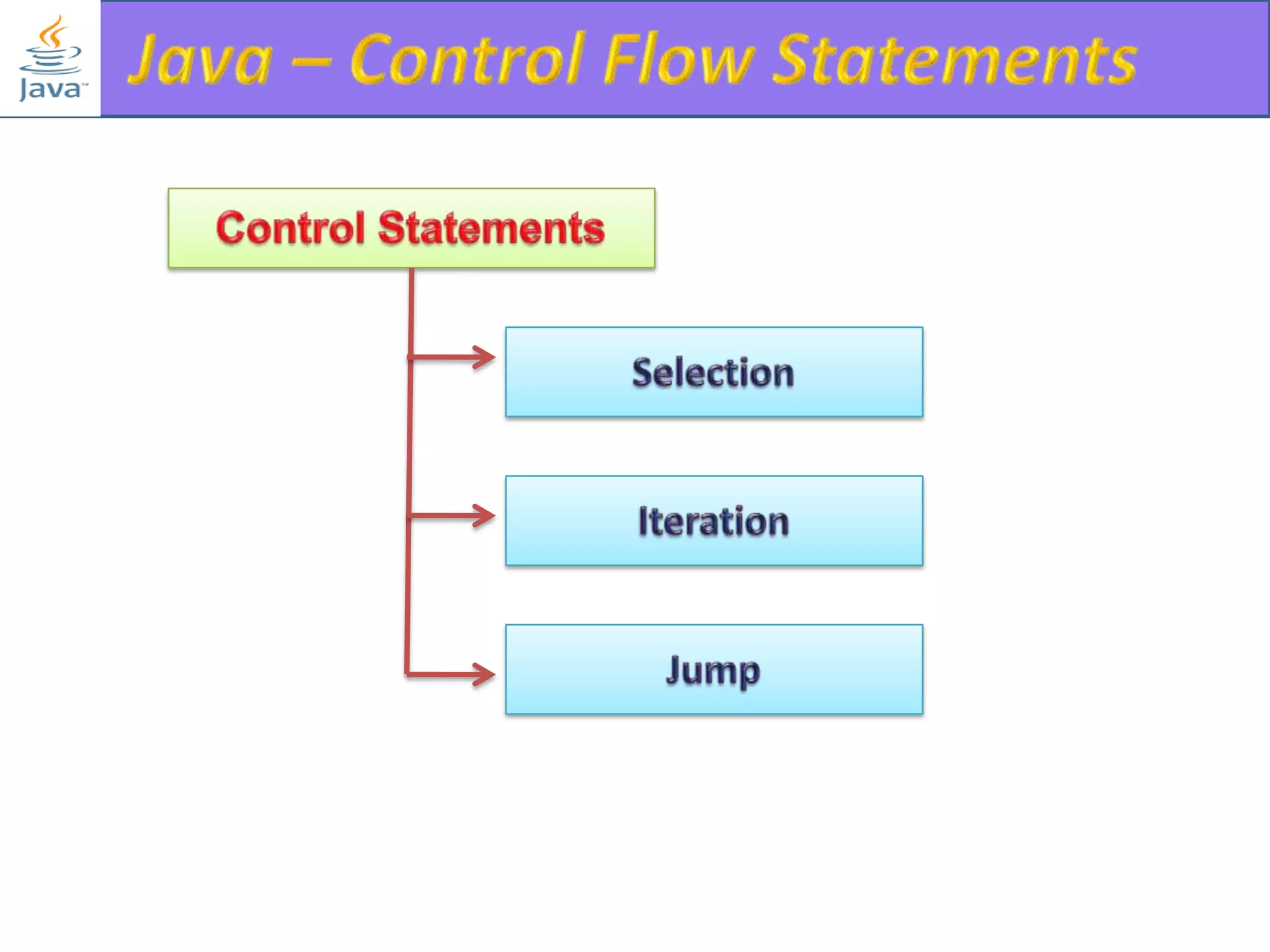
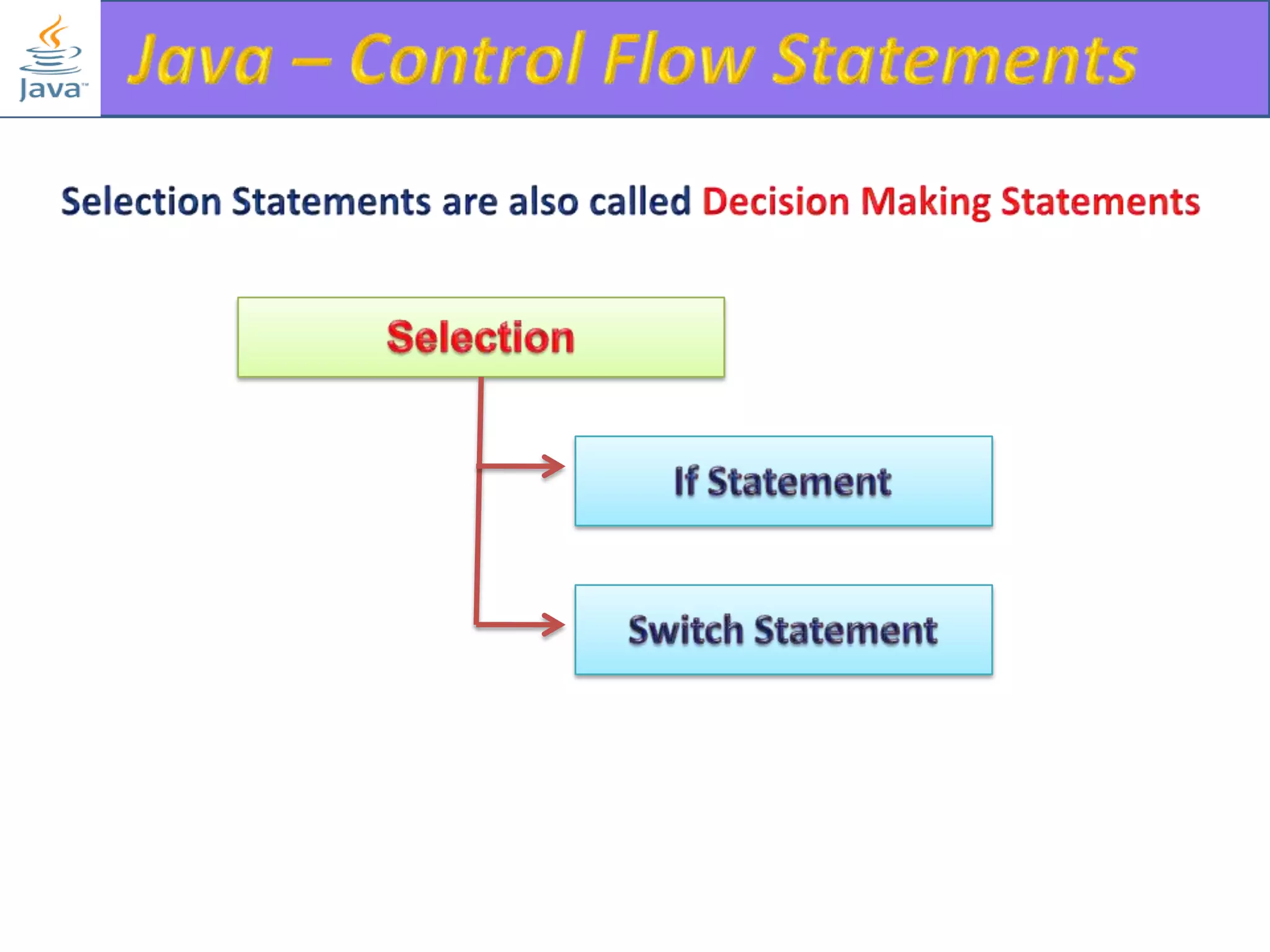
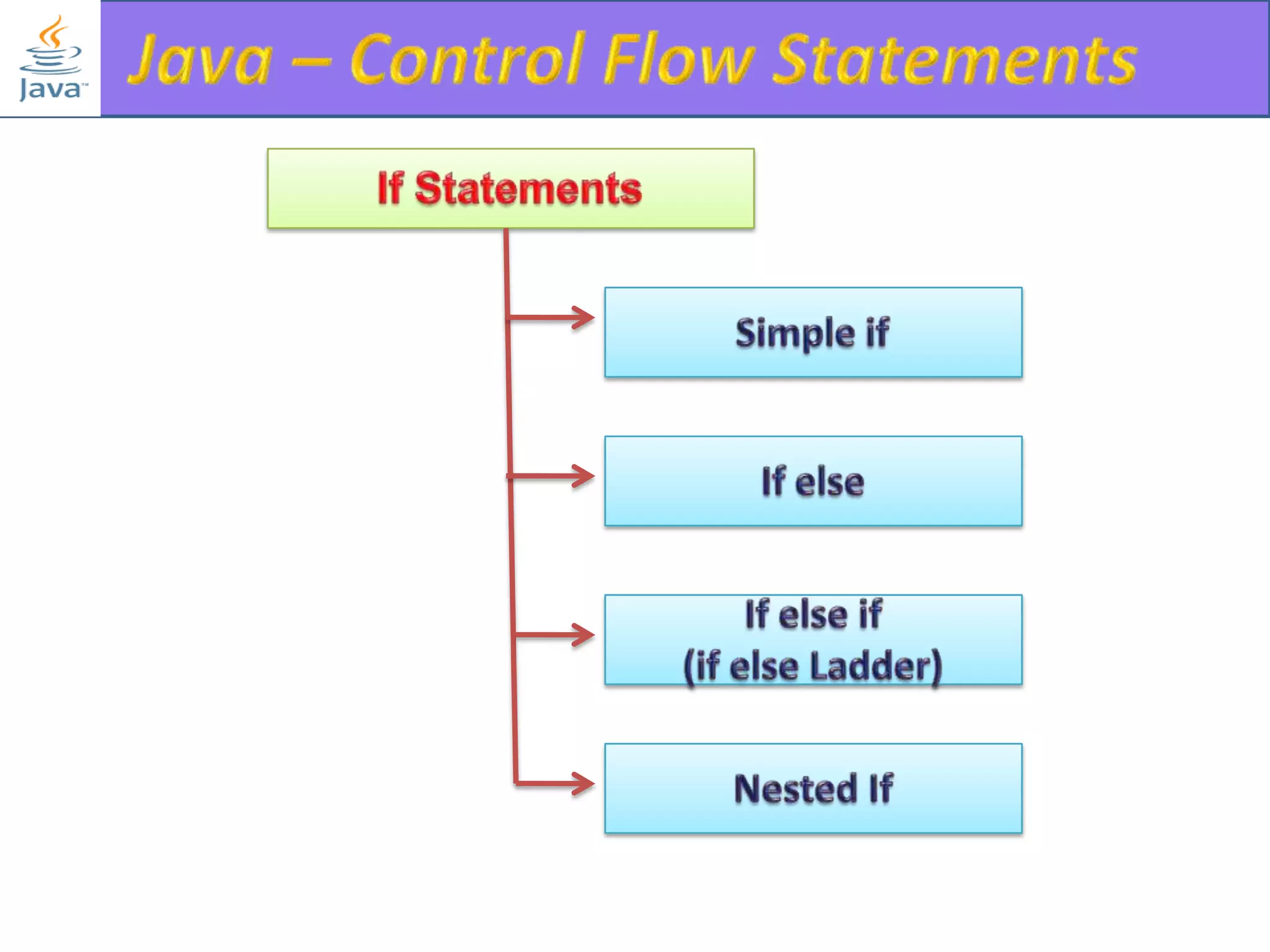
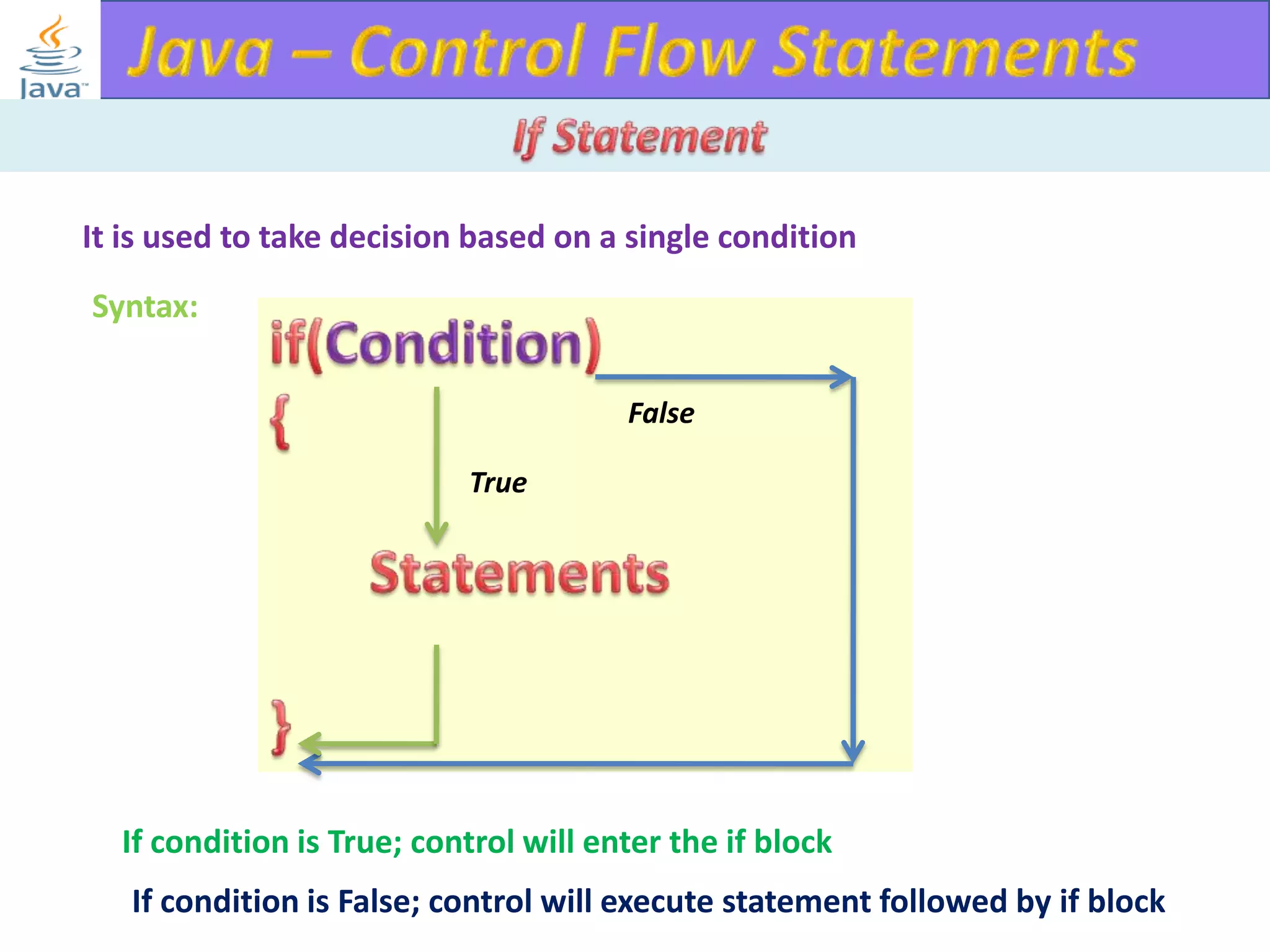
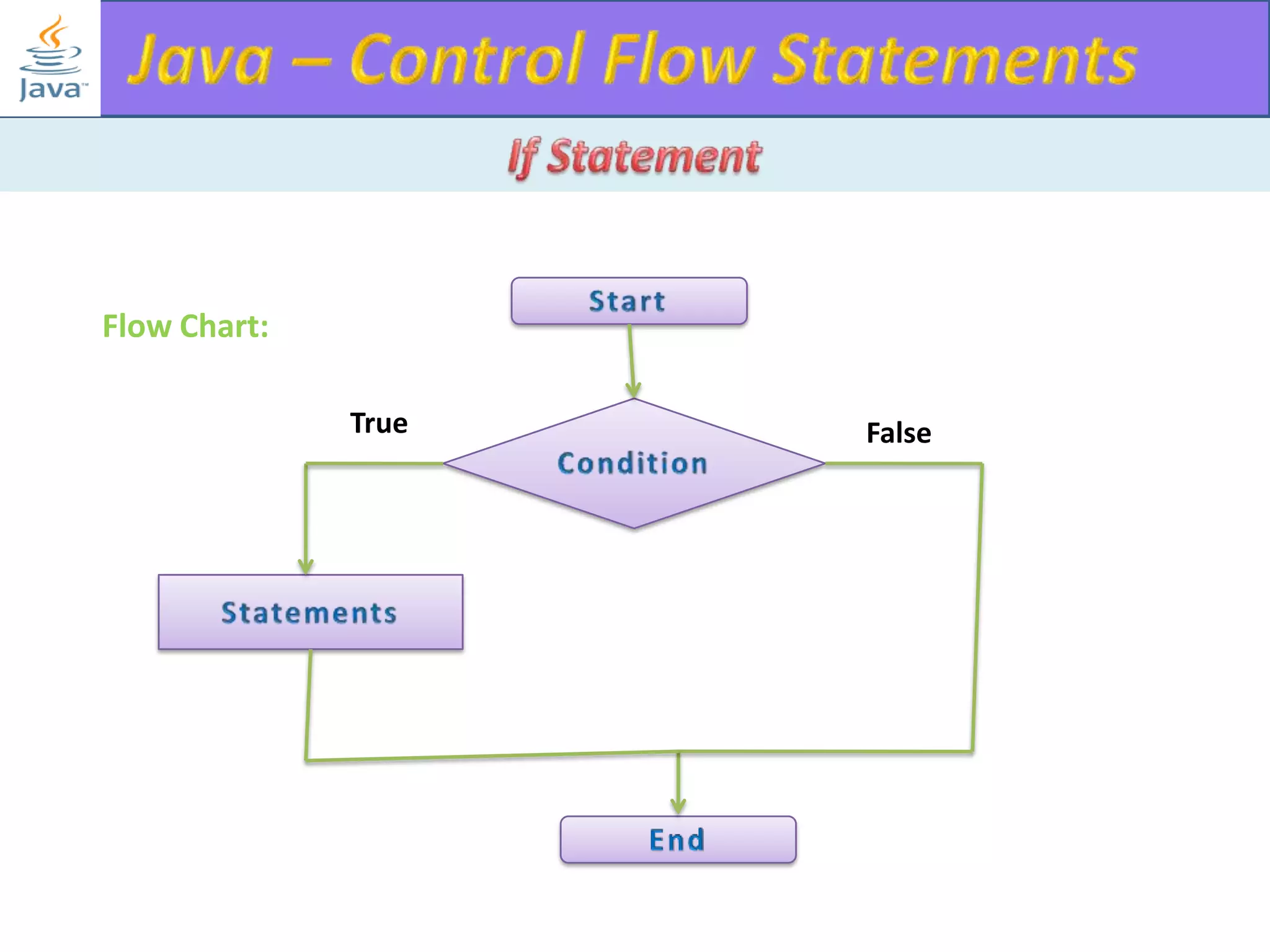
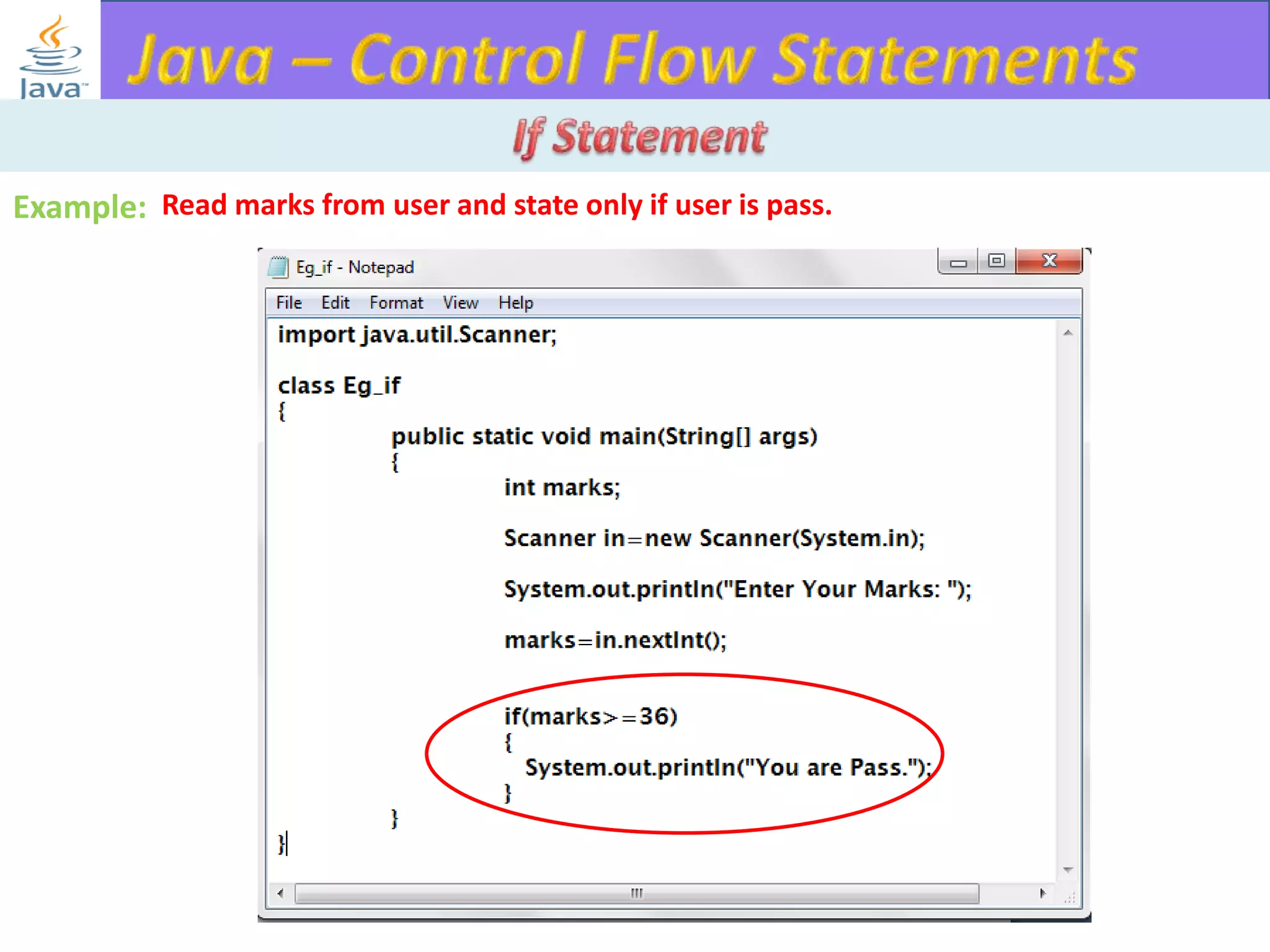
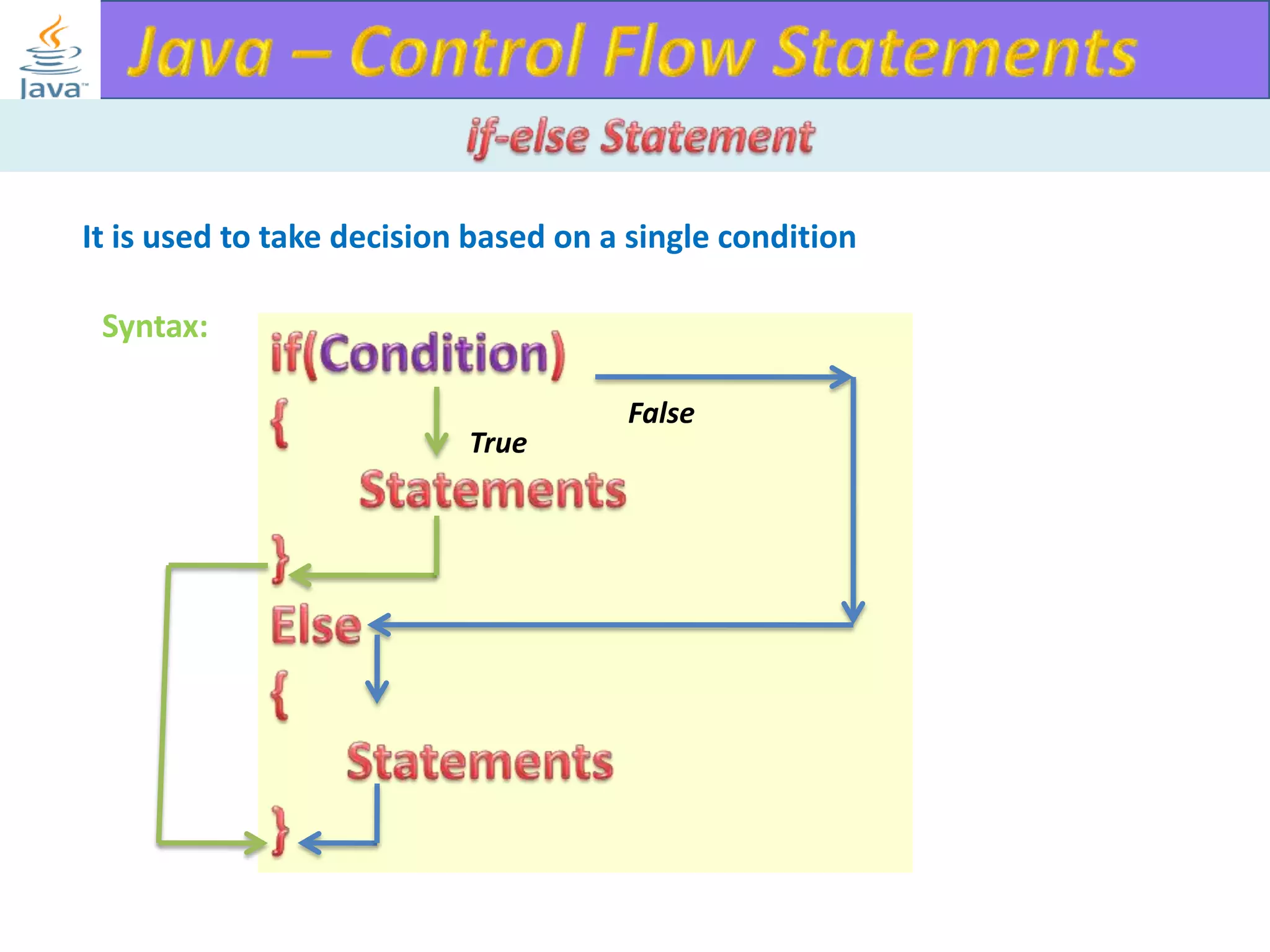
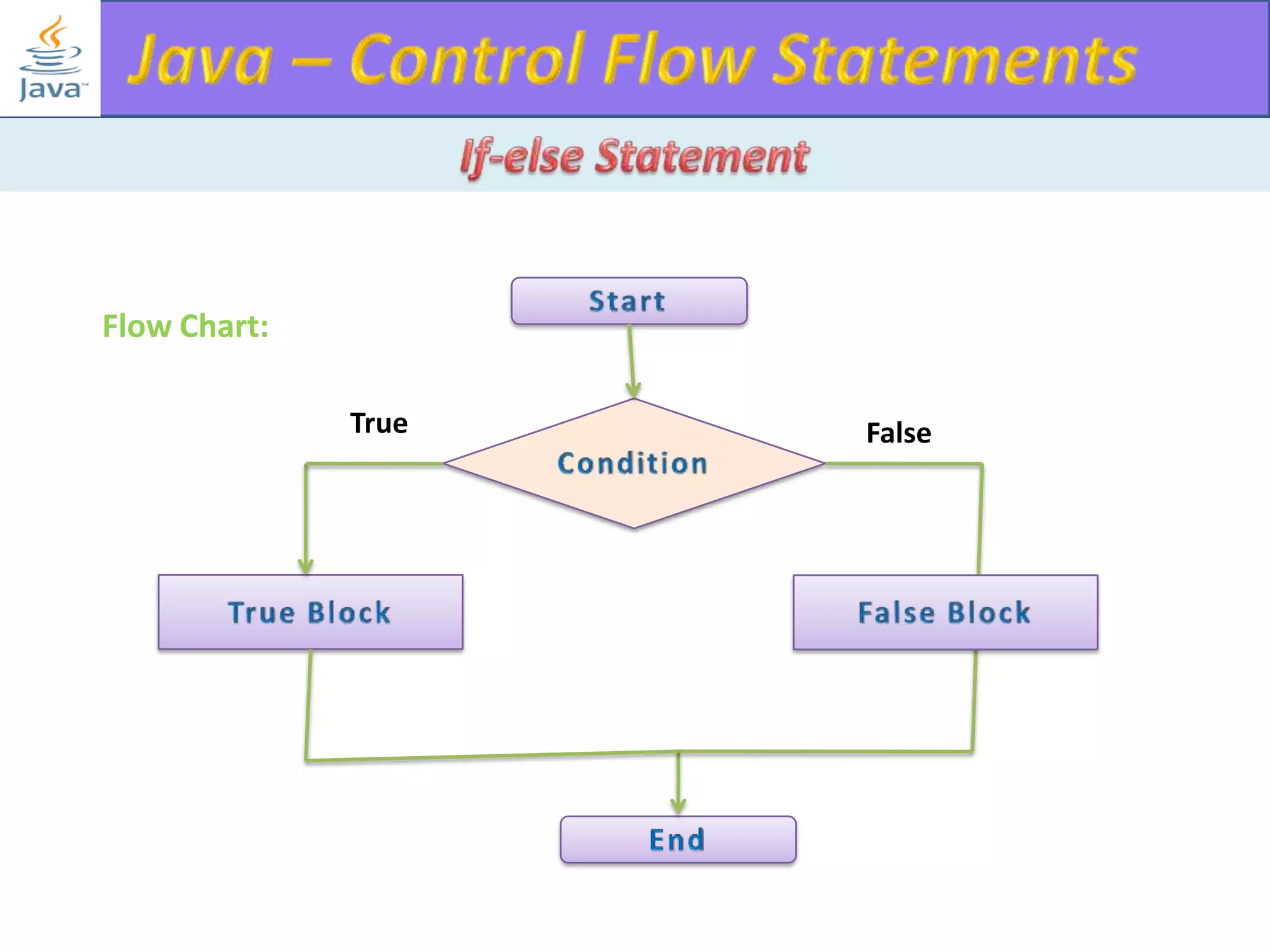
