The document provides a comprehensive guide to learning Python, including resources, fundamental concepts, and practical examples. It covers installation procedures, essential libraries, web scraping, and database interactions using SQLite, along with code samples for hands-on learning. Additionally, it offers recommendations for books and online documentation to enhance learners' understanding of Python programming.

































![FOR
for i in [0, 1, 2, 3, 4]:
print i
!
items = [0, 1, 2, 3, 4]
for i in items:
print i
!
for i in range(5):
print i
!
!
!
chars = 'SAHFI'
for i, c in enumerate(chars):
print i, c
!
!
words = ('Samsung', 'Apple',
'HP', 'Foxconn', 'IBM')
for c, w in zip(chars, words):
print c, w
13](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/learning-python-from-data-public-130728195724-phpapp01/75/Learning-Python-from-Data-37-2048.jpg)






![LIST COMPREHENSION
[
n
for n in range(2, 100)
if not any(n % i == 0 for i in range(2, n))
]
21](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/learning-python-from-data-public-130728195724-phpapp01/75/Learning-Python-from-Data-45-2048.jpg)






















![DEF AGAIN
def parse_to_school_list(path):
school_list = []
with open(path) as f:
next(f)
next(f)
for school in csv.DictReader(f):
school_list.append(school)
!
return school_list[:-2]
36](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/learning-python-from-data-public-130728195724-phpapp01/75/Learning-Python-from-Data-70-2048.jpg)
![+ COMPREHENSION
def parse_to_school_list(path='schools.csv'):
with open(path) as f:
next(f)
next(f)
school_list = [school for school in
csv.DictReader(f)][:-2]
!
return school_list
37](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/learning-python-from-data-public-130728195724-phpapp01/75/Learning-Python-from-Data-71-2048.jpg)
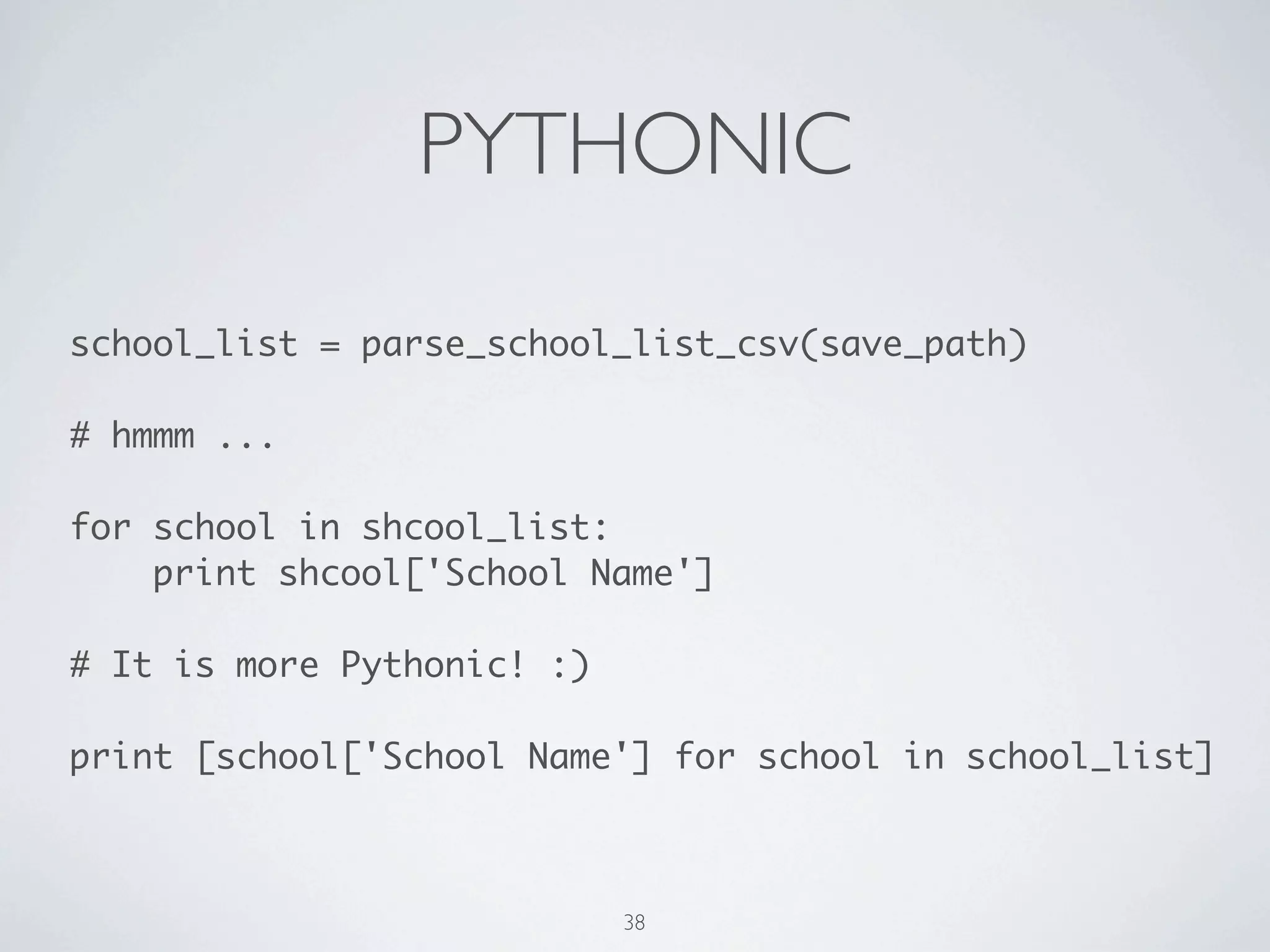
![PYTHONIC
school_list = parse_to_school_list(save_path)
!
# hmmm ...
!
for school in shcool_list:
print shcool['School Name']
!
# It is more Pythonic! :)
!
print [school['School Name'] for school in school_list]
39](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/learning-python-from-data-public-130728195724-phpapp01/75/Learning-Python-from-Data-73-2048.jpg)
![GROUP BY
from itertools import groupby
!
# You MUST sort it.
keyfunc = lambda school: school['County']
school_list.sort(key=keyfunc)
!
for county, schools in groupby(school_list, keyfunc):
for school in schools:
print '%s %r' % (county, school)
print '---'
40](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/learning-python-from-data-public-130728195724-phpapp01/75/Learning-Python-from-Data-74-2048.jpg)

