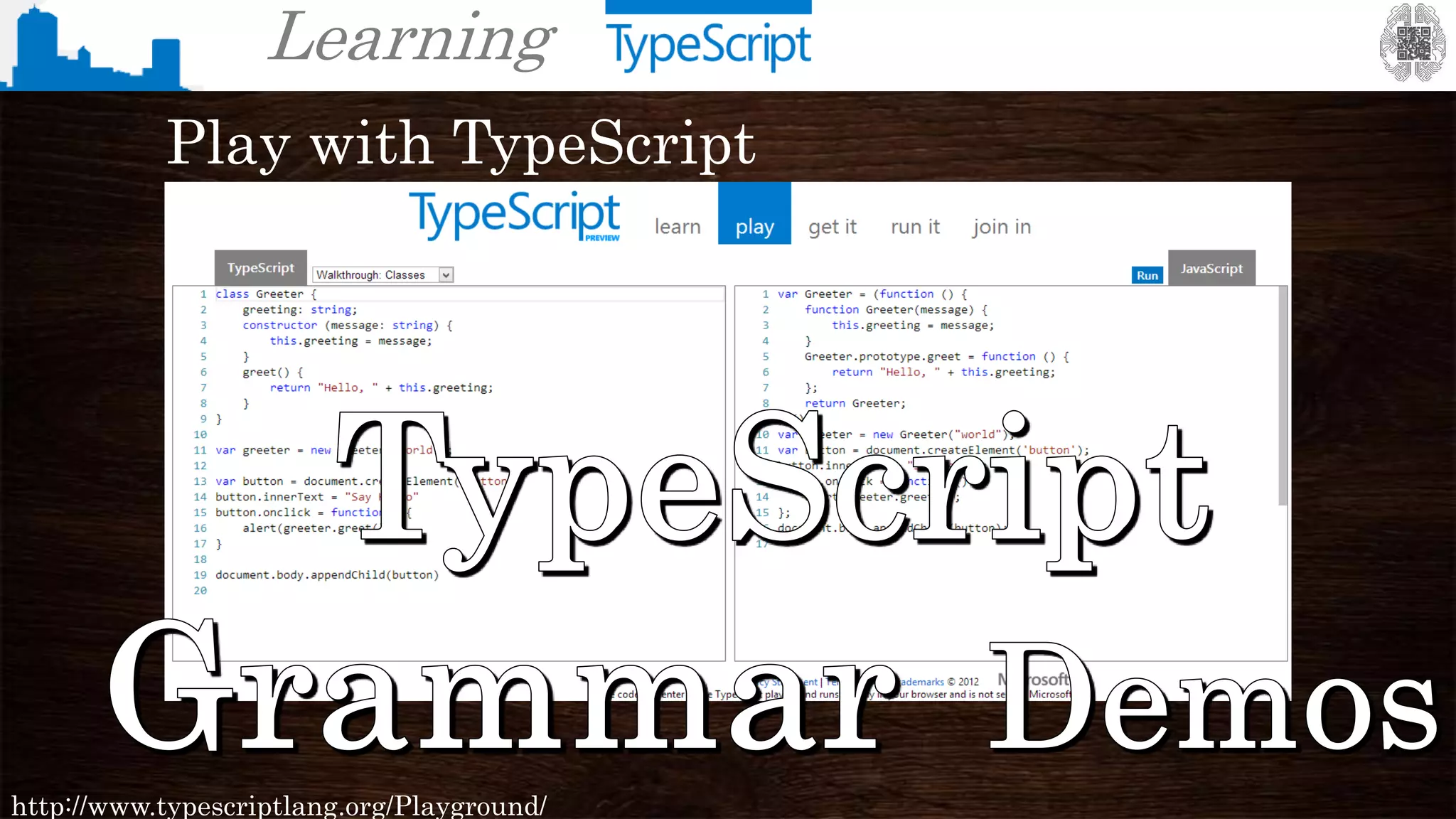
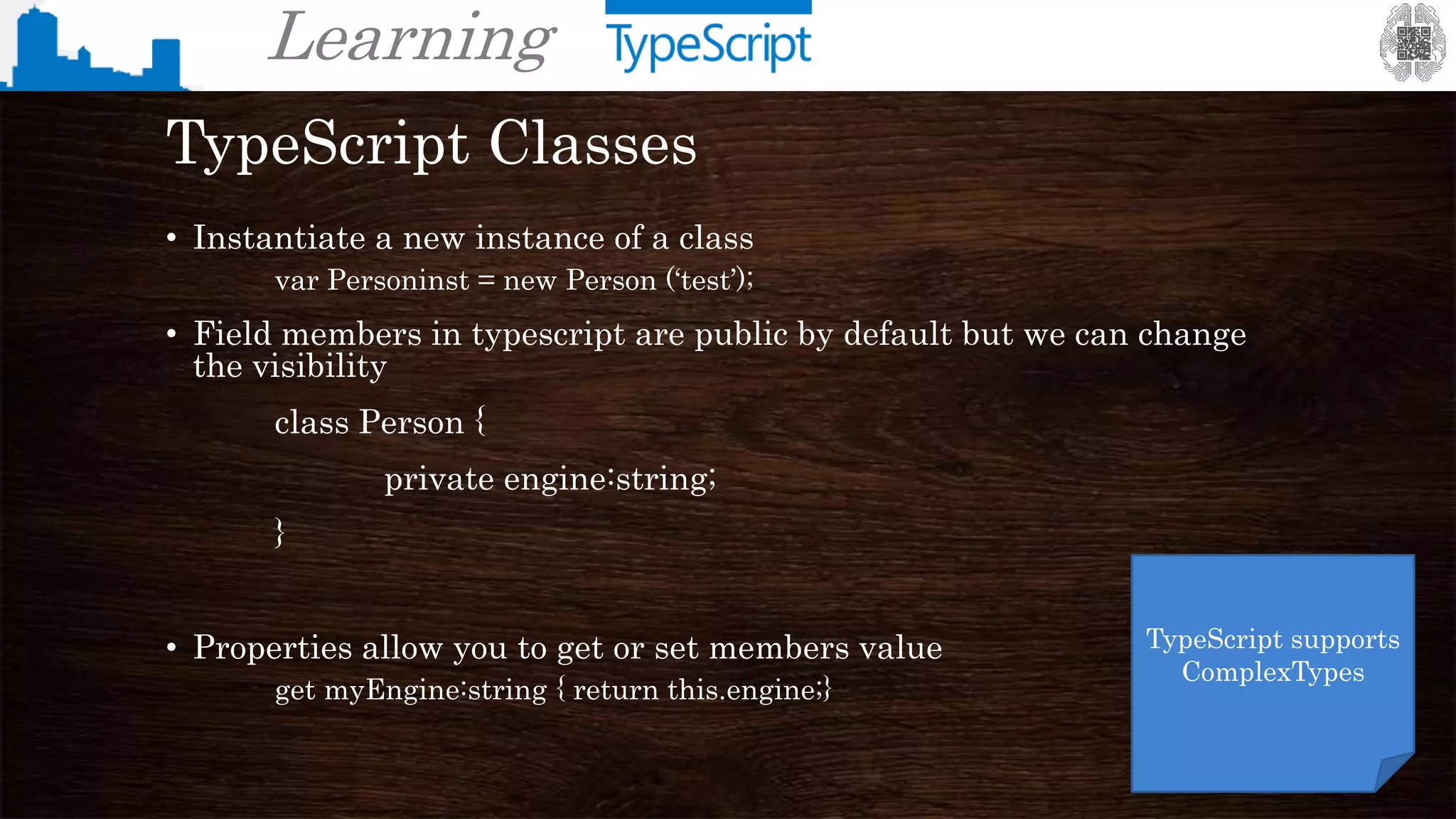
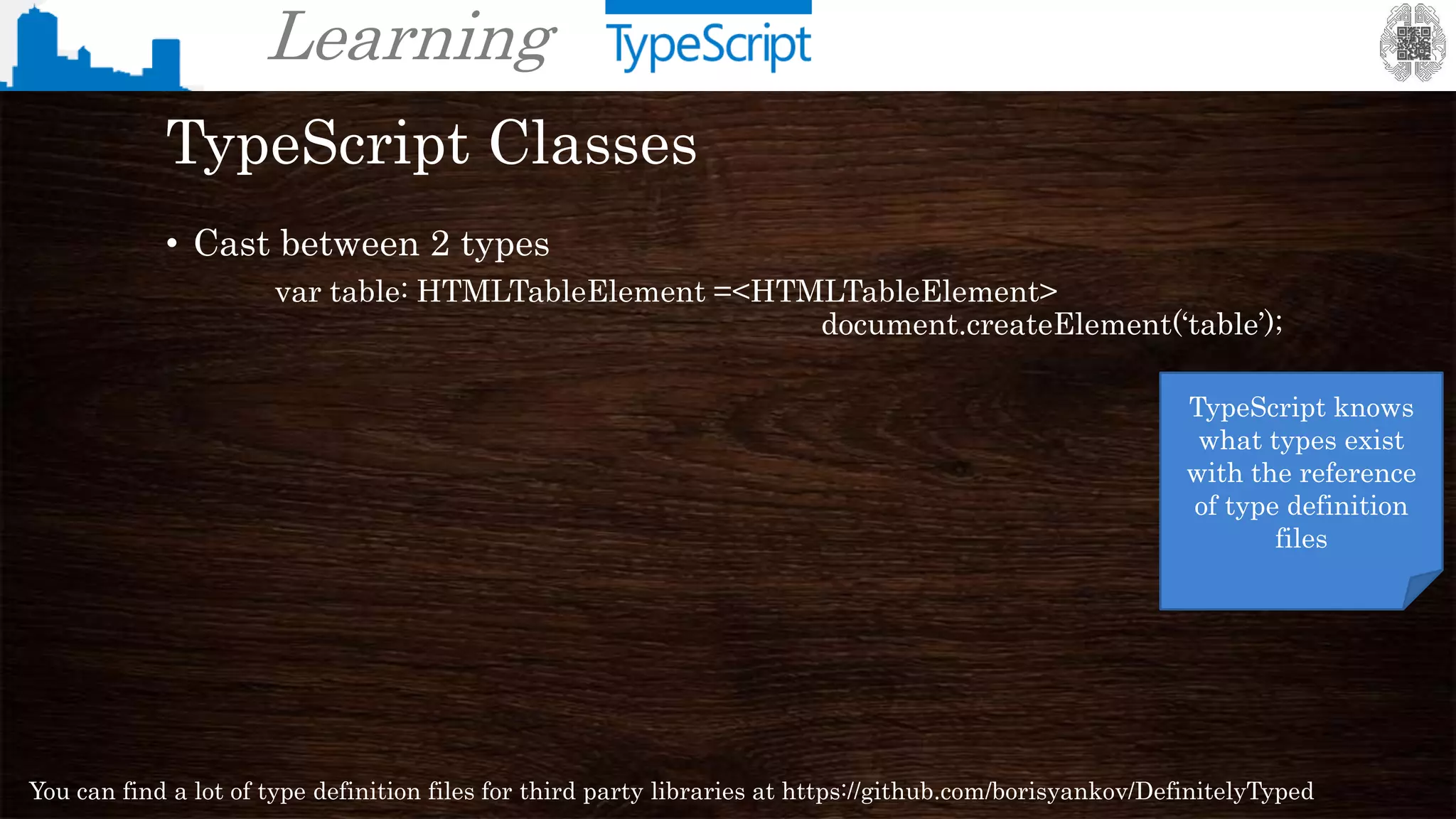
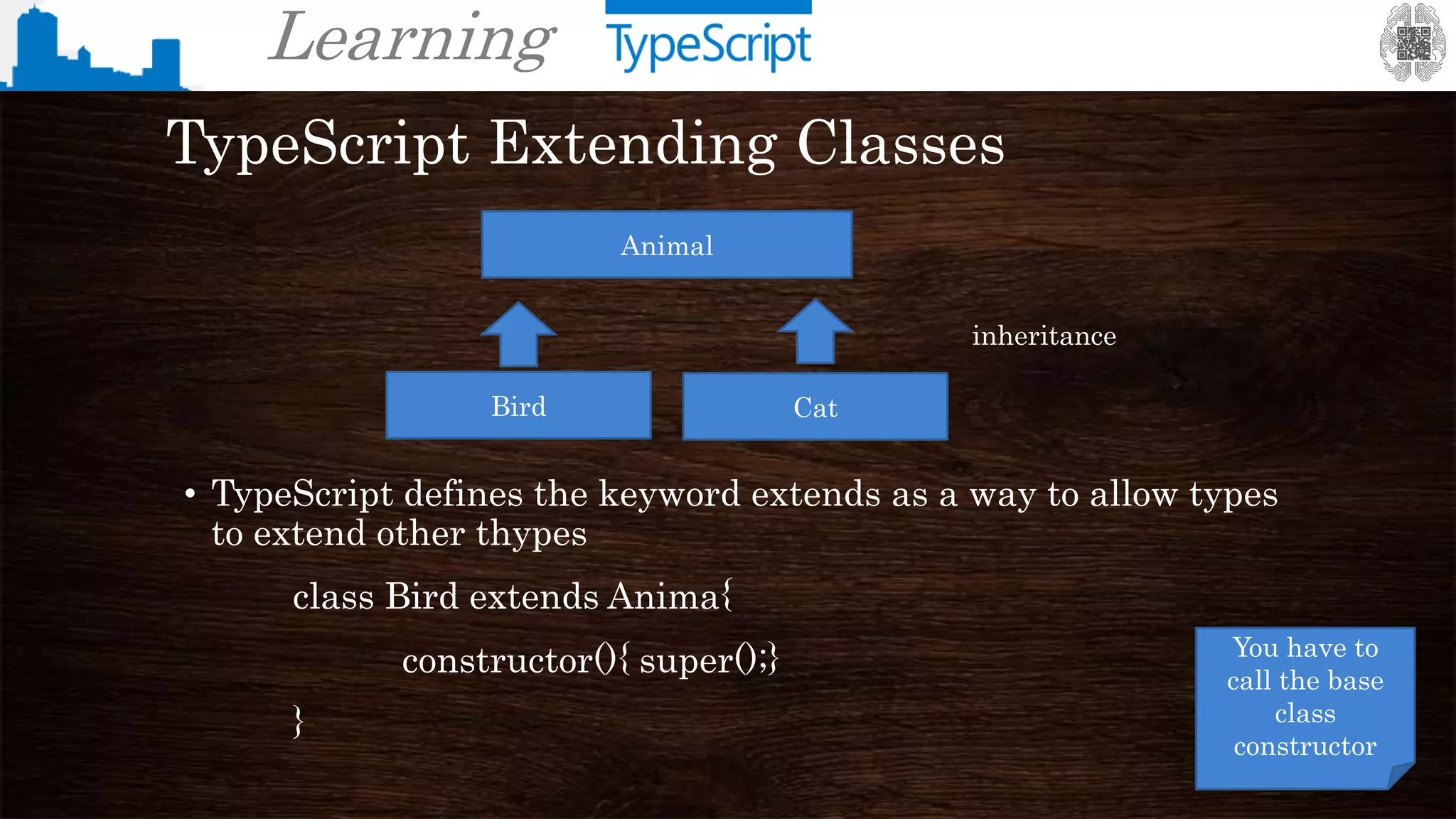
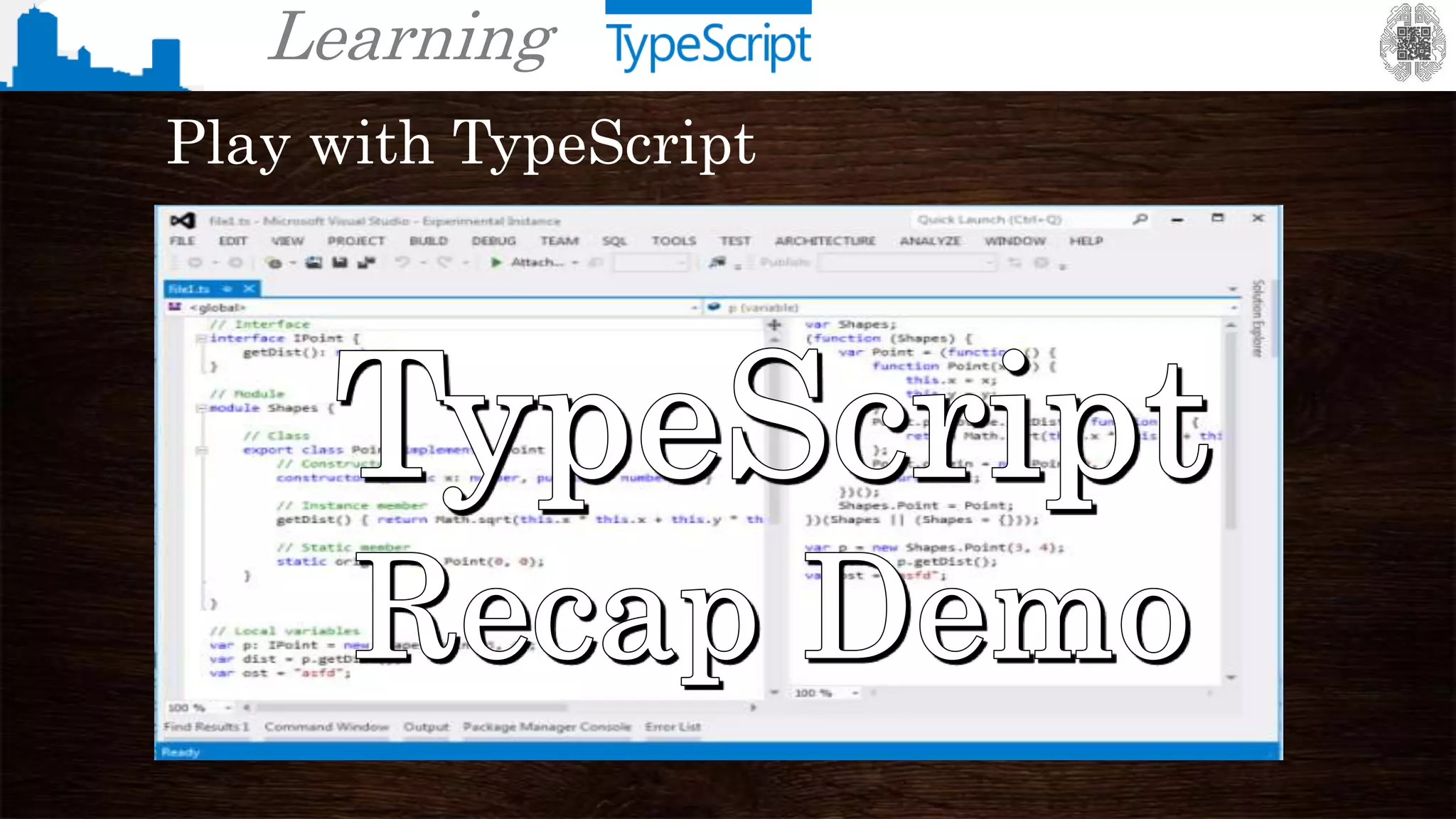
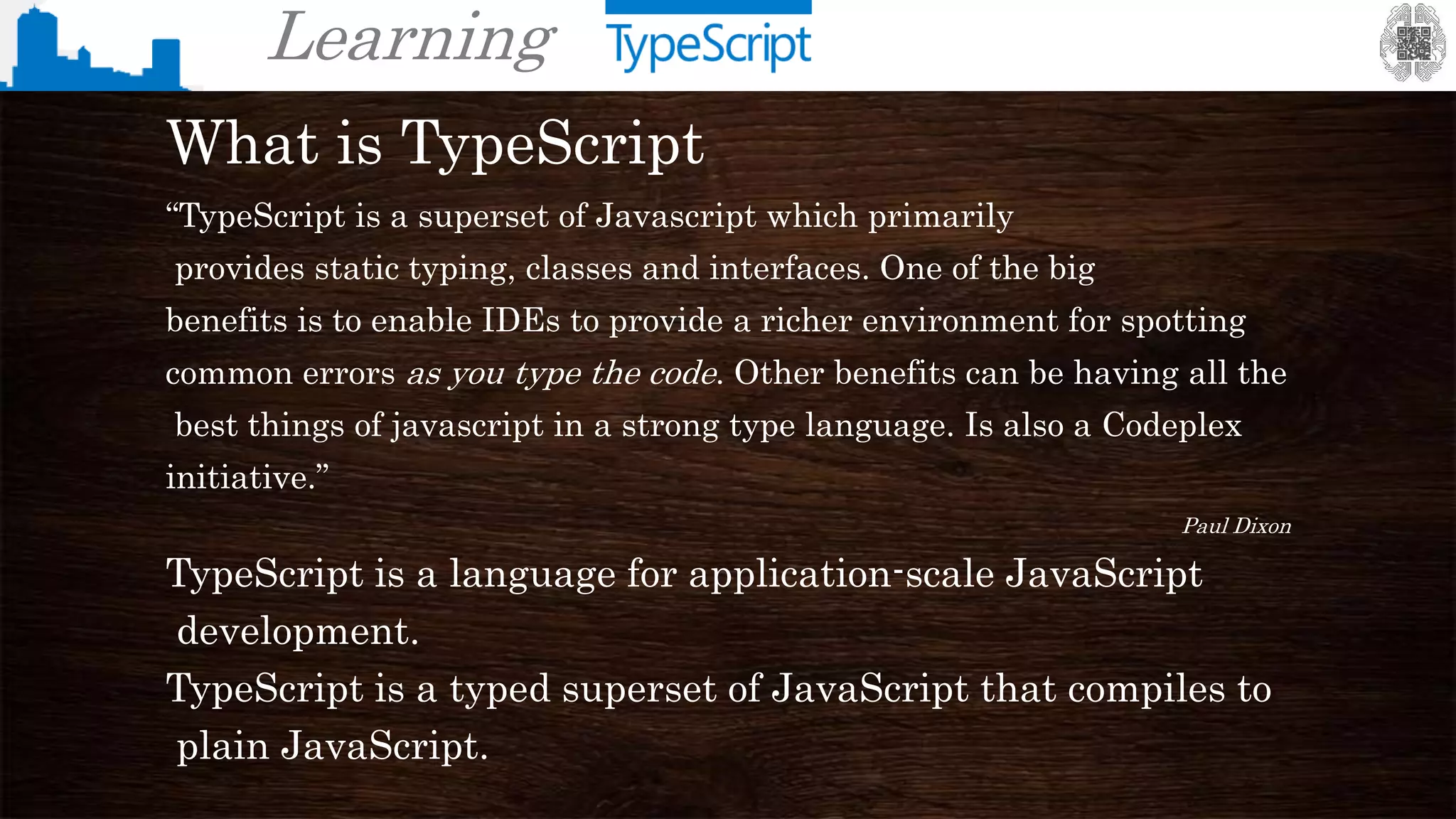
