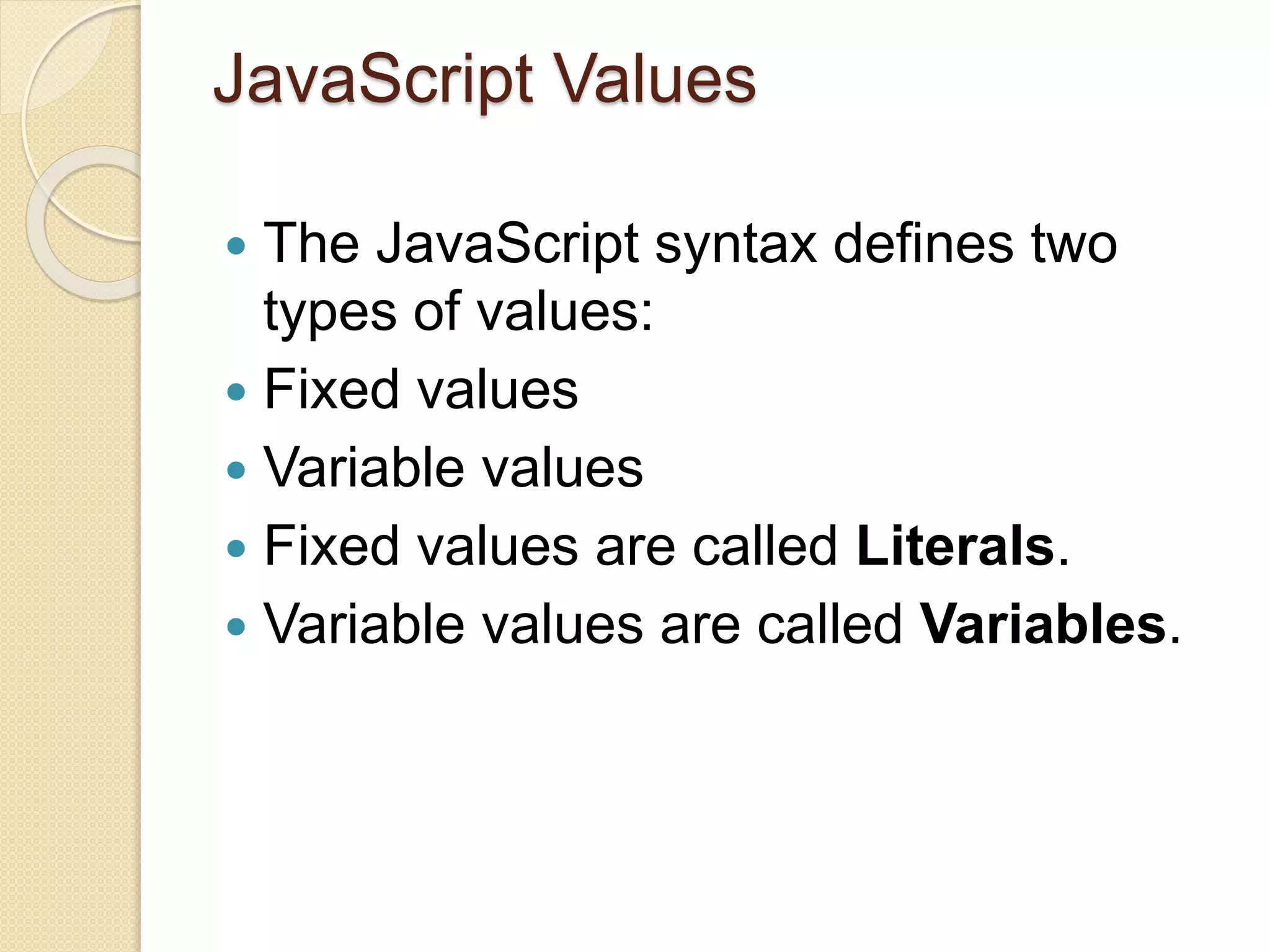
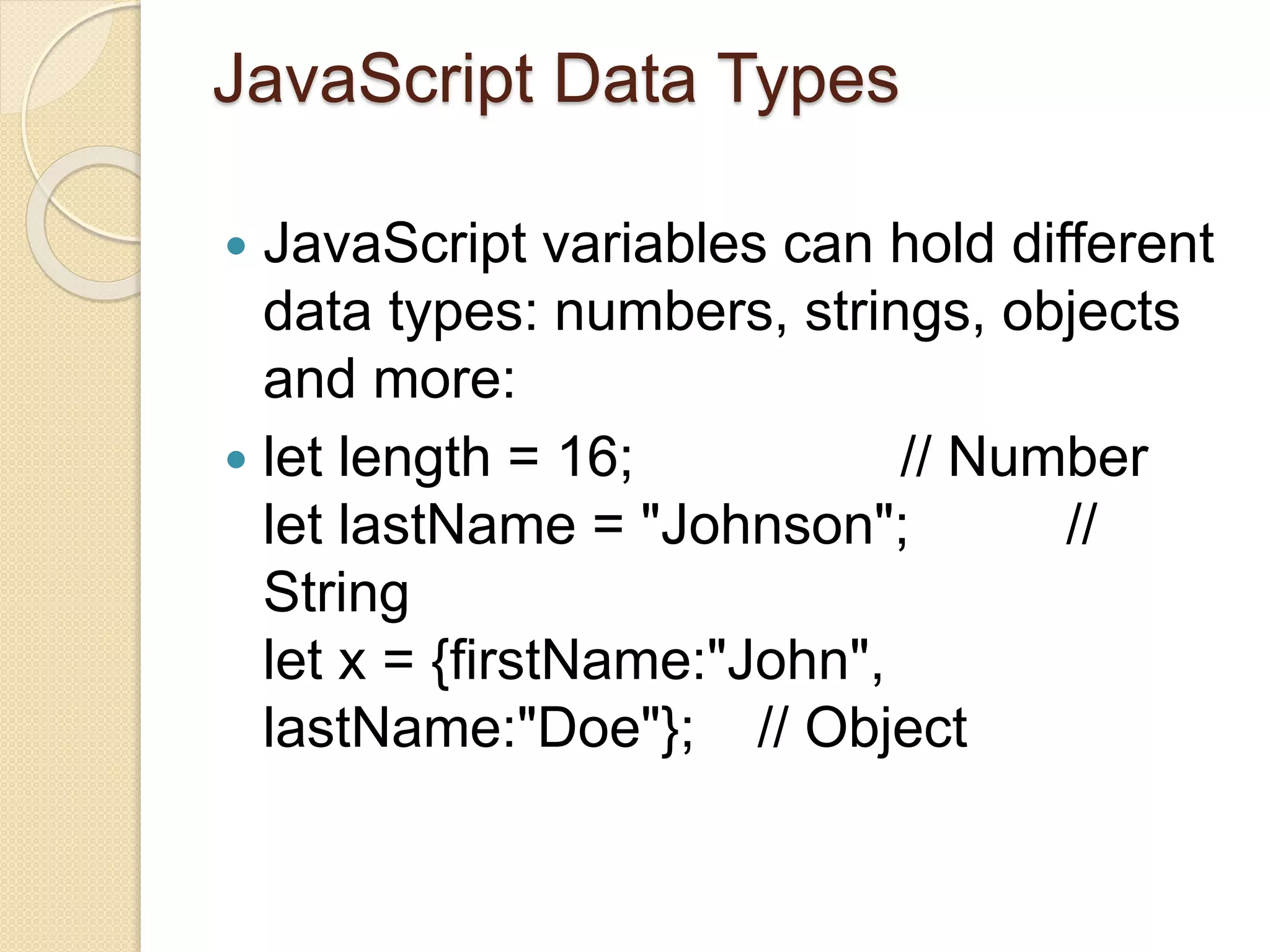
This document provides an introduction and overview of JavaScript. It includes examples of basic JavaScript programs that change HTML content, attribute values, and styles. It discusses advantages of placing scripts in external files and defines key JavaScript concepts like comments, case sensitivity, data types, variables and literals. The document serves as a tutorial for beginners to learn JavaScript fundamentals.