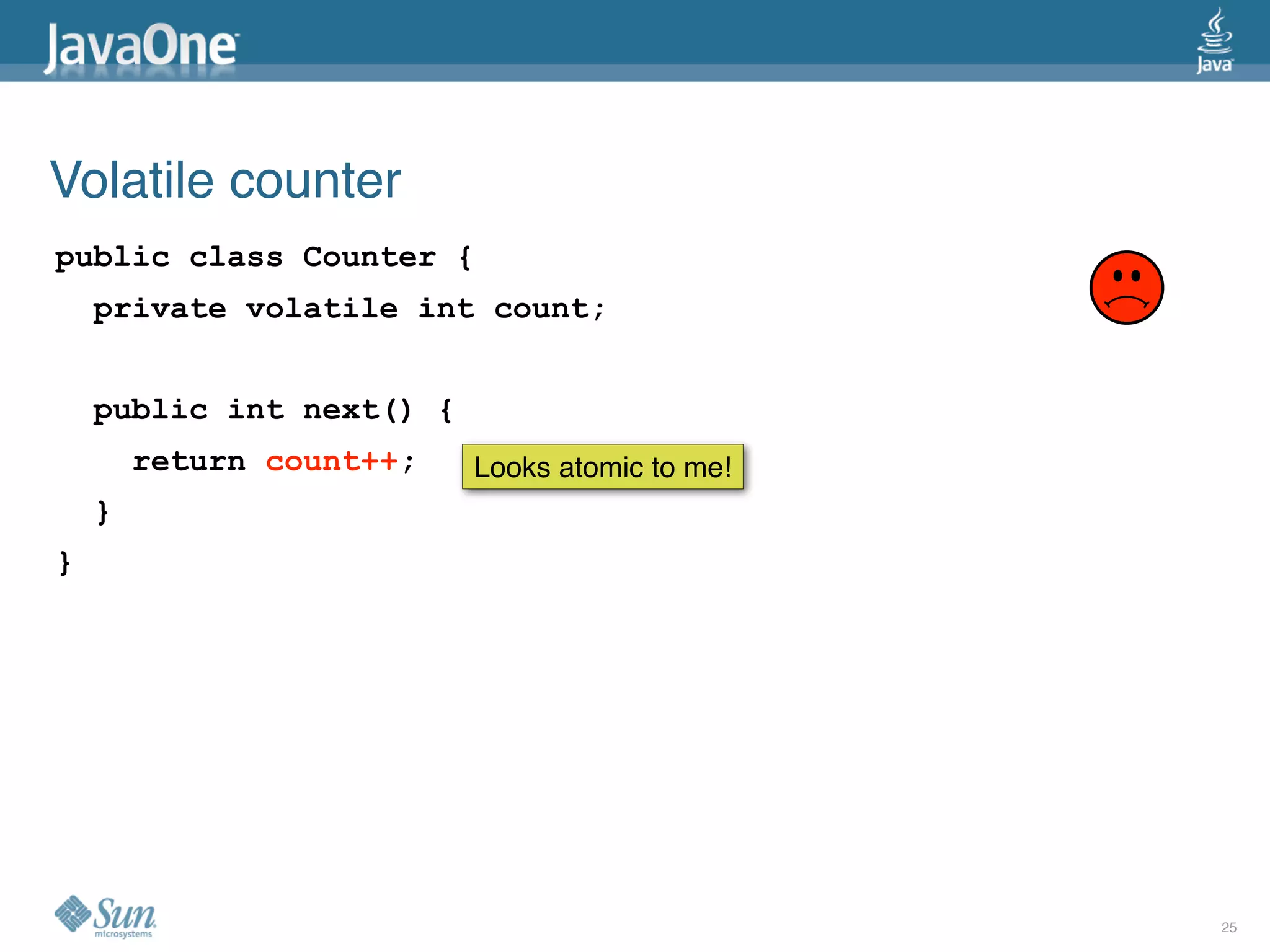
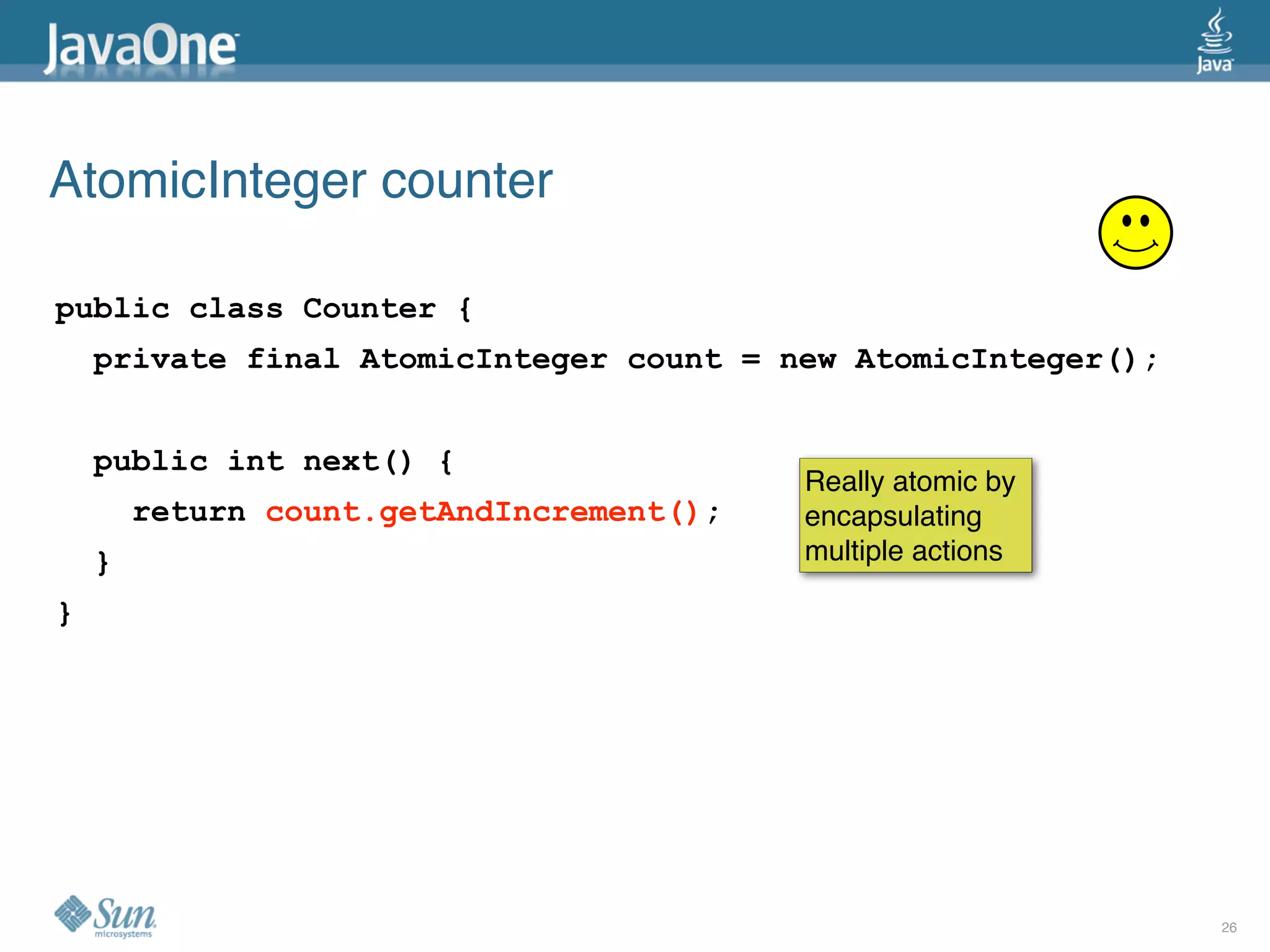
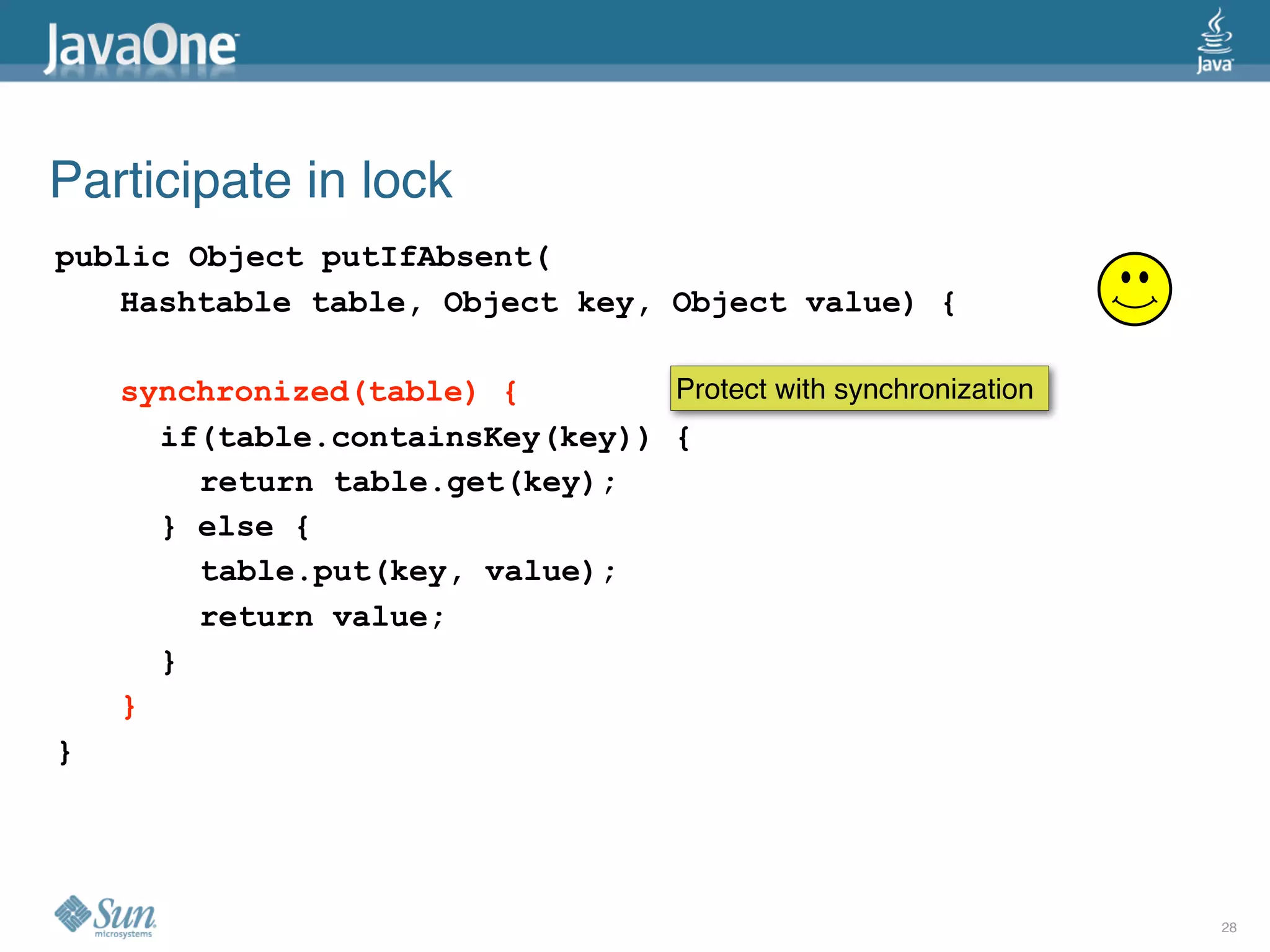
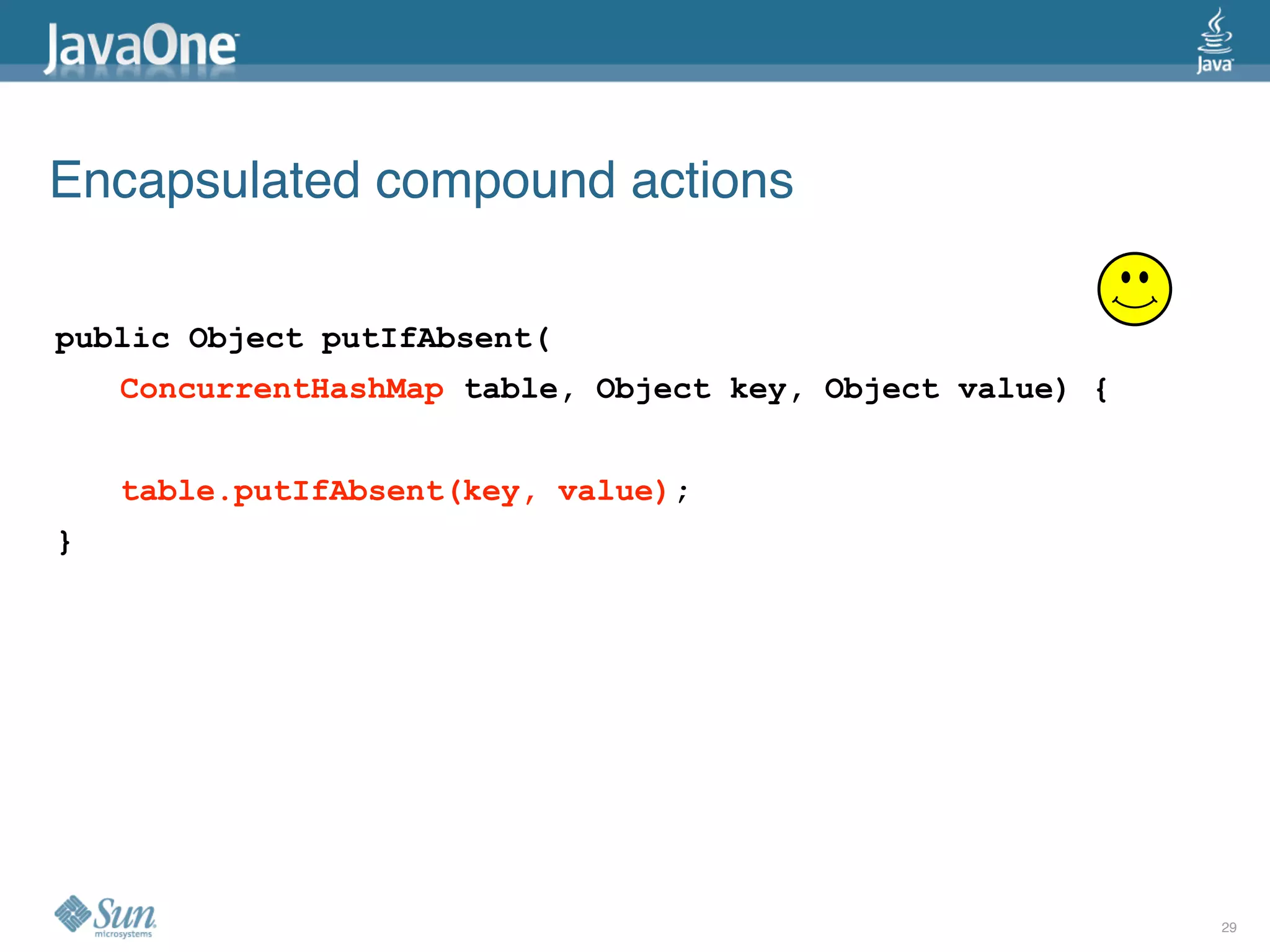
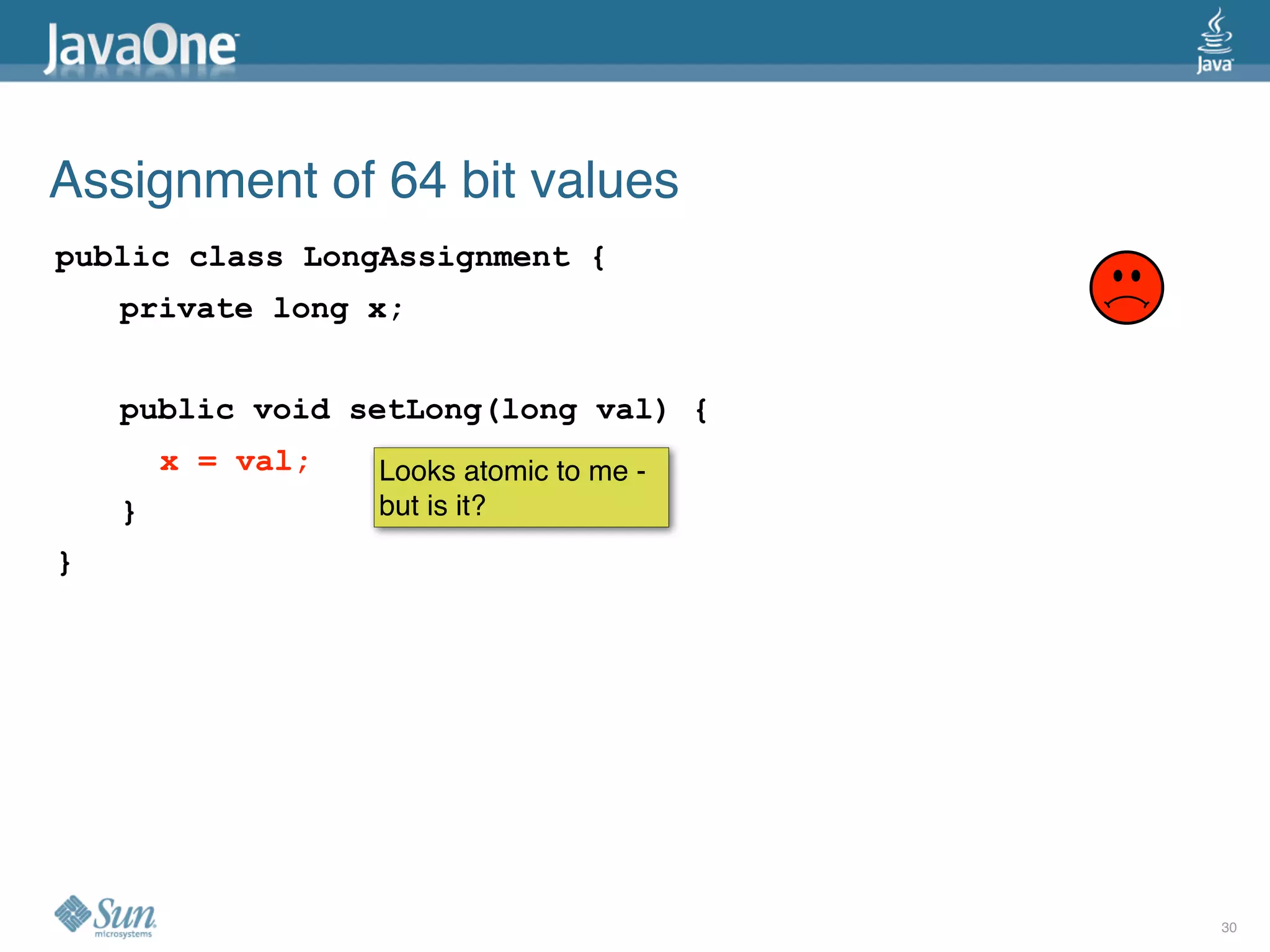
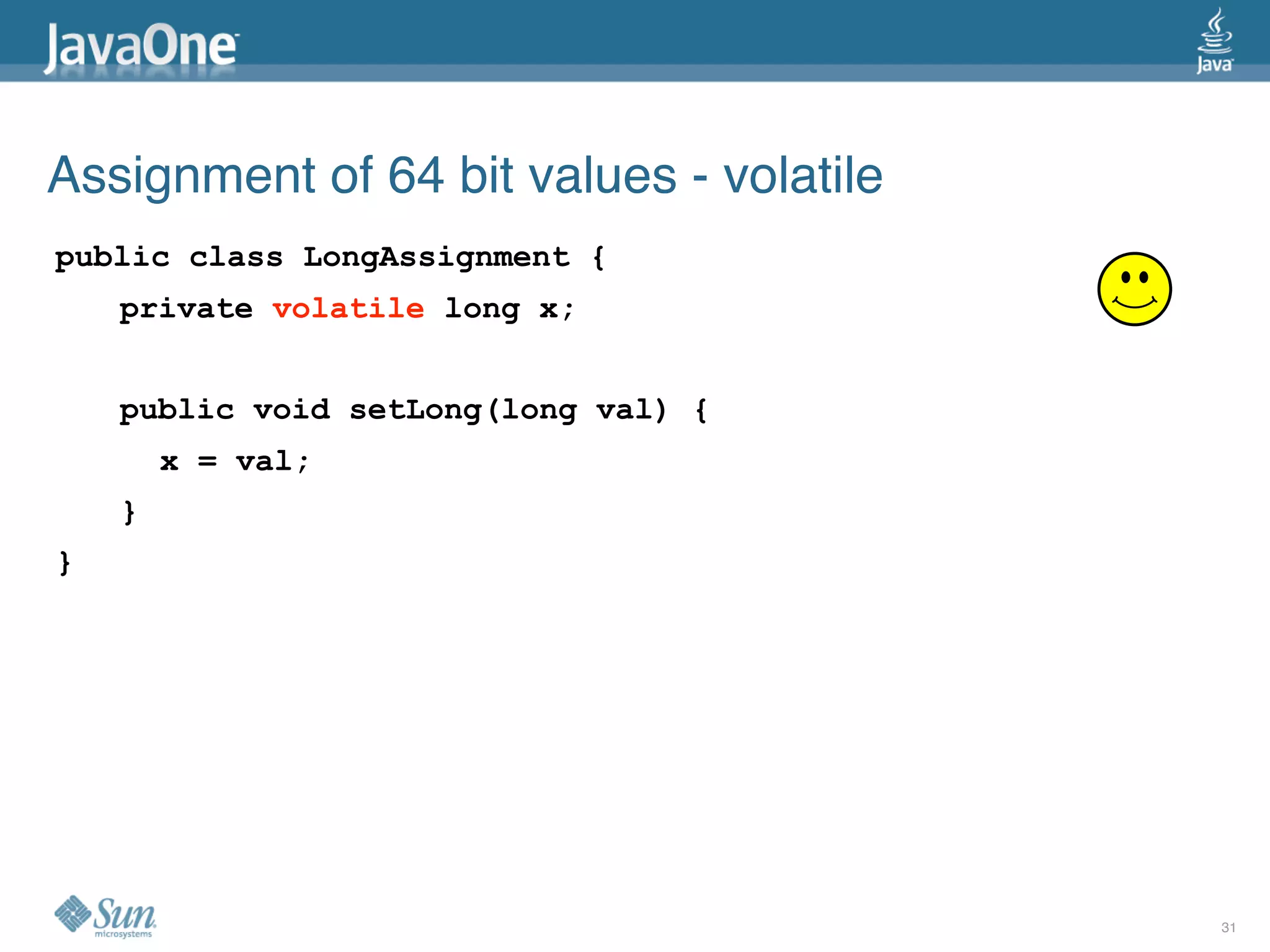
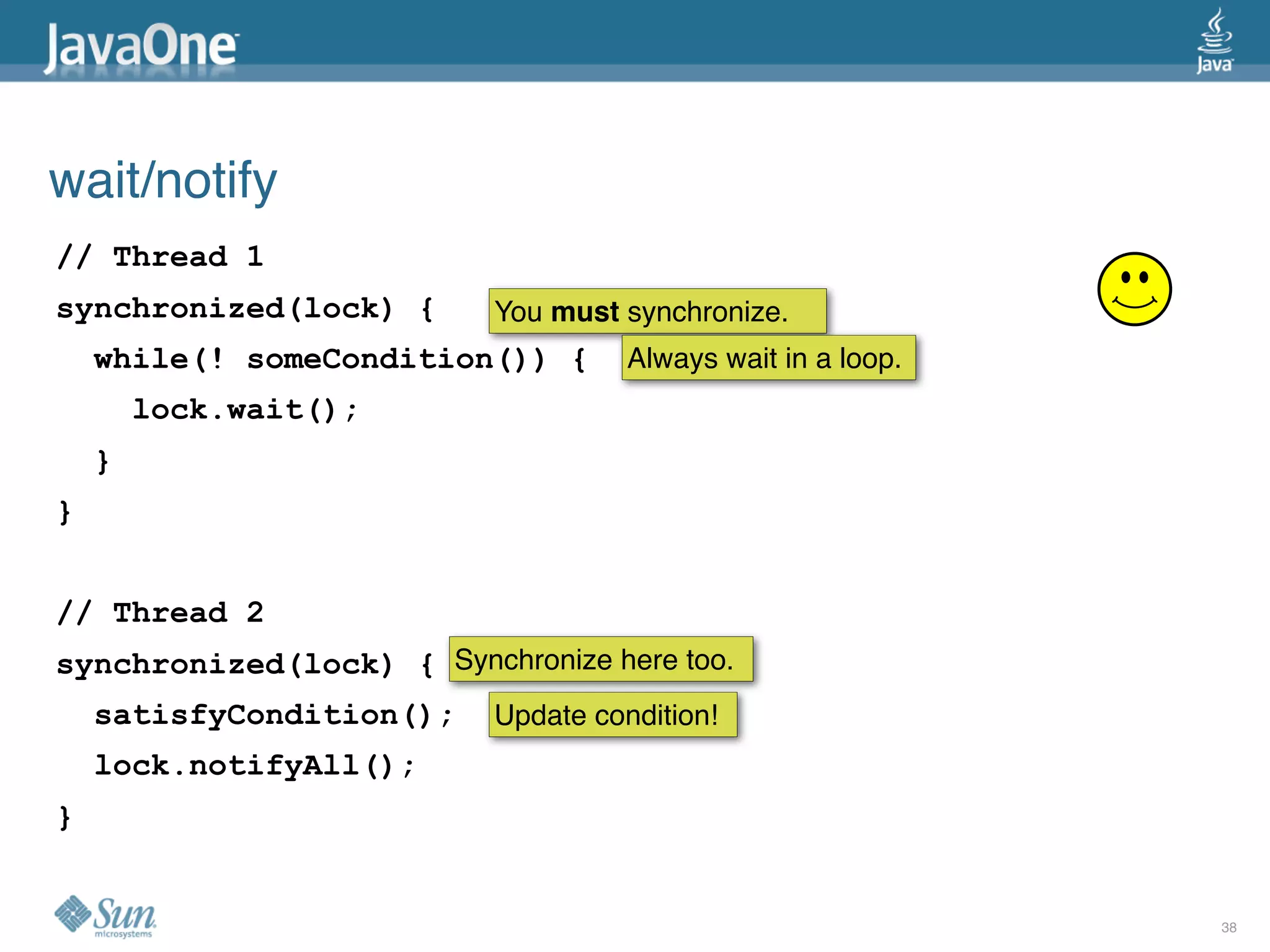
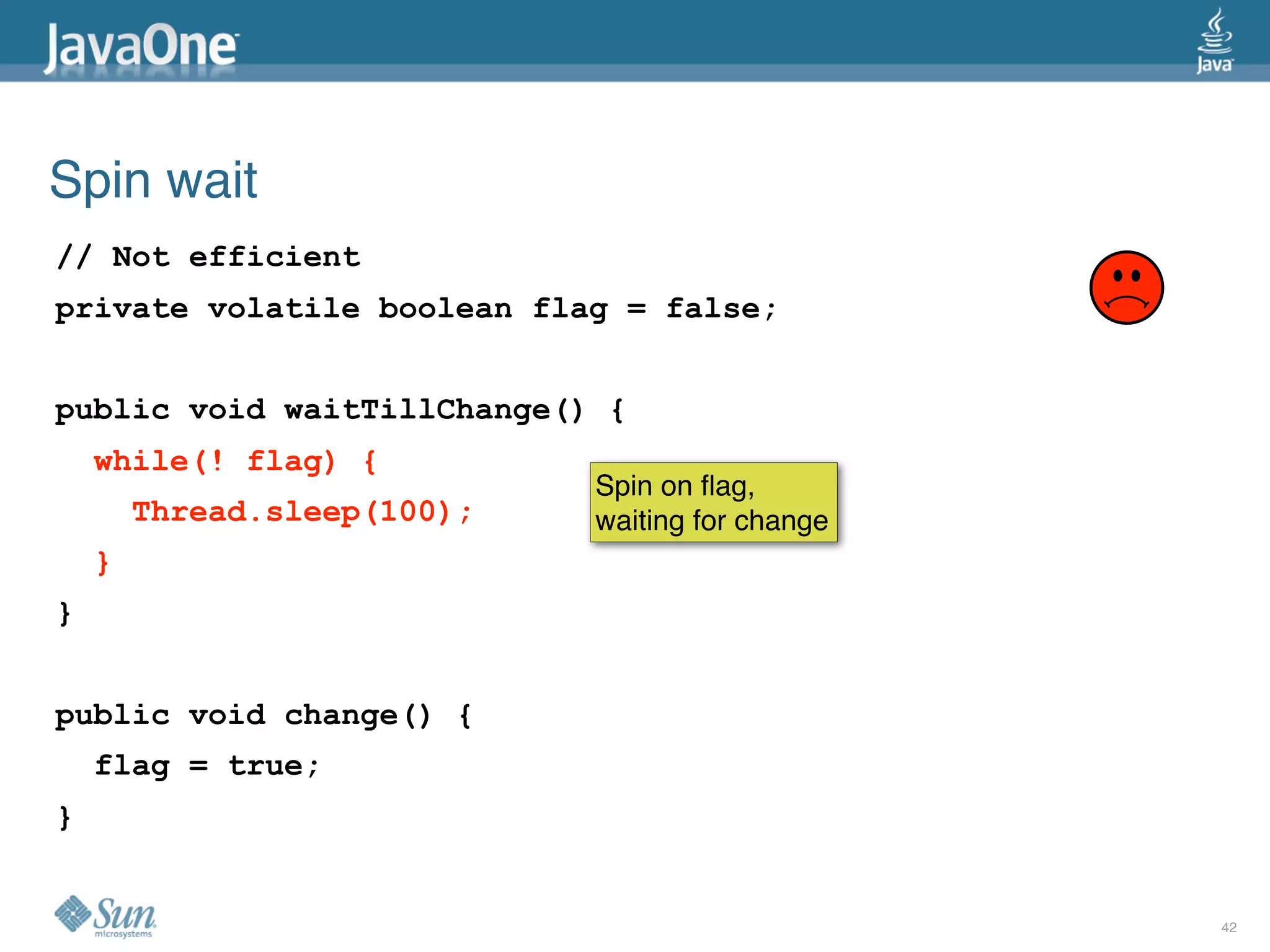
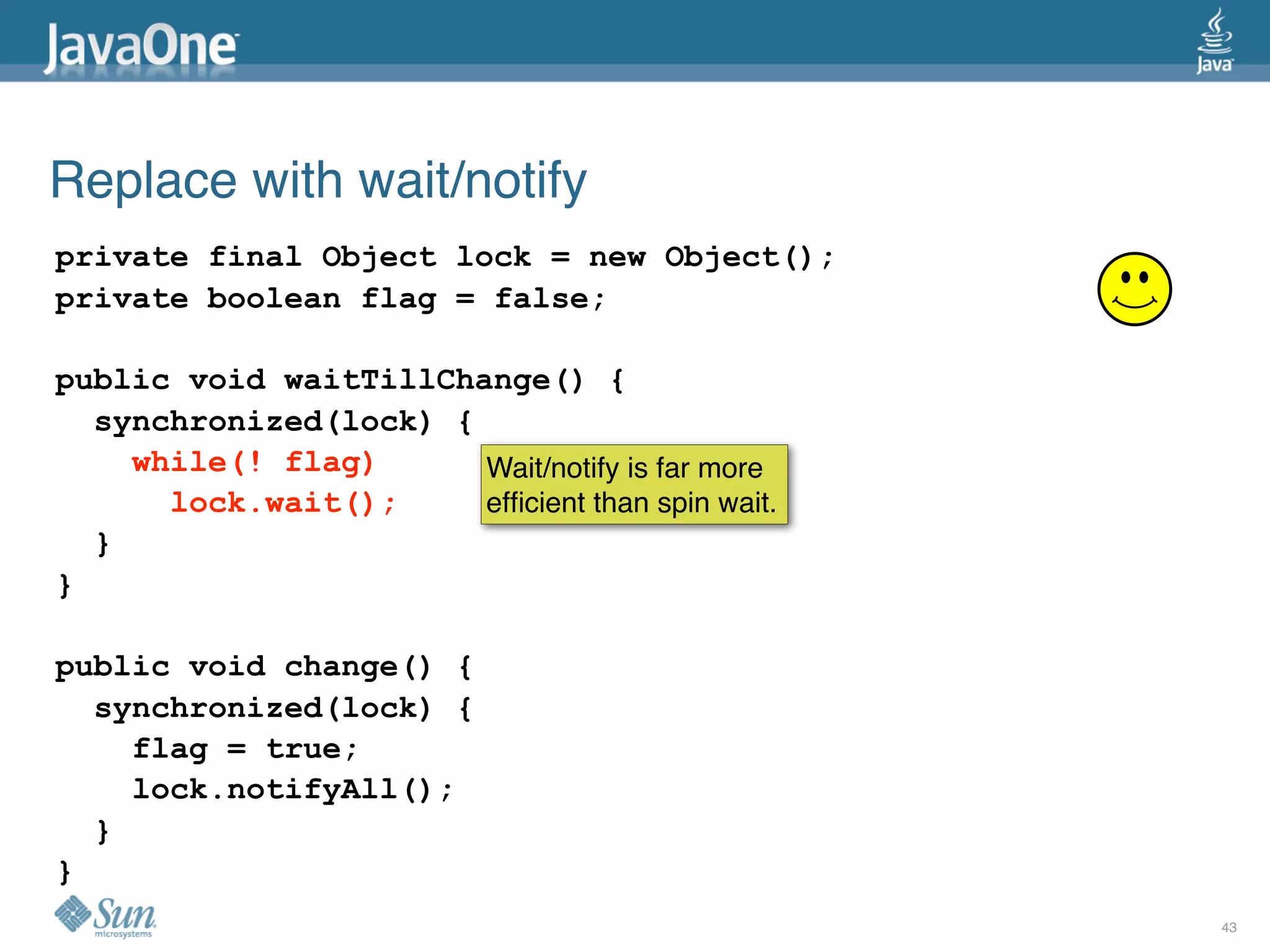
