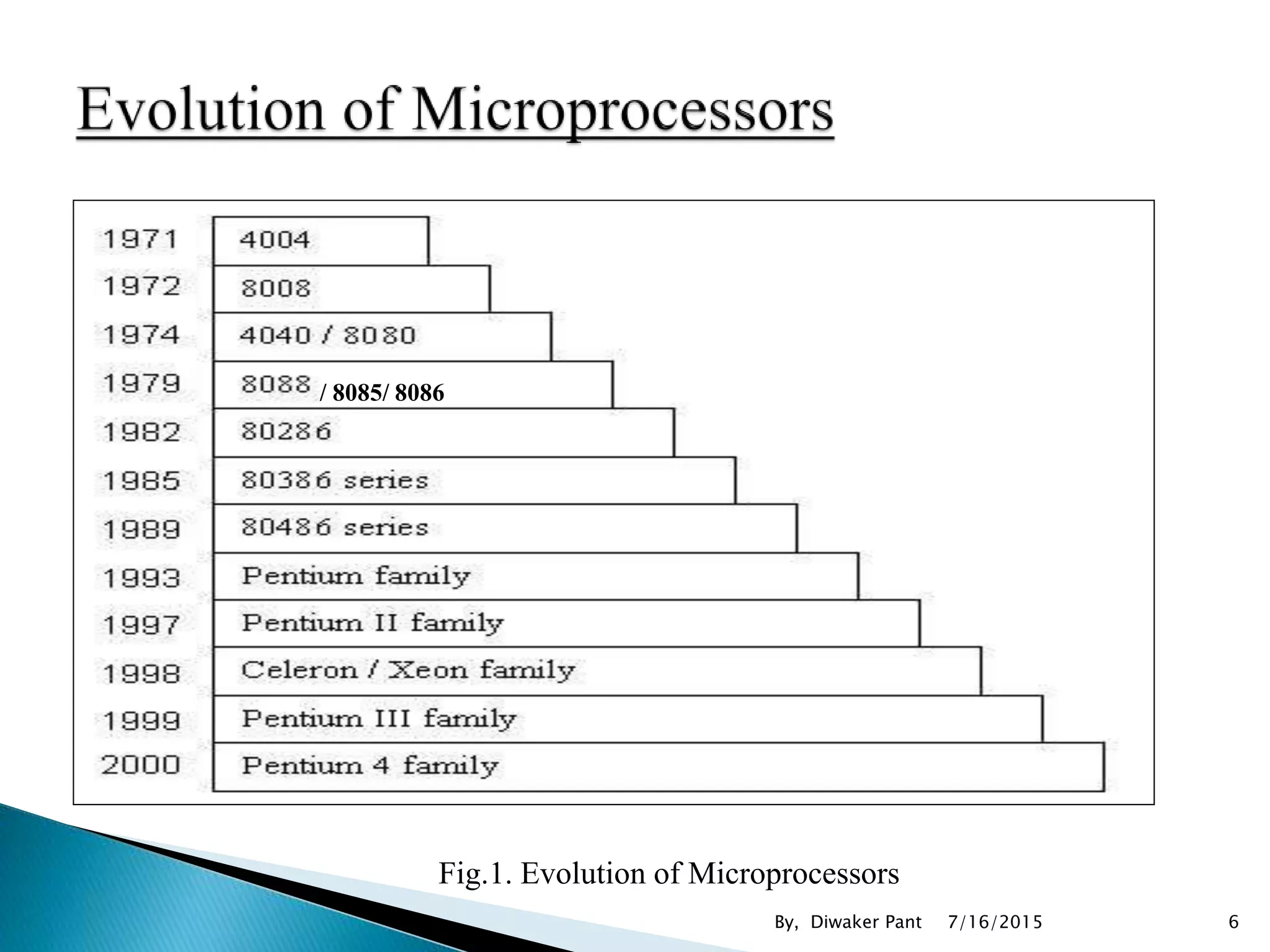
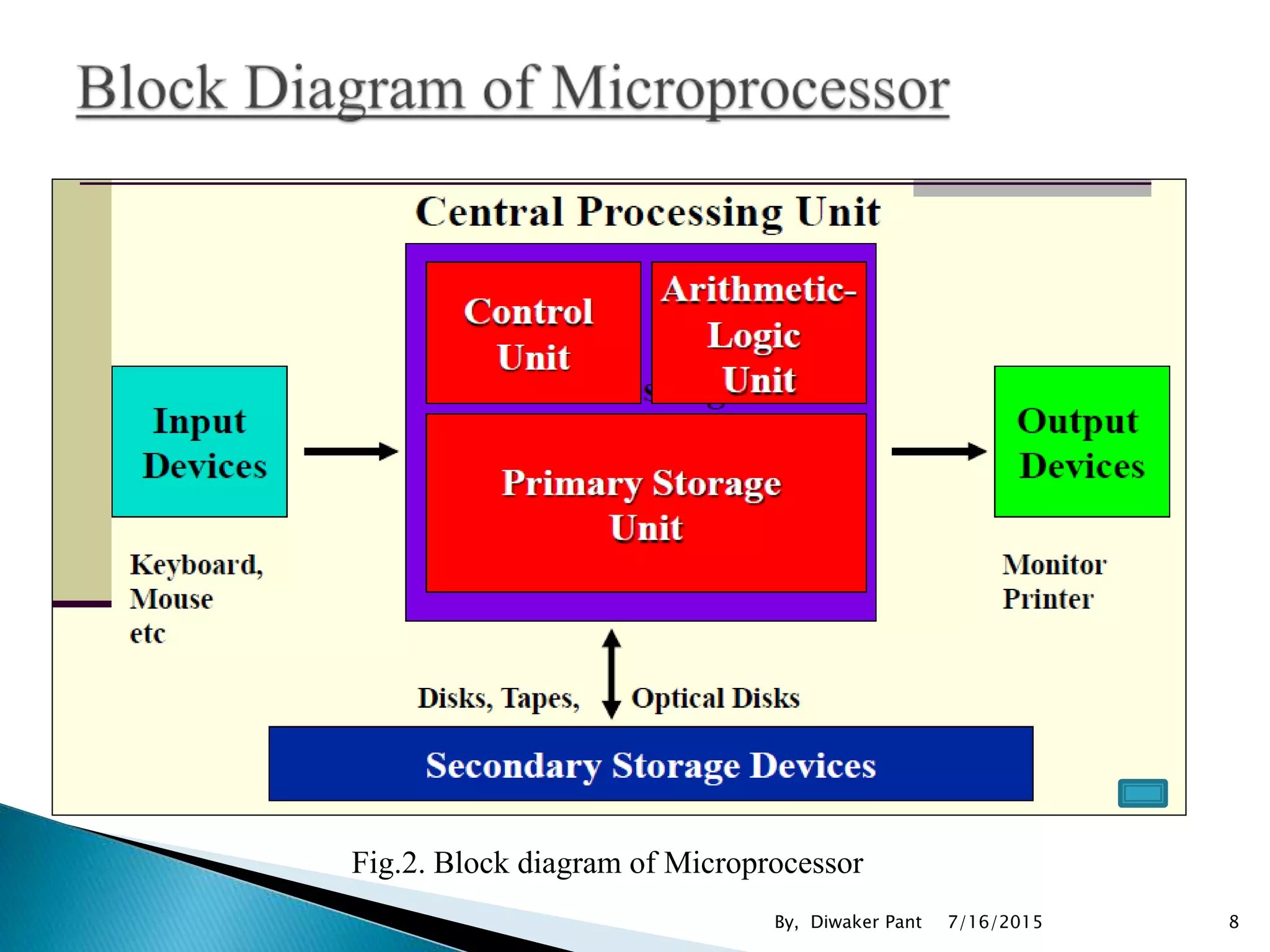
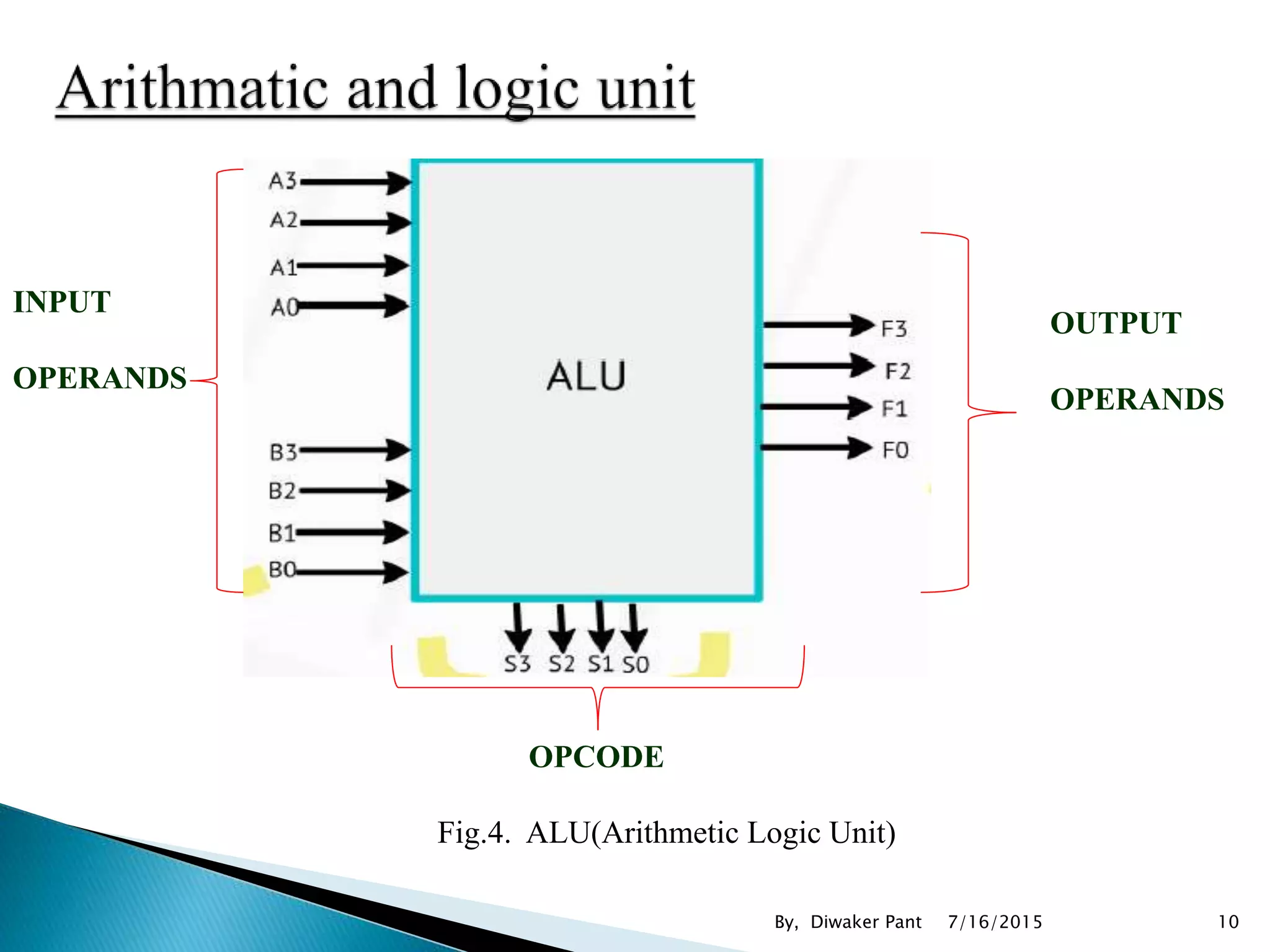
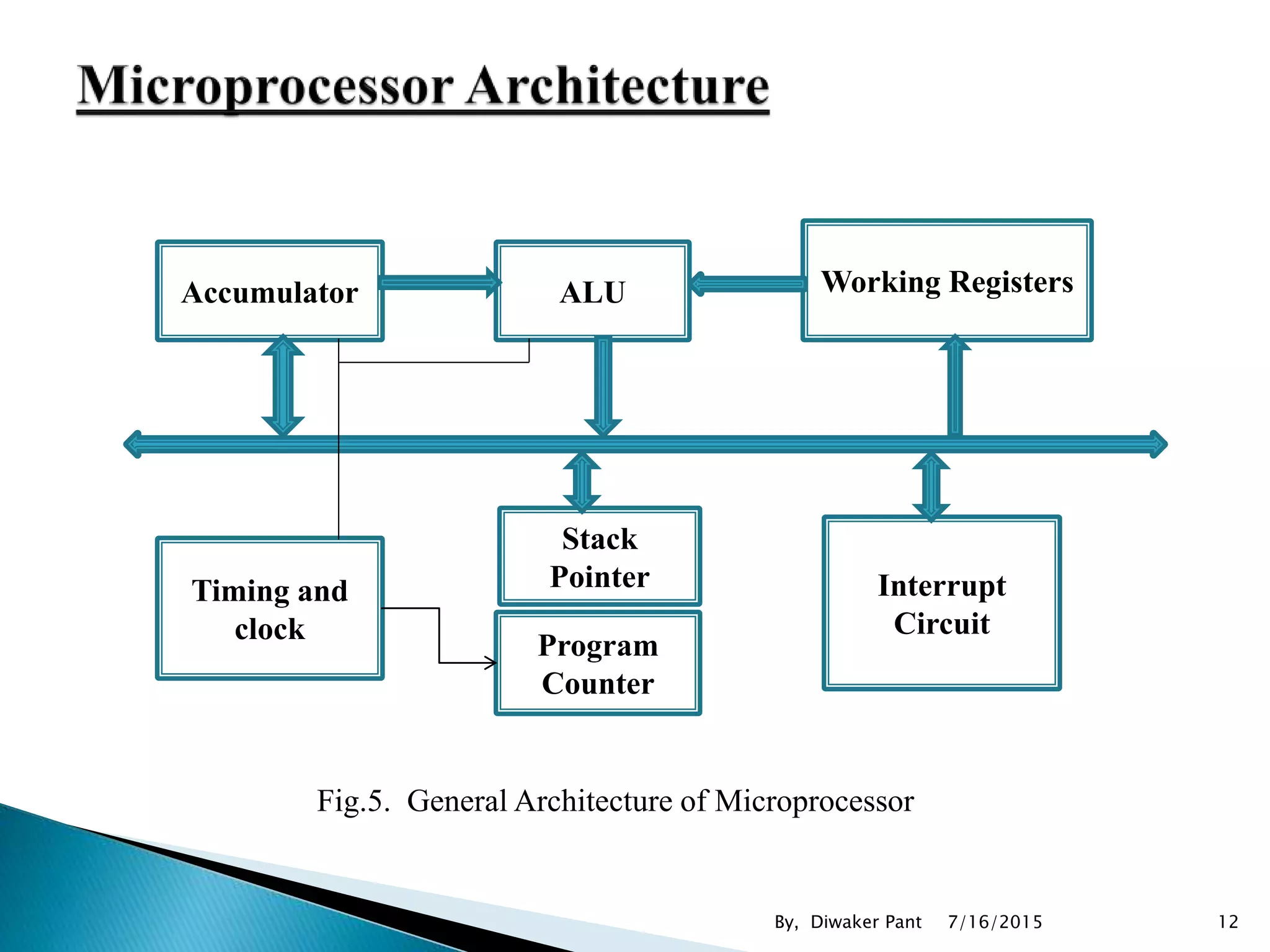
