This document provides a detailed exploration of JavaScript functions, covering topics such as their nature as objects, creation methods (named functions, function expressions, and IIFE), invocation mechanics, scope, execution context, and argument handling. It also discusses the concept of 'this', closures, and techniques like partial application and memoization. The document is technical in nature and delves deeply into the inner workings of JavaScript functions, aiming to enhance understanding and application among developers.





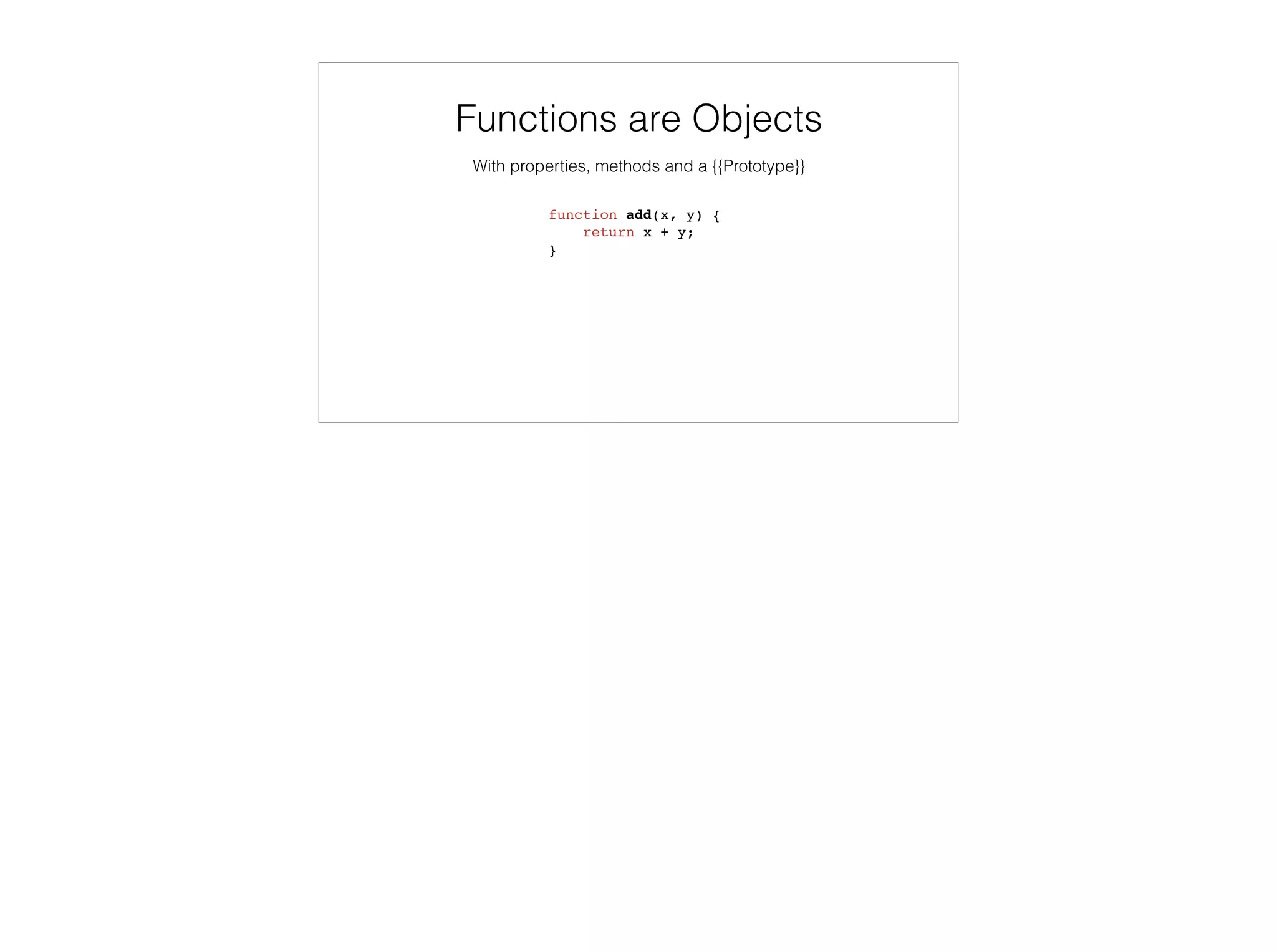

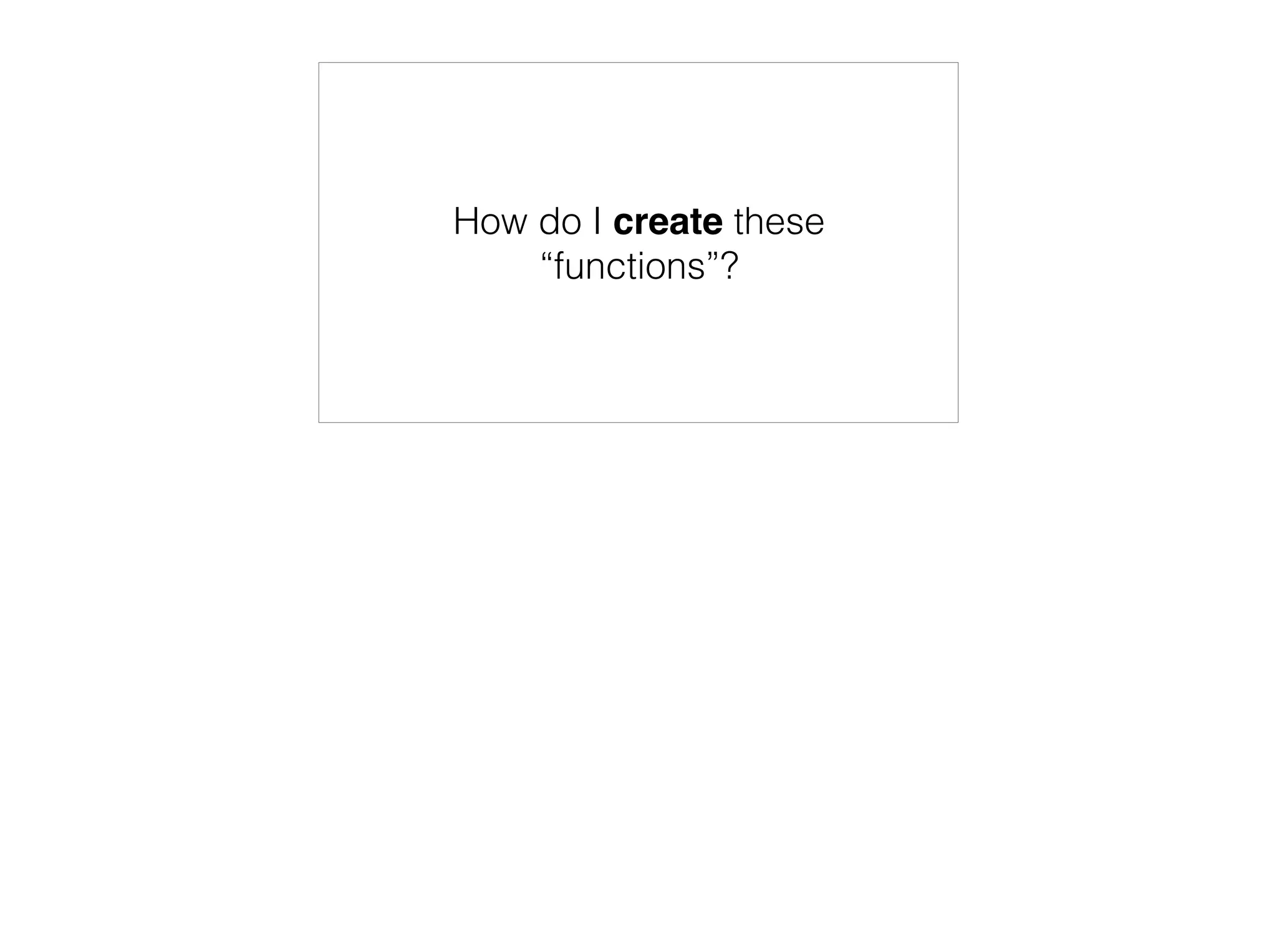


![Agenda
(function printAgenda() {
var topics = [
'What is a Function?',
'How do I create these "functions"?',
'What happens when I invoke a Function?',
'How do I wield this power?'
