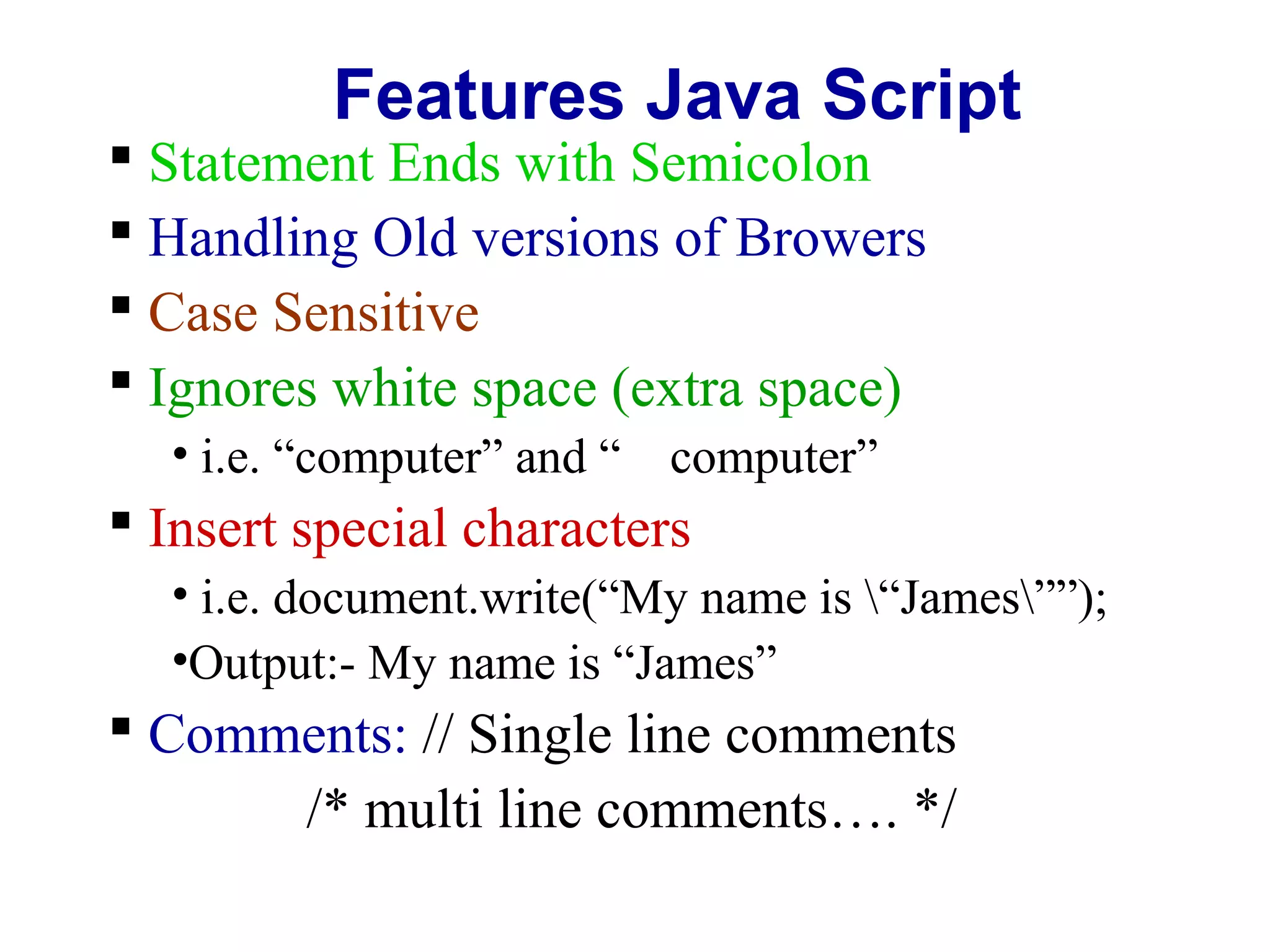
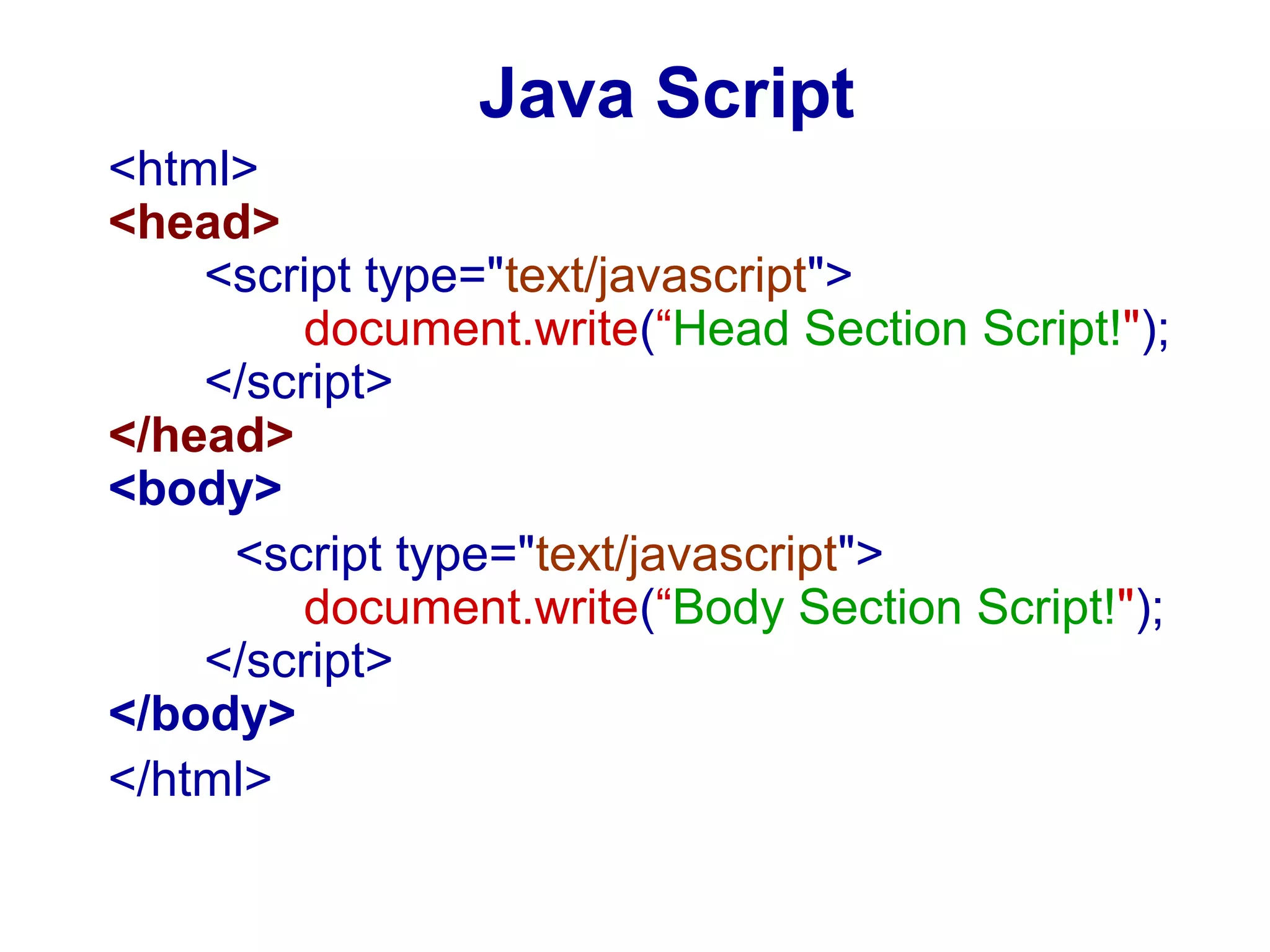
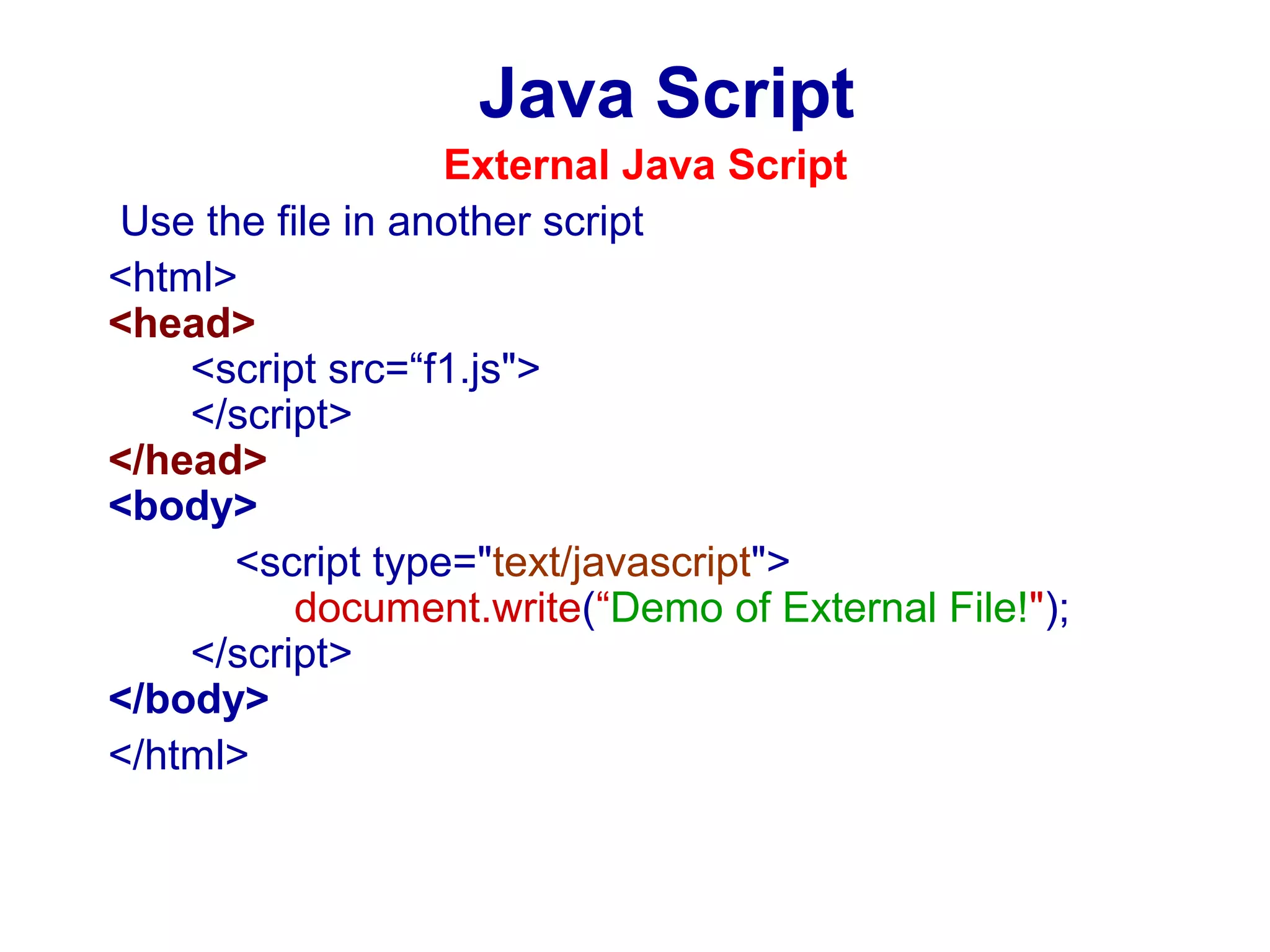
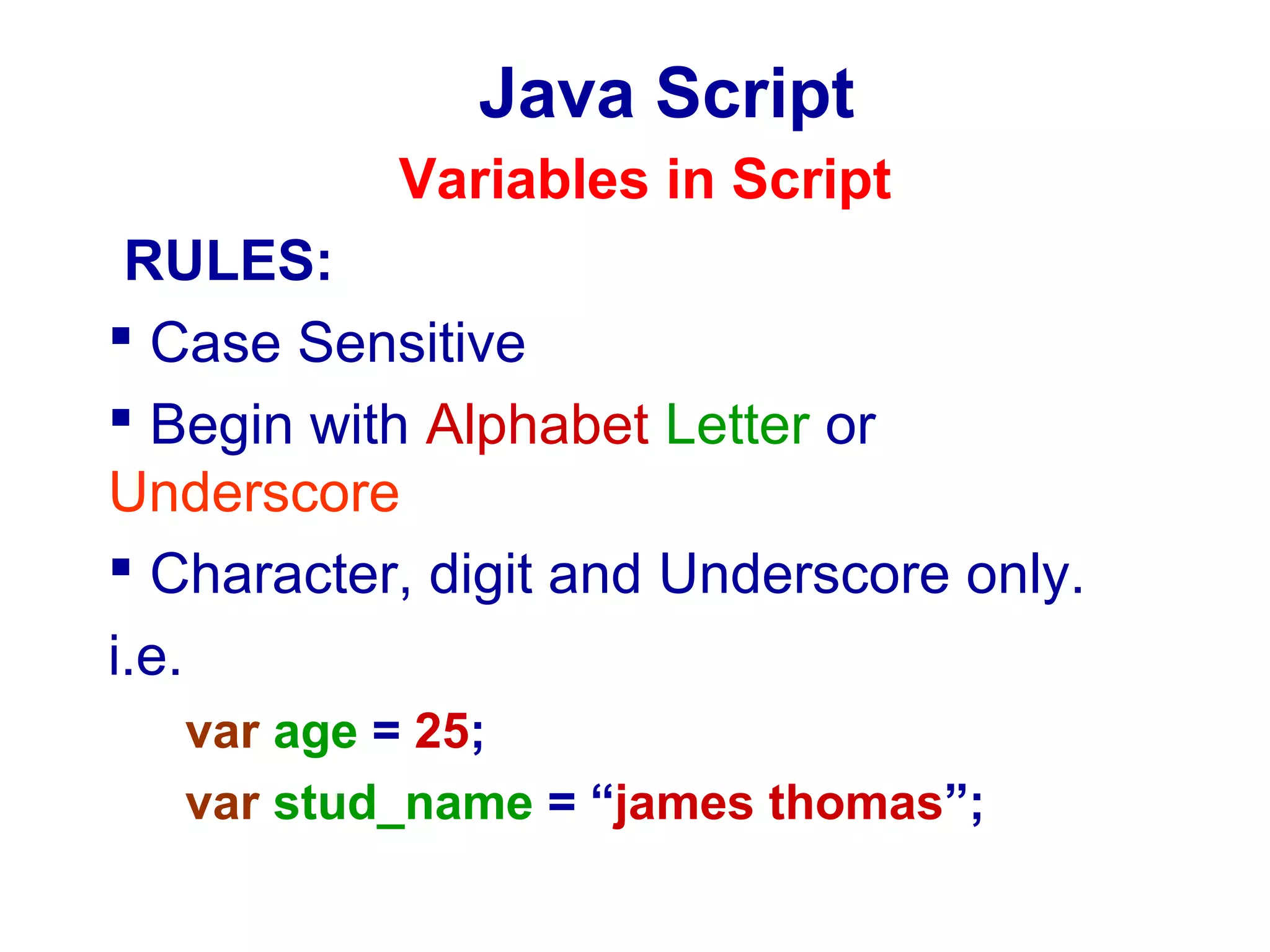