![CLIME
if __name__ == '__main__':
import clime.now
!
--- shell ---
!
$ python csv_clime.py
usage: basename <p>
or: parse-to-school-list <path>
or: save [--path] <url>
!
It contains some userful function for parsing data from
government.
42](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/learning-python-from-data-public-130728195724-phpapp01/75/Learning-Python-from-Data-76-2048.jpg)





![XPATH
titles = root.xpath('/html/head/title')
print titles[0].text
!
title_texts = root.xpath('/html/head/title/text()')
print title_texts[0]
!
as_ = root.xpath('//a')
print as_
print [a.get('href') for a in as_]
49](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/learning-python-from-data-public-130728195724-phpapp01/75/Learning-Python-from-Data-83-2048.jpg)


![DEF FIND_URLS
def find_urls(content):
root = etree.HTML(content)
return [
a.attrib['href'] for a in root.xpath('//a')
if 'href' in a.attrib
]
52](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/learning-python-from-data-public-130728195724-phpapp01/75/Learning-Python-from-Data-86-2048.jpg)
![BFS 1/2
NEW = 0
QUEUED = 1
VISITED = 2
!
def search_urls(url):
!
url_queue = [url]
url_state_map = {url: QUEUED}
!
while url_queue:
!
url = url_queue.pop(0)
print url
53](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/learning-python-from-data-public-130728195724-phpapp01/75/Learning-Python-from-Data-87-2048.jpg)
![BFS 2/2
# continue the previous page
try:
found_urls = find_urls(get(url))
except Exception, e:
url_state_map[url] = e
print 'Exception: %s' % e
except KeyboardInterrupt, e:
return url_state_map
else:
for found_url in found_urls:
if not url_state_map.get(found_url, NEW):
url_queue.append(found_url)
url_state_map[found_url] = QUEUED
url_state_map[url] = VISITED
54](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/learning-python-from-data-public-130728195724-phpapp01/75/Learning-Python-from-Data-88-2048.jpg)
![DEQUE
from collections import deque
...
!
def search_urls(url):
url_queue = deque([url])
...
while url_queue:
!
url = url_queue.popleft()
print url
...
55](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/learning-python-from-data-public-130728195724-phpapp01/75/Learning-Python-from-Data-89-2048.jpg)



