Kotlin is a modern programming language that was created by JetBrains as a replacement for Java, with some key advantages:
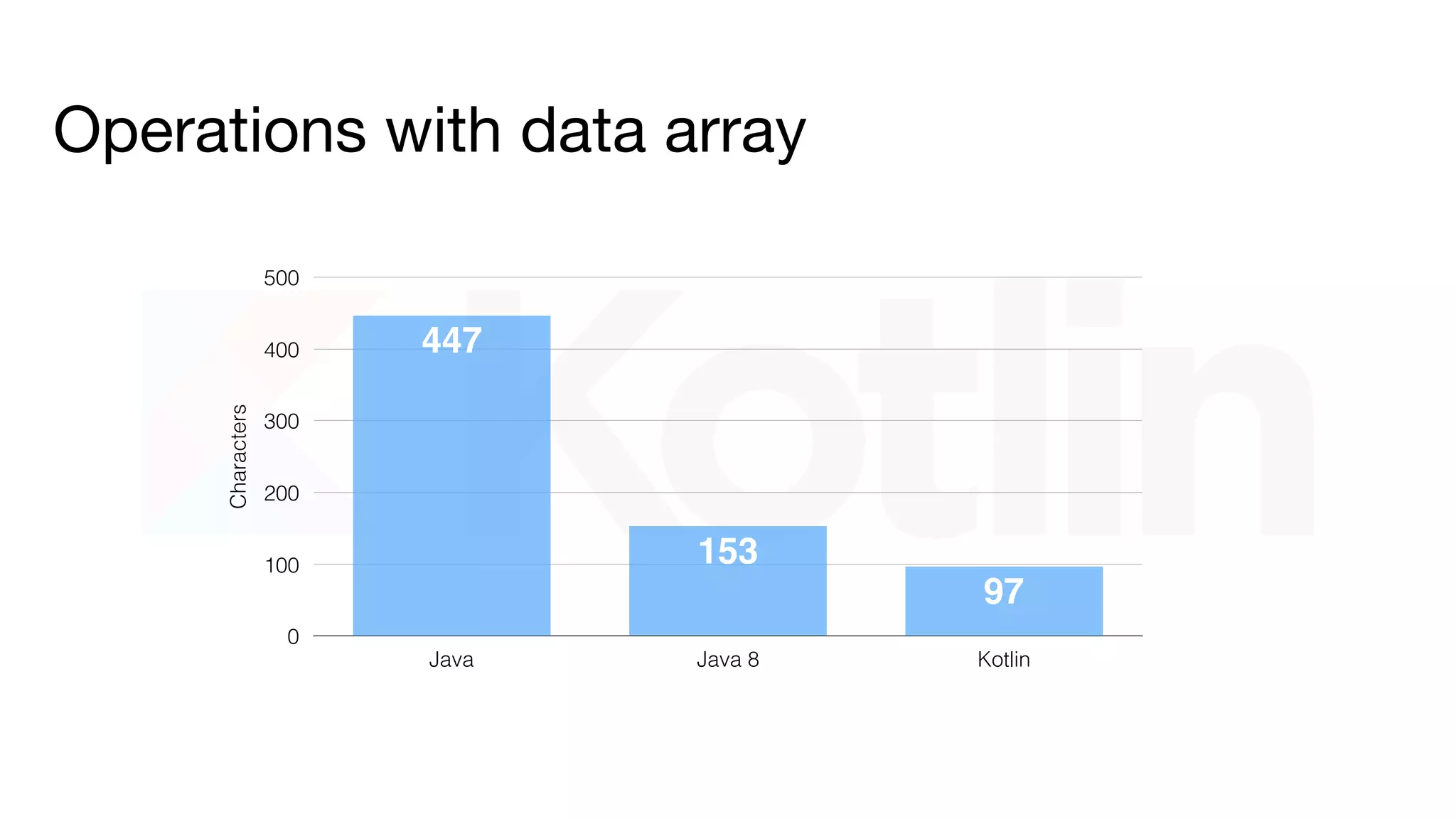
- It simplifies development tasks like creating data classes and working with collections. Kotlin also reduces the amount of code needed for common operations.
