Embed presentation
Downloaded 1,233 times




![ MERGE SORT (A,p,r) //divide
if p < r
then q= [ (p + r) / 2 ]
MERGE SORT(A,p,q)
MERGER SORT(A,q + 1,r)
MERGE(A,p,q,r)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mergesortalgorithm-160901095302/75/Merge-sort-algorithm-5-2048.jpg)
![Merge(array A, int p, int q, int r)
{
array B[p..r] //temp array taken
i = k = p // initialize pointers
j = q+1
while (i <= q and j <= r)
{
if (A[i] <= A[j]) B[k++] = A[i++]
else B[k++] = A[j++]
}
while (i <= q)
B[k++] = A[i++] // copy any leftover to B
while (j <= r)
B[k++] = A[j++]
for i = p to r
A[i] = B[i] // copy B back to A
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mergesortalgorithm-160901095302/75/Merge-sort-algorithm-6-2048.jpg)


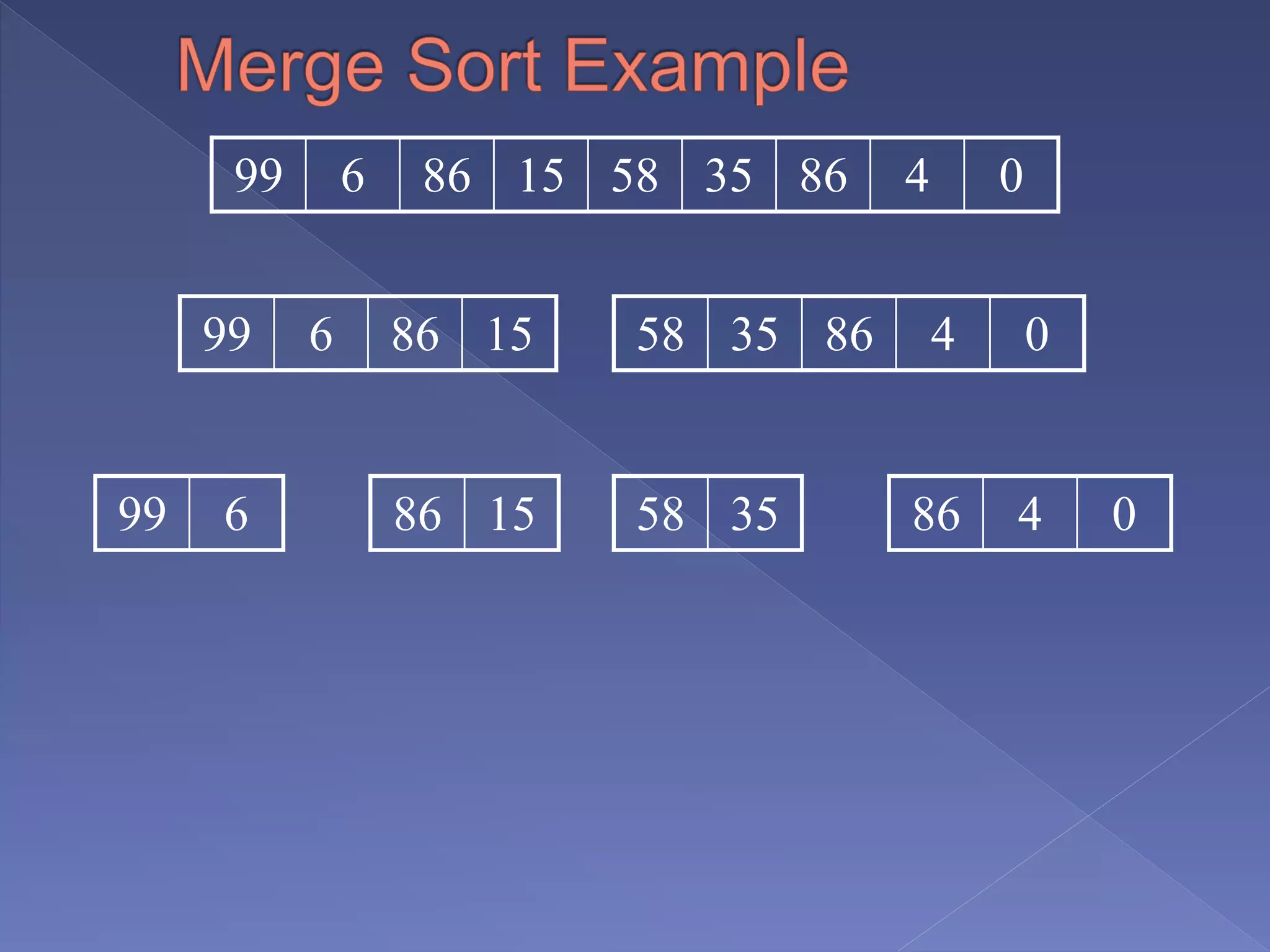
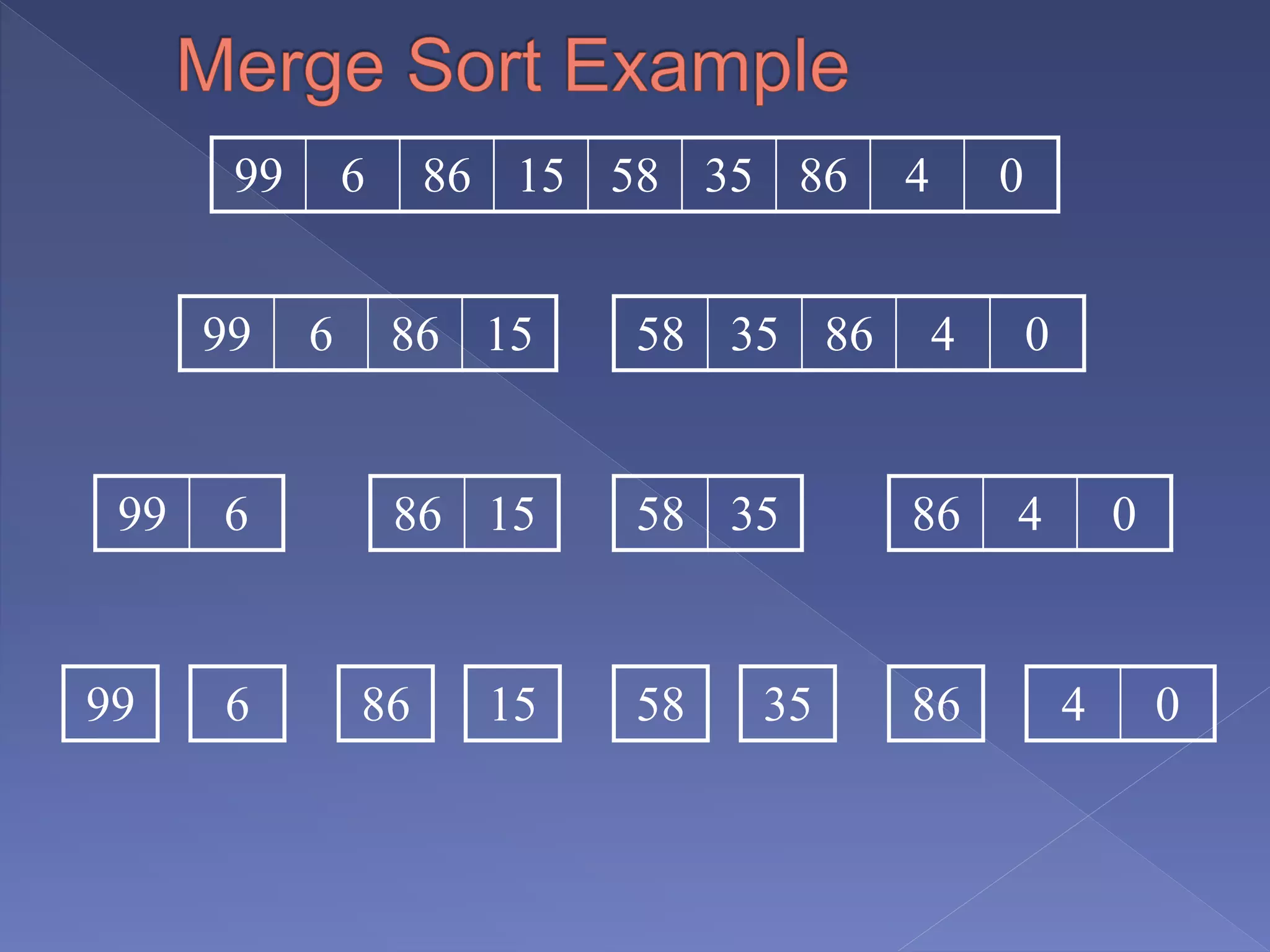
