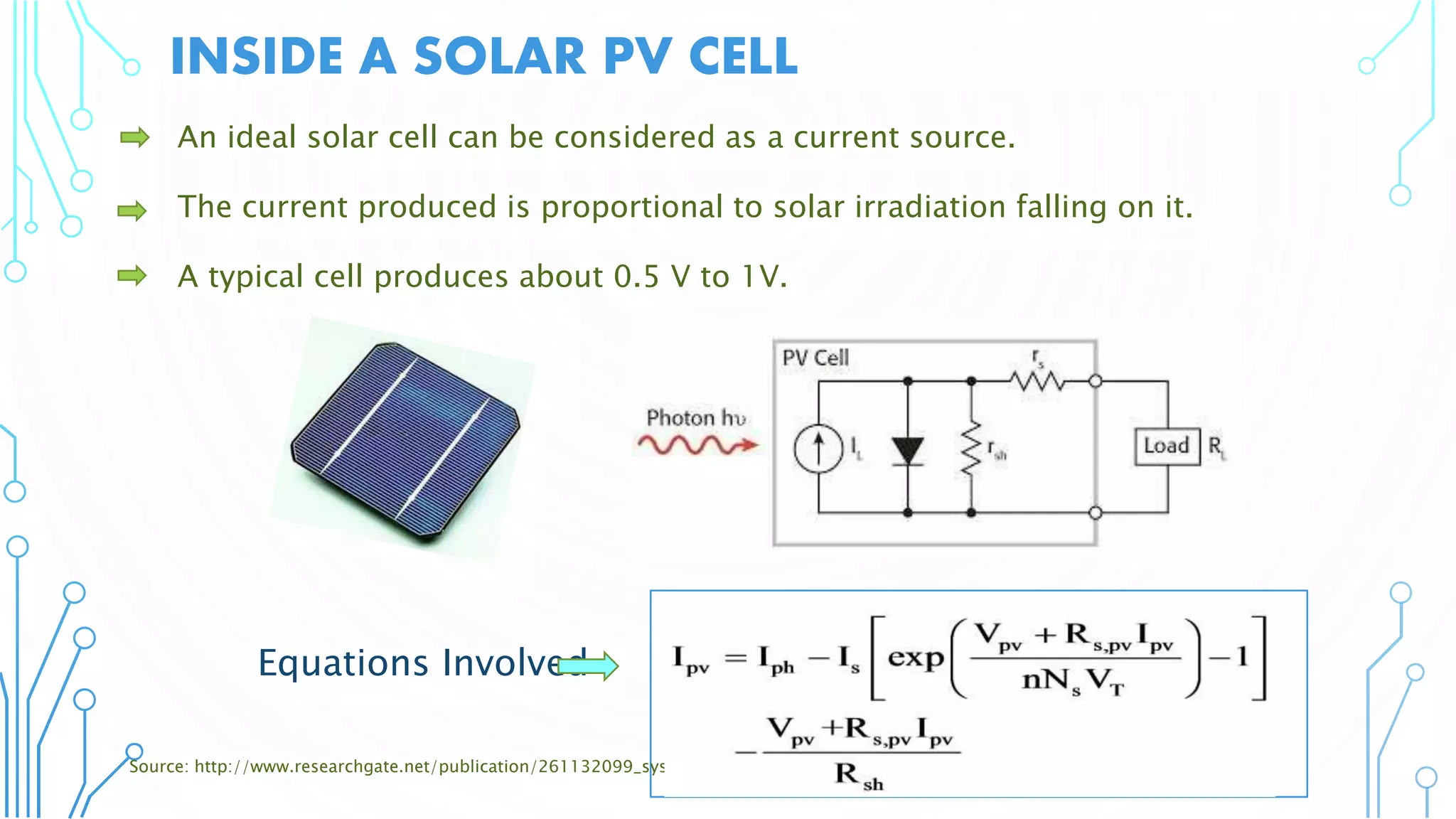
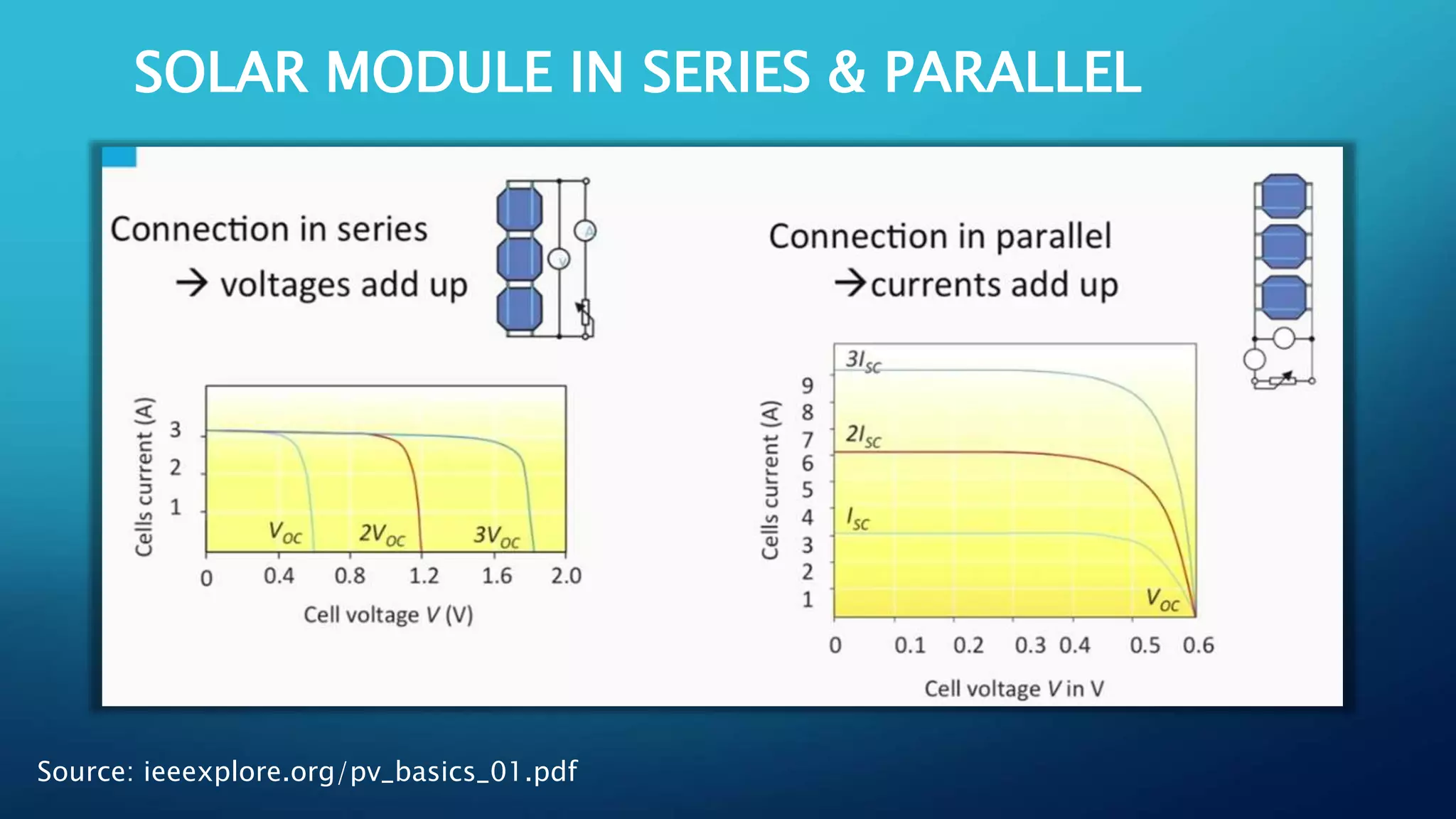
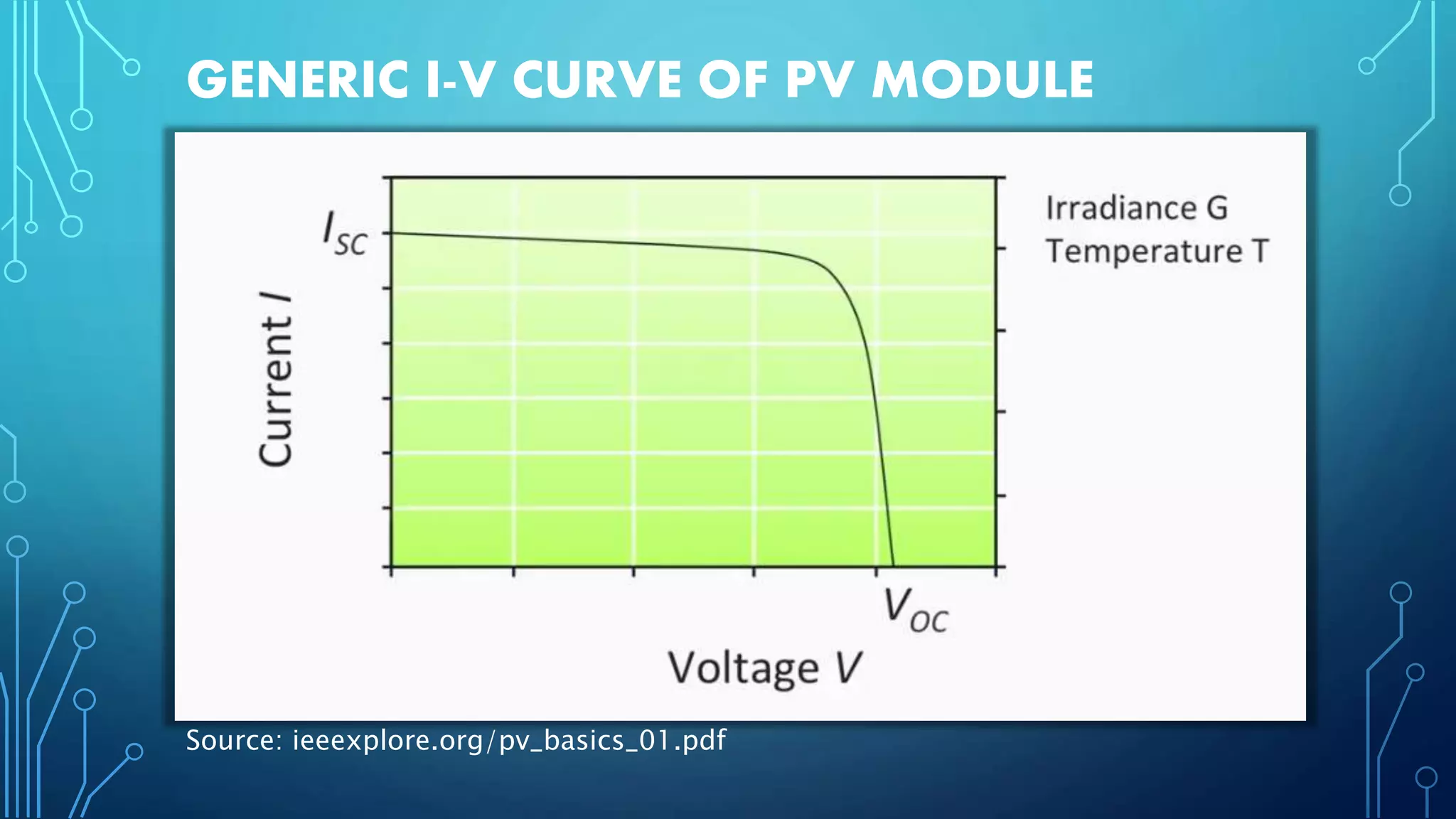
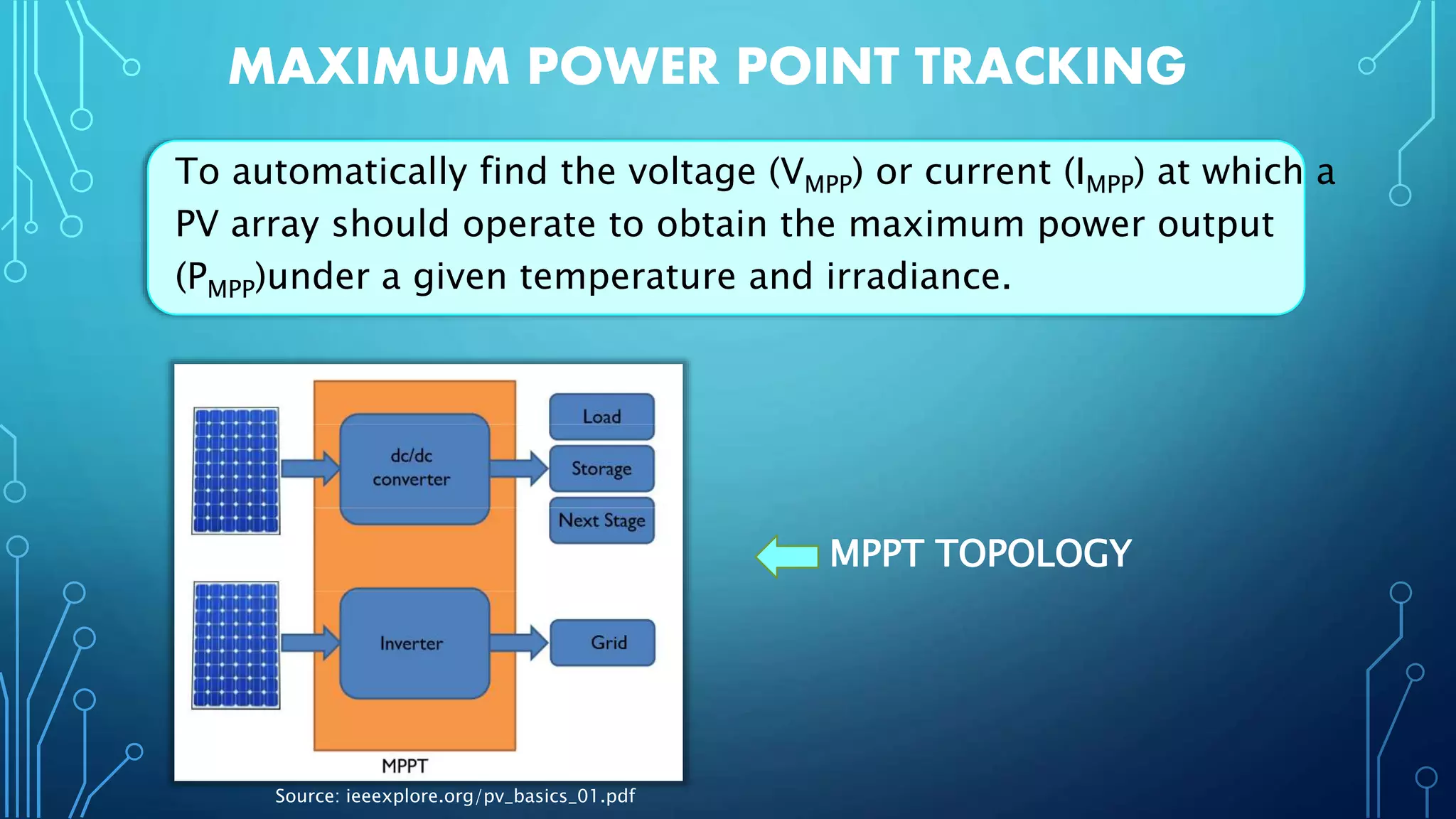
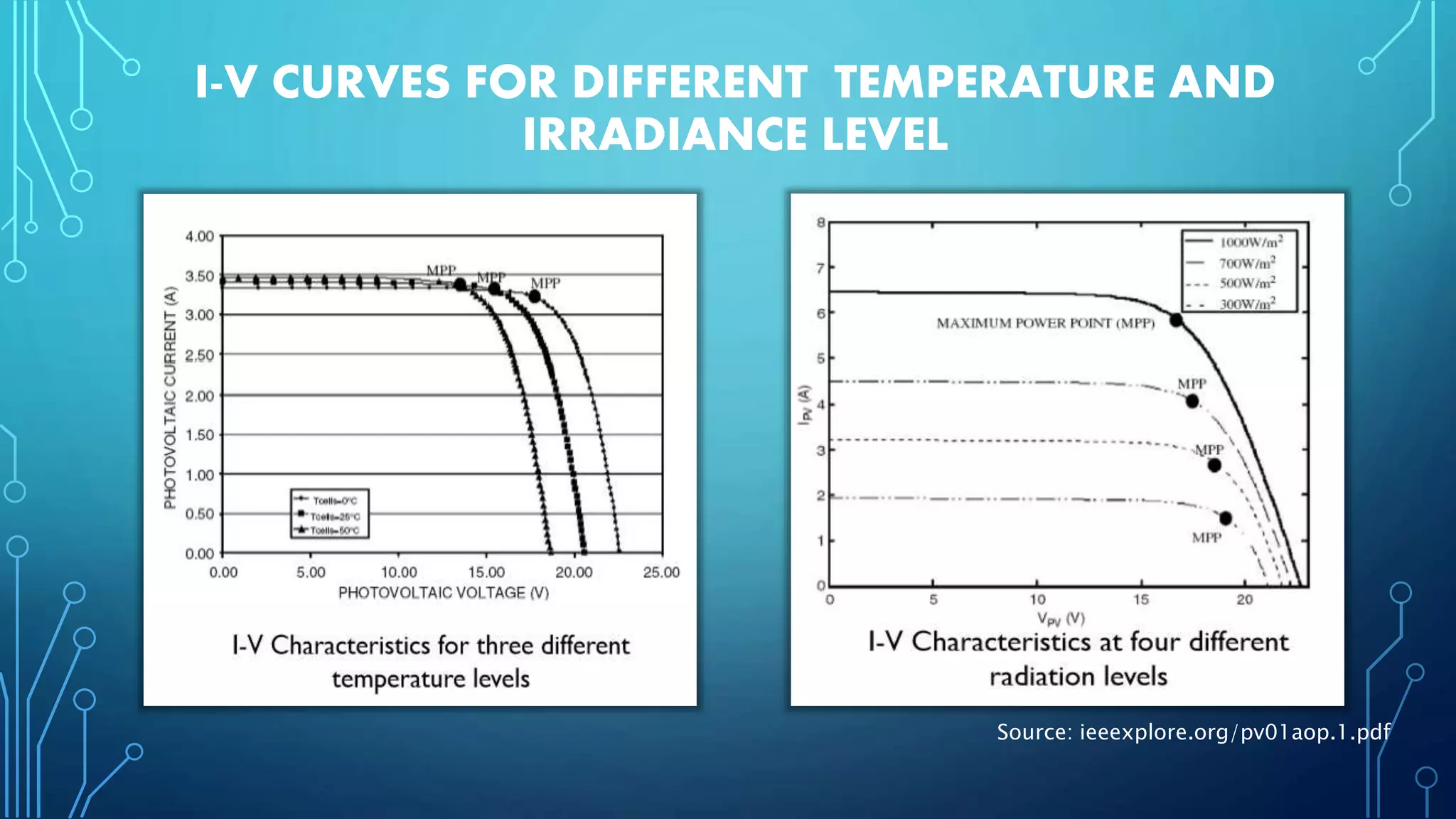
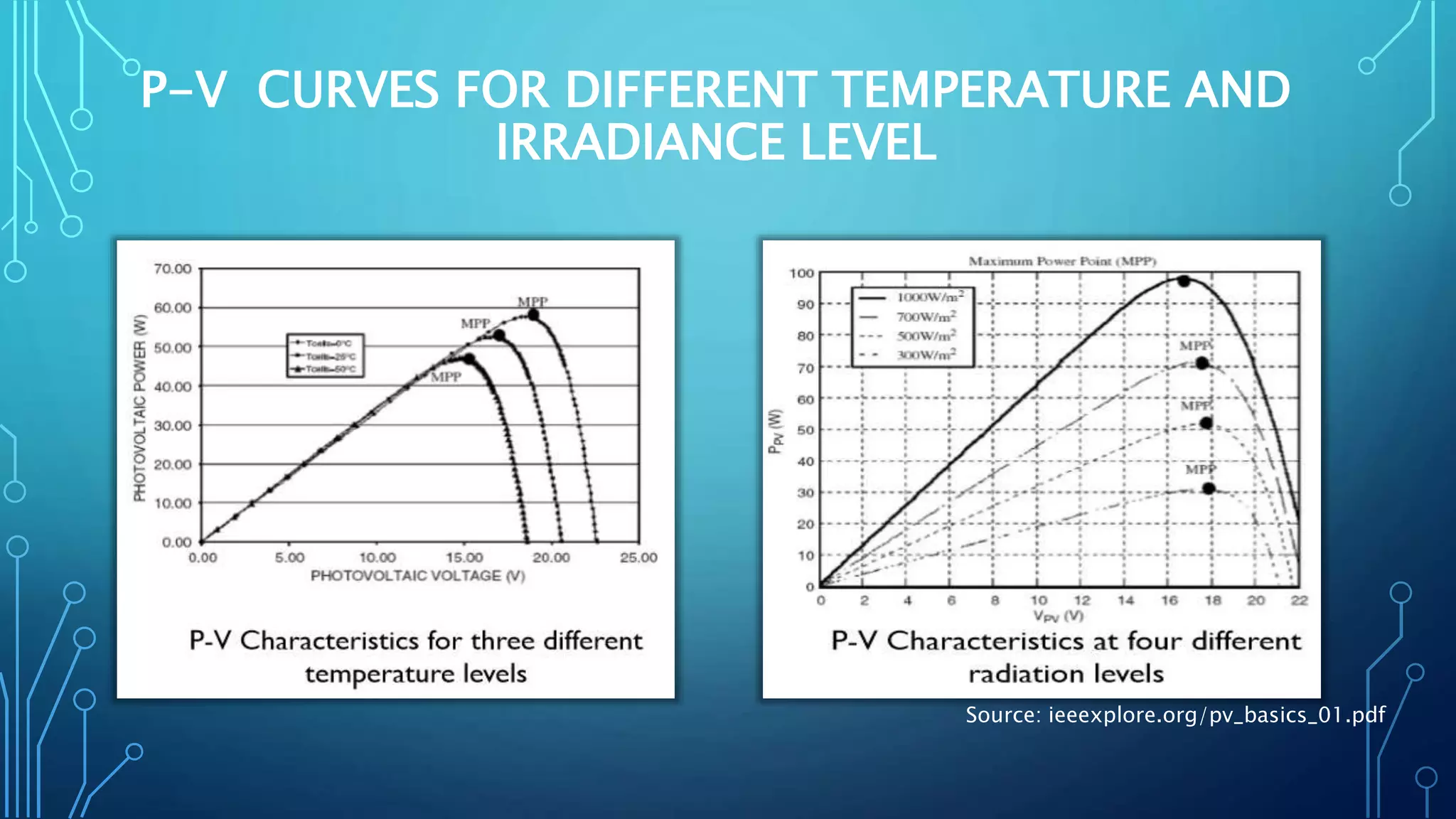
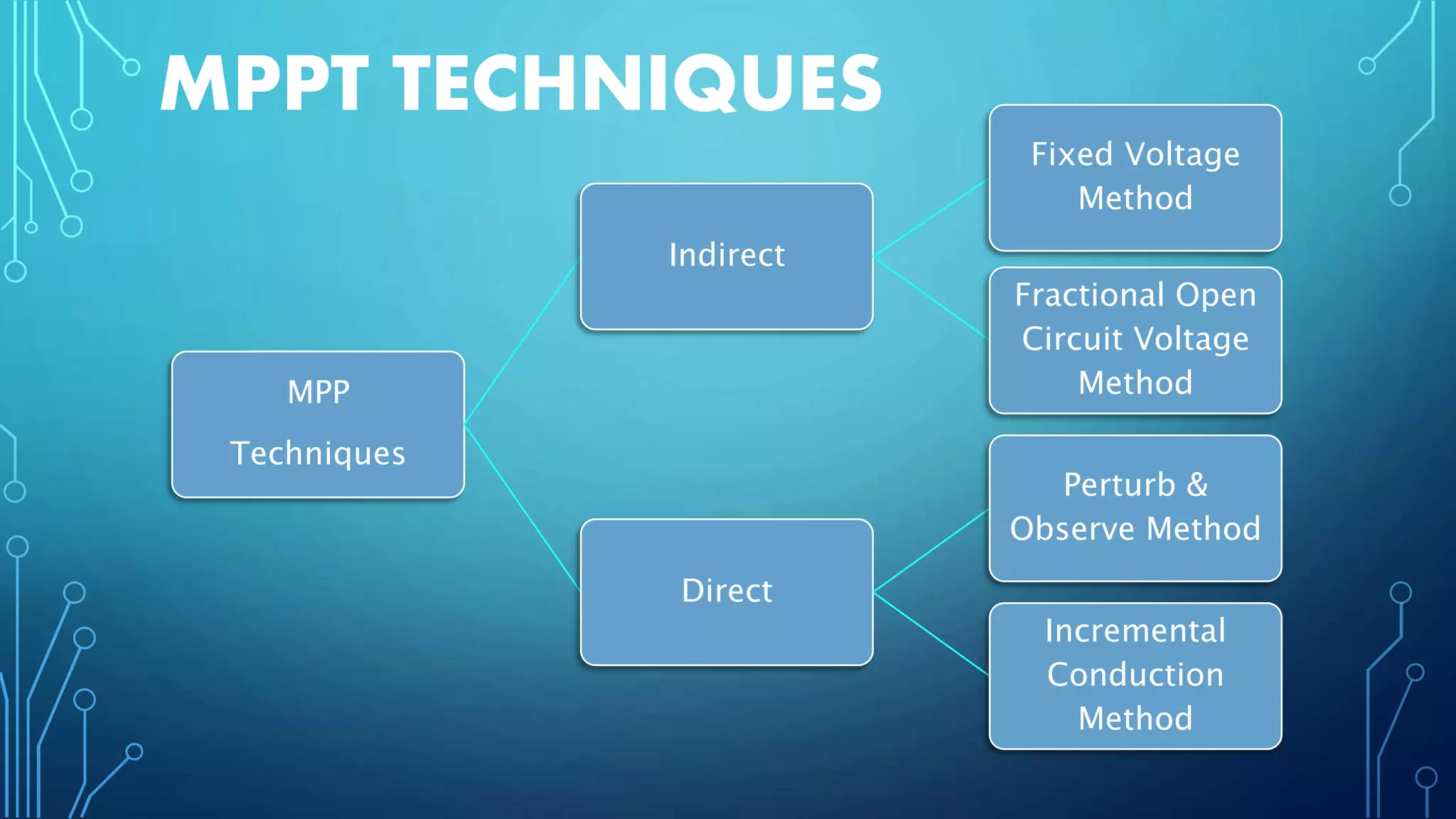
