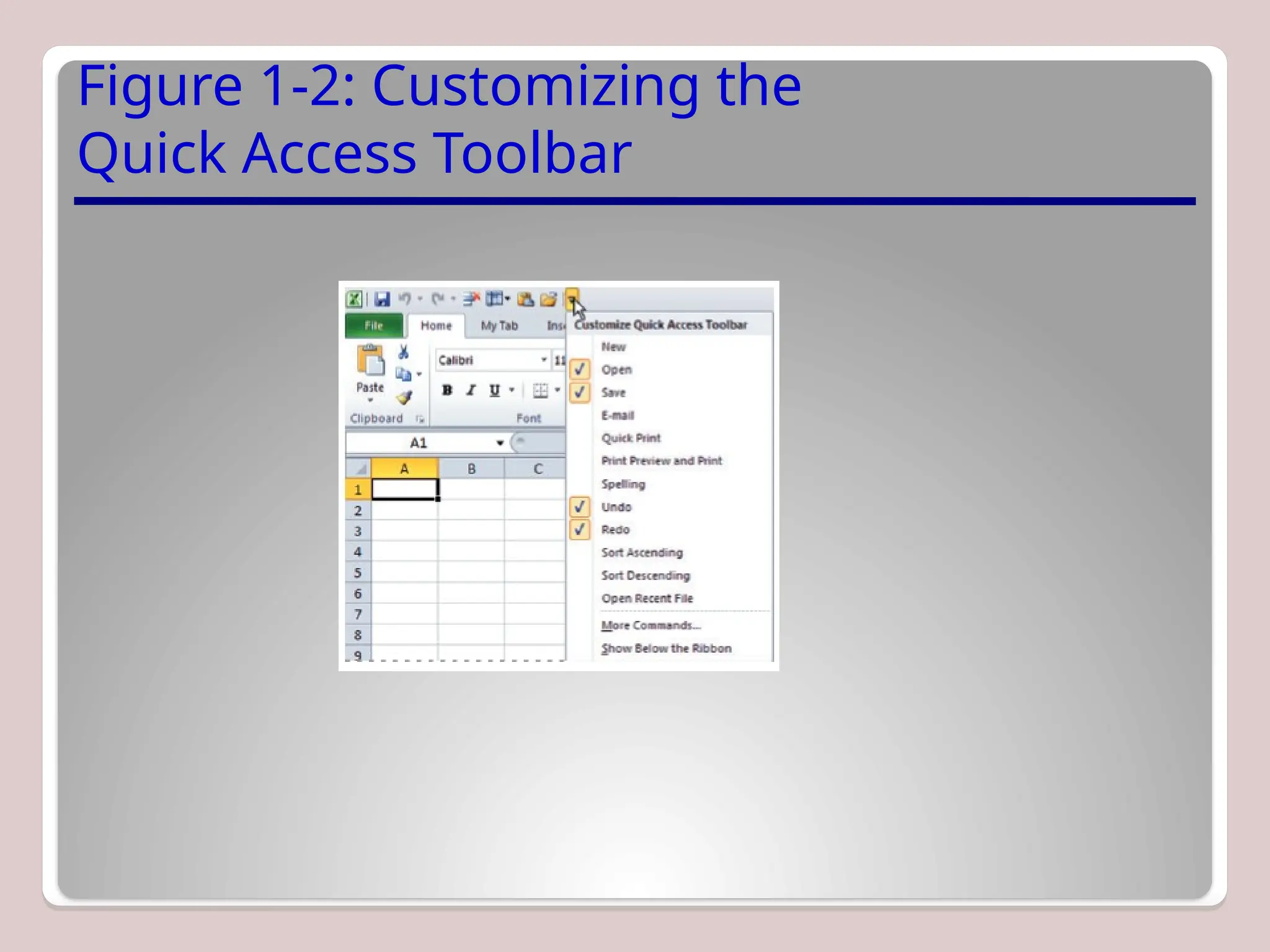
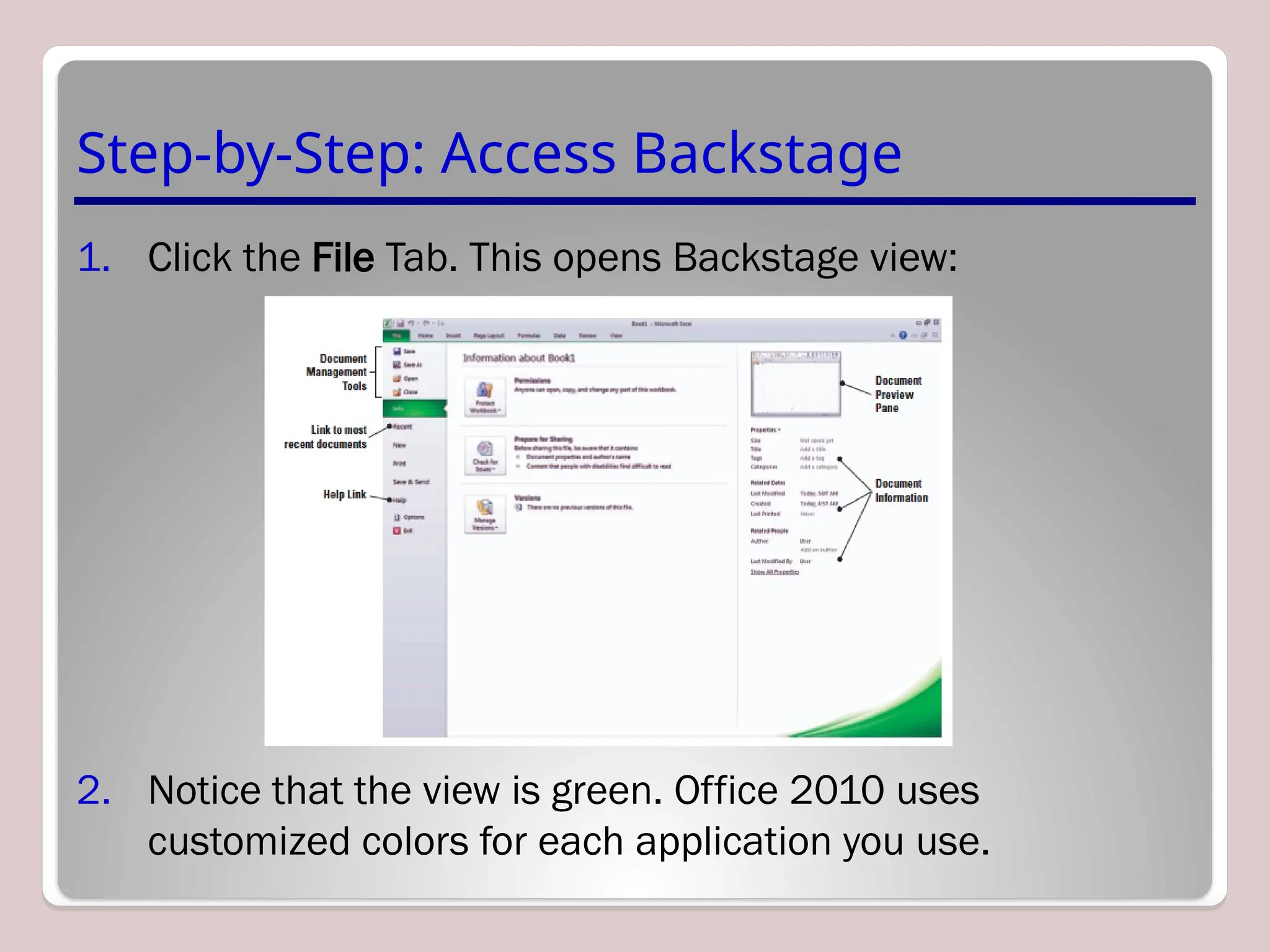
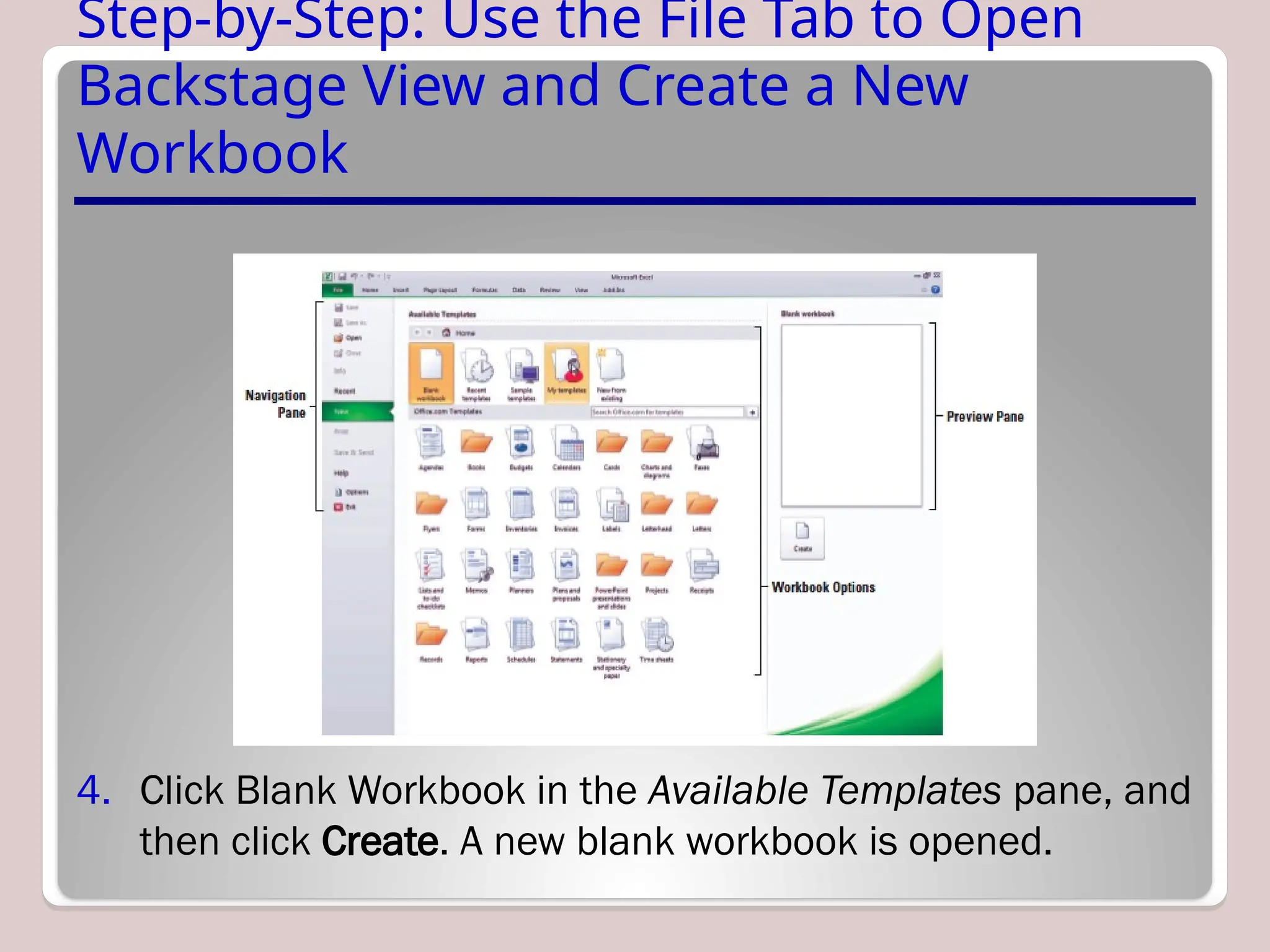
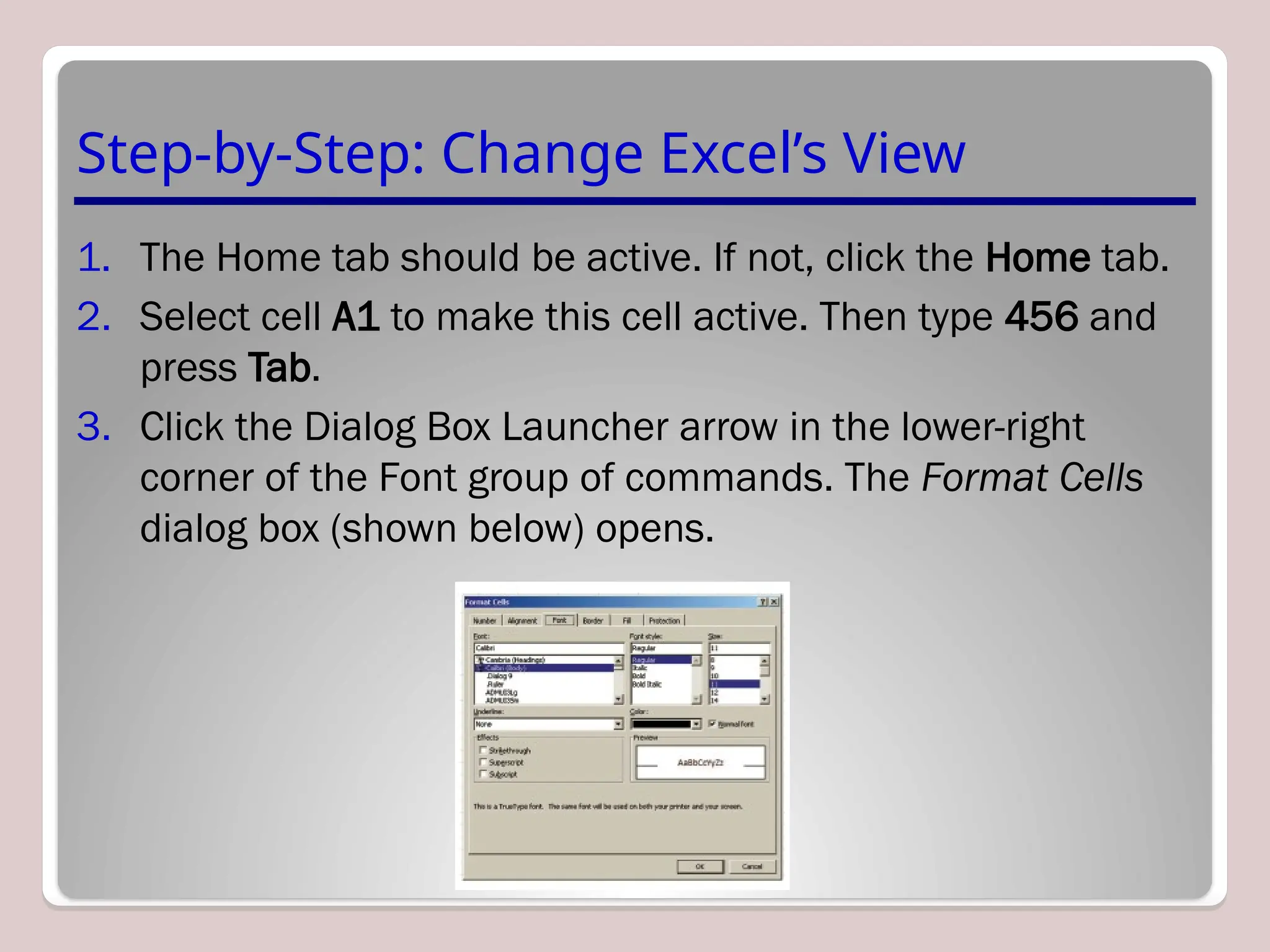