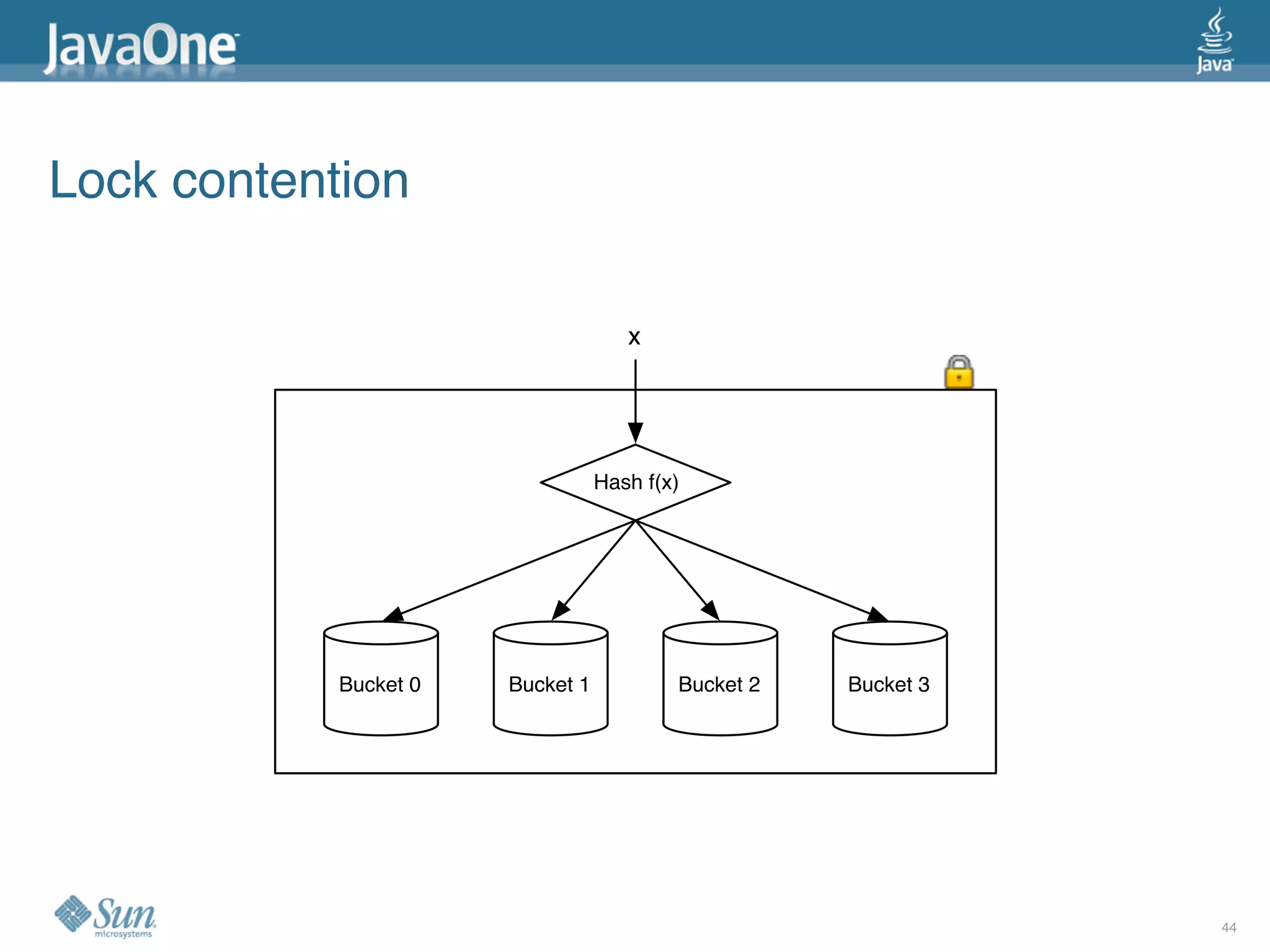
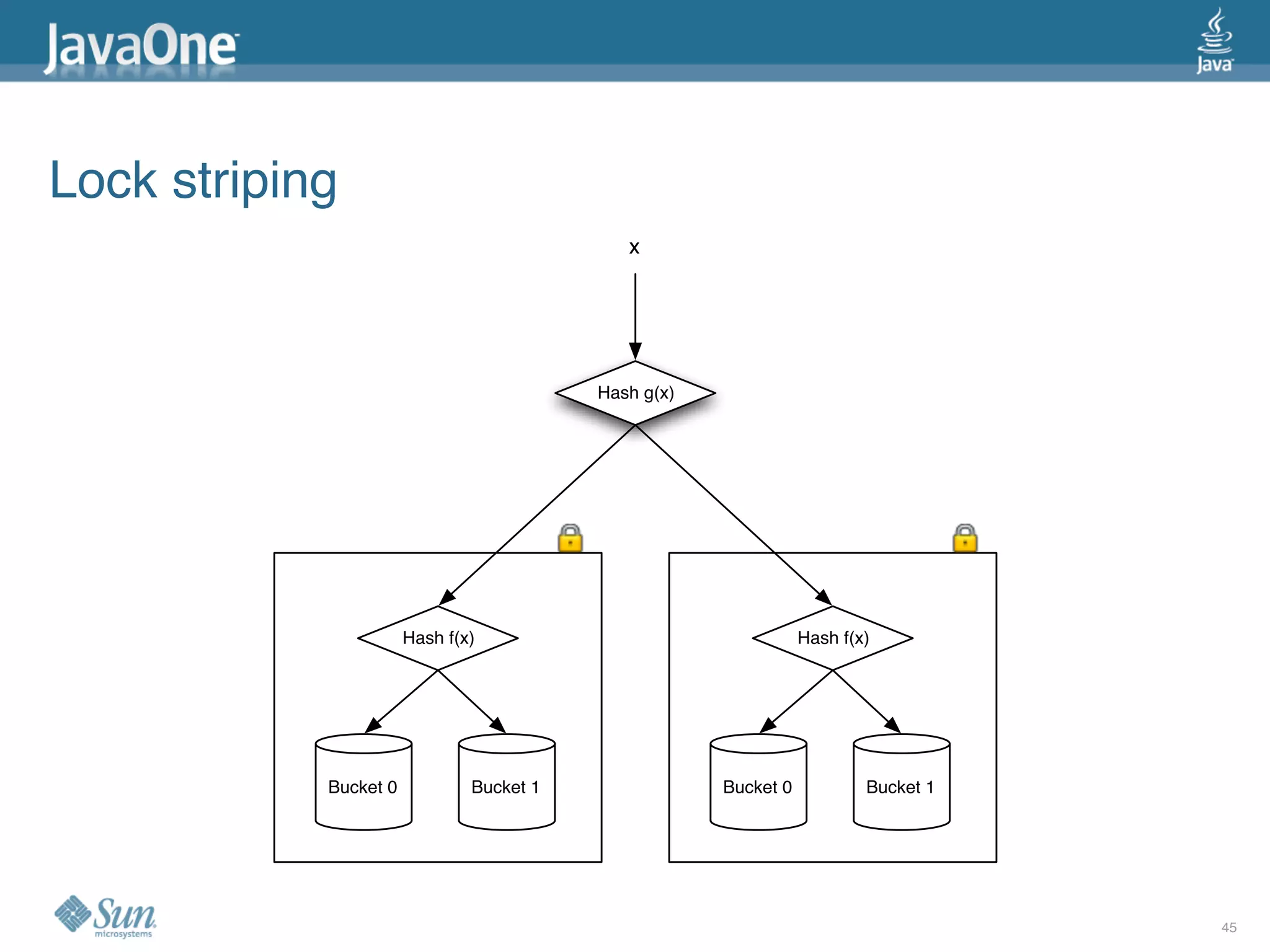
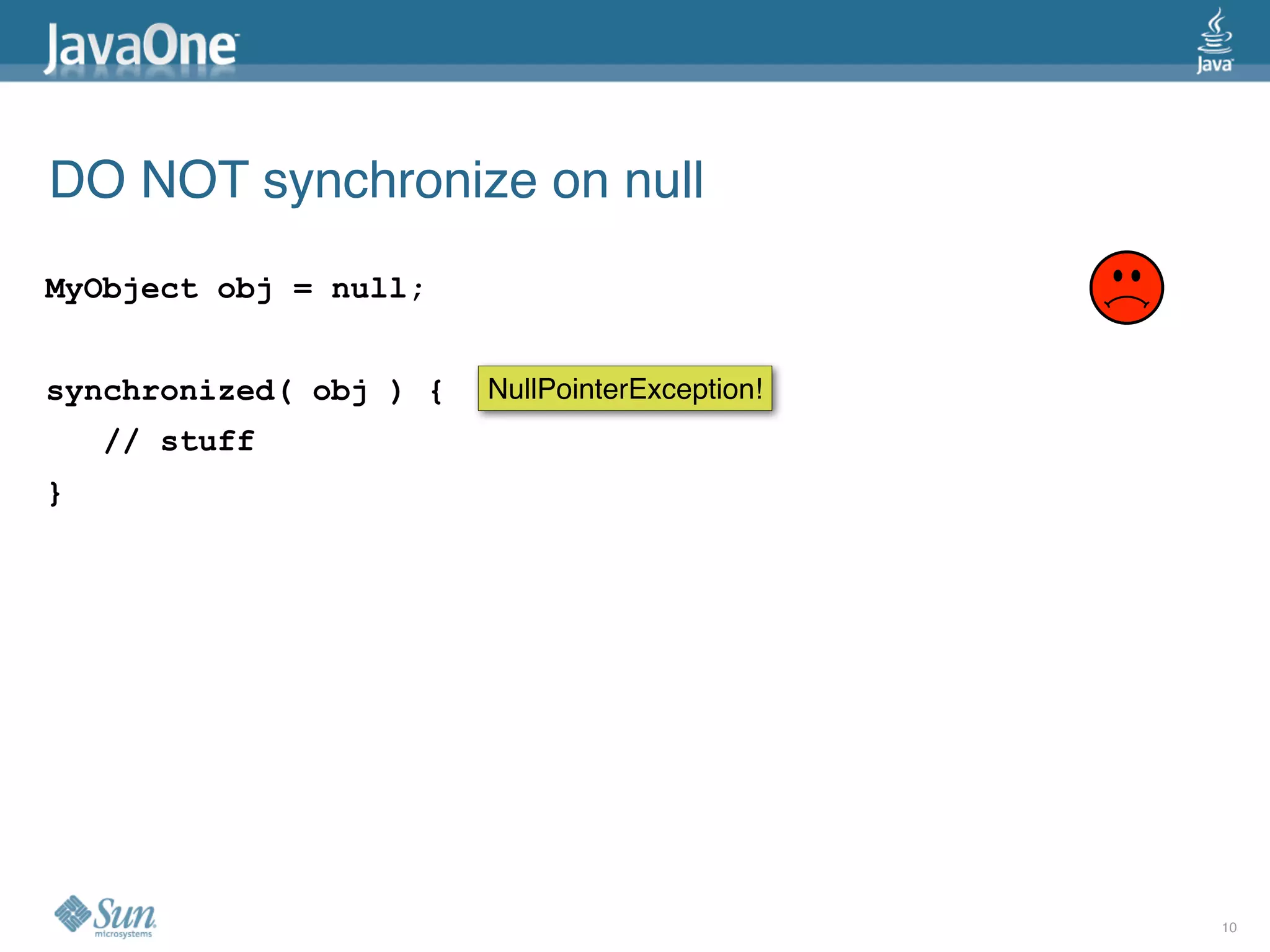
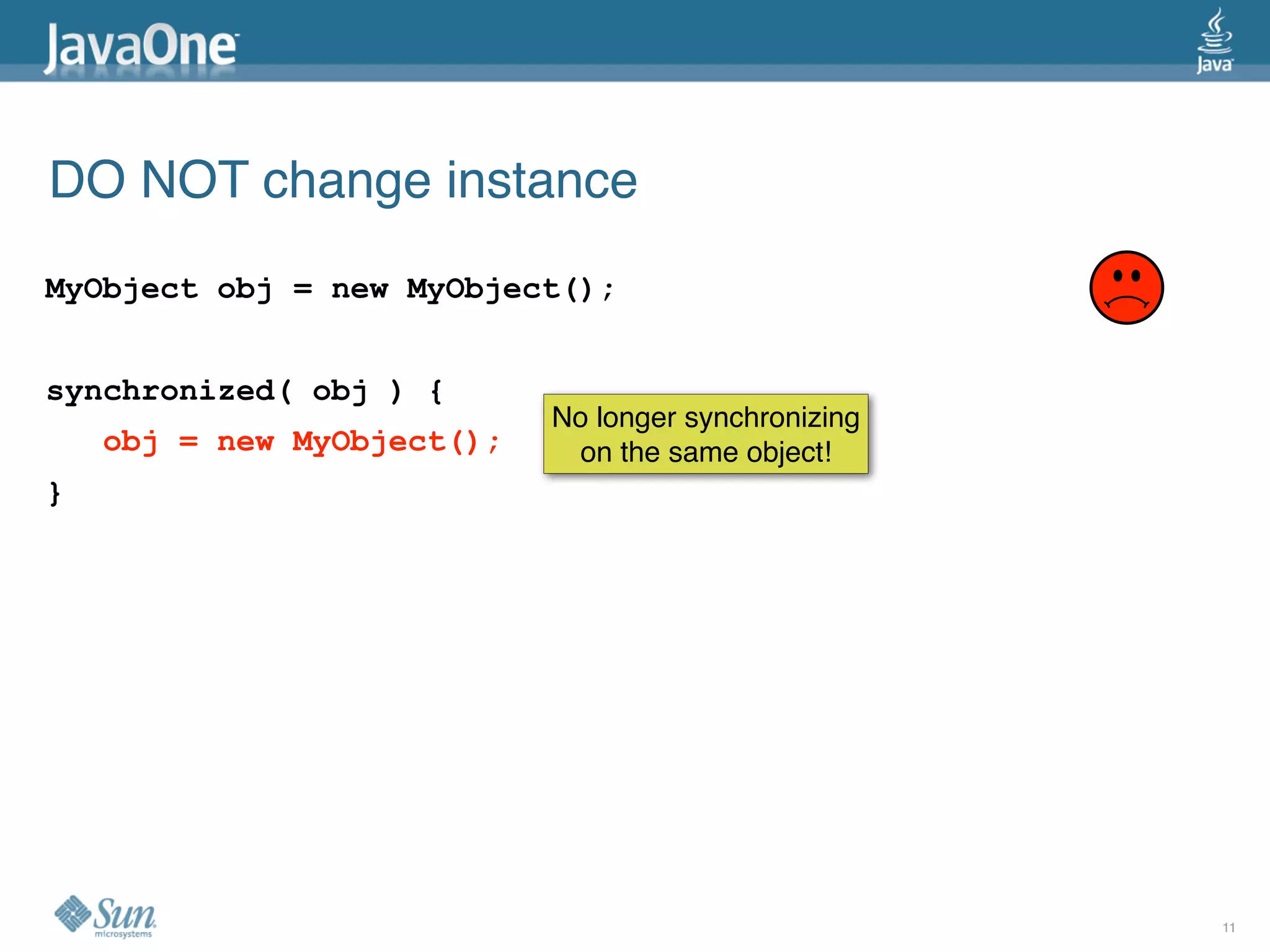
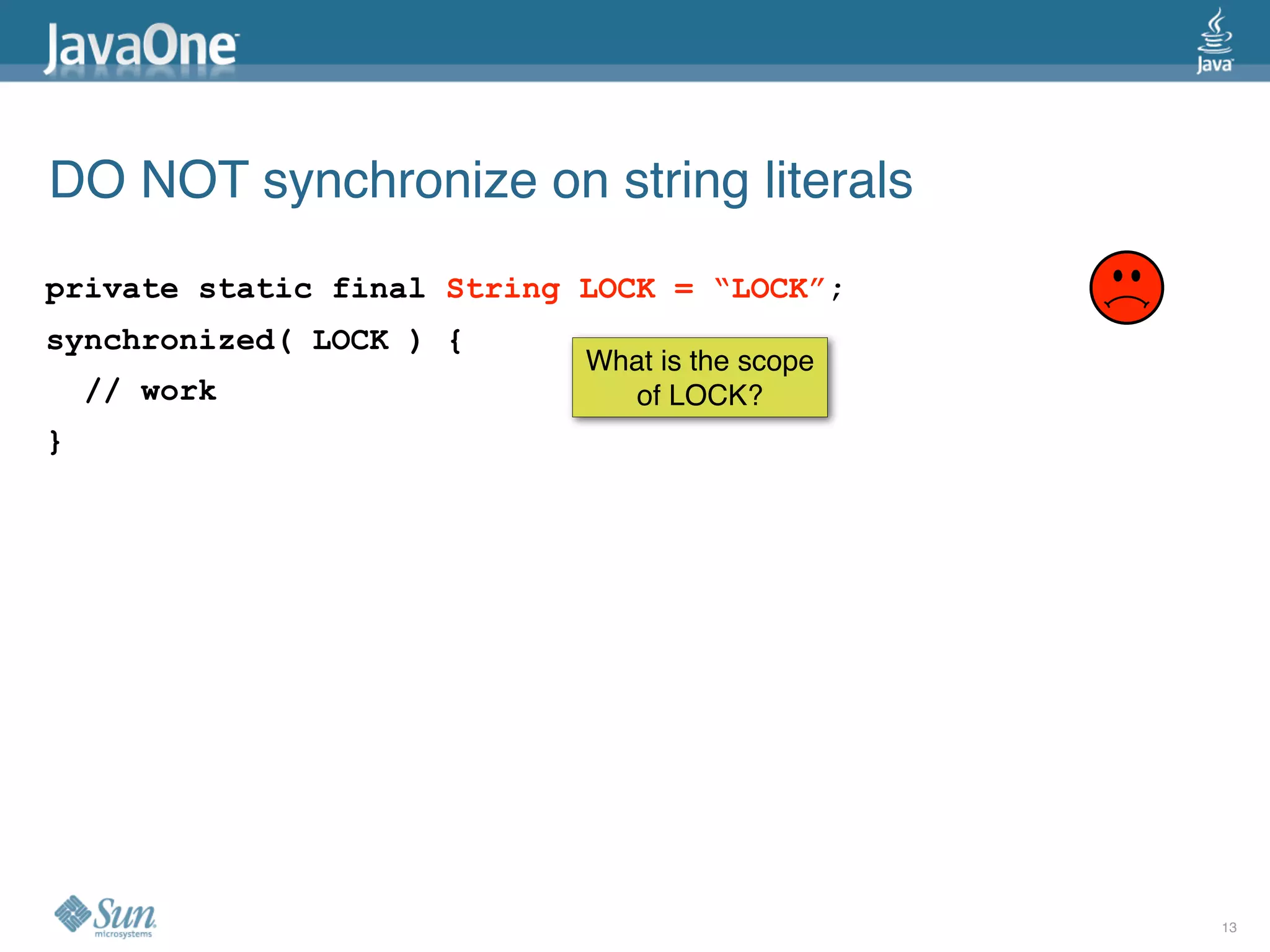
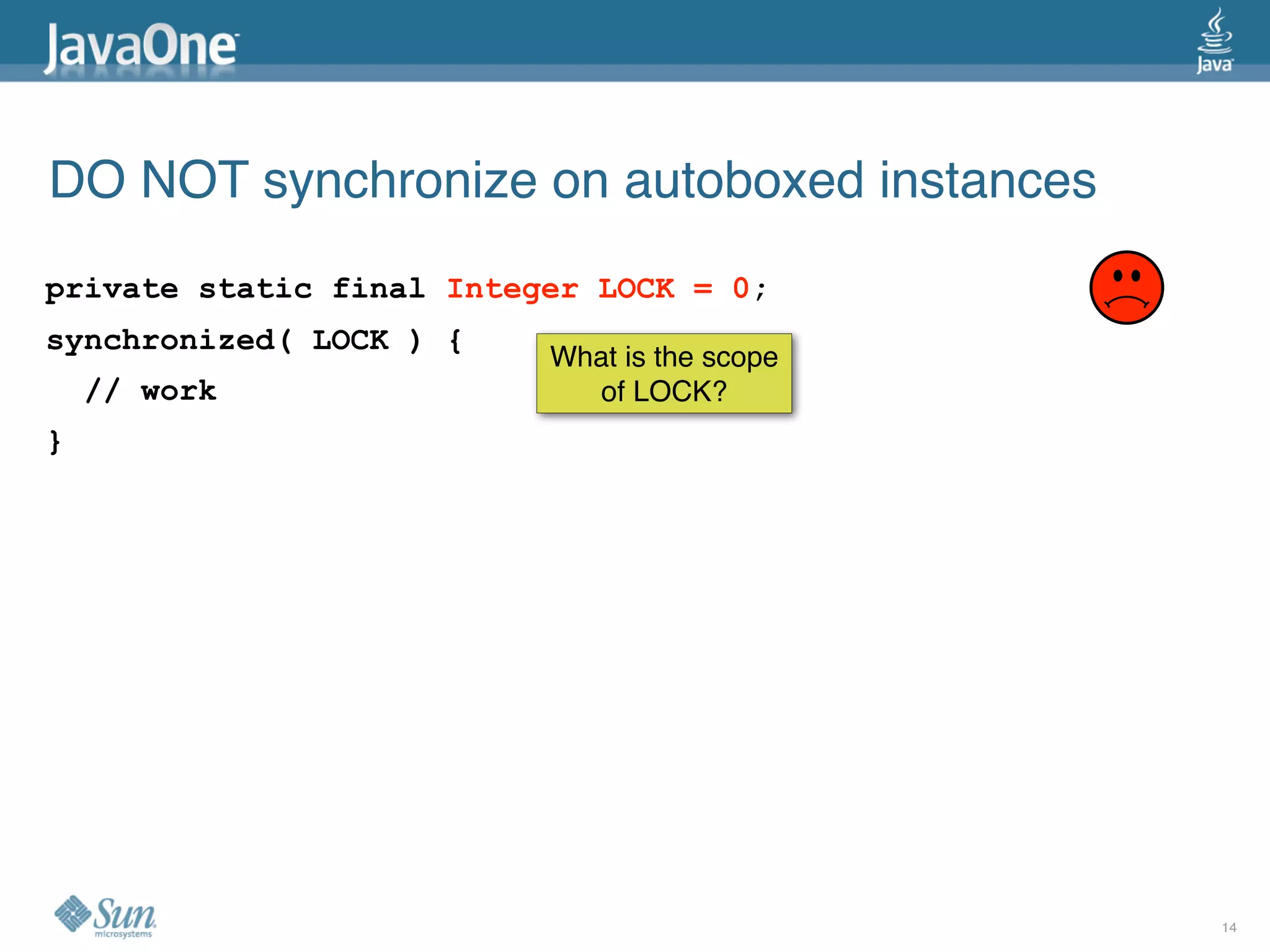
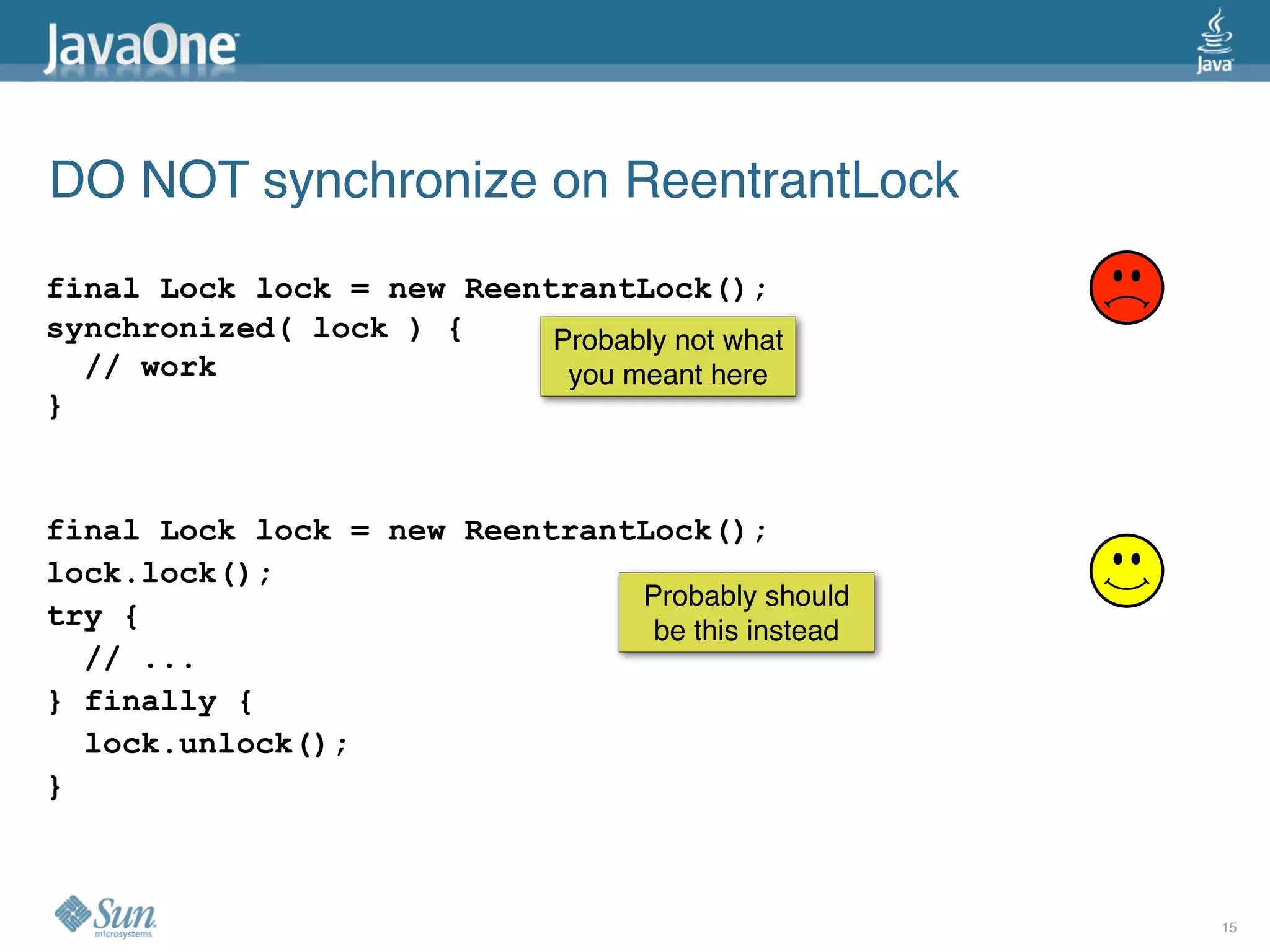
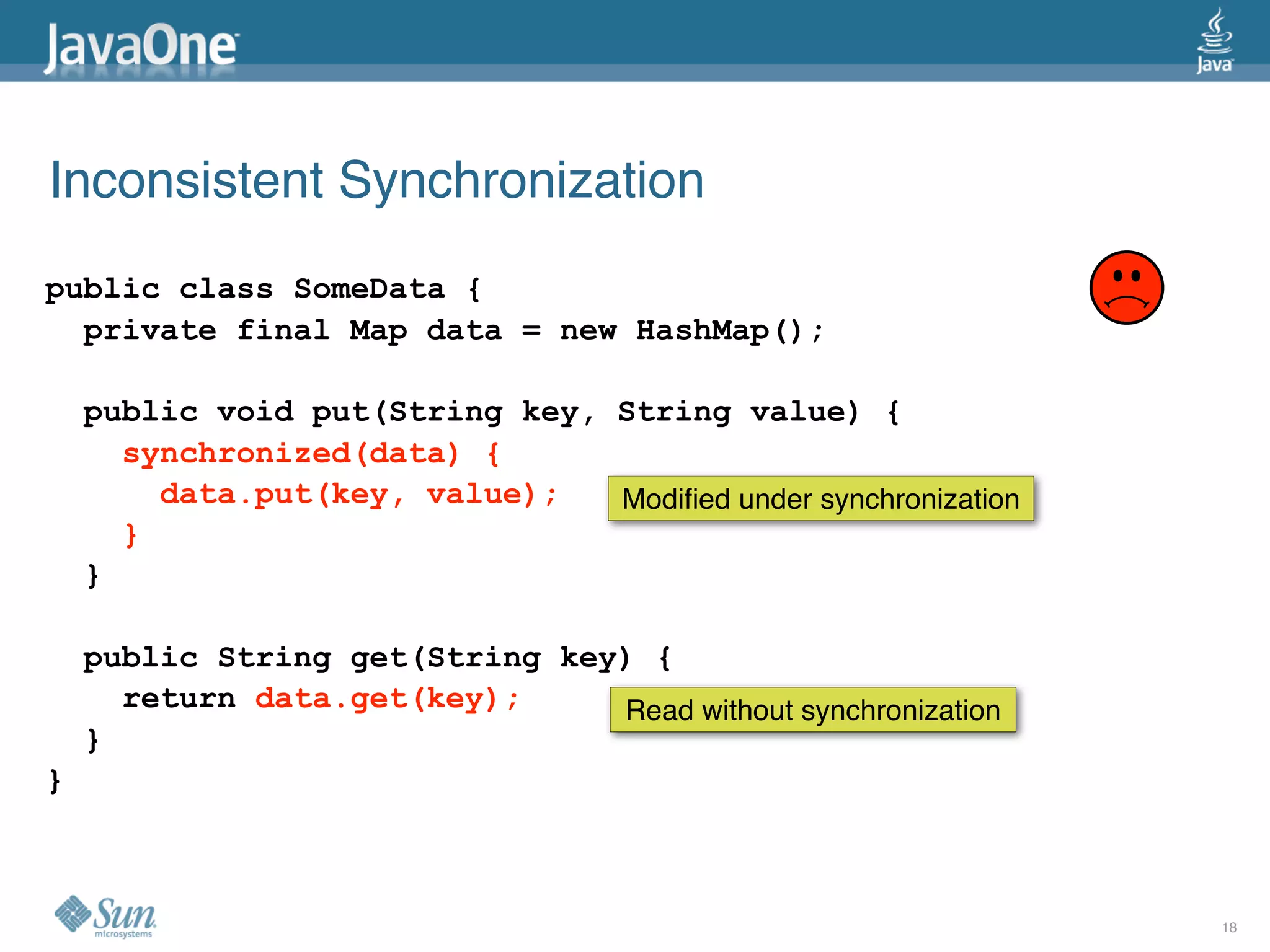
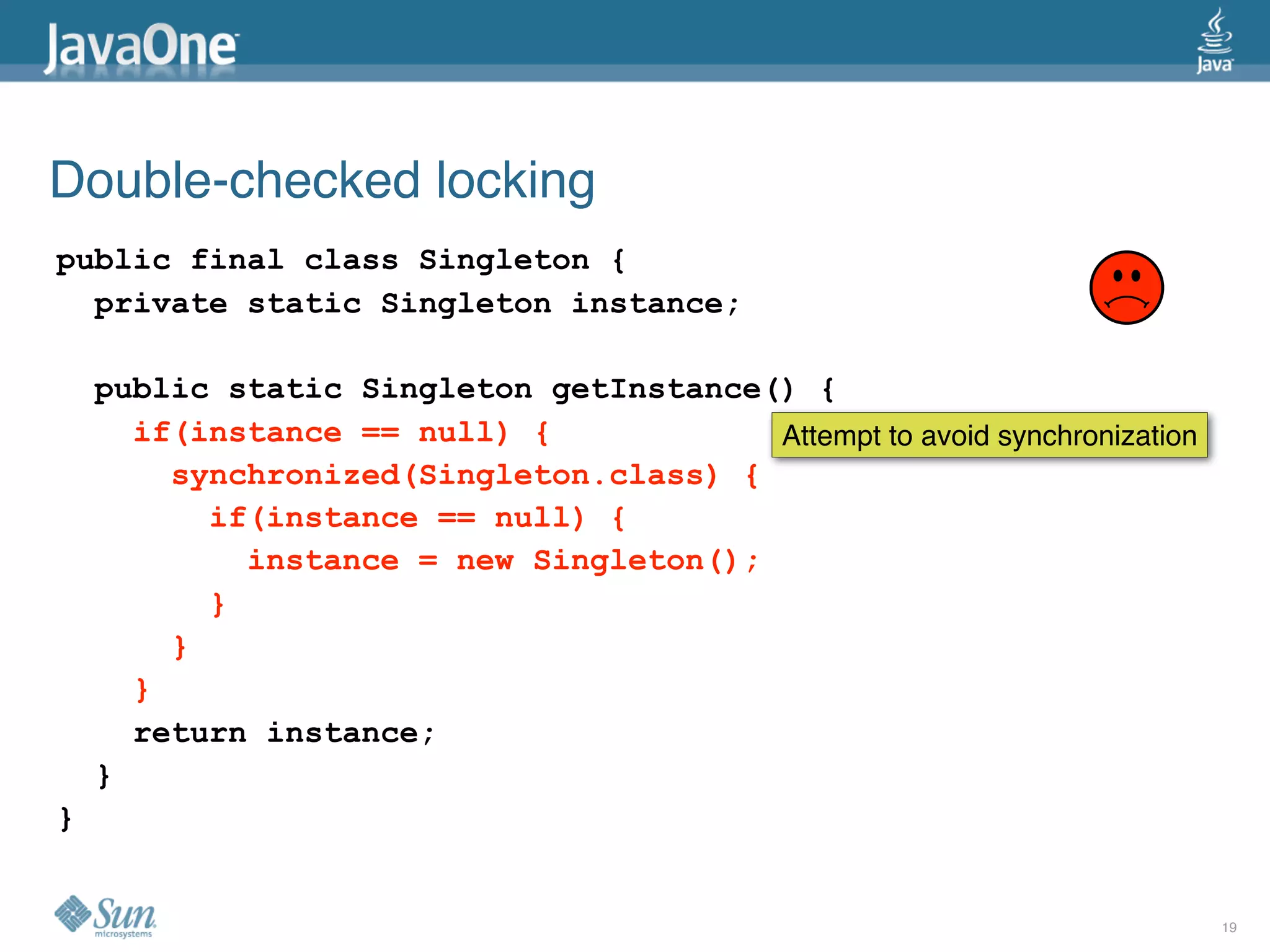
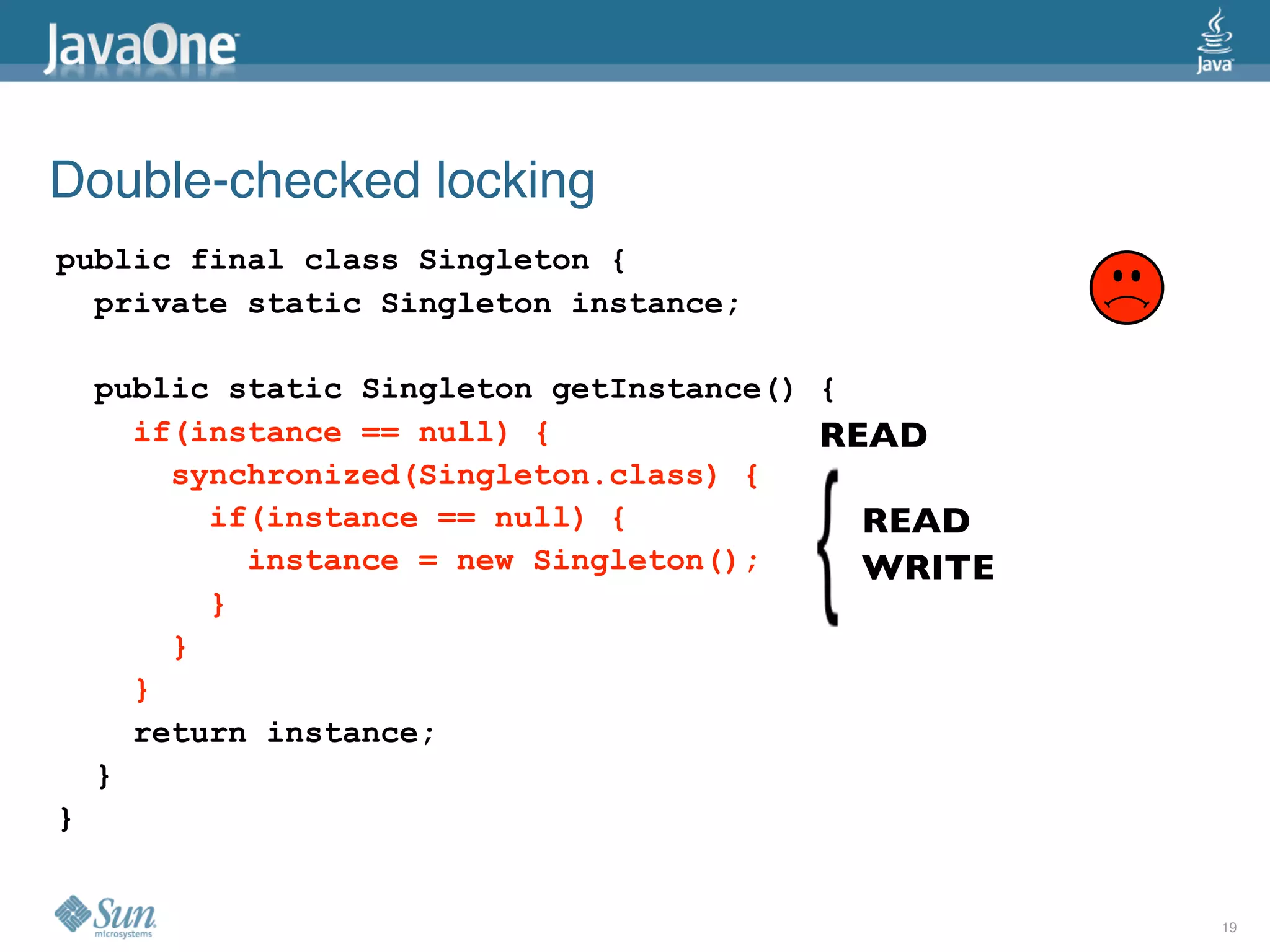