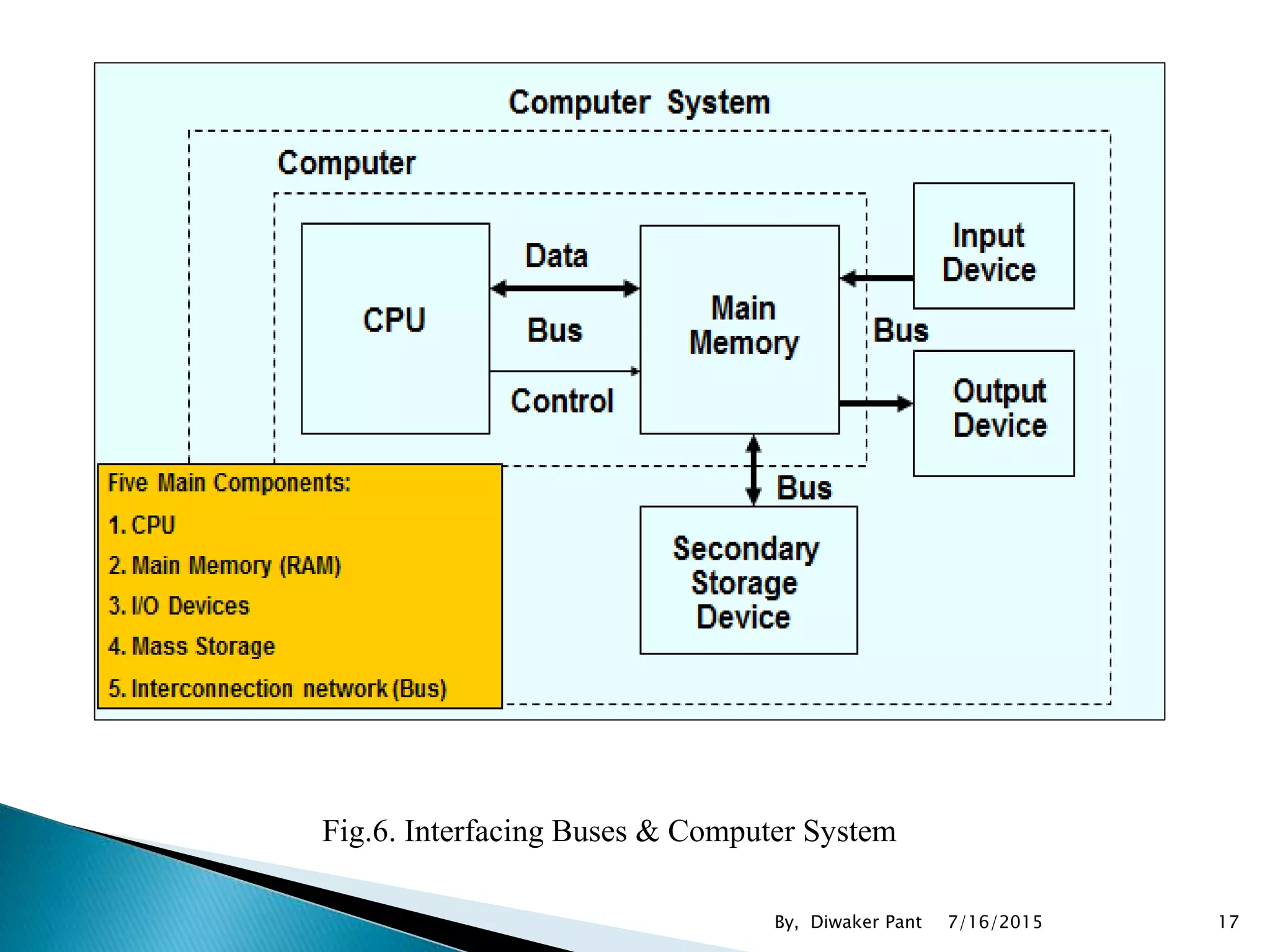
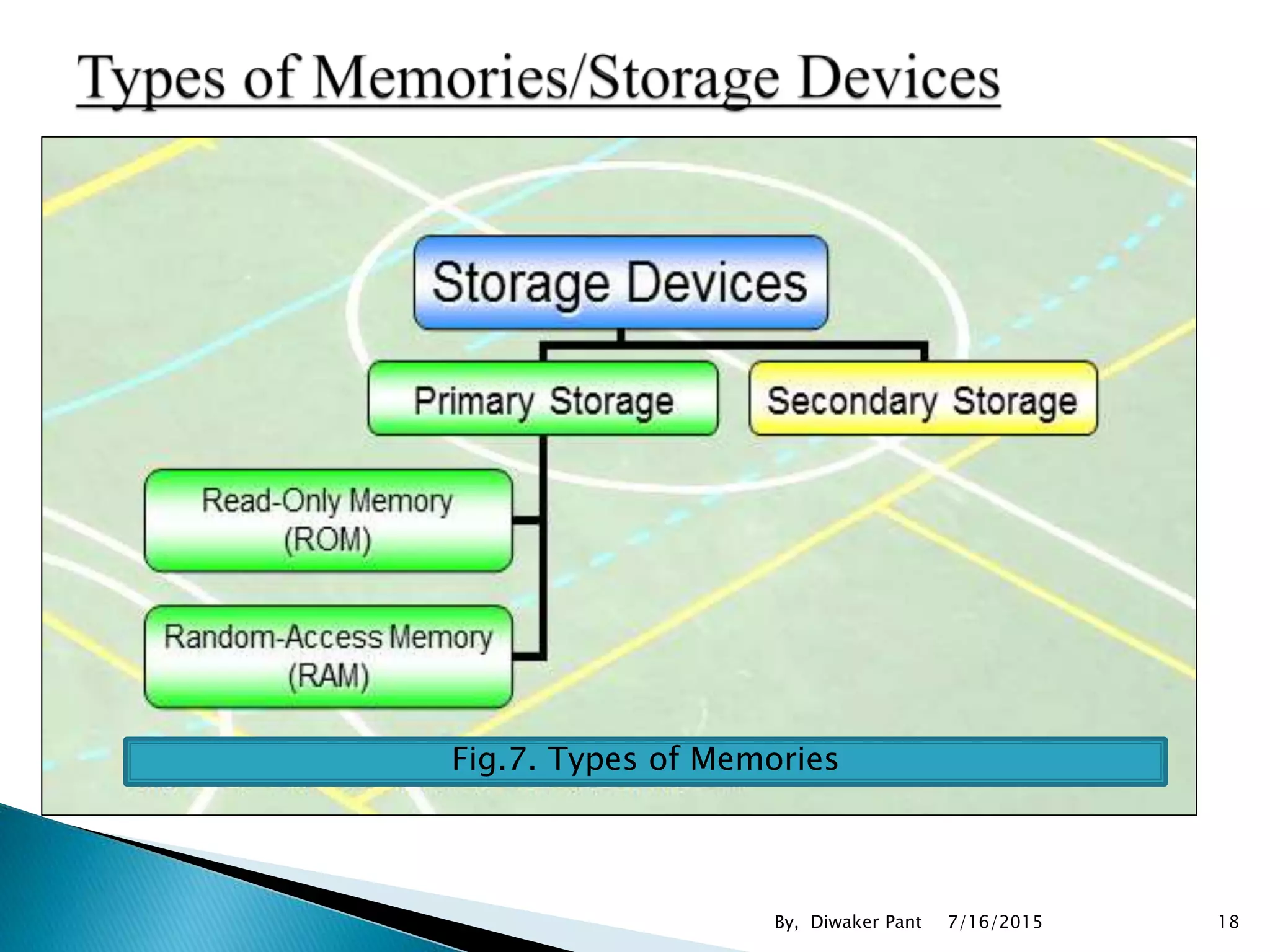
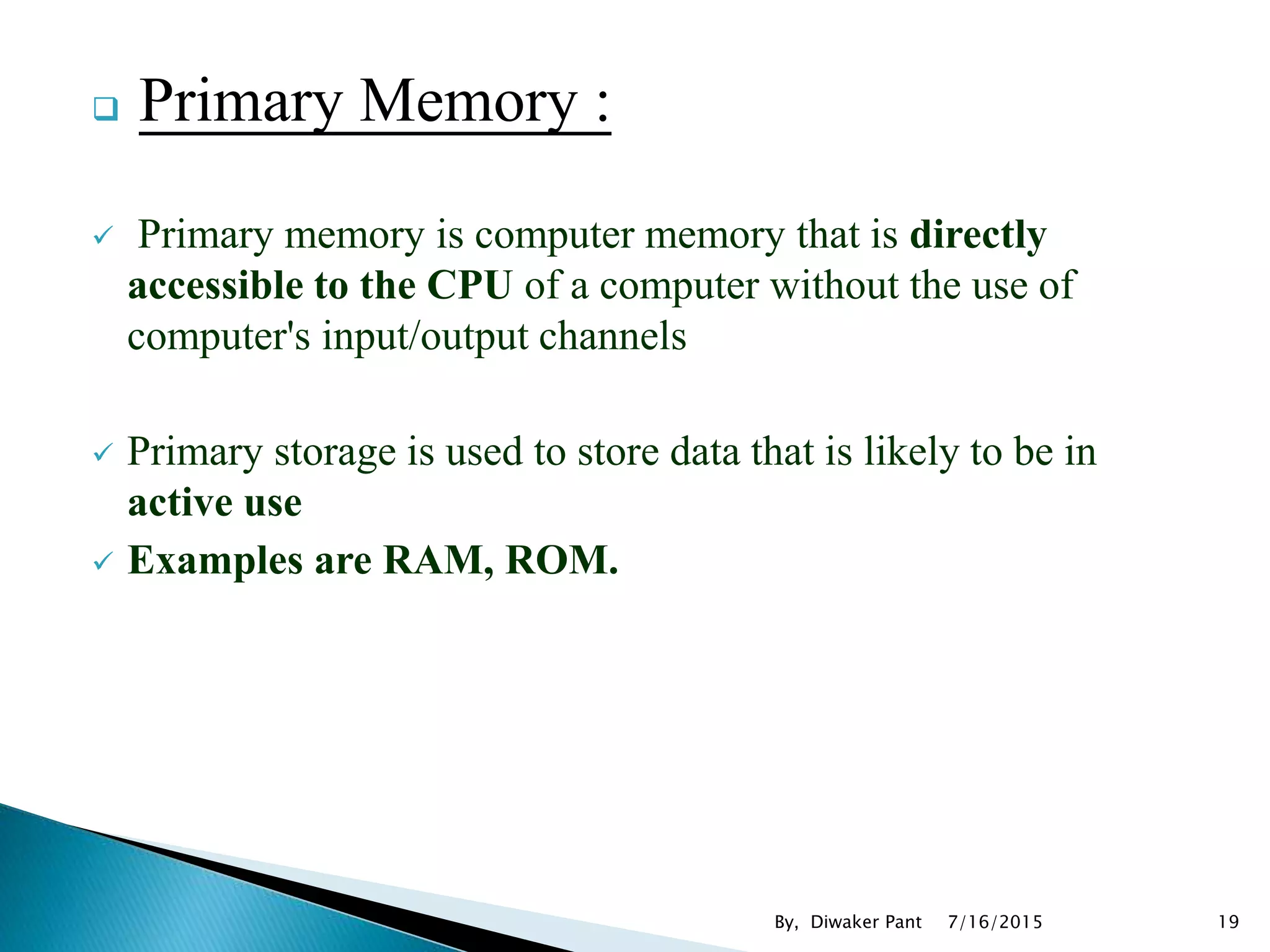
