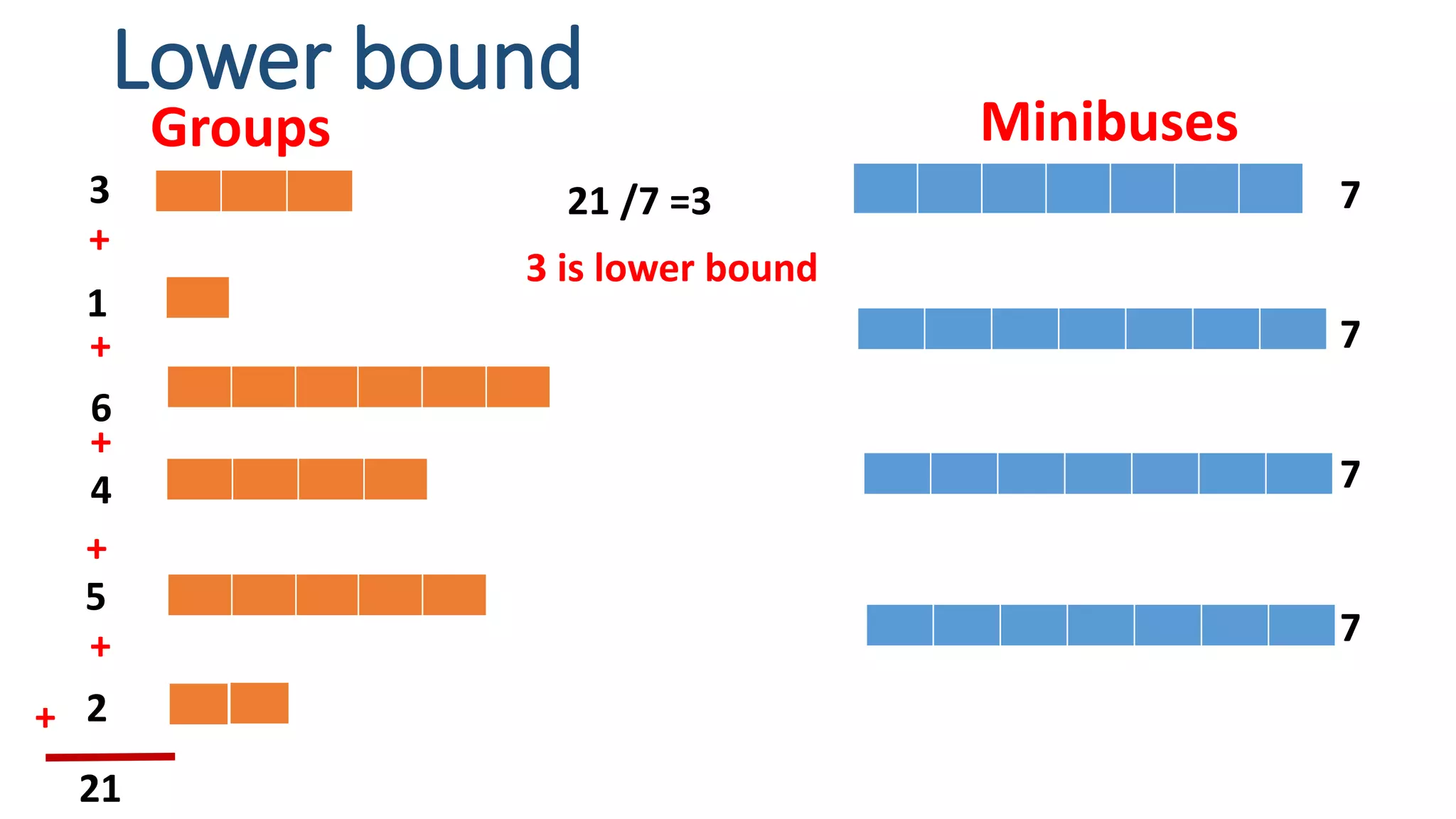
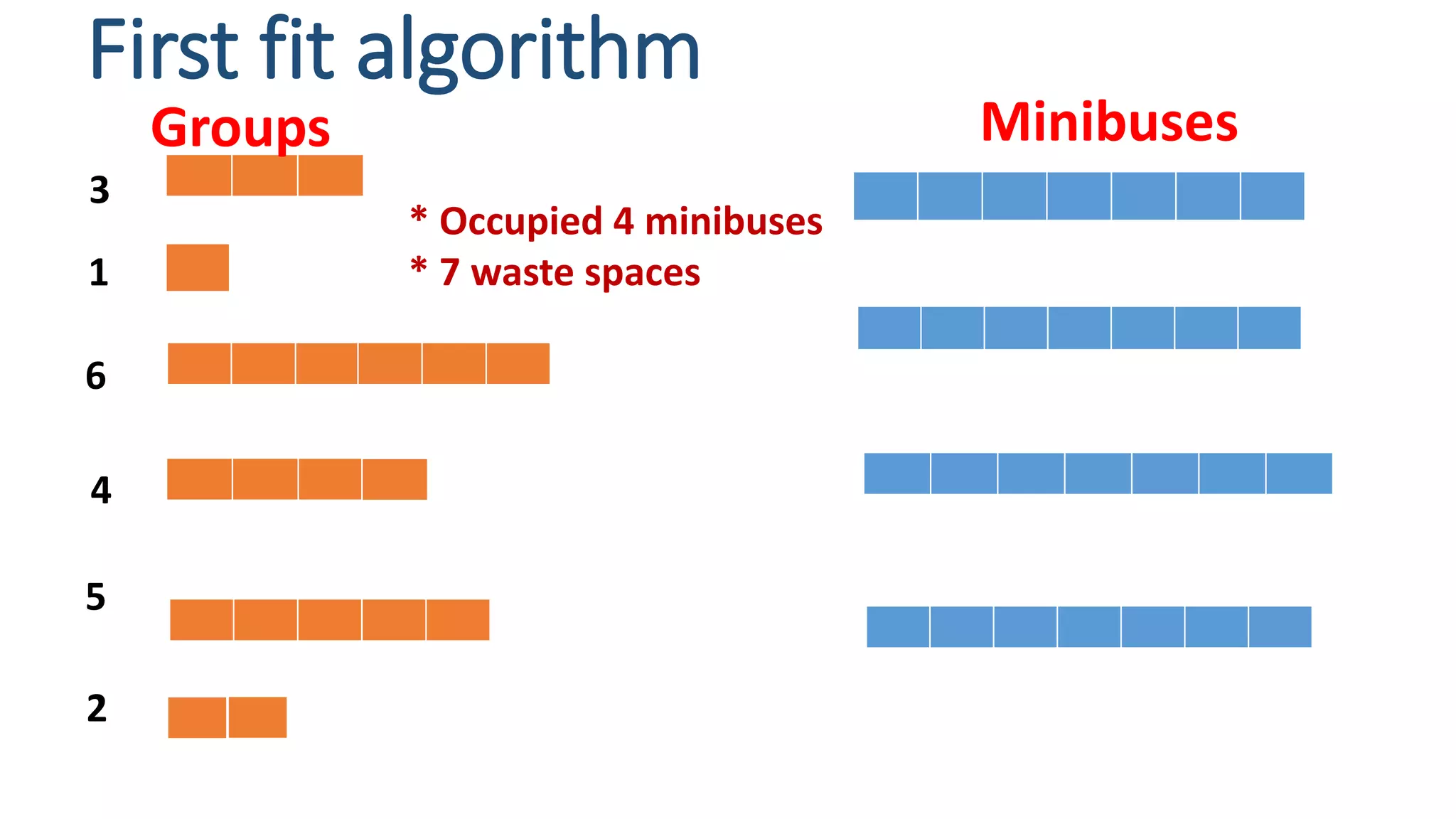
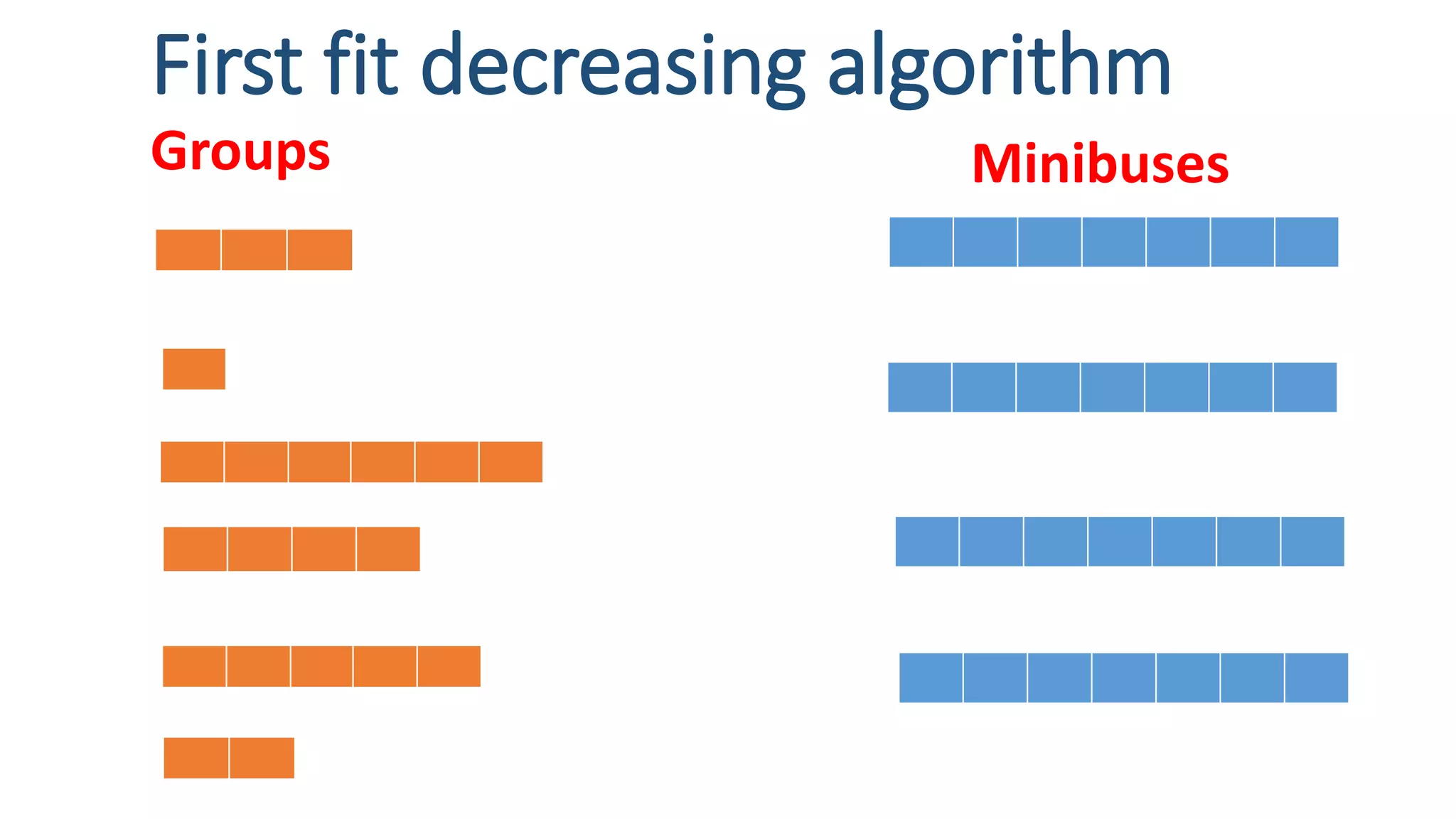
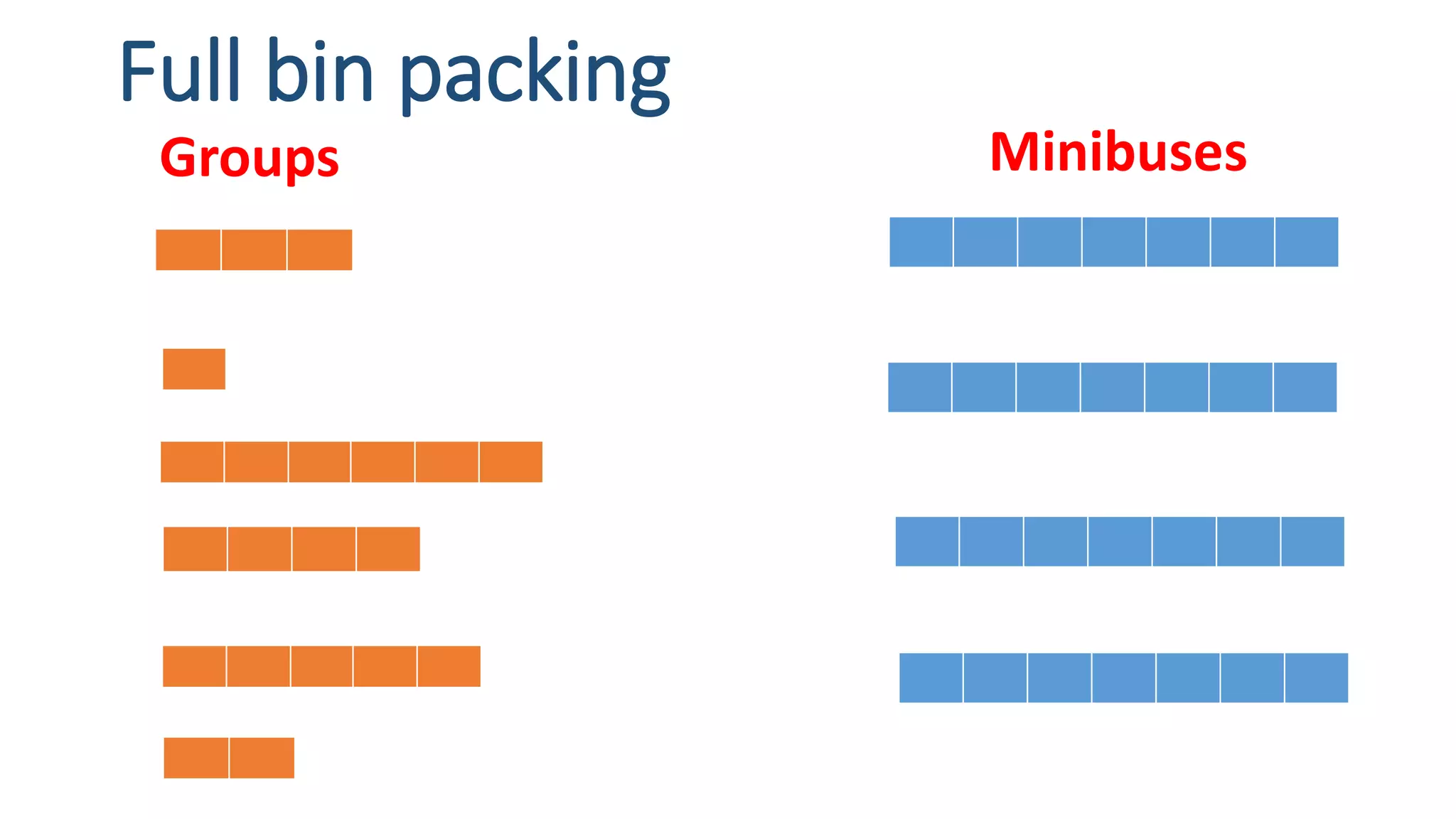
This document discusses two NP problems: graph coloring and bin packing. It provides pseudocode for a graph coloring algorithm that uses backtracking to try all possible color combinations. The algorithm has a runtime of O(m*n) where m is the number of colors and n is the number of vertices. It also describes the bin packing problem of fitting groups of people onto buses and presents lower bound, first fit, first fit decreasing and full bin packing algorithms to solve it, noting their tradeoffs between speed and optimality.

![n 0 1 2 3
0 1 1 0 1
1 1 1 1 1
2 0 1 1 1
3 1 1 1 1
3 2
10 Graphcolor(int k)
{
for(Int c =1 ;c<=m;c++)
{
if (isSafe(k,c)){
x[k]=c;
if((k+1))<n)
Graphcolor(k+1)
else
print x[]; return
}
}
}
k =Current node
c =colour
n = total nodes
0 1 2
1 2 3X[k]=
ifSafe(int k, int c)
{
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
if(G[k][i] ==1 && c==x[i])
{
return false;
}
}
return true;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/daa-190131074307/75/Non-Deterministic-and-Deterministic-Problems-3-2048.jpg)