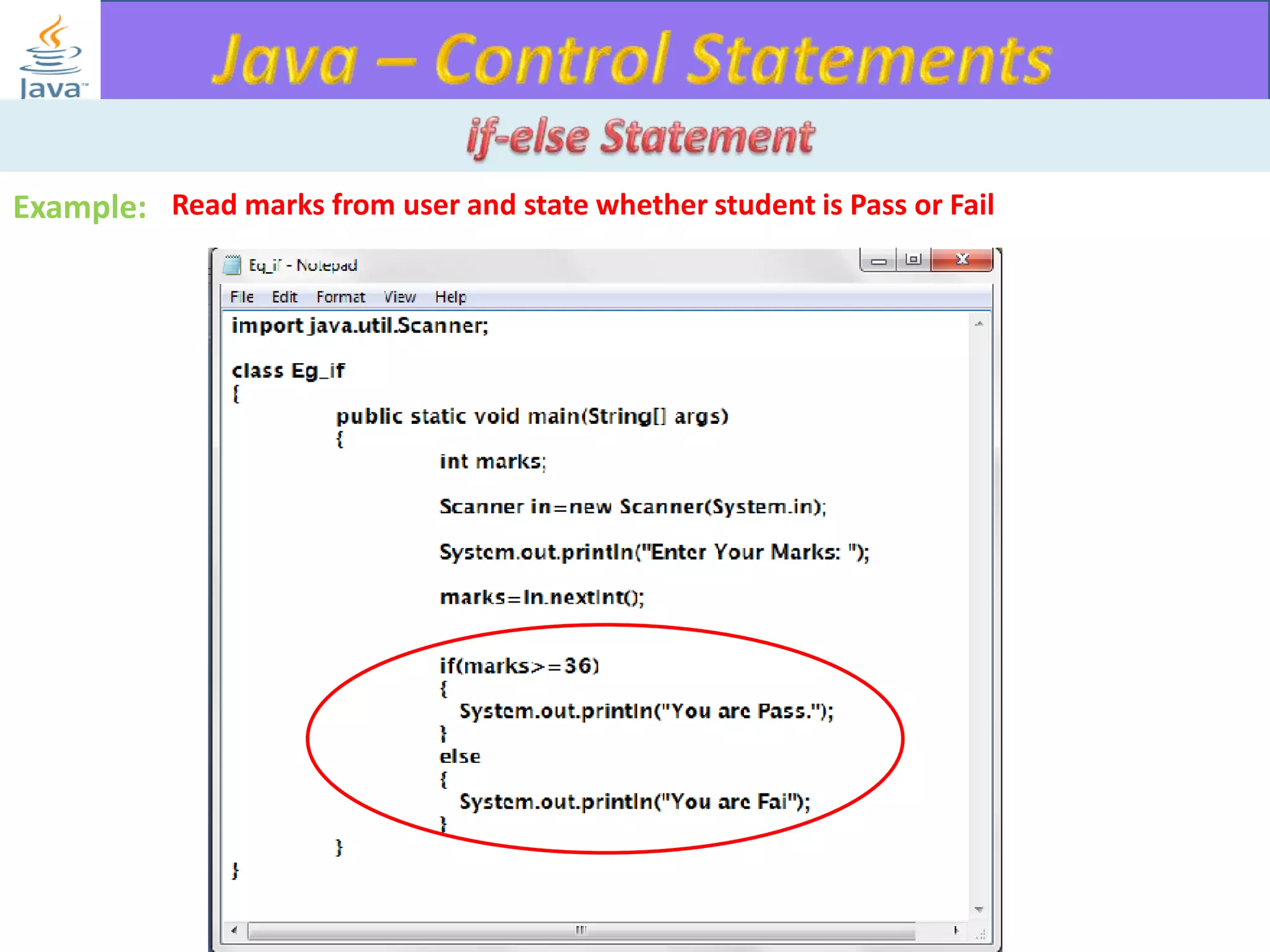
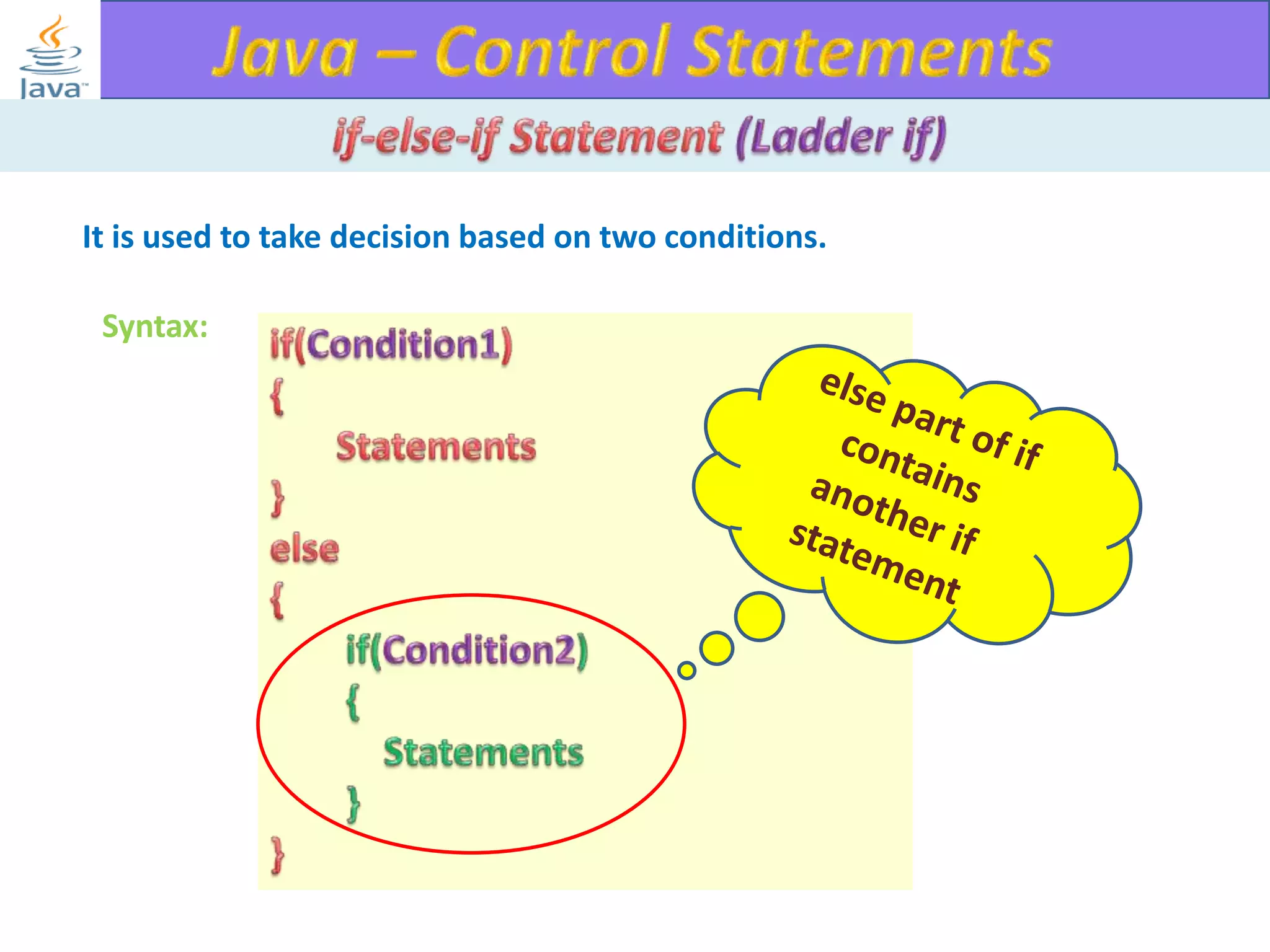
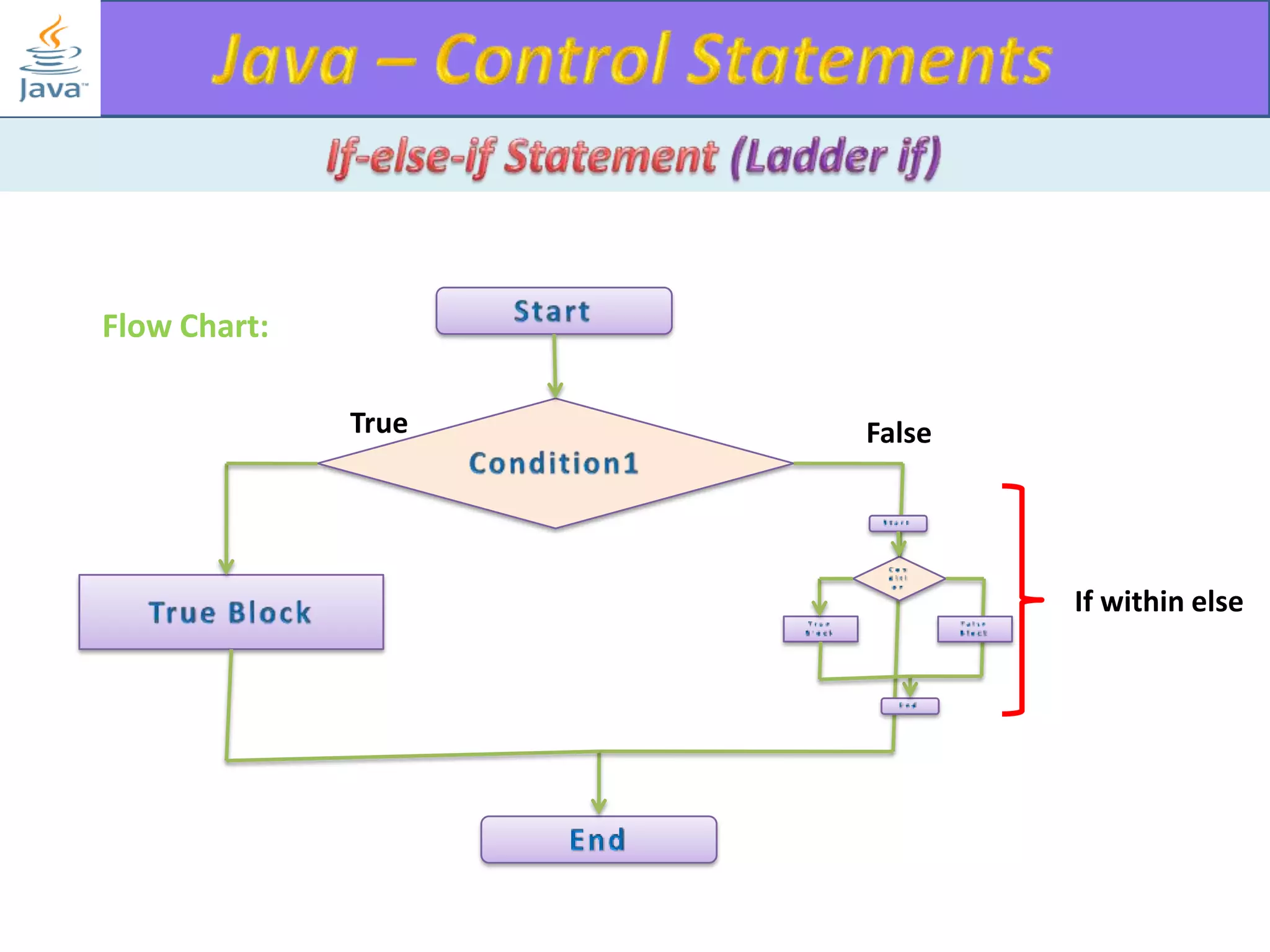
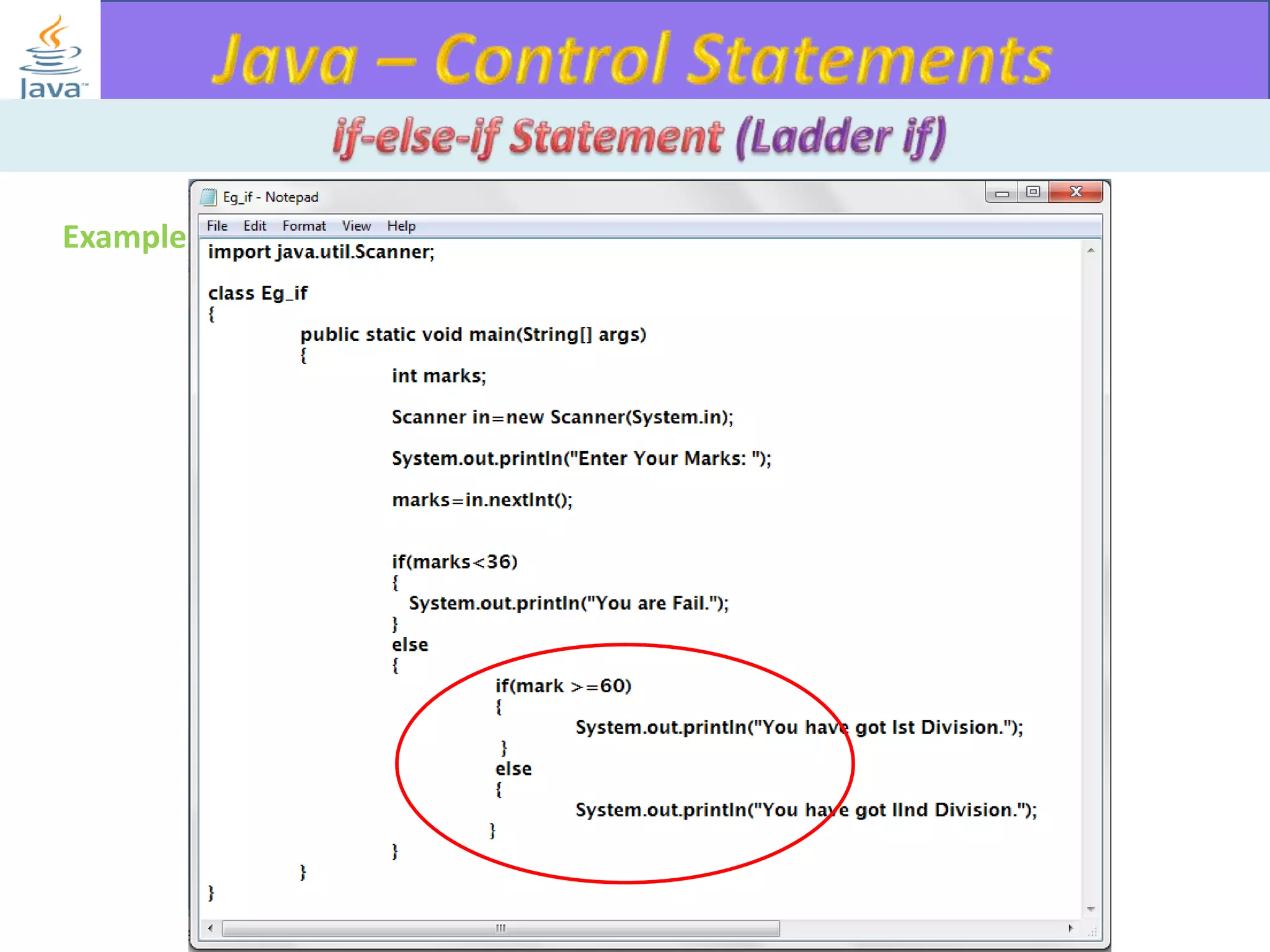
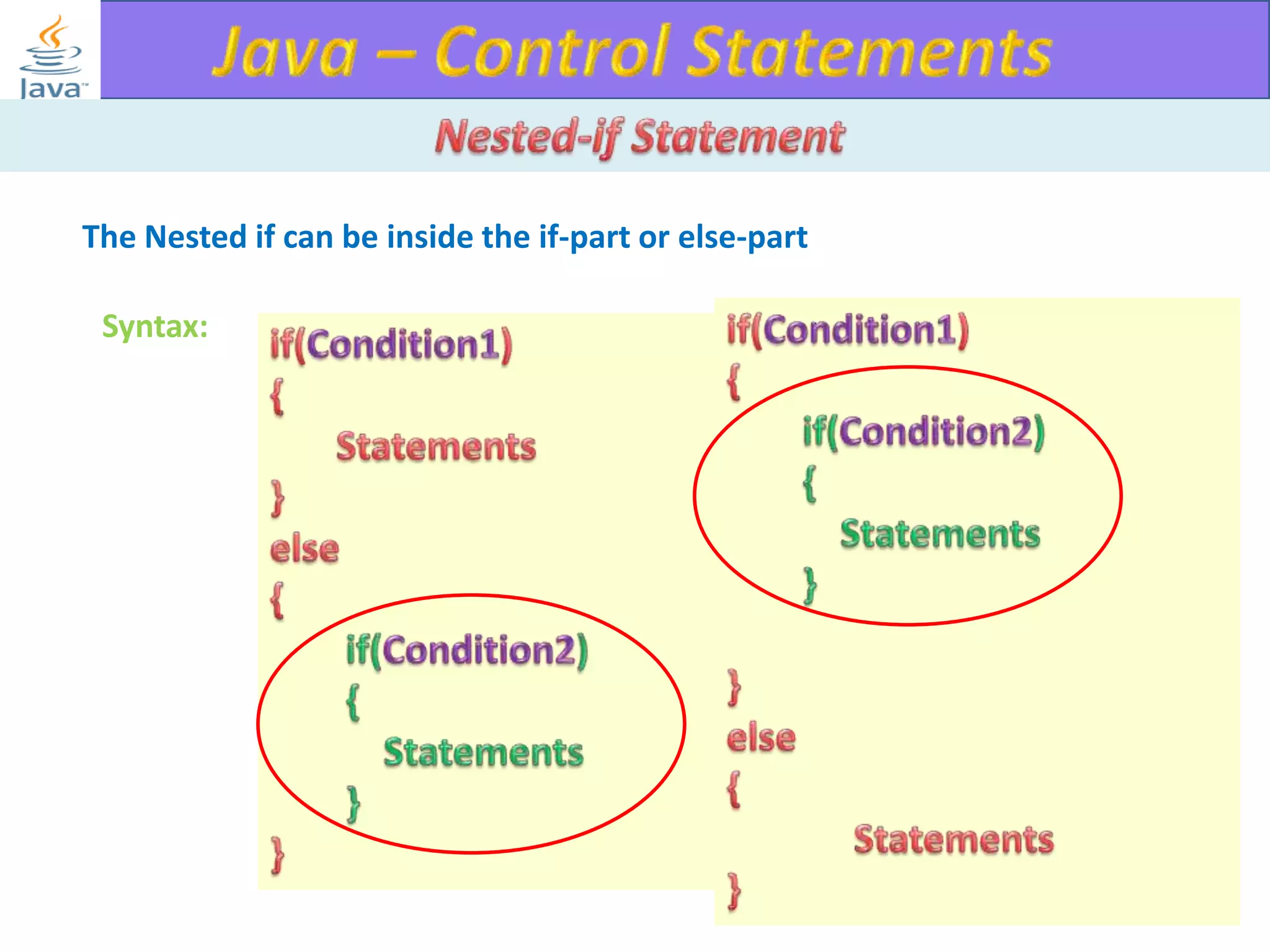
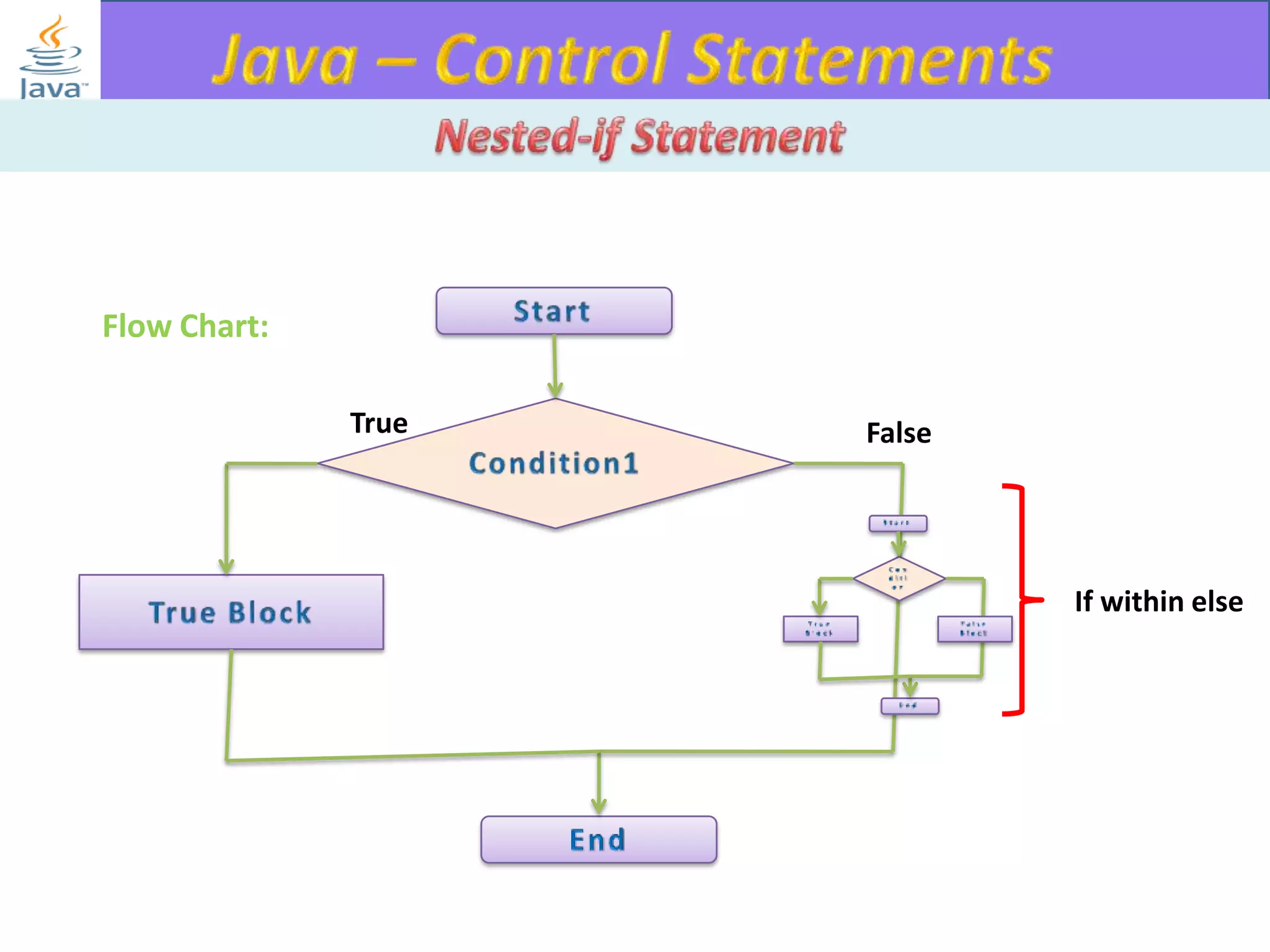
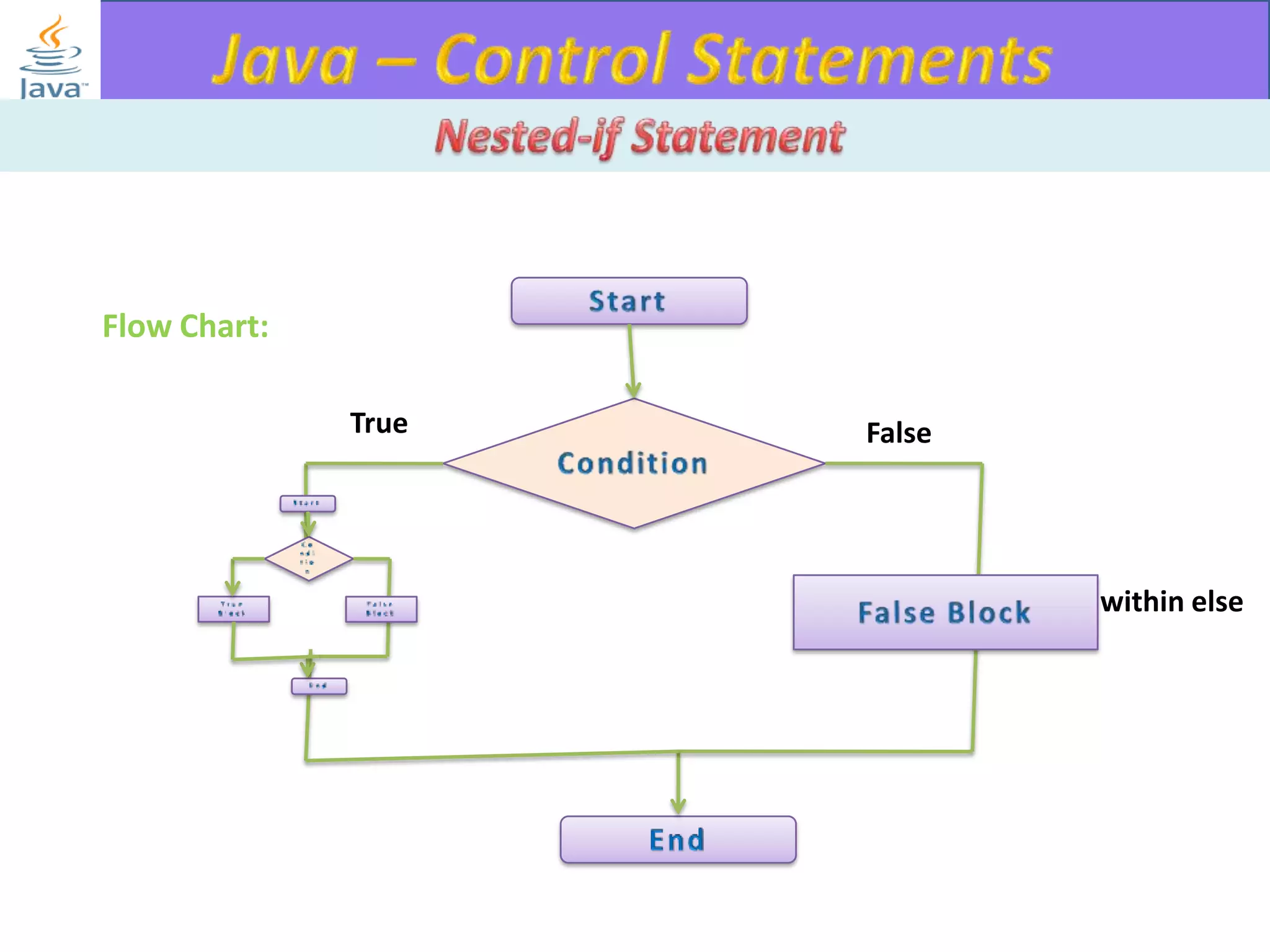
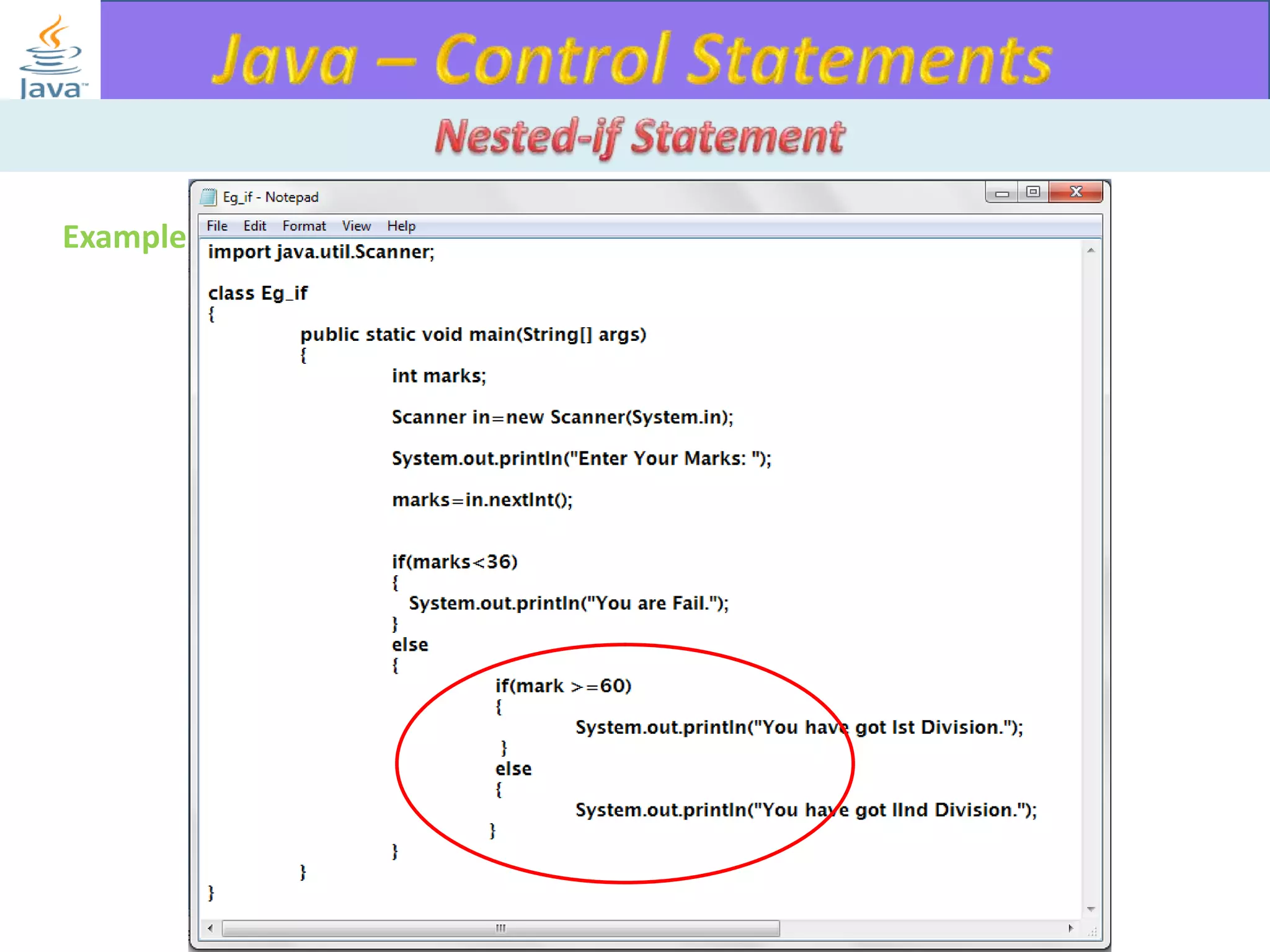
