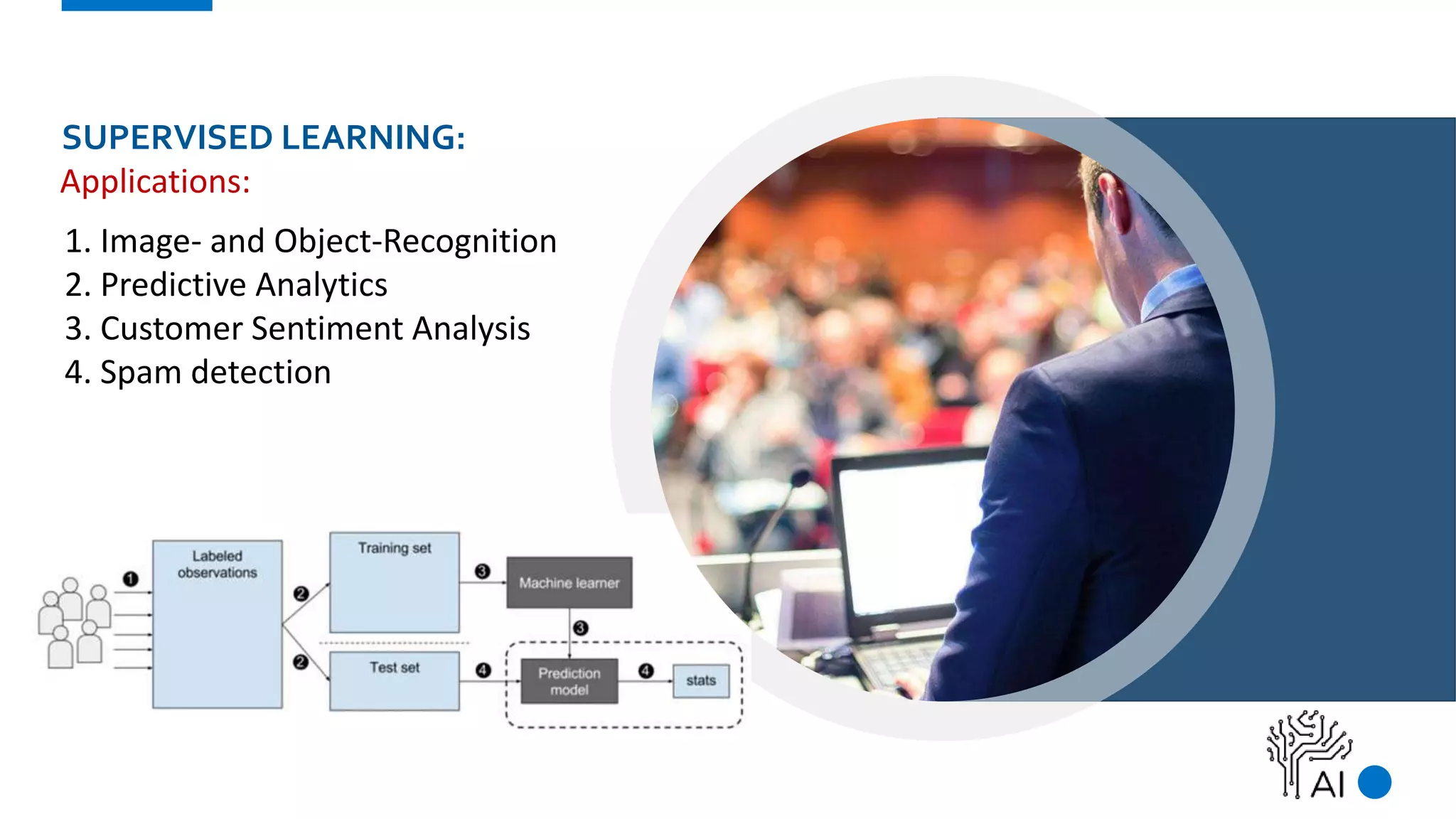
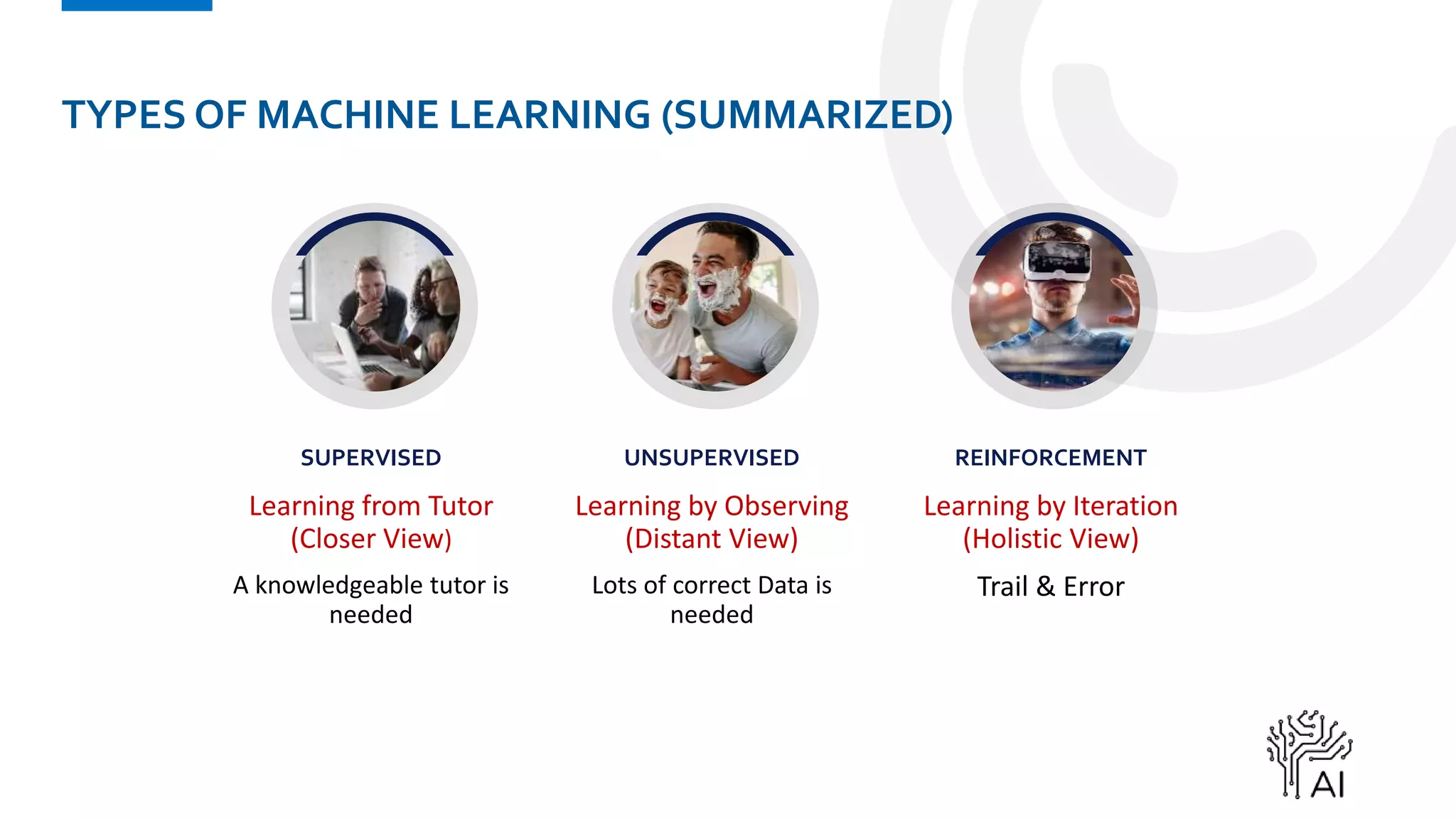
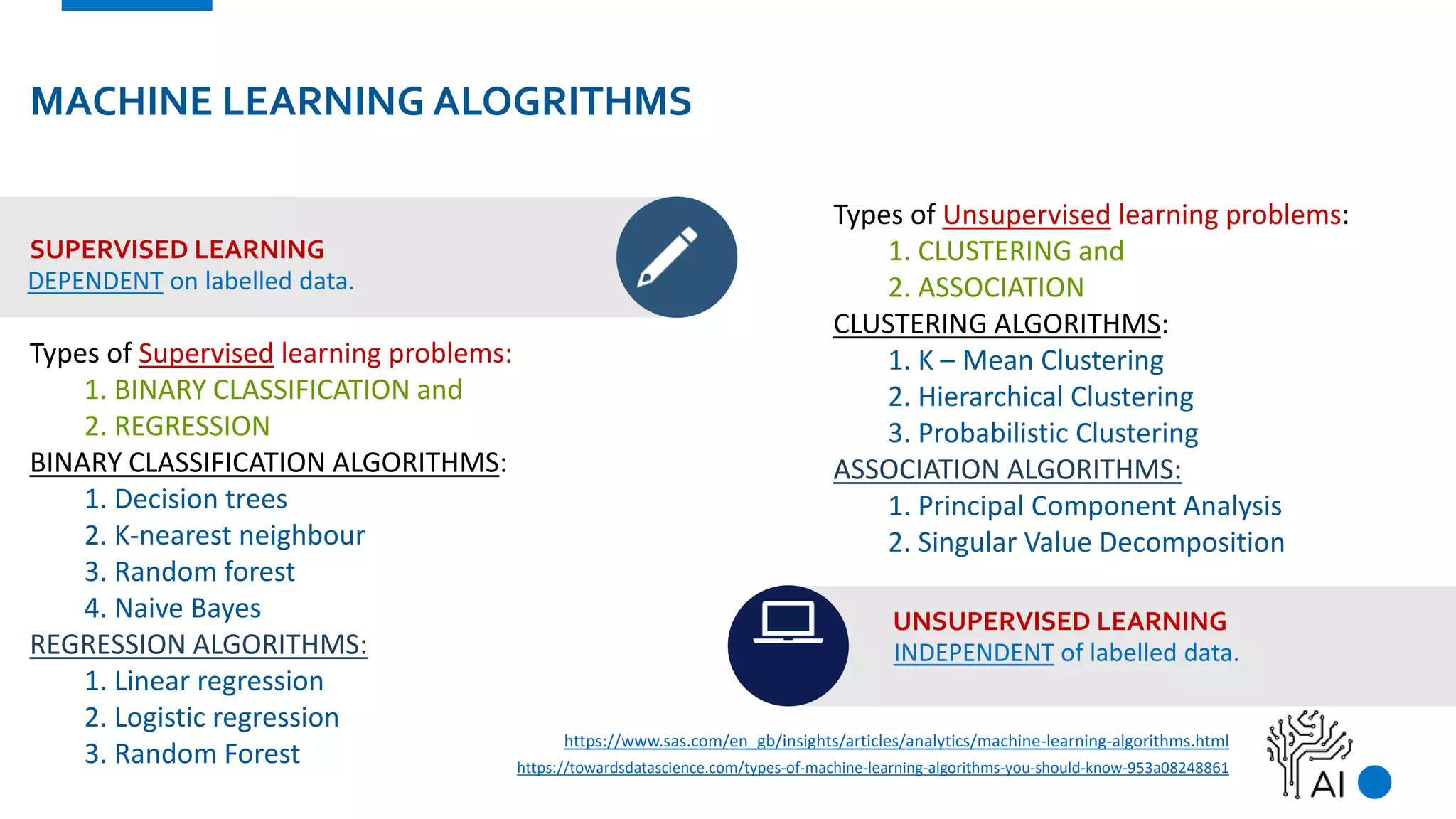