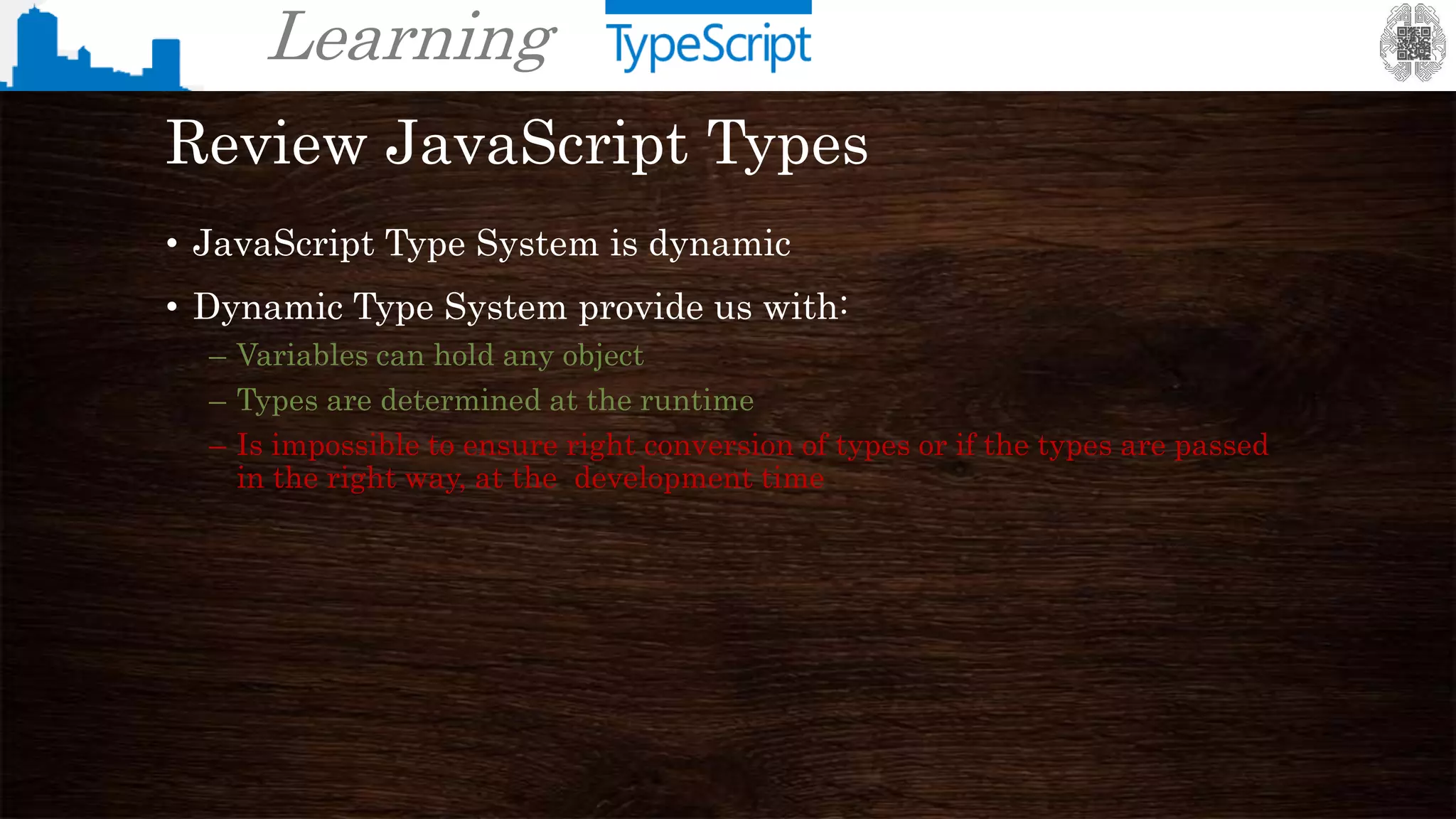
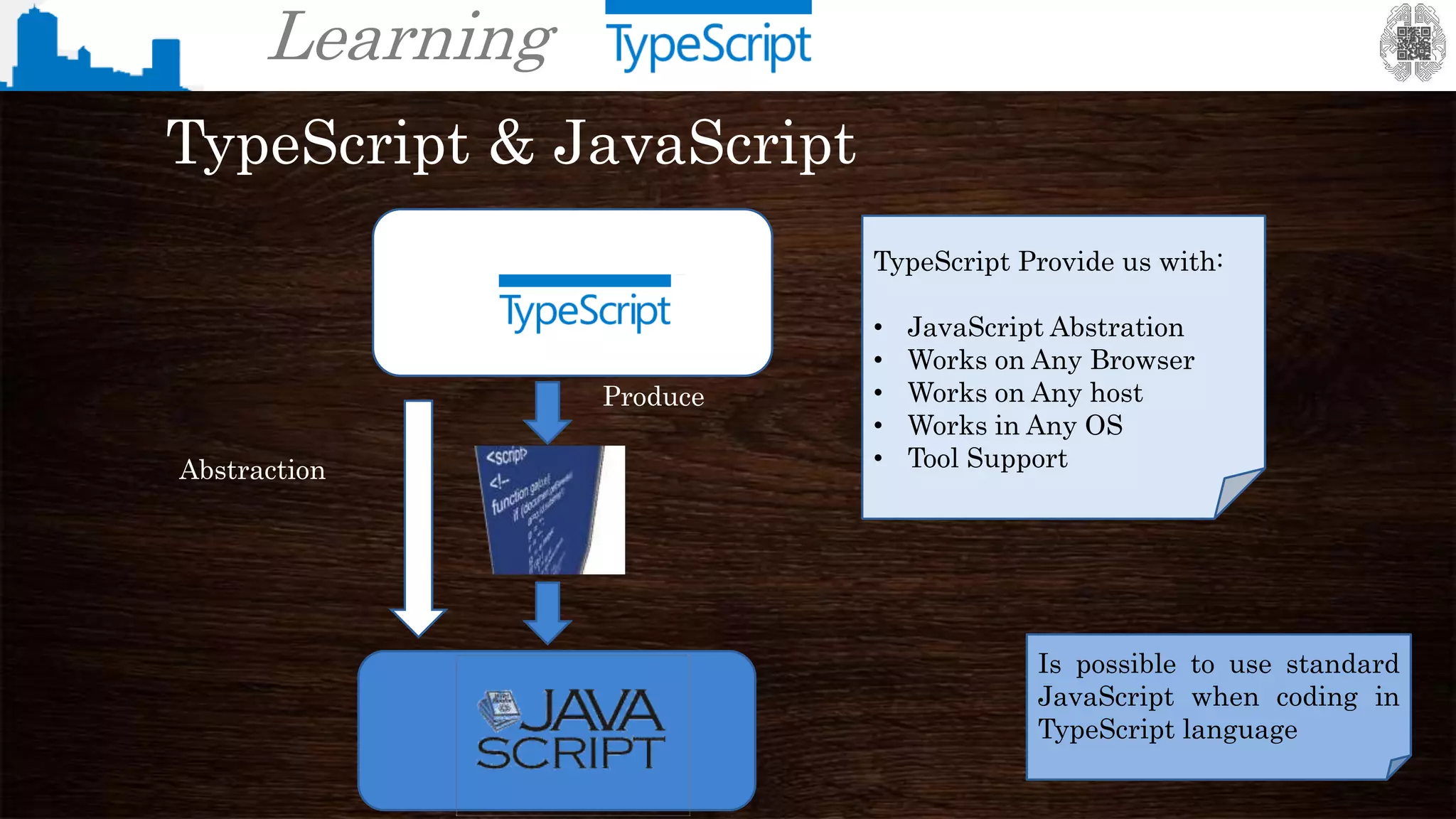
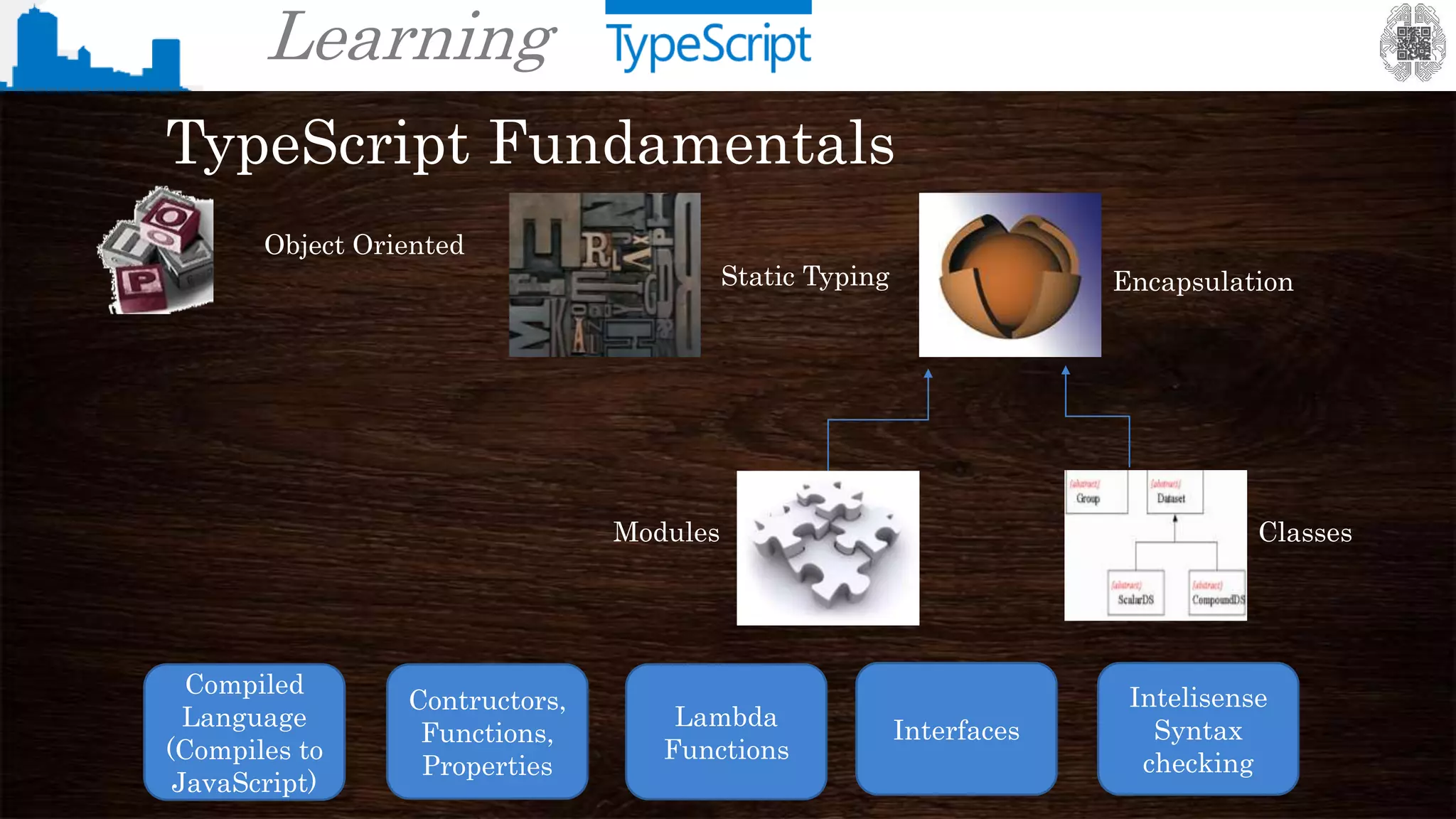
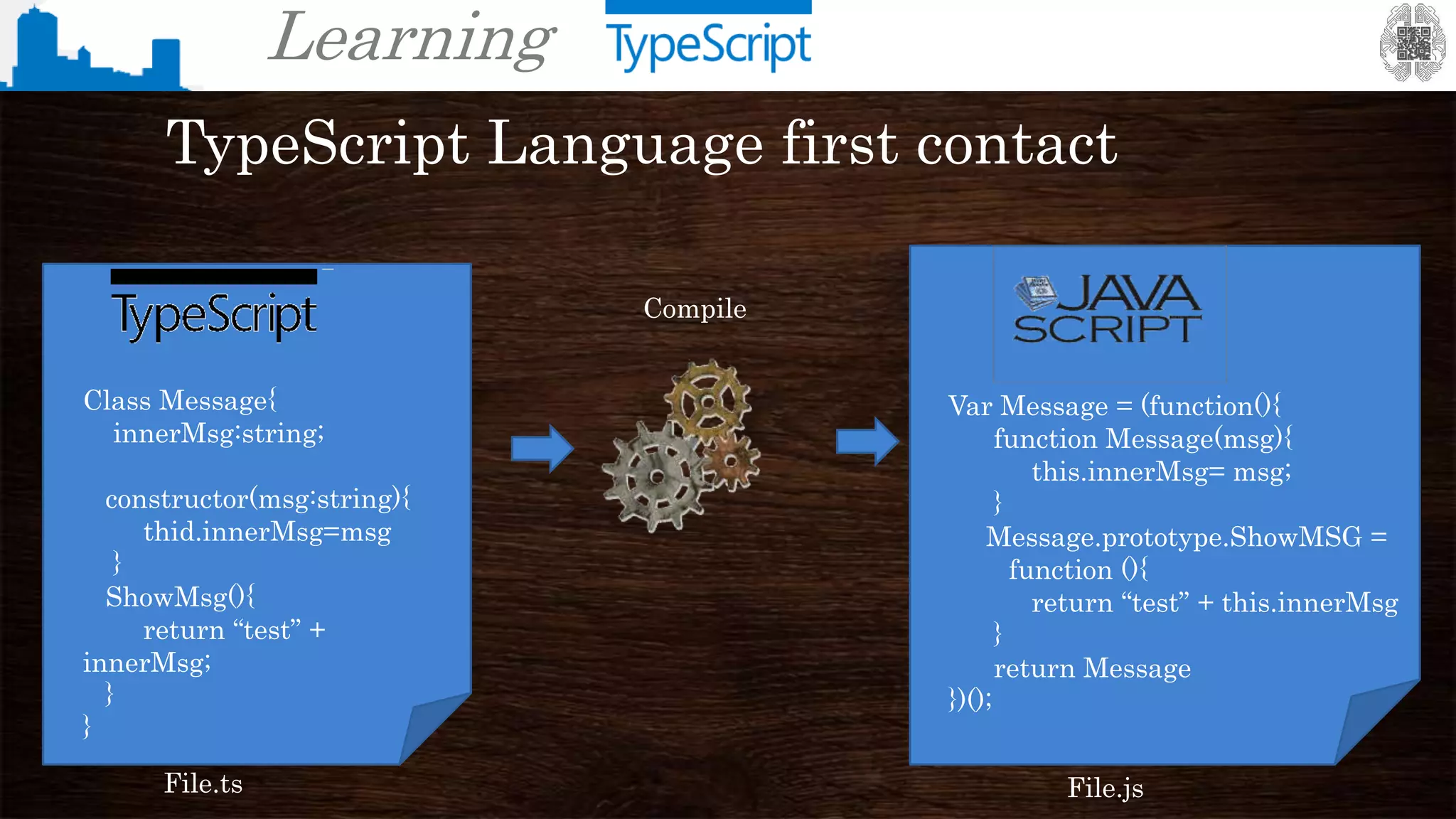
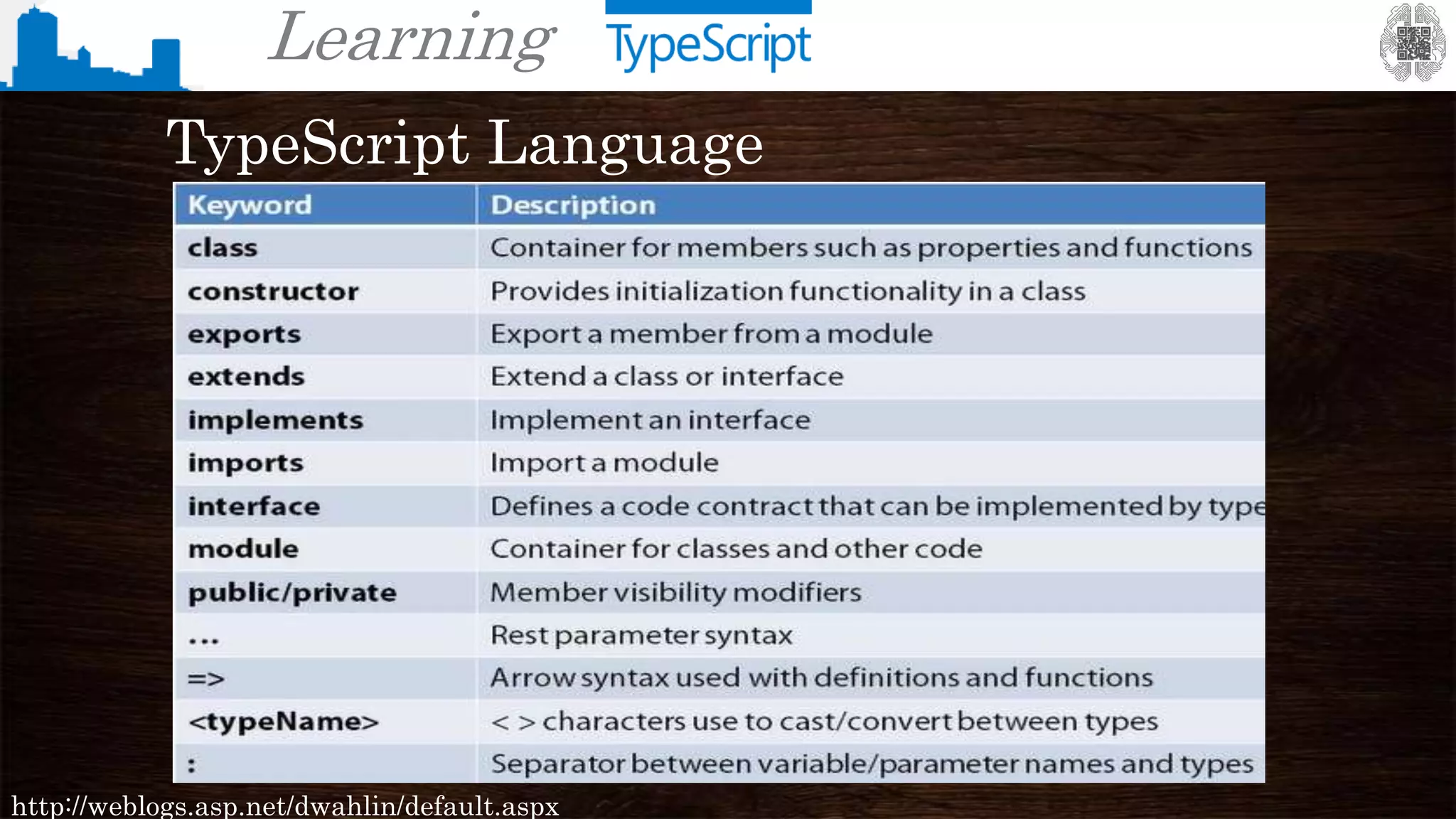
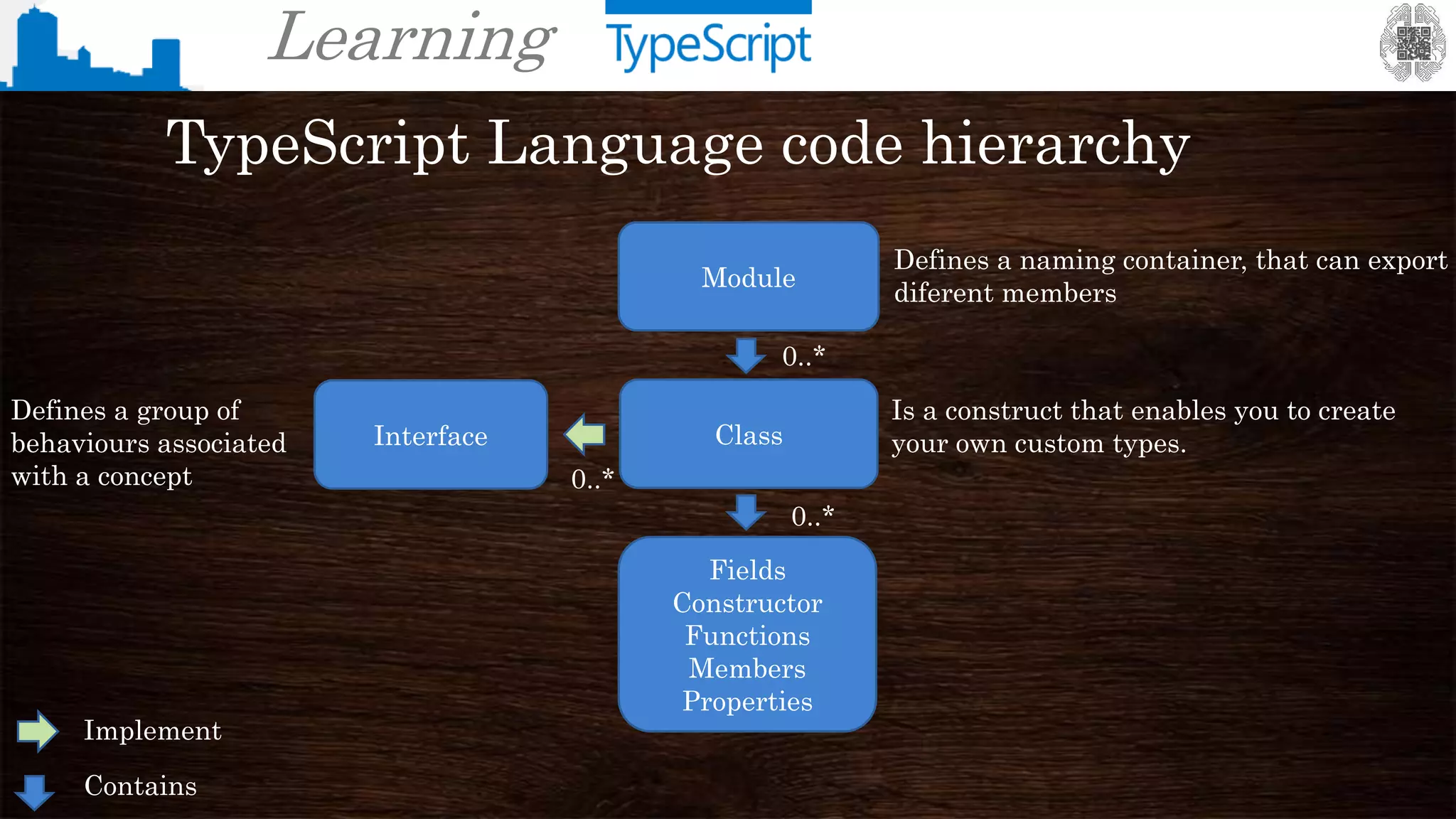