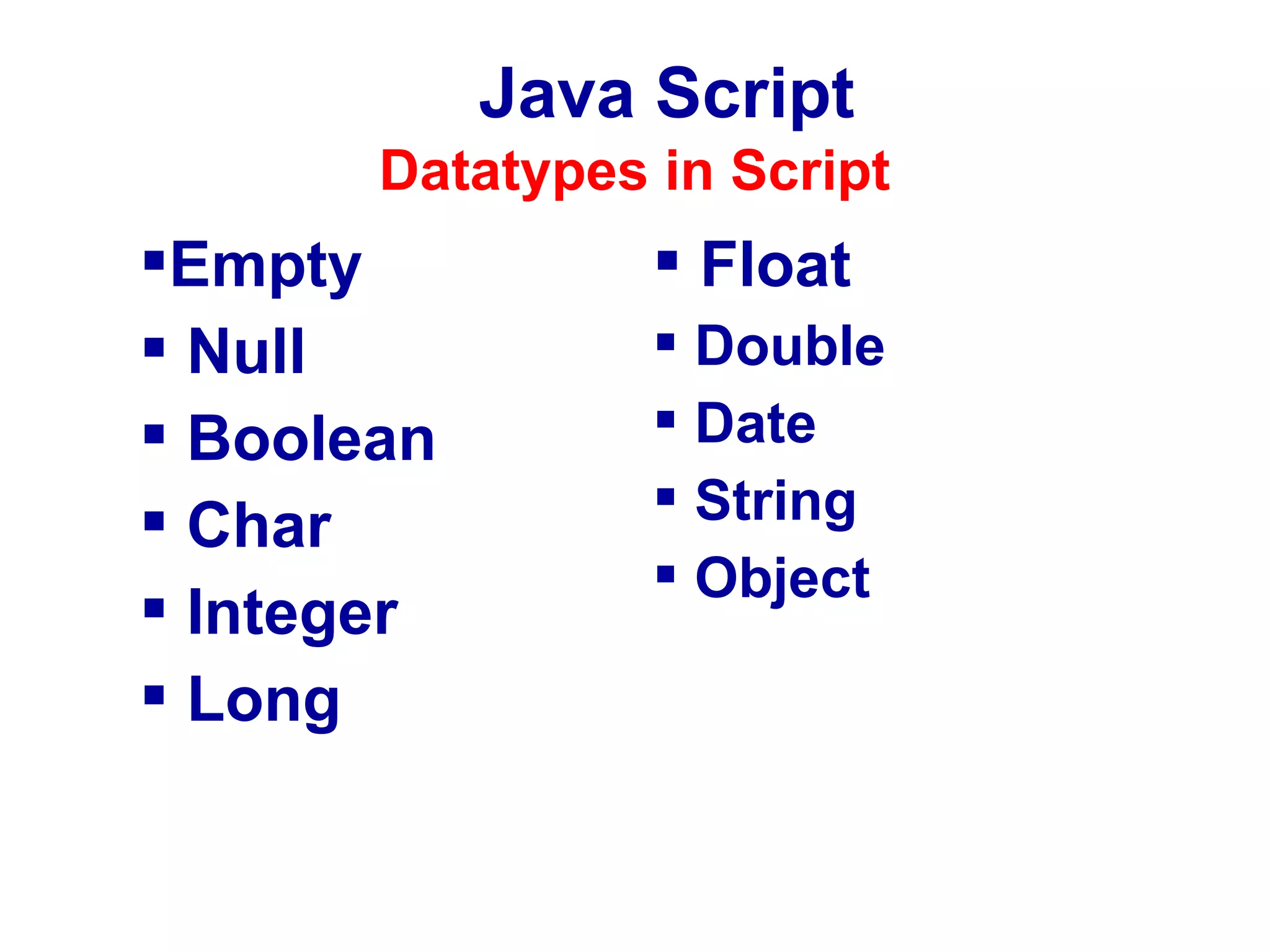
JavaScript was designed to add interactivity to HTML pages. It is a scripting language that is usually embedded directly into HTML pages and allows programmers to put dynamic text and react to events. JavaScript can be used to validate data, detect the visitor's browser, create cookies, and read and write HTML elements. It uses semicolons, handles old browser versions, is case sensitive, and ignores whitespace. Variables can be local or global and datatypes include empty, null, boolean, char, integer, long, float, double, date, string, and object. JavaScript supports operators, conditional statements, looping statements, and functions.