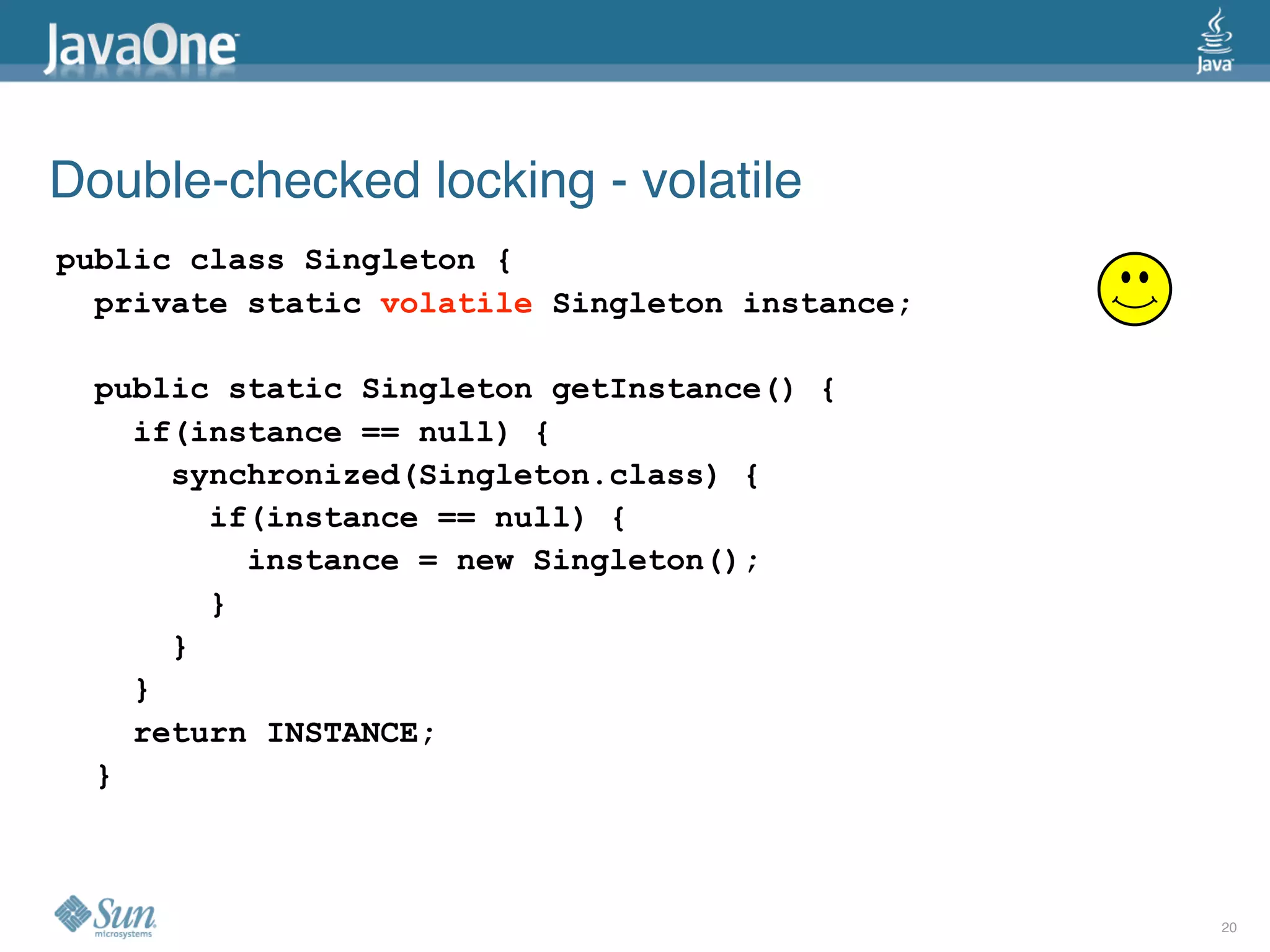
The document discusses common concurrency problems in Java such as shared mutable data without locking, visibility issues, lack of atomicity, and unsafe publication that can cause bugs, and provides examples of how to correctly implement locking, visibility, atomic operations, and safe publication to avoid concurrency problems.





