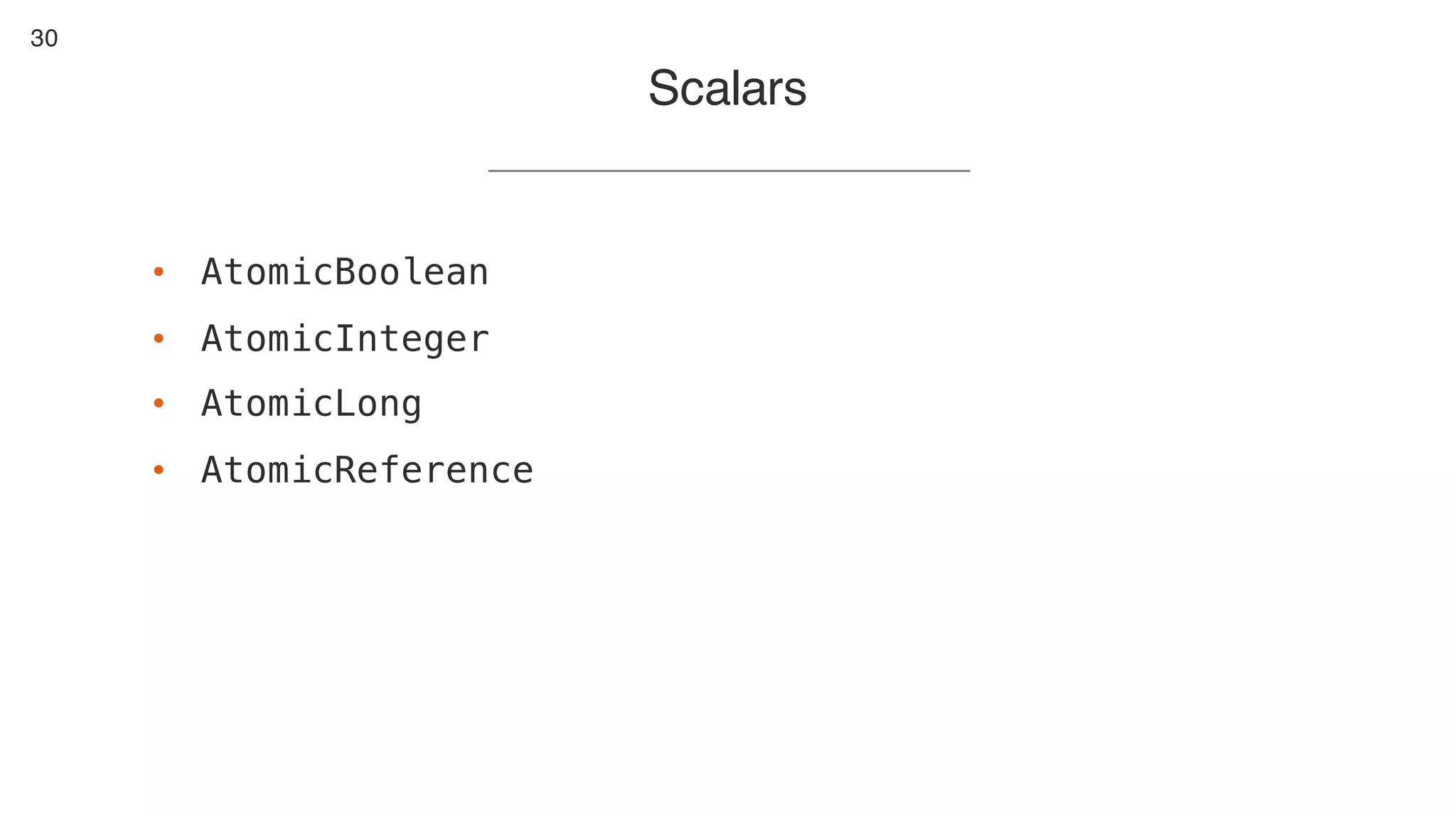
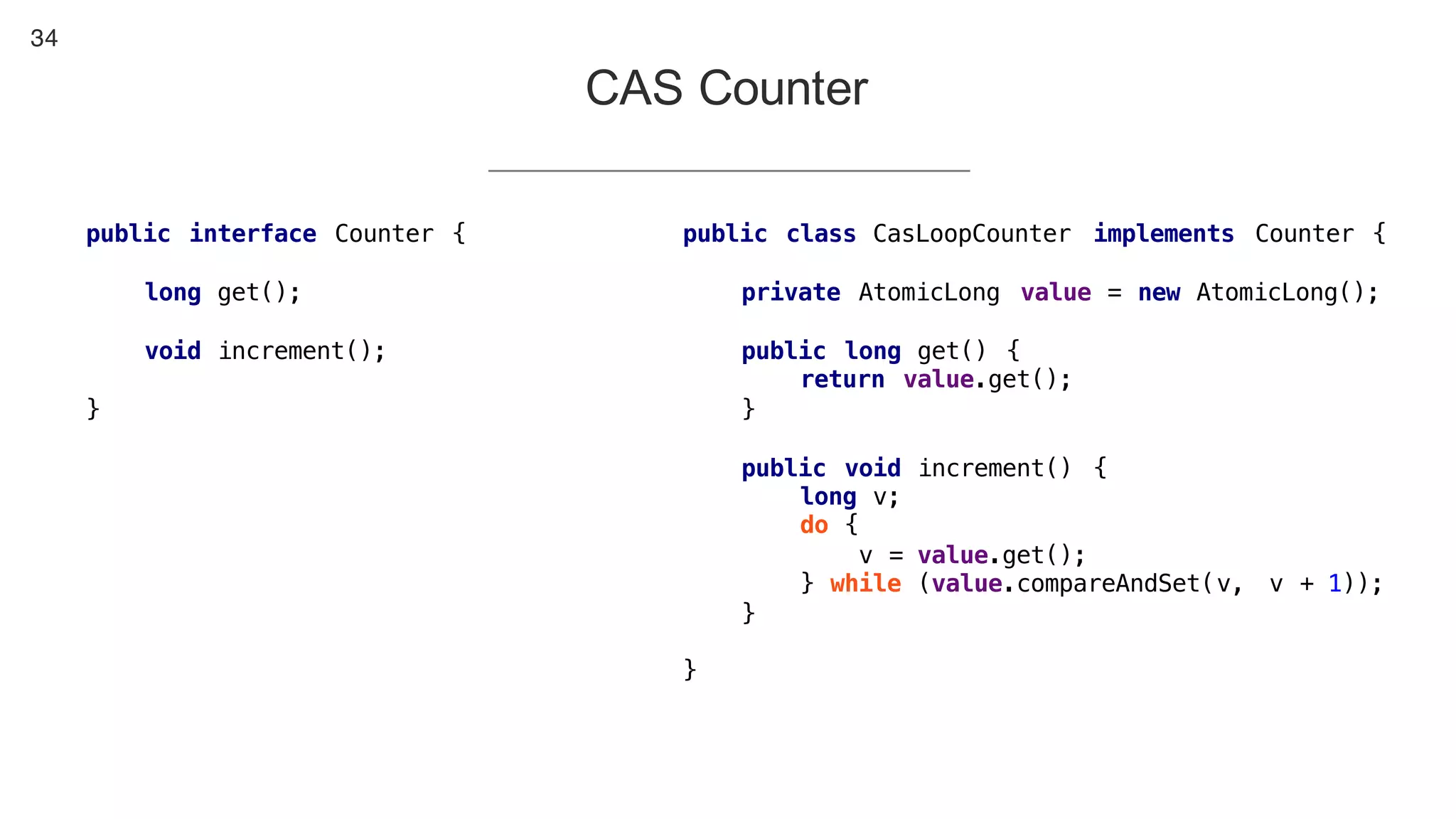
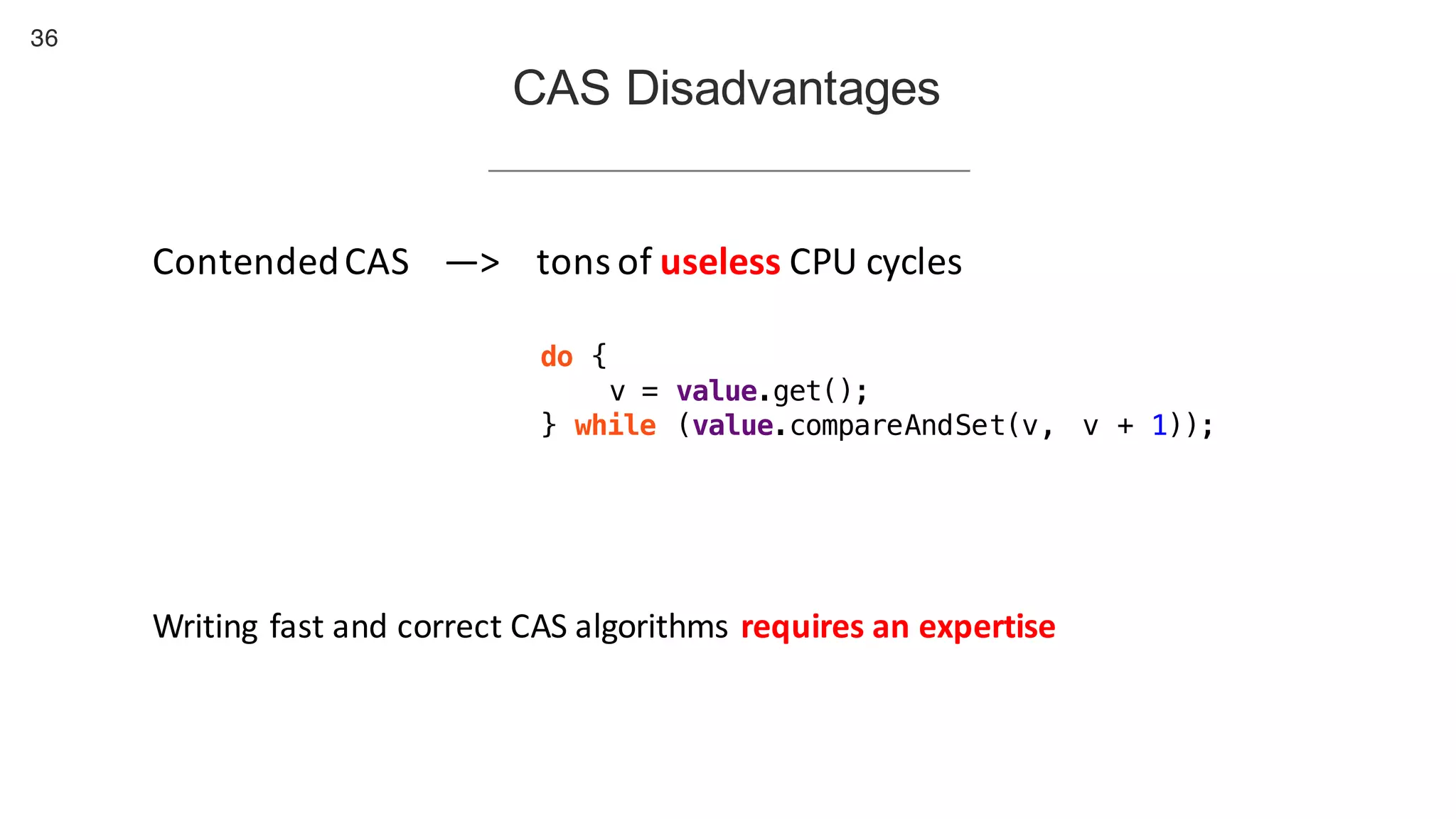