- Kotlin works seamlessly with Java code and is fully interoperable. It is also compatible with existing Java tools and platforms.
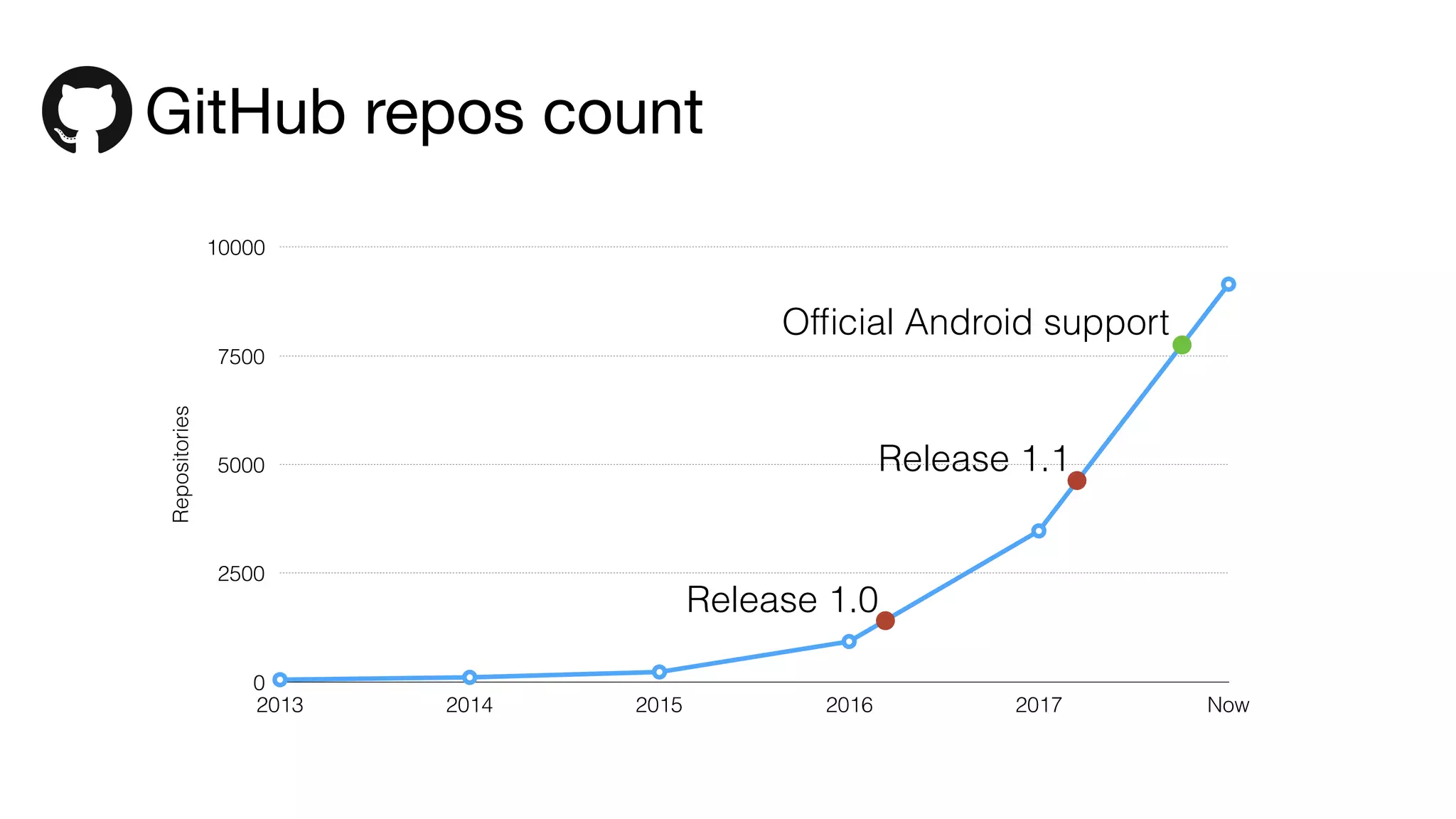
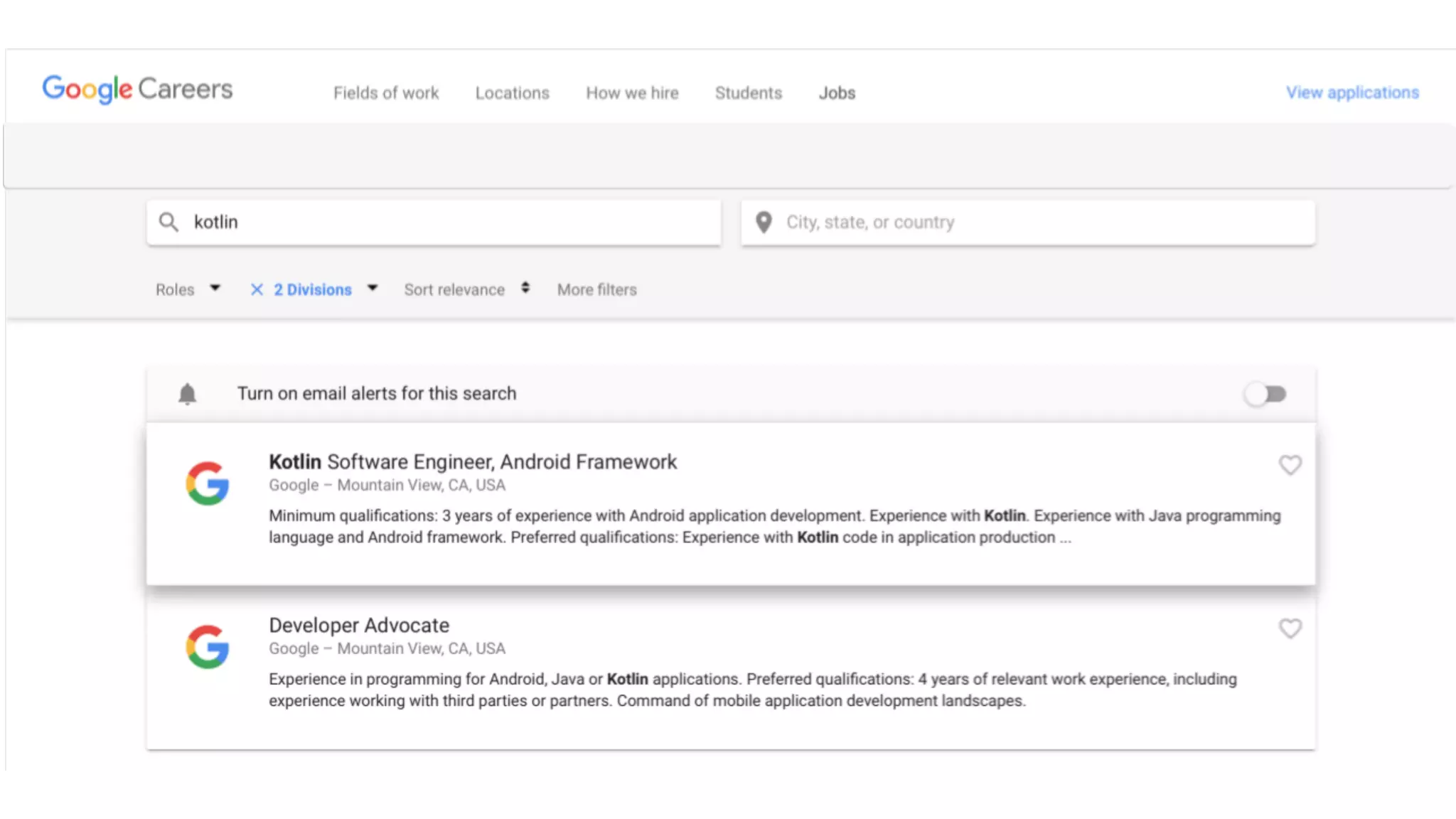
- The language has seen growing adoption since its 1.0 release in 2016 and is now officially supported by Google for Android development. Many large companies and open source projects use Kotlin due to its improvements over Java.