];
return topics.join("n");
})();
// => 'What is a Function?',
// => 'How do I create these "functions"?,
// => 'What happens when I invoke a Function?',
// => 'How do I wield this power?"](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascriptfunctions-150516001136-lva1-app6891/75/JavaScript-Functions-13-2048.jpg)


















![Scopes
var globalVar = 'found in global scope';
function global_function() {
var localVar = 'found in global_function';
function inner_function() {
var innerVar = 'found in inner_function';
console.log(globalVar, localVar, innerVar);
console.log(notFoundAnywhere);
}
inner_function();
}
global_function();
global scope
globalVar: ‘found in global scope’
global_function: [Function]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascriptfunctions-150516001136-lva1-app6891/75/JavaScript-Functions-34-2048.jpg)
![Scopes
var globalVar = 'found in global scope';
function global_function() {
var localVar = 'found in global_function';
function inner_function() {
var innerVar = 'found in inner_function';
console.log(globalVar, localVar, innerVar);
console.log(notFoundAnywhere);
}
inner_function();
}
global_function();
global scope
globalVar: ‘found in global scope’
global_function: [Function]
global_function scope](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascriptfunctions-150516001136-lva1-app6891/75/JavaScript-Functions-35-2048.jpg)
![Scopes
var globalVar = 'found in global scope';
function global_function() {
var localVar = 'found in global_function';
function inner_function() {
var innerVar = 'found in inner_function';
console.log(globalVar, localVar, innerVar);
console.log(notFoundAnywhere);
}
inner_function();
}
global_function();
global scope
globalVar: ‘found in global scope’
global_function: [Function]
localVar: ‘found in global_function’
inner_function: [Function]
global_function scope](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascriptfunctions-150516001136-lva1-app6891/75/JavaScript-Functions-36-2048.jpg)
![Scopes
var globalVar = 'found in global scope';
function global_function() {
var localVar = 'found in global_function';
function inner_function() {
var innerVar = 'found in inner_function';
console.log(globalVar, localVar, innerVar);
console.log(notFoundAnywhere);
}
inner_function();
}
global_function();
global scope
globalVar: ‘found in global scope’
global_function: [Function]
localVar: ‘found in global_function’
inner_function: [Function]
global_function scope
inner_functon scope](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascriptfunctions-150516001136-lva1-app6891/75/JavaScript-Functions-37-2048.jpg)
![Scopes
var globalVar = 'found in global scope';
function global_function() {
var localVar = 'found in global_function';
function inner_function() {
var innerVar = 'found in inner_function';
console.log(globalVar, localVar, innerVar);
console.log(notFoundAnywhere);
}
inner_function();
}
global_function();
global scope
globalVar: ‘found in global scope’
global_function: [Function]
