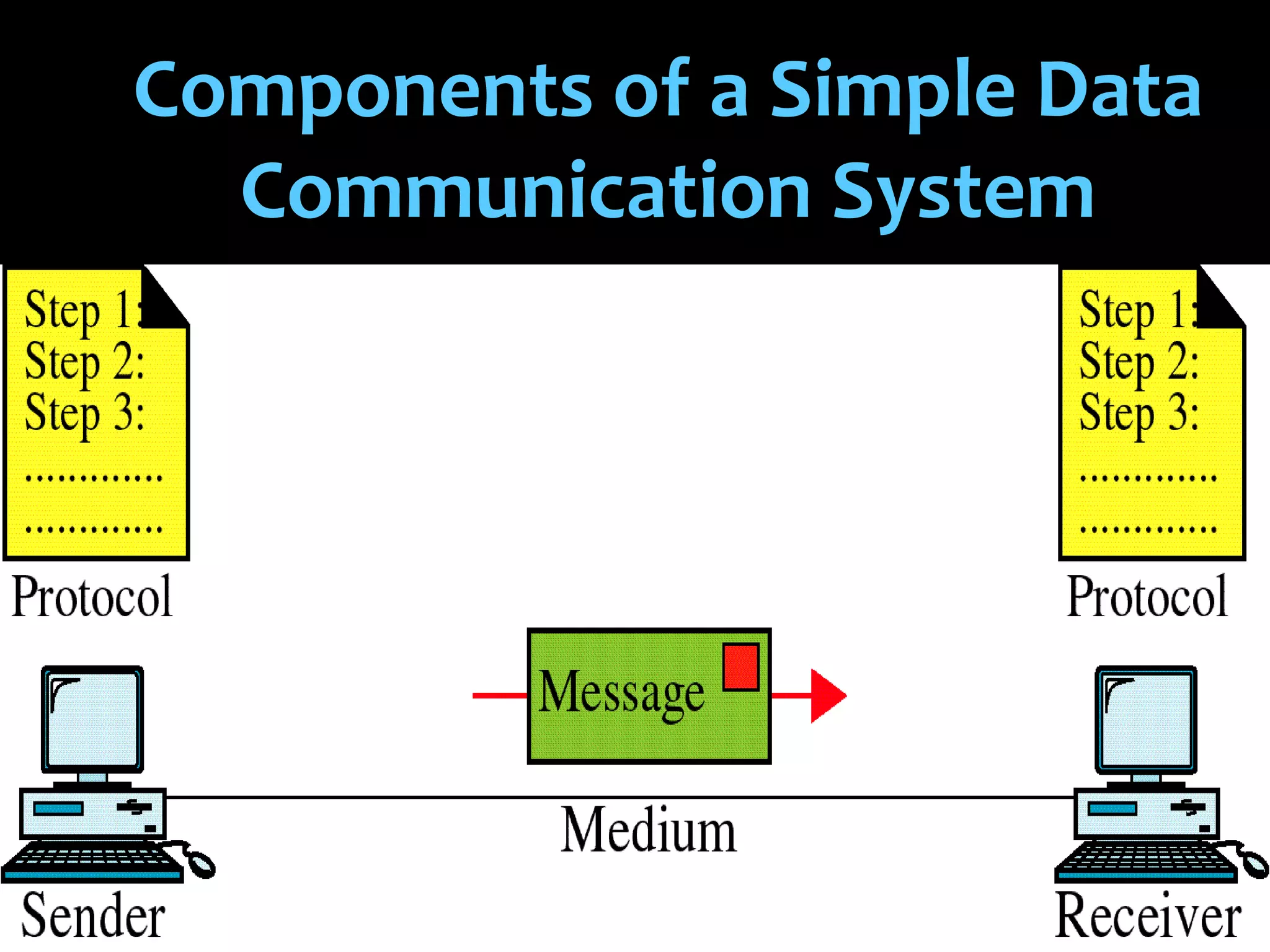
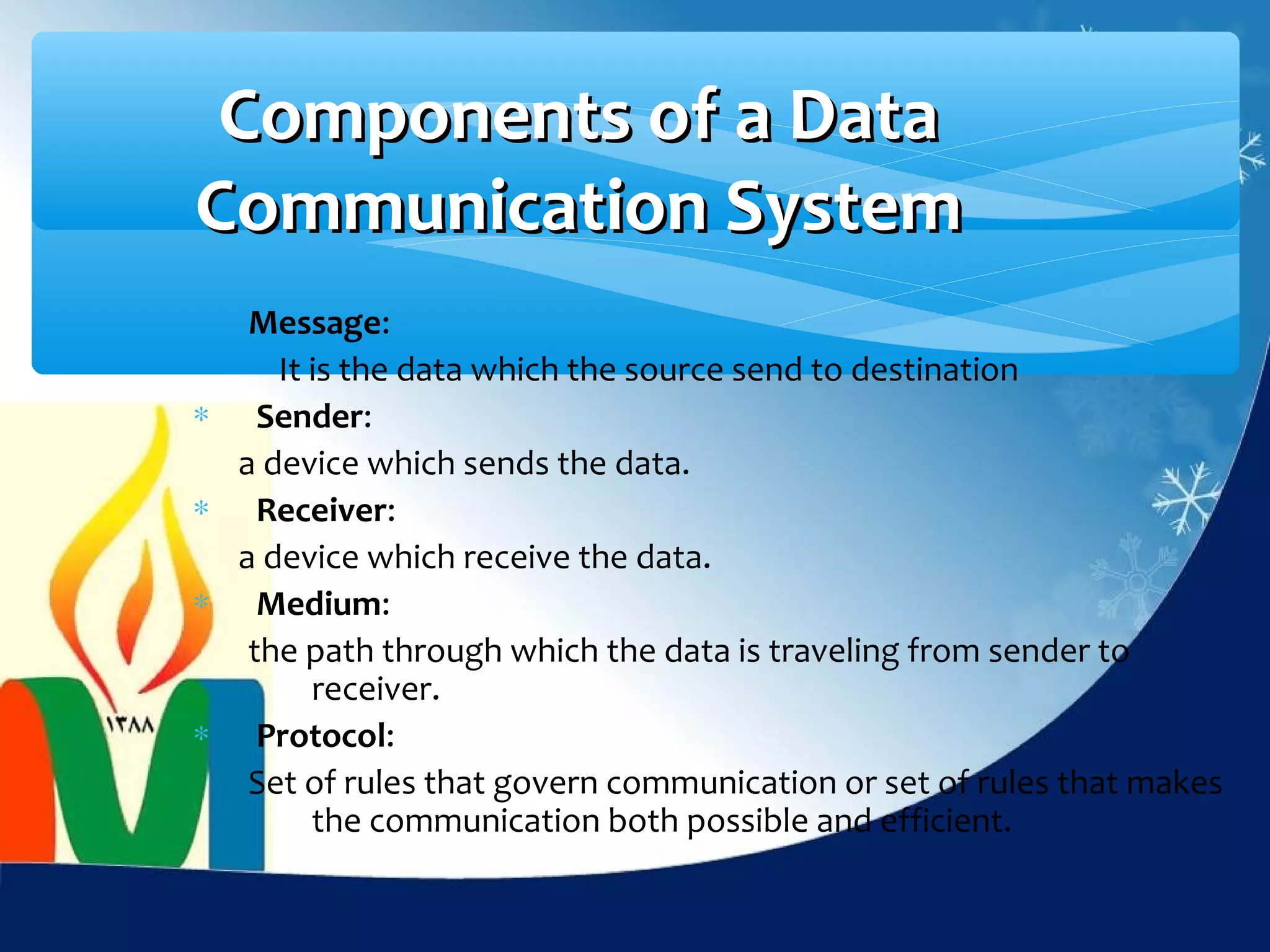
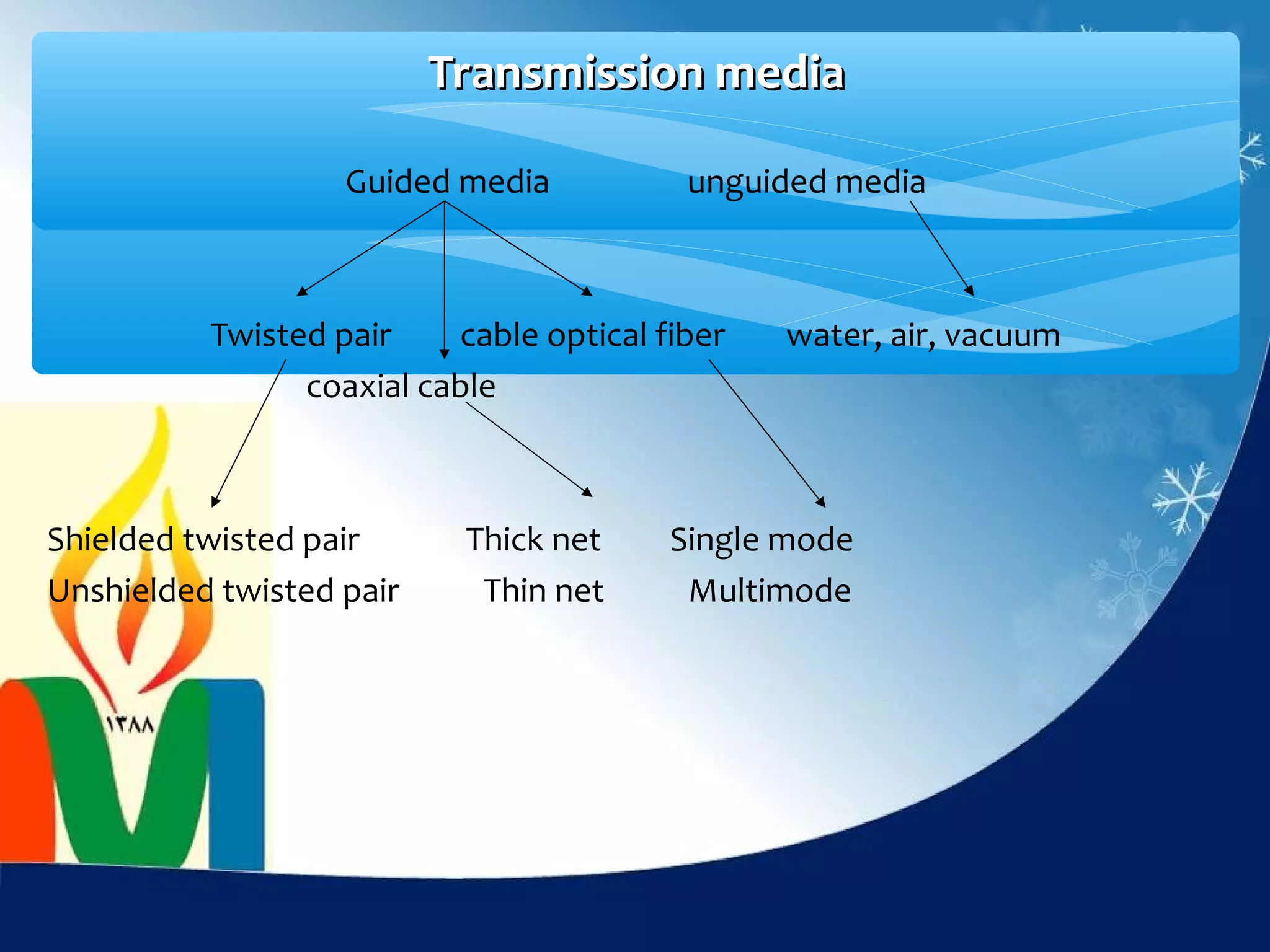
