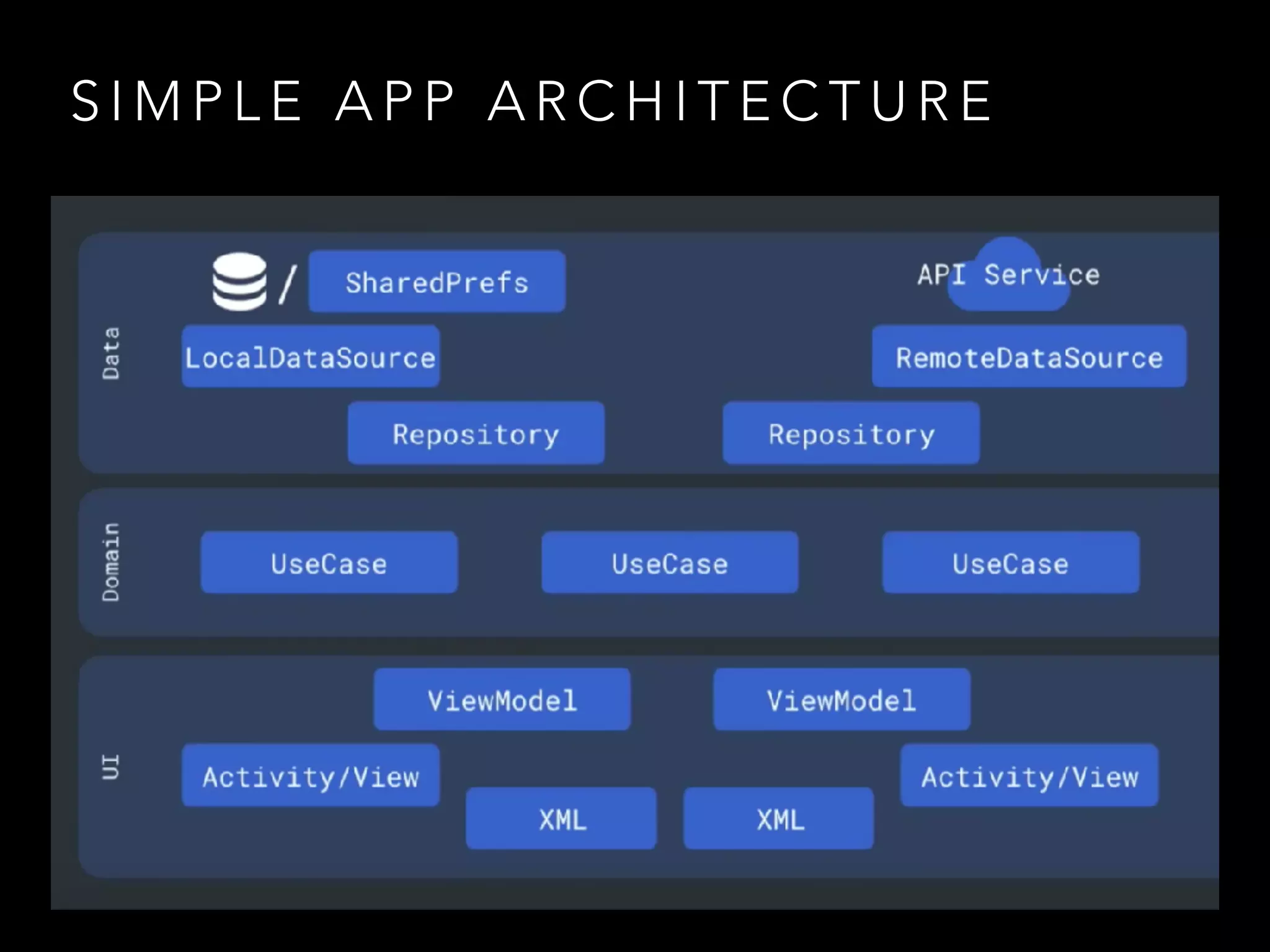
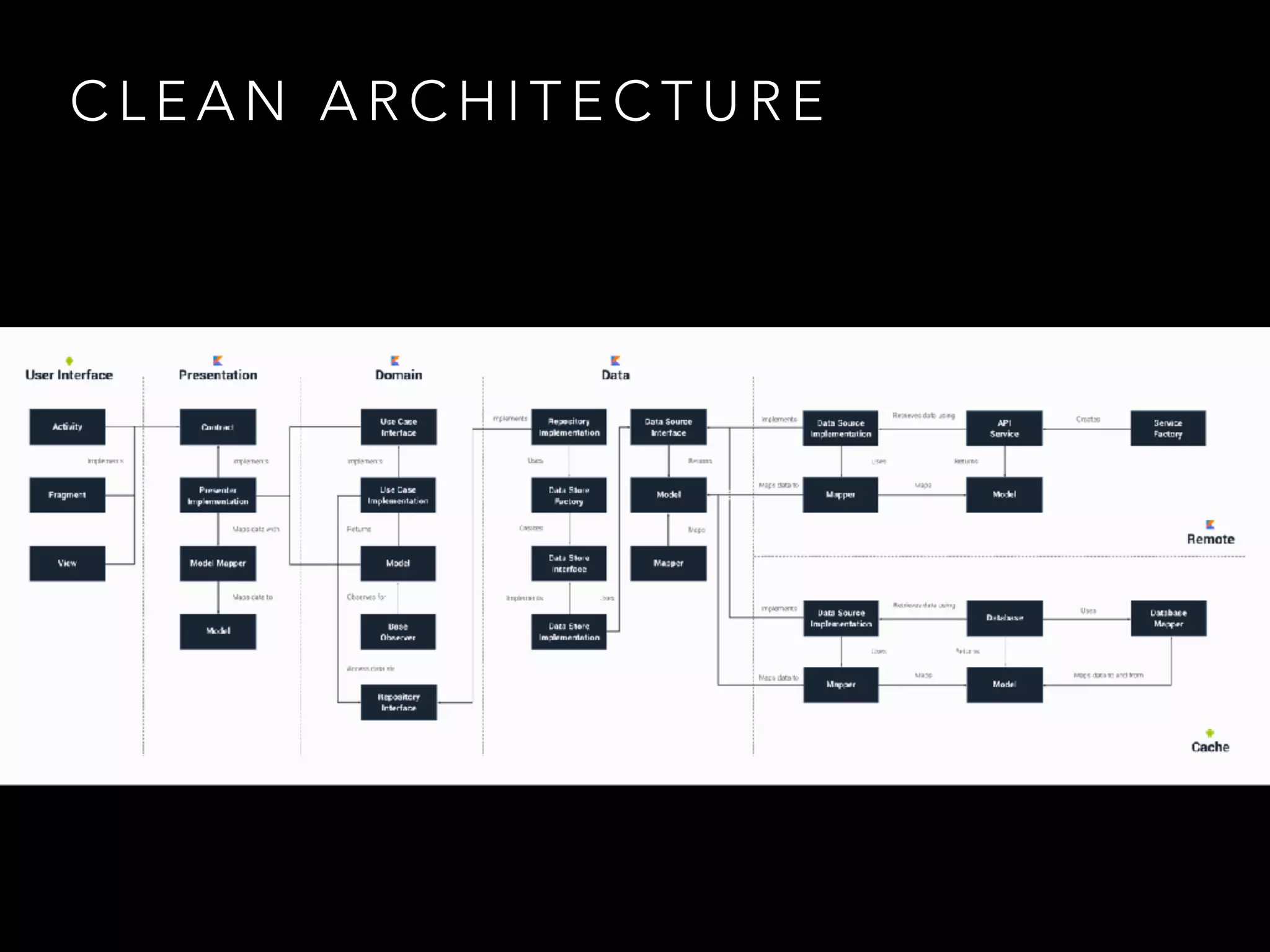
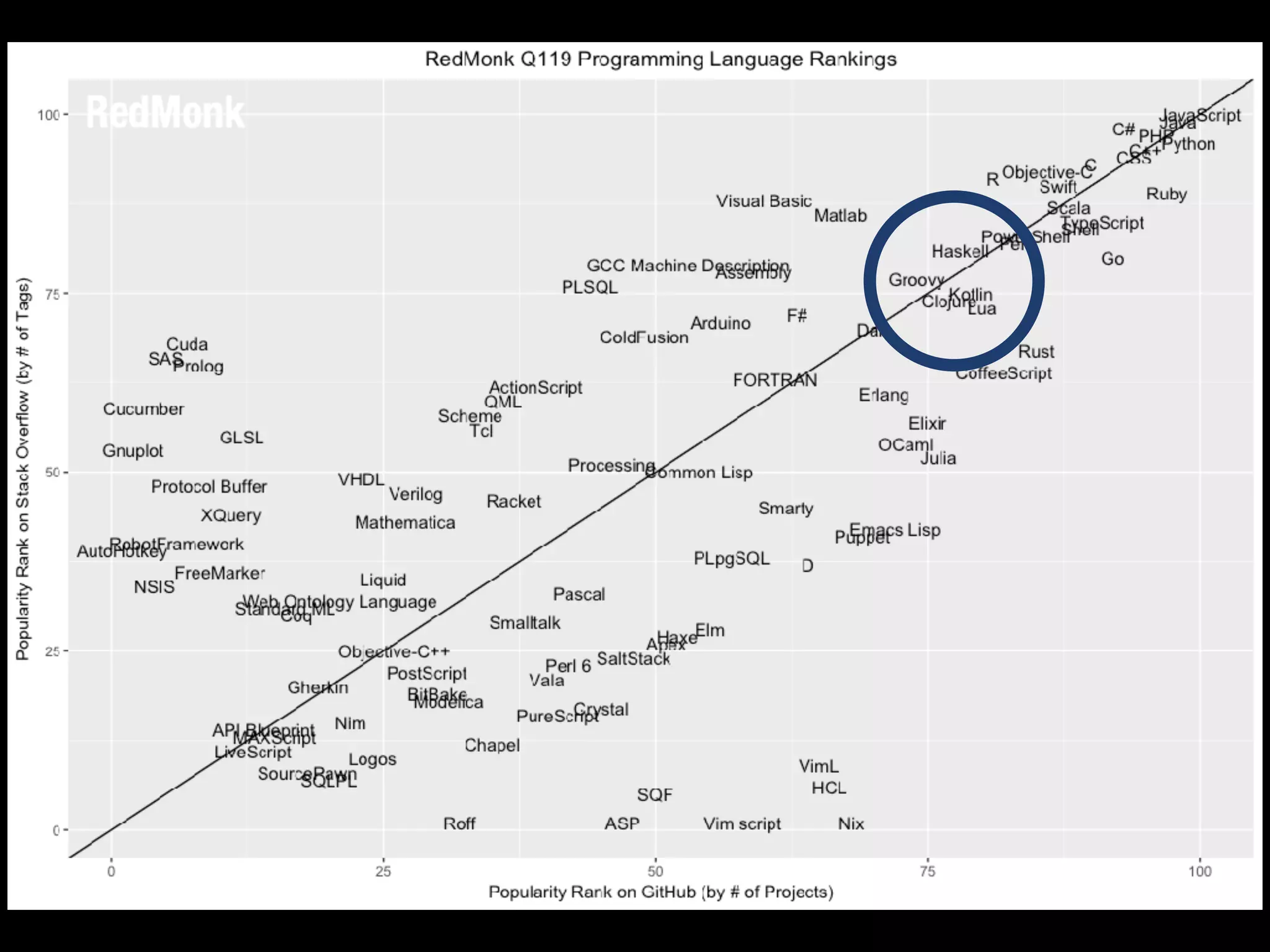
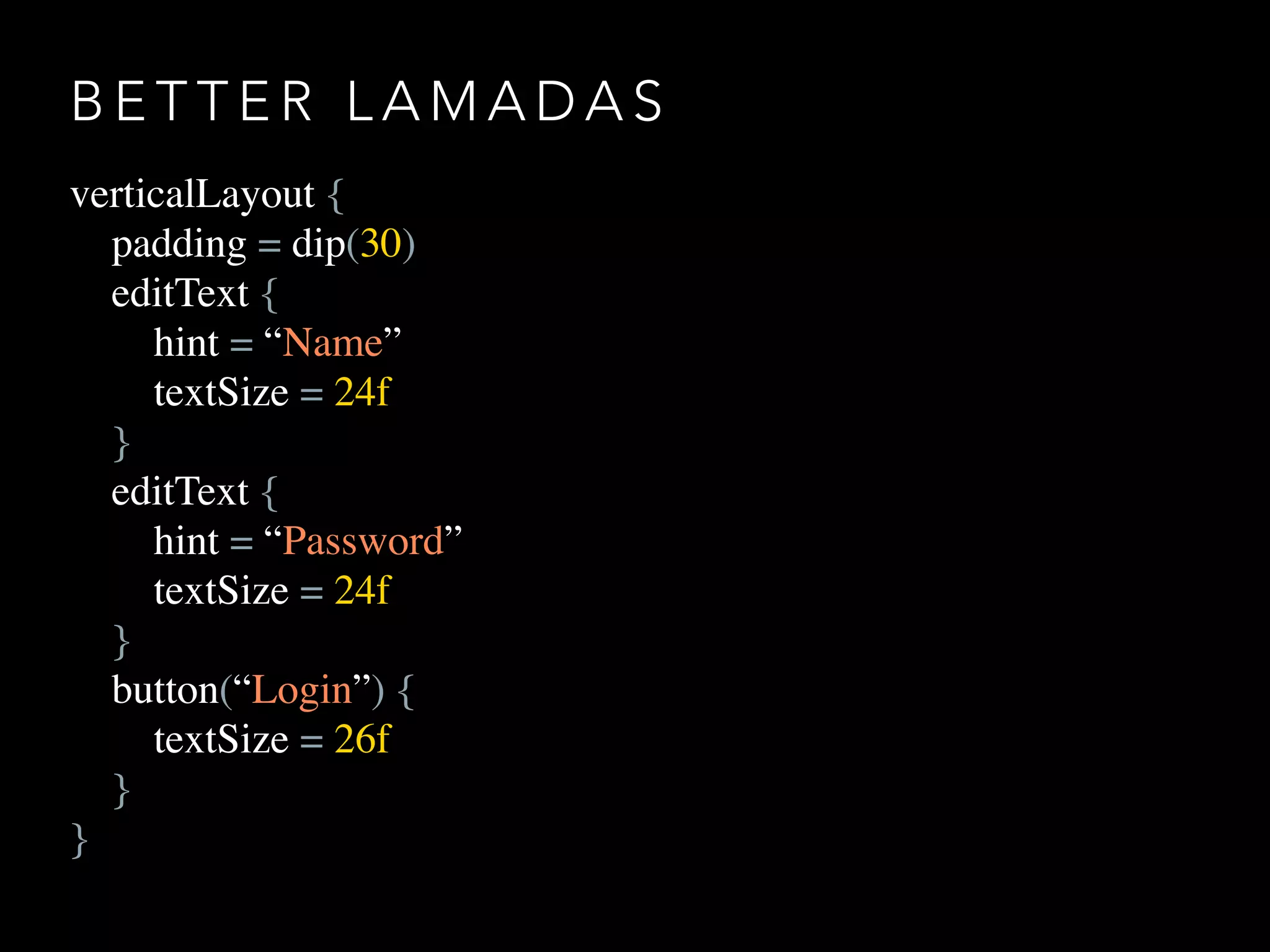
The document provides an overview of Kotlin programming language, focusing on its features and advantages for Android development. It covers topics such as syntax, type inference, null safety, extension functions, and the benefits of using Kotlin over Java. Additionally, it includes examples of using Kotlin for cleaner, more efficient code in Android applications.

































![O P E R AT O R O V E R L O A D I N G
// Original
bitmap.getPixel(100, 100)
// KTX
bitmap[100, 100]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sitkotlinmarch25-190613152922/75/Kotlin-for-Android-Developers-36-2048.jpg)