The document provides an overview of TypeScript, a superset of JavaScript that adds static typing and other features for large-scale application development. It highlights the benefits of using TypeScript for building robust and maintainable code, alongside its fundamental concepts such as classes, interfaces, and type annotations. Additionally, it discusses tools for TypeScript development and includes examples of syntax and type definitions.










![Learning
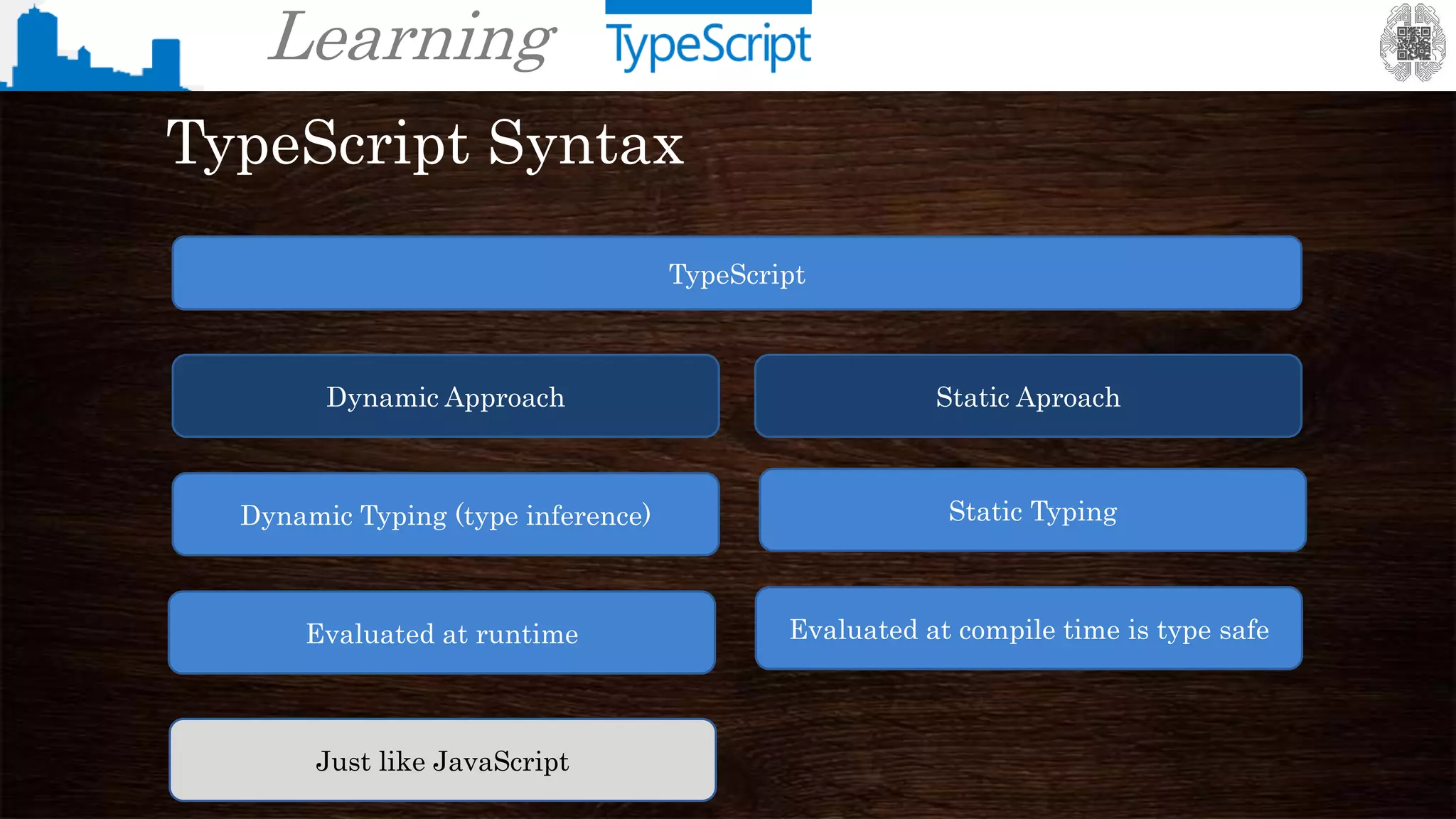