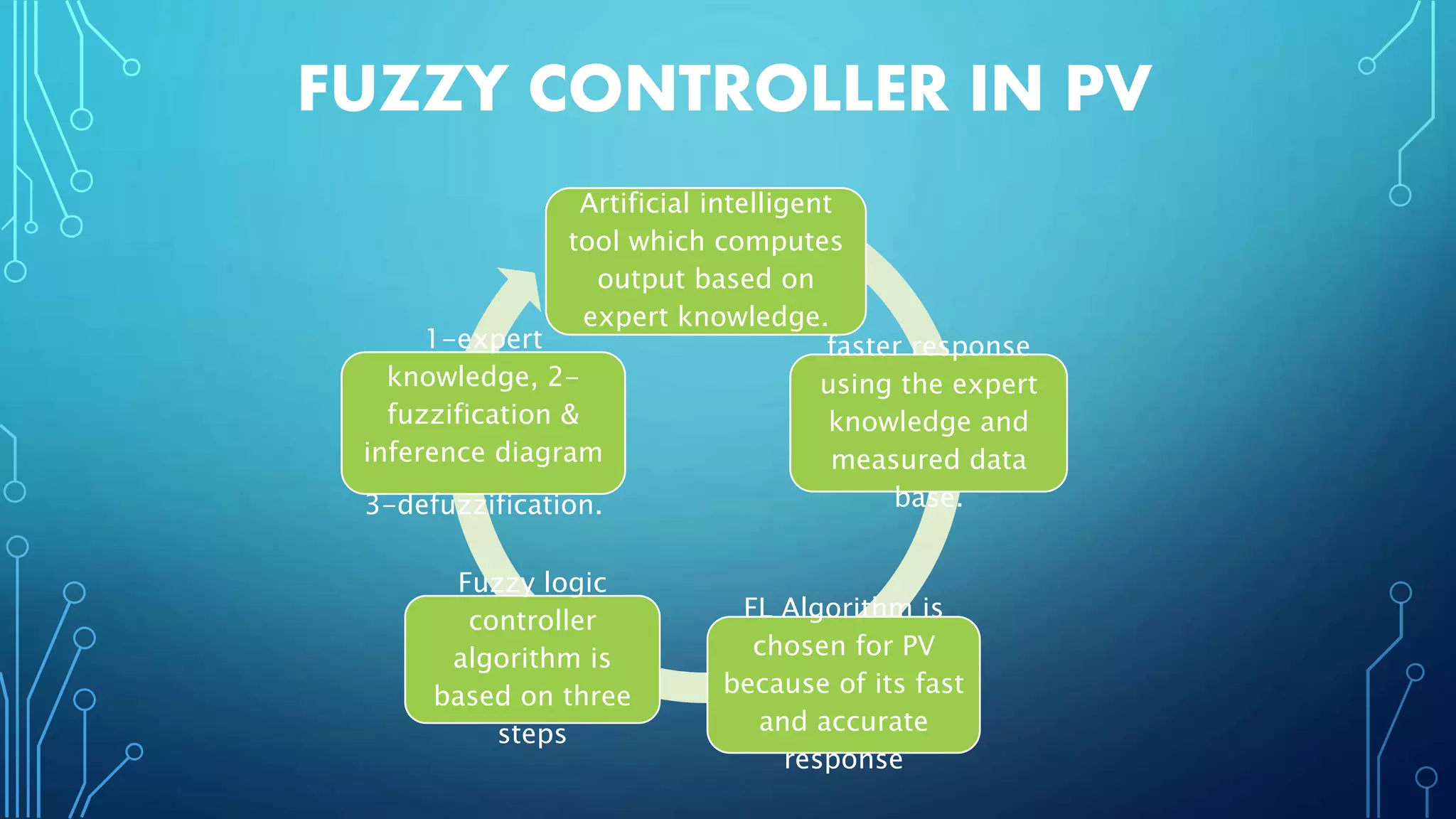
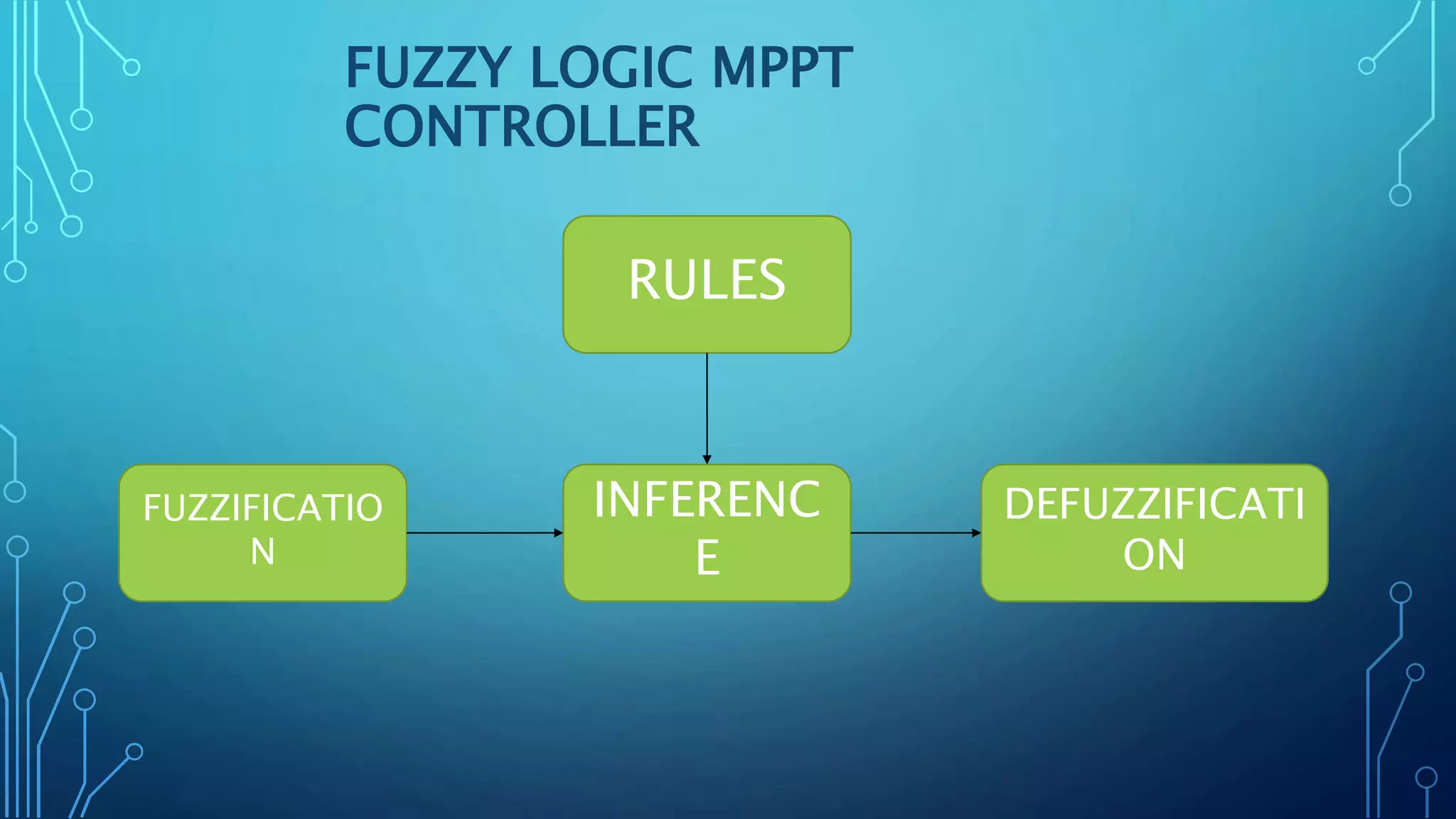
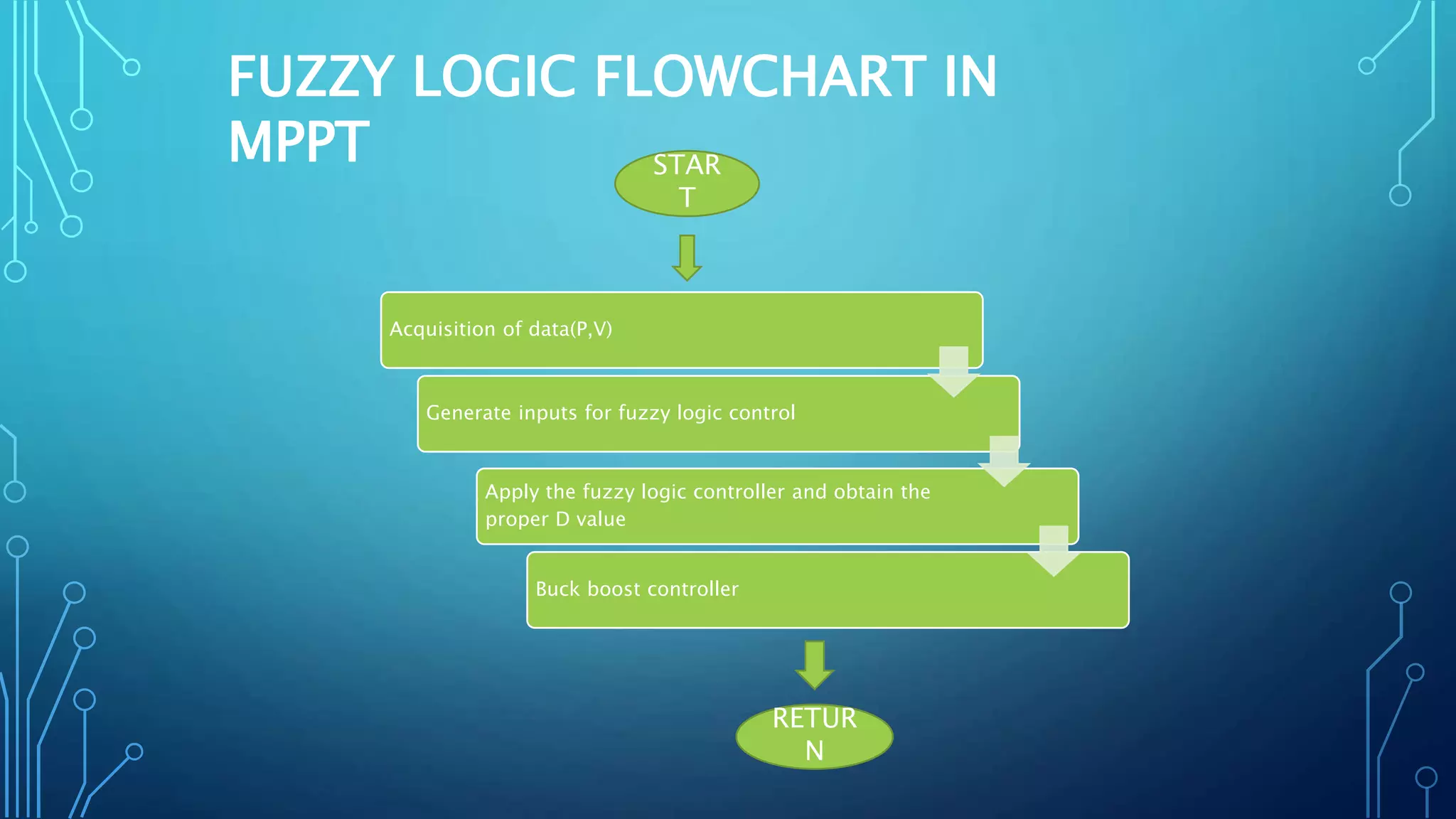
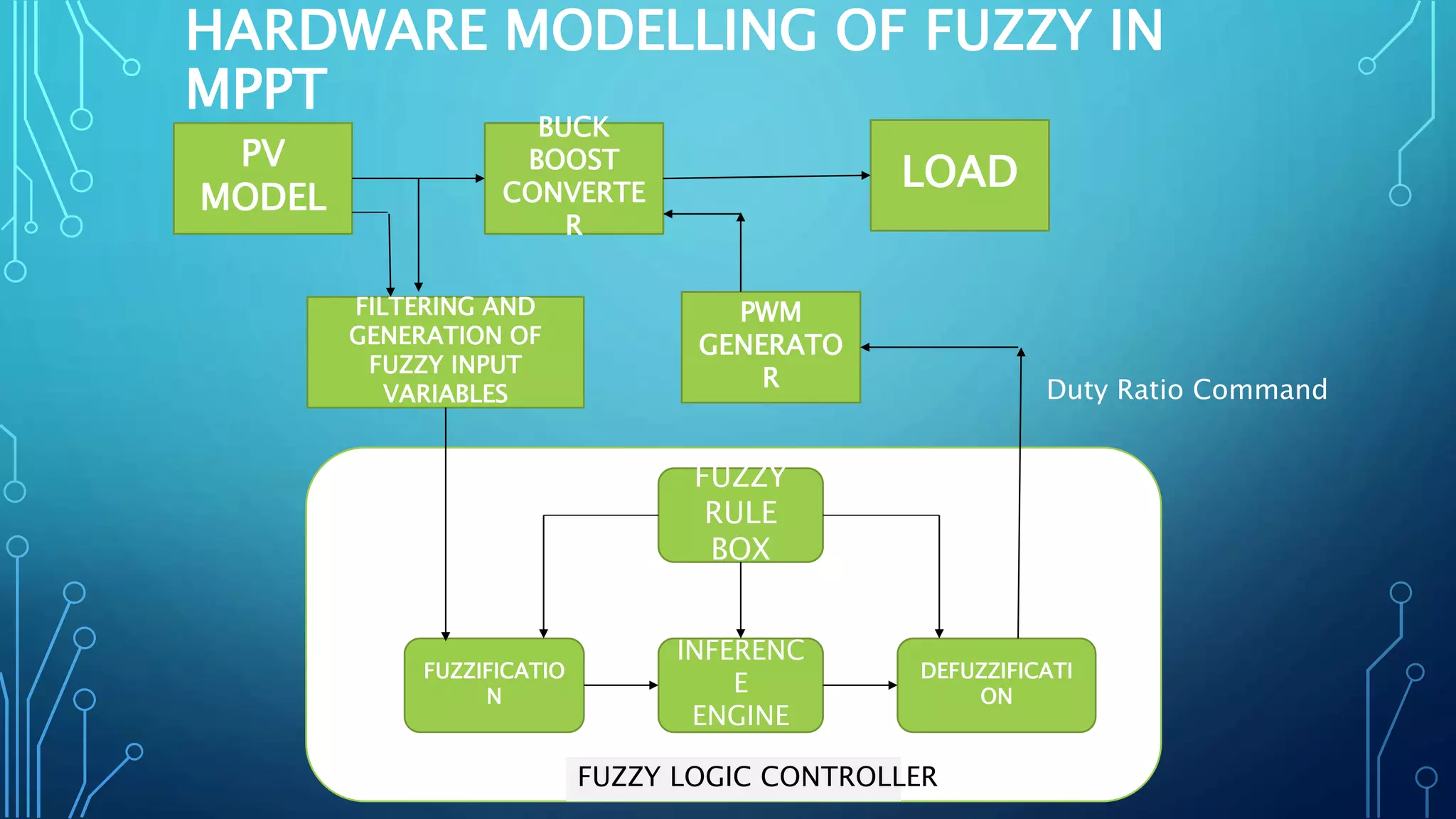
This document discusses harnessing solar energy through an MPPT (maximum power point tracking) based control system using fuzzy logic. It begins