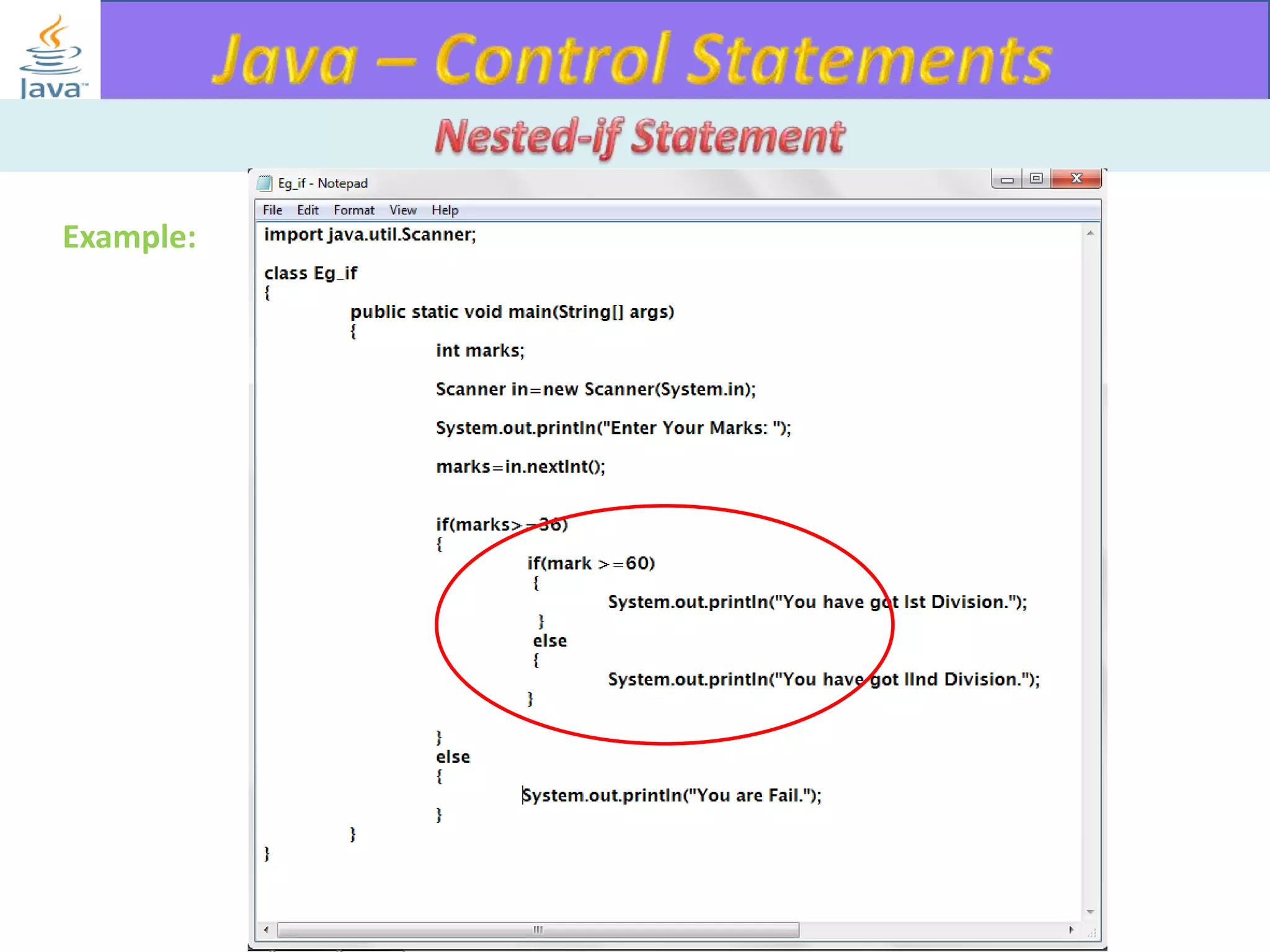
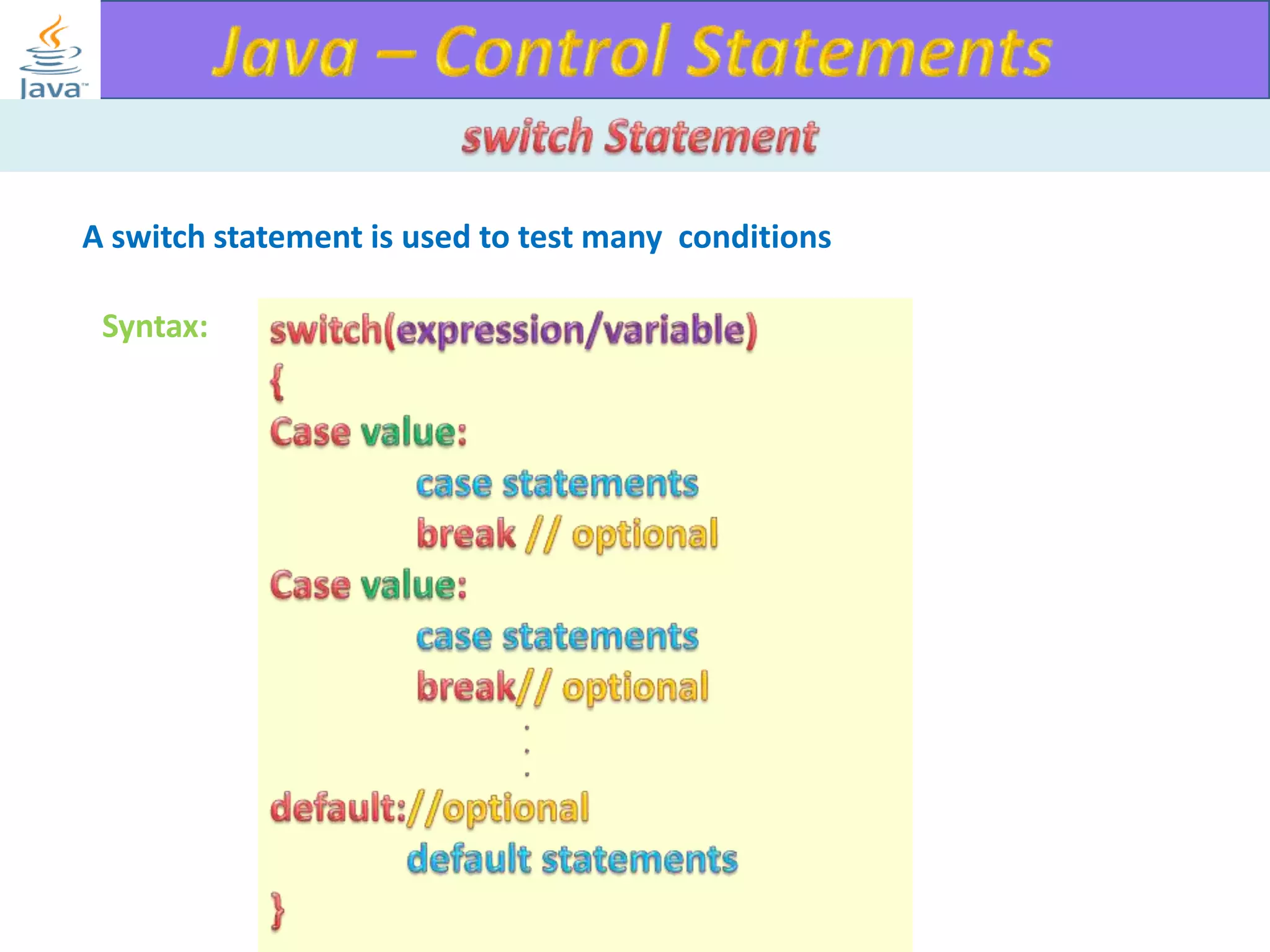
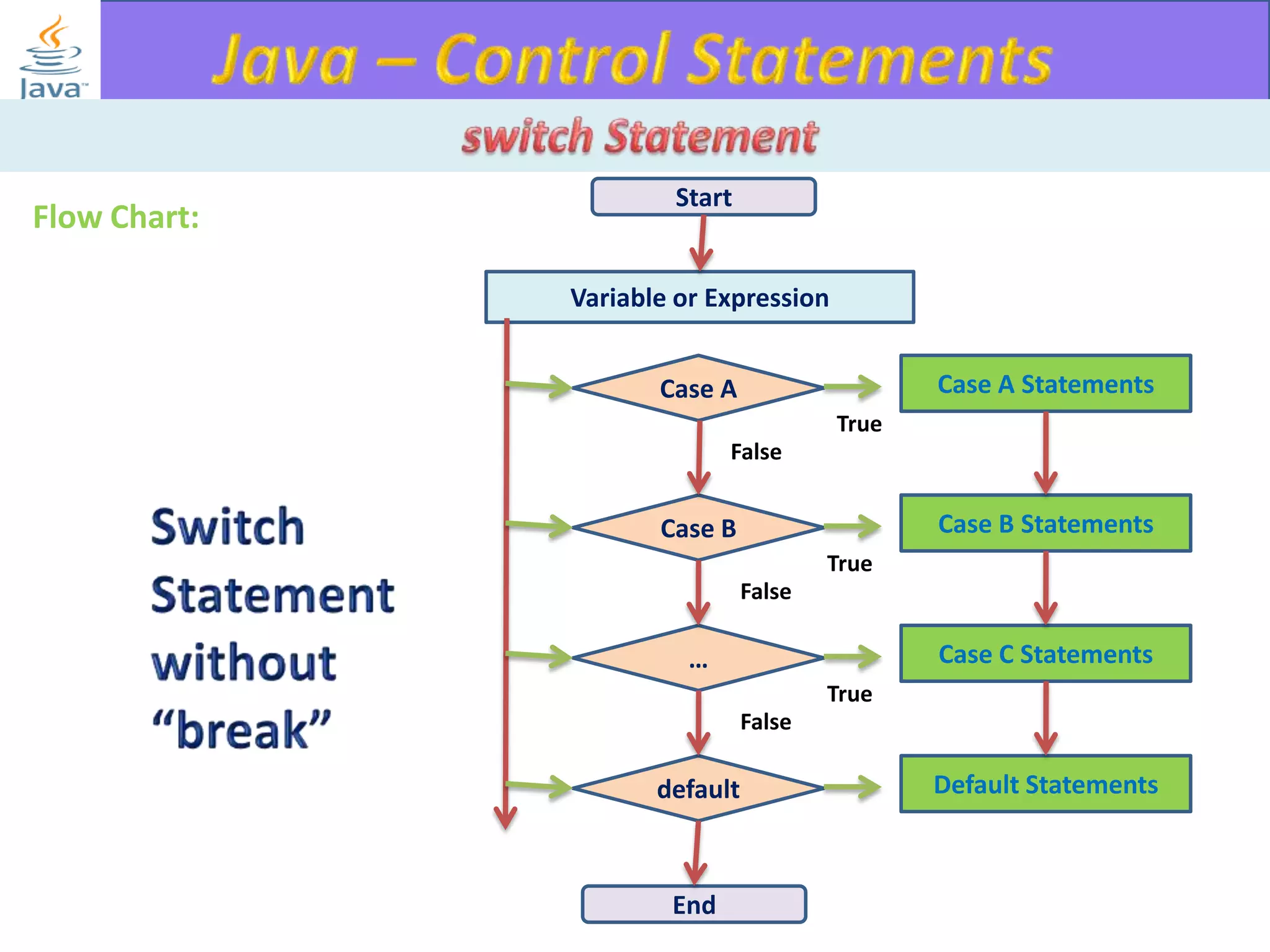
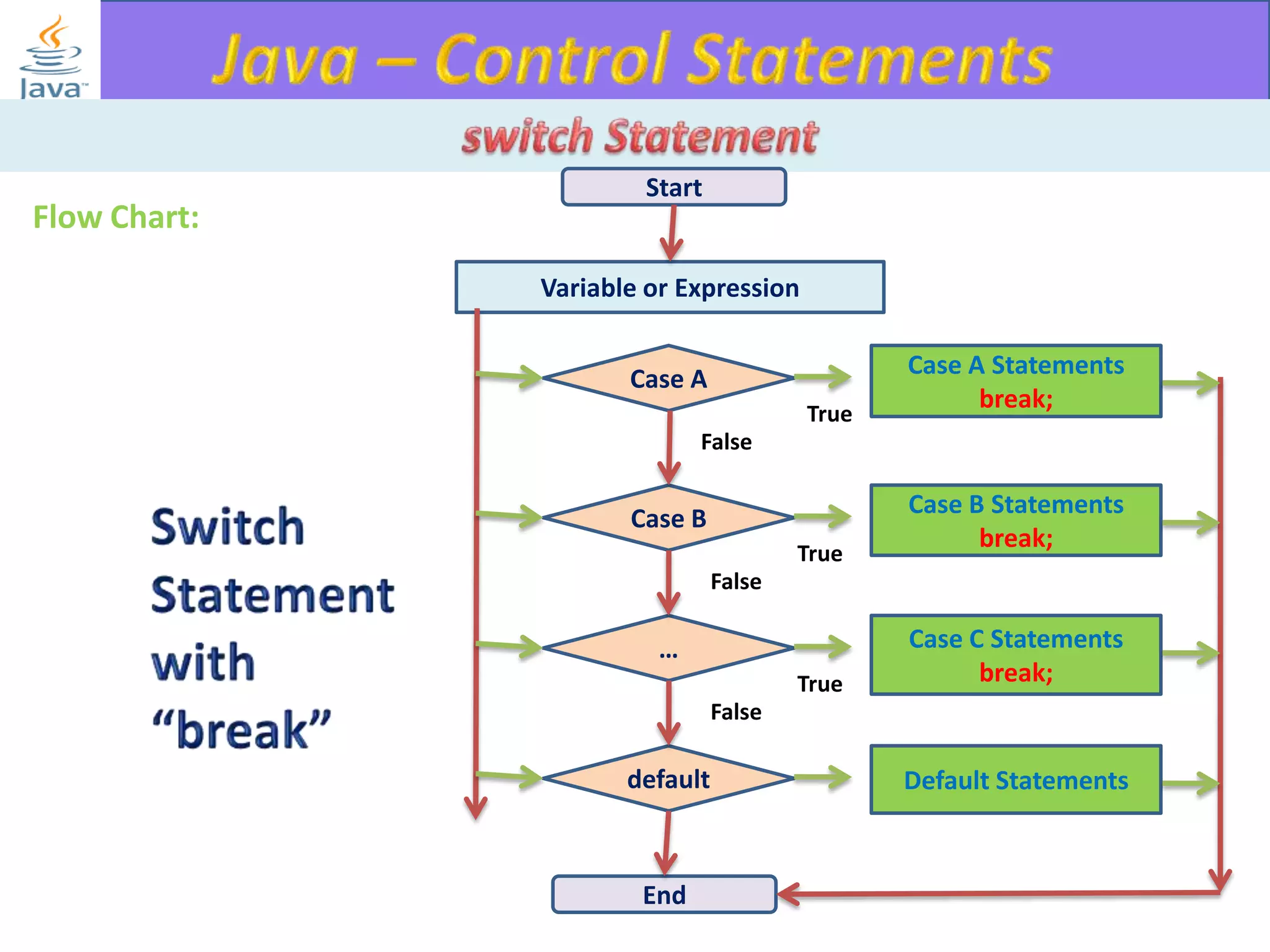
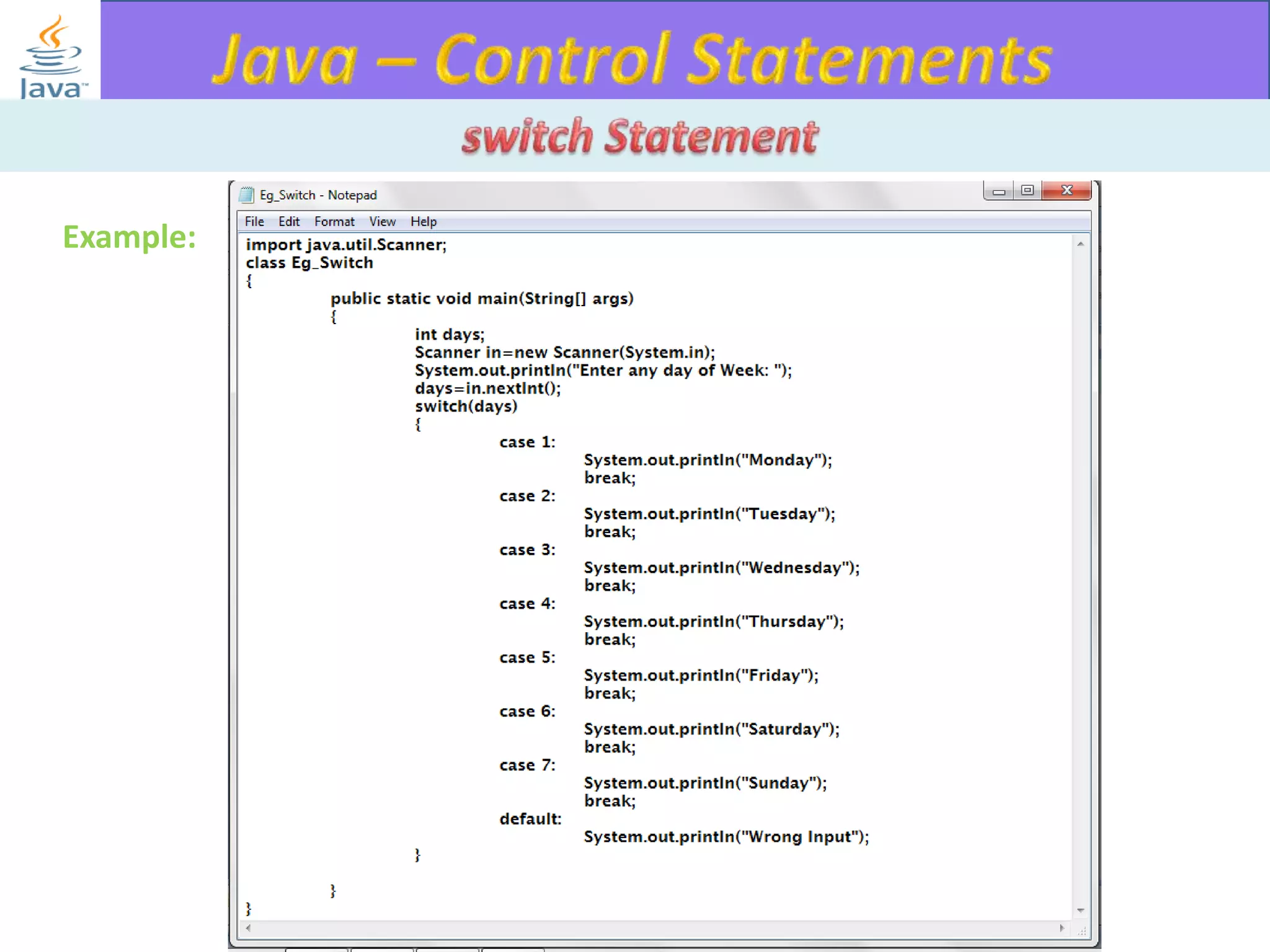
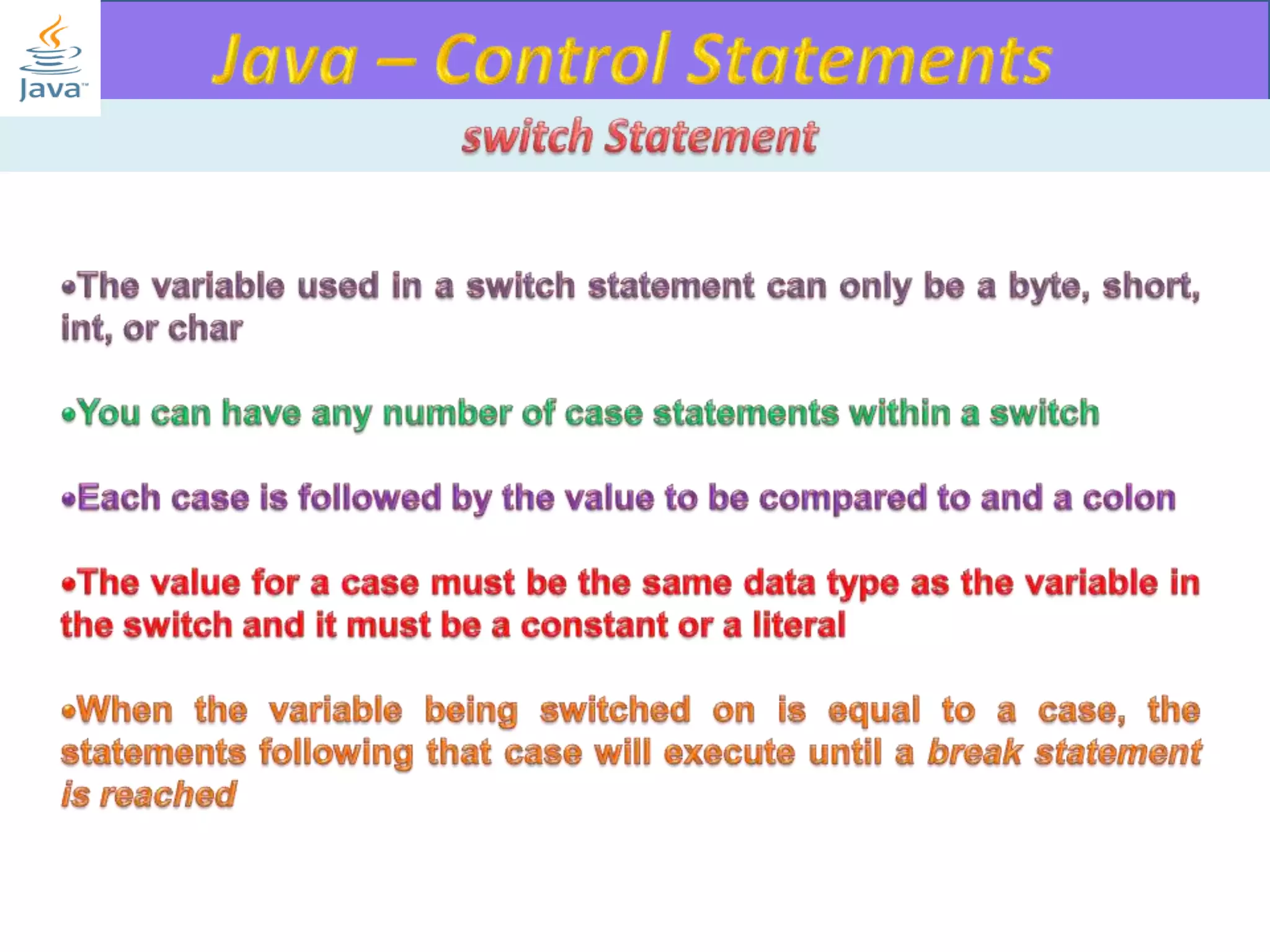
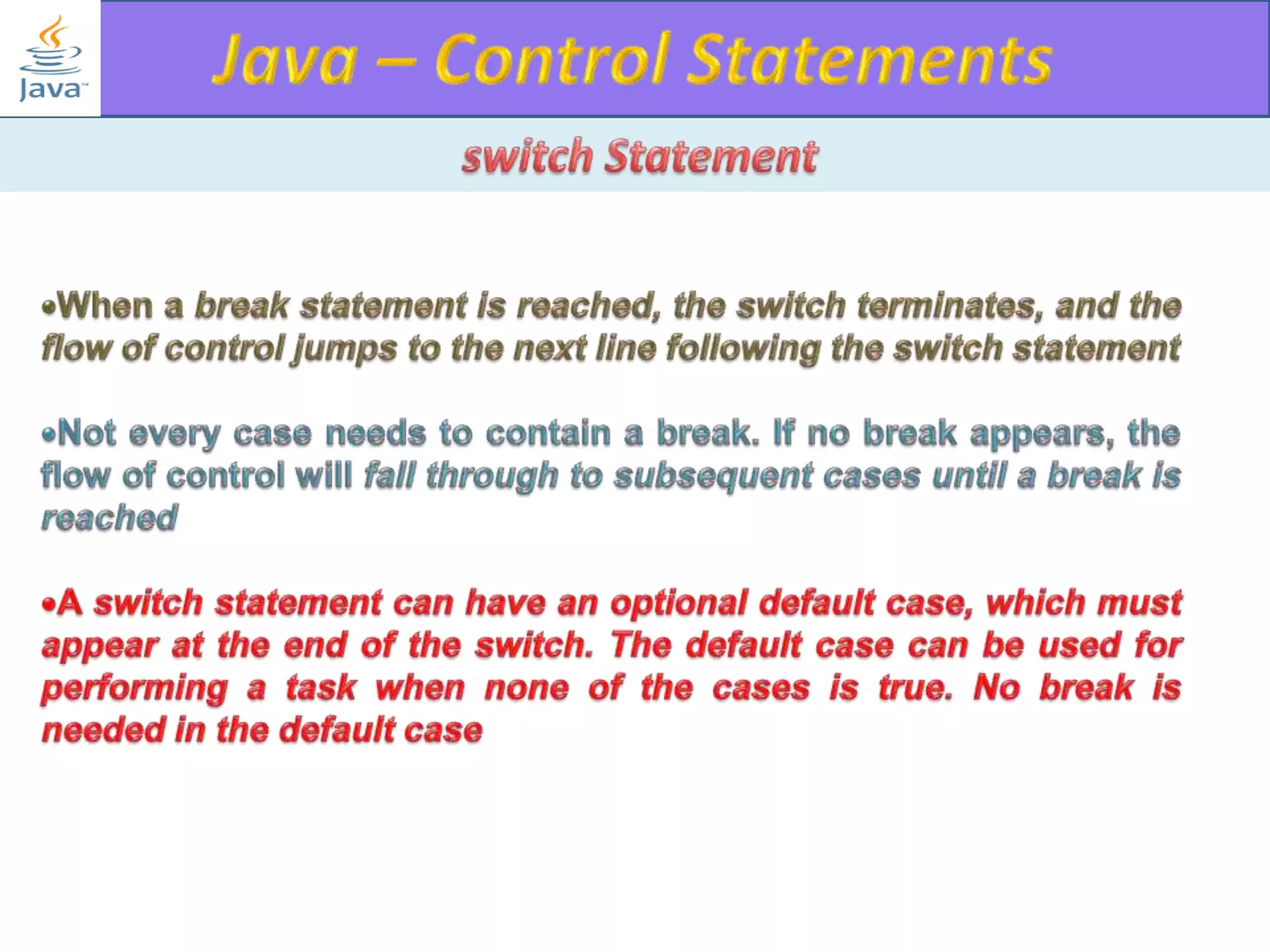
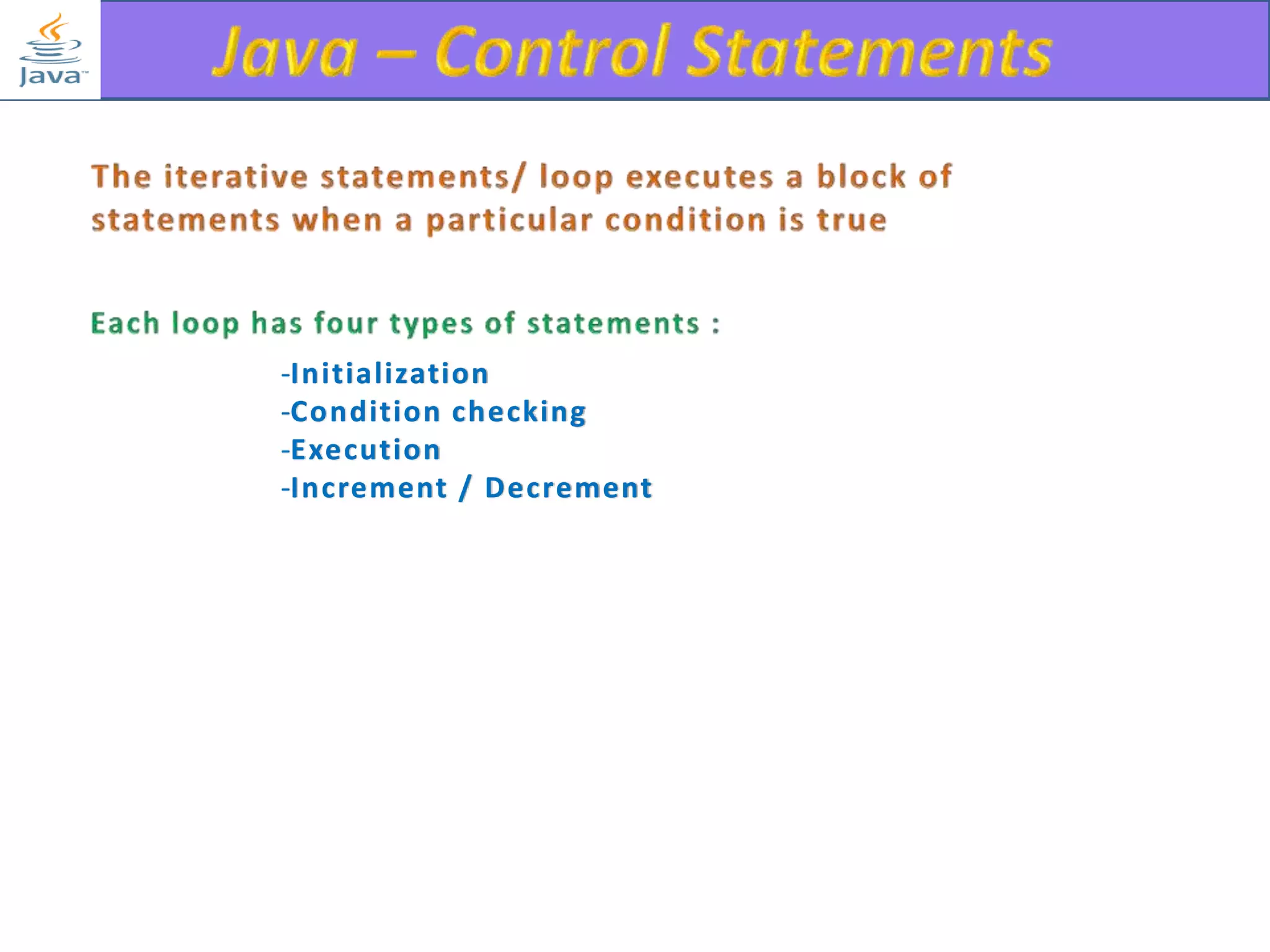
