This document discusses key concepts related to Java programming including:
1) It describes how a Java program works by explaining the roles of the Java compiler, bytecode, interpreter, and native code conversion.
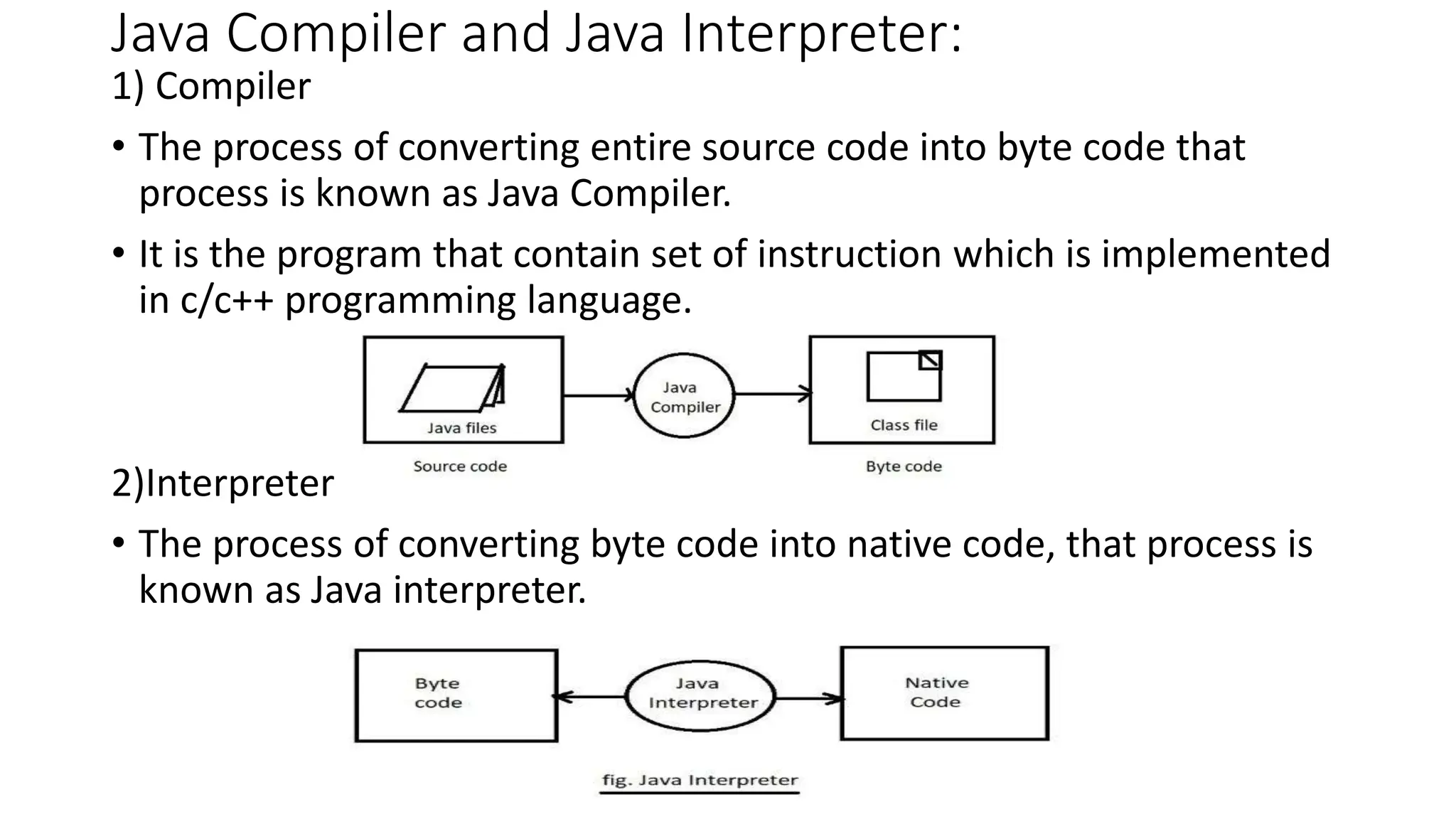
2) It defines the Java compiler and interpreter, explaining that the compiler converts source code to bytecode while the interpreter converts bytecode to native code.