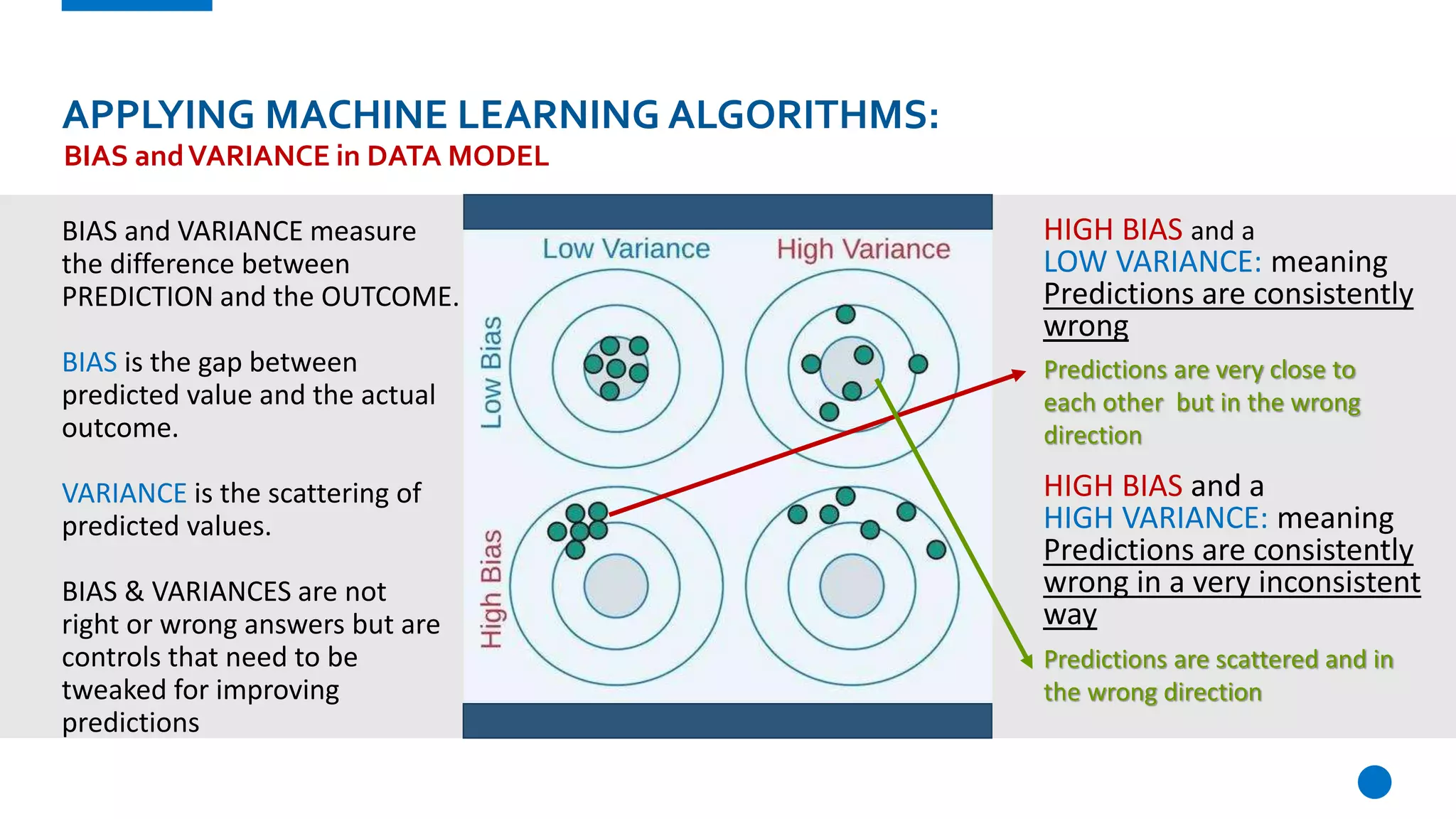
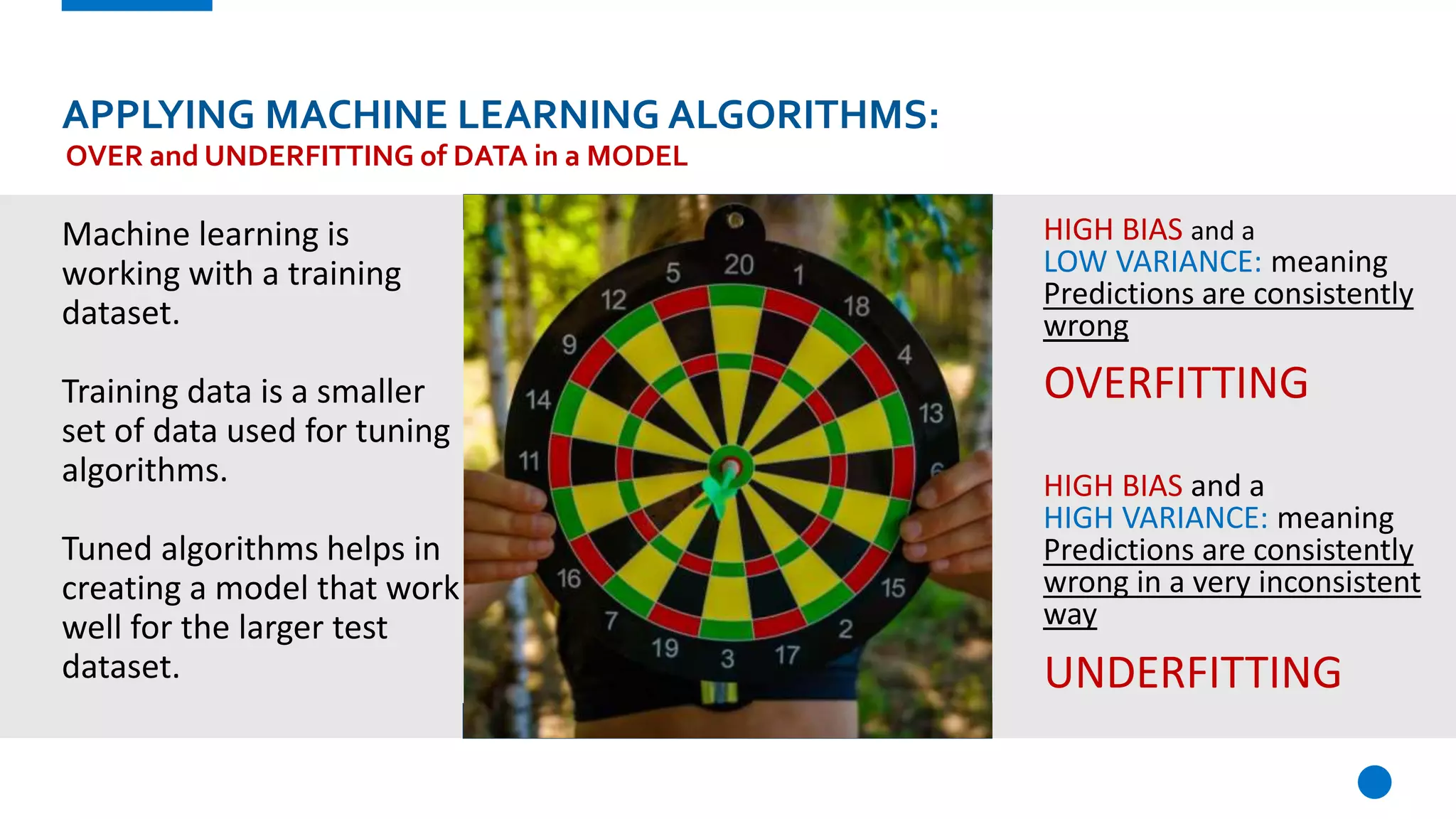
