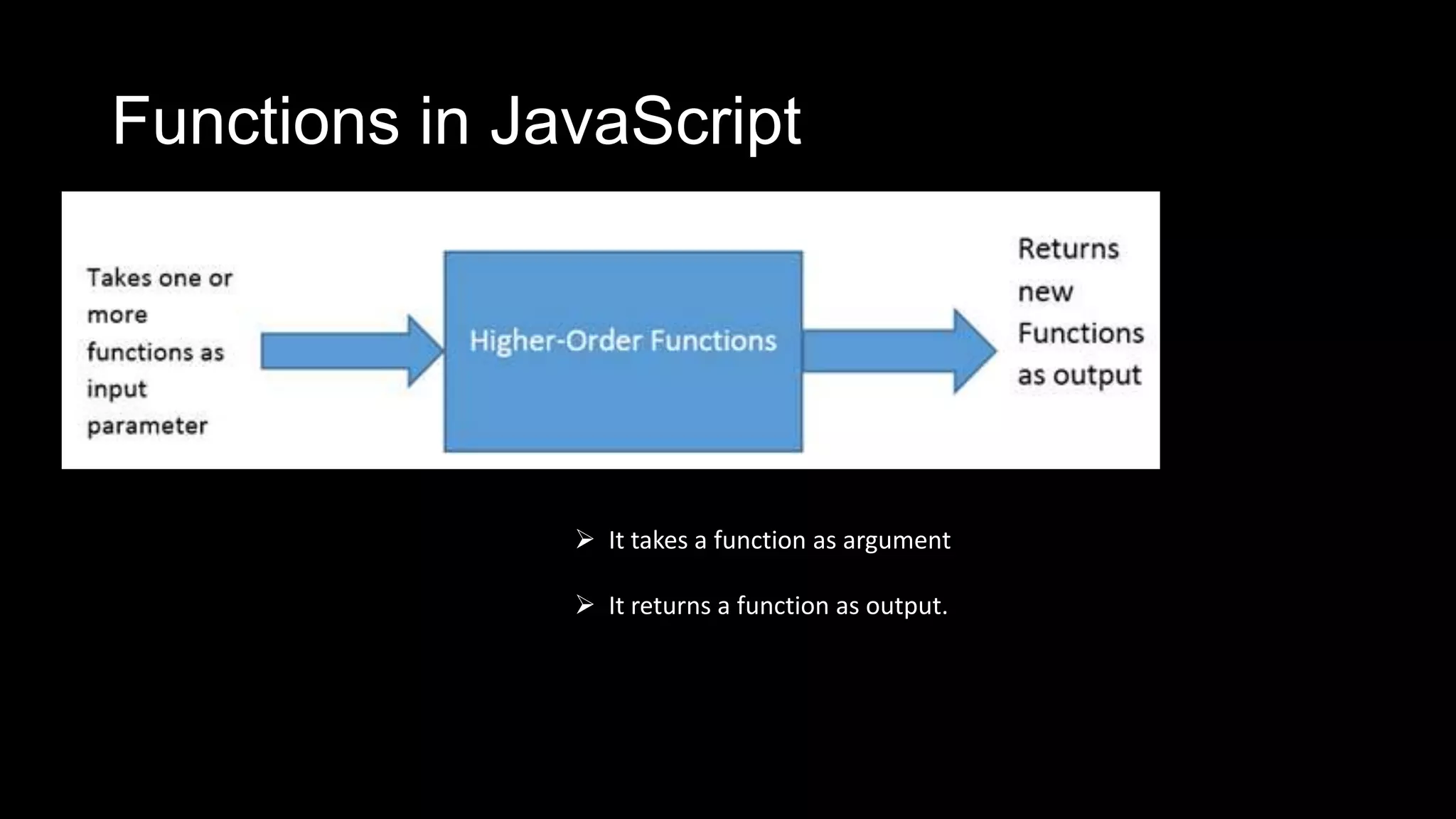
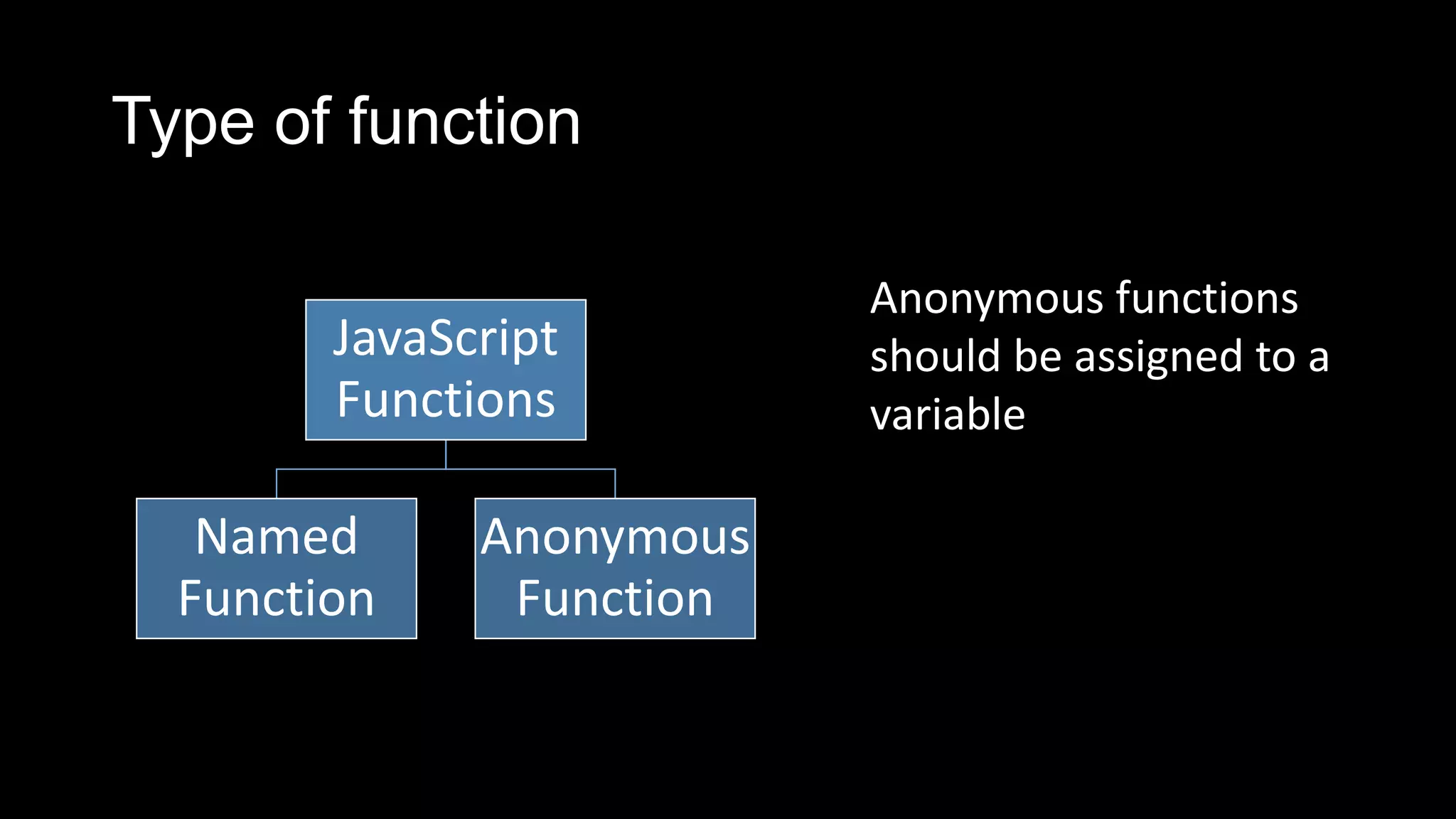
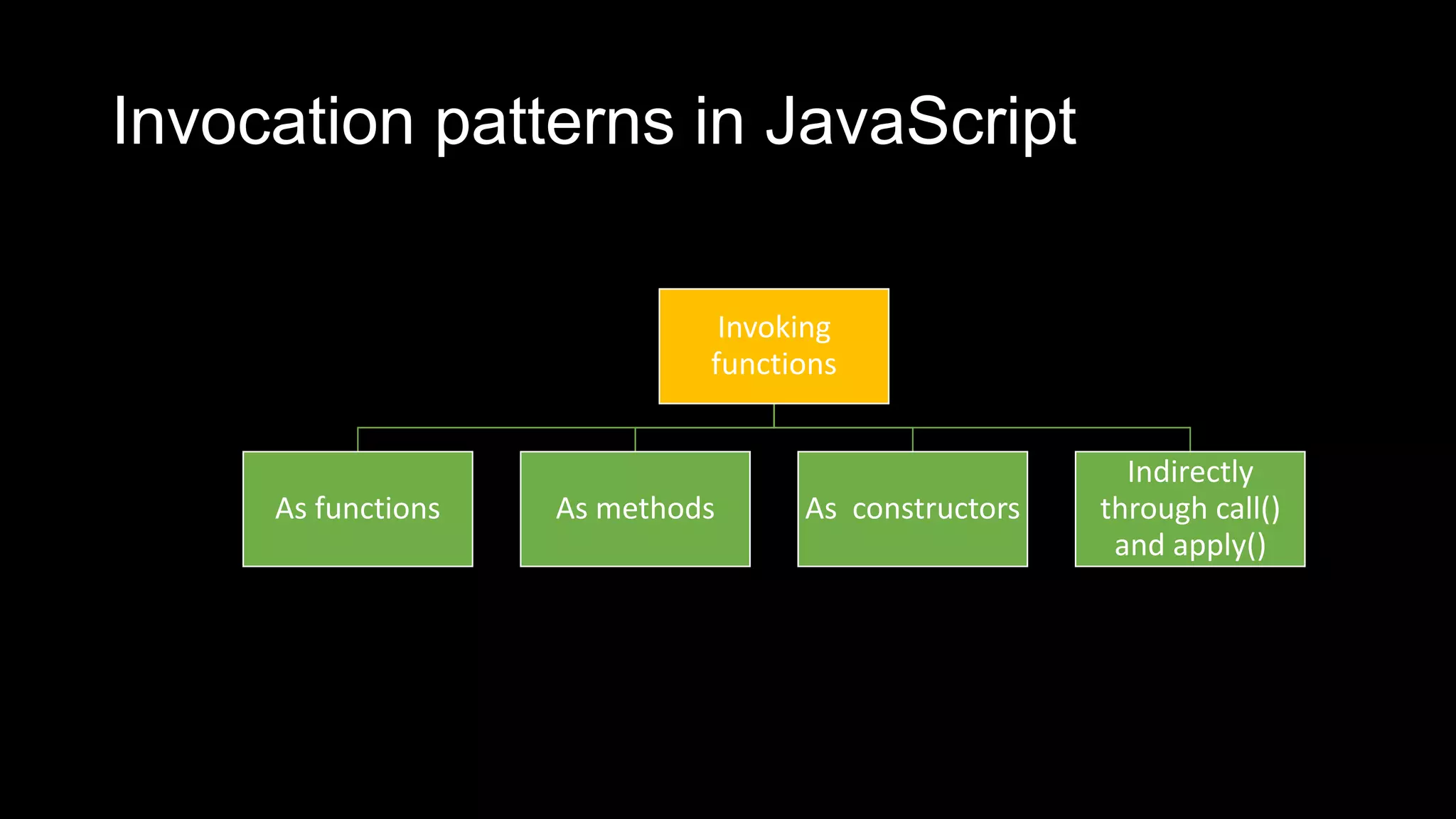
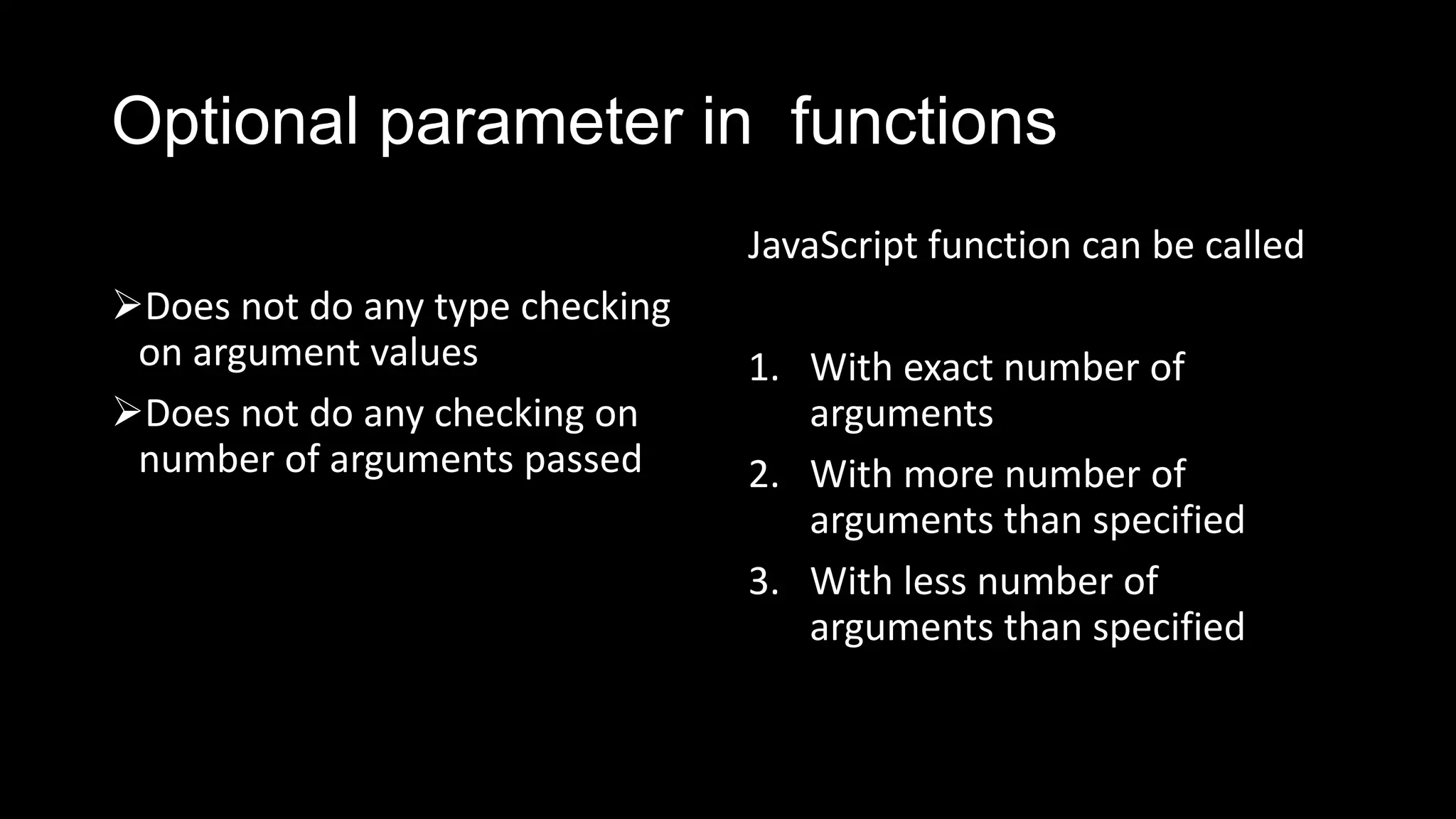