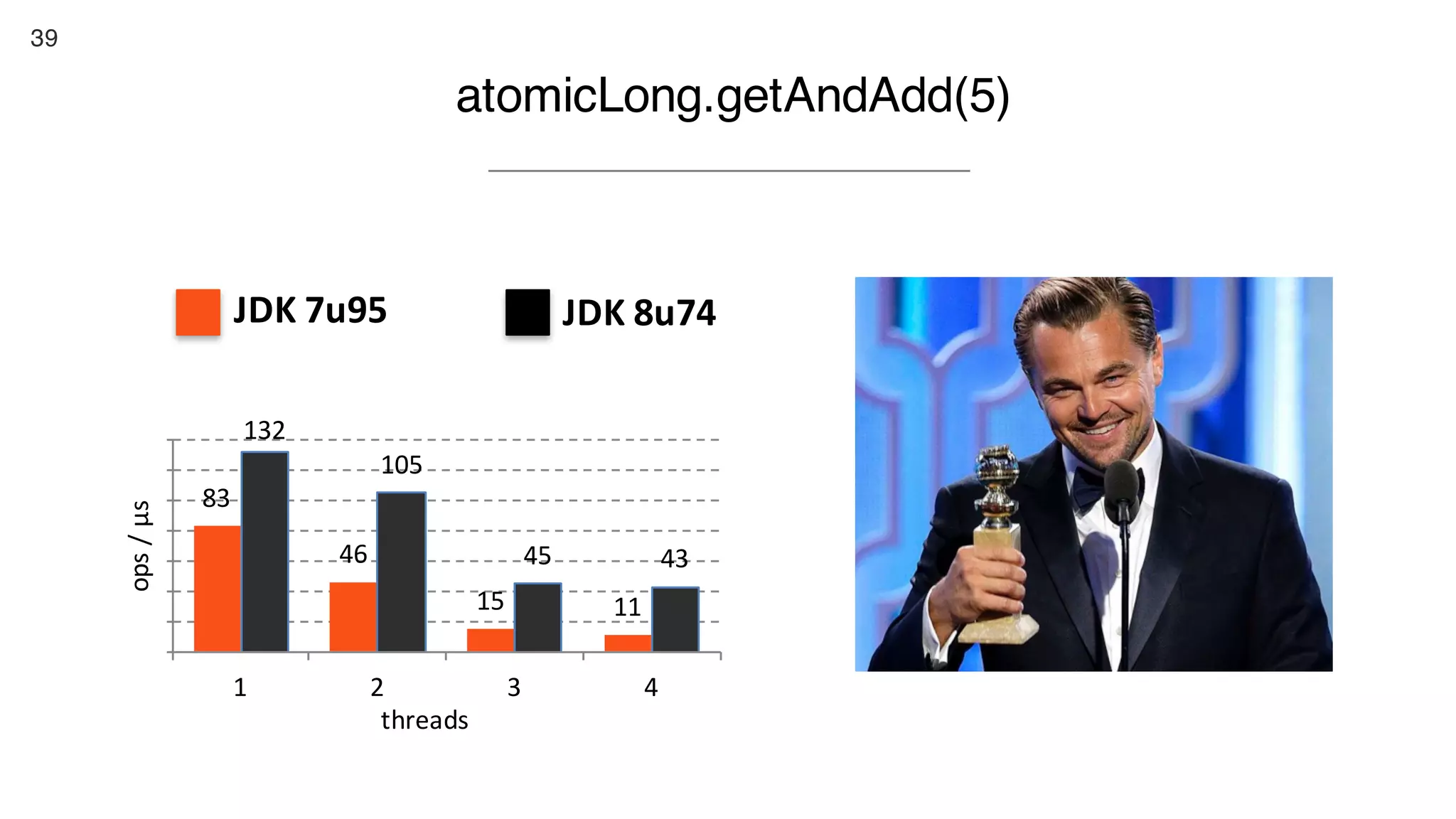
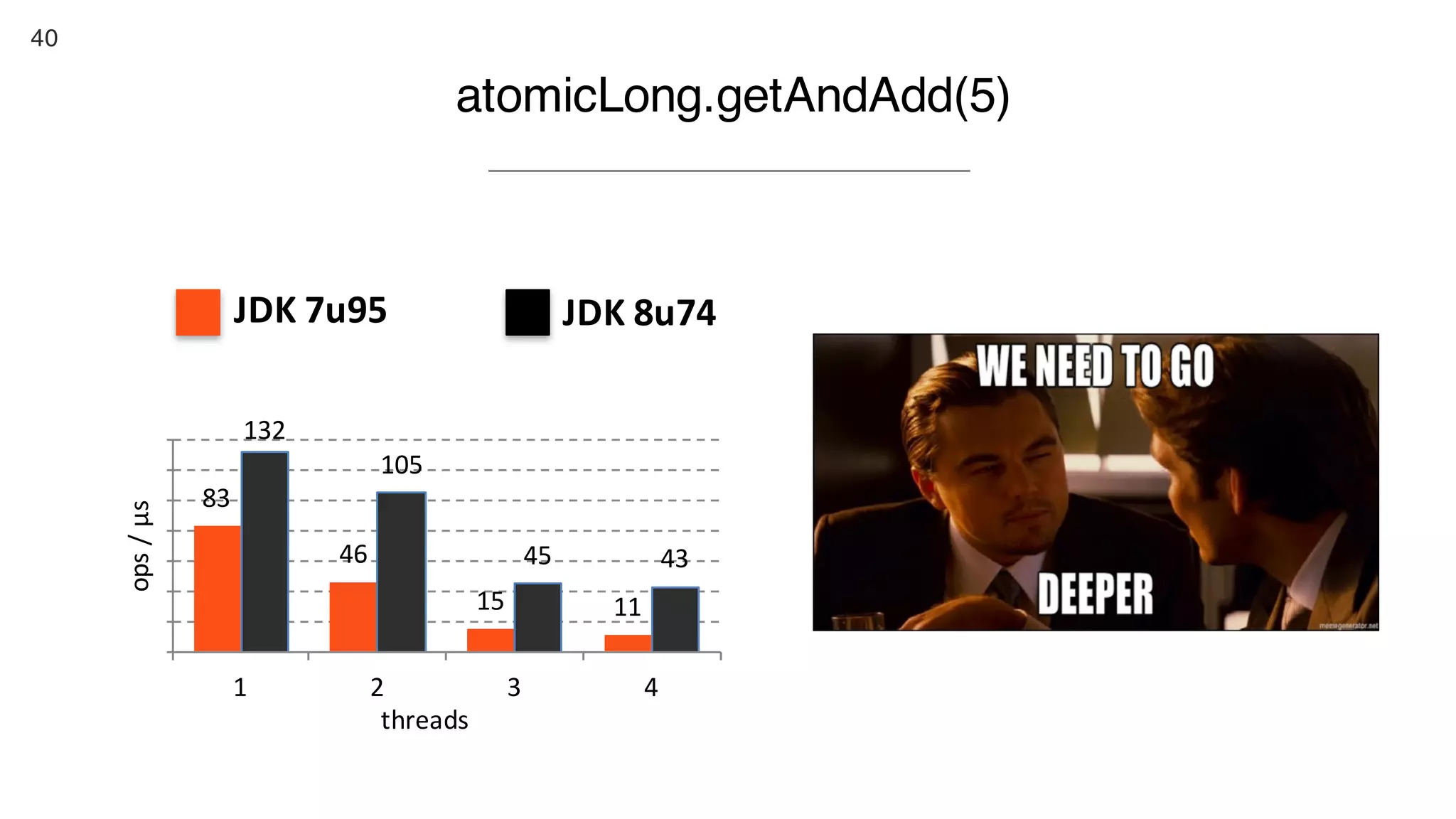
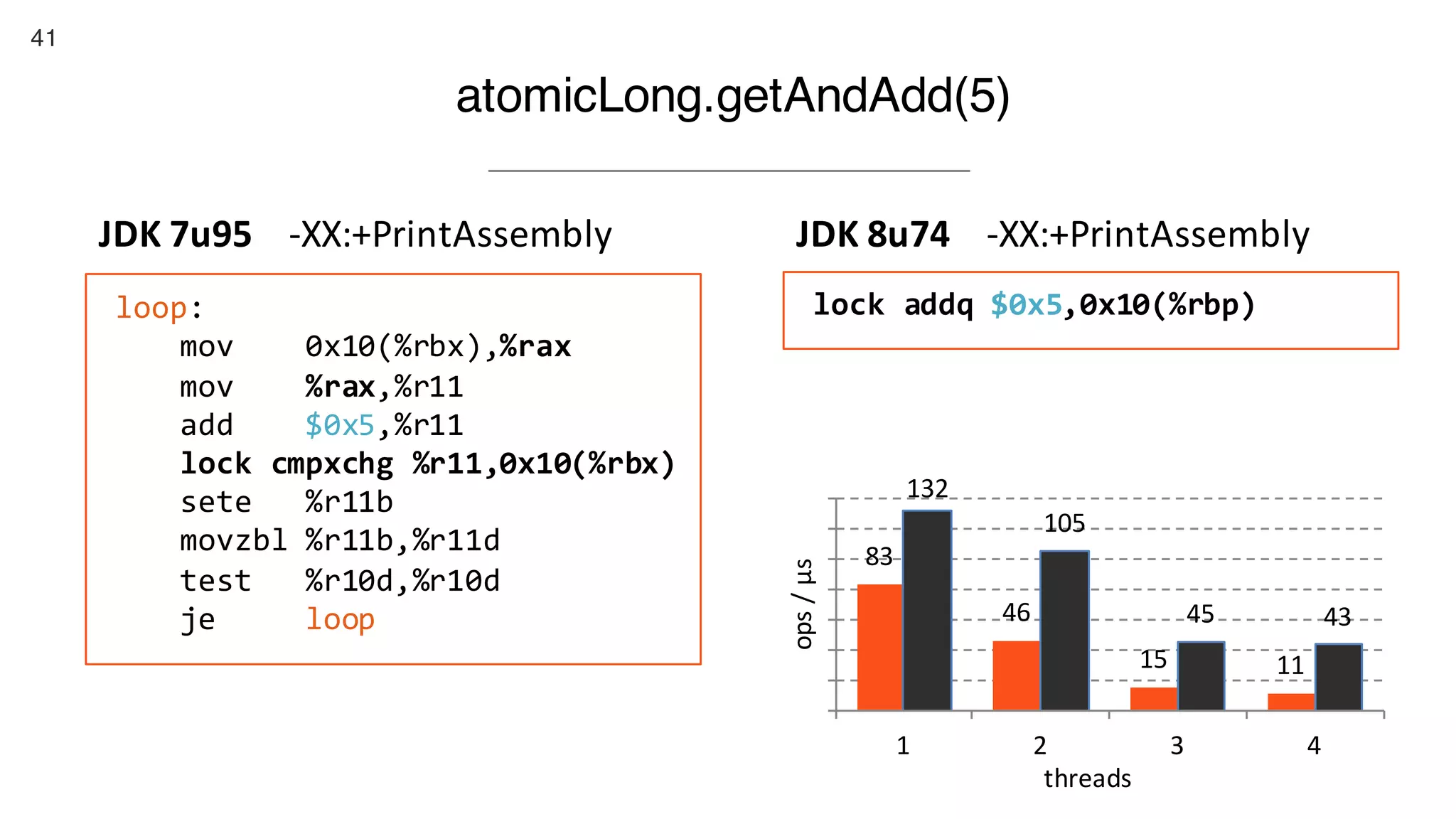
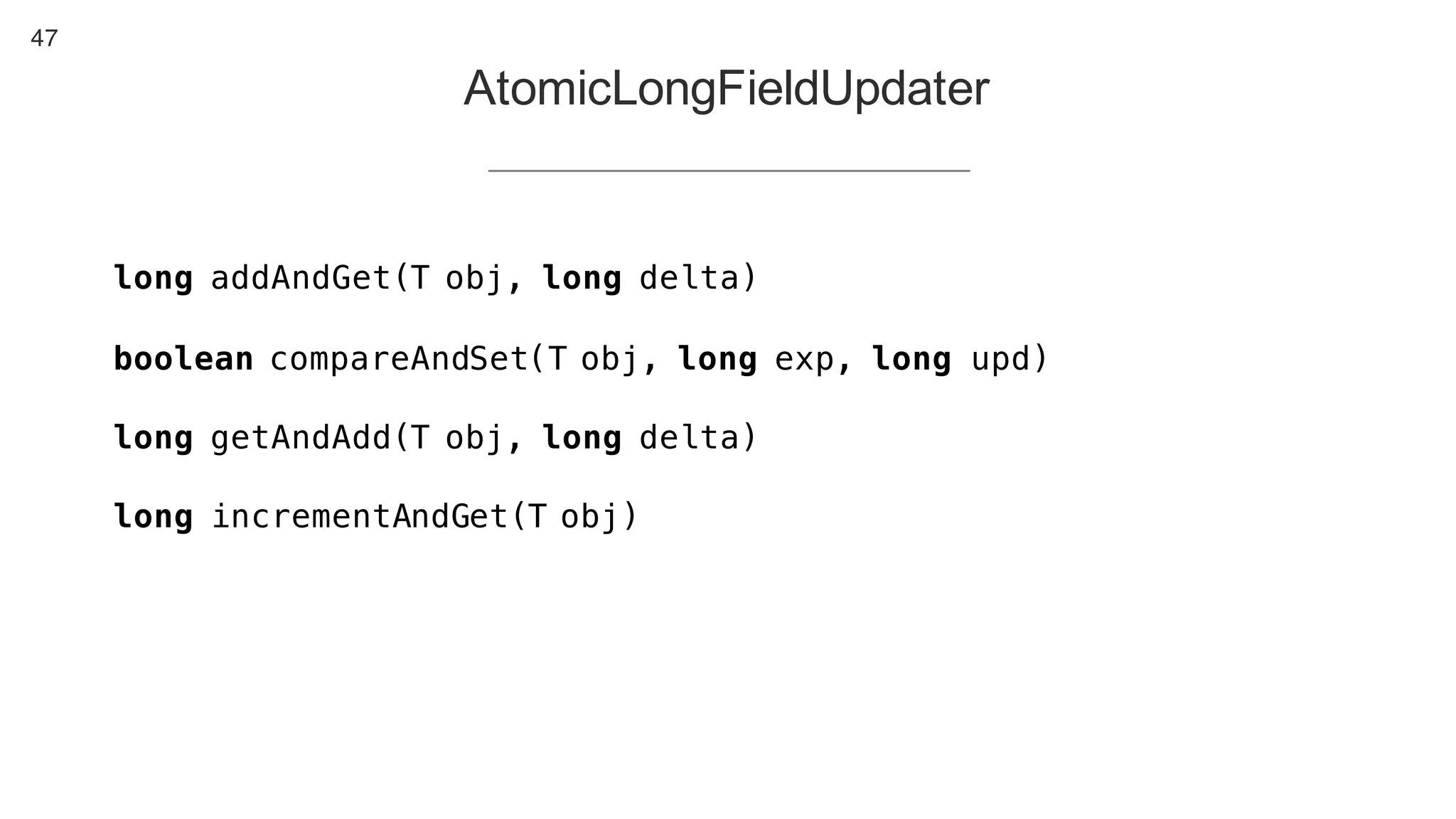
