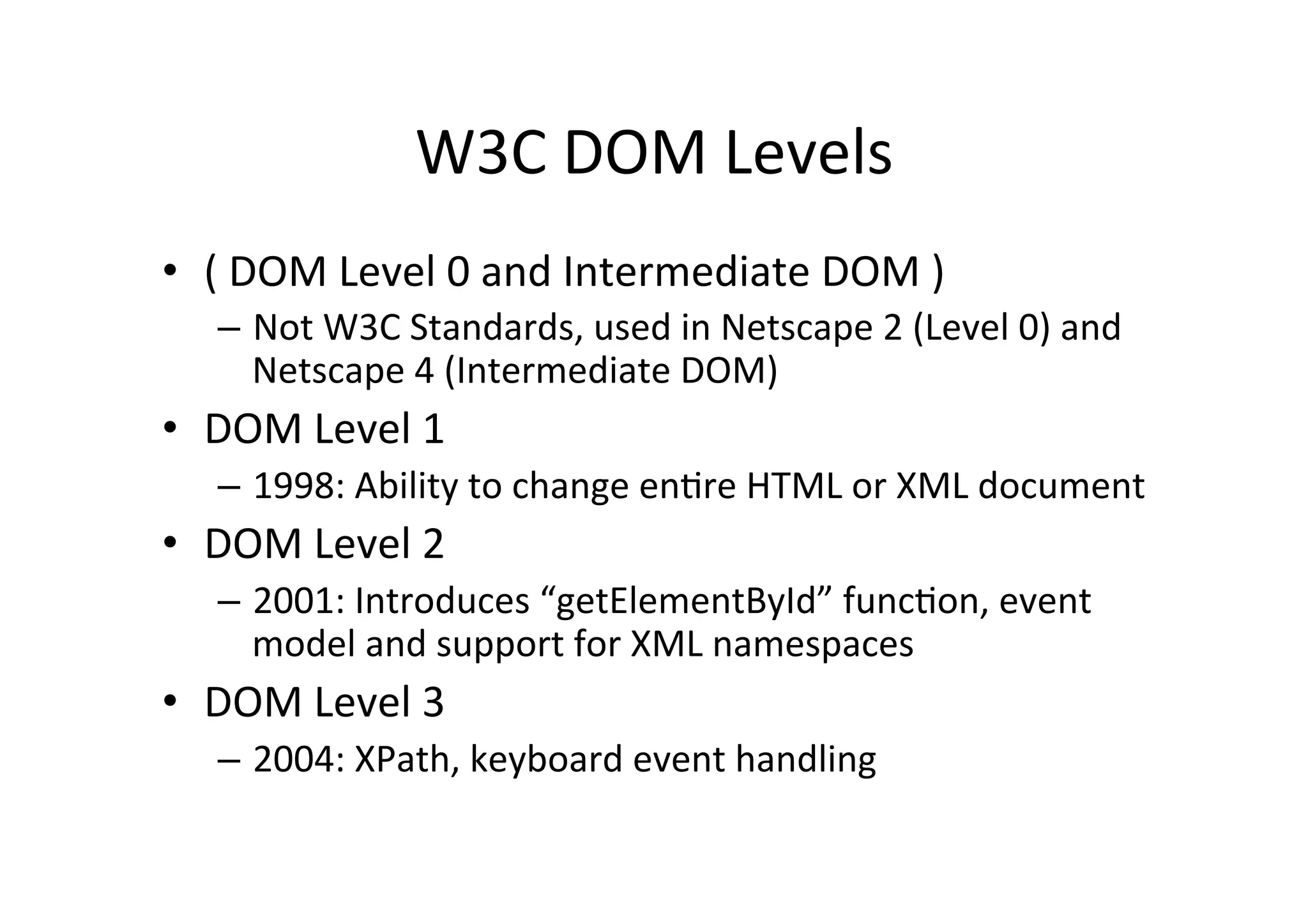
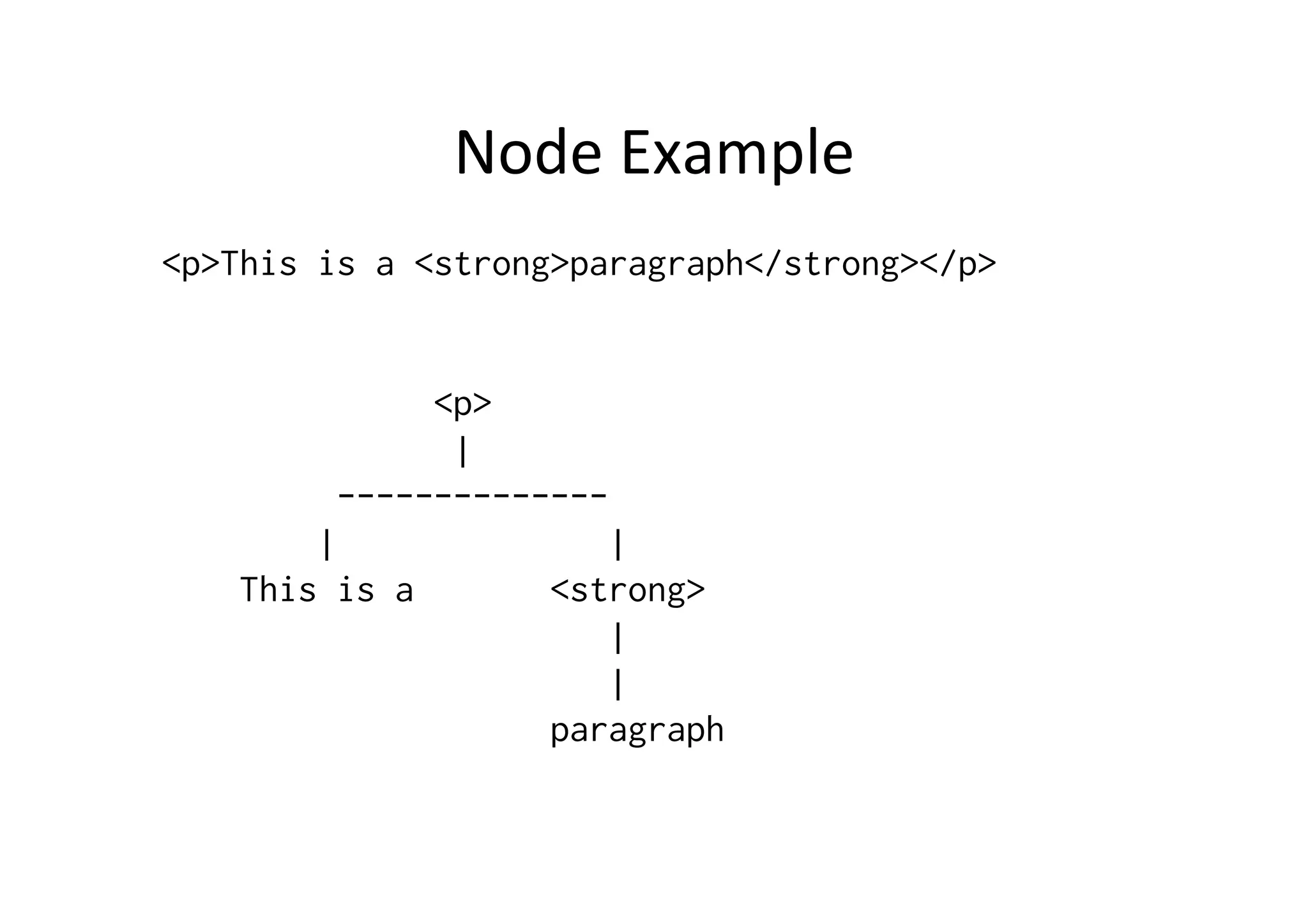
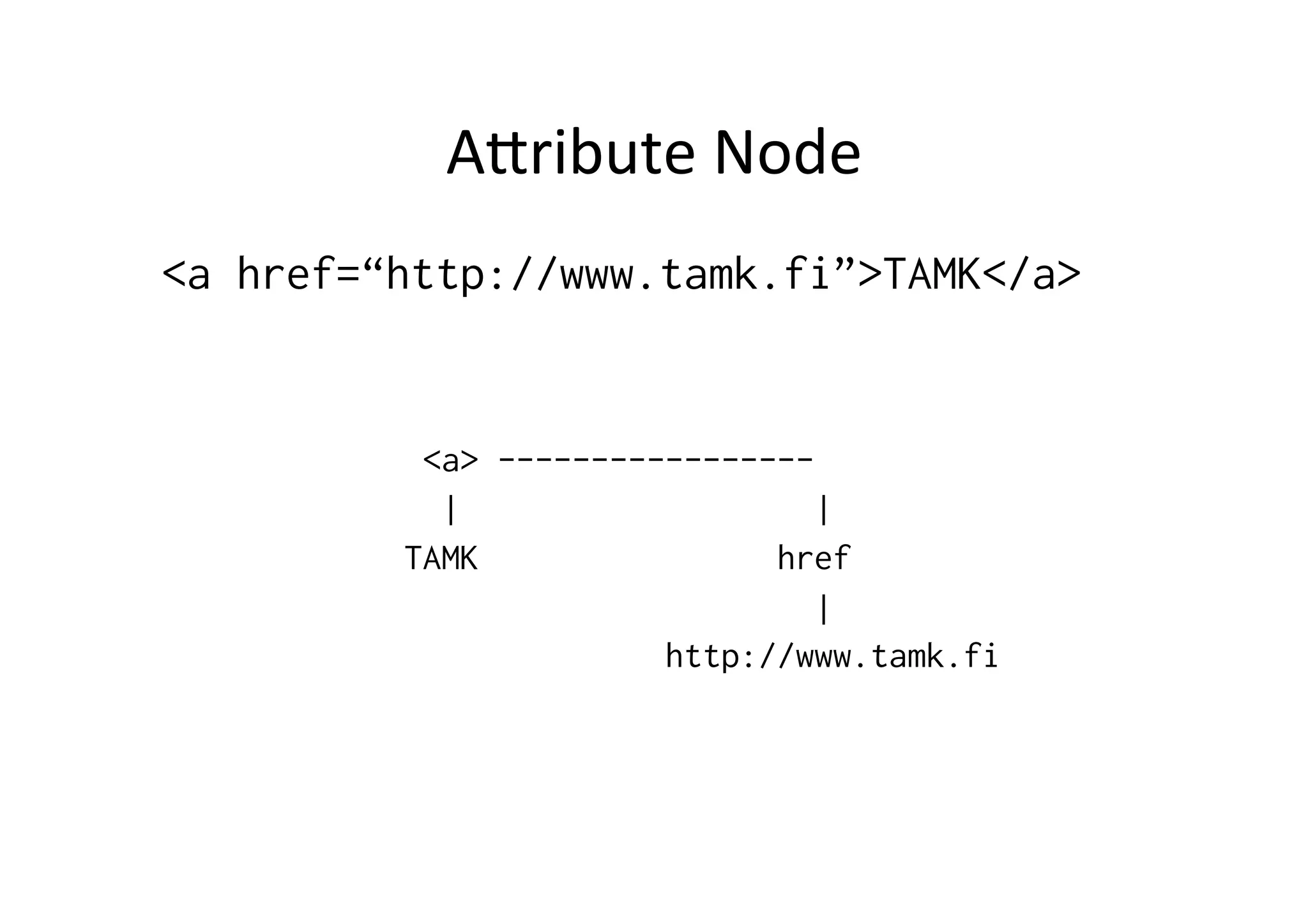
The document discusses the Document Object Model (DOM) and how it can be used with JavaScript to dynamically manipulate HTML and XML documents. It provides an overview of the DOM levels defined by the W3C, DOM node types like elements and text, and methods for accessing and modifying the DOM tree like getElementById() and setAttribute(). It also includes examples of how to add, remove and change DOM nodes with JavaScript.




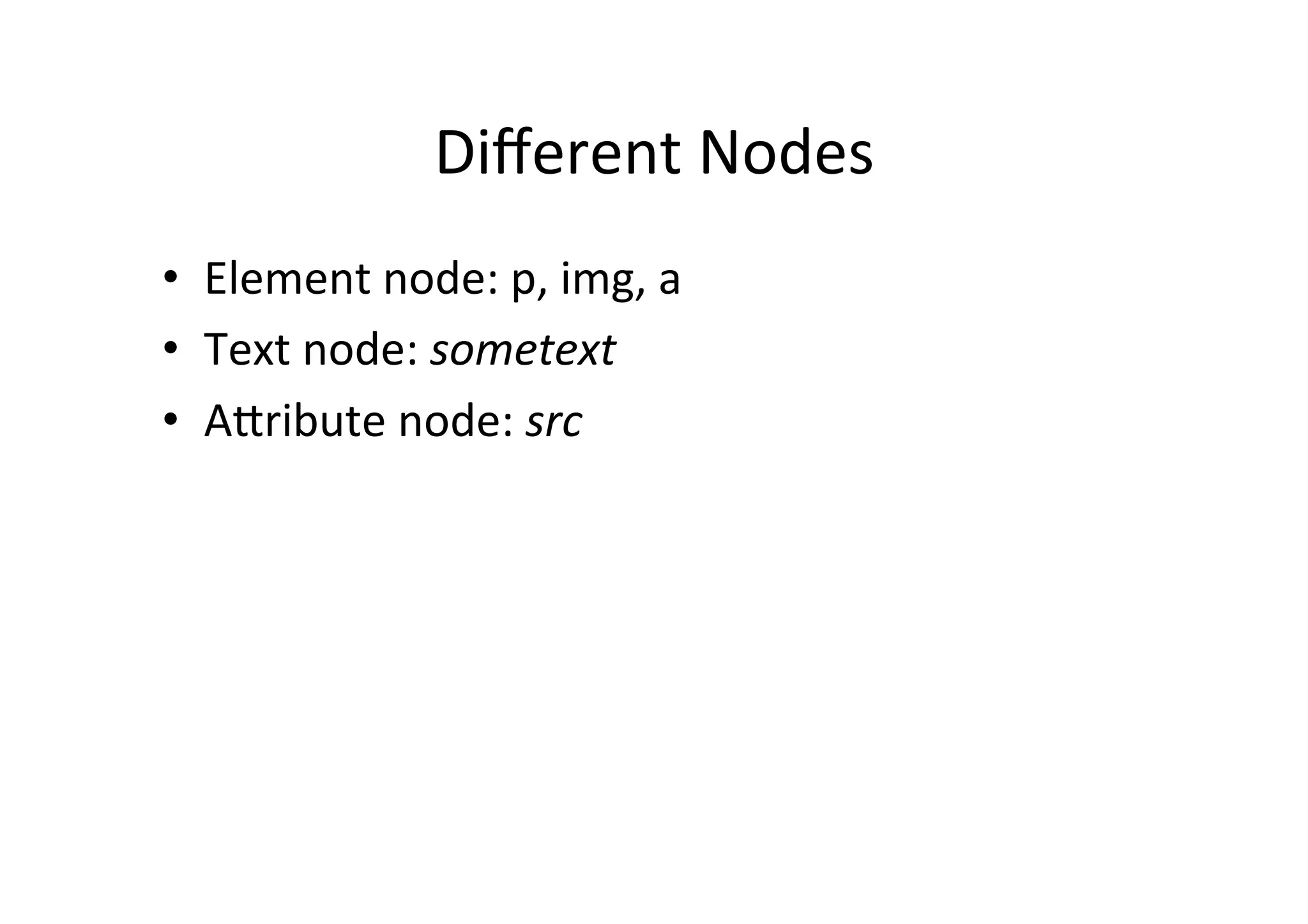
![DOM
Level
1:
To
Access
DOM
tree
• X
can
be
some
node
– var parent = x.parentNode;