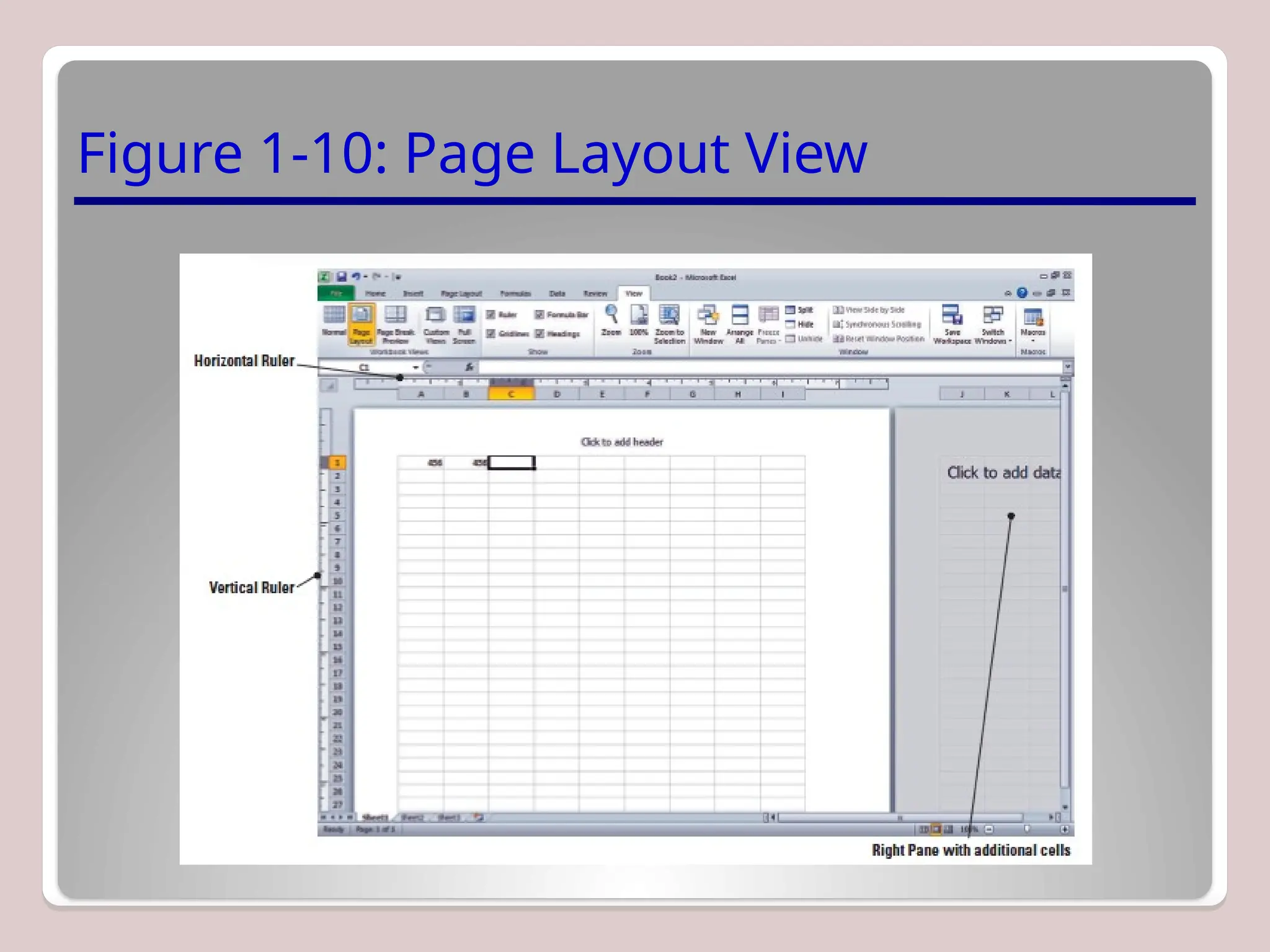
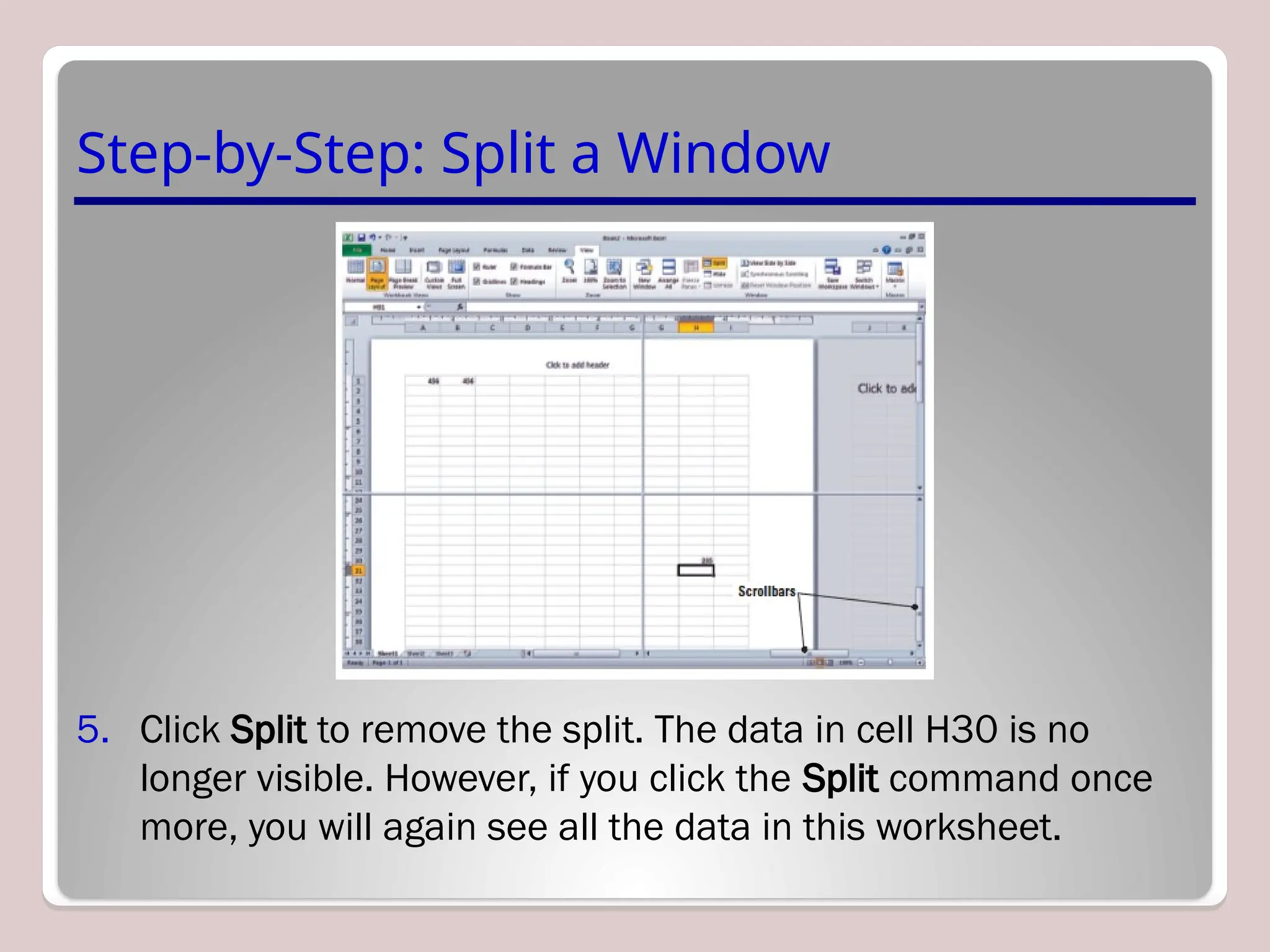
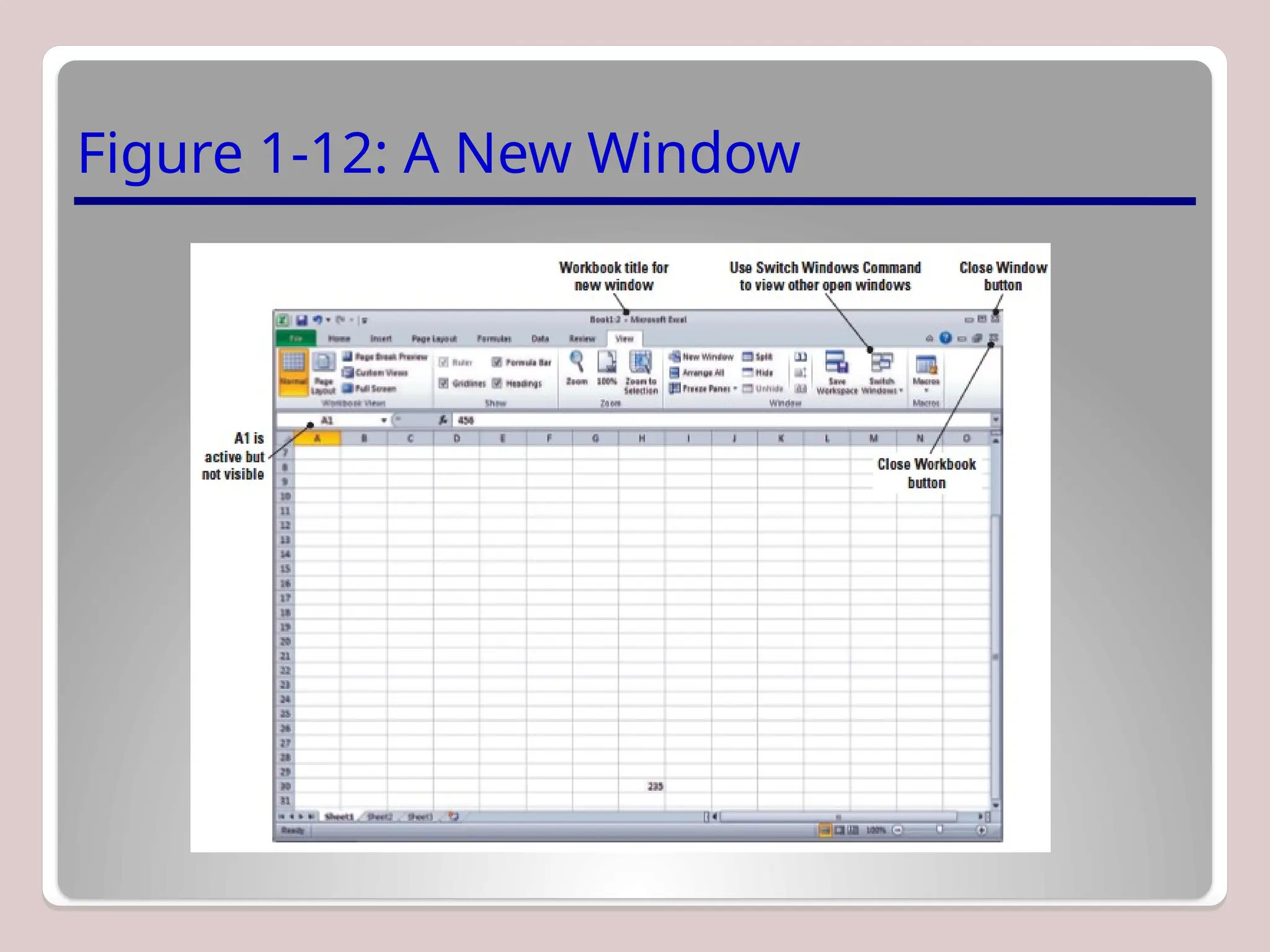
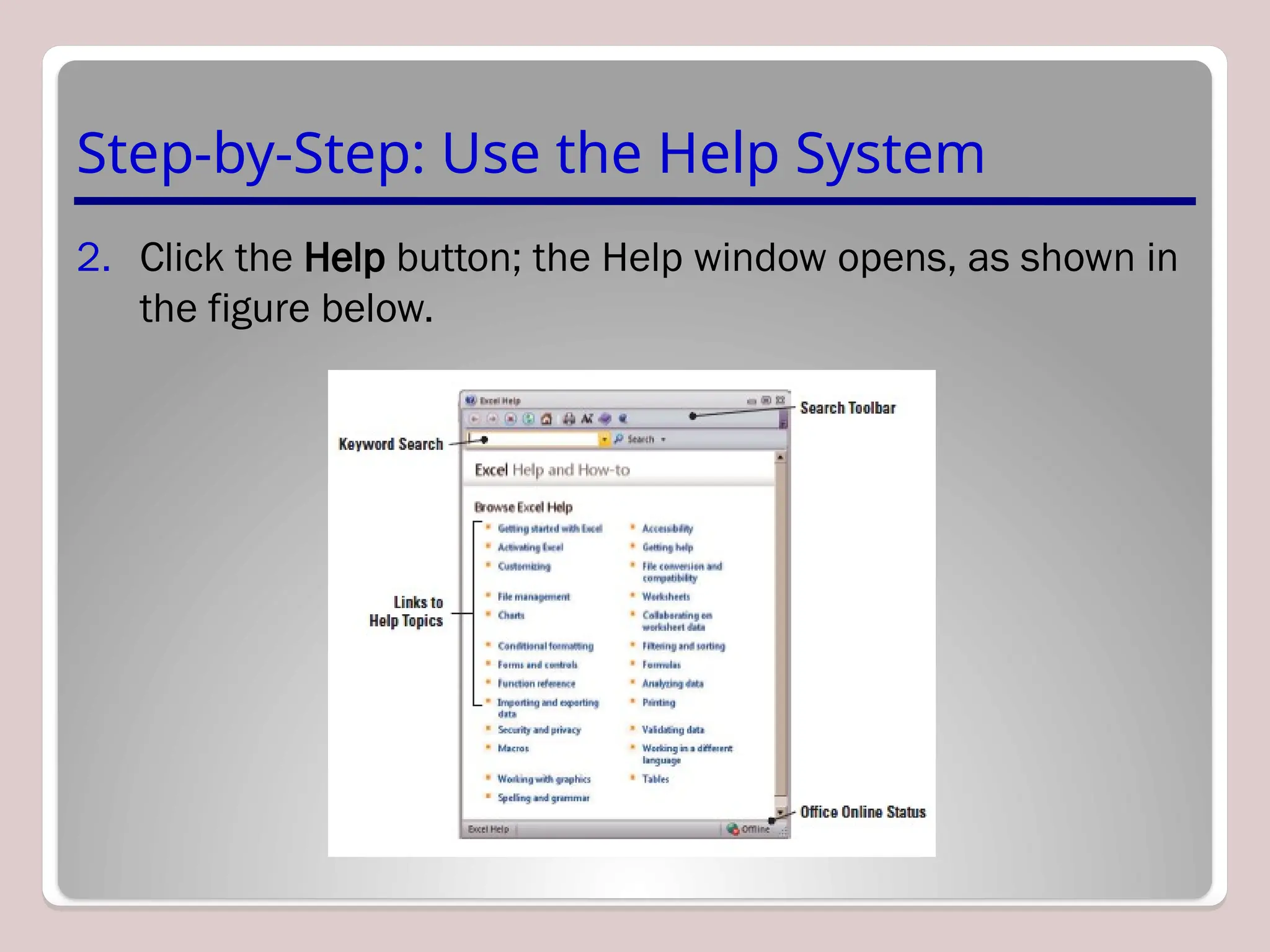