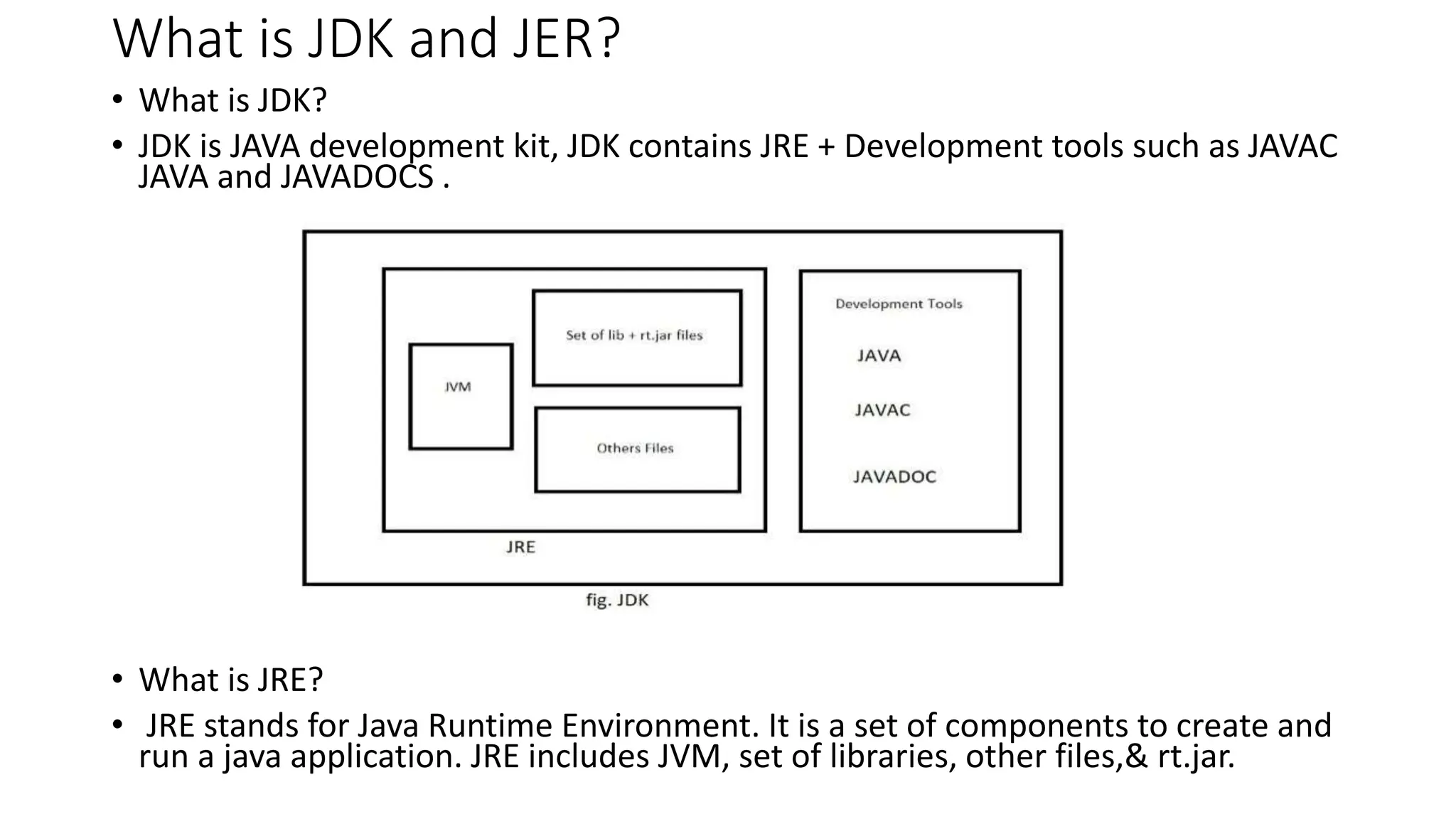
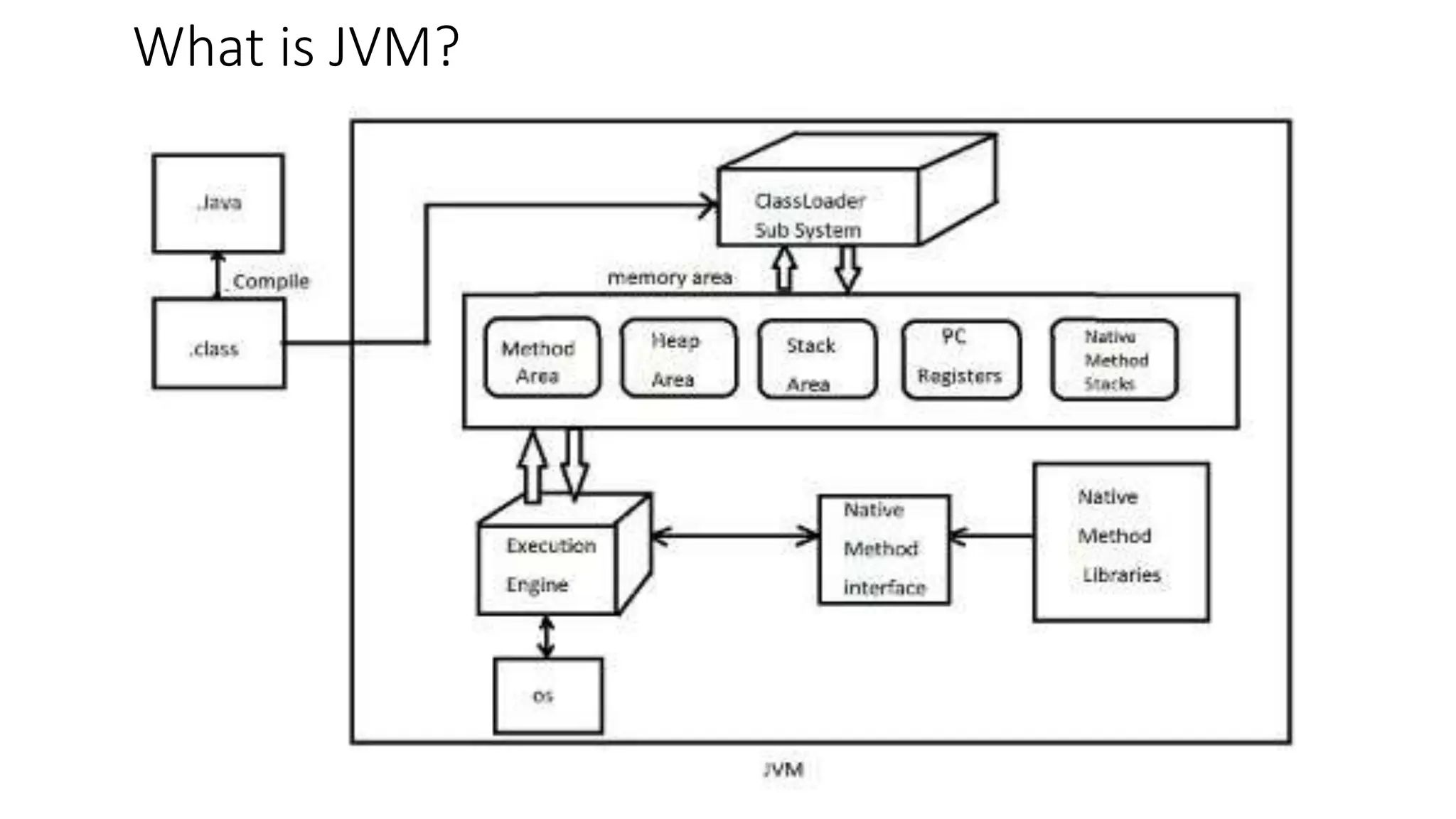
3) It outlines the Java Development Kit (JDK), Java Runtime Environment (JRE), and Java Virtual Machine (JVM), explaining their functions in developing and running Java applications.