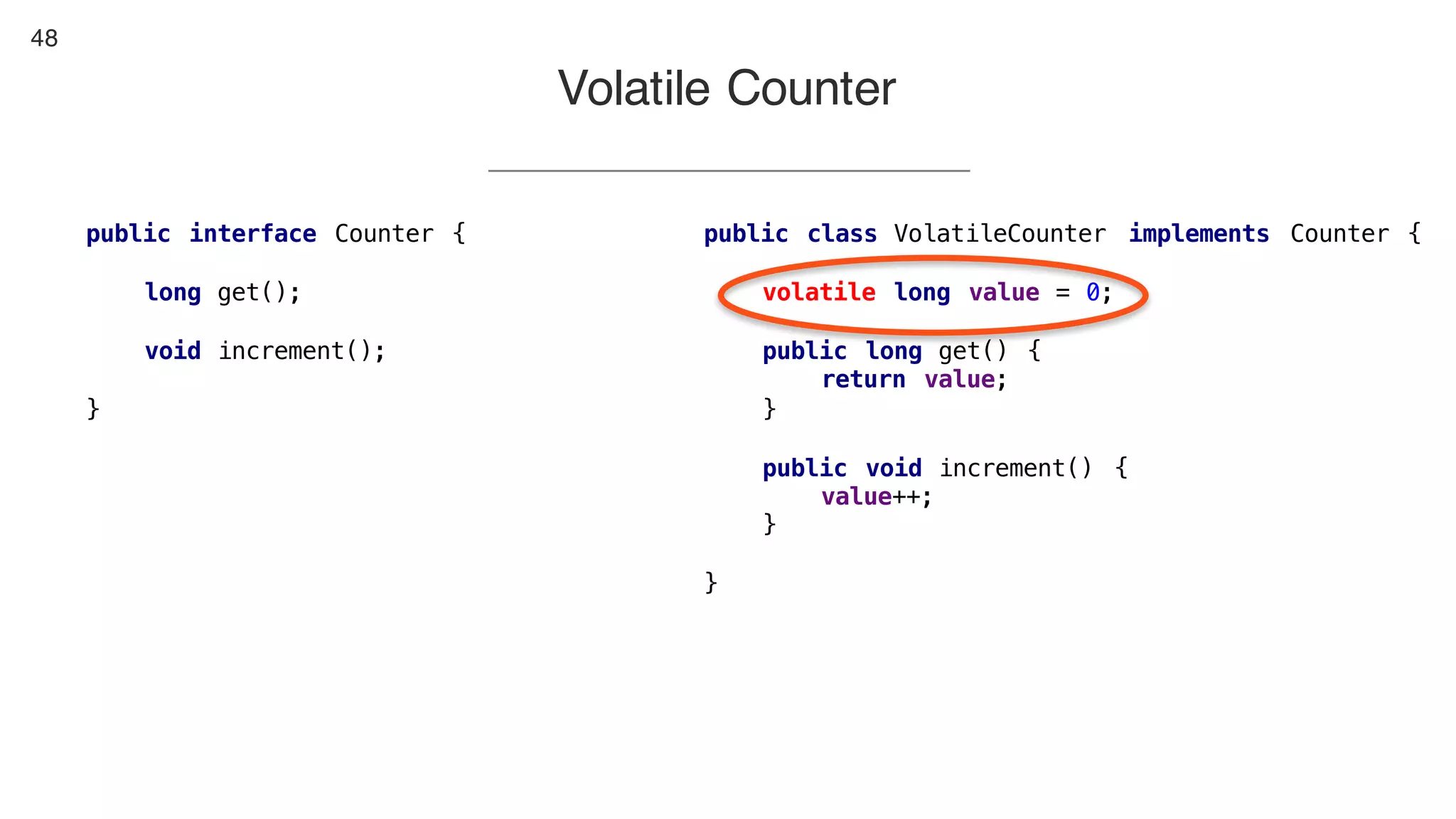
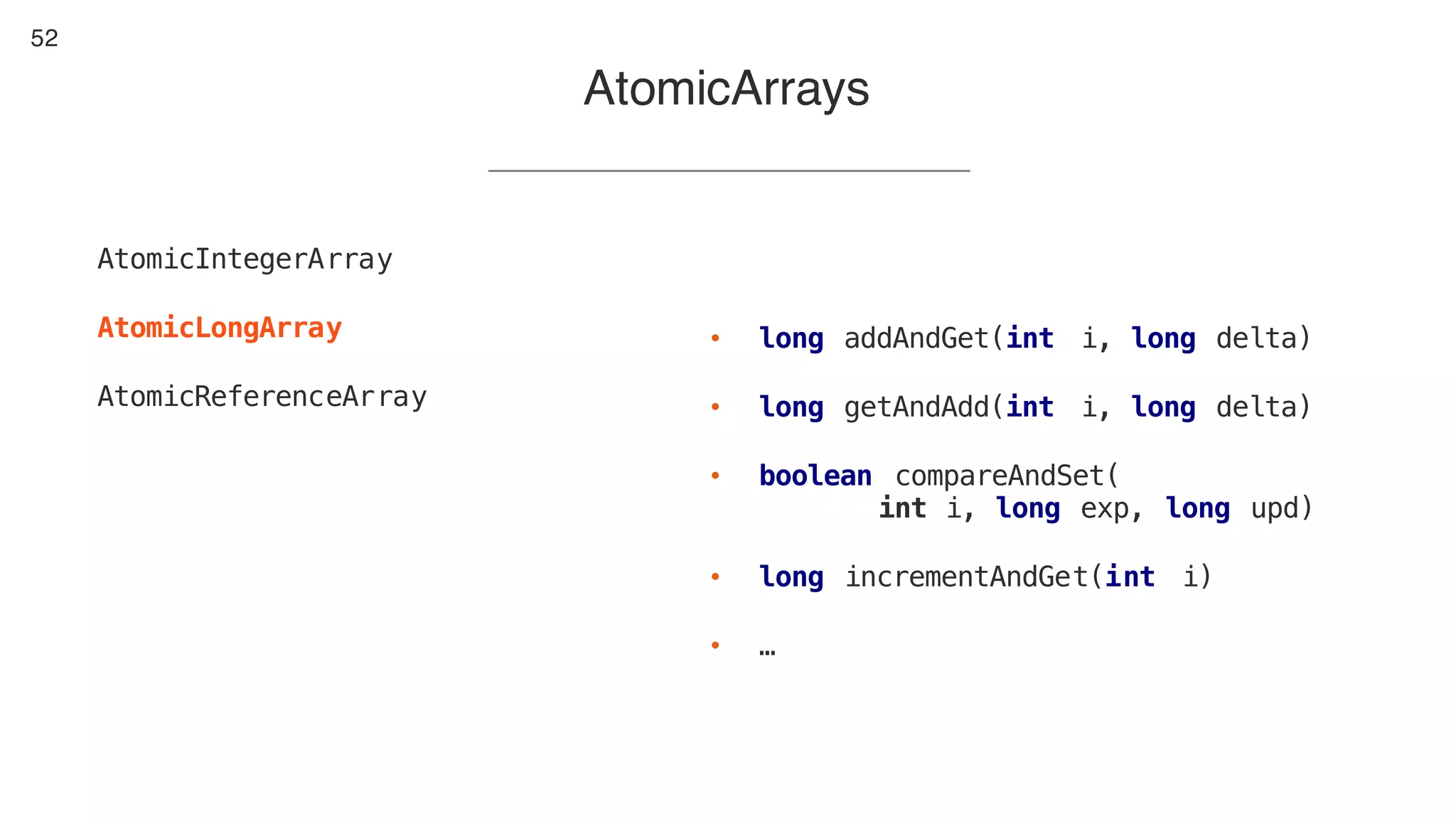
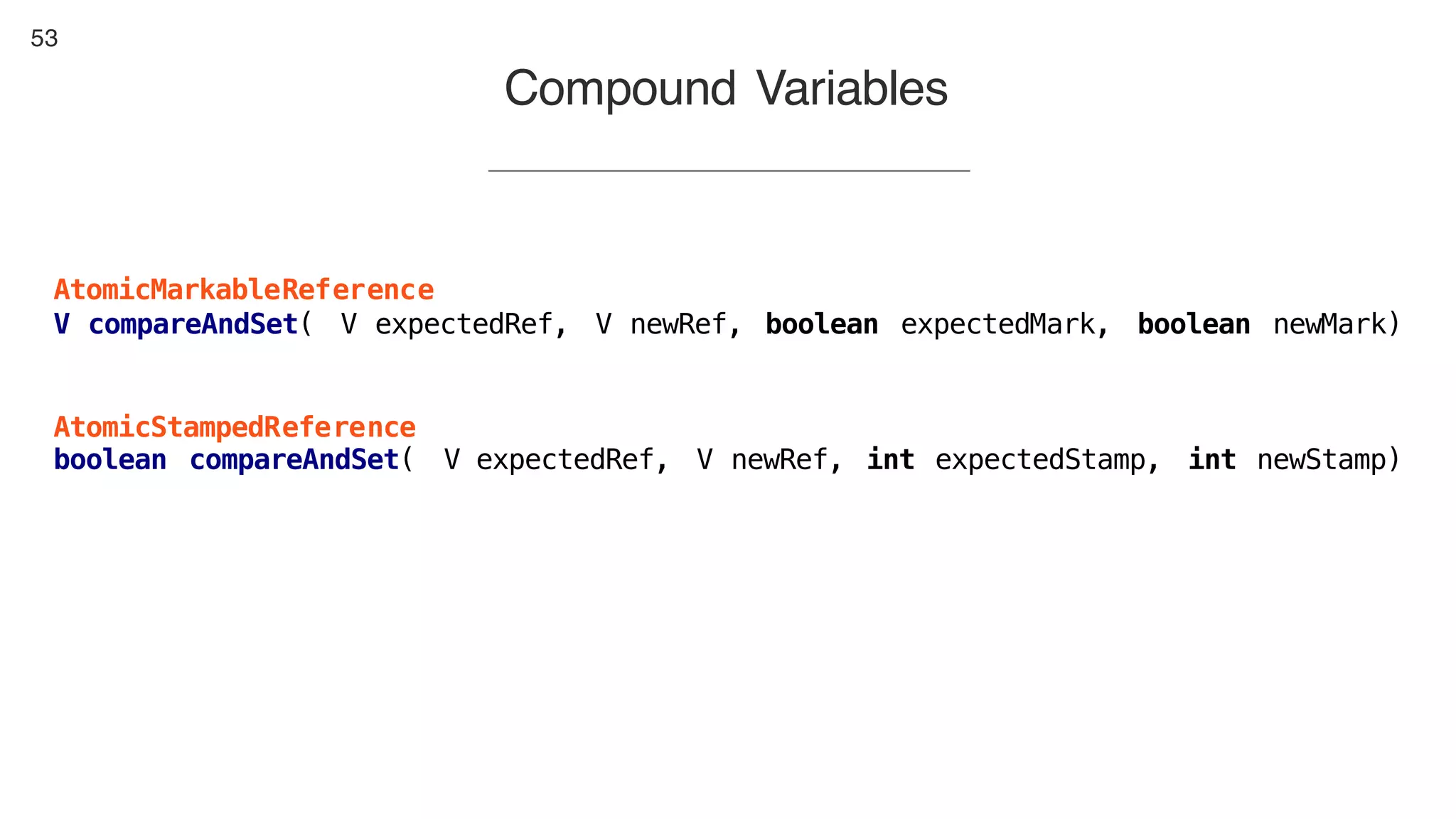