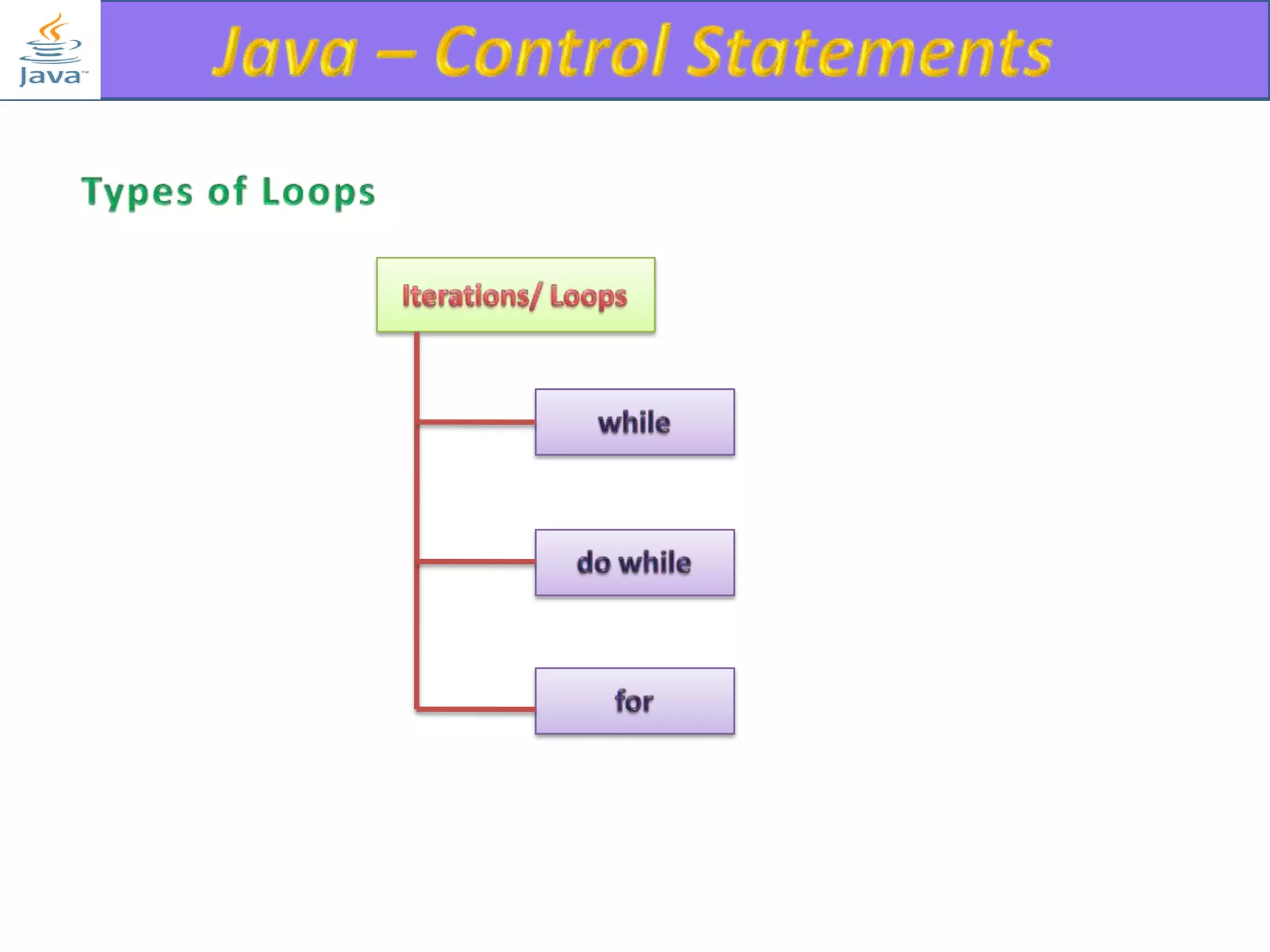
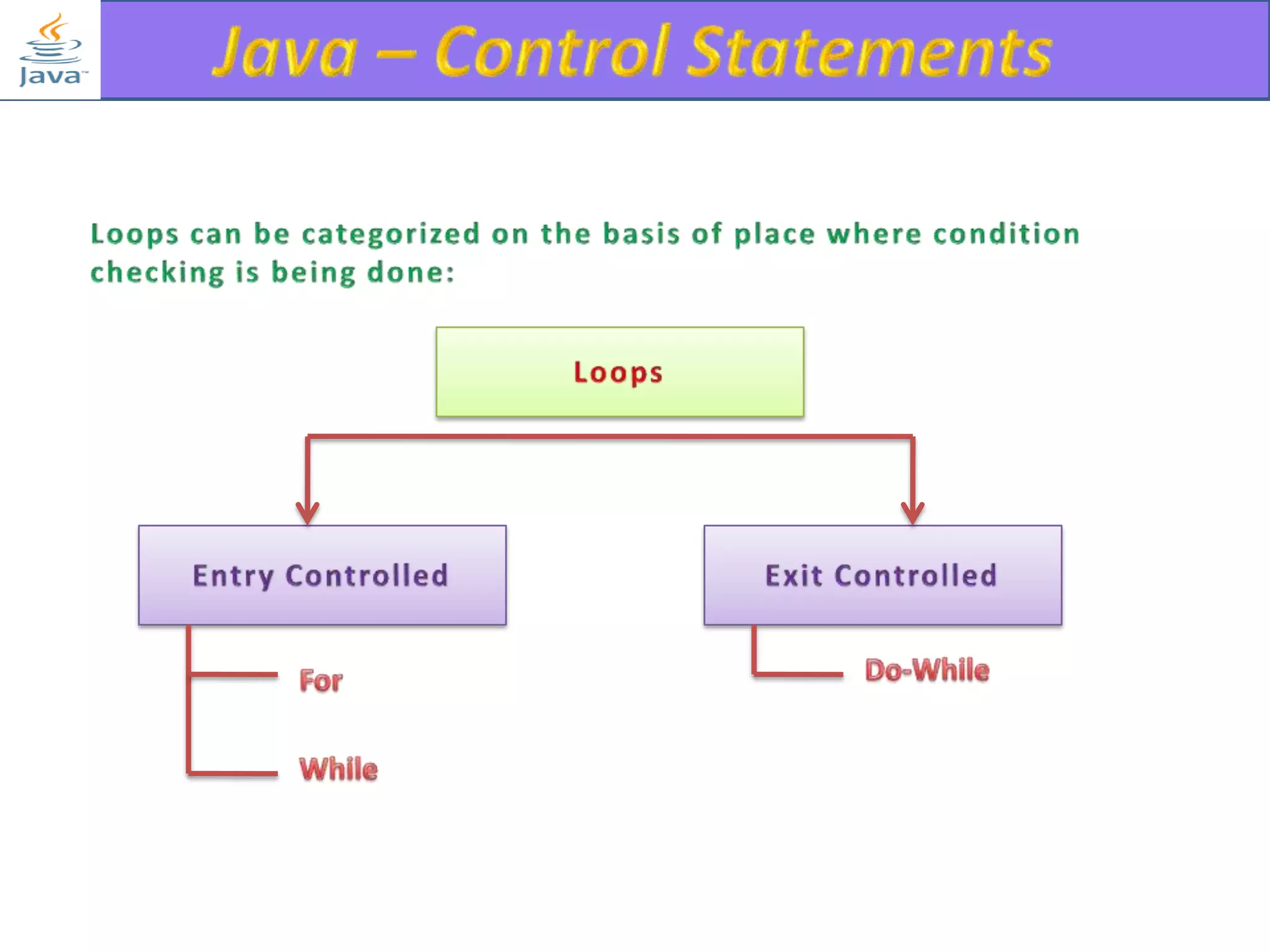
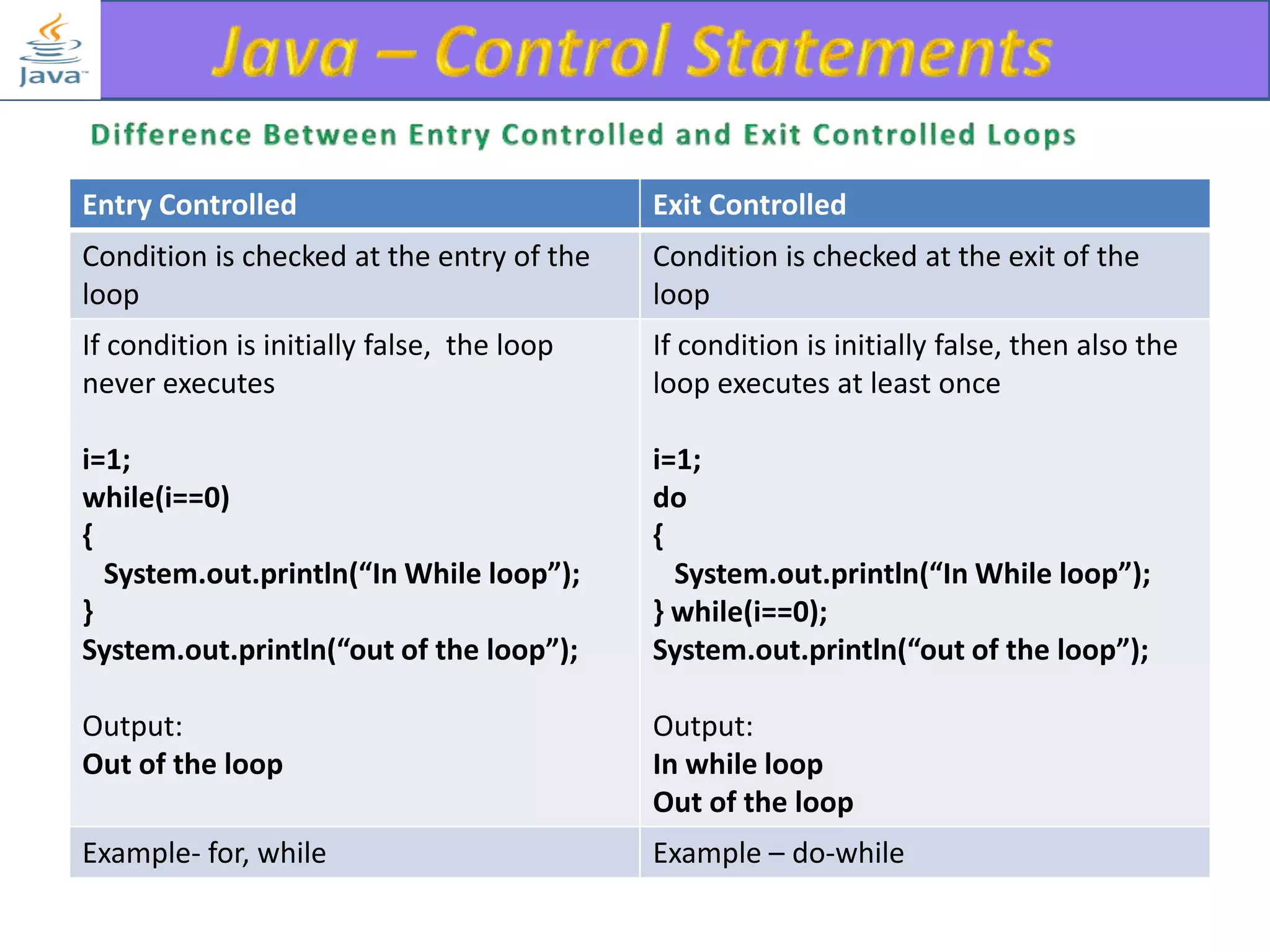
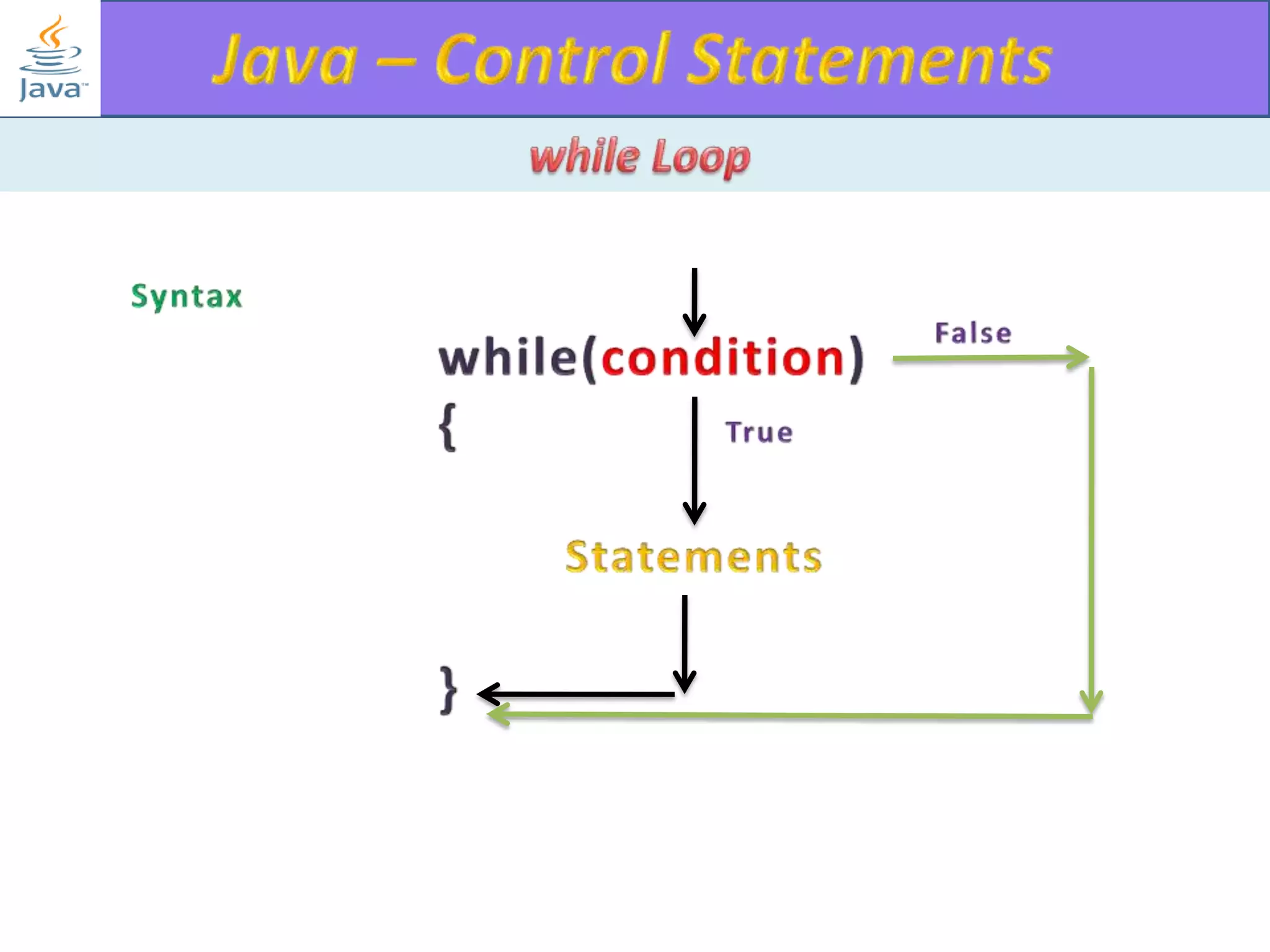
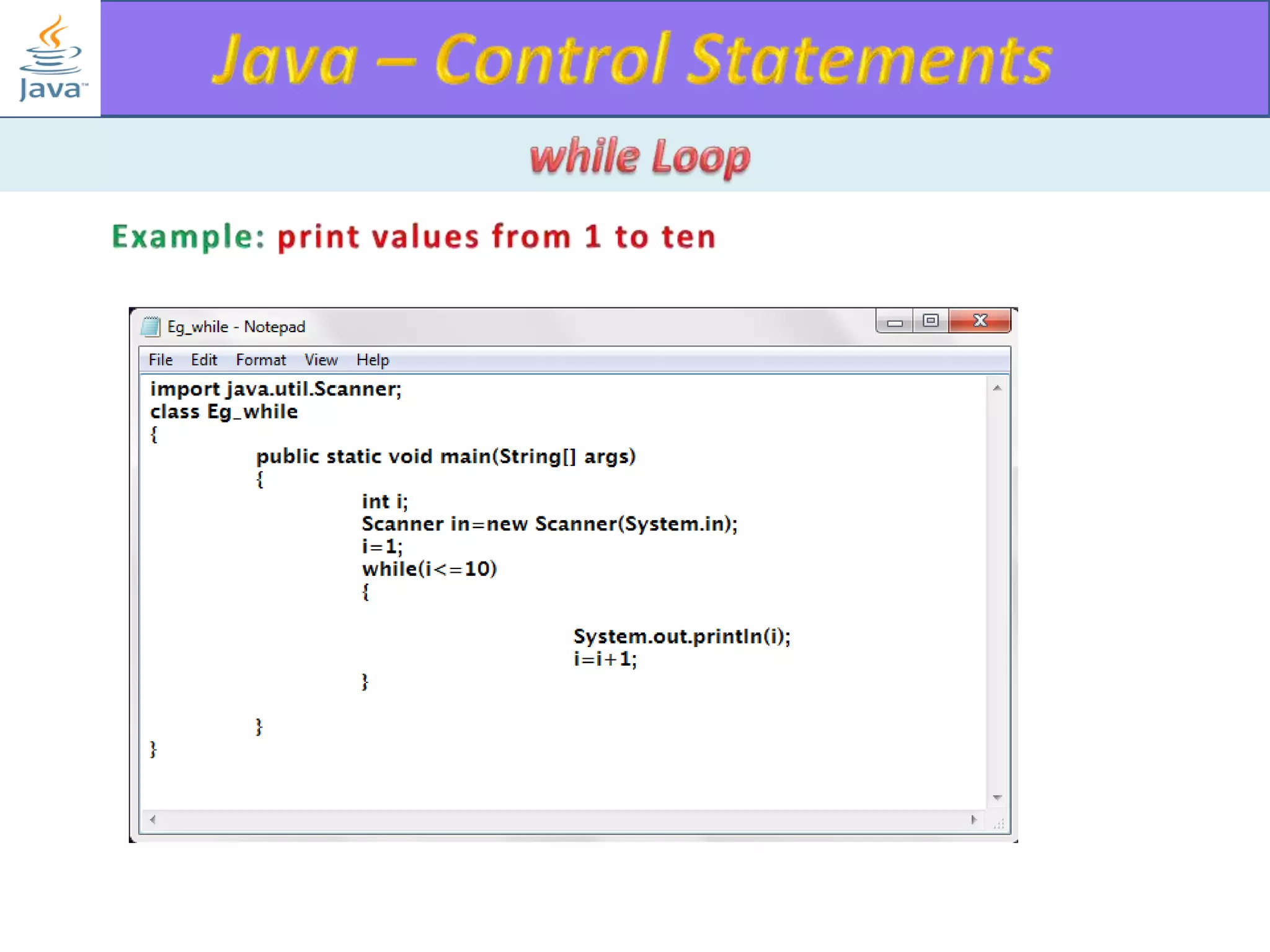
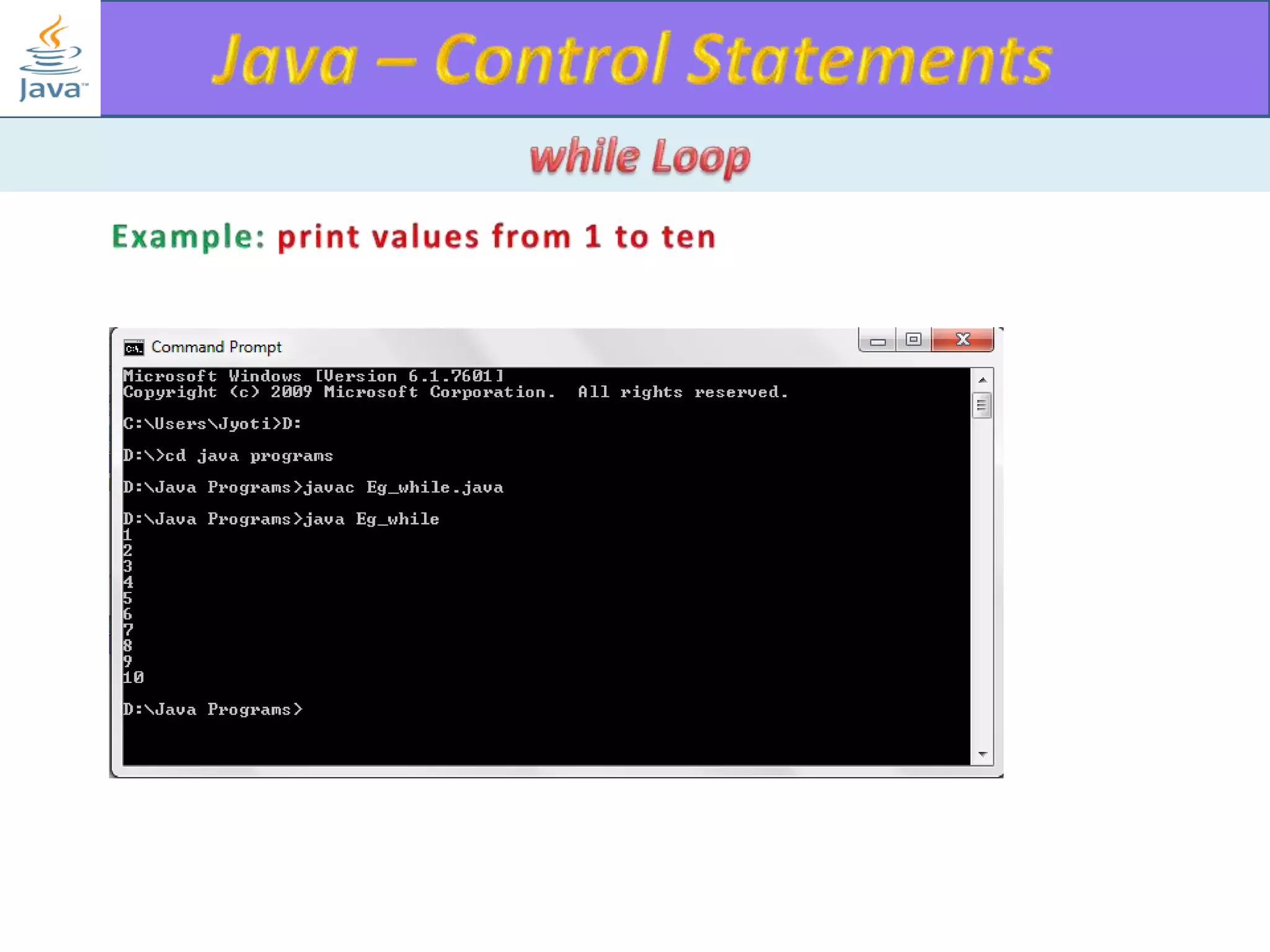
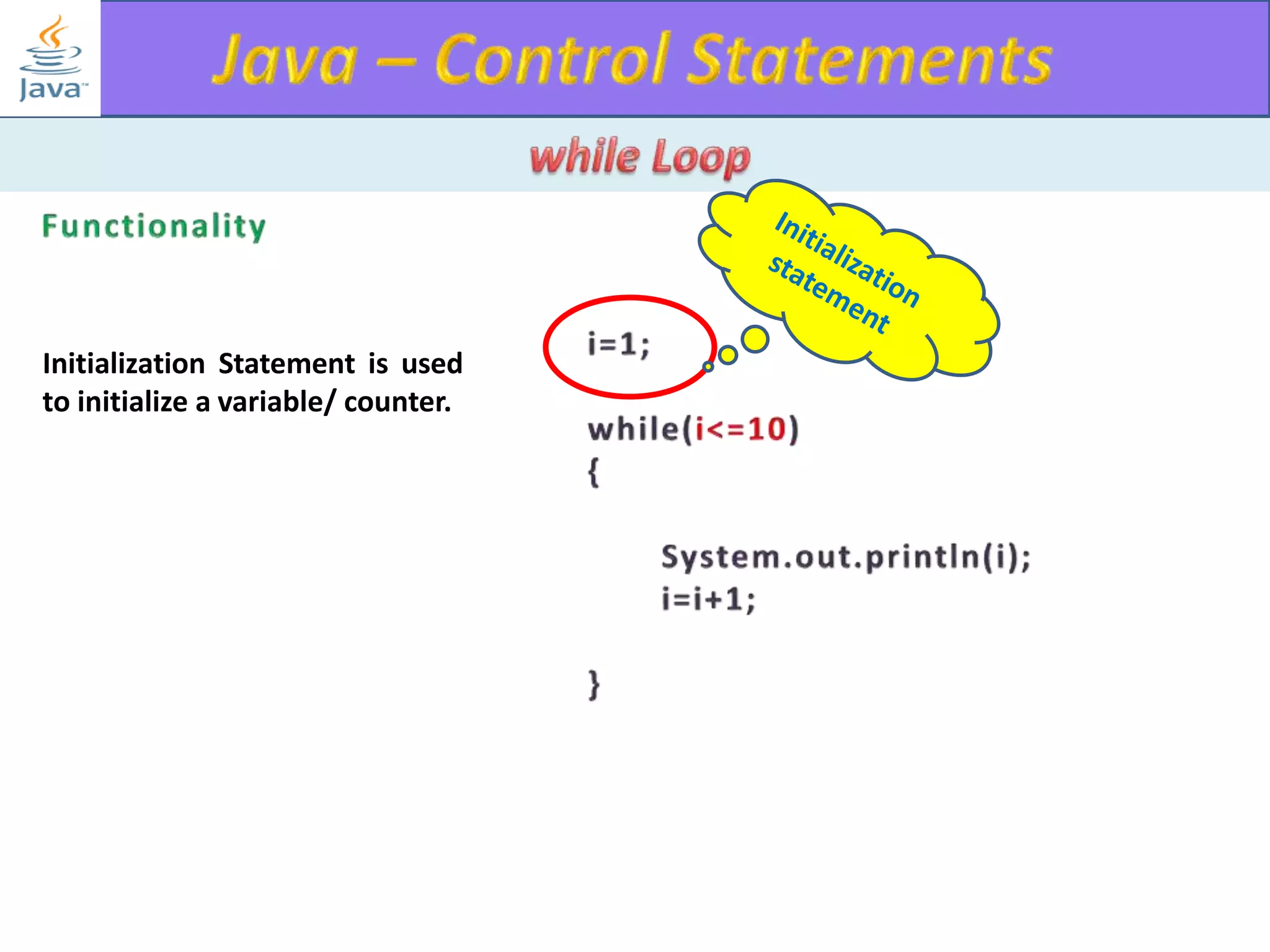
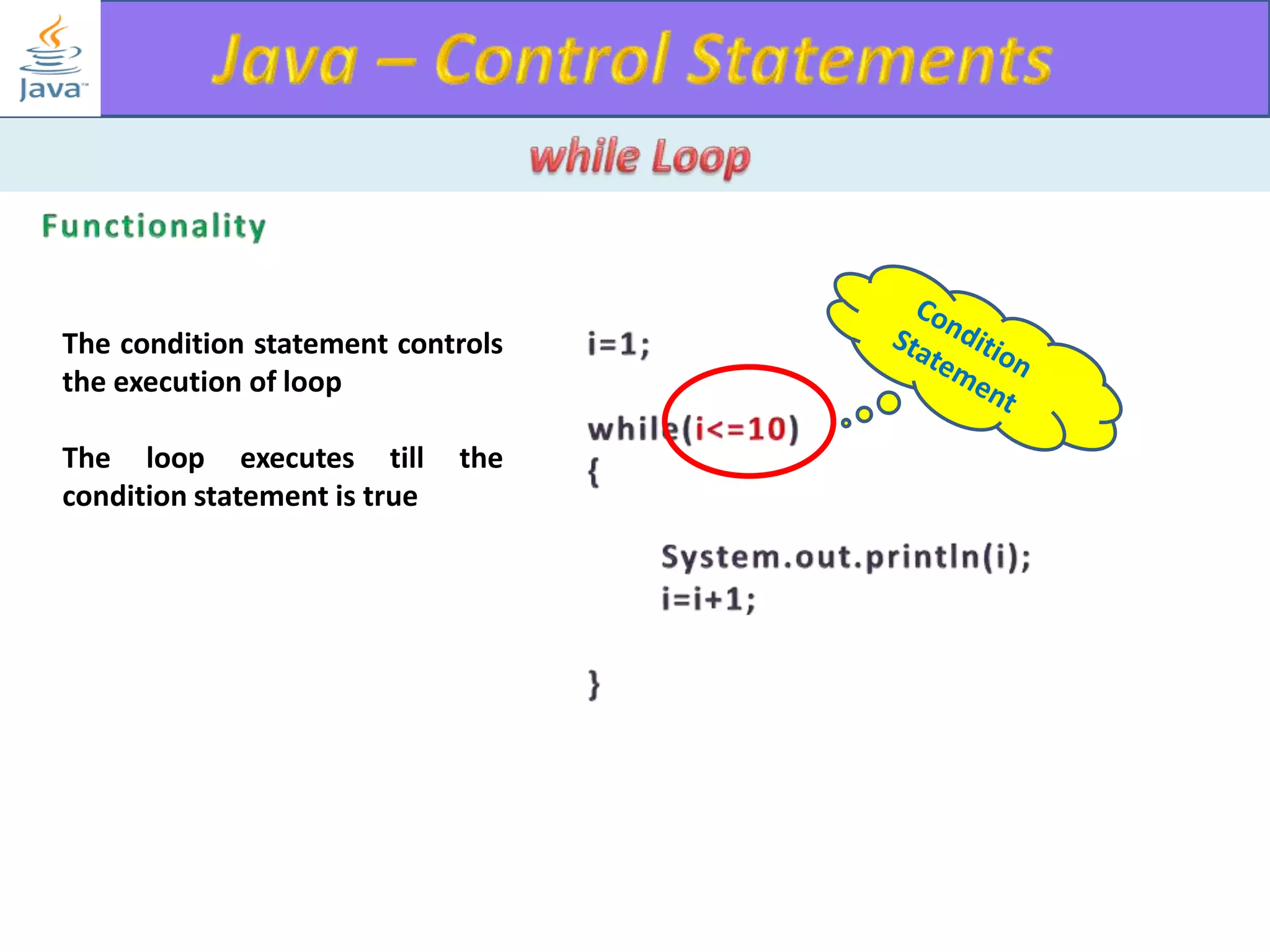