![Mutable Statics
public class MutableStatics {
FORMAT is mutable
private static final DateFormat FORMAT =
DateFormat.getDateInstance(DateFormat.MEDIUM);
public static Date parse(String str)
throws ParseException {
...and this mutates it
return FORMAT.parse(str);
outside synchronization
}
public static void main(String arg[]) {
MutableStatics.parse(“Jan 1, 2000”);
}
}
7](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javaoneconcurrencygotchas090610192215phpapp02-124772711099-phpapp02/75/Javaoneconcurrencygotchas-090610192215-Phpapp02-8-2048.jpg)
![Mutable Statics - instance per call
public class MutableStatics {
public static Date parse(String str)
throws ParseException {
DateFormat format =
DateFormat.getDateInstance(DateFormat.MEDIUM);
return format.parse(str);
}
public static void main(String arg[]) {
MutableStatics.parse(“Jan 1, 2000”);
}
}
8](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javaoneconcurrencygotchas090610192215phpapp02-124772711099-phpapp02/75/Javaoneconcurrencygotchas-090610192215-Phpapp02-9-2048.jpg)





![Racy single-check
public final class String {
private int hash; // default to 0
private final char[] value; // immutable
public int hashCode() {
int h = hash;
if(h == 0) {
// ... compute value for h from data
hash = h;
}
return h;
}
}
22](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javaoneconcurrencygotchas090610192215phpapp02-124772711099-phpapp02/75/Javaoneconcurrencygotchas-090610192215-Phpapp02-24-2048.jpg)
![volatile arrays
public final class VolatileArray {
private volatile boolean[] vals;
public void flip(int i) {
vals[i] = true; Is the value of vals[i]
} visible to other threads?
public boolean flipped(int i) {
return vals[i];
}
}
23](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javaoneconcurrencygotchas090610192215phpapp02-124772711099-phpapp02/75/Javaoneconcurrencygotchas-090610192215-Phpapp02-25-2048.jpg)