localVar: ‘found in global_function’
inner_function: [Function]
innerVar: ‘found in inner_function’
global_function scope
inner_functon scope](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascriptfunctions-150516001136-lva1-app6891/75/JavaScript-Functions-38-2048.jpg)
![Scopes
var globalVar = 'found in global scope';
function global_function() {
var localVar = 'found in global_function';
function inner_function() {
var innerVar = 'found in inner_function';
console.log(globalVar, localVar, innerVar);
console.log(notFoundAnywhere);
}
inner_function();
}
global_function();
// => found in global scope, found in global_function, found in inner_function
// => undefined
global scope
globalVar: ‘found in global scope’
global_function: [Function]
localVar: ‘found in global_function’
inner_function: [Function]
innerVar: ‘found in inner_function’
global_function scope
inner_functon scope](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascriptfunctions-150516001136-lva1-app6891/75/JavaScript-Functions-39-2048.jpg)

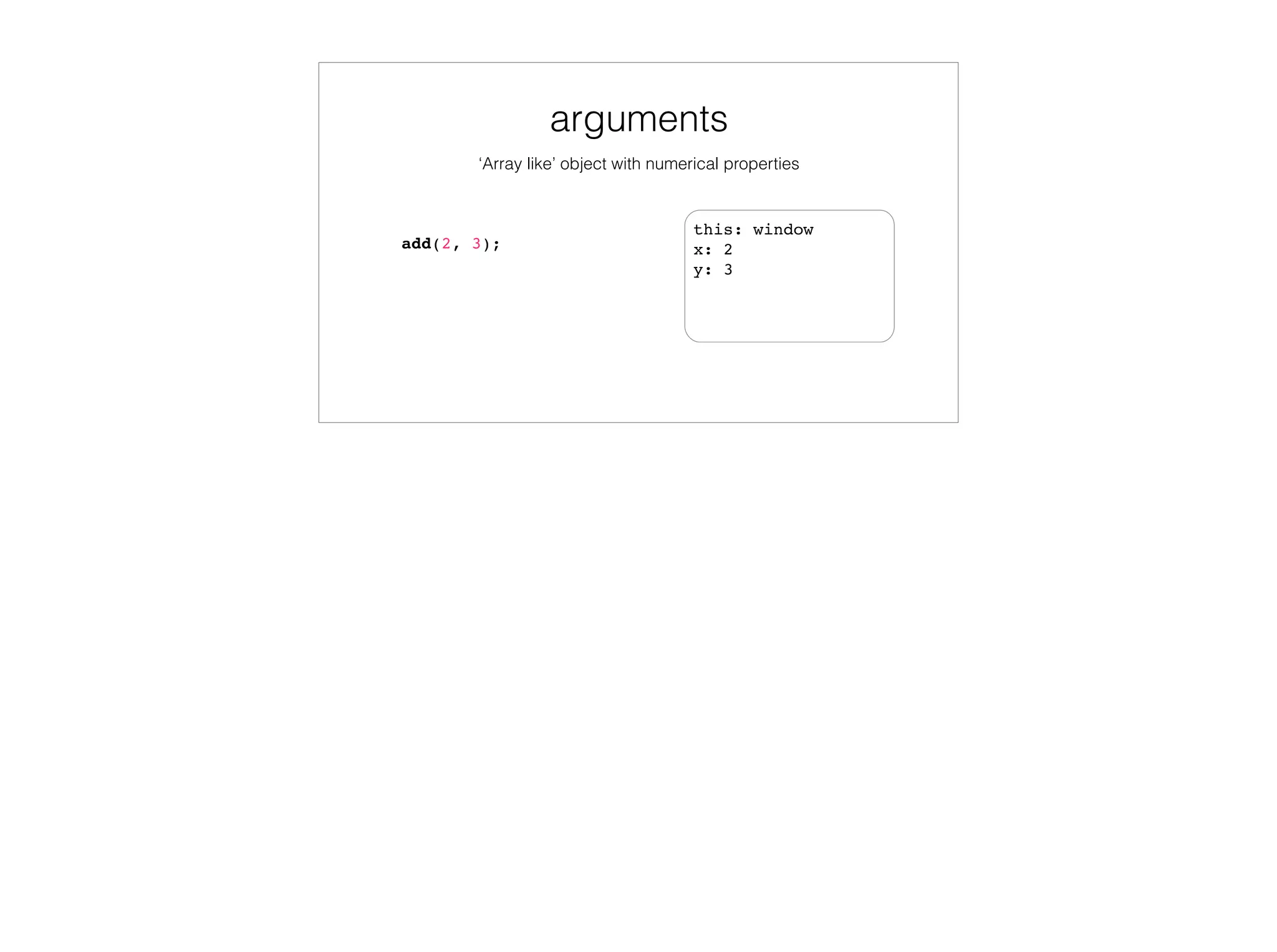
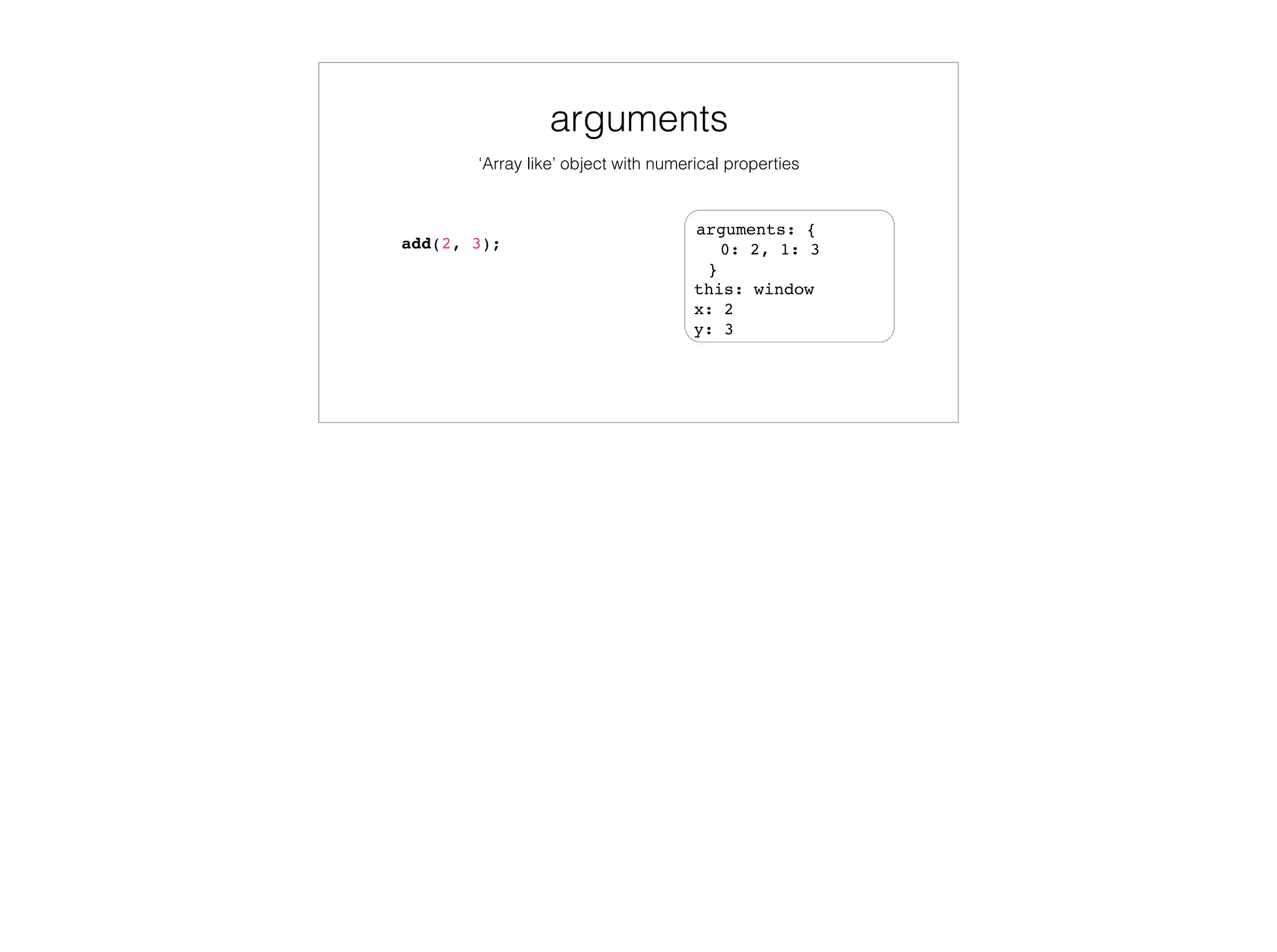




![As element attributes
<button id="calculate" onmouseover="this.style['border-color'] = 'blue';">
Calculate
</button>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascriptfunctions-150516001136-lva1-app6891/75/JavaScript-Functions-49-2048.jpg)
![As element attributes
this === calculate;
// => true
<button id="calculate" onmouseover="this.style['border-color'] = 'blue';">
Calculate
</button>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascriptfunctions-150516001136-lva1-app6891/75/JavaScript-Functions-50-2048.jpg)










![Declaration and Hoisting
function concat() {
return " ".join(to_array(arguments));
function to_array(args) {
var words = [];
for (var i = 0; i < args.length; i++) {
words.push(args[i]);
}
return words;
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascriptfunctions-150516001136-lva1-app6891/75/JavaScript-Functions-61-2048.jpg)
![Declaration and Hoisting
functions are declared
function concat() {
return " ".join(to_array(arguments));
function to_array(args) {
var words = [];
for (var i = 0; i < args.length; i++) {
words.push(args[i]);
}
return words;
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascriptfunctions-150516001136-lva1-app6891/75/JavaScript-Functions-62-2048.jpg)
![Declaration and Hoisting
functions are declared
variables are declared
function concat() {
return " ".join(to_array(arguments));
function to_array(args) {
var words = [];
for (var i = 0; i < args.length; i++) {
words.push(args[i]);
}
return words;
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascriptfunctions-150516001136-lva1-app6891/75/JavaScript-Functions-63-2048.jpg)
![Declaration and Hoisting
function concat() {
return " ".join(to_array(arguments));
function to_array(args) {
var words = [];
for (var i = 0; i < args.length; i++) {
words.push(args[i]);
}
return words;
}
}
function concat() {
function to_array(args) {
var words = [],
i;