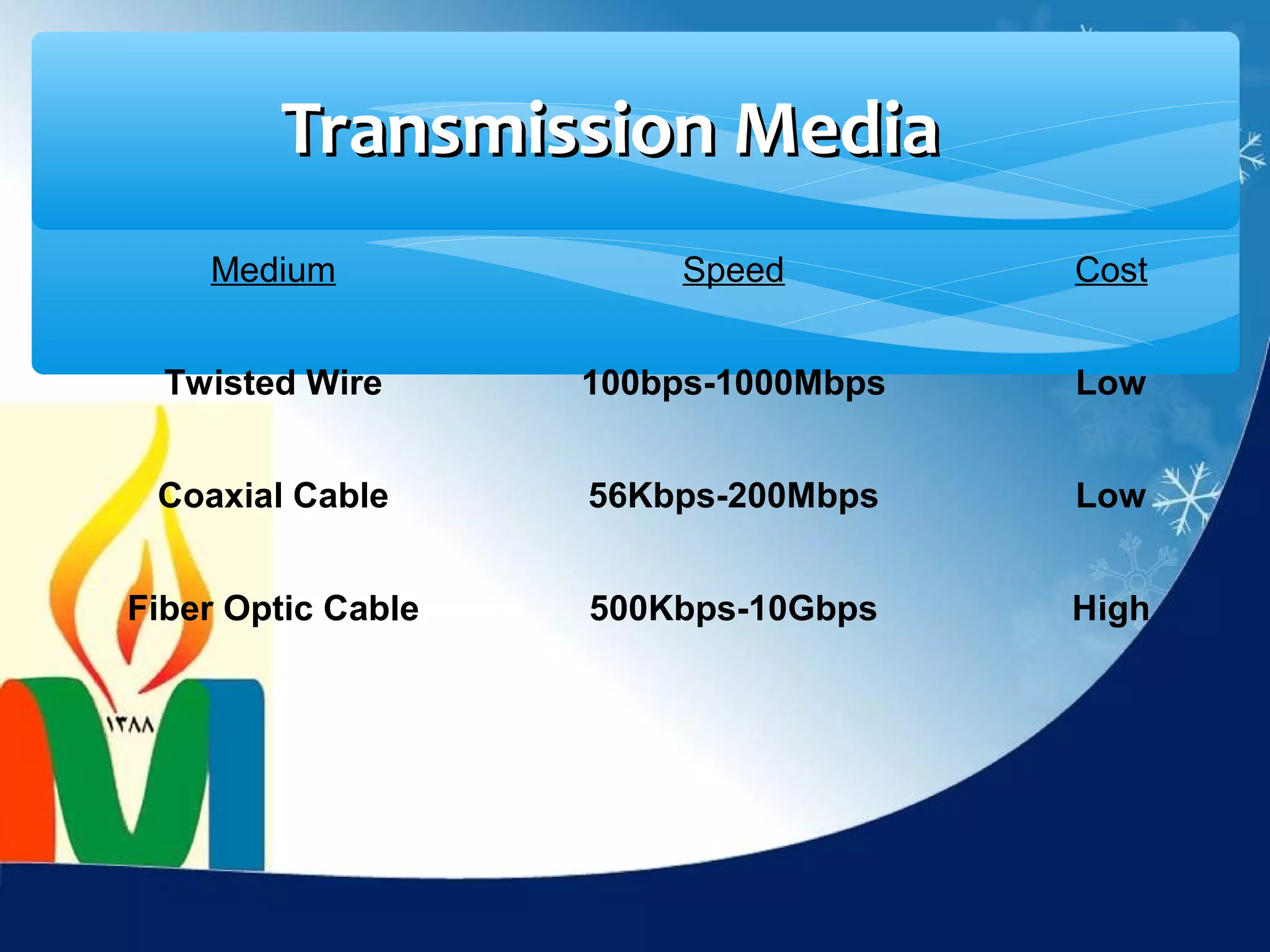
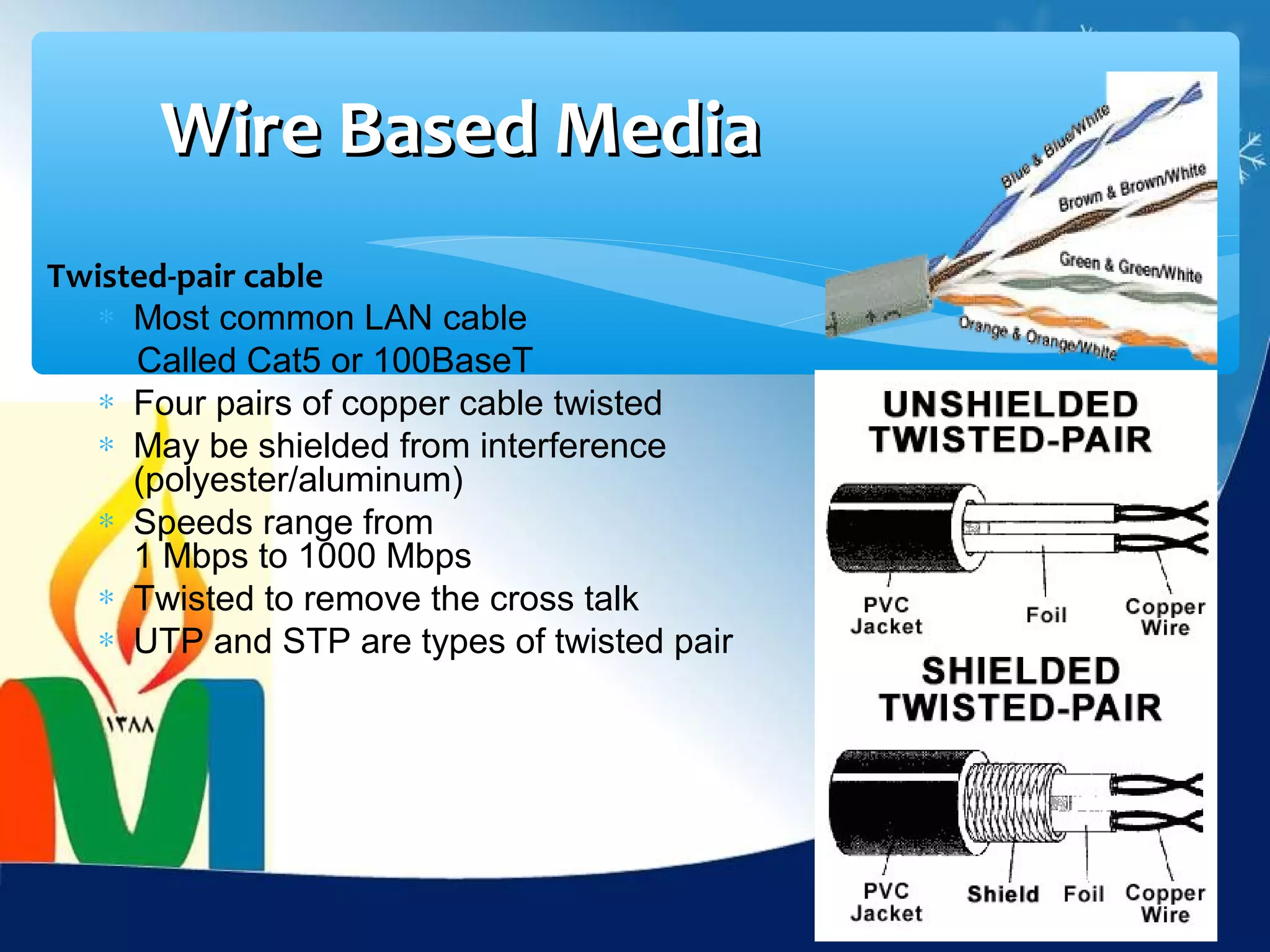
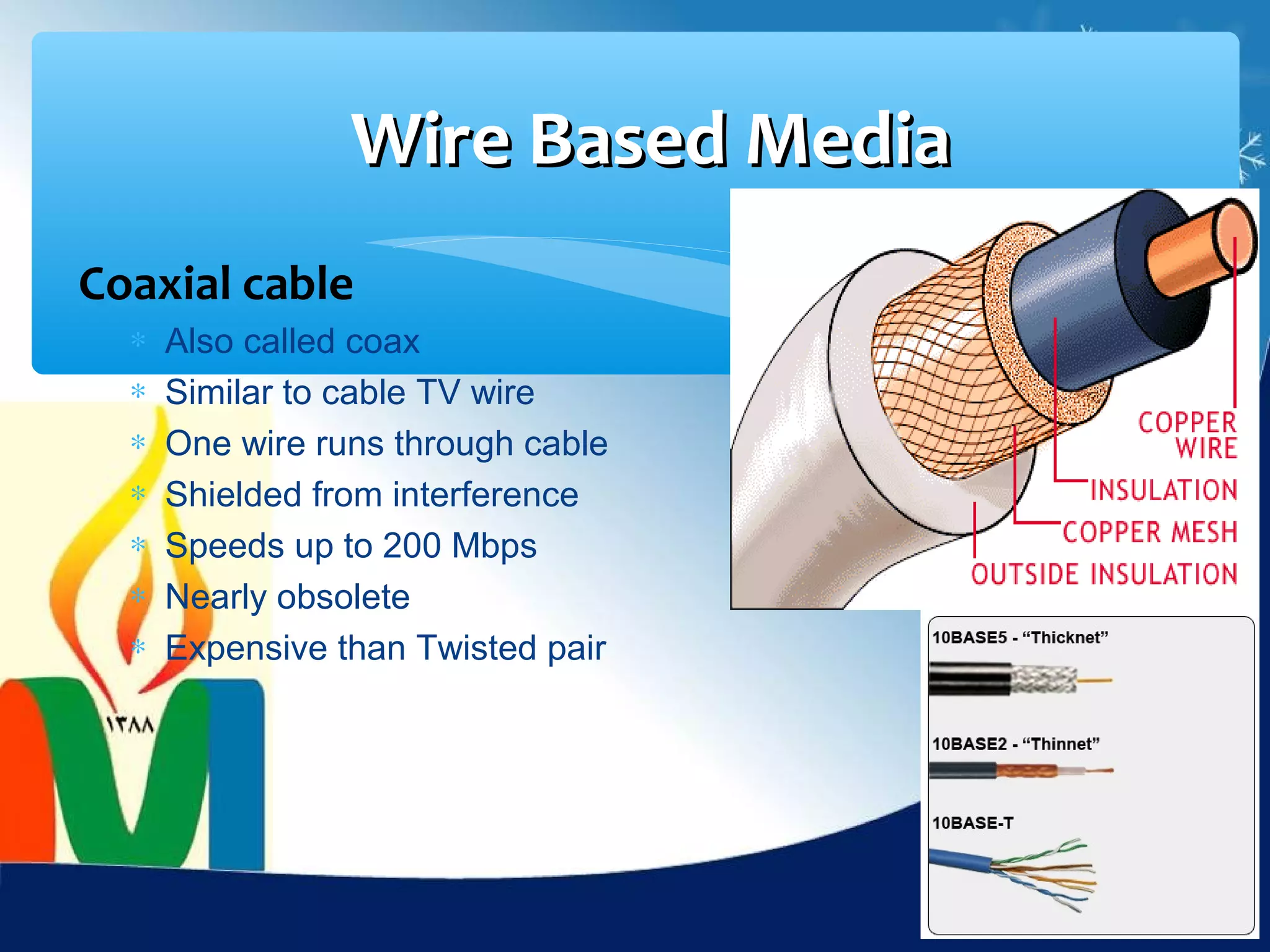