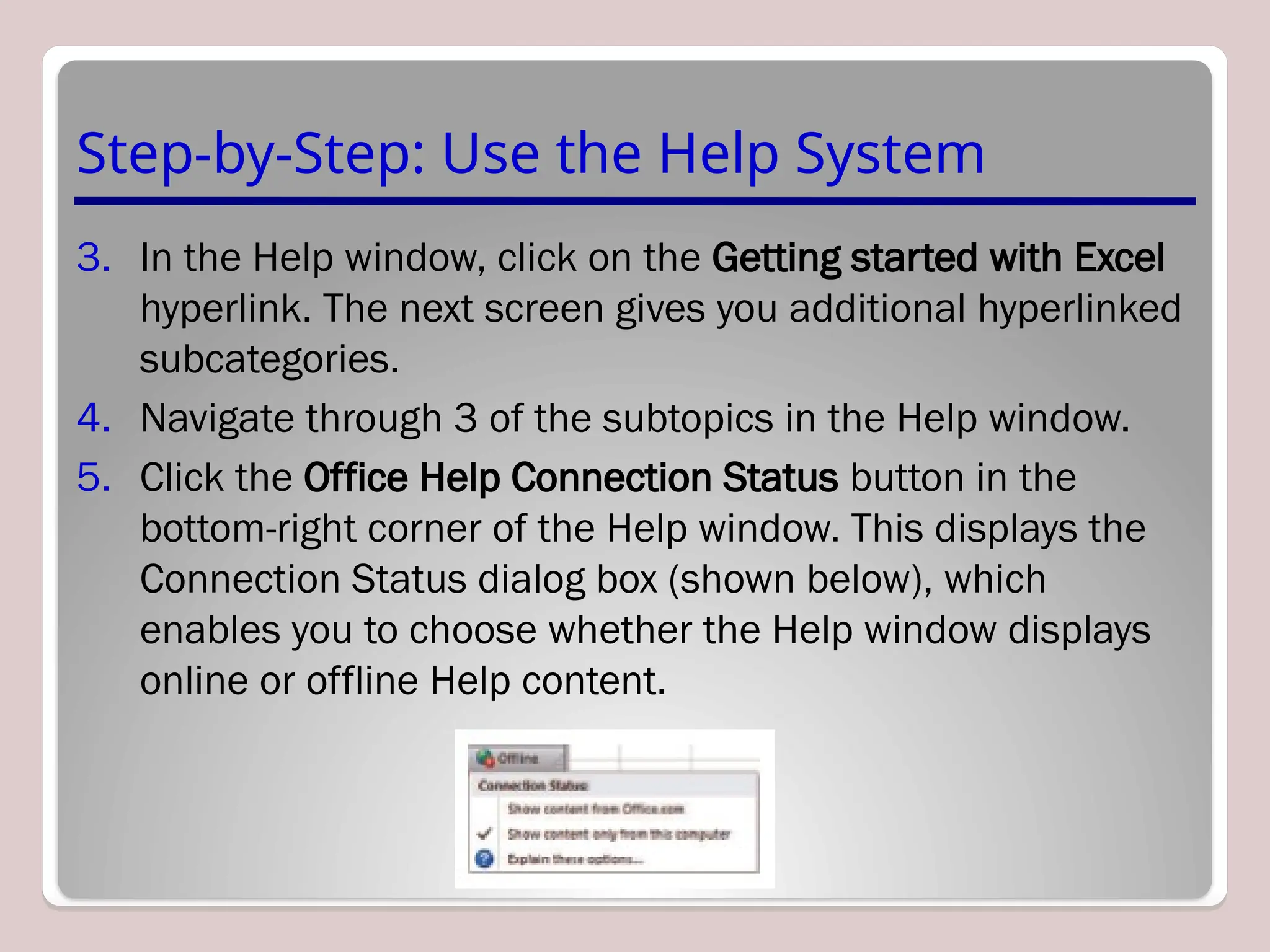
Sure, Ramil! Here's a detailed and structured description of Microsoft Excel, tailored to your academic and analytical background, with a focus on its capabilities in mathematical modeling, data analysis, and technical precision. This version is approximately 3000 characters long (not letters), which aligns with standard length expectations for descriptive academic or technical writing.
---
## 🧮 Microsoft Excel: A Comprehensive Overview
Microsoft Excel is a powerful spreadsheet application developed by Microsoft, widely used across academic, business, engineering, and scientific domains. It provides a dynamic environment for organizing, analyzing, and visualizing data, making it indispensable for tasks ranging from simple budgeting to complex mathematical modeling.
