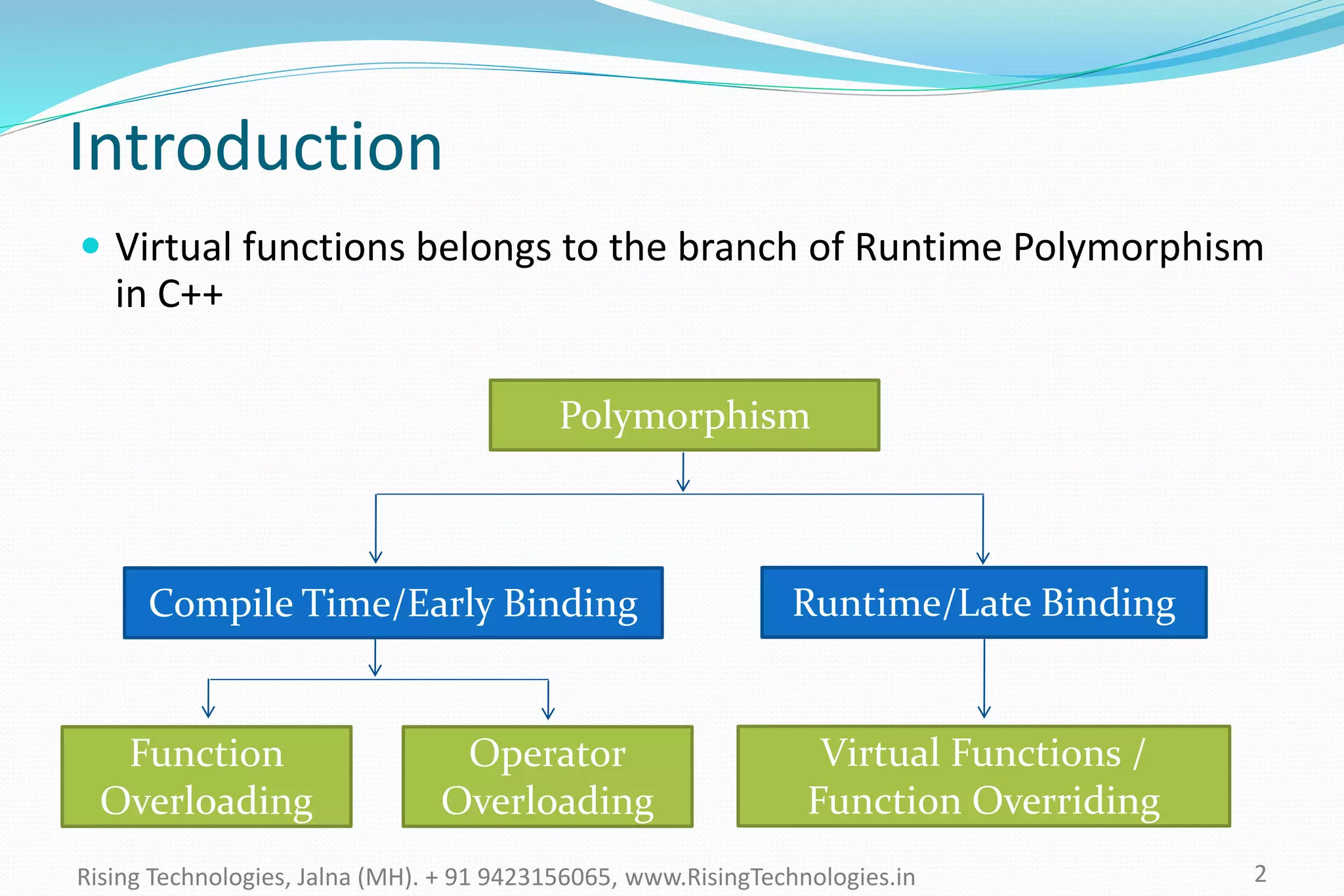
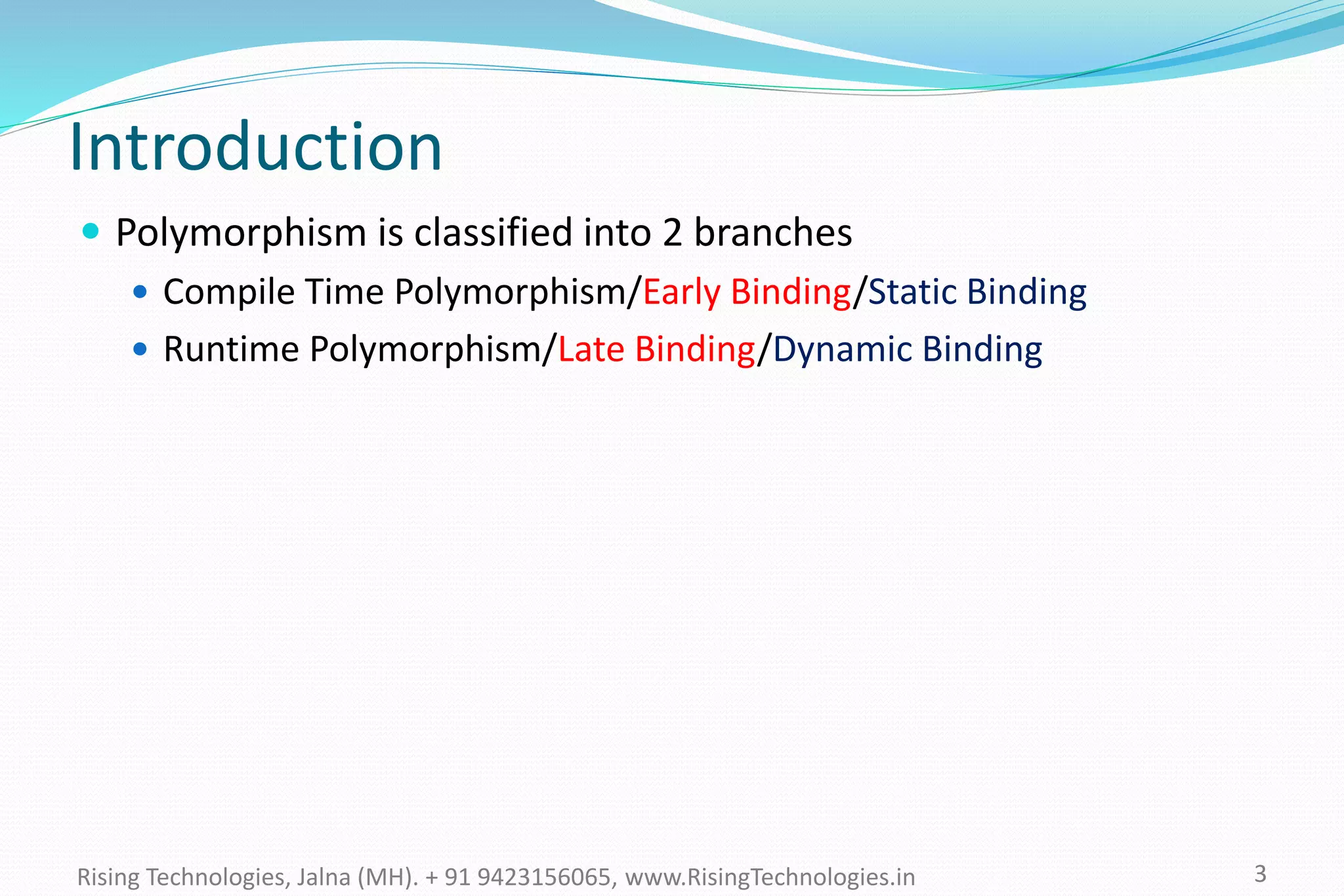
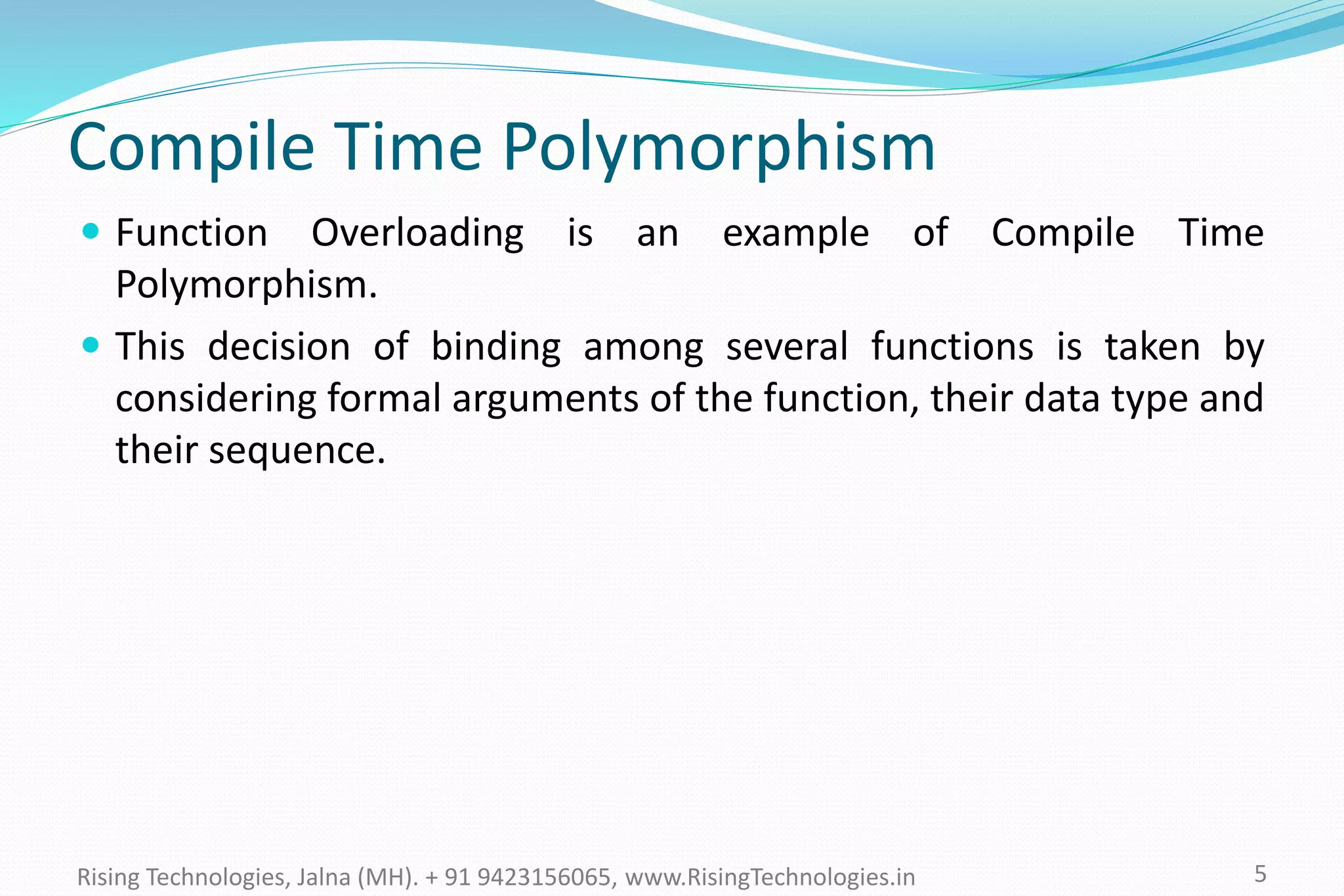