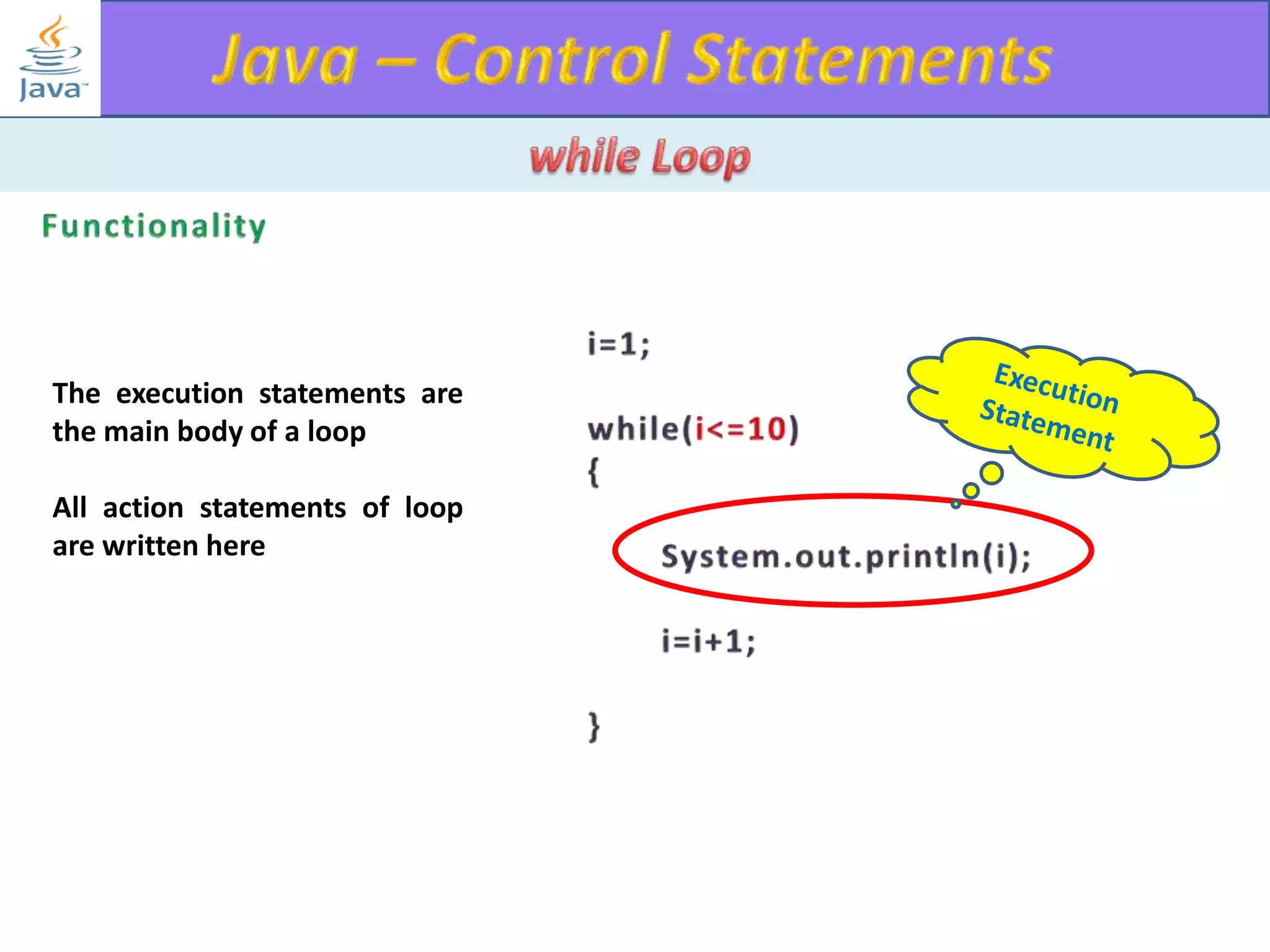
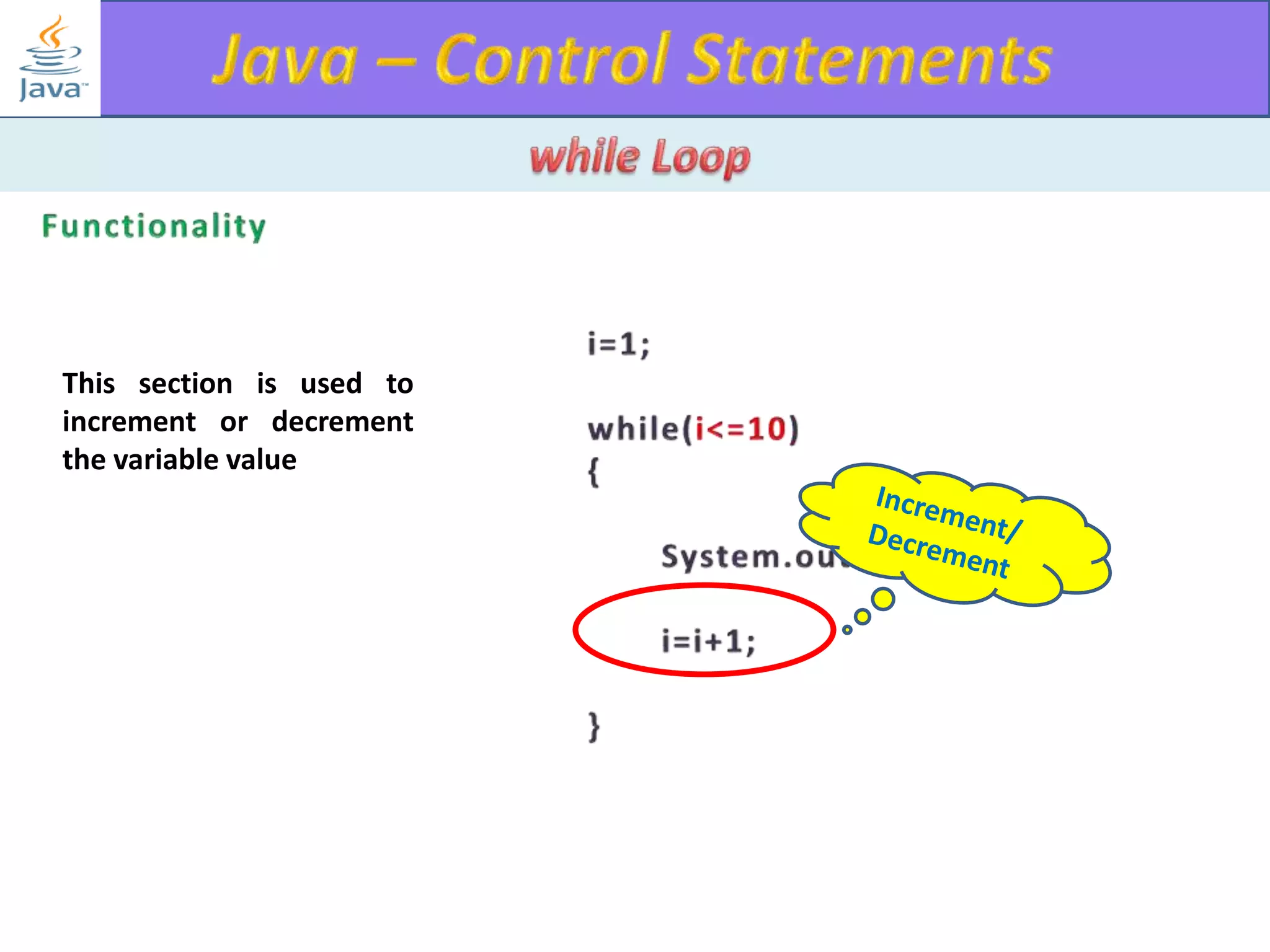
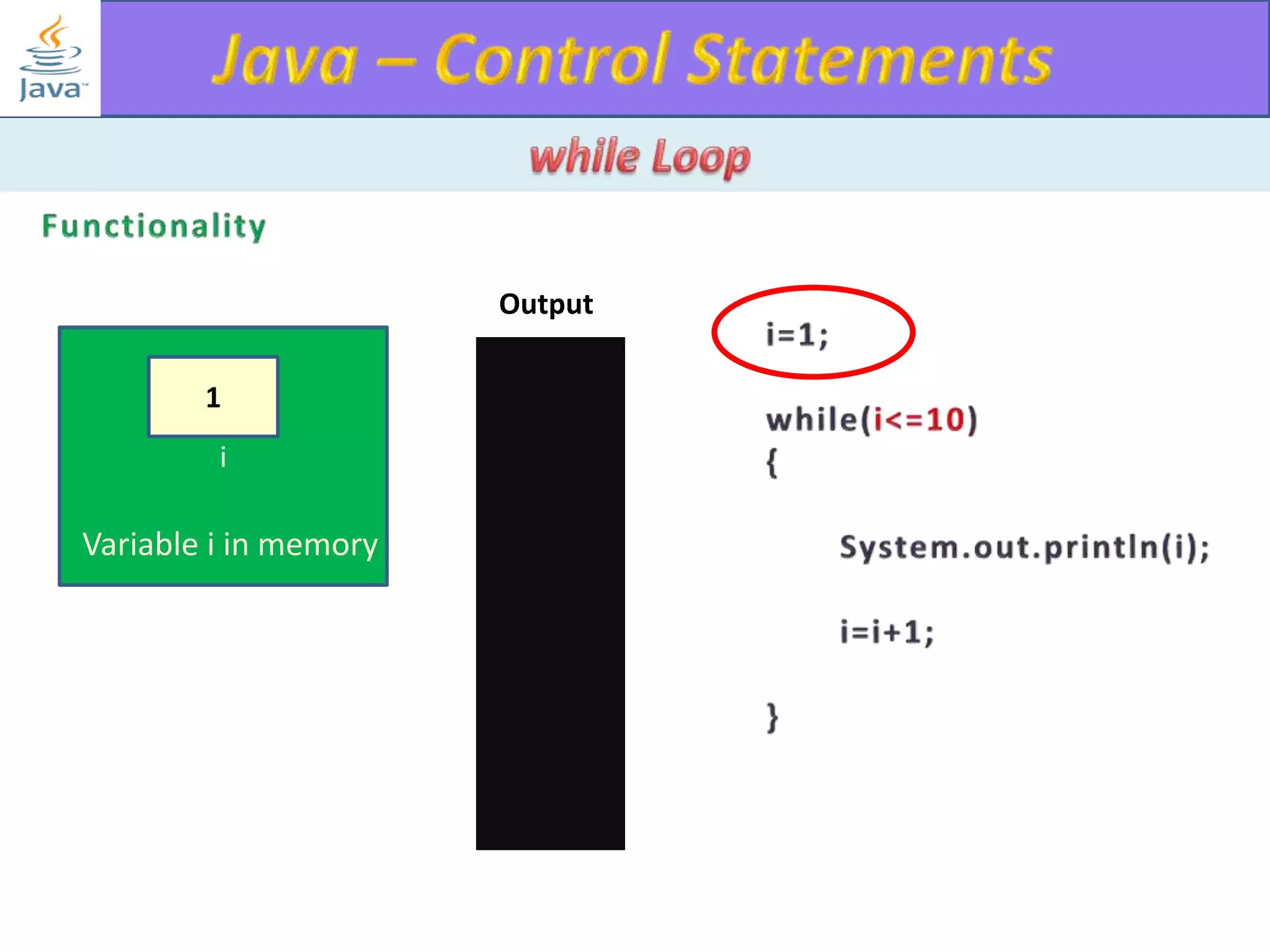
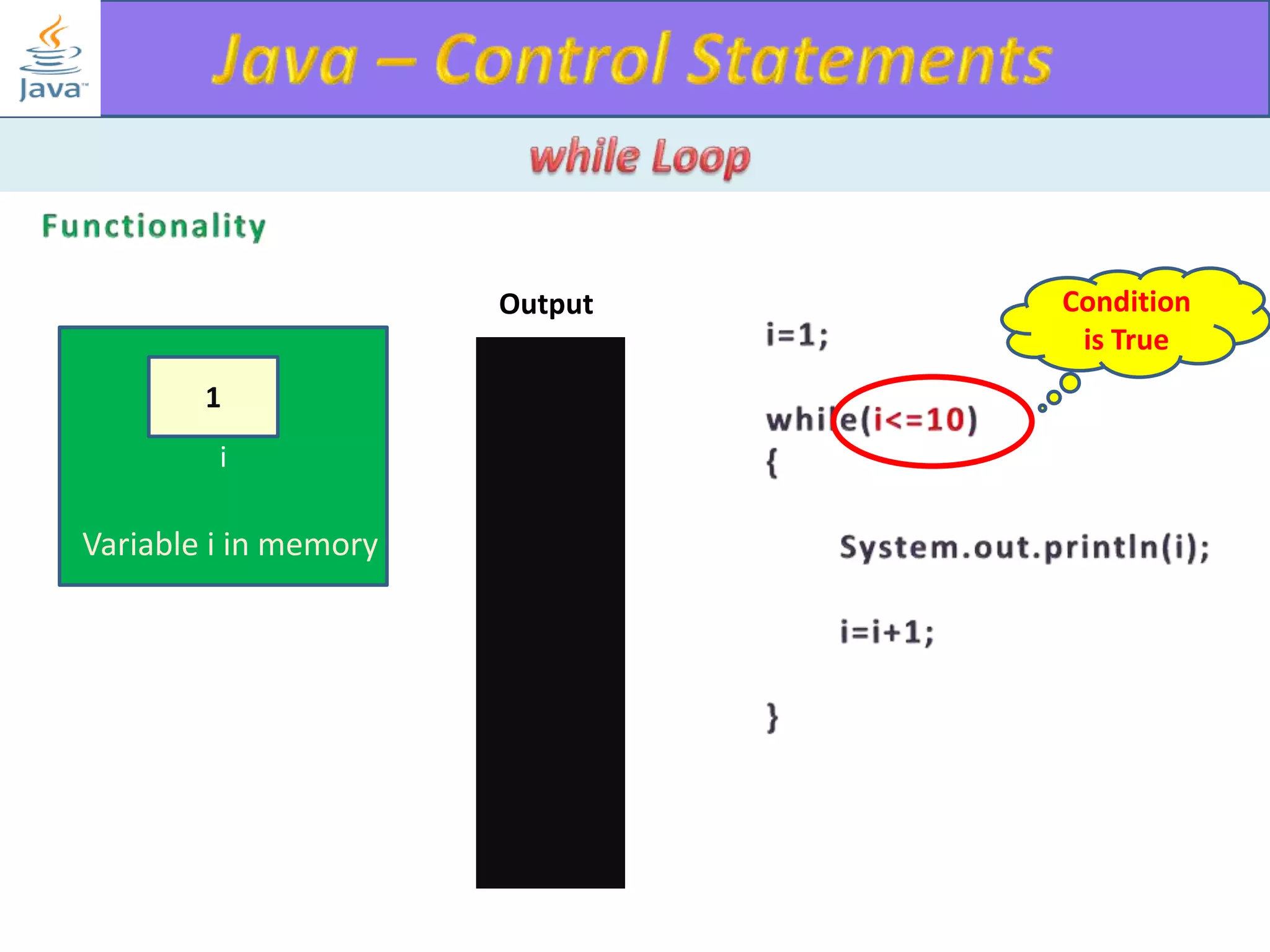
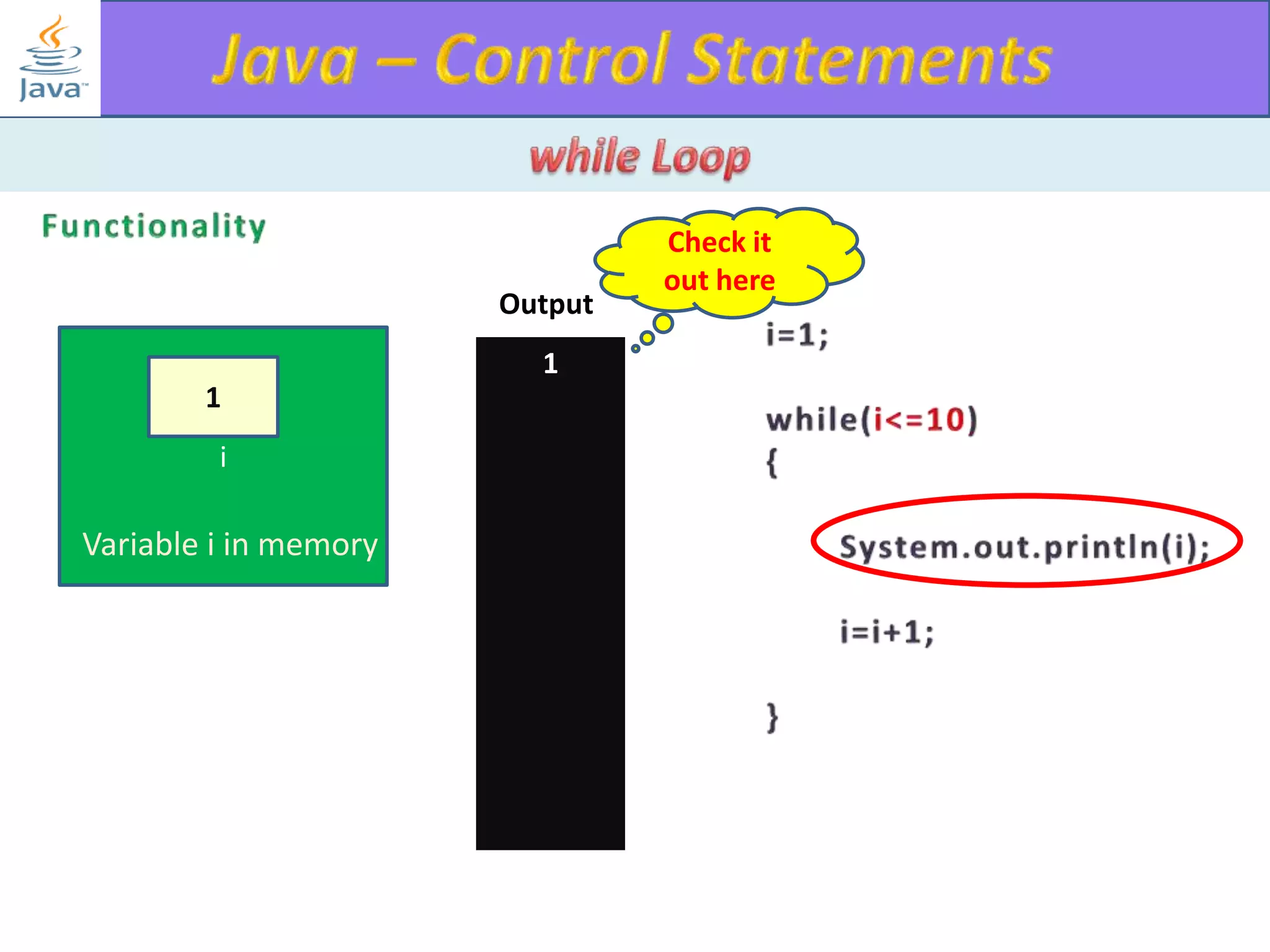
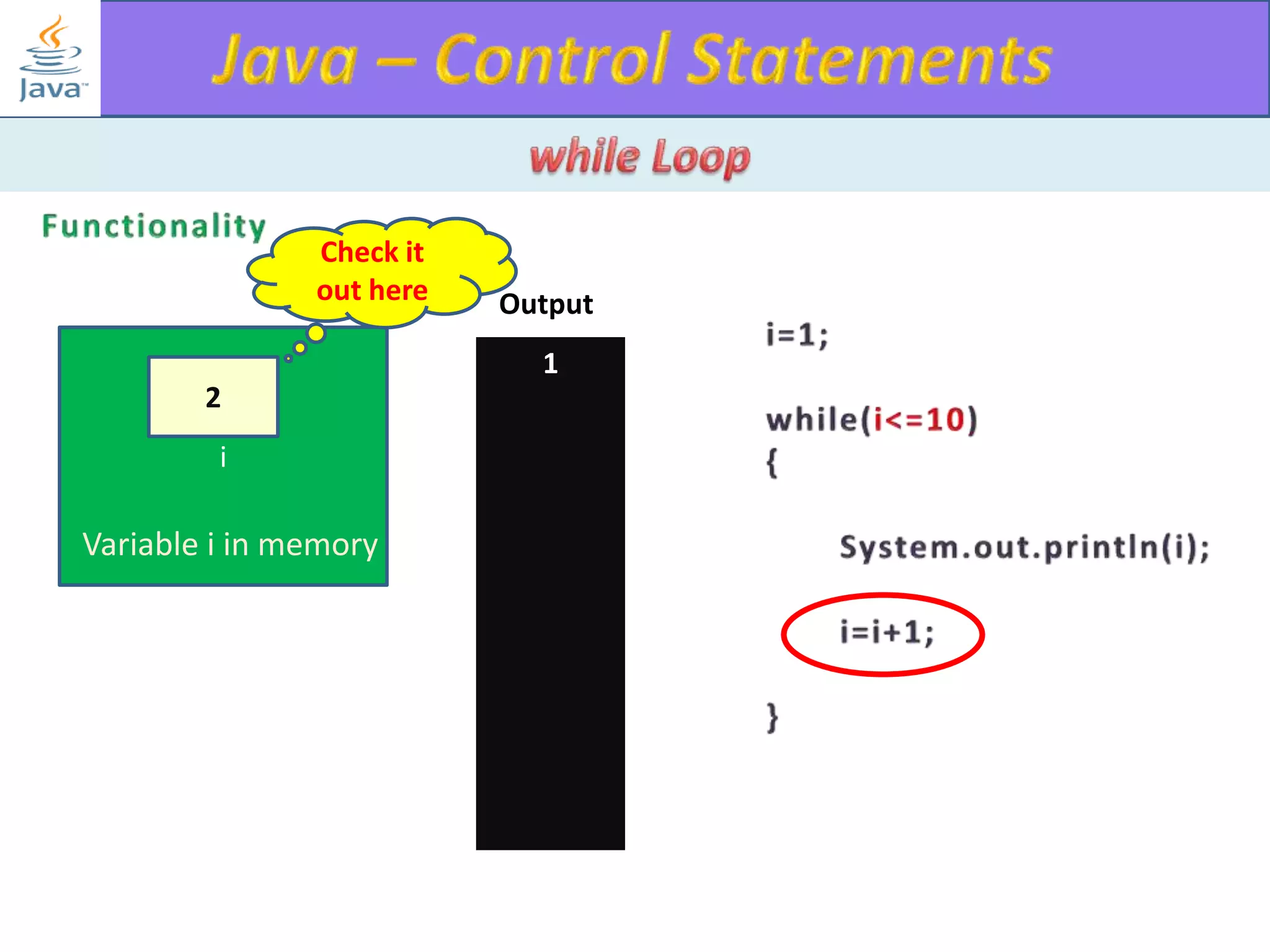
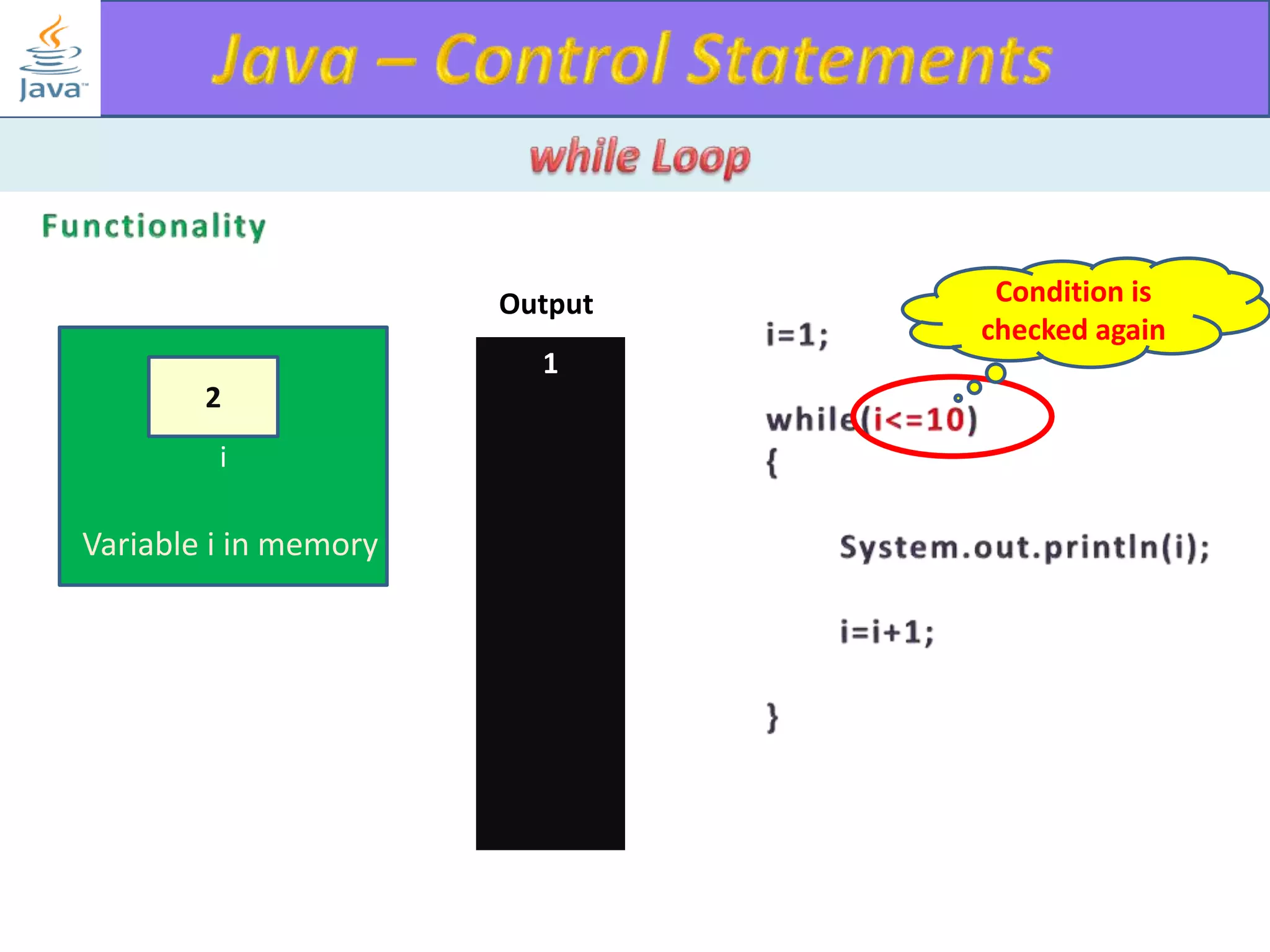
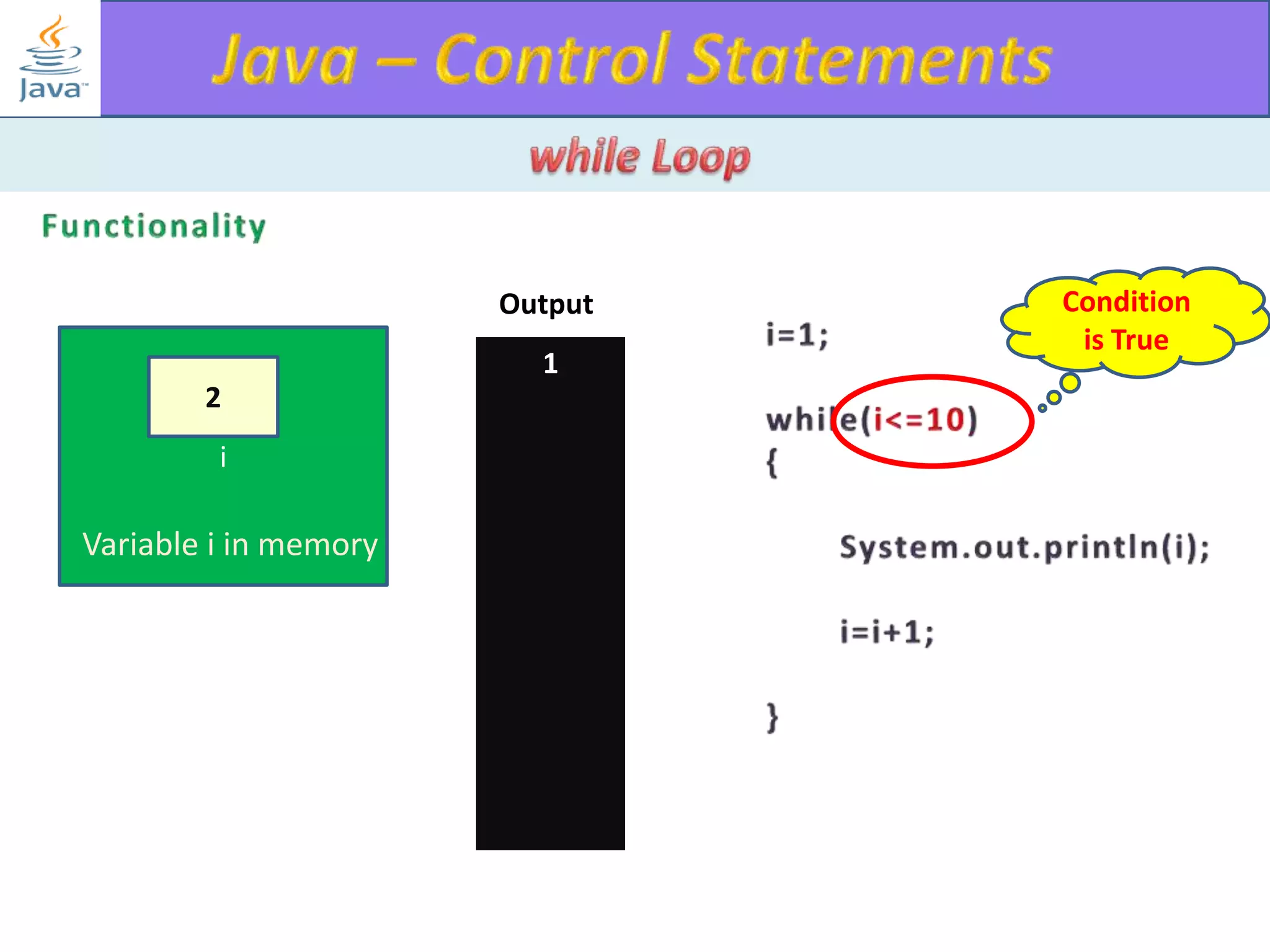