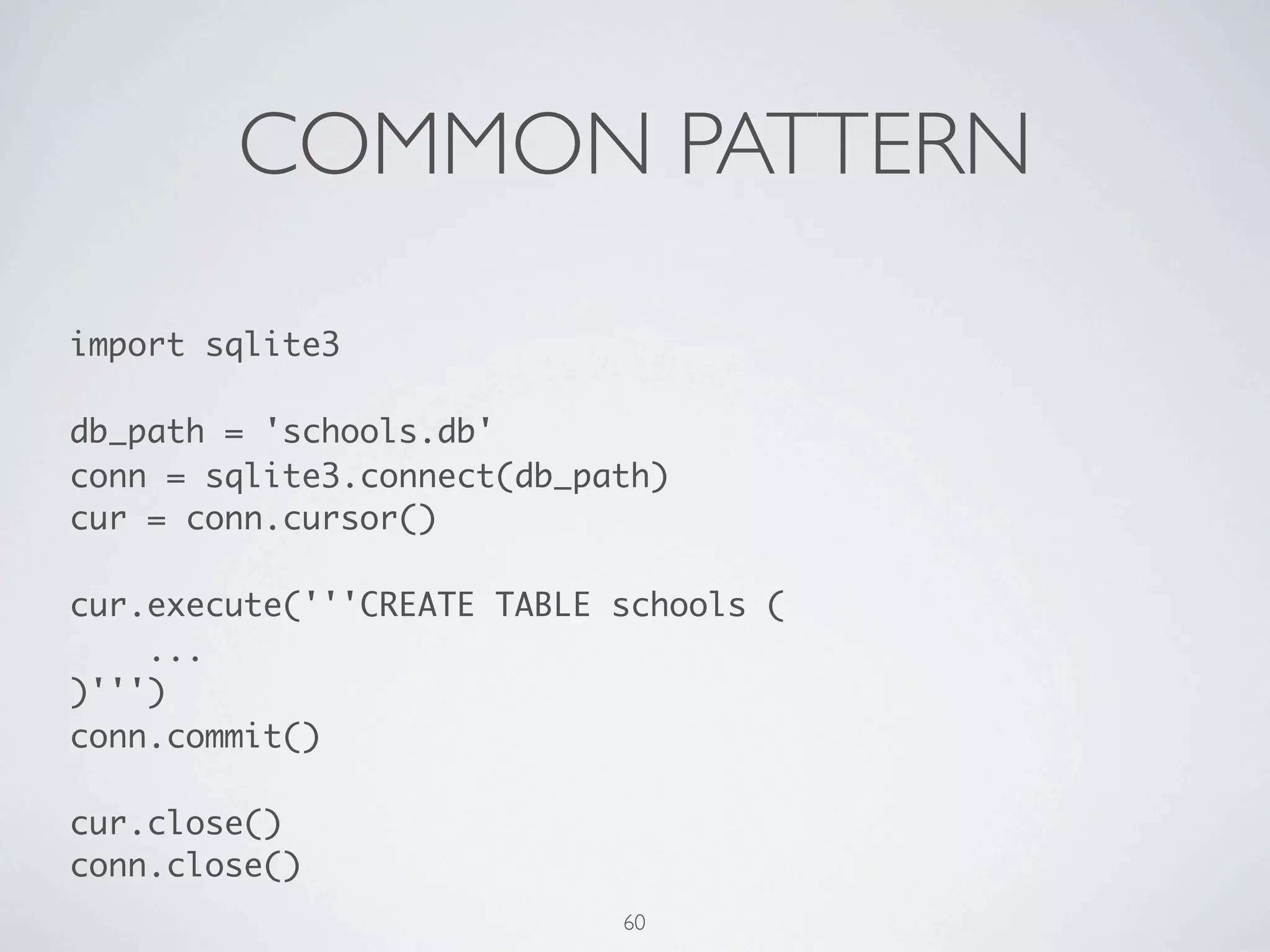






![ROW FACTORY
# SQLite only: Let you convert tuple into dict. It is
`DictCursor` in some other connectors.
!
def dict_factory(cursor, row):
d = {}
for idx, col in enumerate(cursor.description):
d[col[0]] = row[idx]
return d
!
...
con.row_factory = dict_factory
...
67](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/learning-python-from-data-public-130728195724-phpapp01/75/Learning-Python-from-Data-101-2048.jpg)