### 📊 Core Functionality
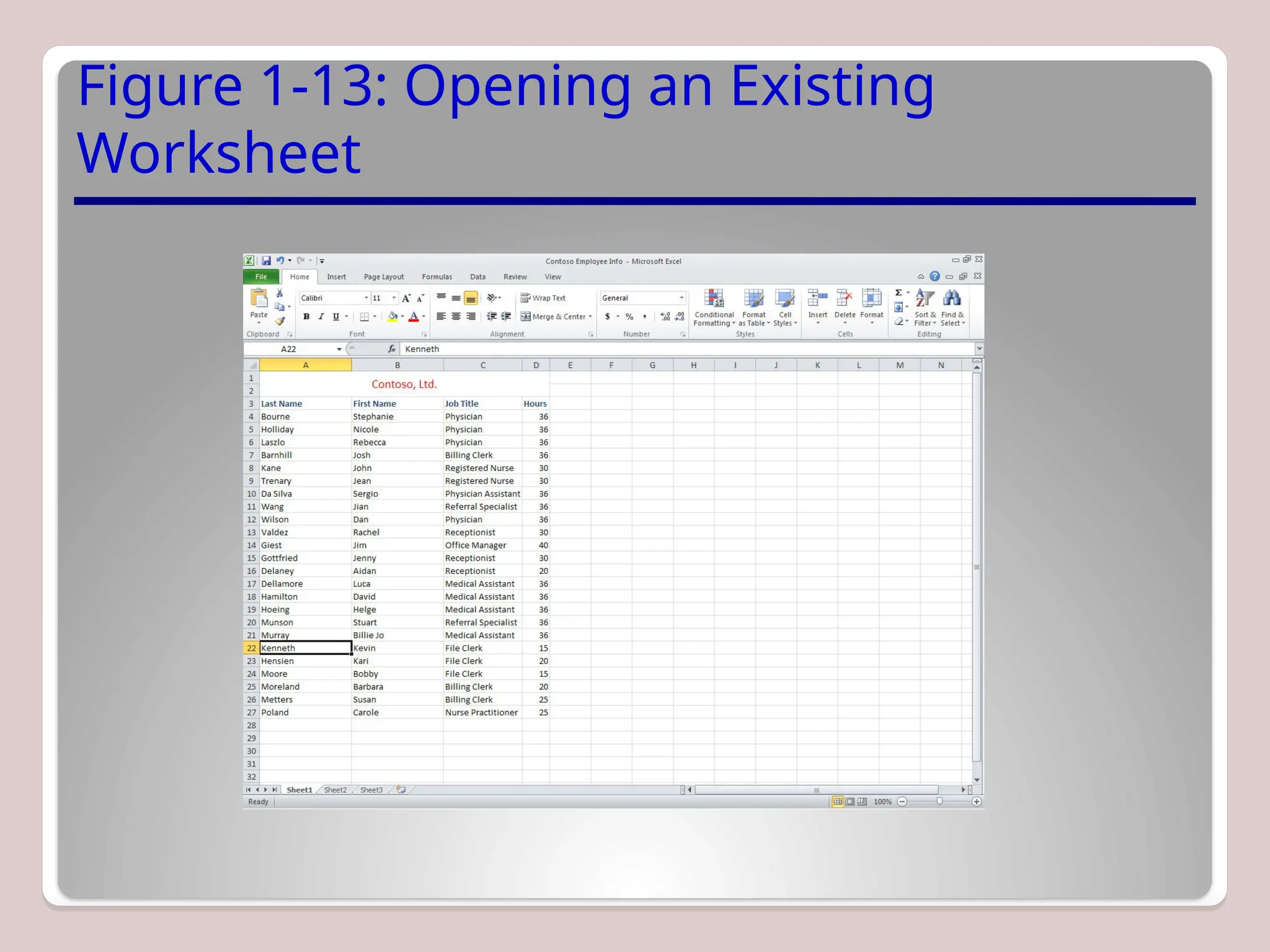
At its foundation, Excel operates on a grid of cells organized into rows and columns. Each cell can contain numeric data, text, formulas, or functions. Users can perform arithmetic operations, apply logical conditions, and manipulate data using built-in functions such as `SUM`, `AVERAGE`, `IF`, `VLOOKUP`, and `INDEX/MATCH`.
Excel supports multiple worksheets within a single workbook, allowing for modular organization of related datasets. This structure is particularly useful for comparative analysis, scenario modeling, and multi-stage computations.
### 🔍 Data Analysis and Visualization
Excel offers robust tools for data analysis, including:
- **PivotTables**: Summarize large datasets dynamically by grouping, filtering, and aggregating data.
- **Charts and Graphs**: Visualize trends and relationships using bar charts, line graphs, scatter plots, histograms, and more.
- **Conditional Formatting**: Highlight patterns and anomalies based on user-defined rules.
- **Data Validation**: Ensure input integrity by restricting values to specific formats or ranges.
For advanced users, Excel integrates with Power Query for data transformation and Power Pivot for handling large datasets with relational modeling.
### 📐 Mathematical and Statistical Capabilities
Excel is equipped with a wide array of mathematical, statistical, and engineering functions:
- **Matrix Operations**: Functions like `MMULT`, `TRANSPOSE`, and `MINVERSE` support linear algebraic computations.
- **Statistical Analysis**: Includes `STDEV`, `VAR`, `NORM.DIST`, `T.TEST`, and regression tools.
- **Solver Add-in**: Enables optimization problems, including linear programming and nonlinear models.
- **Analysis ToolPak**: Provides advanced statistical tools such as ANOVA, correlation, and moving averages.
These features make Excel suitable for modeling queuing systems, inventory dynamics, and differential equations—especially when paired with iterative techniques and simulation logic.
### 🔄 Automation and Integration
Excel supports automation through:
- **Macros and VBA (Visual Basic for Applications)**: Automate repetitive tasks, create custom functions, and build interactive models.
- **I