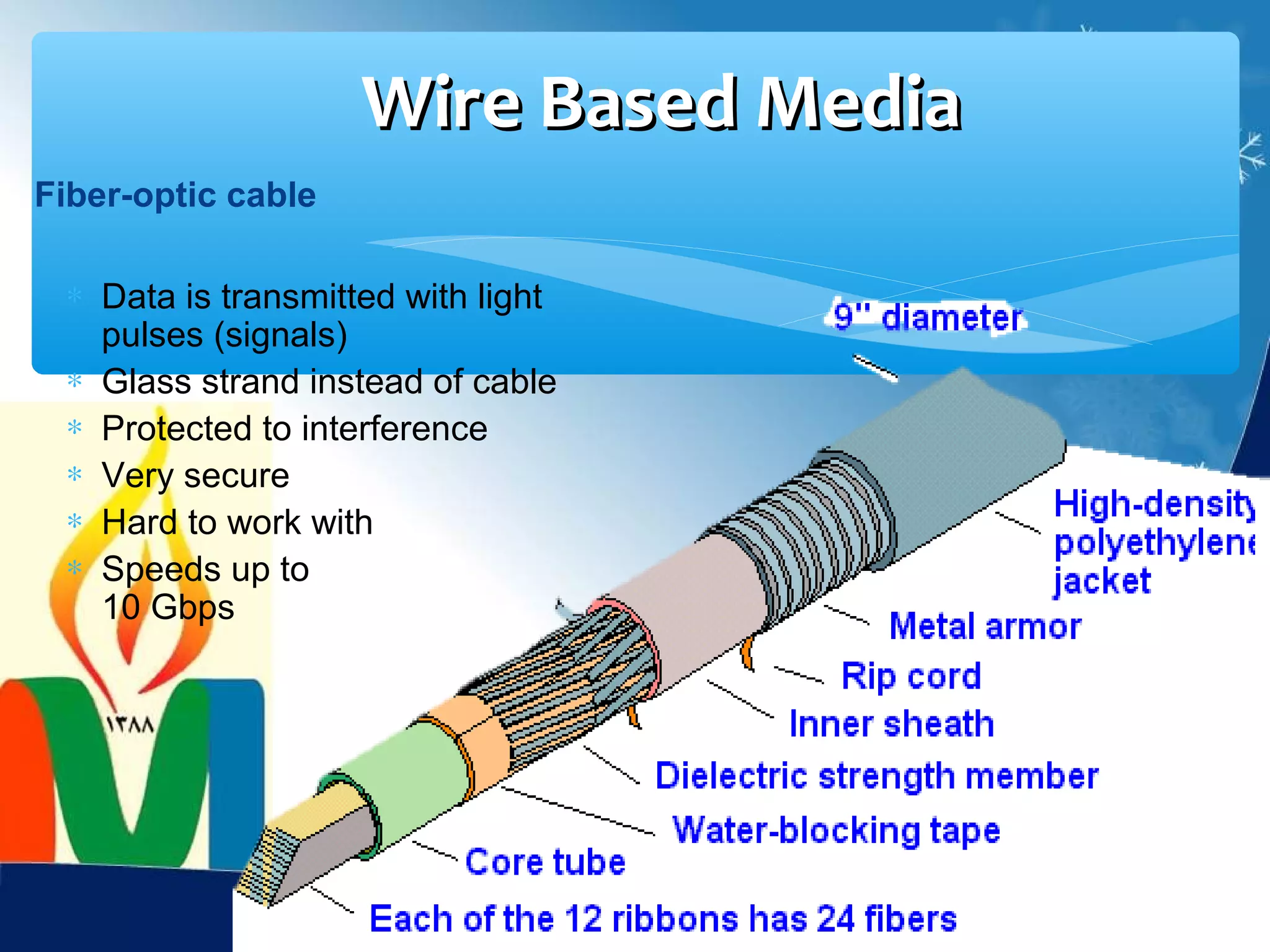
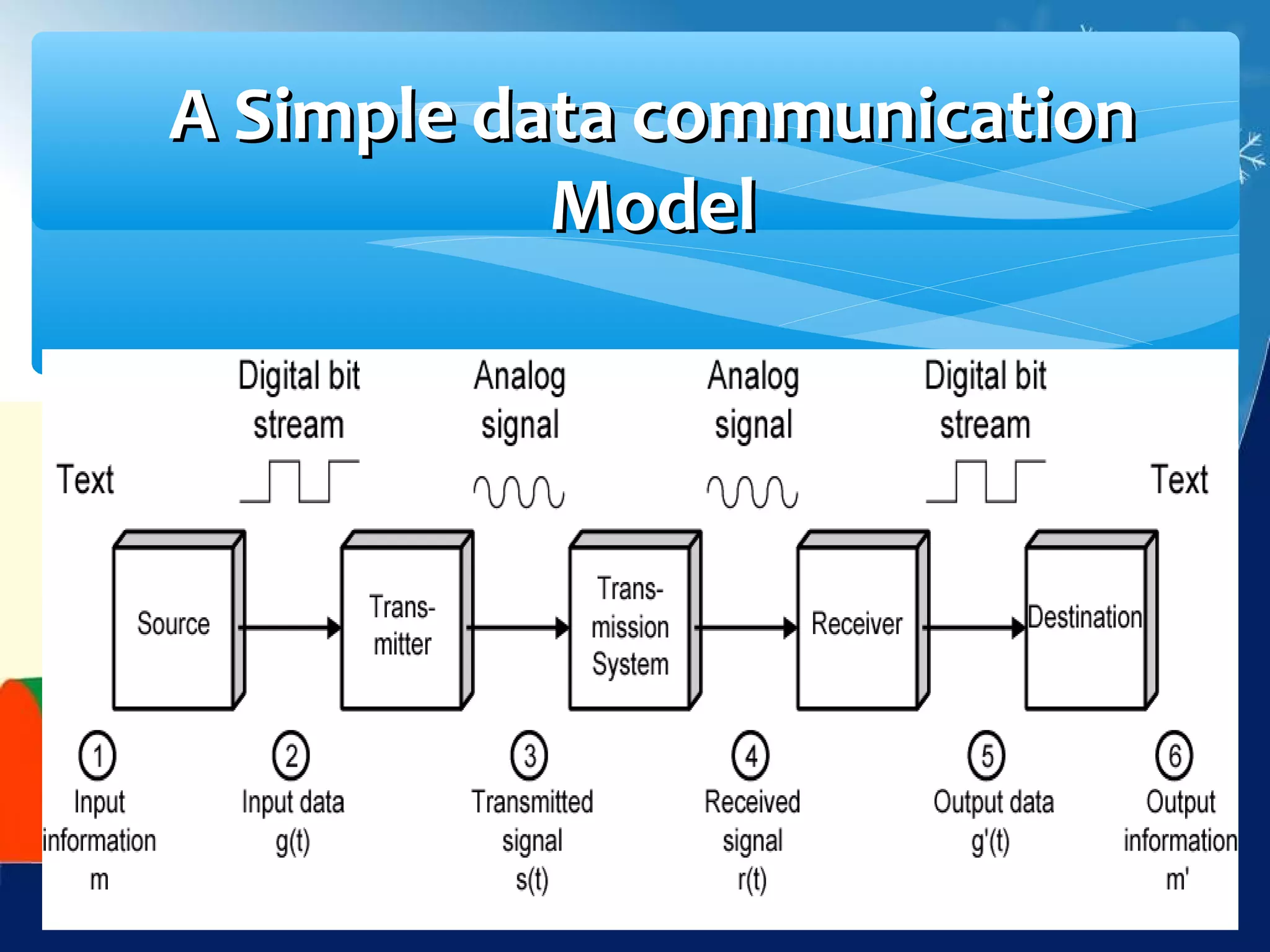
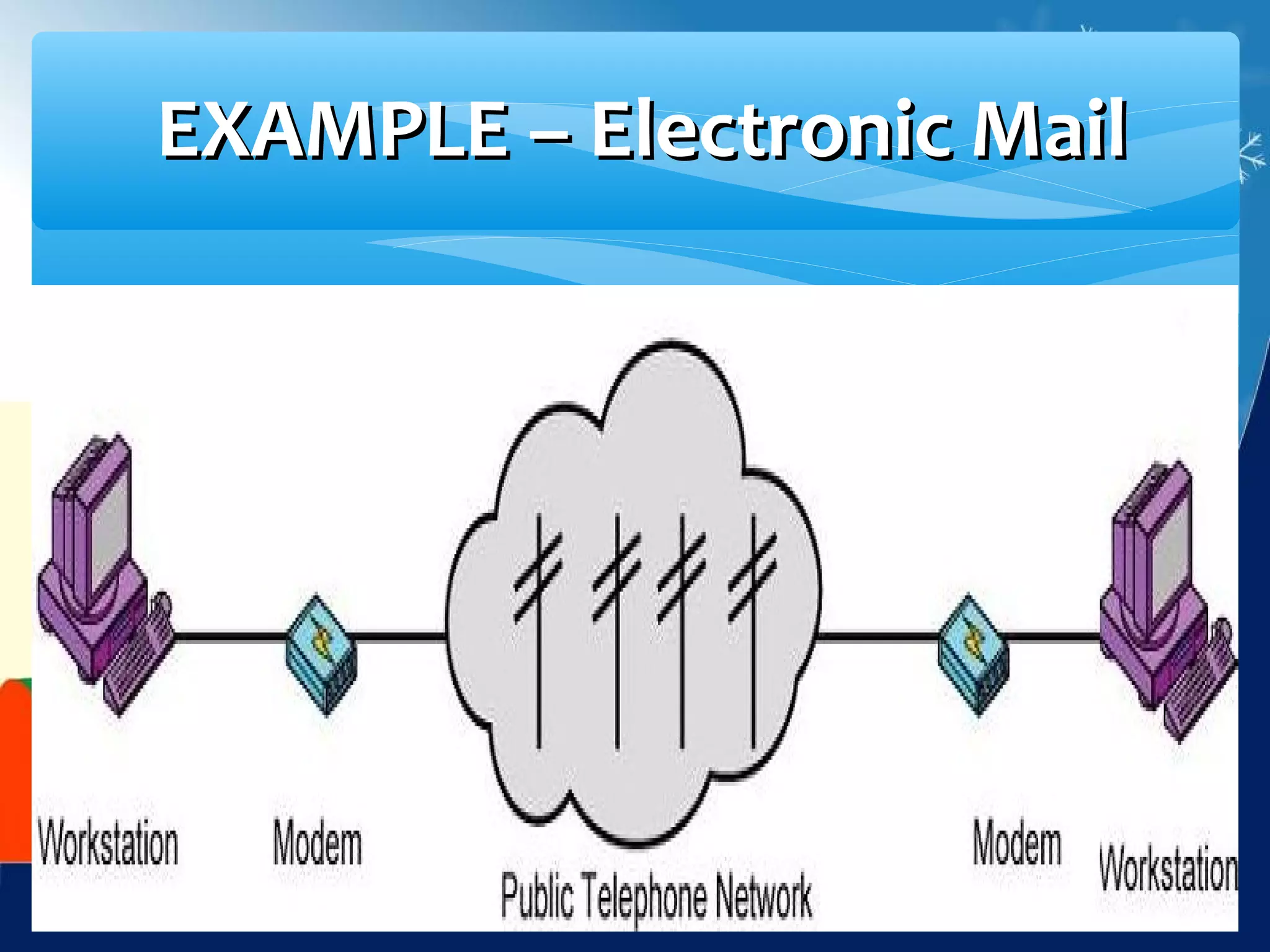