for (i = 0; i < args.length; i++) {
words.push(args[i]);
}
return words;
}
return " ".join(to_array(arguments));
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascriptfunctions-150516001136-lva1-app6891/75/JavaScript-Functions-64-2048.jpg)












![var colors = enumer('RED', 'GREEN', ‘BLUE’),
selectedColor = ‘RED’;
colors.contains(selectedColor);
// => true
selectedColor = ‘YELLOW’;
colors.contains(selectedColor);
// => false
function enumer() {
function contains (value) {
return this.hasOwnProperty(value);
}
var i, numValues = arguments.length,
values = {};
for (i = 0; i < numValues; i++) {
values[arguments[i]] = arguments[i];
}
values.contains = contains;
return values;
}
Variadic Functions](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascriptfunctions-150516001136-lva1-app6891/75/JavaScript-Functions-79-2048.jpg)
![var colors = enumer('RED', 'GREEN', ‘BLUE’),
selectedColor = ‘RED’;
colors.contains(selectedColor);
// => true
selectedColor = ‘YELLOW’;
colors.contains(selectedColor);
// => false
function enumer() {
function contains (value) {
return this.hasOwnProperty(value);
}
var i, numValues = arguments.length,
values = {};
for (i = 0; i < numValues; i++) {
values[arguments[i]] = arguments[i];
}
values.contains = contains;
return values;
}
Variadic Functions](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascriptfunctions-150516001136-lva1-app6891/75/JavaScript-Functions-80-2048.jpg)
![var colors = enumer('RED', 'GREEN', ‘BLUE’),
selectedColor = ‘RED’;
colors.contains(selectedColor);
// => true
selectedColor = ‘YELLOW’;
colors.contains(selectedColor);
// => false
function enumer() {
function contains (value) {
return this.hasOwnProperty(value);
}
var i, numValues = arguments.length,
values = {};
for (i = 0; i < numValues; i++) {
values[arguments[i]] = arguments[i];
}
values.contains = contains;
return values;
}
Variadic Functions](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascriptfunctions-150516001136-lva1-app6891/75/JavaScript-Functions-81-2048.jpg)
![var colors = enumer('RED', 'GREEN', ‘BLUE’),
selectedColor = ‘RED’;
colors.contains(selectedColor);
// => true
selectedColor = ‘YELLOW’;
colors.contains(selectedColor);
// => false
function enumer() {
function contains (value) {
return this.hasOwnProperty(value);
}
var i, numValues = arguments.length,
values = {};
for (i = 0; i < numValues; i++) {
values[arguments[i]] = arguments[i];
}
values.contains = contains;
return values;
}
Variadic Functions](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascriptfunctions-150516001136-lva1-app6891/75/JavaScript-Functions-82-2048.jpg)







![function memoize(func, context) {
var results = {},
wrapper = function () {
var args = Array.prototype.slice.call(arguments, 0),
key = ':'.join(args);
if (!results.hasOwnProperty(key)) {
results[key] = func.apply(context, args);
}
return results[key];
};
return wrapper;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascriptfunctions-150516001136-lva1-app6891/75/JavaScript-Functions-90-2048.jpg)