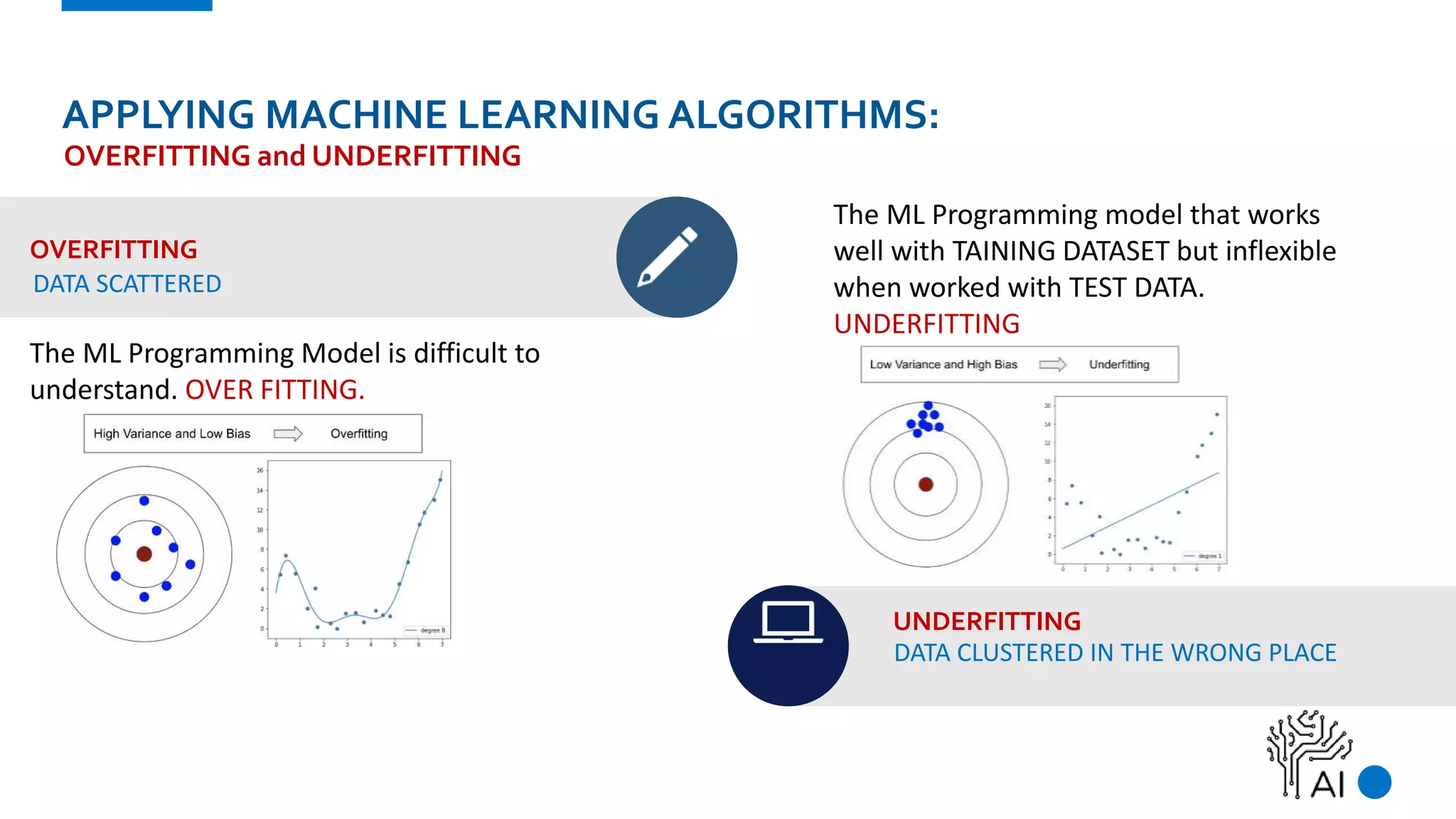
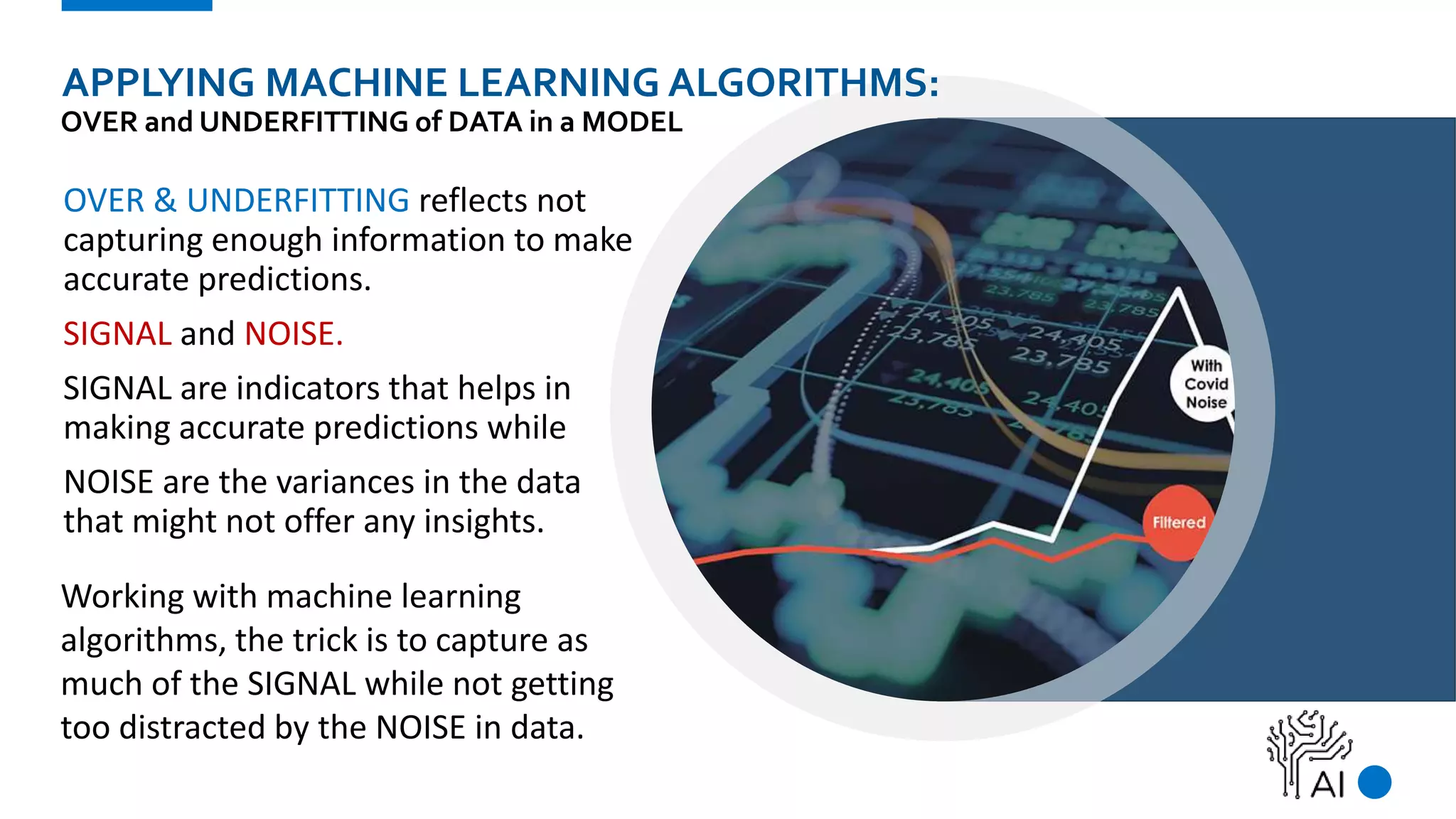
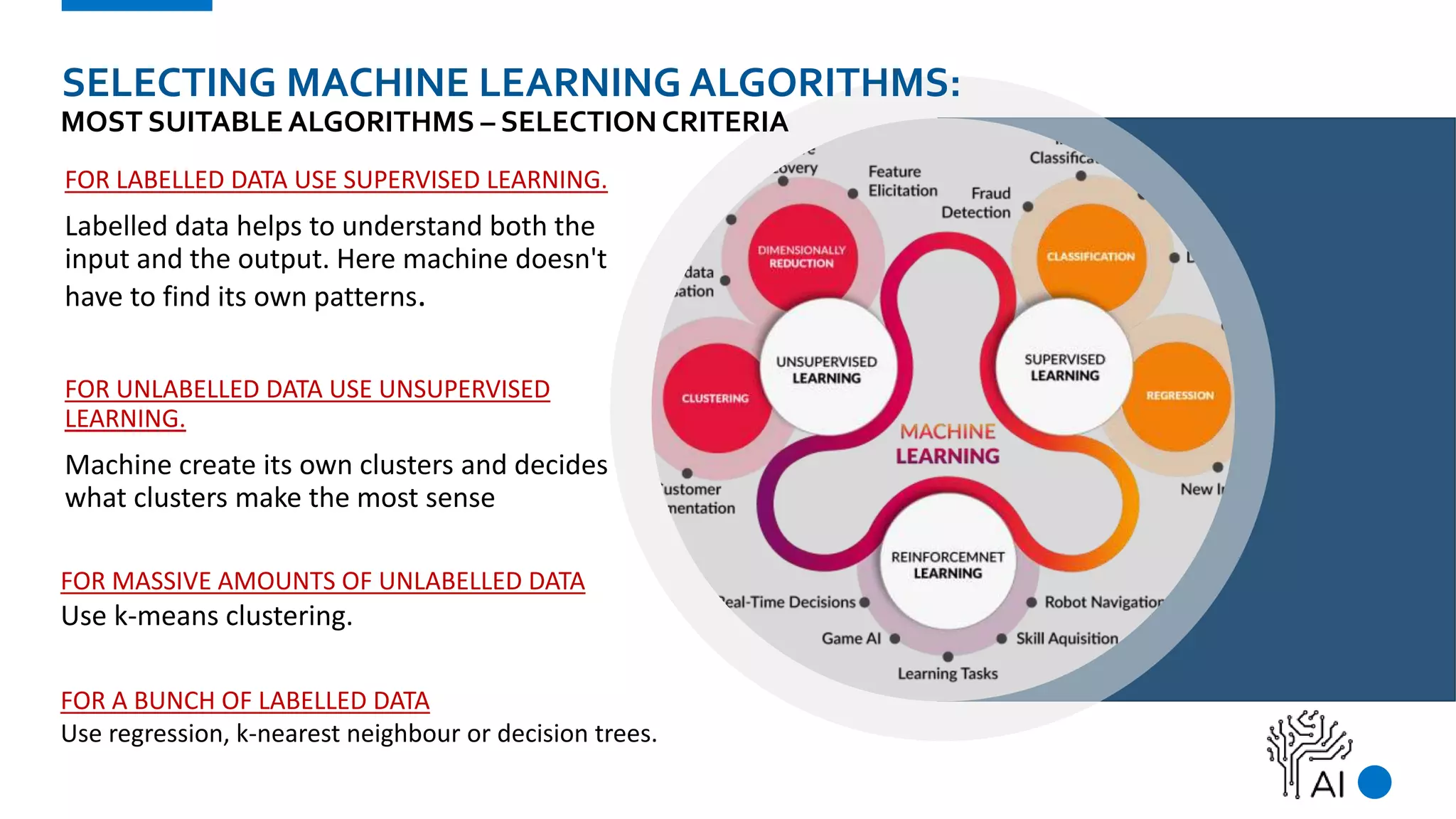
The document provides an overview of machine learning, defining it as a method where algorithms learn patterns from data without explicit instructions. It elaborates on different types of machine learning, including supervised, unsupervised, and reinforcement learning, as well as the importance of algorithms and hyper-parameters in model training and predictions. Additionally, it discusses challenges like bias, variance, overfitting, and underfitting when applying machine learning algorithms.