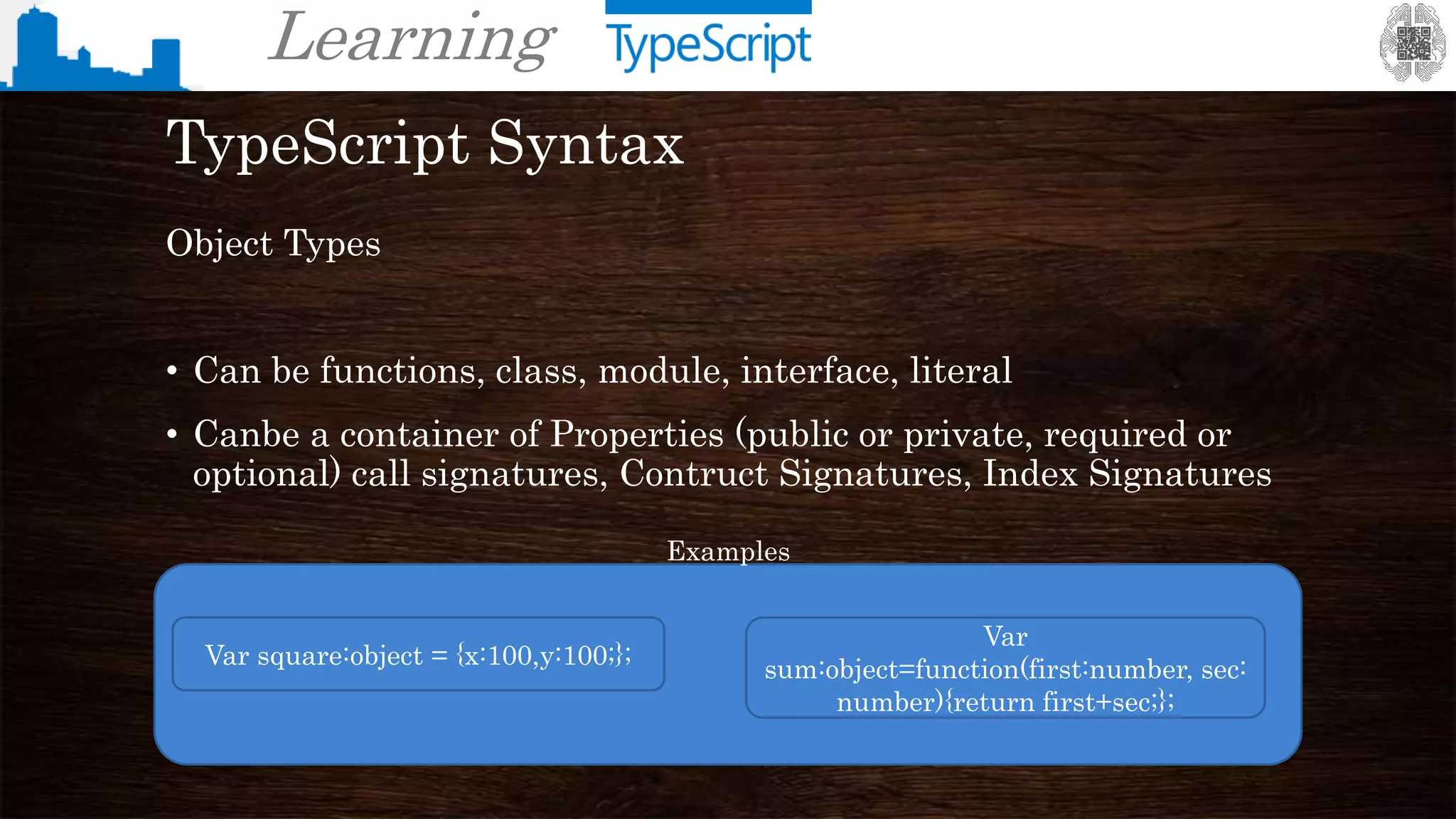
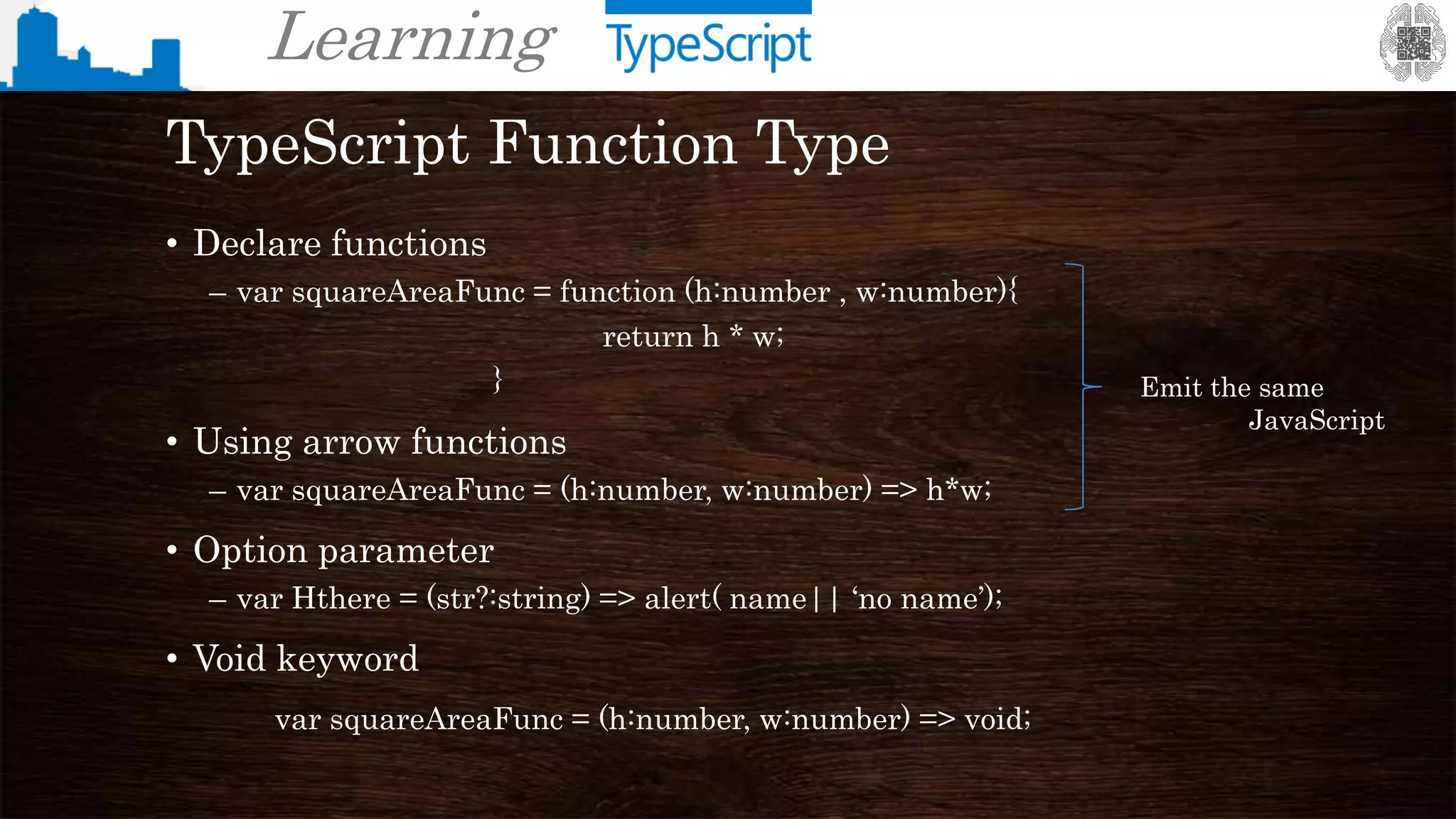
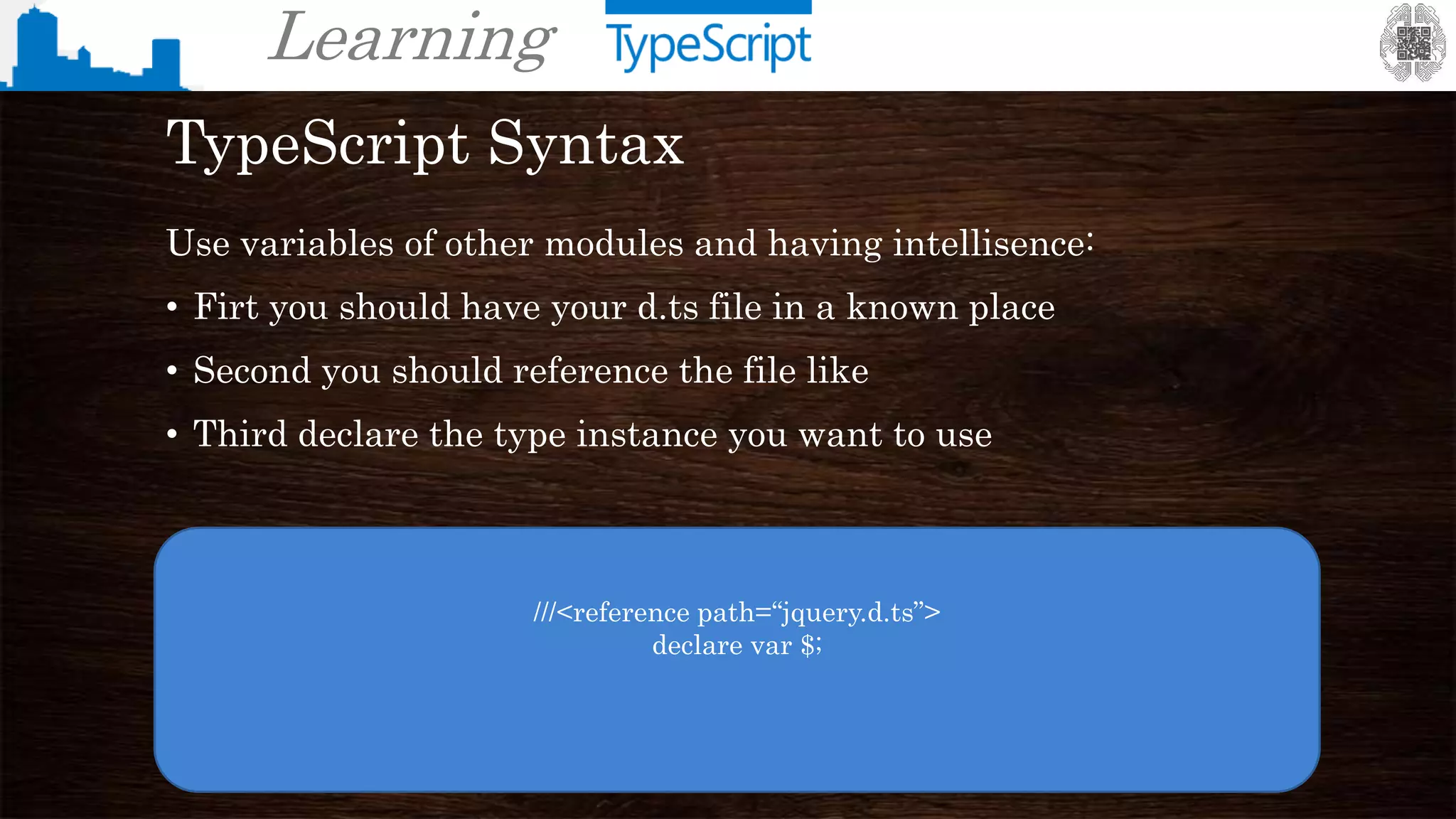
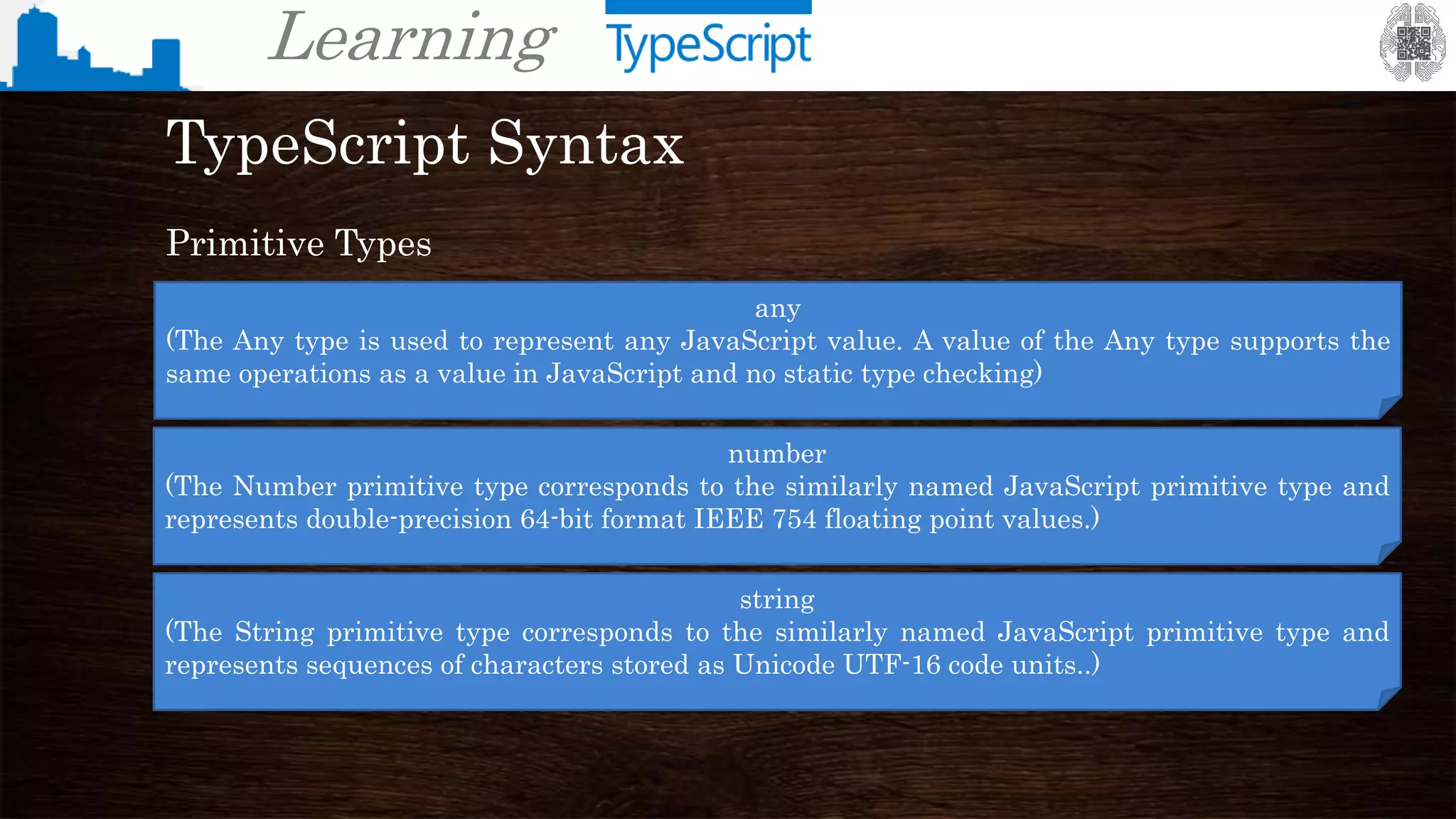
TypeScript Syntax
Primitive Types
null
(The Null type is a subtype of all types, except the Void and Undefined types. This means that
null is considered a valid value for all primitive and object types, including even the Number and
Boolean primitive types)
undefined
(The Undefined type corresponds to the similarly named JavaScript primitive type and is the
type of the undefined literal.)
Type Arrays
(Represents a container of values of a specific static or dynamic type. In the second case we ca
illustrate with the following example:
var names: string[] = [‗Antonio‘,‘John‘,‘Manuel‘];
To índex the array you use the following notation
names[num] ;
Where num is the índex in the array starting at 0 for the first elemento)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/learningtypescript-130120173150-phpapp02/75/Learning-typescript-21-2048.jpg)