This document provides an overview of Linux shell scripting concepts including:
- Using Vagrant to create and manage virtual machines for testing shell scripts
- The basics of shell script syntax like naming, permissions, comments and variables
- Common shell commands like echo, read, if/then conditional statements, loops and positional parameters
- Redirection of standard input/output and pipes to connect commands
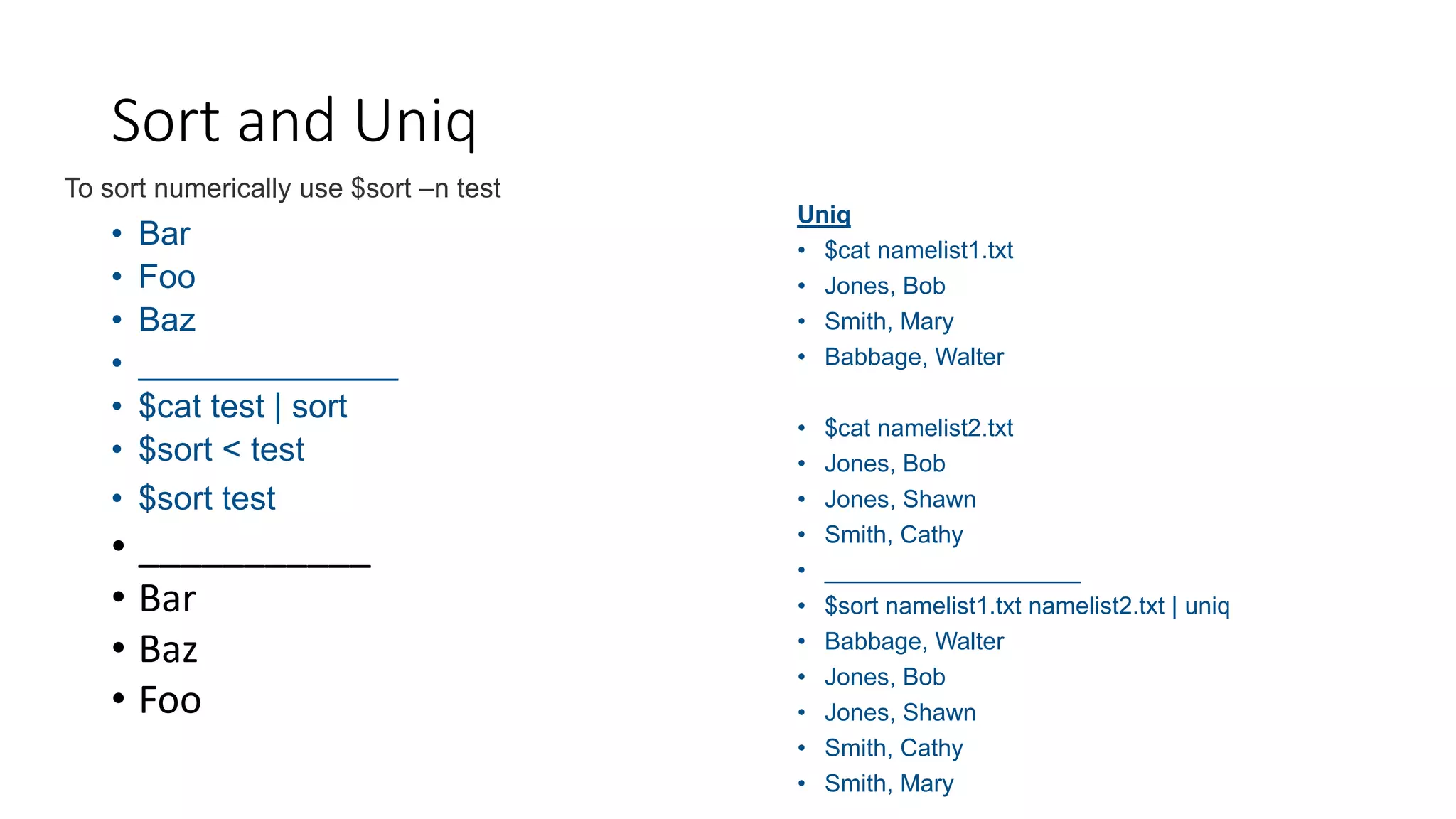
- Basic text processing tools like cut, sort, uniq and awk
- Functions and case statements for reusability and conditional logic





![Getting Help for Shell Builtins
• Type: type [-afptP] name [name…]
• For each NAME, indicate how it would be interpreted if used as a command
name.
• Help: help [-s] [pattern …]
• Display helpful information about builtin commands](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/linuxshellscripting2-221213122258-2ef72a0c/75/Linux-Shell-Scripting-pptx-6-2048.jpg)



![The if statement
• if [[ COMMANDS ]]
then
COMMANDS
else
COMMANDS
fi](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/linuxshellscripting2-221213122258-2ef72a0c/75/Linux-Shell-Scripting-pptx-10-2048.jpg)

![Sanity Checking
if [[ “${UID}” –ne 0 ]]
then
echo ‘Please run as root.’ >&2
exit 1
fi](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/linuxshellscripting2-221213122258-2ef72a0c/75/Linux-Shell-Scripting-pptx-12-2048.jpg)


![The for Loop
for VARIABLE in LIST
do
COMMANDS
done
The while Loop
while [[ COMMANDS ]]
do
COMMANDS
done](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/linuxshellscripting2-221213122258-2ef72a0c/75/Linux-Shell-Scripting-pptx-16-2048.jpg)