![function memoize(func, context) {
var results = {},
wrapper = function () {
var args = Array.prototype.slice.call(arguments, 0),
key = ':'.join(args);
if (!results.hasOwnProperty(key)) {
results[key] = func.apply(context, args);
}
return results[key];
};
return wrapper;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascriptfunctions-150516001136-lva1-app6891/75/JavaScript-Functions-91-2048.jpg)












![var funcs = [];
for (var i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
funcs.push(function () {
console.log(i);
});
}
for (var j = 0; j < 5; j++) {
funcs[j]();
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascriptfunctions-150516001136-lva1-app6891/75/JavaScript-Functions-104-2048.jpg)
![// => 5
// => 5
// => 5
// => 5
// => 5
var funcs = [];
for (var i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
funcs.push(function () {
console.log(i);
});
}
for (var j = 0; j < 5; j++) {
funcs[j]();
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascriptfunctions-150516001136-lva1-app6891/75/JavaScript-Functions-105-2048.jpg)
![// => 5
// => 5
// => 5
// => 5
// => 5
var funcs = [];
for (var i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
funcs.push(function () {
console.log(i);
});
}
for (var j = 0; j < 5; j++) {
funcs[j]();
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascriptfunctions-150516001136-lva1-app6891/75/JavaScript-Functions-106-2048.jpg)
![// => 0
// => 1
// => 2
// => 3
// => 4
var funcs = [];
for (var i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
funcs.push((function (i) {
return function () {
console.log(i);
};
})(i));
}
for (var j = 0; j < 5; j++) {
funcs[j]();
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascriptfunctions-150516001136-lva1-app6891/75/JavaScript-Functions-107-2048.jpg)
![// => 0
// => 1
// => 2
// => 3
// => 4
var funcs = [];
for (var i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
funcs.push((function (i) {
return function () {
console.log(i);
};
})(i));
}
for (var j = 0; j < 5; j++) {
funcs[j]();
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascriptfunctions-150516001136-lva1-app6891/75/JavaScript-Functions-108-2048.jpg)



![Encapsulation: A Better enumer
var colors = enumer('RED', 'GREEN', 'BLUE');
colors.contains('RED');
// => true
colors.contains('YELLOW');
// => false
function enumer() {
function contains (value) {
return this.hasOwnProperty(value);
}
var i, numValues = arguments.length,
values = {};
for (i = 0; i < numValues; i++) {
values[arguments[i]] = arguments[i];
}
values.contains = contains;
return values;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascriptfunctions-150516001136-lva1-app6891/75/JavaScript-Functions-112-2048.jpg)
![Encapsulation: A Better enumer
var colors = enumer('RED', 'GREEN', 'BLUE');
colors.contains('RED');
// => true
colors.contains('YELLOW');
// => false
colors.YELLOW = 'YOLO';
colors.contains('YELLOW');
// => true
function enumer() {
function contains (value) {
return this.hasOwnProperty(value);
}