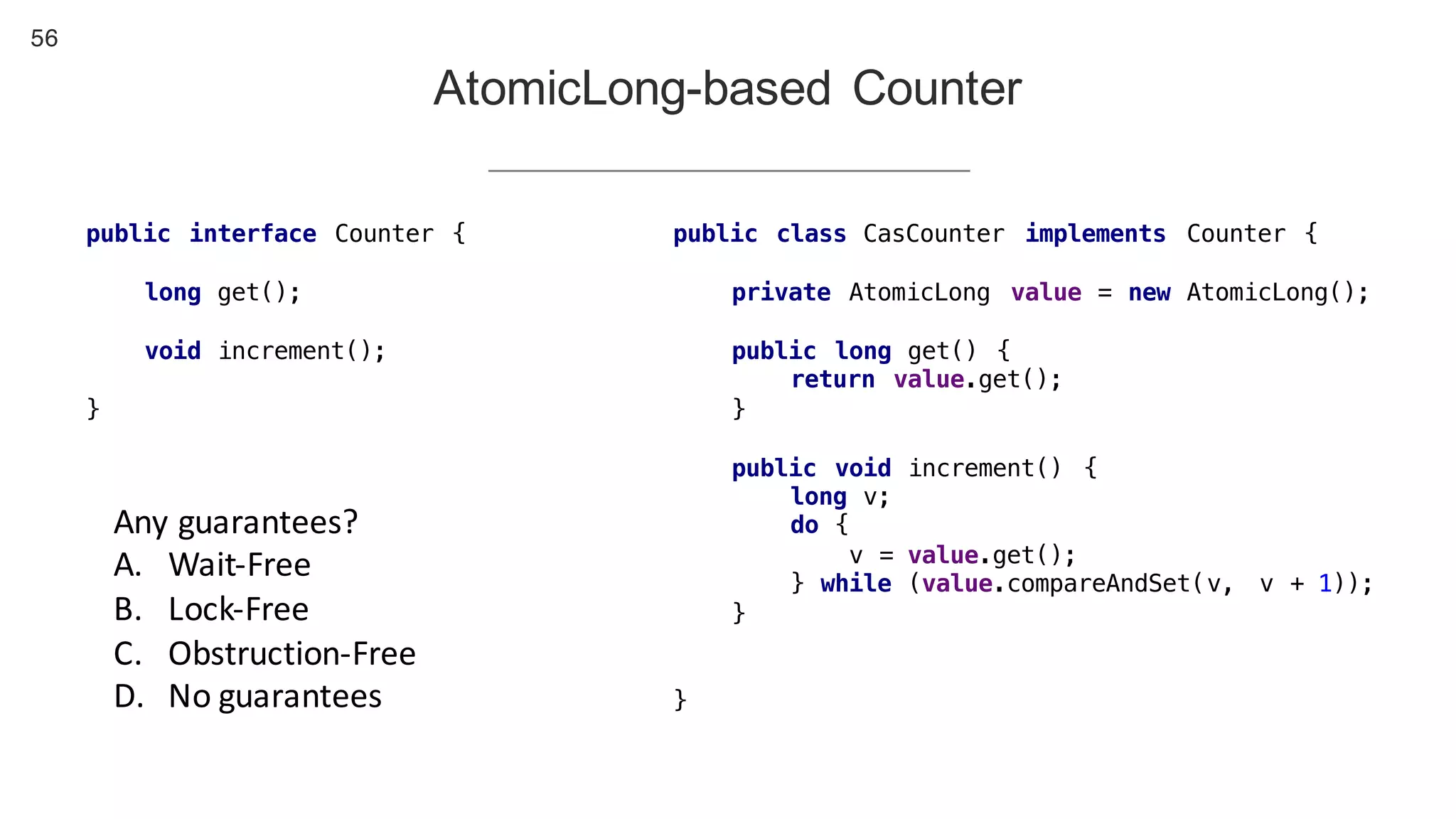
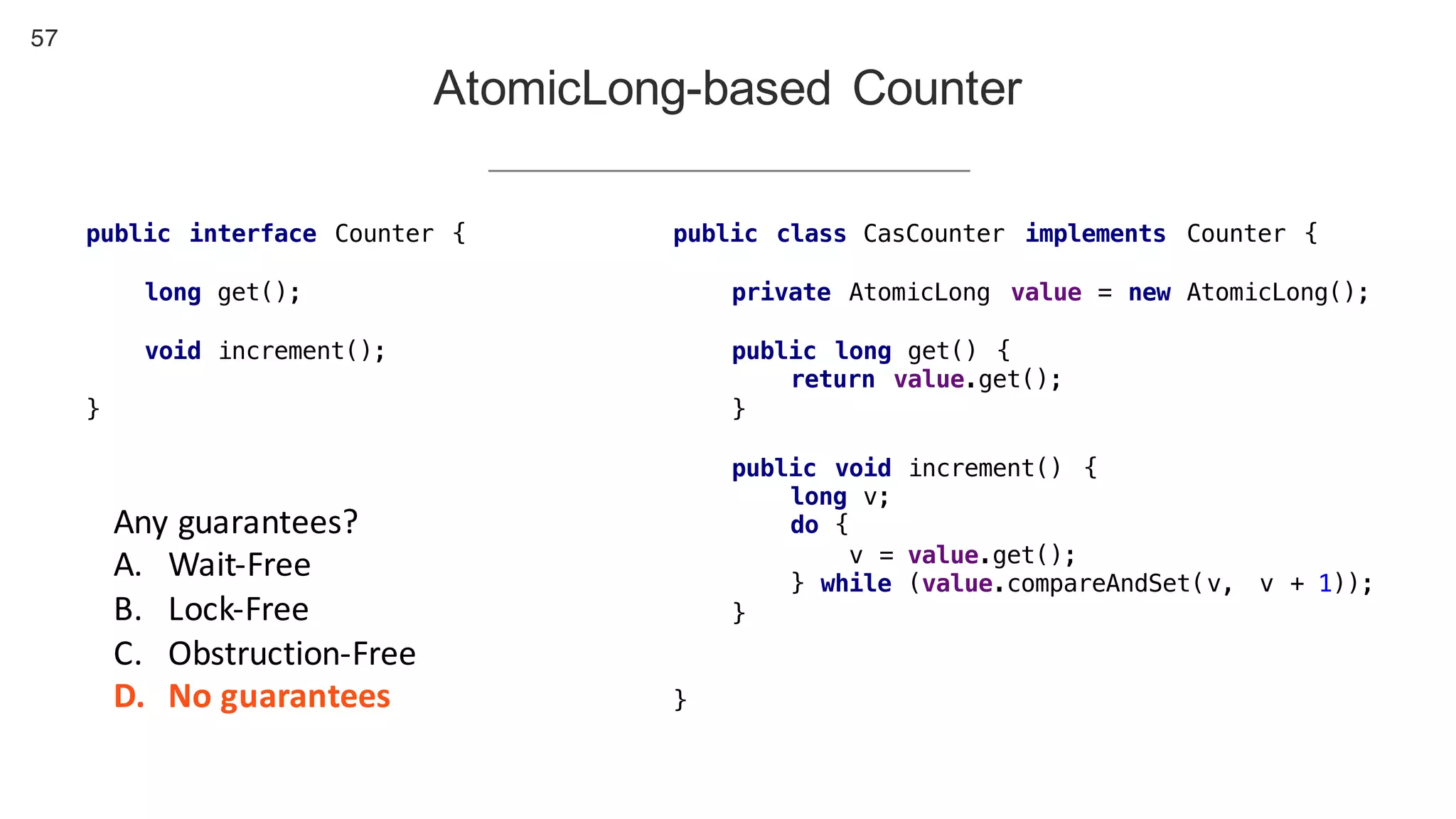
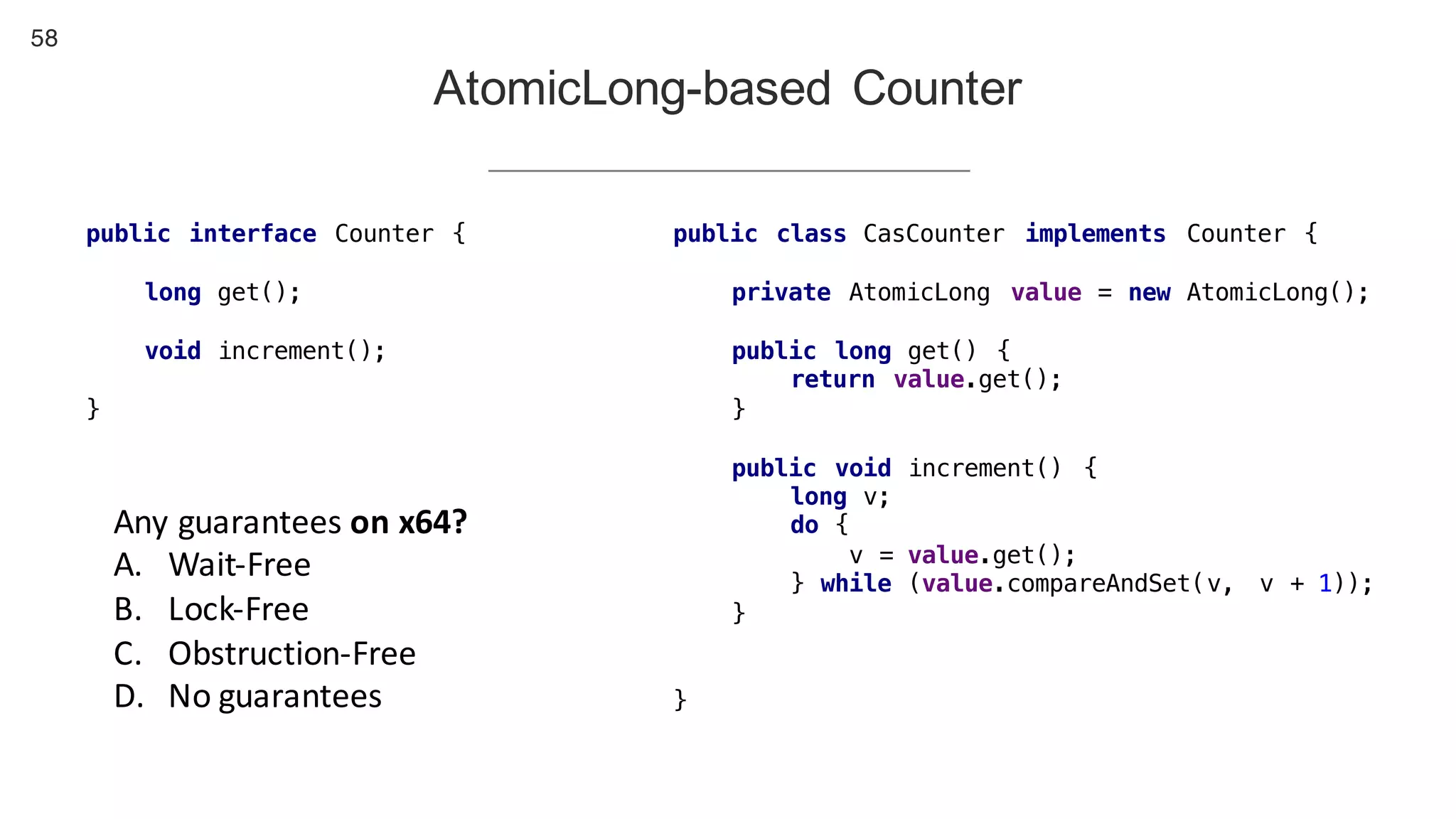
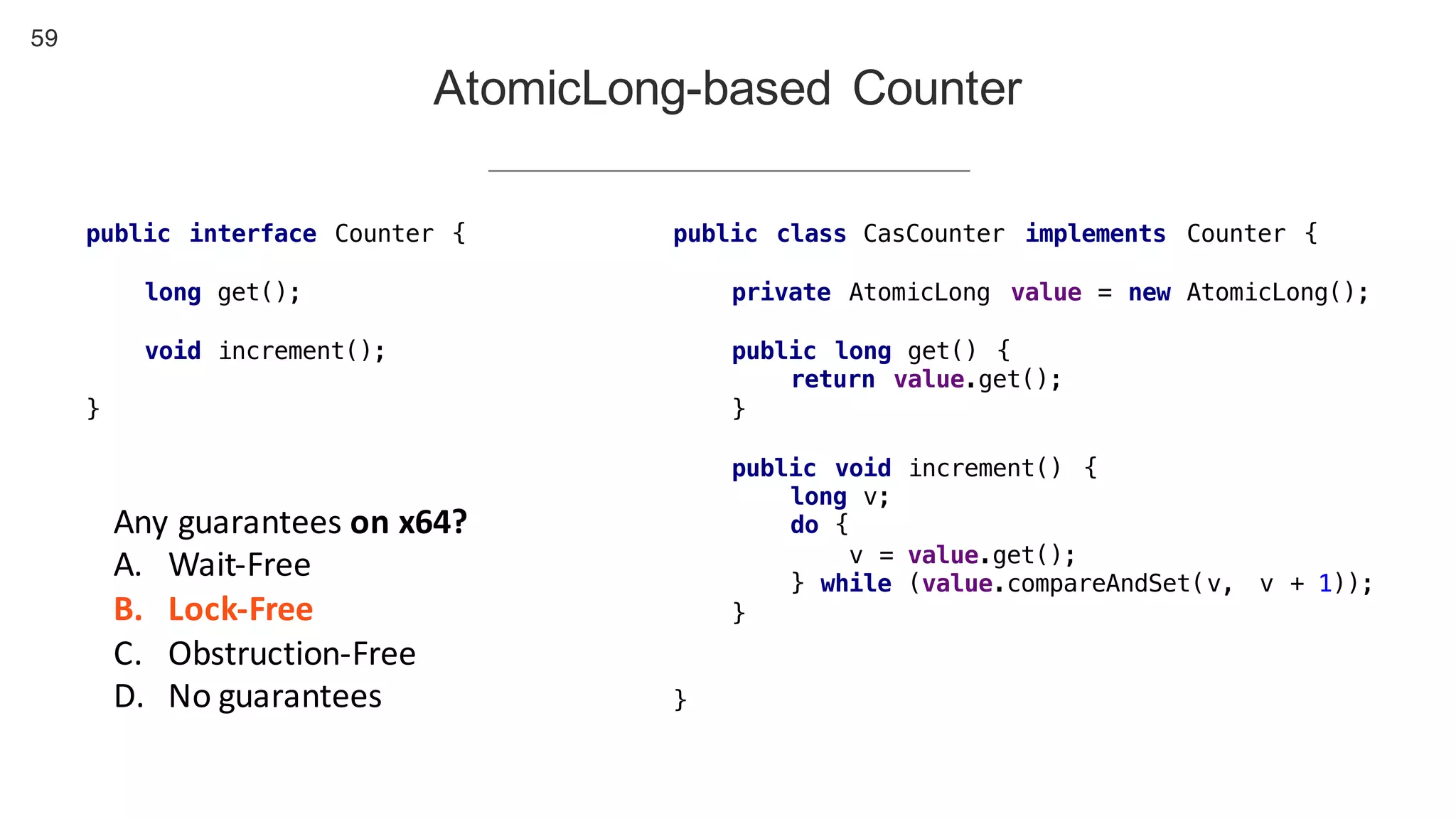
This document contains notes from a presentation on non-blocking synchronization. It introduces concepts like concurrency, locking, compare-and-swap (CAS) operations, and how they are implemented in Java using classes like AtomicLong. CAS allows updating shared memory without locking, but can involve retries if the expected value changes. Java provides various atomic data structures like scalars, arrays, and accumulators that have lock-free or obstruction-free guarantees. Non-blocking data structures like lock-free stacks and queues are also discussed.