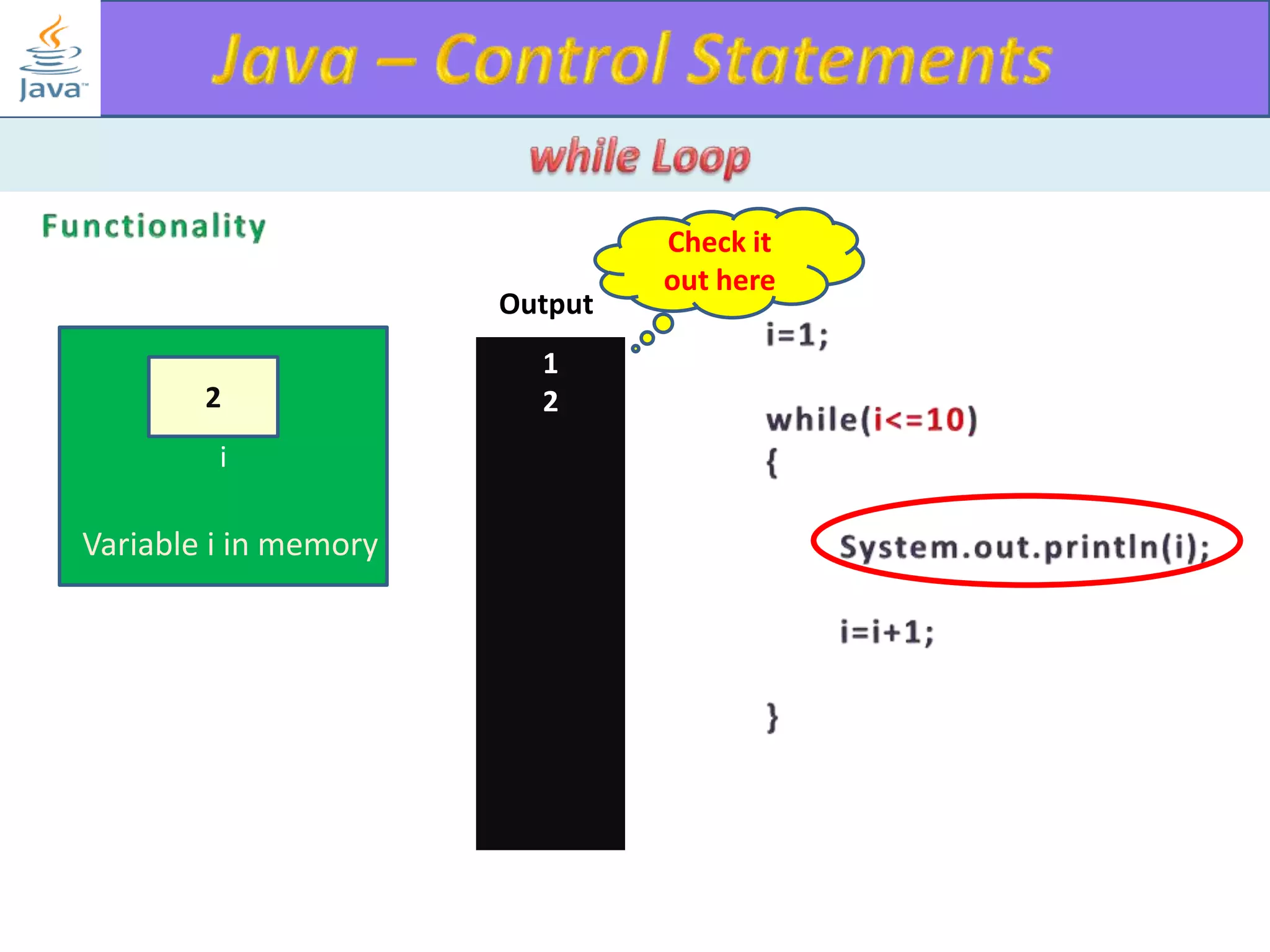
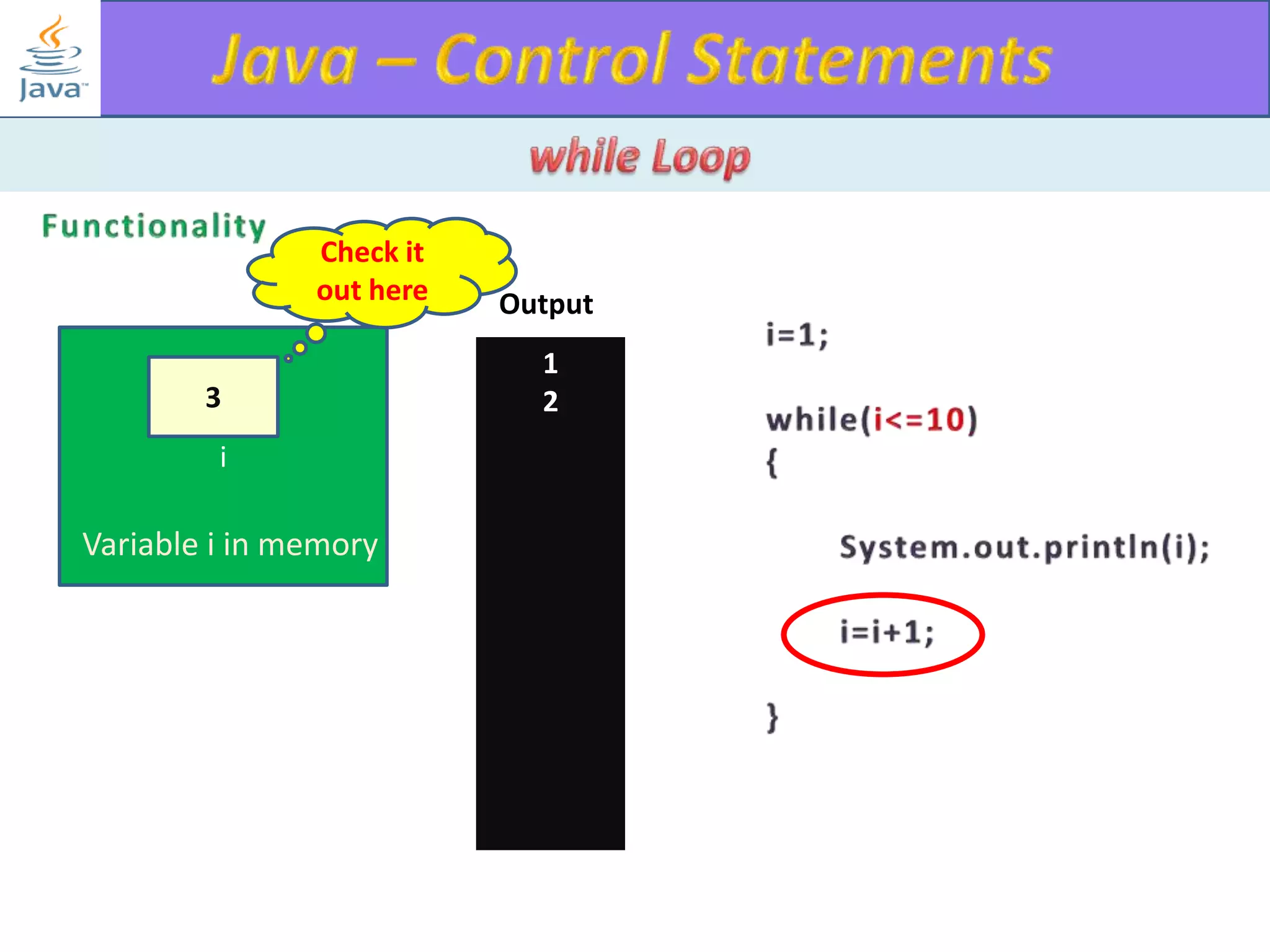
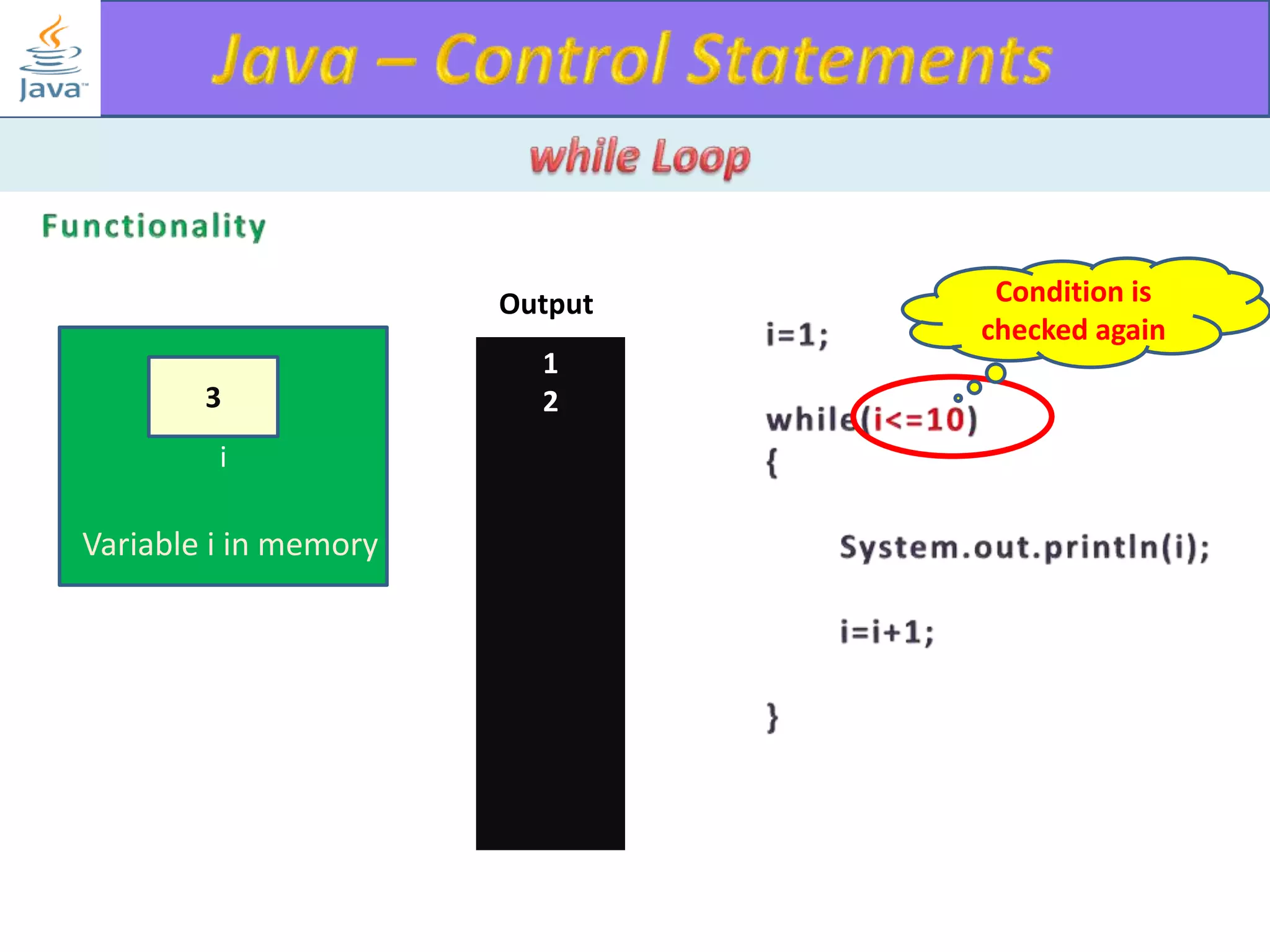
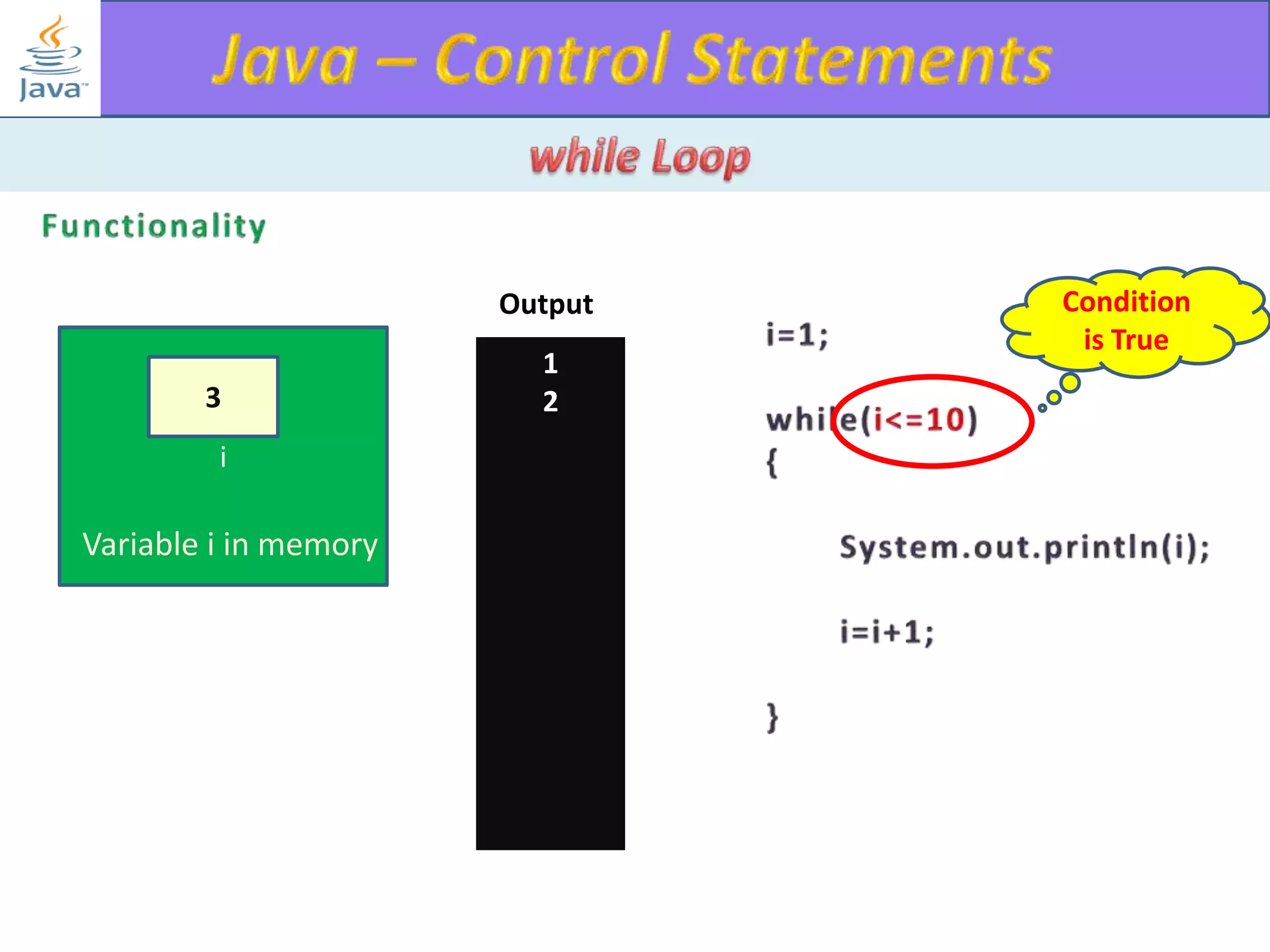
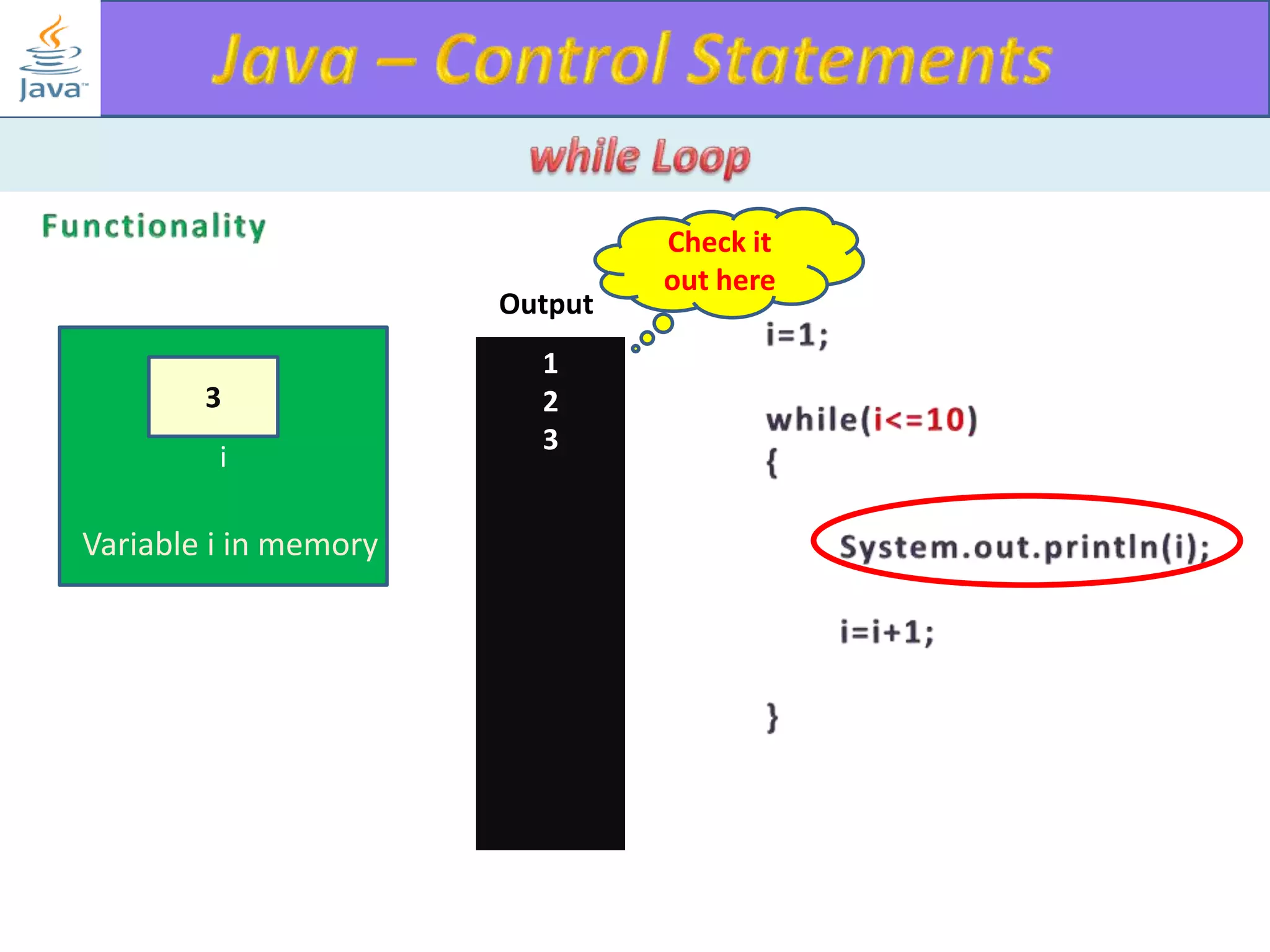
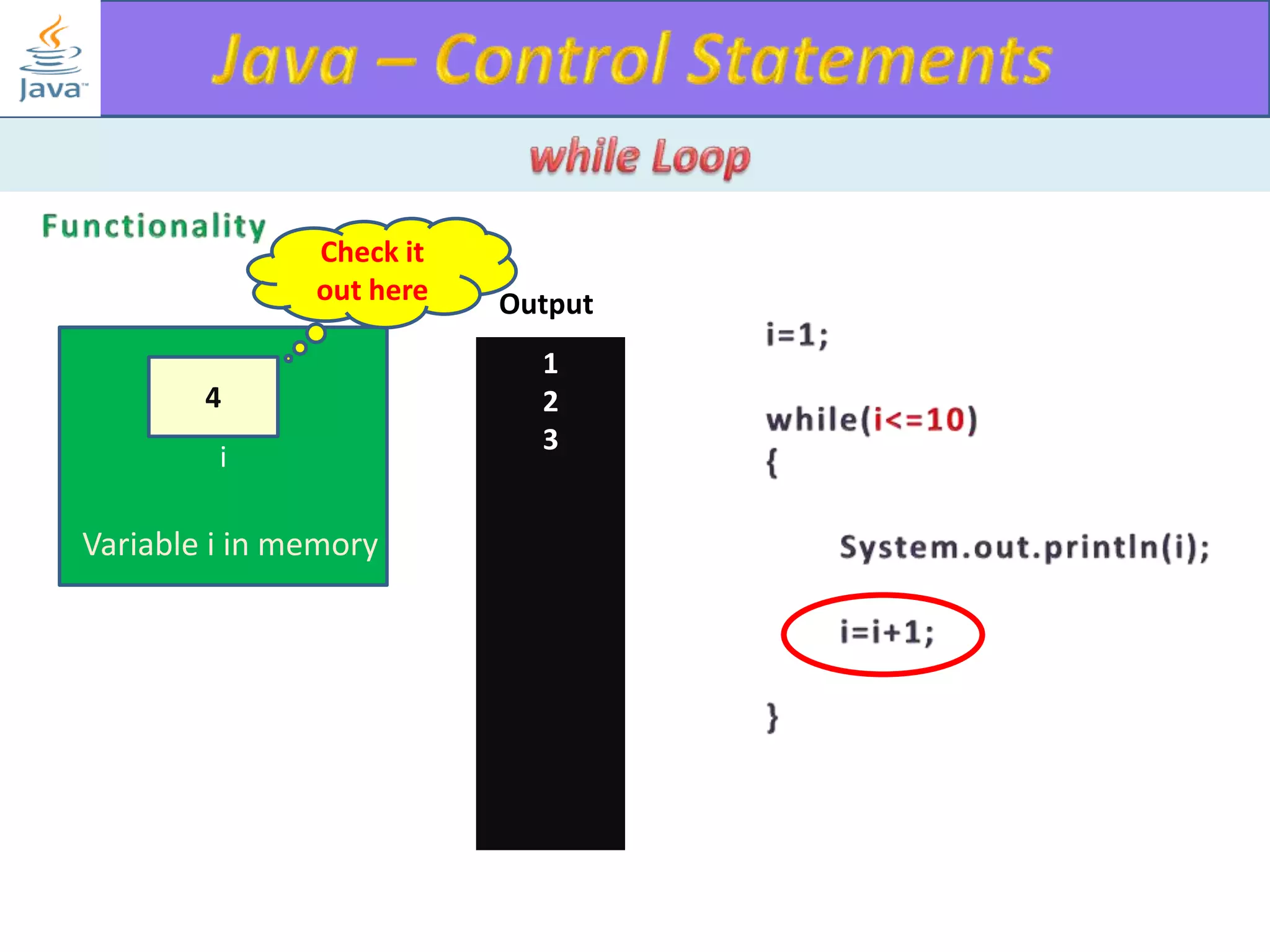
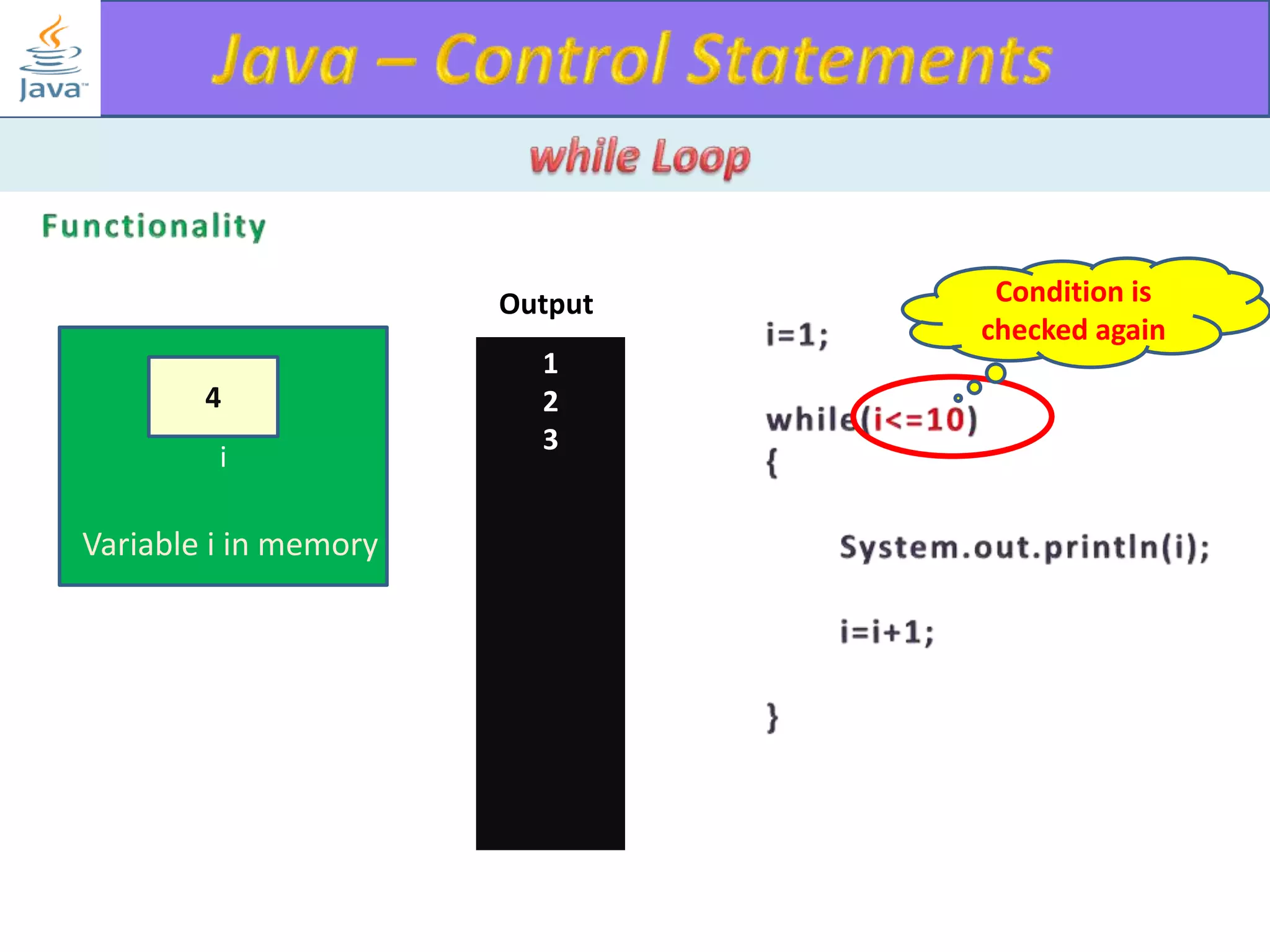
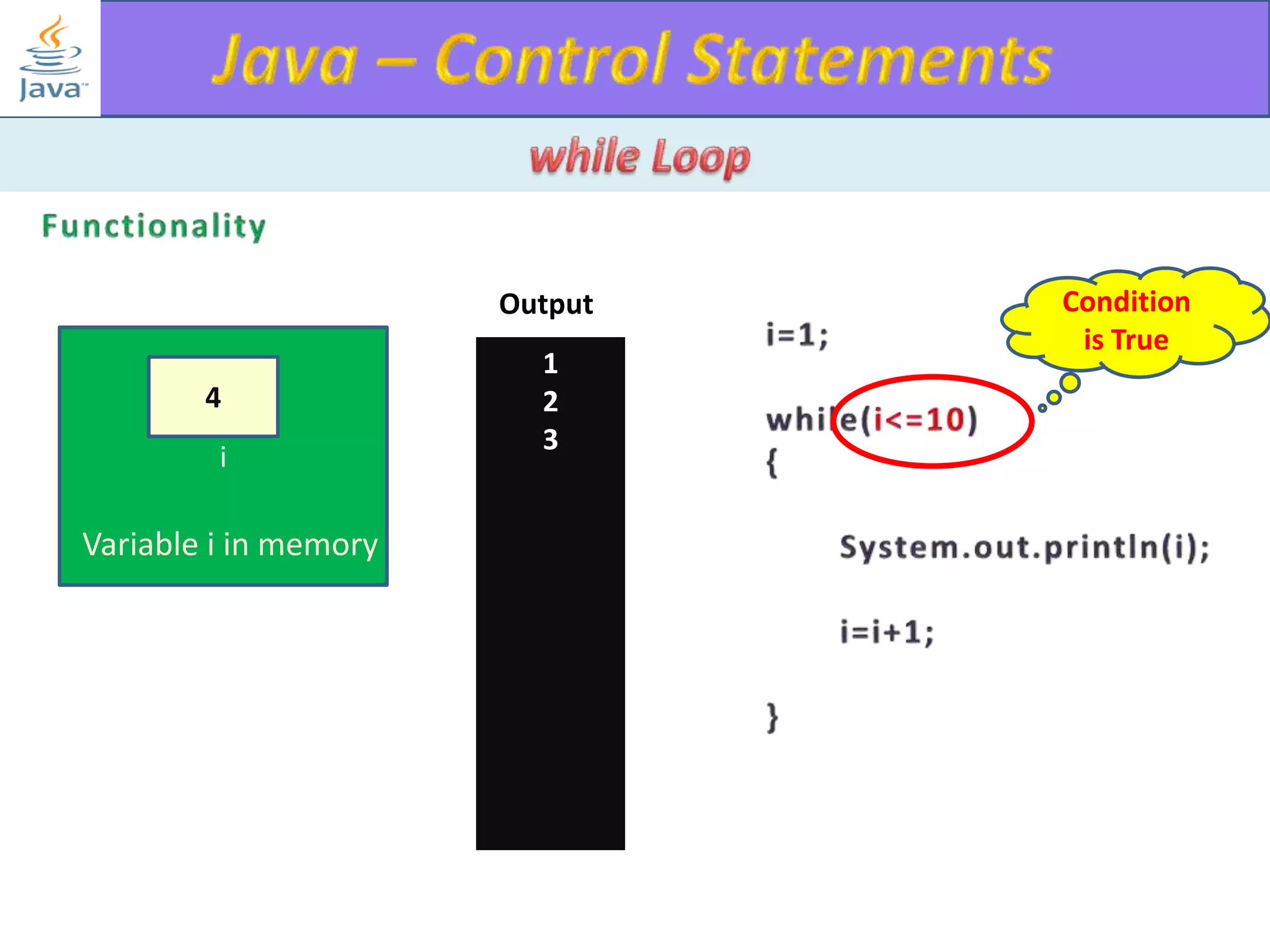