with basics of solar photovoltaics including PV cells, modules, and arrays. It then covers MPPT techniques such as perturb and observe method and incremental conductance method. Finally, it discusses implementing fuzzy logic for MPPT control, including fuzzification, inference, and defuzzification steps. The goal is to use fuzzy logic's ability to handle imprecise inputs to provide a fast and accurate MPPT control system.







![REFRENCE
S
[1] Noppadol Khaehintung, Phaophak Sirisuk, and Anatawat Kunakorn, “Grid-connected photovoltaic
system with maximum power point tracking using self-organizing fuzzy logic controller”, IEEE Power
Electronics and Drives Systems, PEDS, Kuala Lumpur, 2005, pp. 517-521.
[2] Huan-Liang Tsai, “Insolation-oriented model of photovoltaic module using MATLAB/SIMULINK”, Solar
Energy 84, 2010, pp. 13181326.
[3] S.Lalouni, D. Rekioua, T. Rekioua, and E. Matagne, “Fuzzy logic control of sand-alone photovoltaic
system with battery storage”, Journal of Power Sources, Volume 193, Issue2, 5 September 2009, pp.
899-907.
[4] V. Salas, E. Olias, A. Barrado, and A. Lazaro, “ Review of the maximum power point tracking algorithms
for stand-alone photovoltaic systems”, Soalr Energy Materials & Solar Cells 90, 2006, pp. 1555-1578.
[5] M.S. Ait Cheikh, C. Larbes, G. F. Tchoketch Kebir, and A. Zerguerras, “Maximum power point tracking
using a fuzzy logic control scheme”, Revue des energies Renouvelables, Vol. 10, 2007, pp. 387-395.
[6] H.J. Möller, ‘Semiconductors for Solar Cells’, Artech House, Inc, Norwood, MA, 1993.
[7] R. Gottschalg, M. Rommel, D.G. Ineld and H. Ryssel, ‘Comparison of Different Methods for the](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalppt-2-150808071002-lva1-app6892/75/MPPT-using-fuzzy-logic-32-2048.jpg)