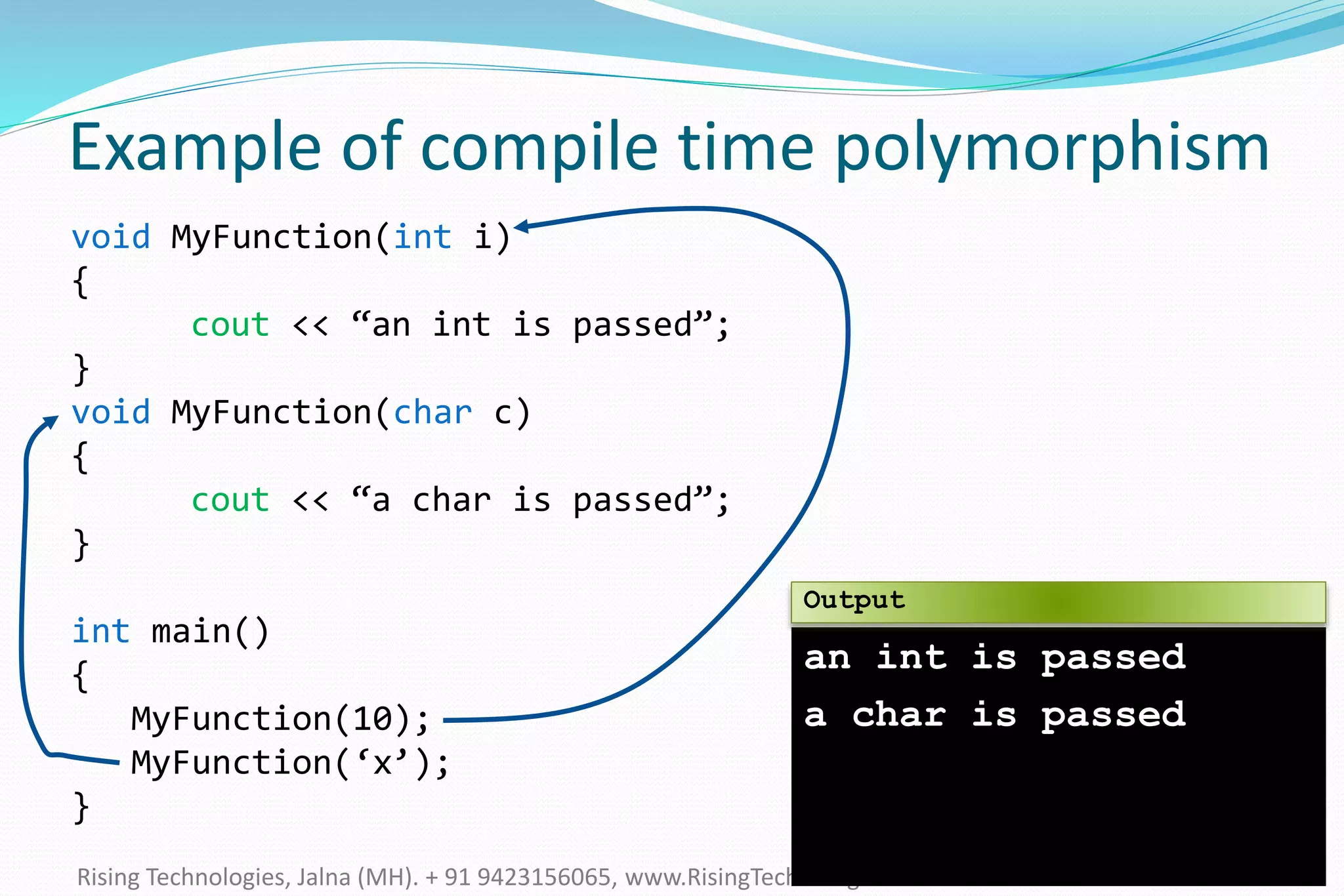
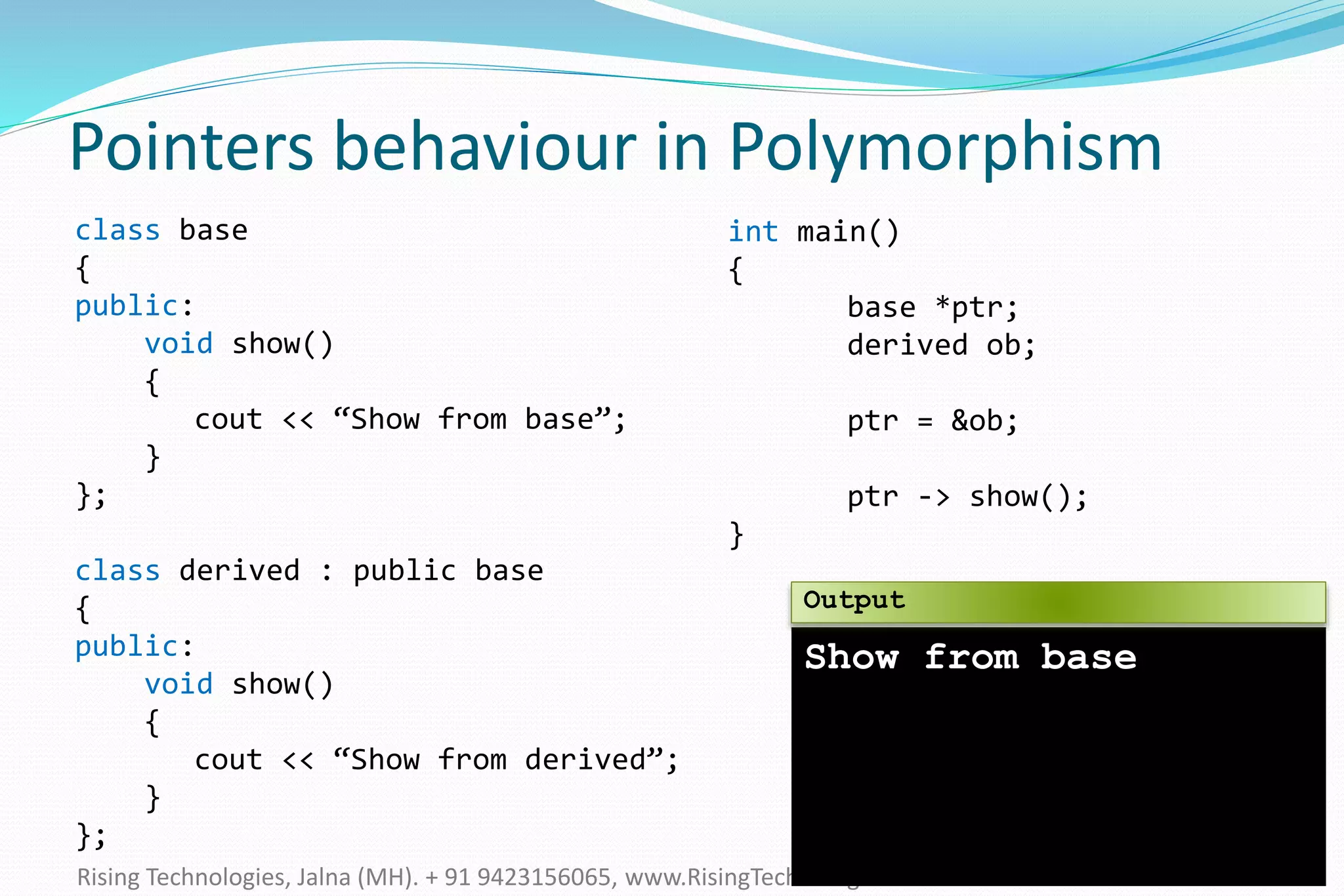
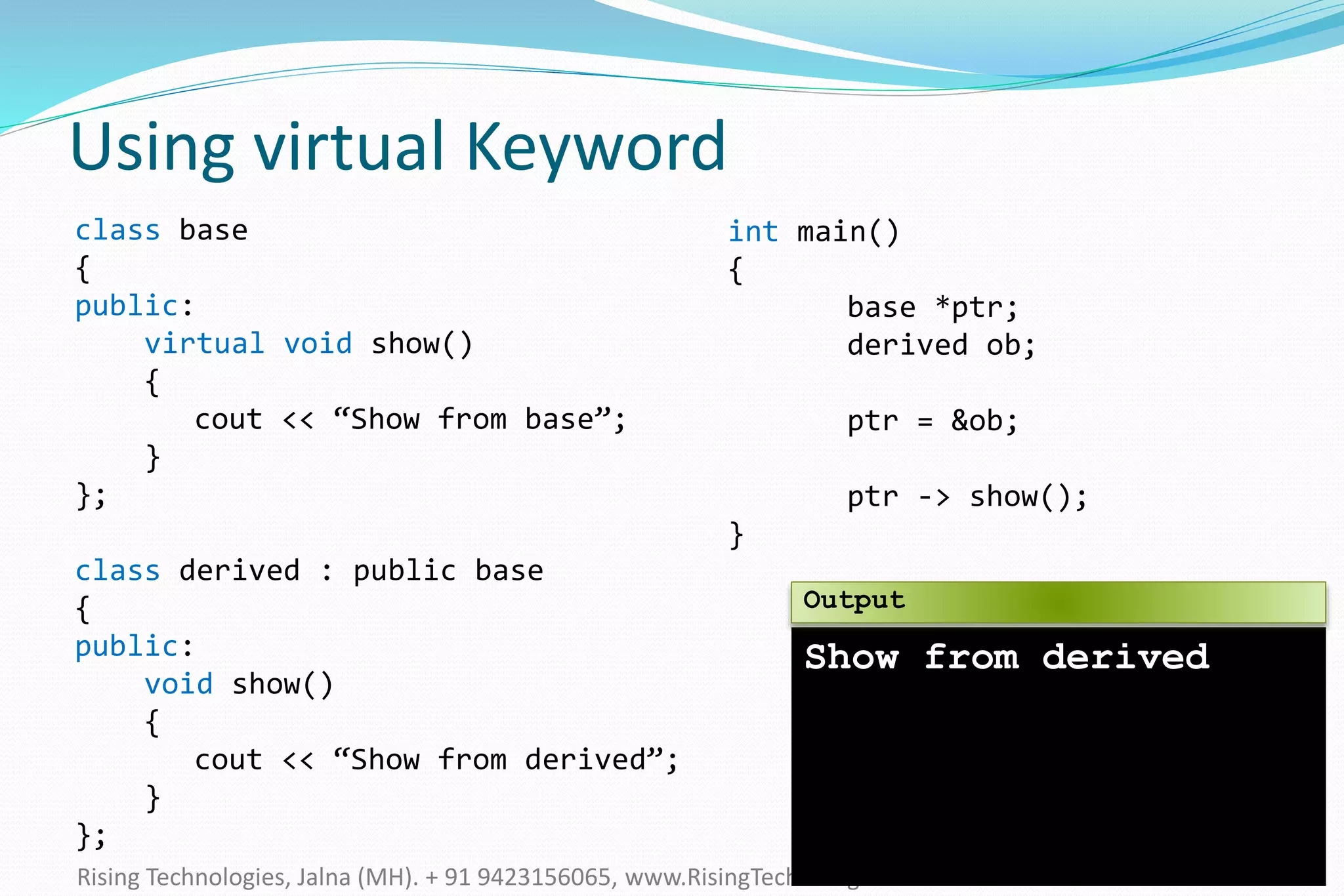