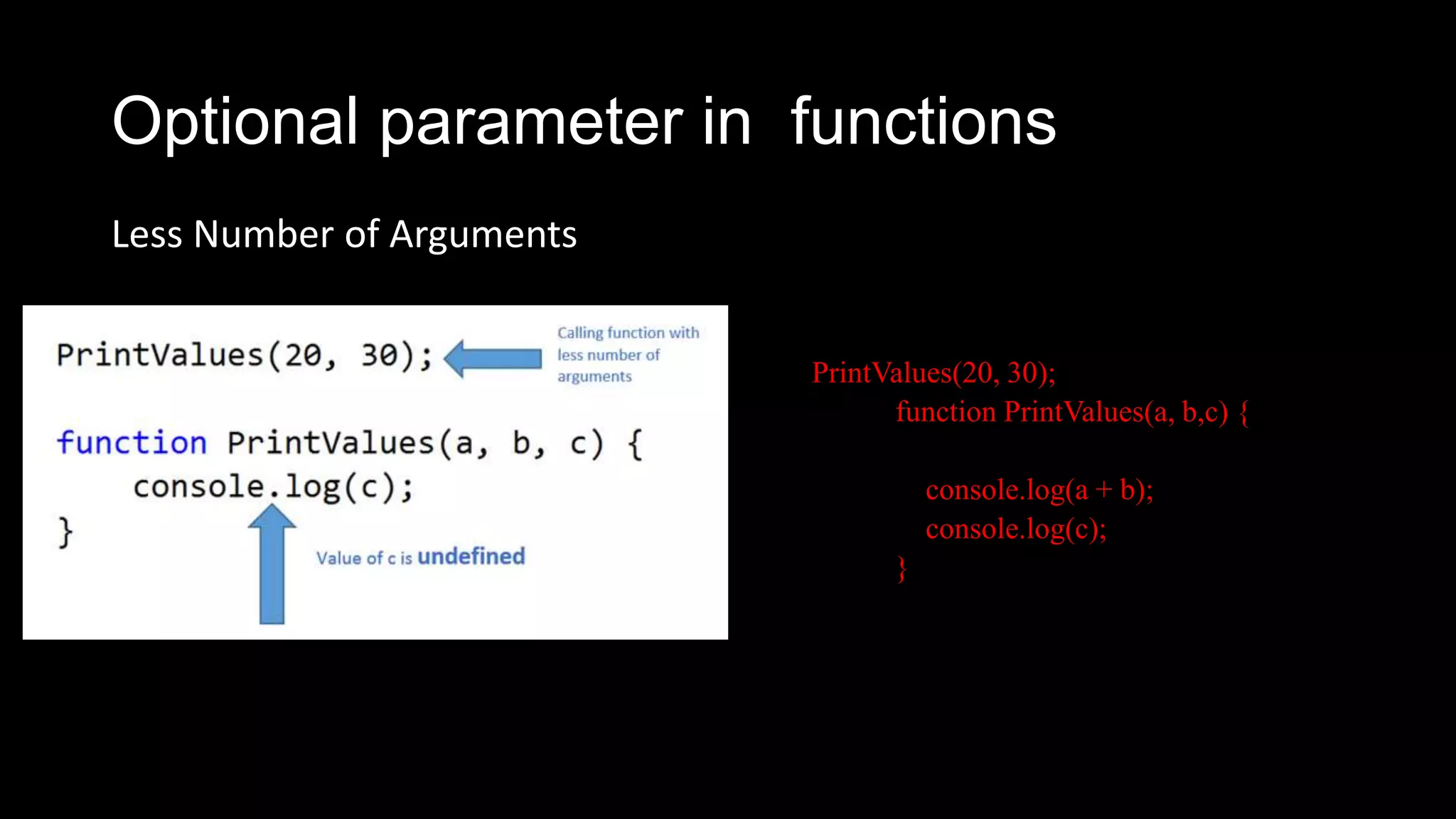
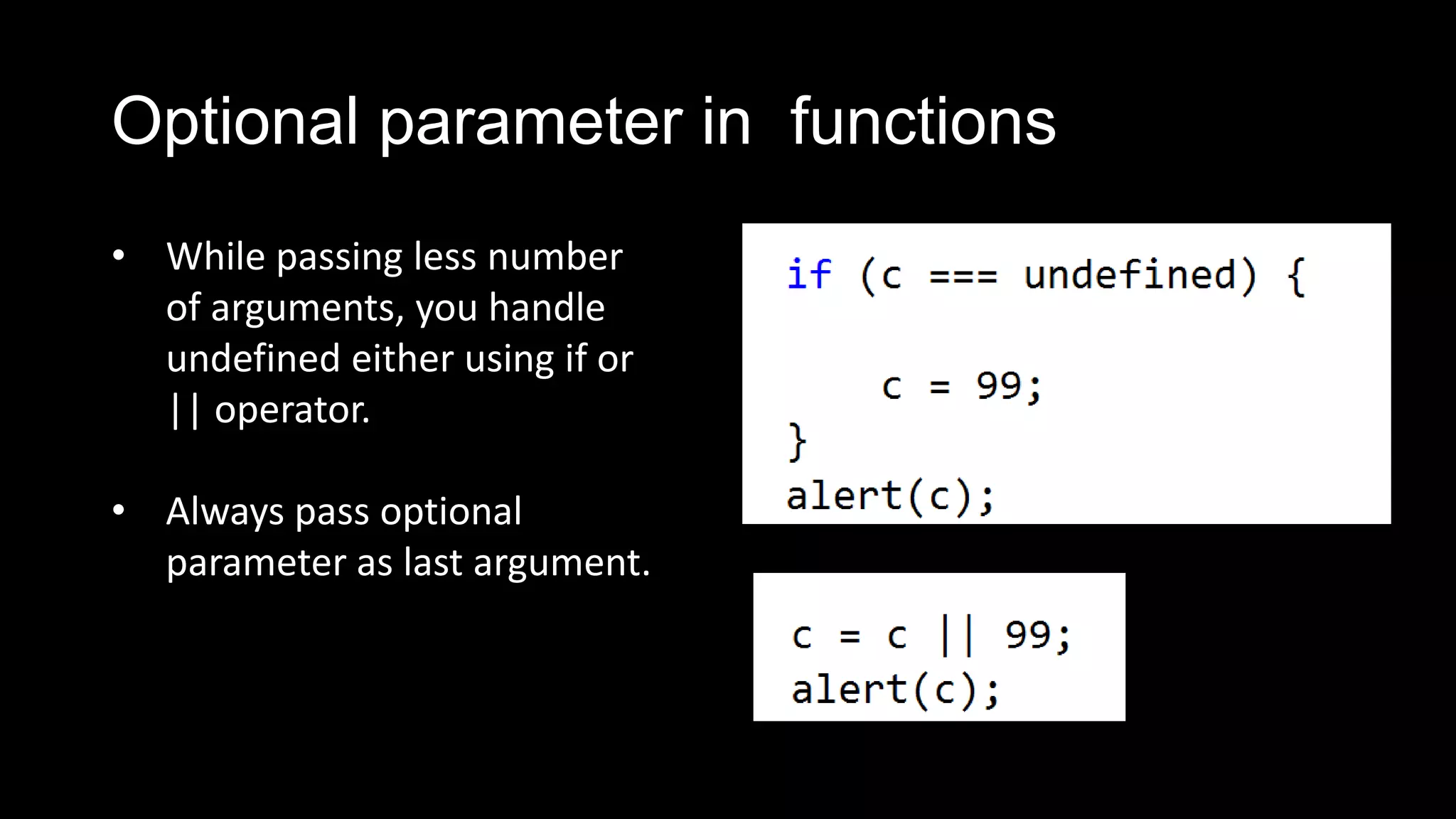
Functions in JavaScript can be named or anonymous. Nested functions can access variables of parent functions but not vice versa. Functions can be stored in variables, passed as parameters, and used in expressions. Functions are passed by value, except for objects which are passed by reference. Functions can be invoked as functions, methods, or constructors and indirectly through call and apply. Optional parameters should be passed last and can be handled with undefined checks. Functions create local scopes for variables except global variables. Functions can be used to organize code into namespaces. Higher order functions take and return other functions.