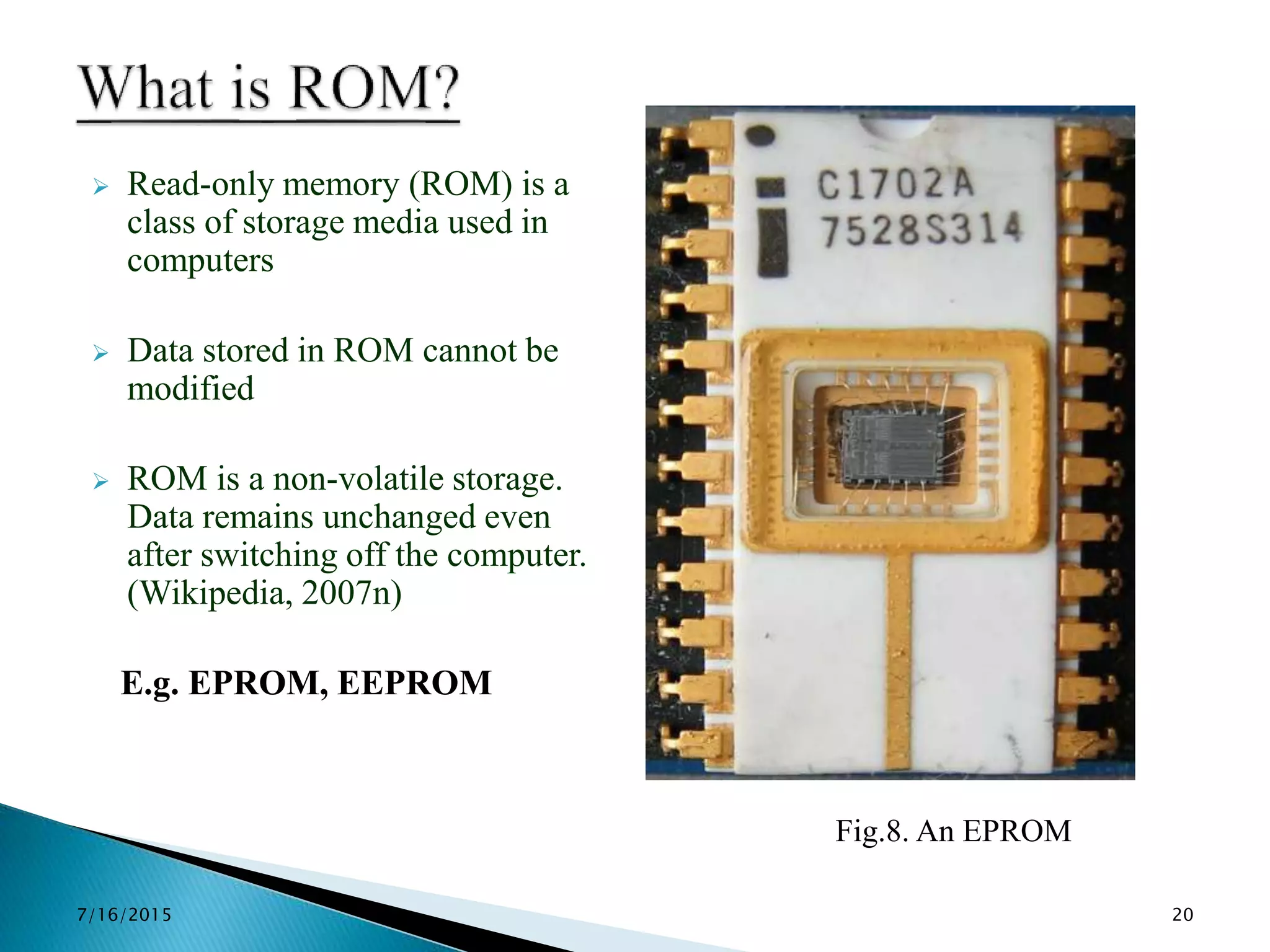
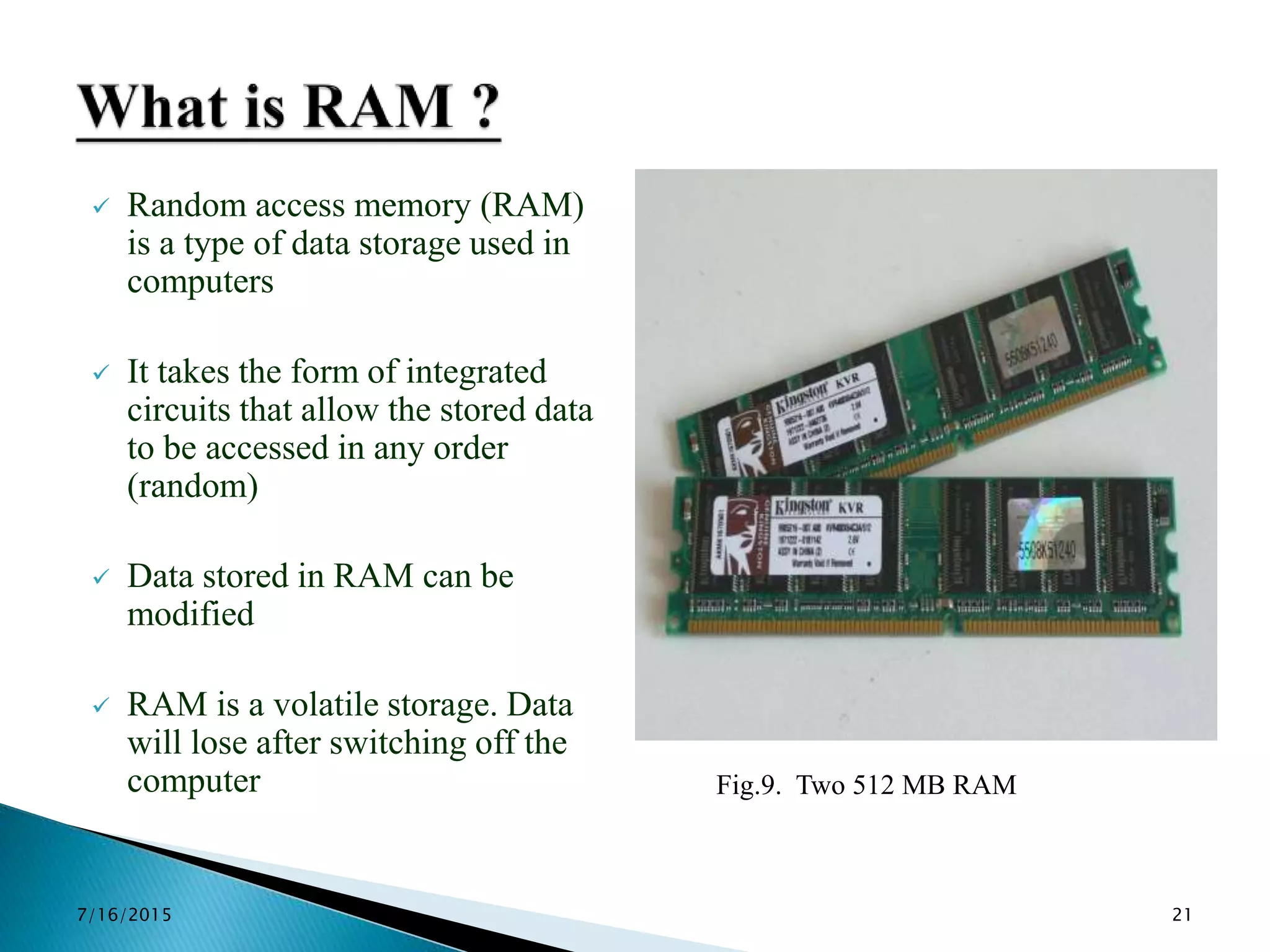
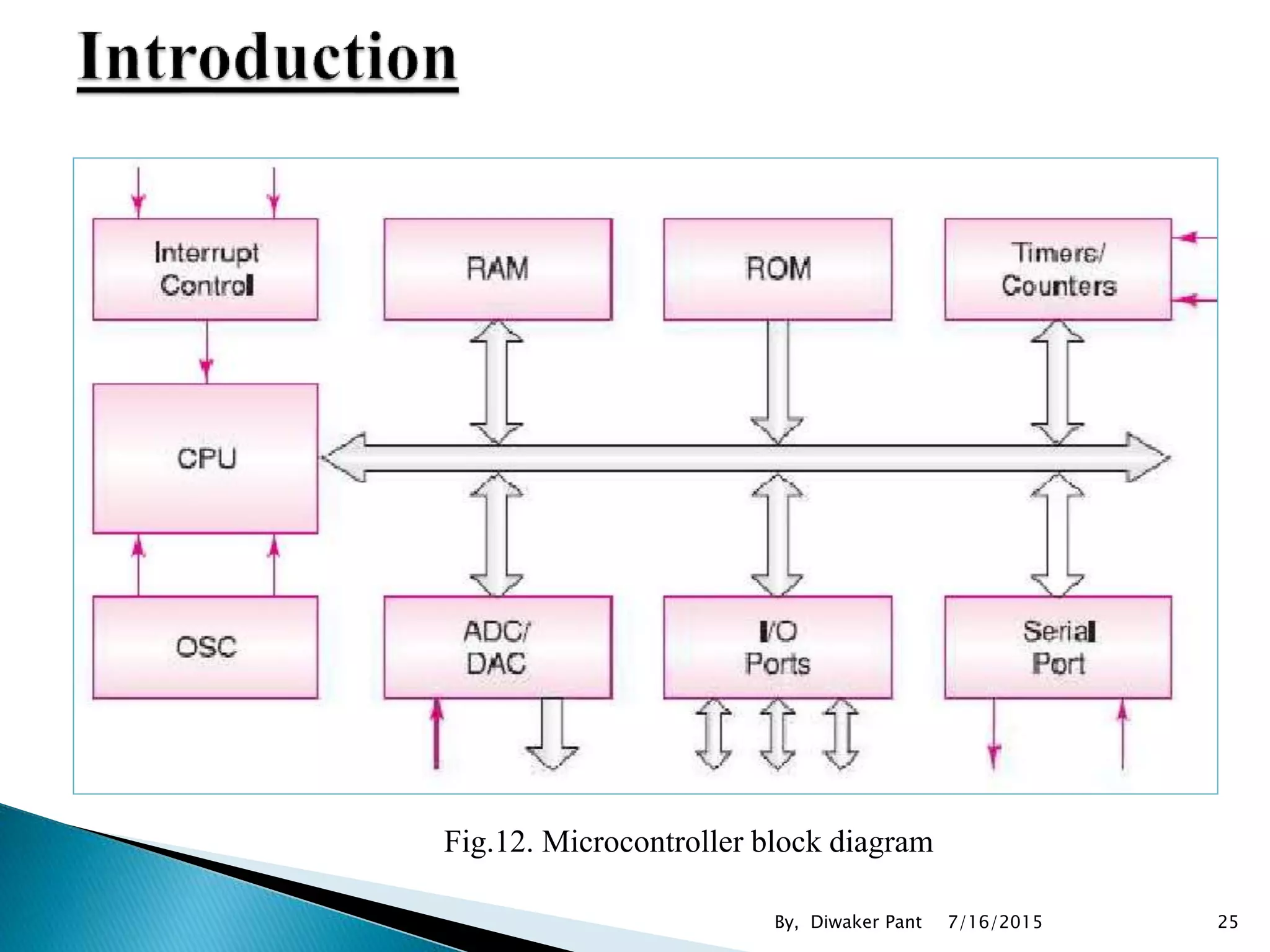
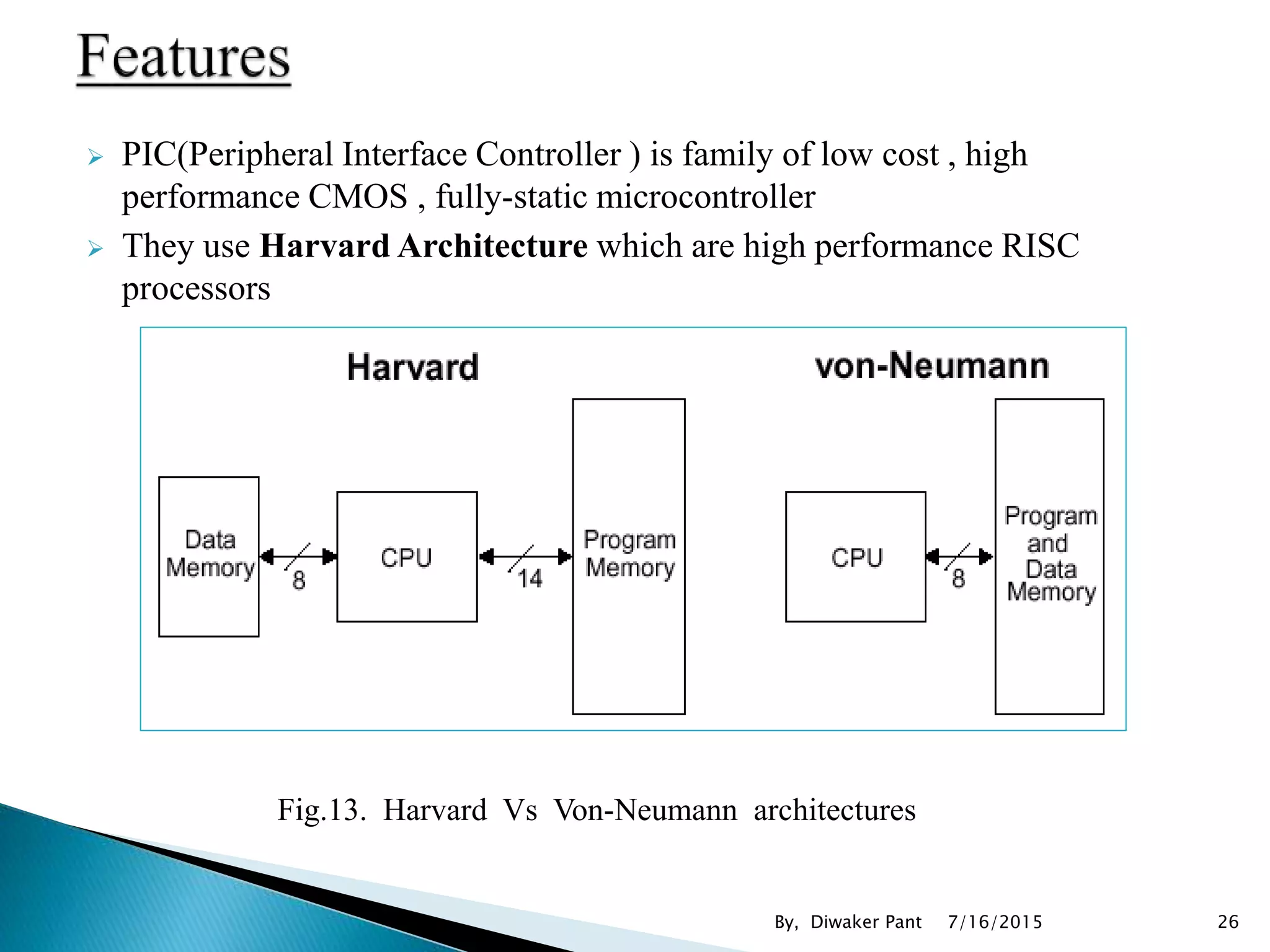