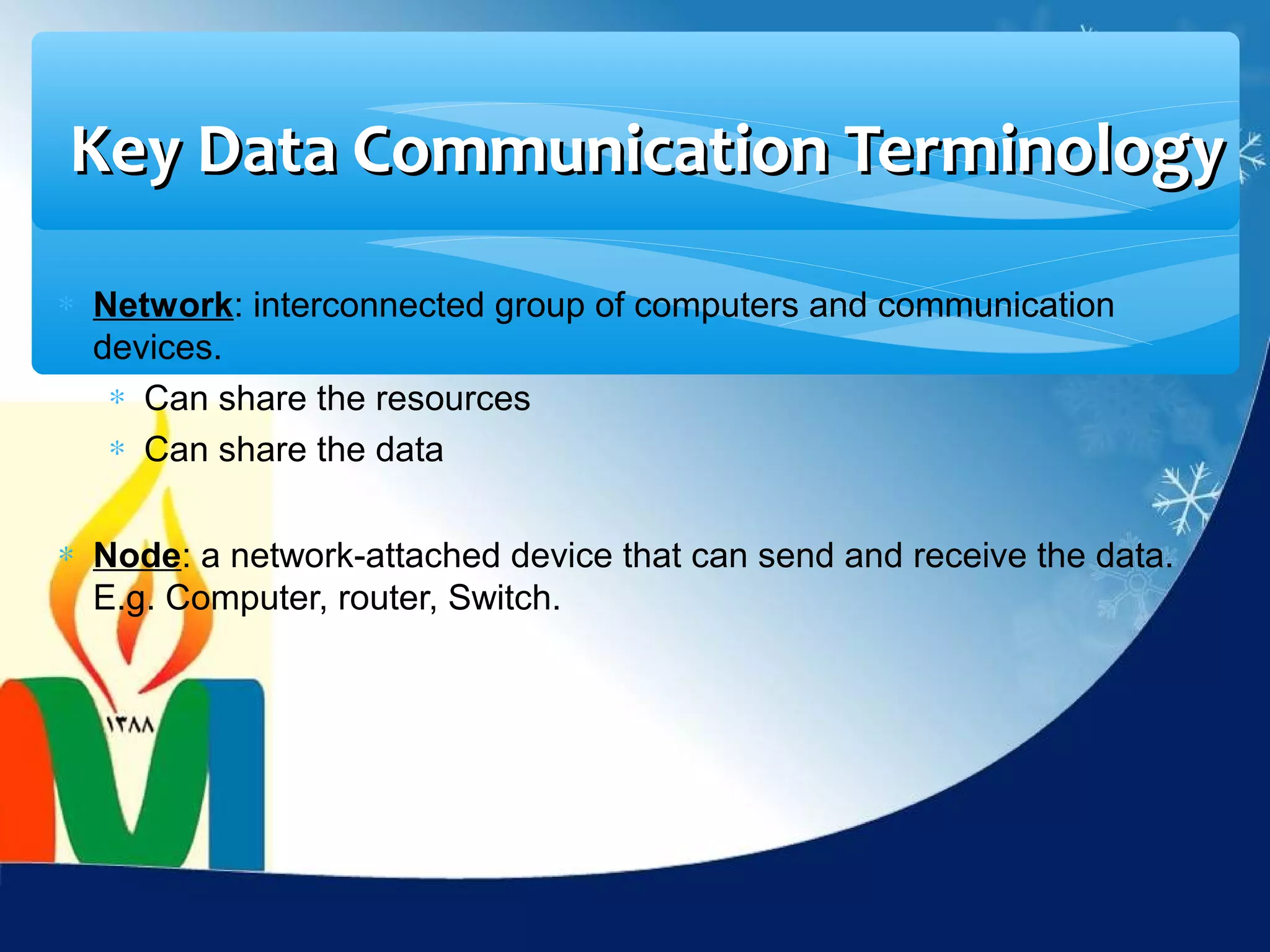
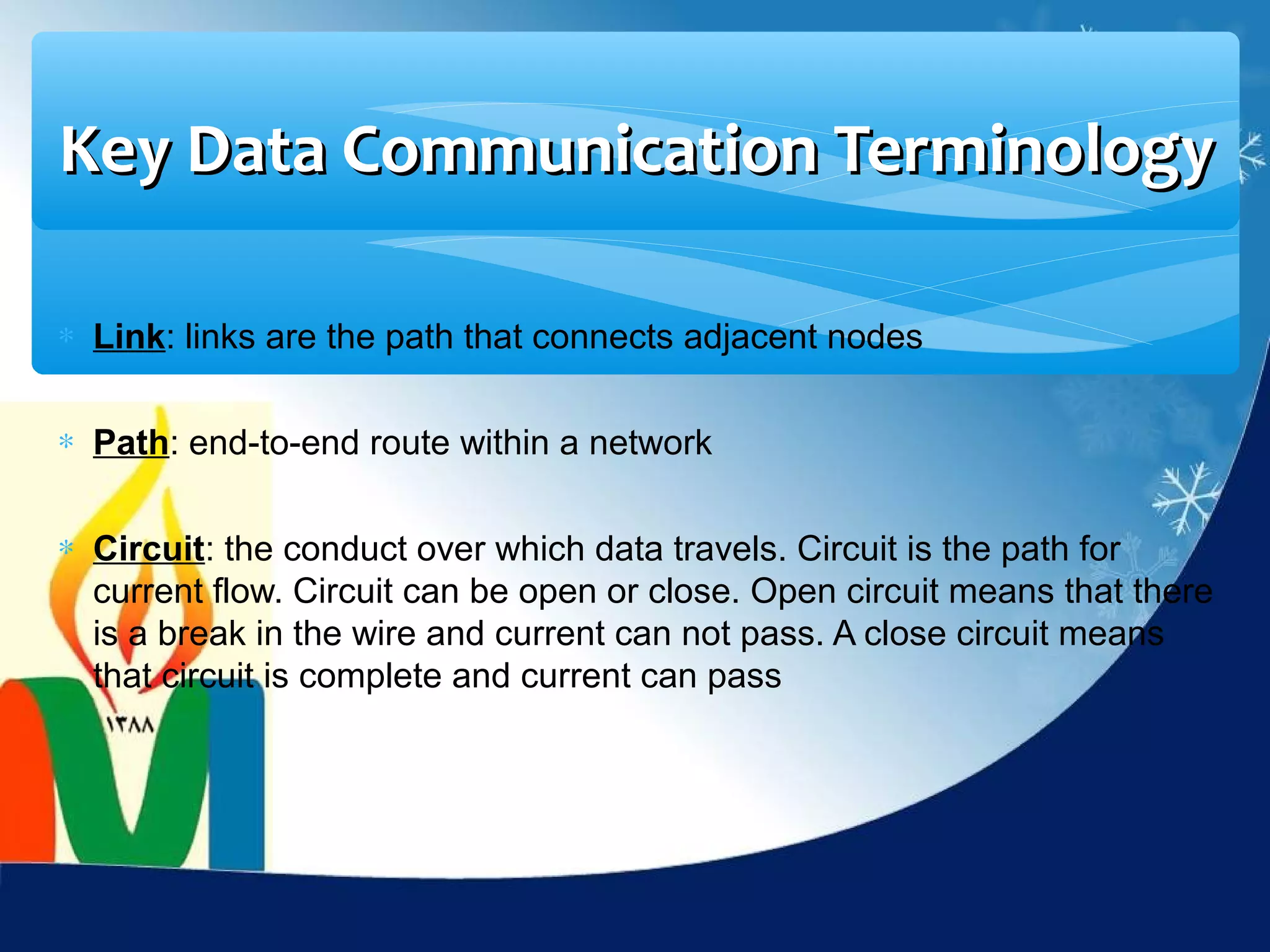
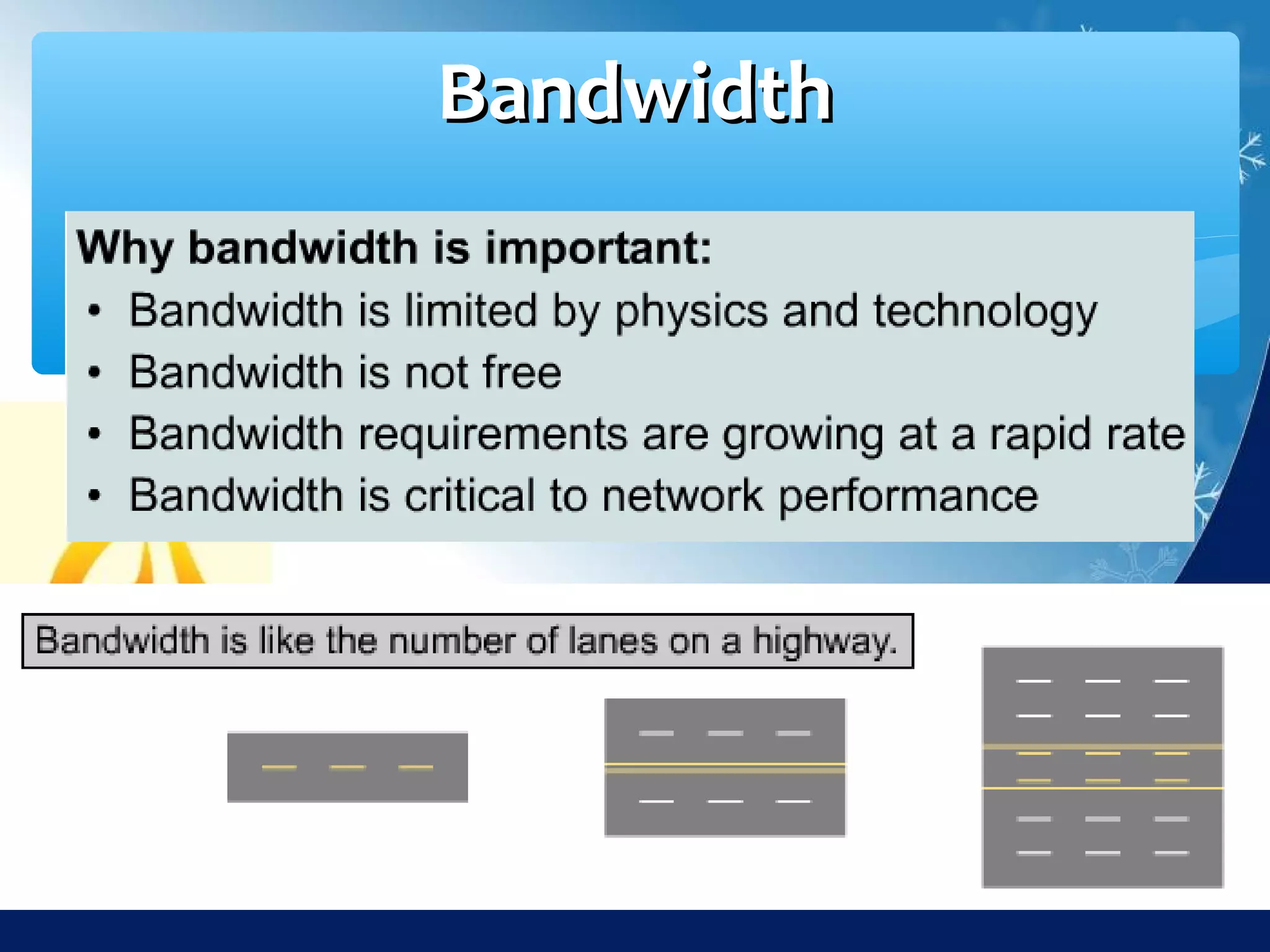