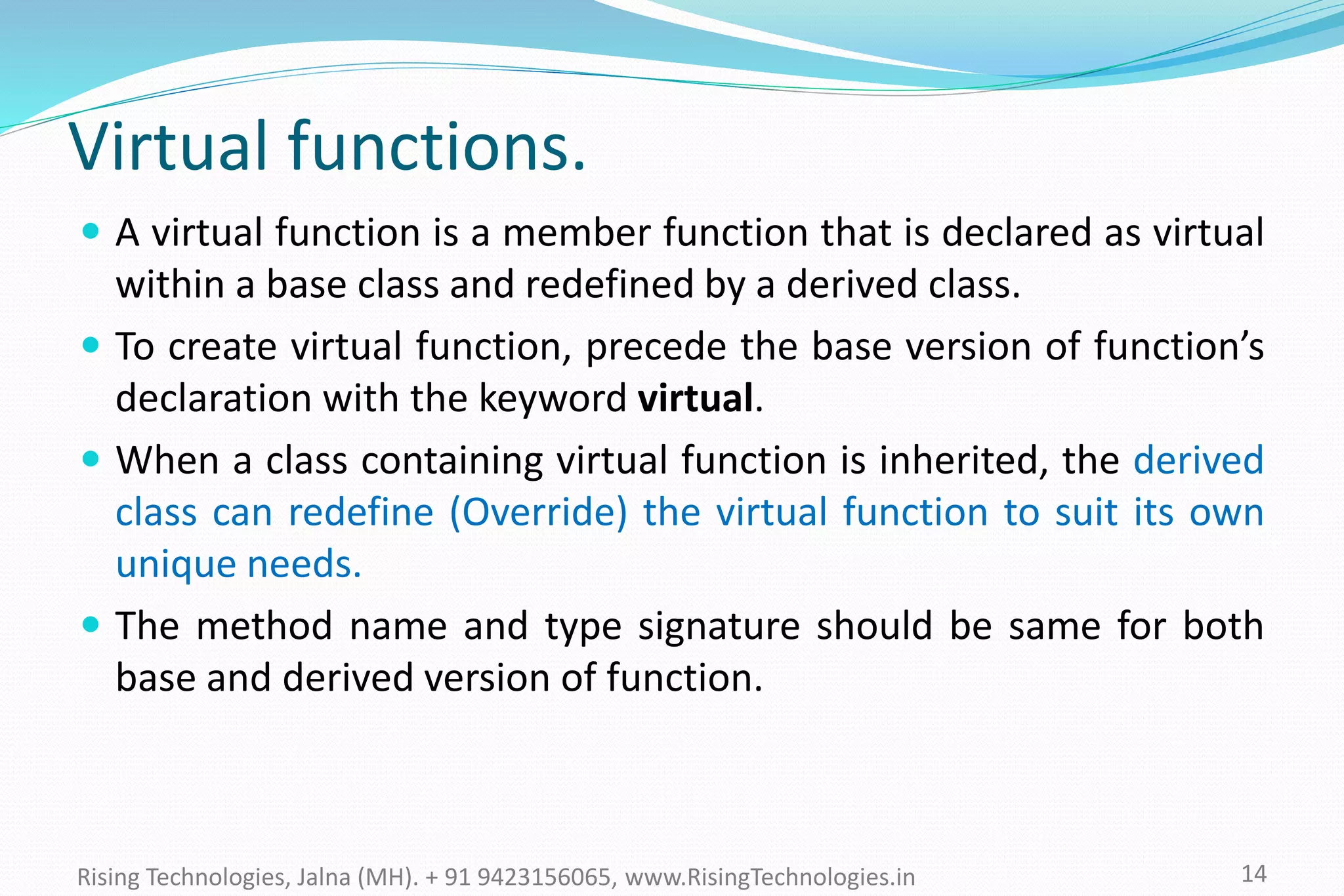
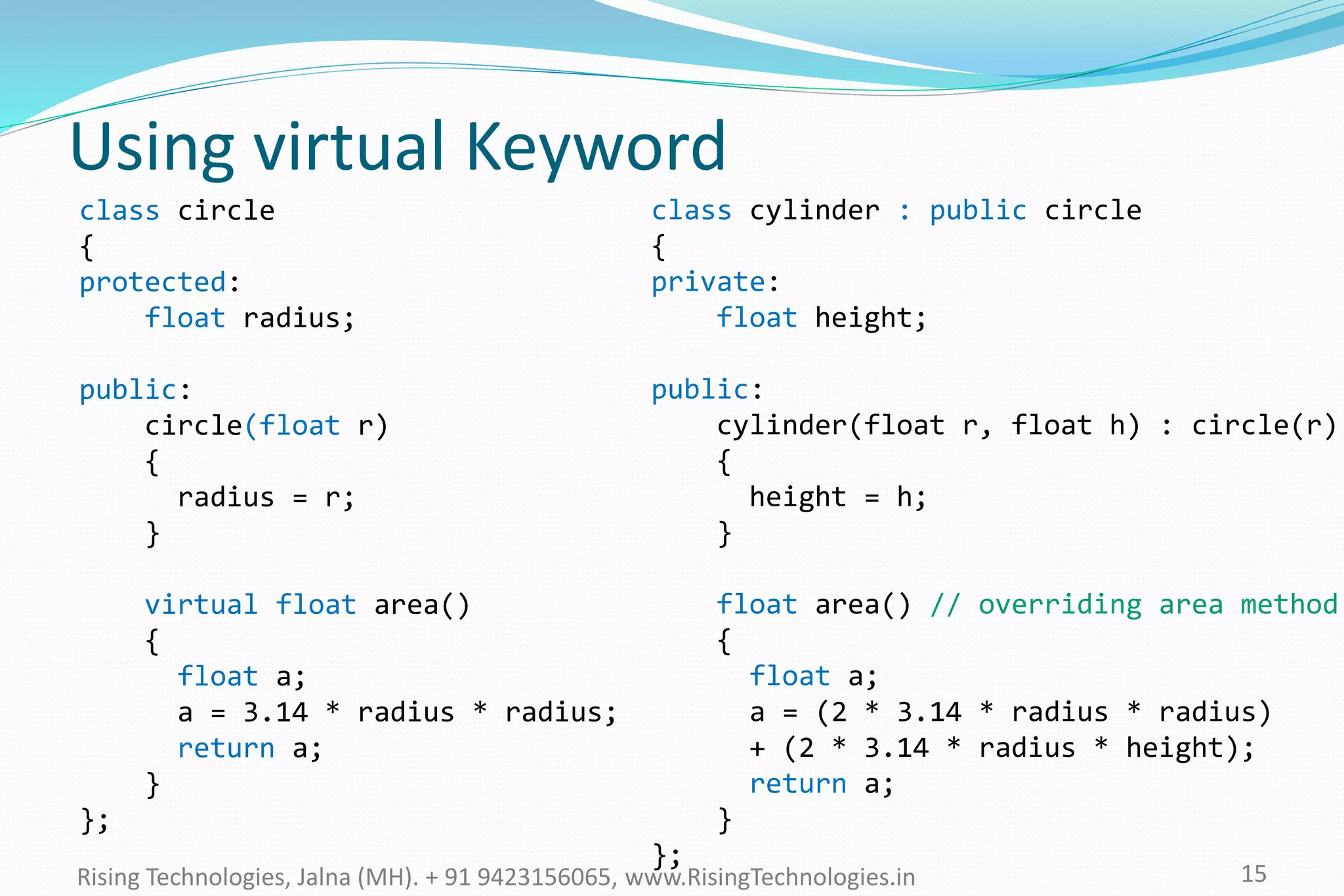
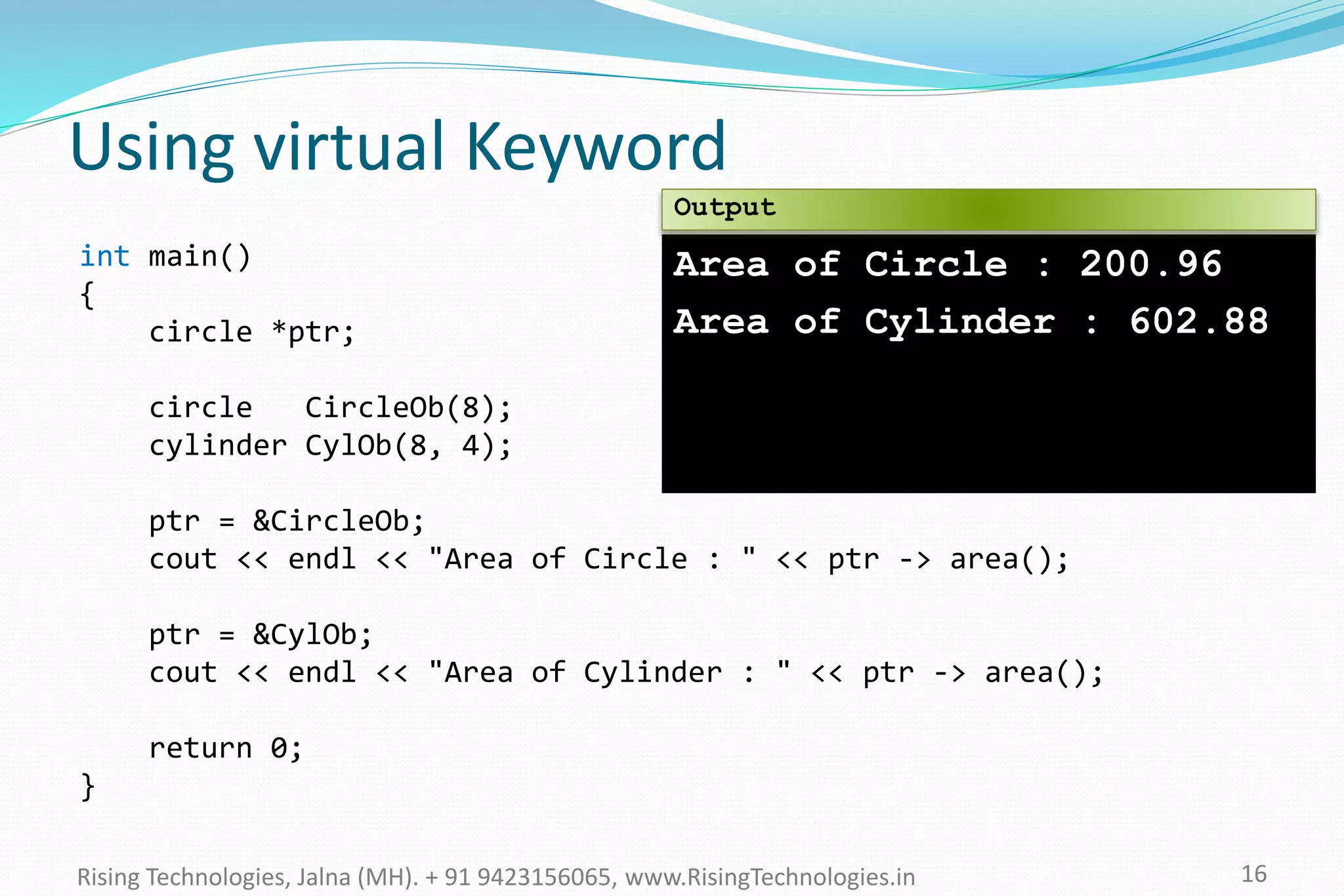