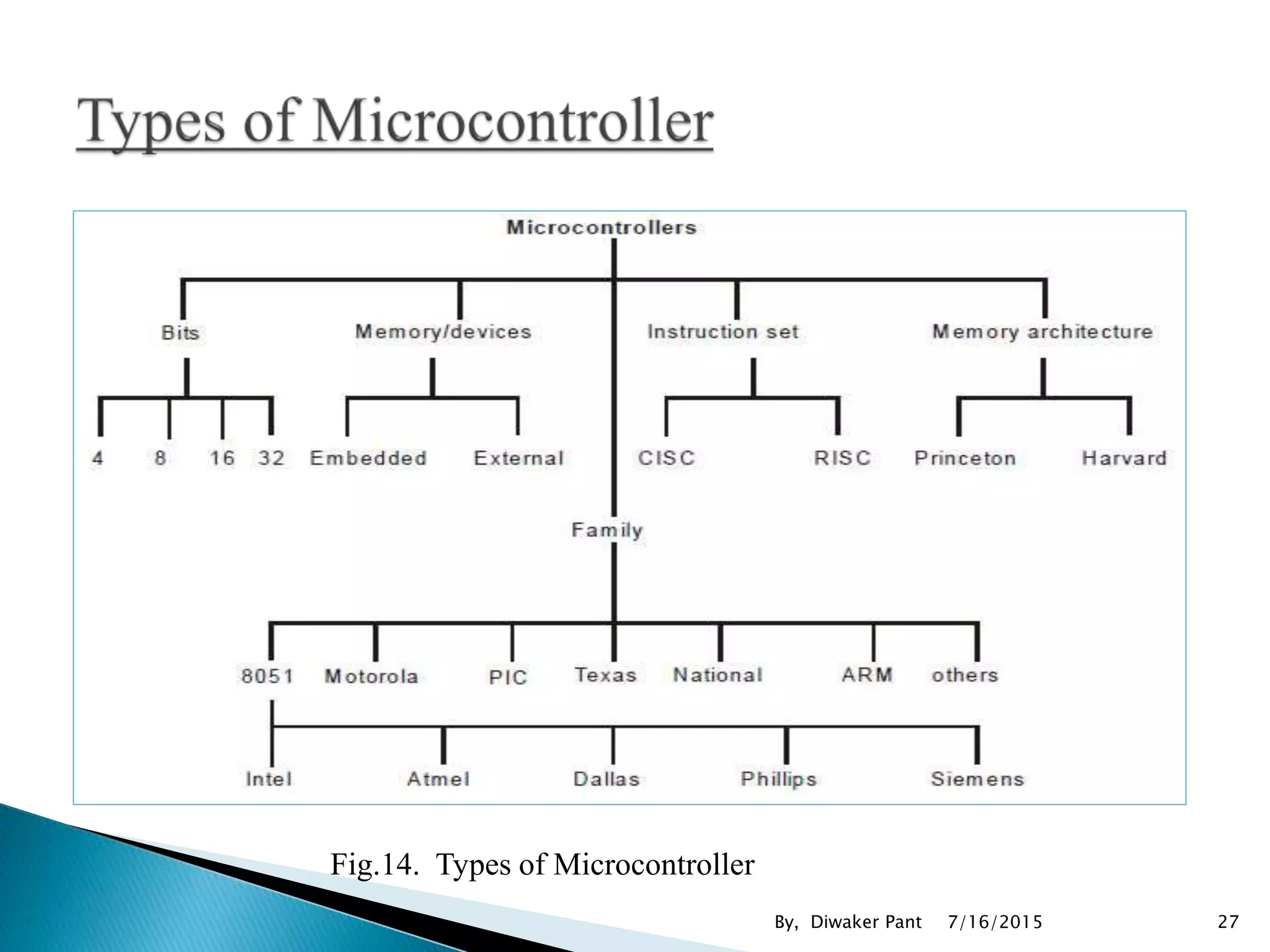
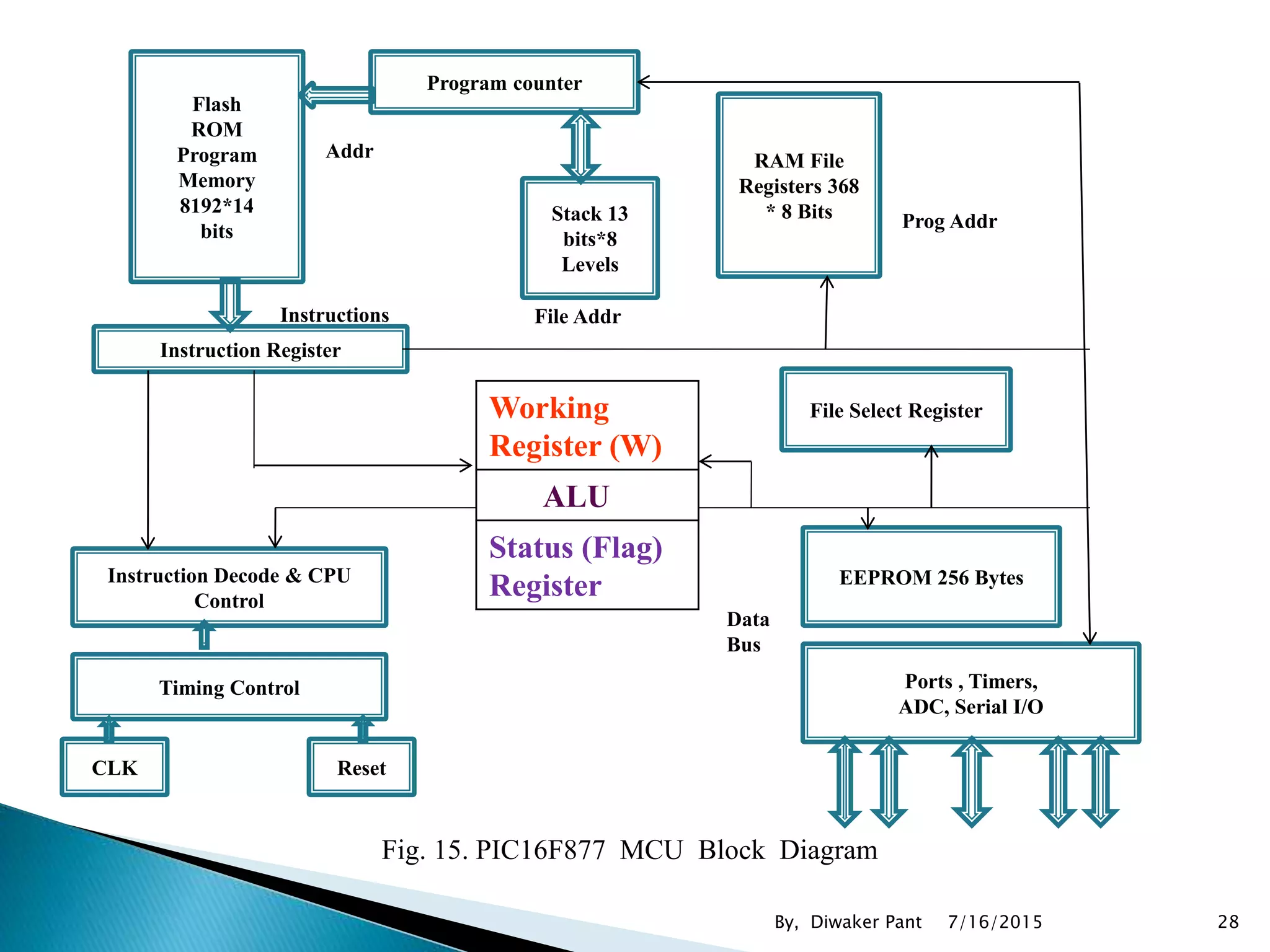
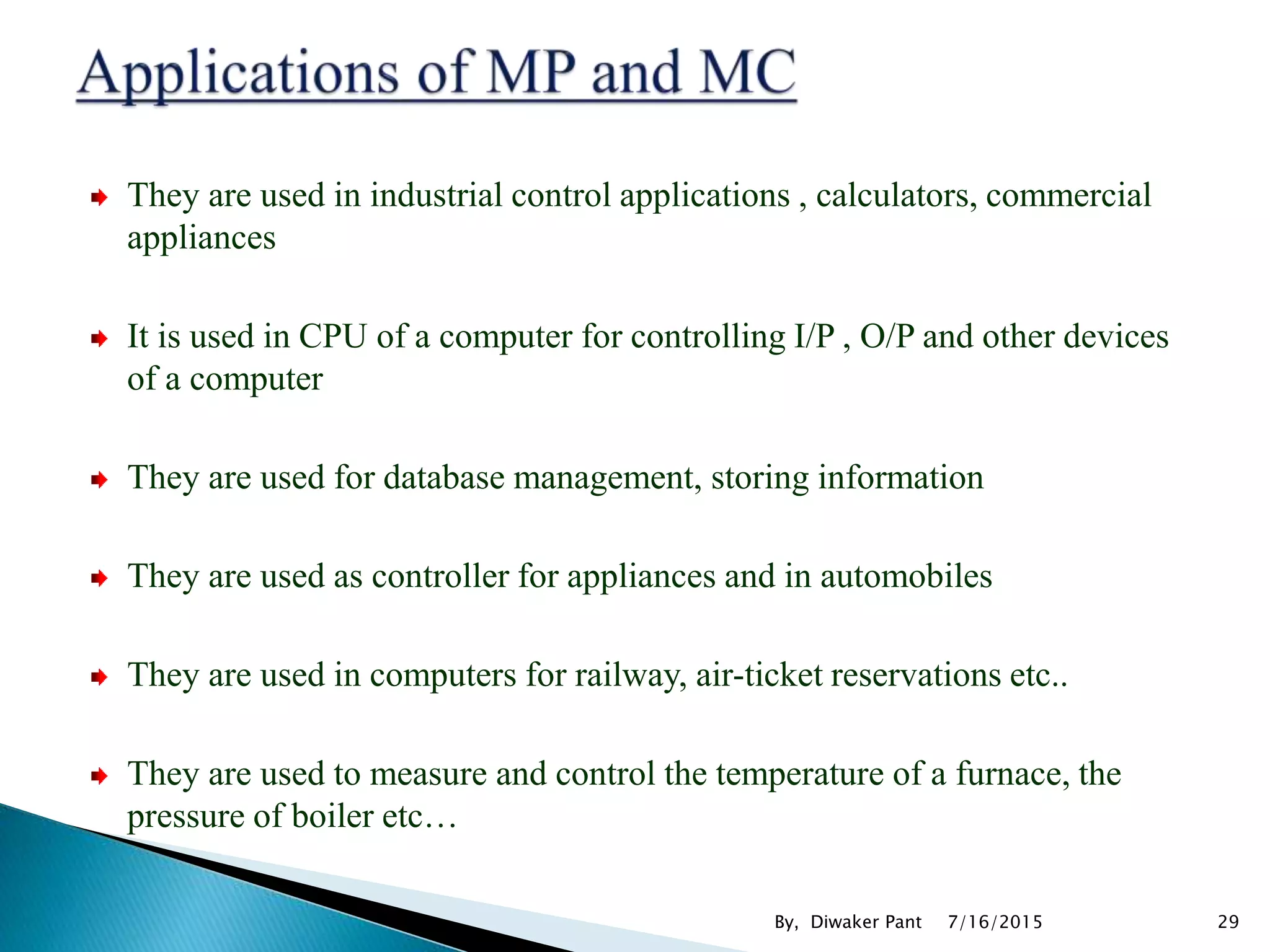