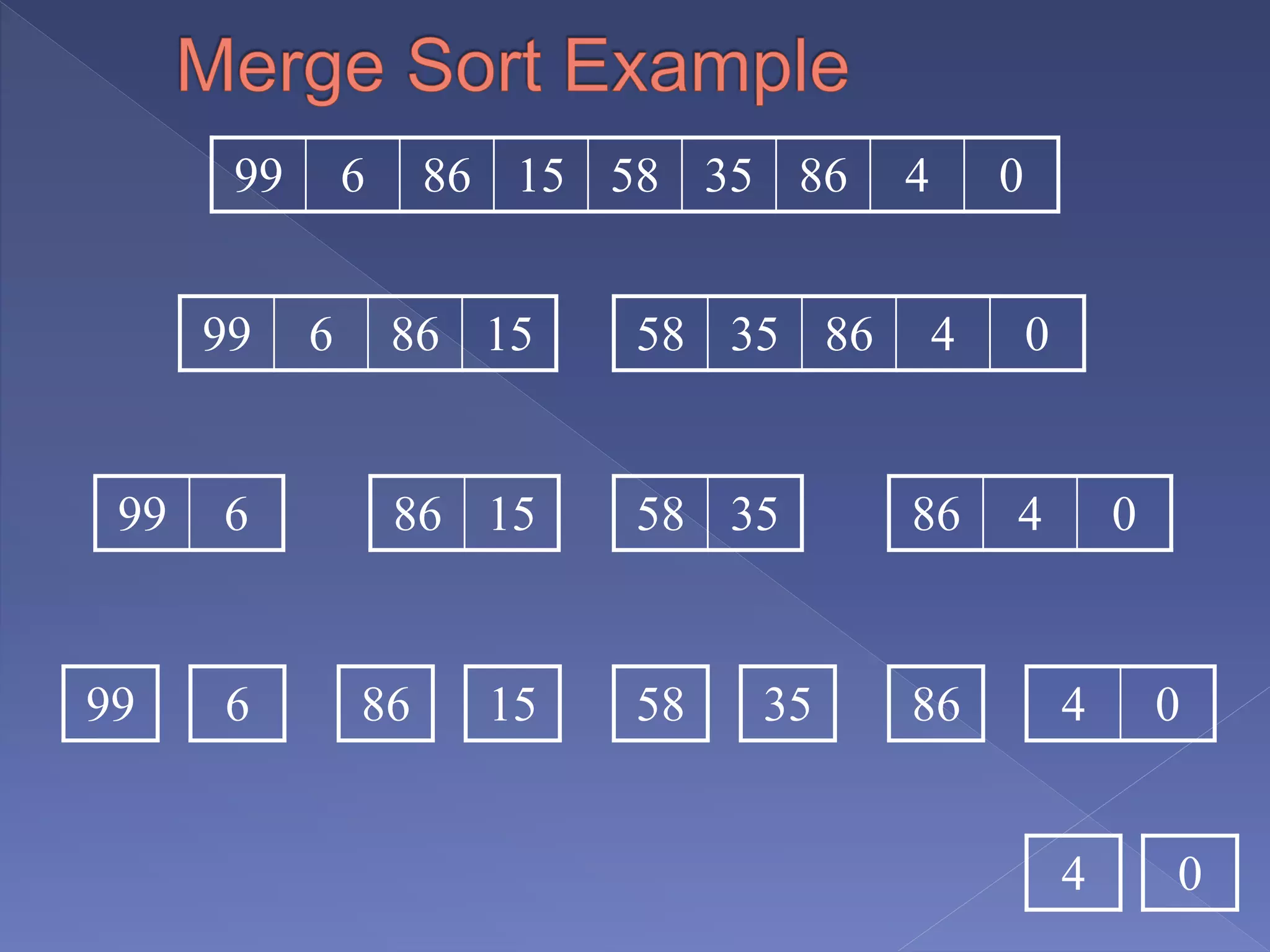
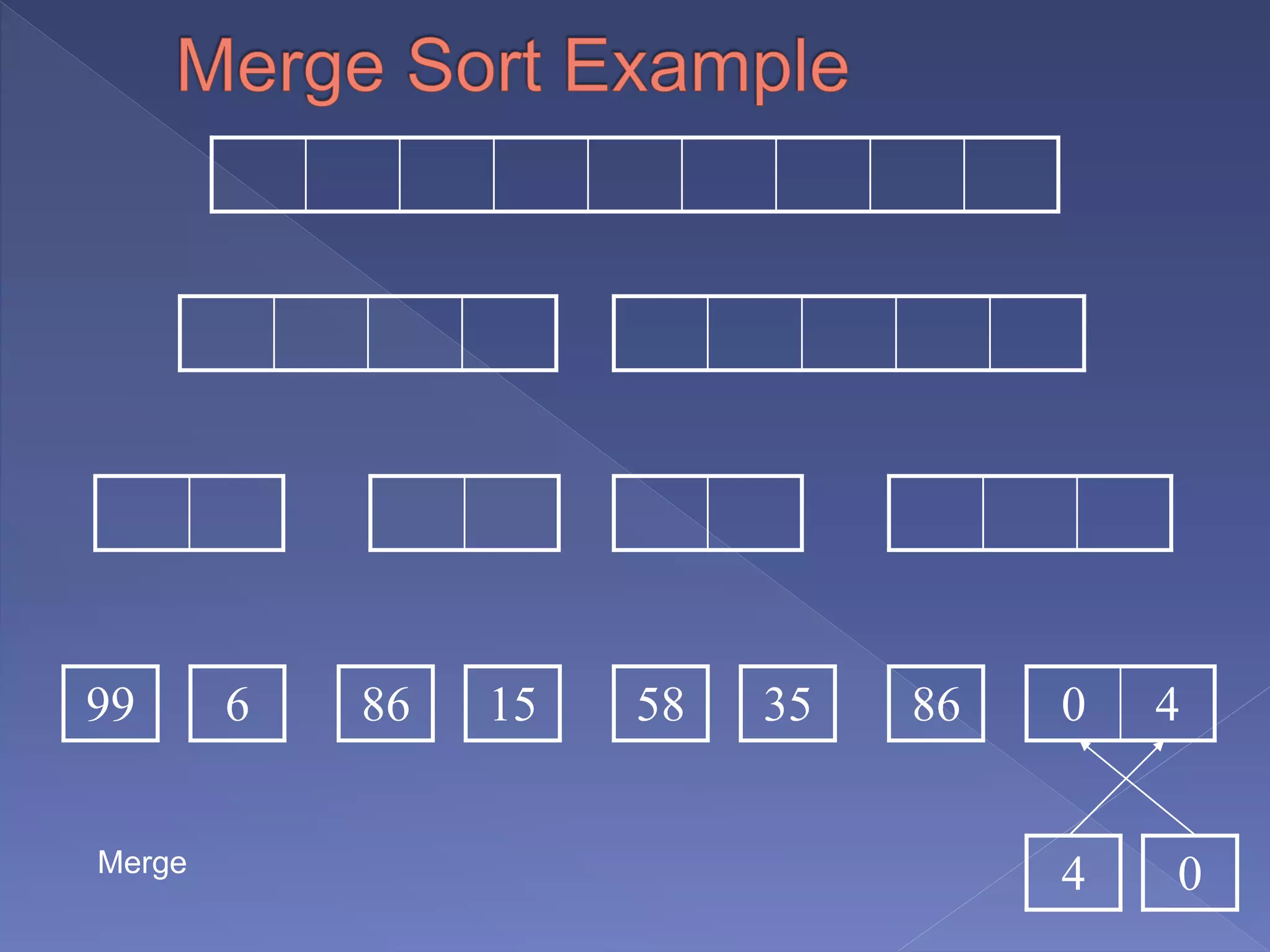
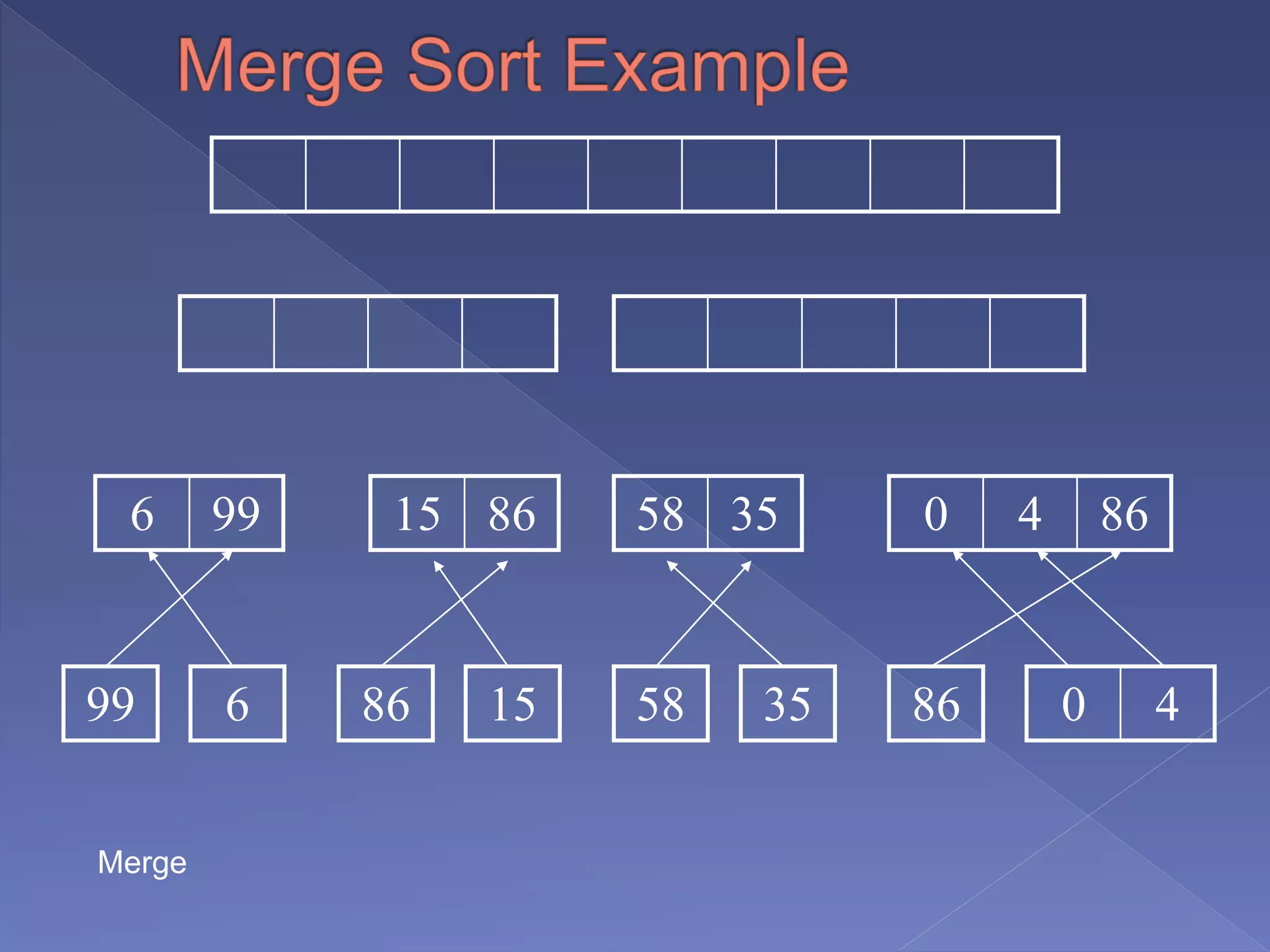
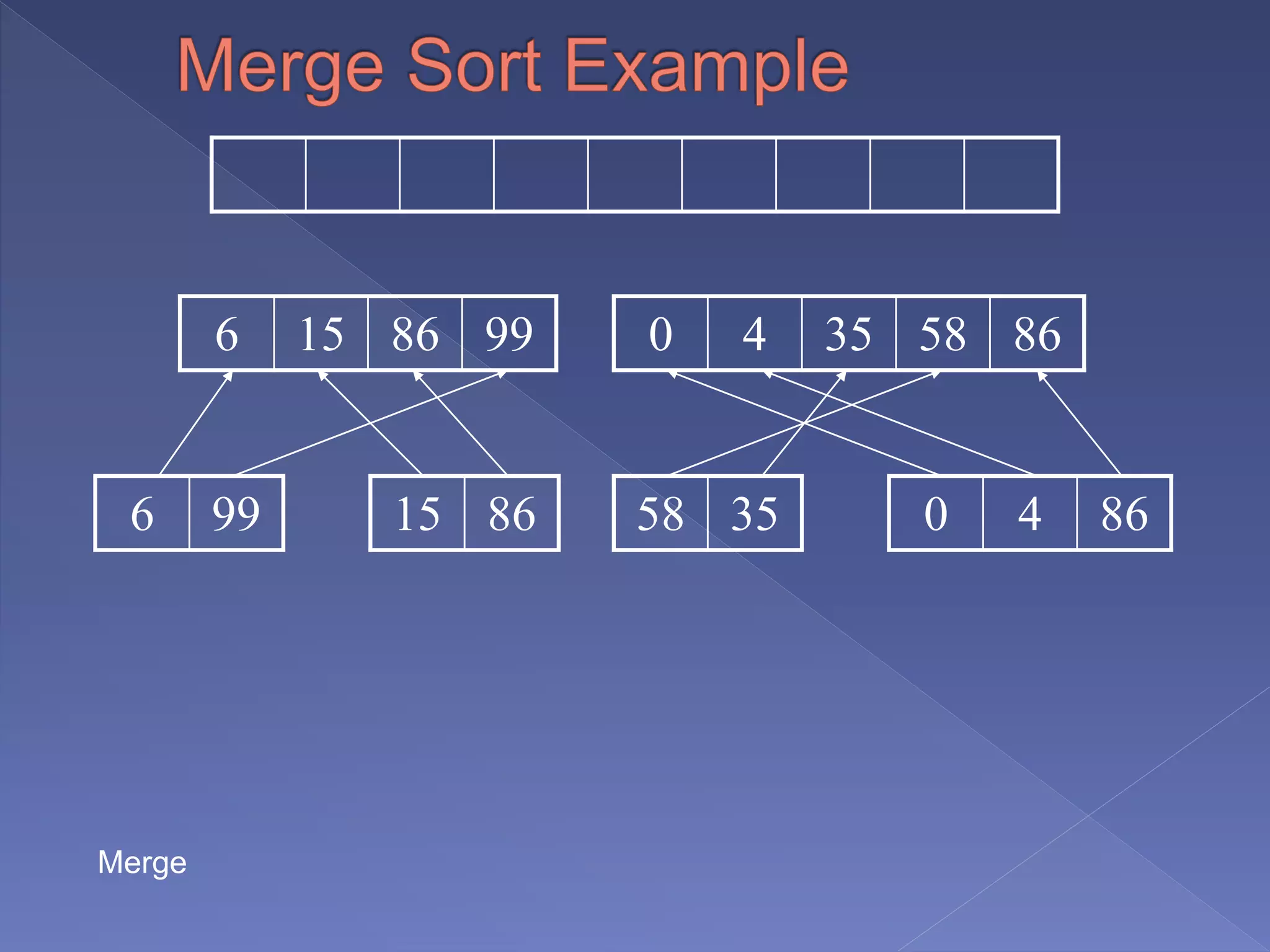
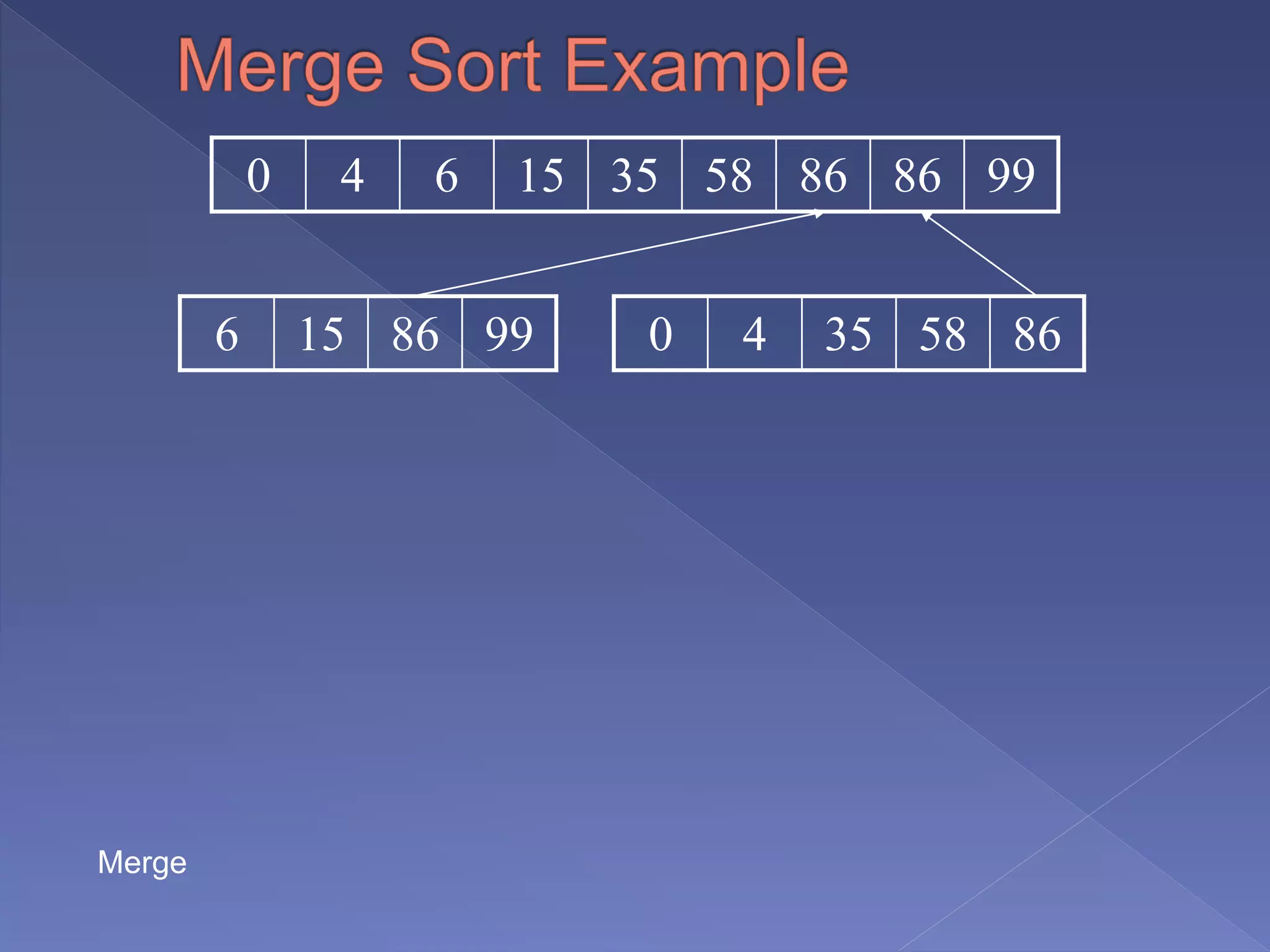
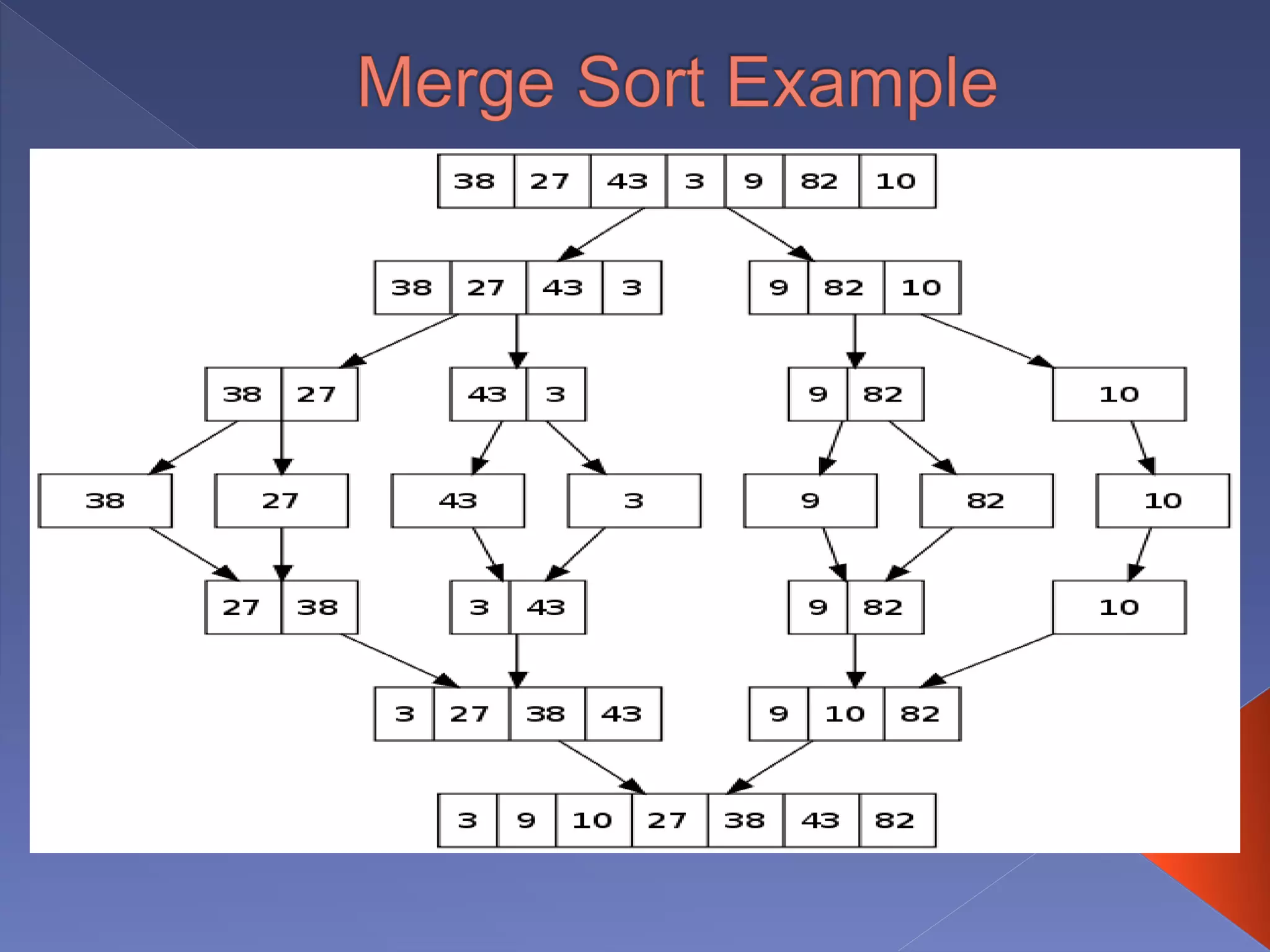

Merge sort is a sorting algorithm based on the divide and conquer technique, with a worst-case time complexity of O(n log n). It works by recursively splitting the array into halves, sorting each half, and then merging them back together in a sorted order. Developed by John von Neumann for EDVAC in 1945, it efficiently handles sorting tasks through its systematic approach.




![ MERGE SORT (A,p,r) //divide
if p < r
then q= [ (p + r) / 2 ]
MERGE SORT(A,p,q)
MERGER SORT(A,q + 1,r)
MERGE(A,p,q,r)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mergesortalgorithm-160901095302/75/Merge-sort-algorithm-5-2048.jpg)
![Merge(array A, int p, int q, int r)
{
array B[p..r] //temp array taken
i = k = p // initialize pointers
j = q+1
while (i <= q and j <= r)
{
if (A[i] <= A[j]) B[k++] = A[i++]
else B[k++] = A[j++]
}
while (i <= q)
B[k++] = A[i++] // copy any leftover to B
while (j <= r)
B[k++] = A[j++]
for i = p to r
A[i] = B[i] // copy B back to A
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mergesortalgorithm-160901095302/75/Merge-sort-algorithm-6-2048.jpg)