– var firstchild = x.childNodes[0];
• How
to
get
reference
to
x?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/js-dom-120318052245-phpapp01/75/JavaScript-and-DOM-10-2048.jpg)
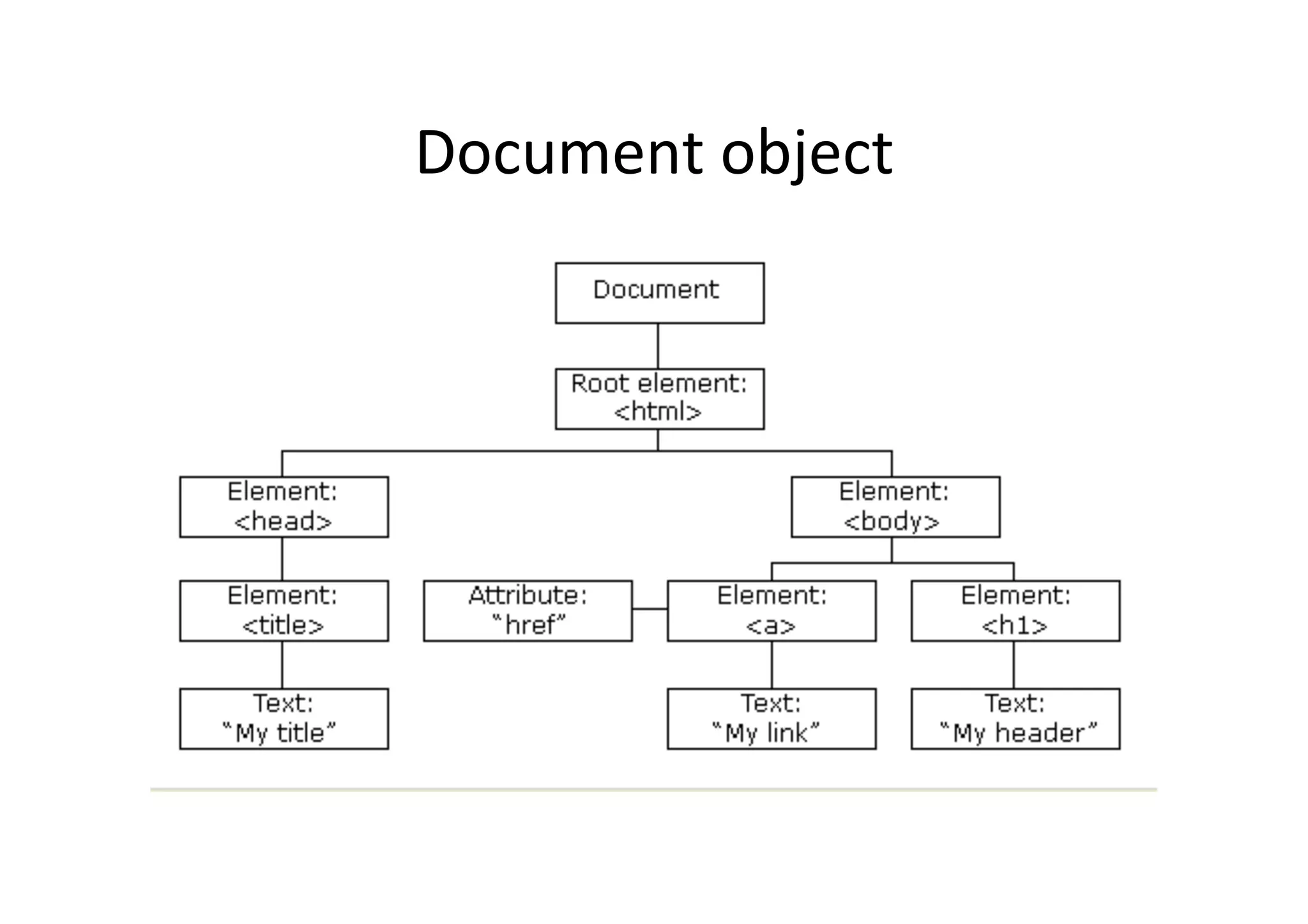
![Access
var title =
document.firstChild.firstChild.lastChild;
// document.html.head.title
var title =
document.firstChild.childNodes[0].childNodes[
0];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/js-dom-120318052245-phpapp01/75/JavaScript-and-DOM-12-2048.jpg)
![Gelng
Element
Easier
Way
var x =
document.getElementsByTagName(‘strong')[0]
var x = document.getElementById('hereweare');](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/js-dom-120318052245-phpapp01/75/JavaScript-and-DOM-13-2048.jpg)
