Embed presentation
Download to read offline



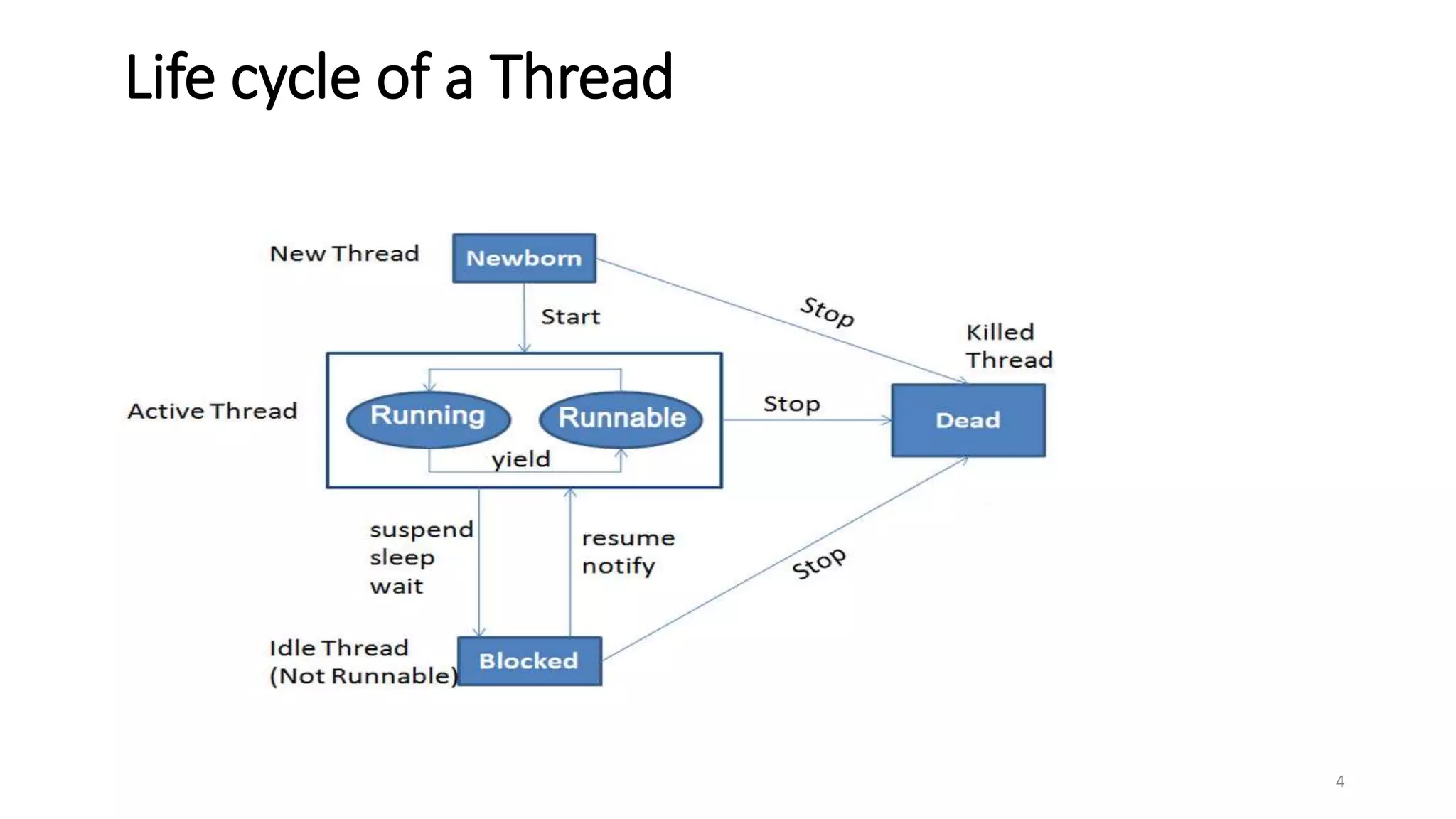

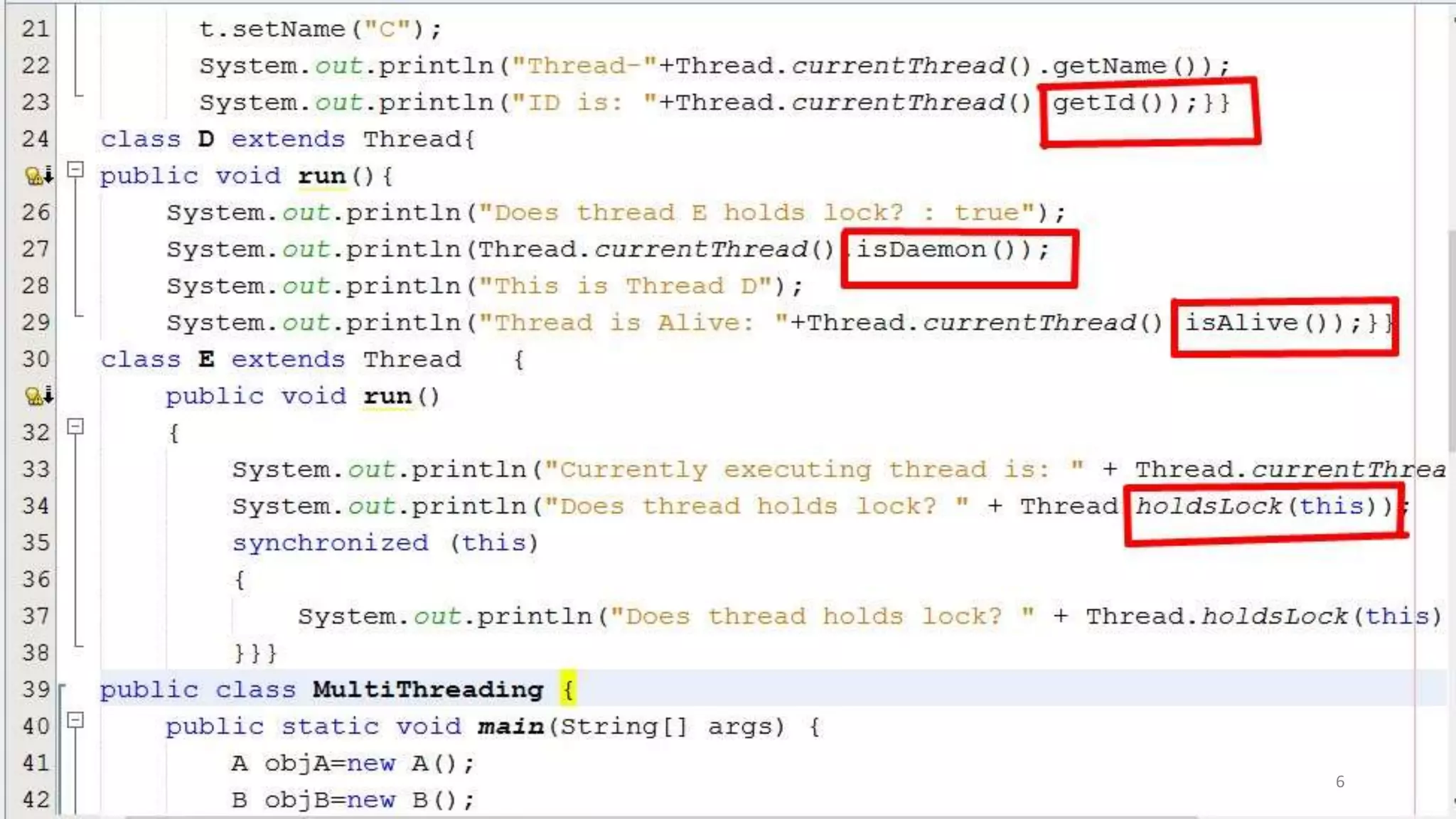
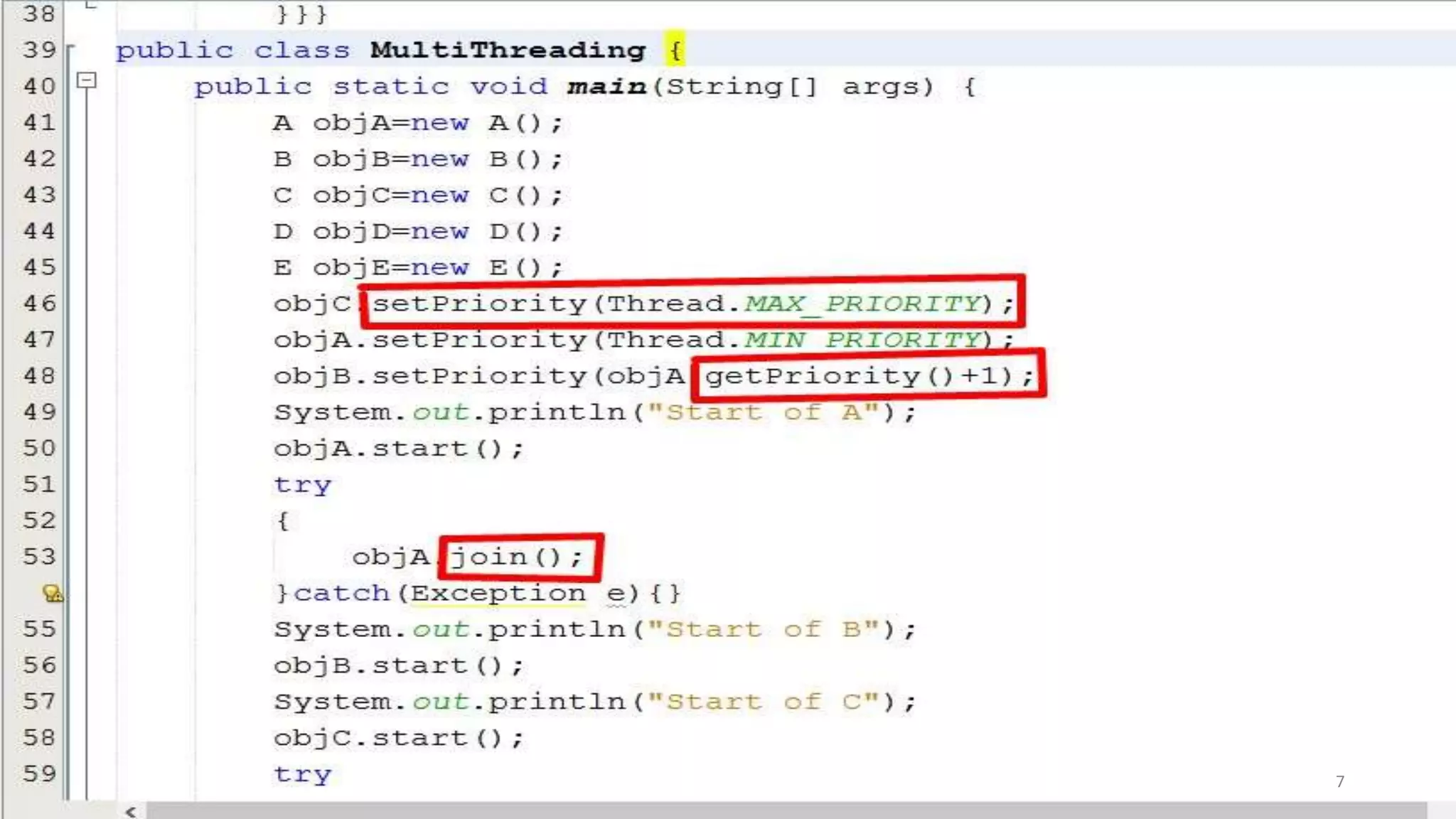