![Functions in JavaScript
Dhananjay Kumar [@debug_mode]
Delhi Chapter Lead
Microsoft MVP
Mindcracker MVP
Telerik Evangelist
http://debugmode.net
FB: Dhananjay.25july@gmail.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascript-130905060837-/75/Java-script-1-2048.jpg)

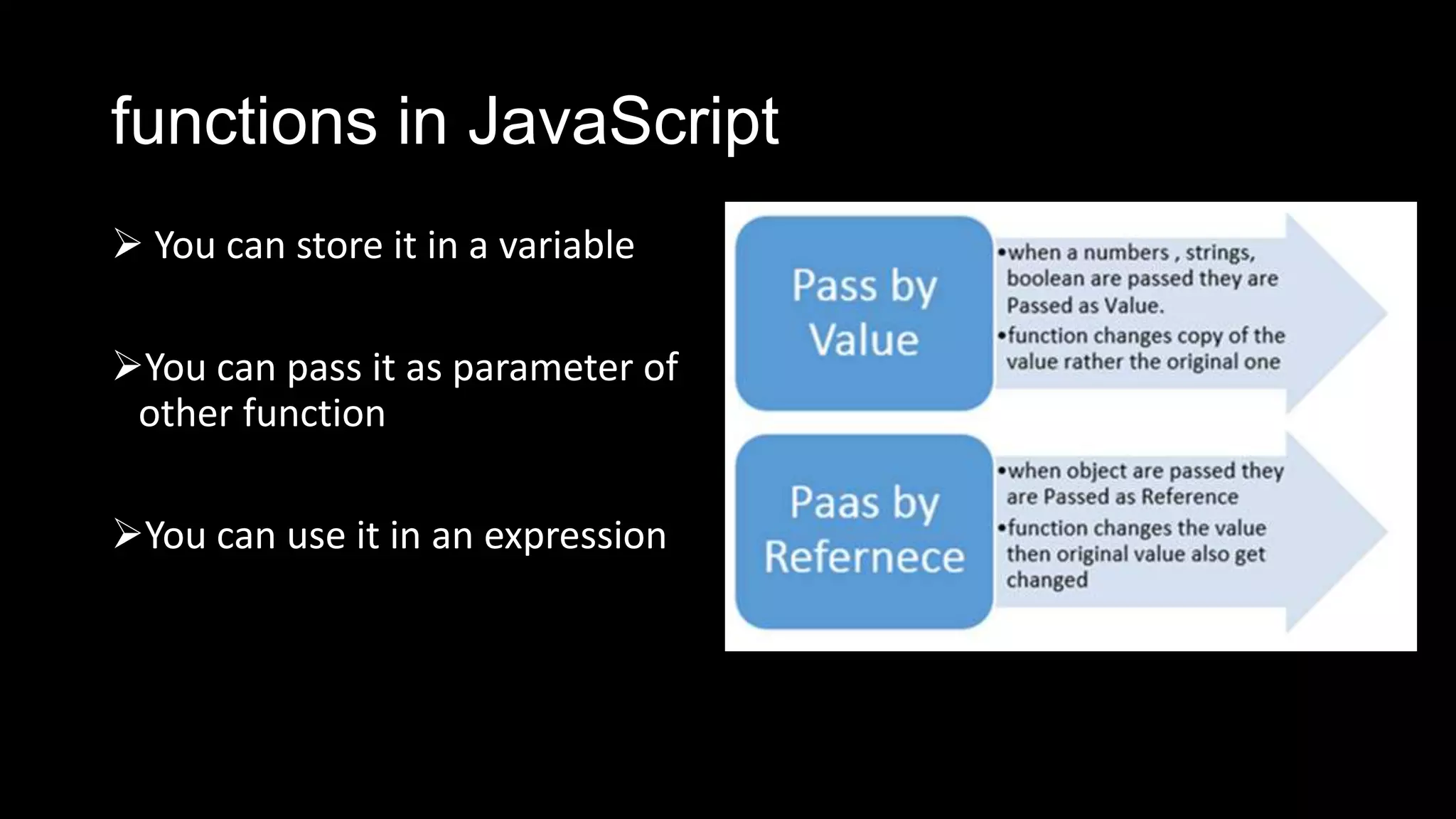
![functions in JavaScript
Pass by Value
var greetingmessage = "Hey DJ";
function showmessage(greetingmessage)
{
greetingmessage = "I am changing
value";
}
showmessage(greetingmessage);
alert(greetingmessage);
Pass By Reference
var arrayofname = ["dj"];
function showmessage(arrayofname) {