var i, numValues = arguments.length,
values = {};
for (i = 0; i < numValues; i++) {
values[arguments[i]] = arguments[i];
}
values.contains = contains;
return values;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascriptfunctions-150516001136-lva1-app6891/75/JavaScript-Functions-113-2048.jpg)
![Encapsulation: A Better enumer
var colors = enumer('RED', 'GREEN', 'BLUE');
colors.contains('RED');
// => true
colors.contains('YELLOW');
// => false
colors.YELLOW = 'YOLO';
colors.contains('YELLOW');
// => true
delete colors.RED;
colors.contains('RED');
// => false
function enumer() {
function contains (value) {
return this.hasOwnProperty(value);
}
var i, numValues = arguments.length,
values = {};
for (i = 0; i < numValues; i++) {
values[arguments[i]] = arguments[i];
}
values.contains = contains;
return values;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascriptfunctions-150516001136-lva1-app6891/75/JavaScript-Functions-114-2048.jpg)
![Encapsulation: A Better enumer
var colors = enumer('RED', 'GREEN', 'BLUE');
colors.contains('RED');
// => true
colors.contains('YELLOW');
// => false
colors.YELLOW = 'YOLO';
colors.contains('YELLOW');
// => true
colors.contains('contains');
// => true
delete colors.RED;
colors.contains('RED');
// => false
function enumer() {
function contains (value) {
return this.hasOwnProperty(value);
}
var i, numValues = arguments.length,
values = {};
for (i = 0; i < numValues; i++) {
values[arguments[i]] = arguments[i];
}
values.contains = contains;
return values;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascriptfunctions-150516001136-lva1-app6891/75/JavaScript-Functions-115-2048.jpg)
![Encapsulation: A Better enumer
var colors = enumer('RED', 'GREEN', 'BLUE');
colors.contains('RED');
// => true
colors.contains('YELLOW');
// => false
function enumer() {
function contains (value) {
return this.hasOwnProperty(value);
}
var i, numValues = arguments.length,
values = {};
for (i = 0; i < numValues; i++) {
values[arguments[i]] = arguments[i];
}
values.contains = contains;
return values;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascriptfunctions-150516001136-lva1-app6891/75/JavaScript-Functions-116-2048.jpg)





























![Encapsulation the JavaScript Way
function Vault(passcode) {
var locked = true,
data = {};
function checkPasscode(attemptedPasscode) {
return attemptedPasscode == passcode;
}
function grantAccess() {
locked = false;
return true;
}
this.isLocked = function () {
return locked;
};
this.lock = function () {
locked = true;
};
// ...
// ...
this.unlock = function (attemptedPasscode) {
checkPasscode(attemptedPasscode) && grantAccess();
};
this.store = function (key, value) {
if (this.isLocked()) {
throw new Error('The vault is locked');
}
data[key] = value;
};
this.retrieve = function (key) {
if (this.isLocked) {
throw new Error('The vault is locked');
}
return data[key];
};
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascriptfunctions-150516001136-lva1-app6891/75/JavaScript-Functions-146-2048.jpg)