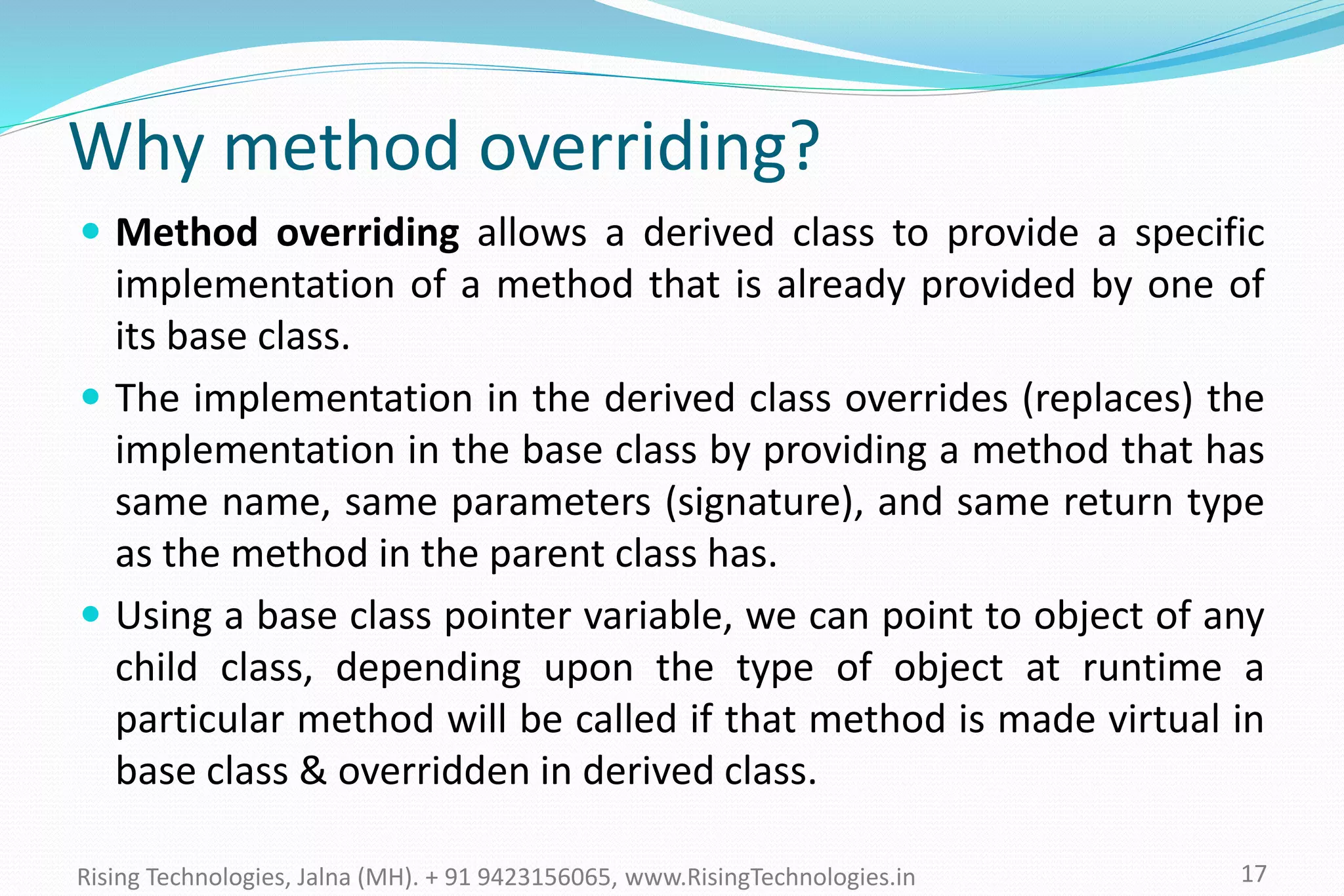
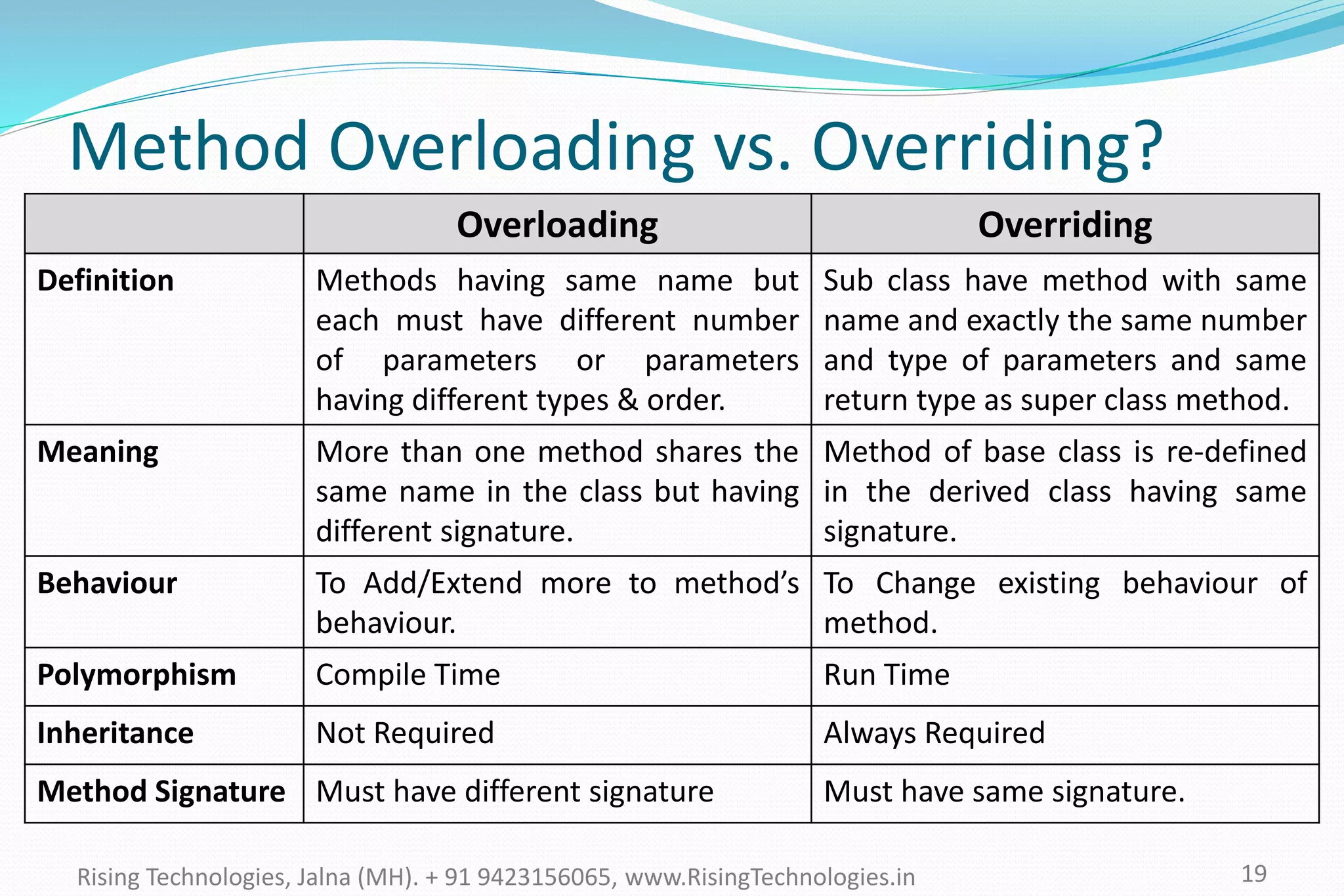