arrayofname[0] = "dhananjay";
}
showmessage(arrayofname);
alert(arrayofname[0]);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascript-130905060837-/75/Java-script-5-2048.jpg)




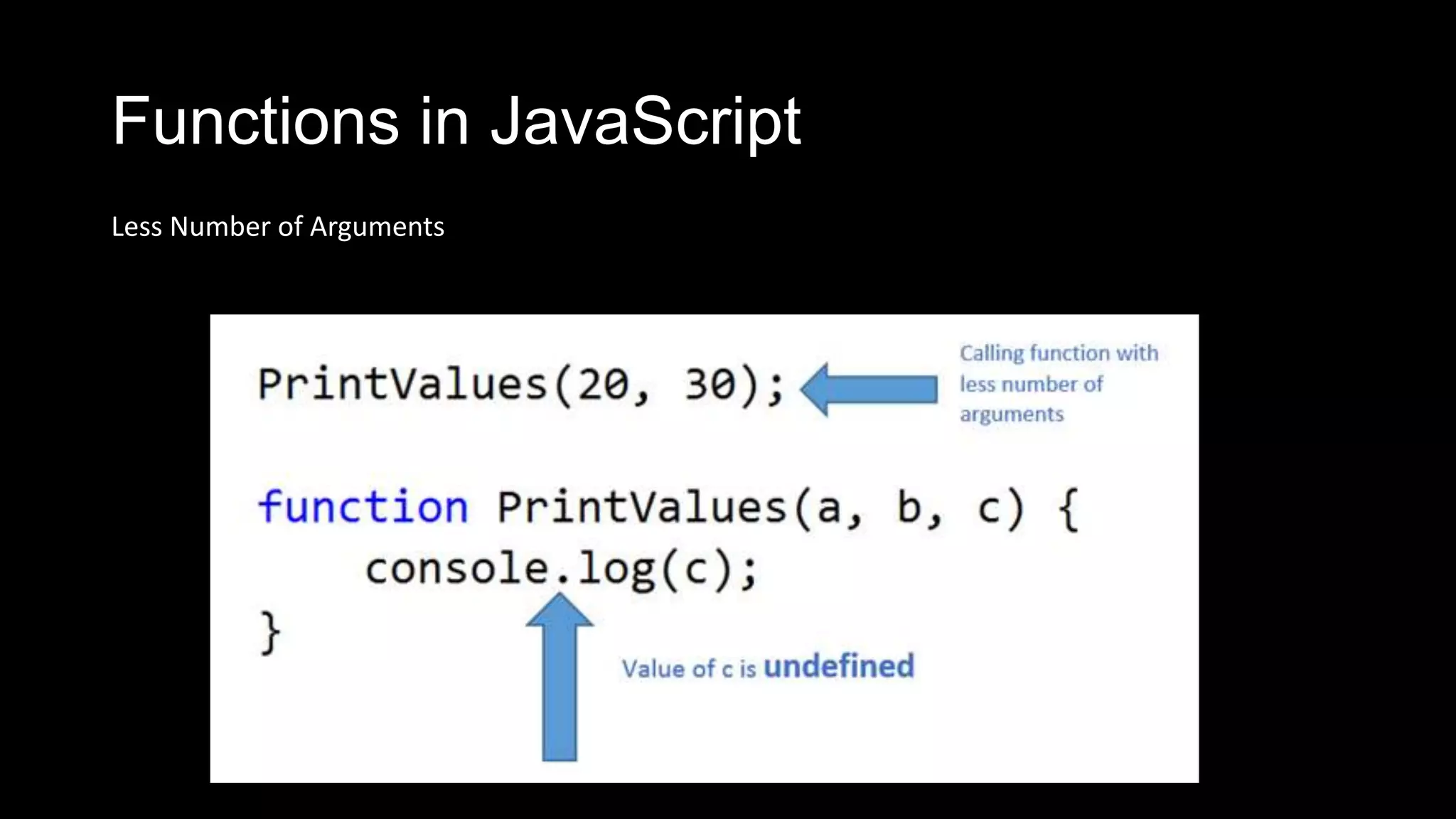
![Optional parameter in functions
More numbers of Arguments
PrintValues(20, 30,40,50,60);
function PrintValues(a, b,c) {
if (arguments.length > 3) {
throw Error("invalid arguments");
}
console.log(a);
console.log(c);
var abc = arguments[4];
console.log(abc);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascript-130905060837-/75/Java-script-14-2048.jpg)