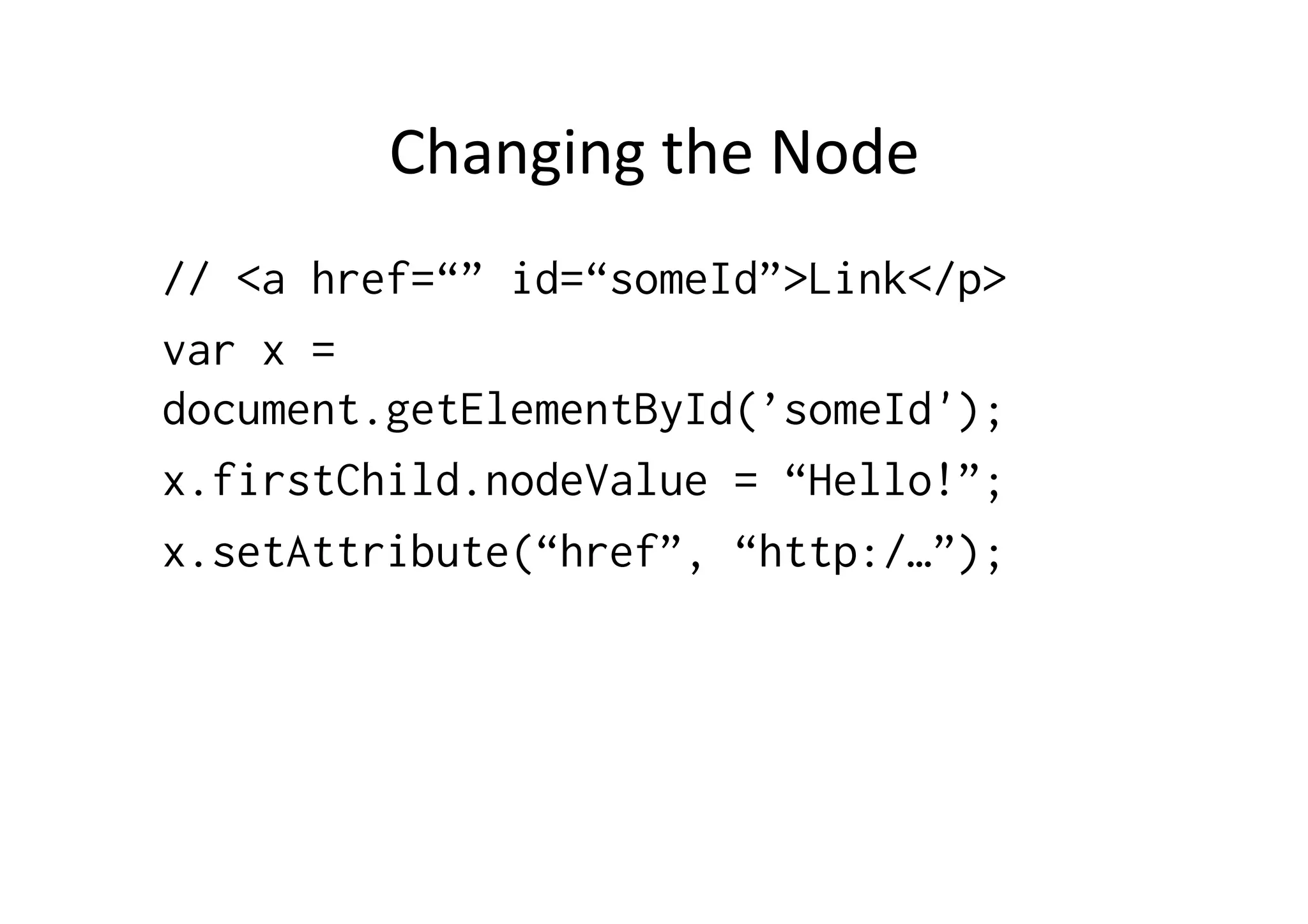

![CreaFng
and
Removing
Nodes
var x = document.createElement(’hr');
document.getElementById('inserthrhere').appendChild(x);
var node = document.getElementById('inserthrhere')
node.removeChild(node.childNodes[0]);
var x = document.createTextNode(’SomeText');
document.getElementById('hereweare').appendChild(x);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/js-dom-120318052245-phpapp01/75/JavaScript-and-DOM-16-2048.jpg)
![<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Strict//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-strict.dtd">