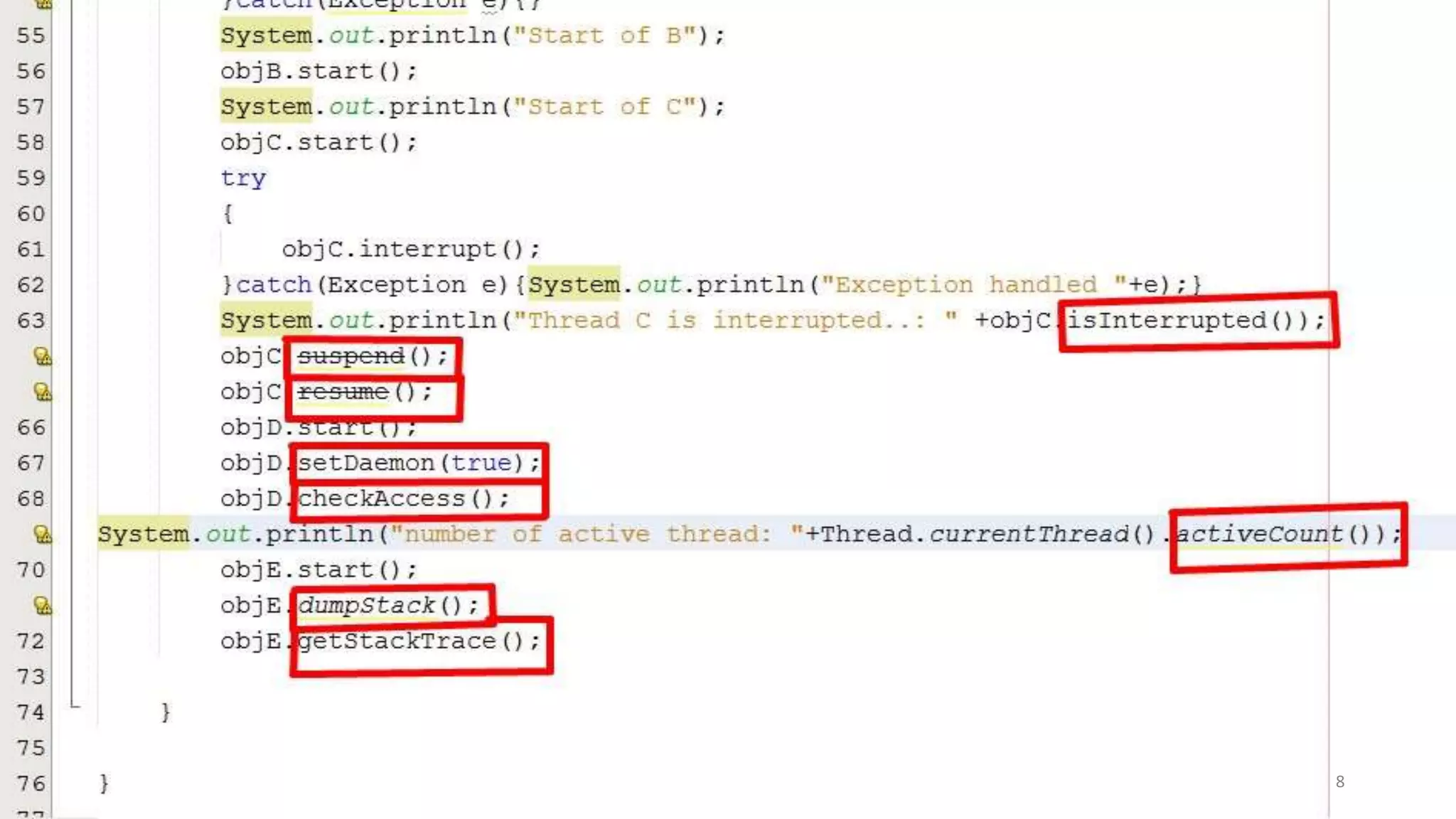



A thread is the smallest unit of processing in a program that allows for parallel execution. Multithreading allows a program to be divided into multiple threads that can run simultaneously, sharing system resources. The advantages of multithreading in Java include performing multiple operations concurrently without blocking the user, improving performance and responsiveness, and better utilizing CPU resources through parallel processing.