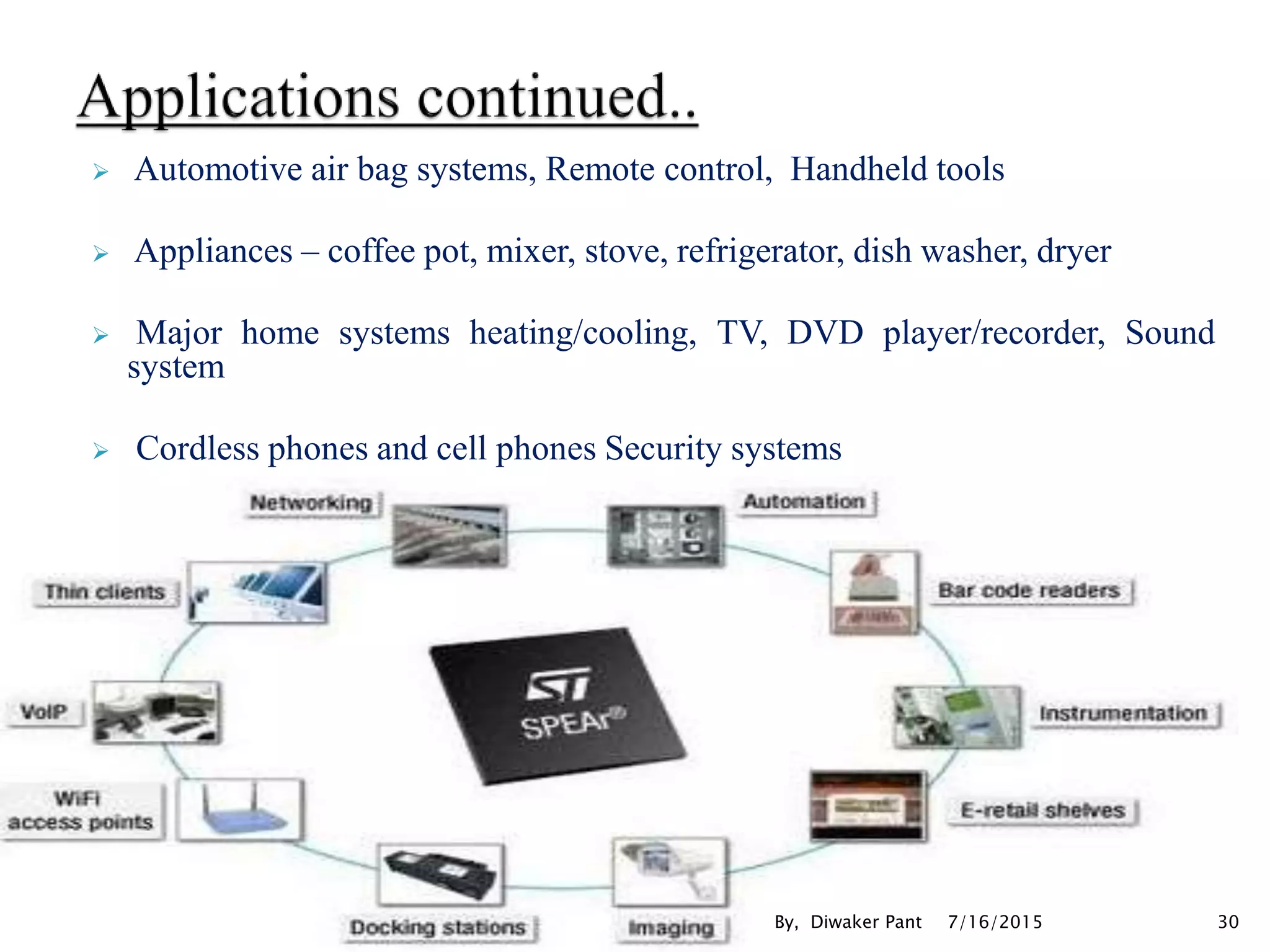
This document provides an overview of microprocessors and microcontrollers. It discusses the evolution of microprocessors from discrete components to integrated circuits. The key components of a microprocessor like the CPU, ALU, and memory are described. Microcontroller fundamentals like PIC microcontrollers and their architecture are also covered. Common applications of microprocessors and microcontrollers are in devices like appliances, automobiles, and industrial control systems. Leading manufacturers of microprocessors and microcontrollers are mentioned.