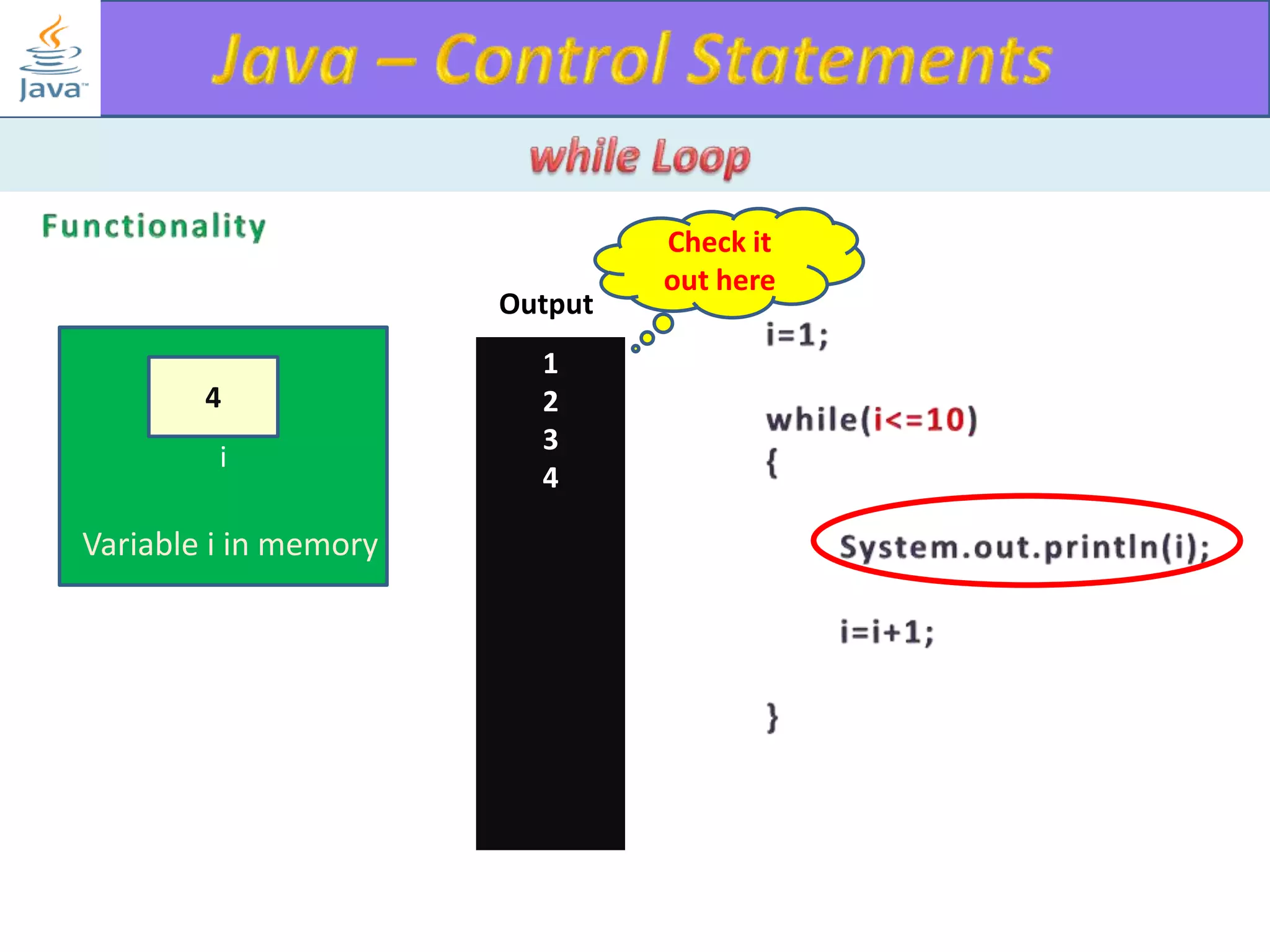
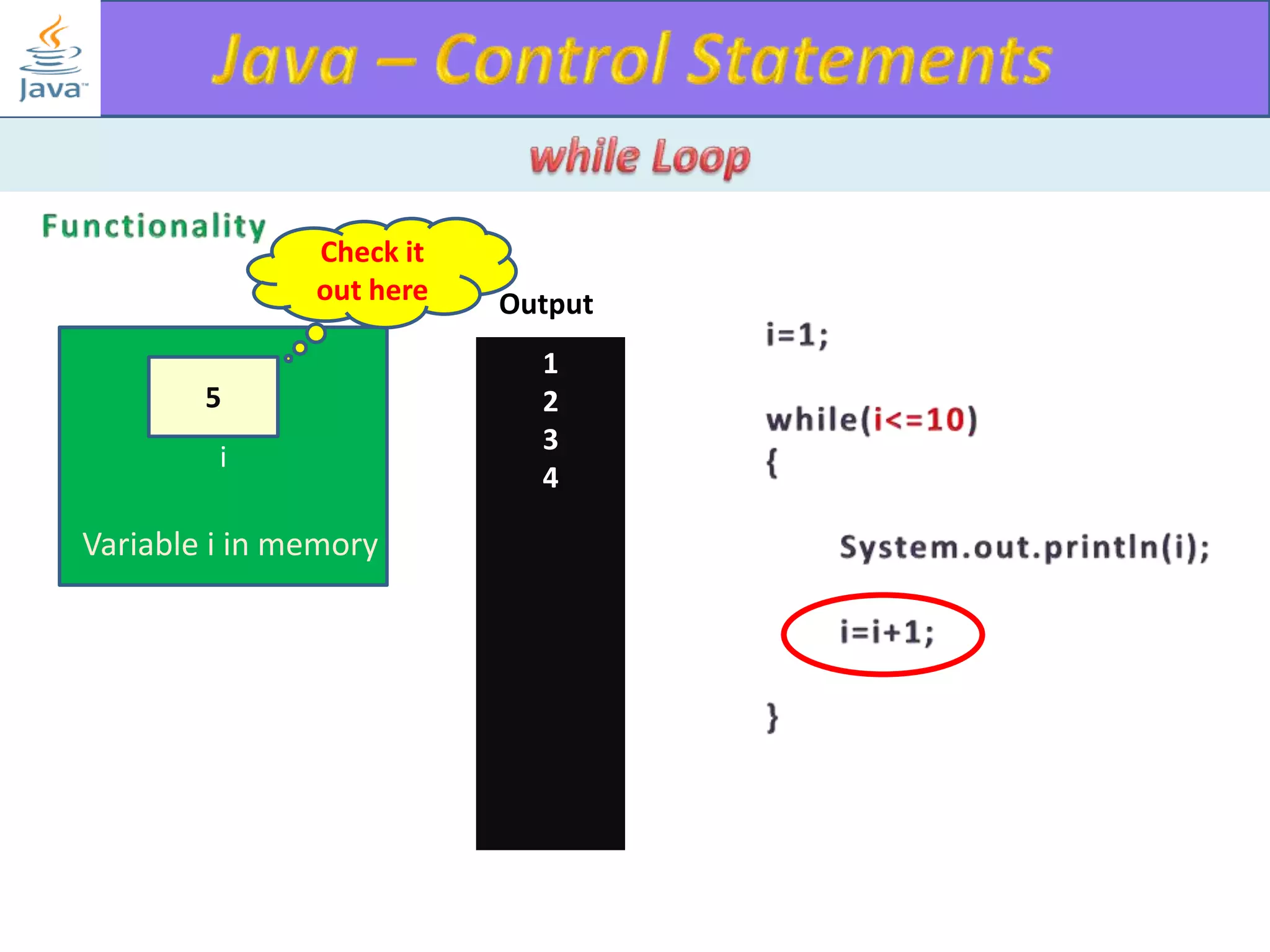
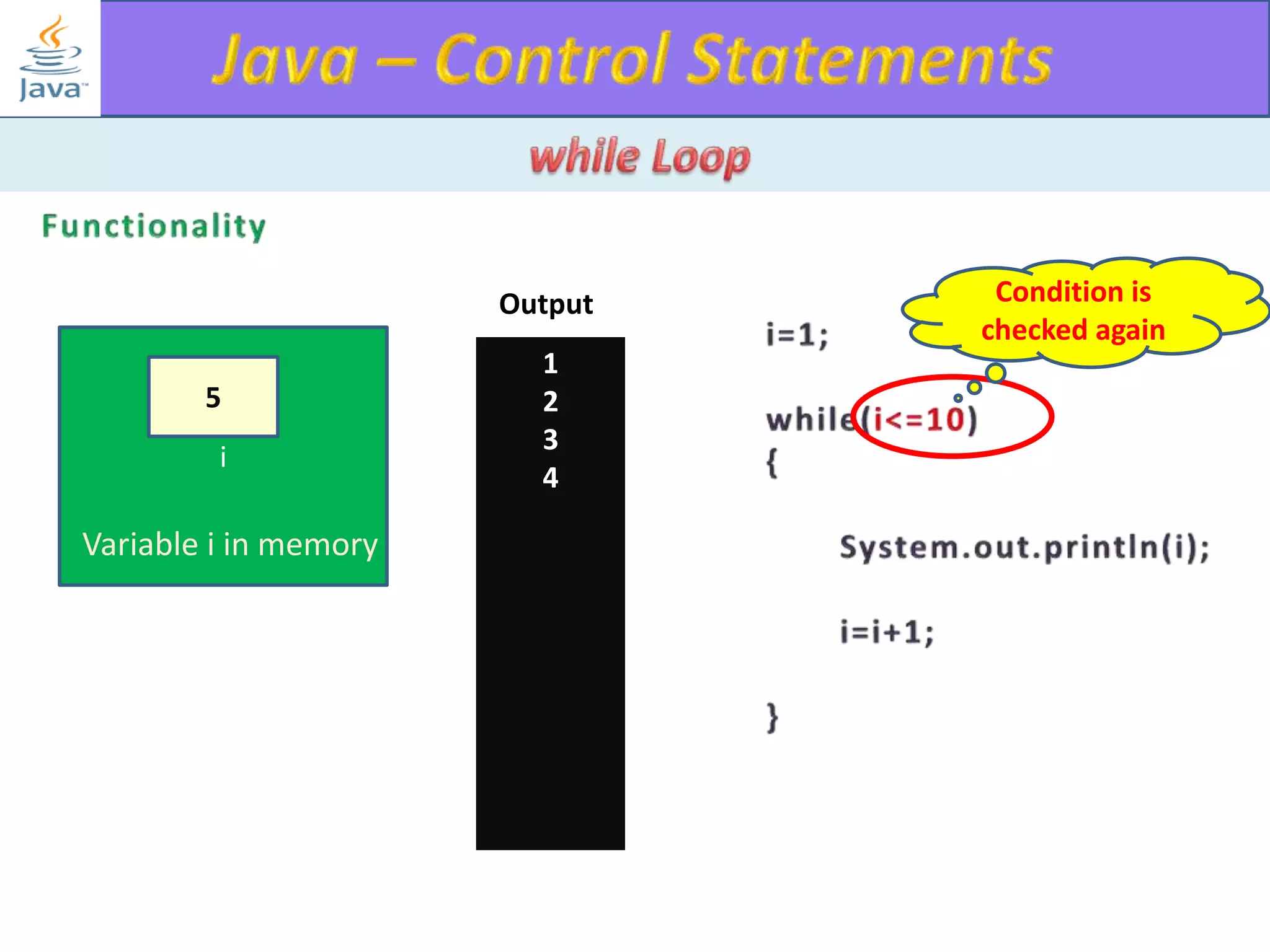
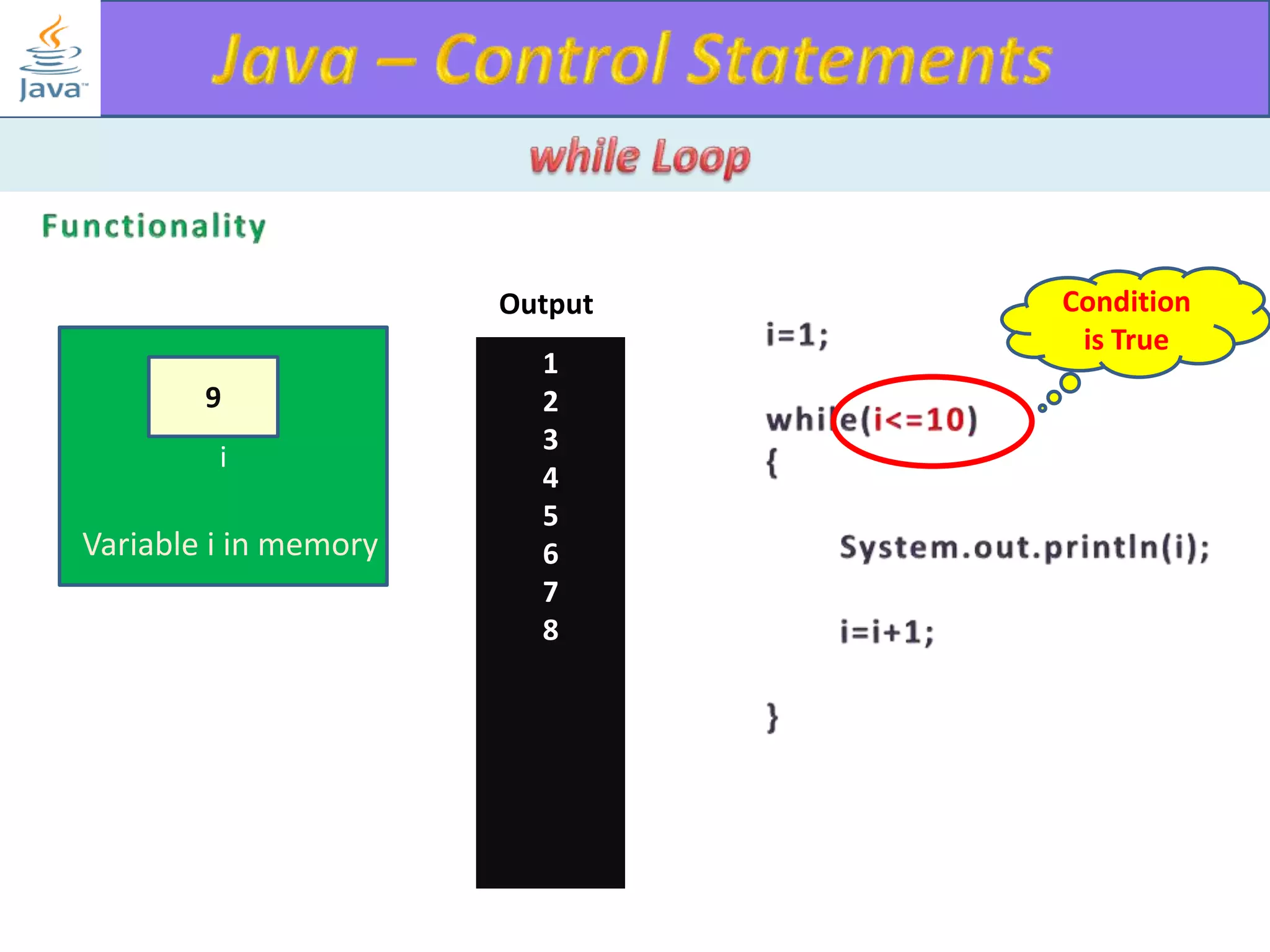
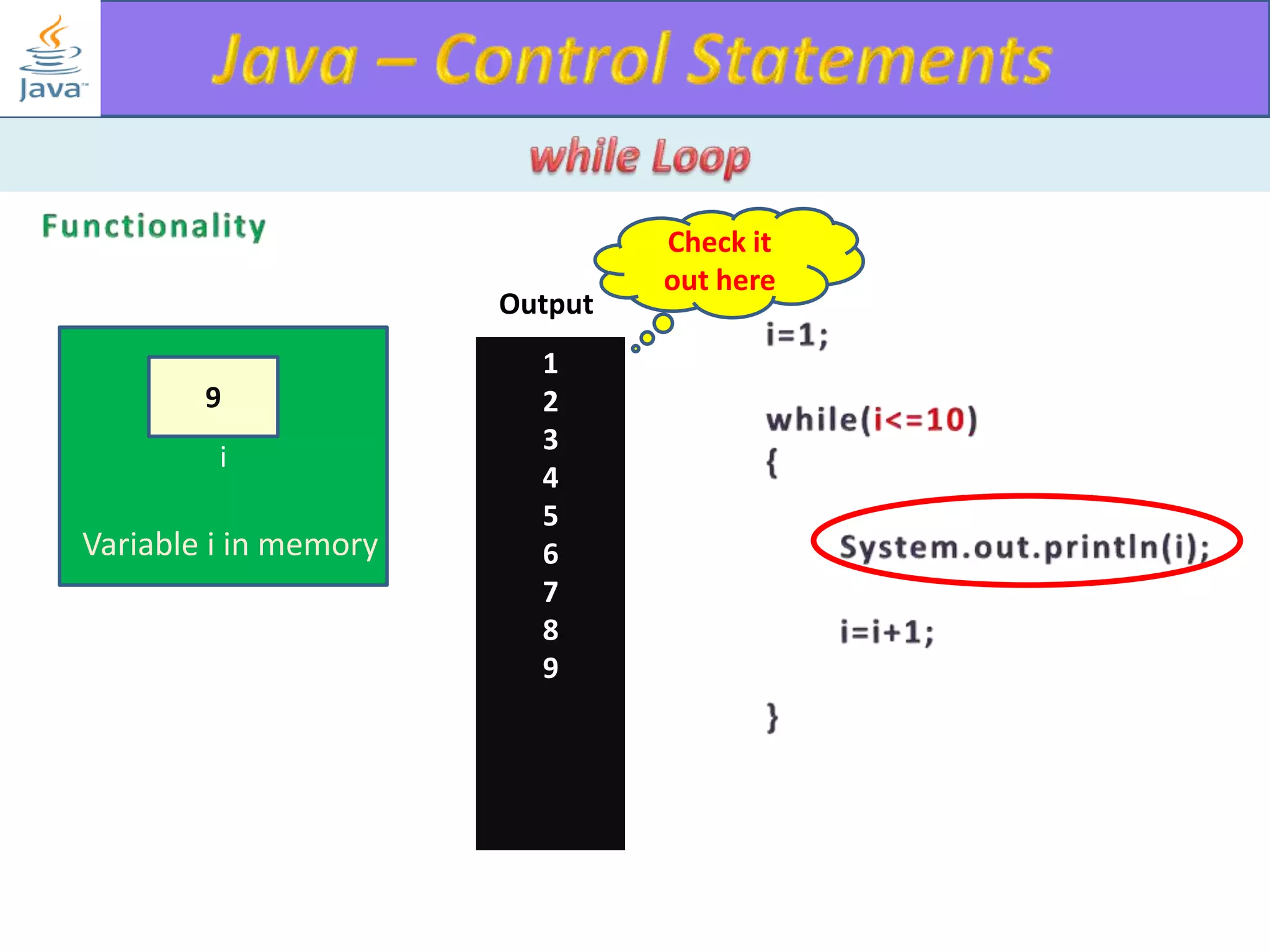
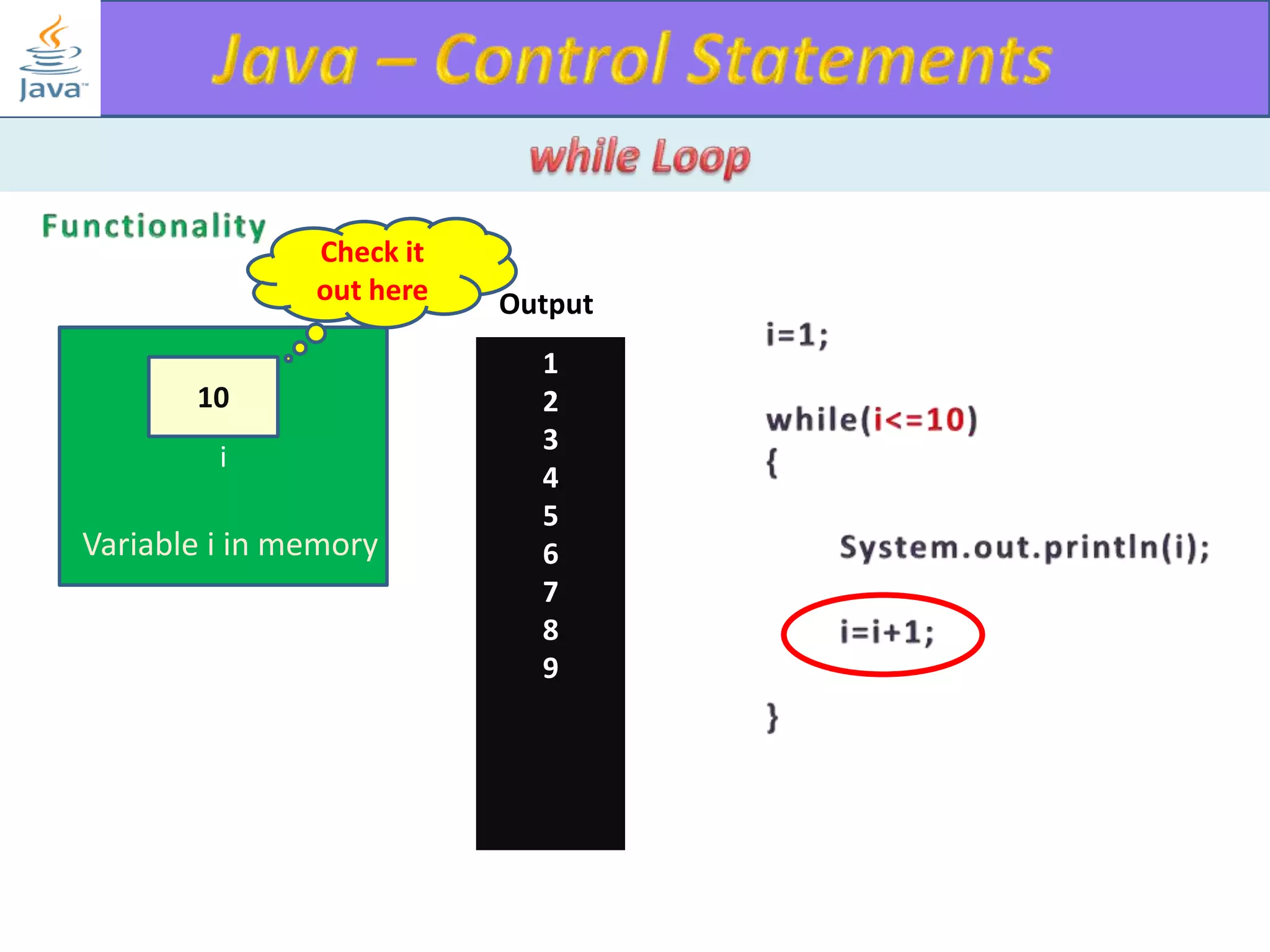
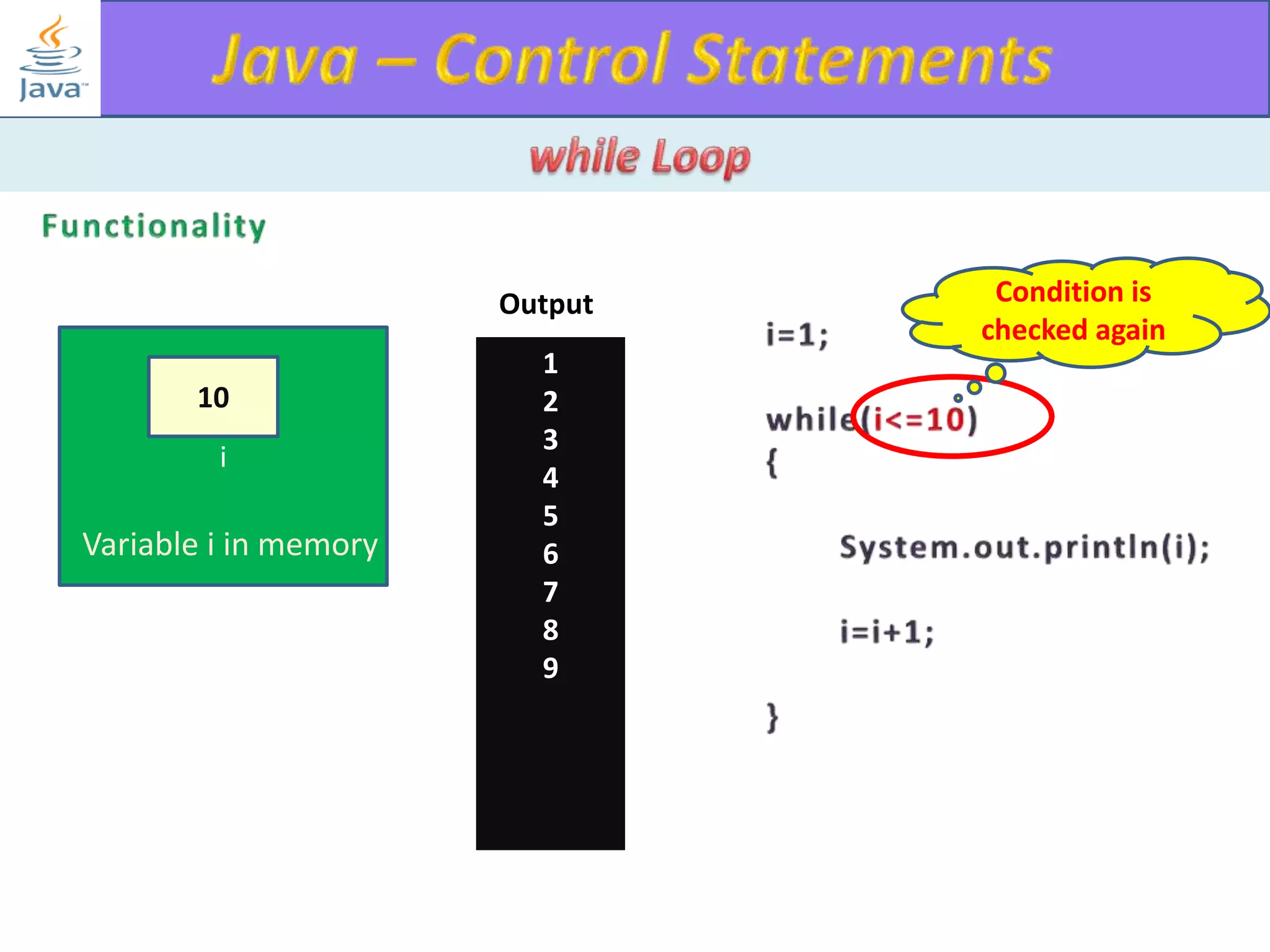
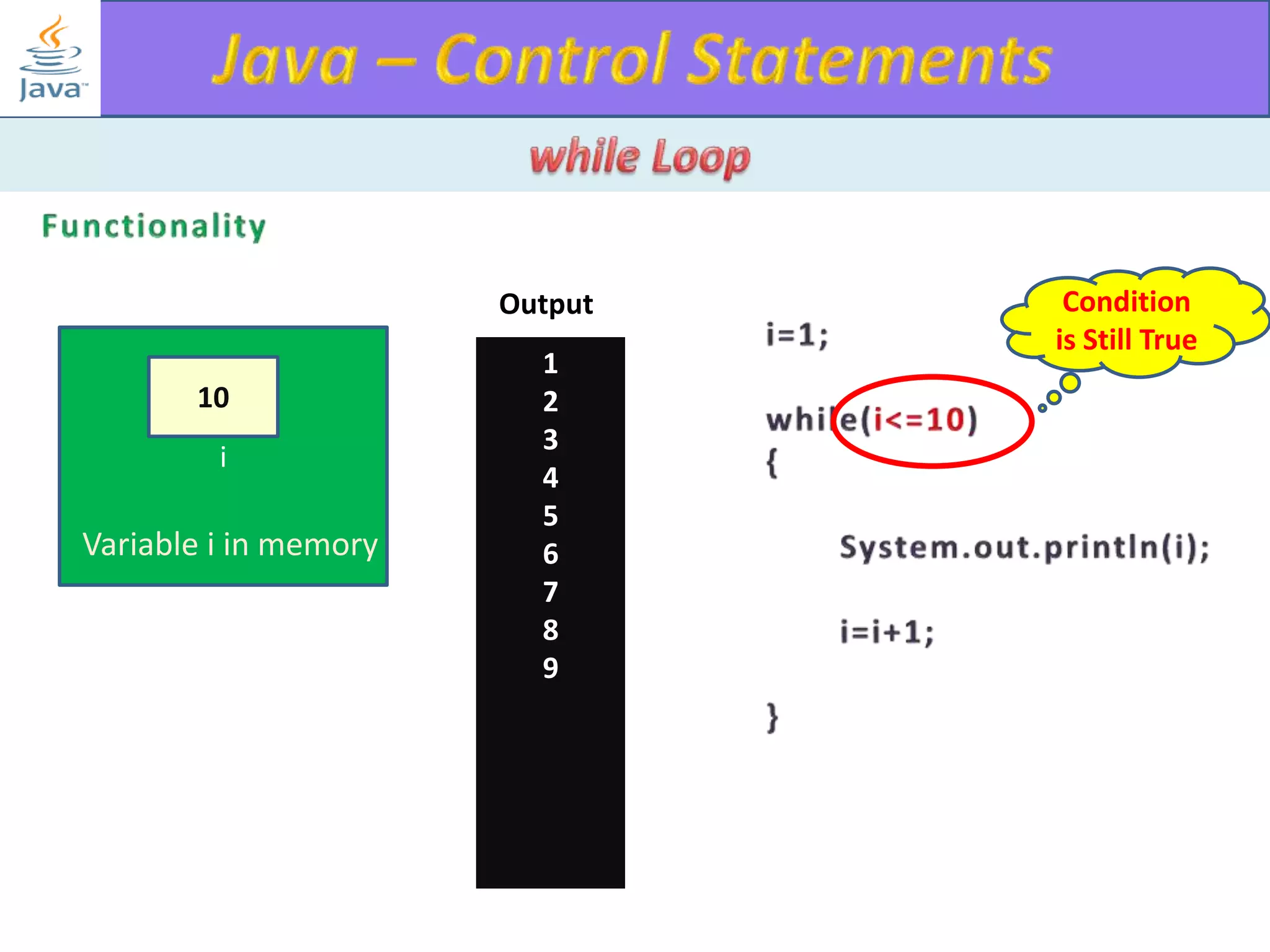