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml">
<head>
<title></title>
<meta http-equiv="content-type" content="application/xhtml+xml; charset=utf-8" />
<script type="text/javascript">
//<![CDATA[
function change()
{
// Get list of ALL <h1> - elements
var listOfHeading1 = window.document.getElementsByTagName("h1");
// Find the first <h1> - element in the list
var heading1 = listOfHeading1[0];
// Get the child - element of the first <h1> - element (Text)
var text = heading1.firstChild;
// Replace the text
text.data = "Hello from JS!";
}
//]]>
</script>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Title</h1>
<input type="submit" onClick="change();" value="click!"/>
</body>
</html>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/js-dom-120318052245-phpapp01/75/JavaScript-and-DOM-17-2048.jpg)
![<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Strict//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-strict.dtd">
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml">
<head>
<title></title>
<meta http-equiv="content-type" content="application/xhtml+xml; charset=utf-8" />
<script type="text/javascript">
//<![CDATA[
function change()
{
// Reference to the table - element
var table = document.getElementById("mytable");
var tr = document.createElement("tr"); // <tr>
var td1 = document.createElement("td"); // <td>
var td1Text = document.createTextNode("New Cell"); // "New Cell"
td1.appendChild(td1Text); // <td>New Cell</td>
var td2 = document.createElement("td"); // <td>
var td2Text = document.createTextNode("New Cell"); // "New Cell"
td2.appendChild(td2Text); // <td>New Cell</td>
tr.appendChild(td1);
tr.appendChild(td2);
table.appendChild(tr);
}
//]]>
</script>
</head>
<body>
<table id="mytable" border="1">
<tr><td> </td><td> </td></tr>
<tr><td> </td><td> </td></tr>
<tr><td> </td><td> </td></tr>
</table>
<input type="submit" onClick="change();" value="Add Row"/>
</body>
</html>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/js-dom-120318052245-phpapp01/75/JavaScript-and-DOM-18-2048.jpg)