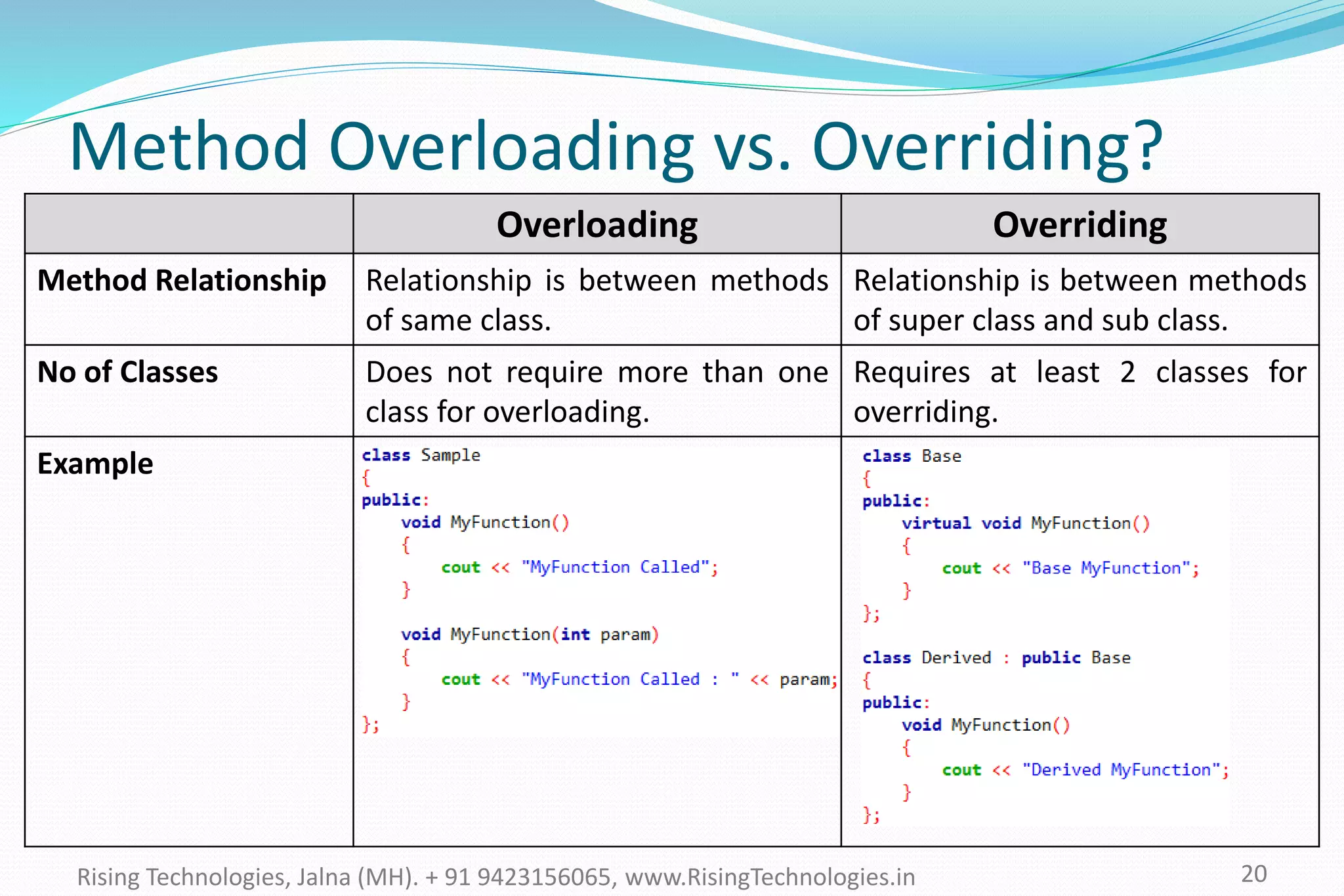
The document explains the concepts of polymorphism in C++, focusing on compile-time and runtime polymorphism. It details the use of virtual functions for achieving runtime polymorphism and the behavior of pointers in relation to base and derived classes. Additionally, it outlines the differences between method overloading and overriding, emphasizing how these techniques facilitate flexible programming through dynamic and static binding.