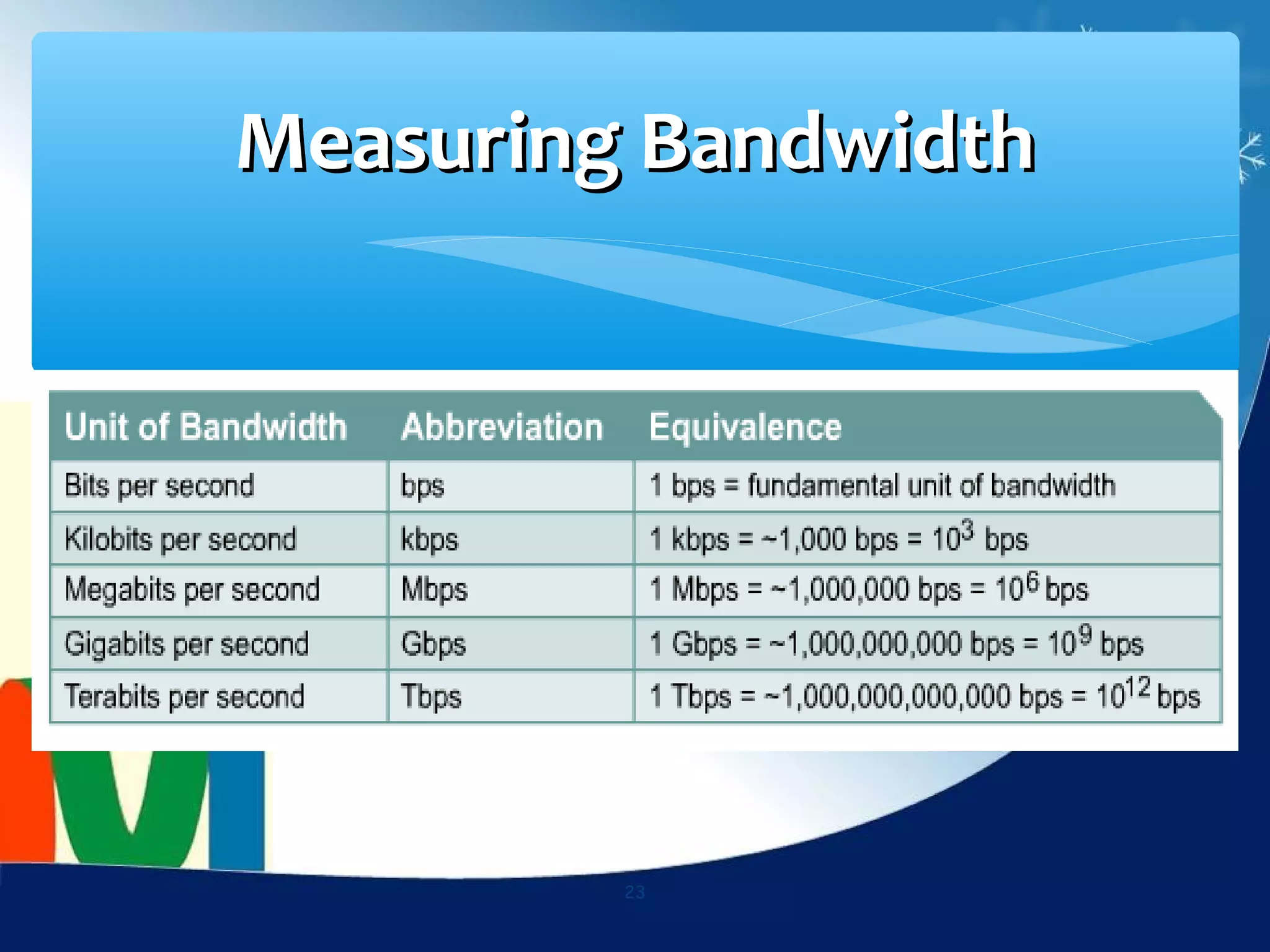
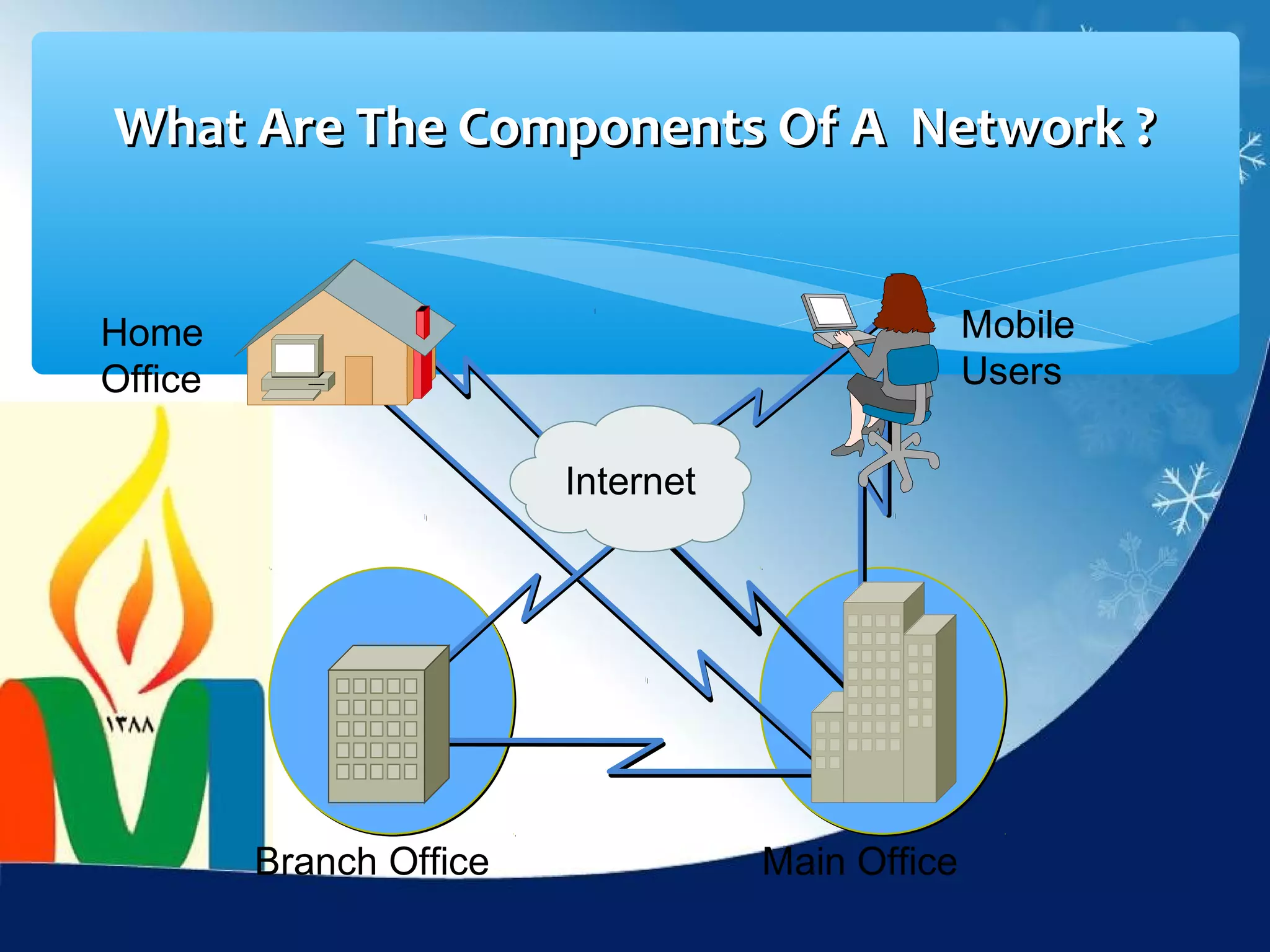
Data communication is the exchange of data between two devices via a transmission medium. It can be either local, when the devices are near each other, or remote, when they are farther apart. A data communication system consists of five main components: a message, sender, receiver, transmission medium, and protocol. It allows for the effective delivery, accuracy, and timeliness of data exchange.