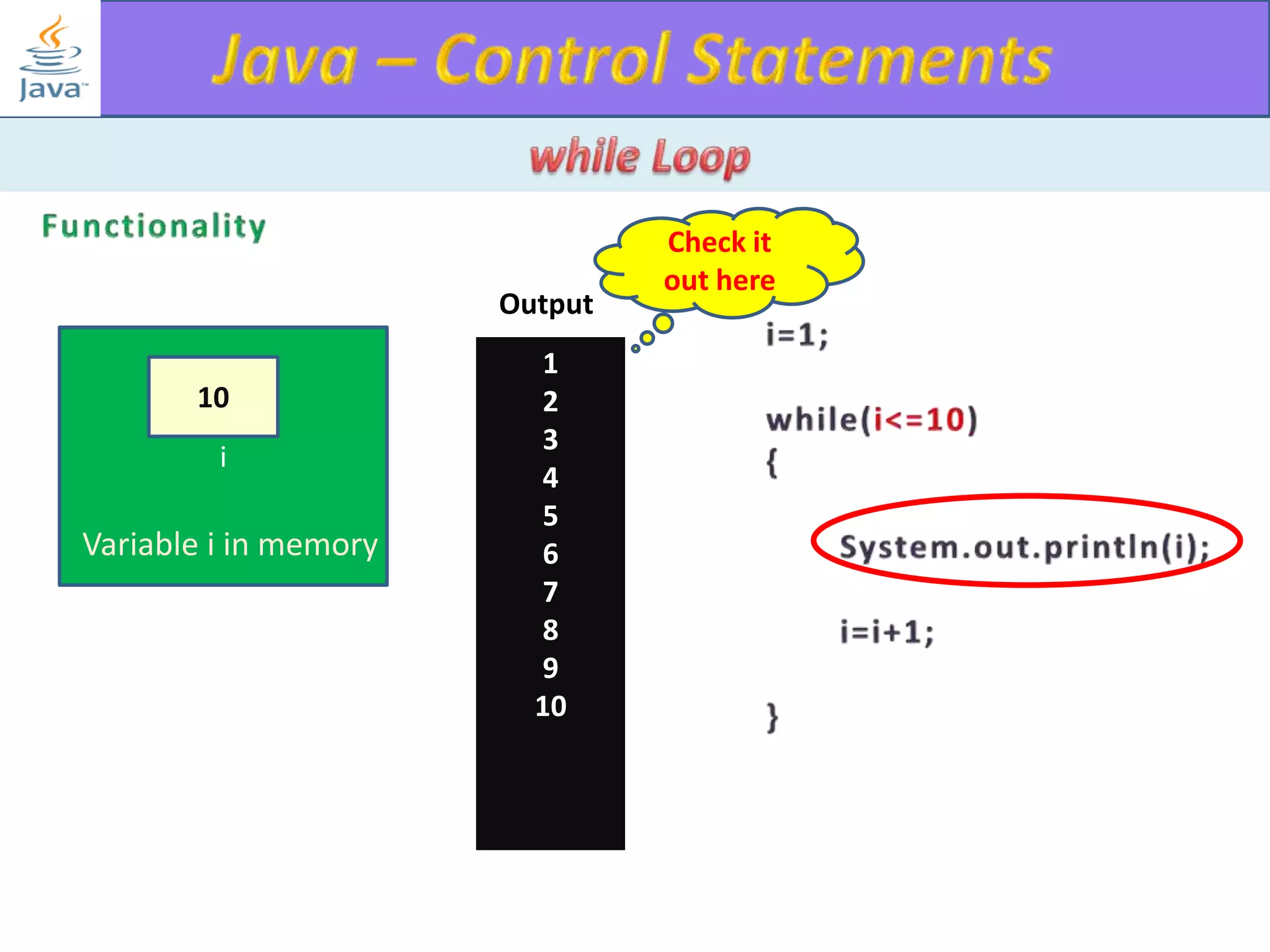
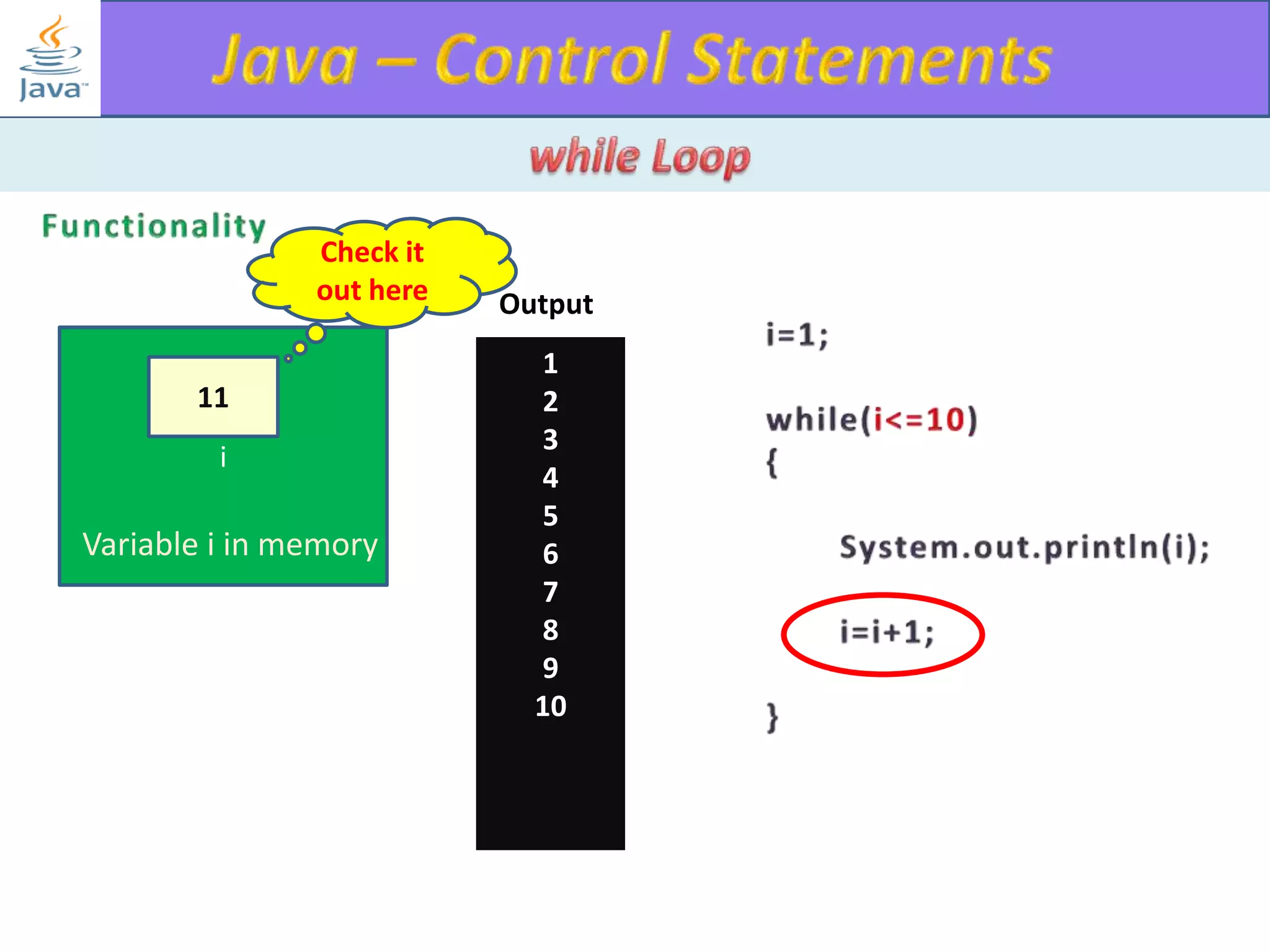
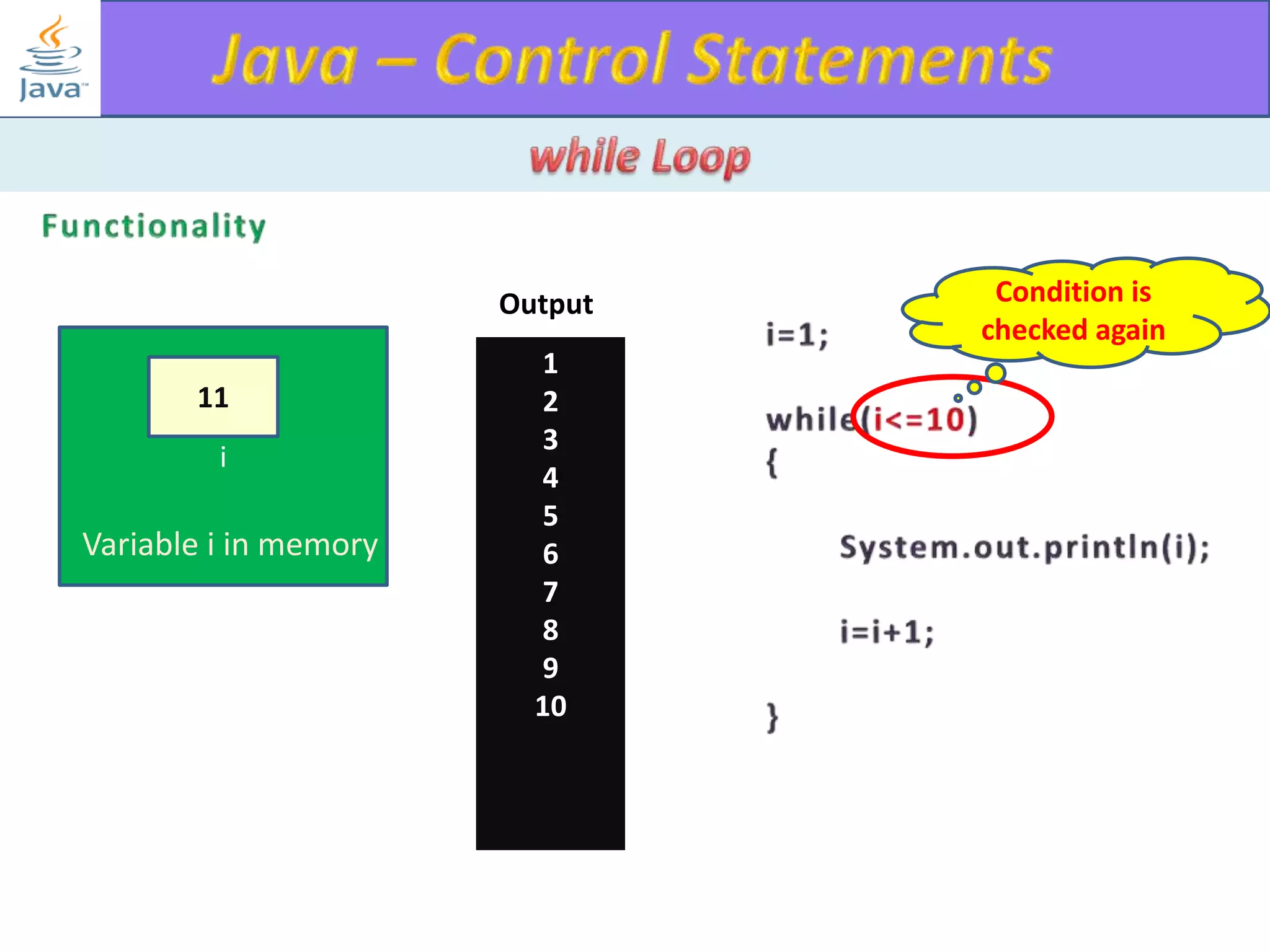
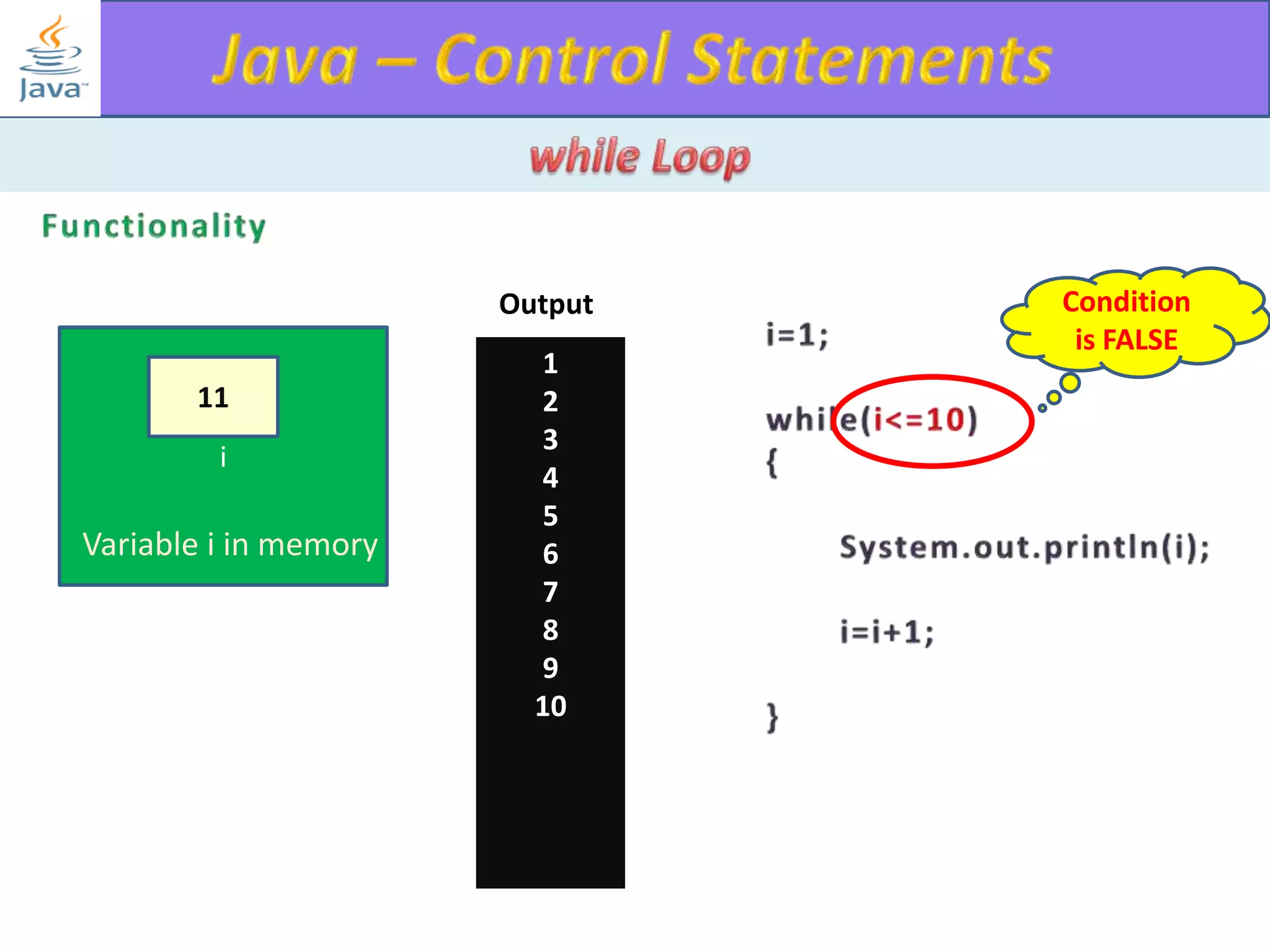
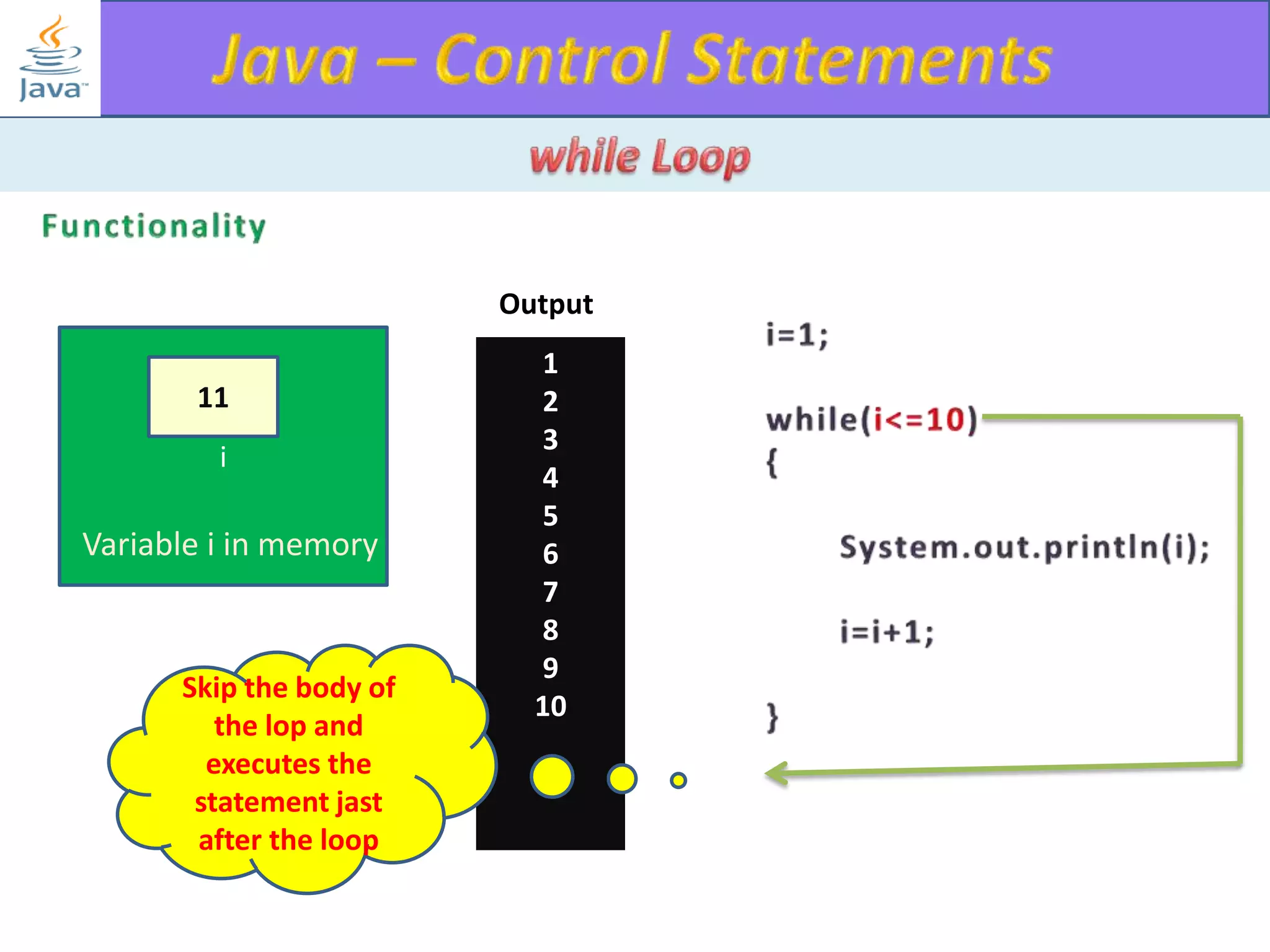
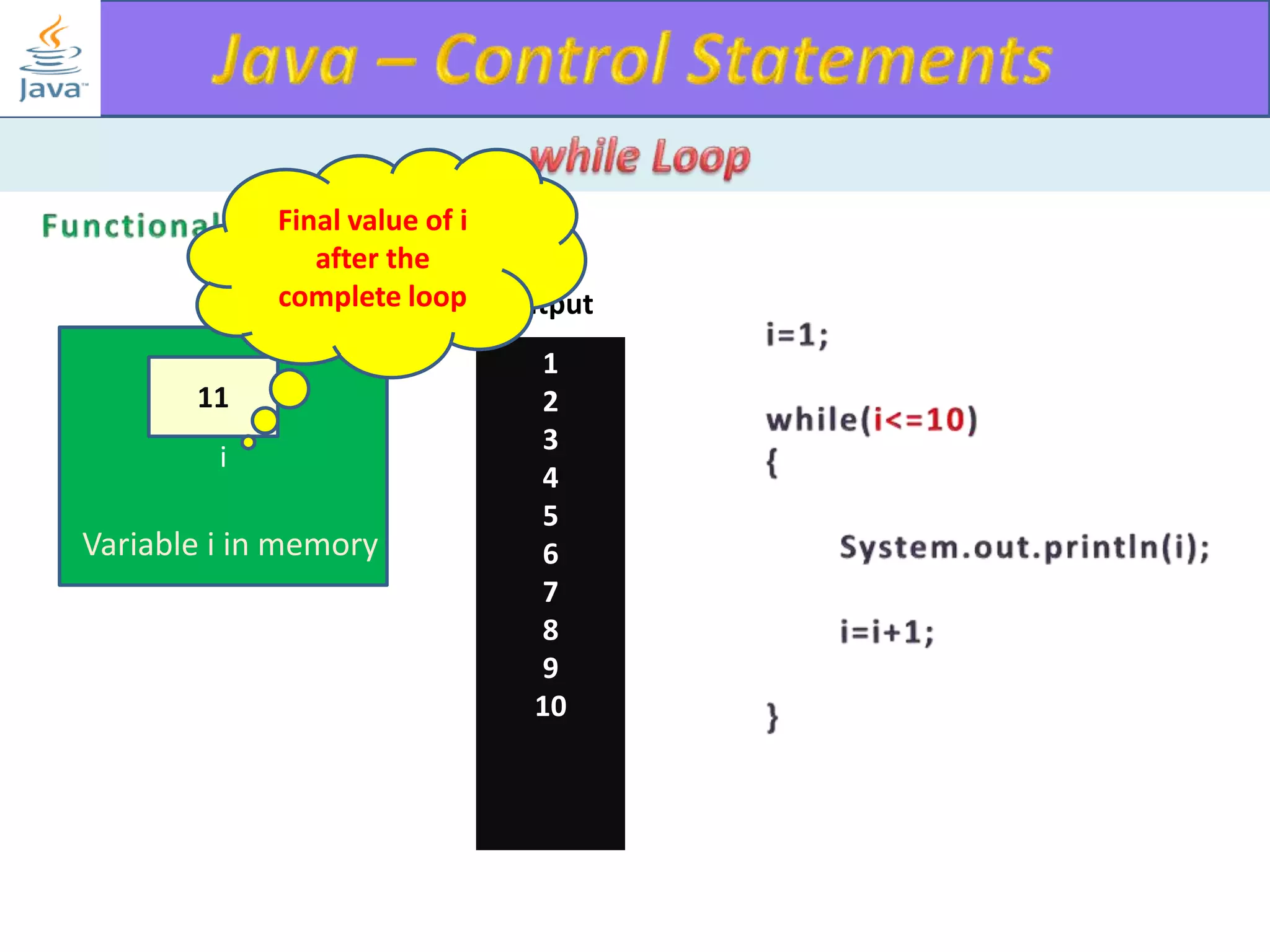
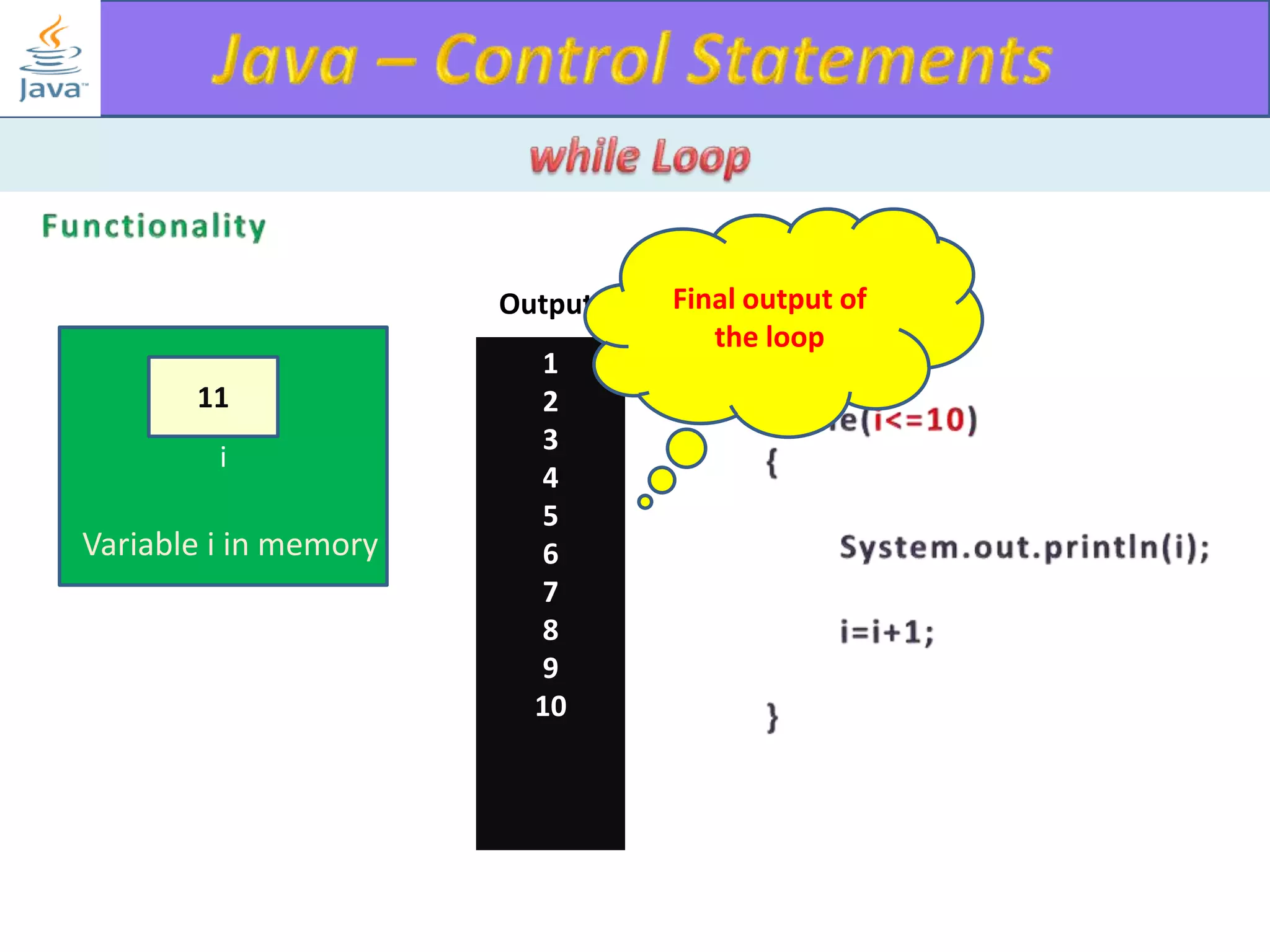
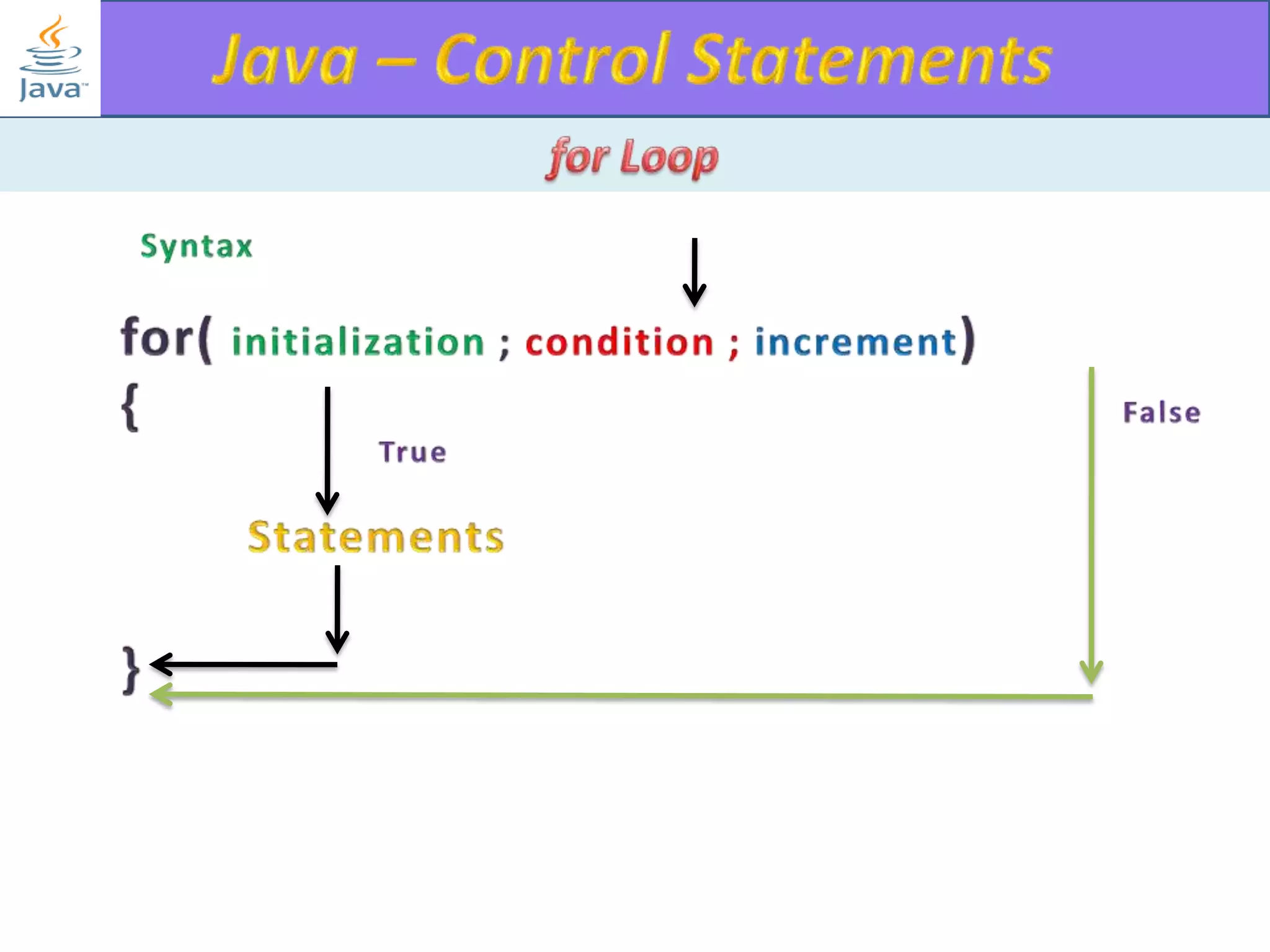
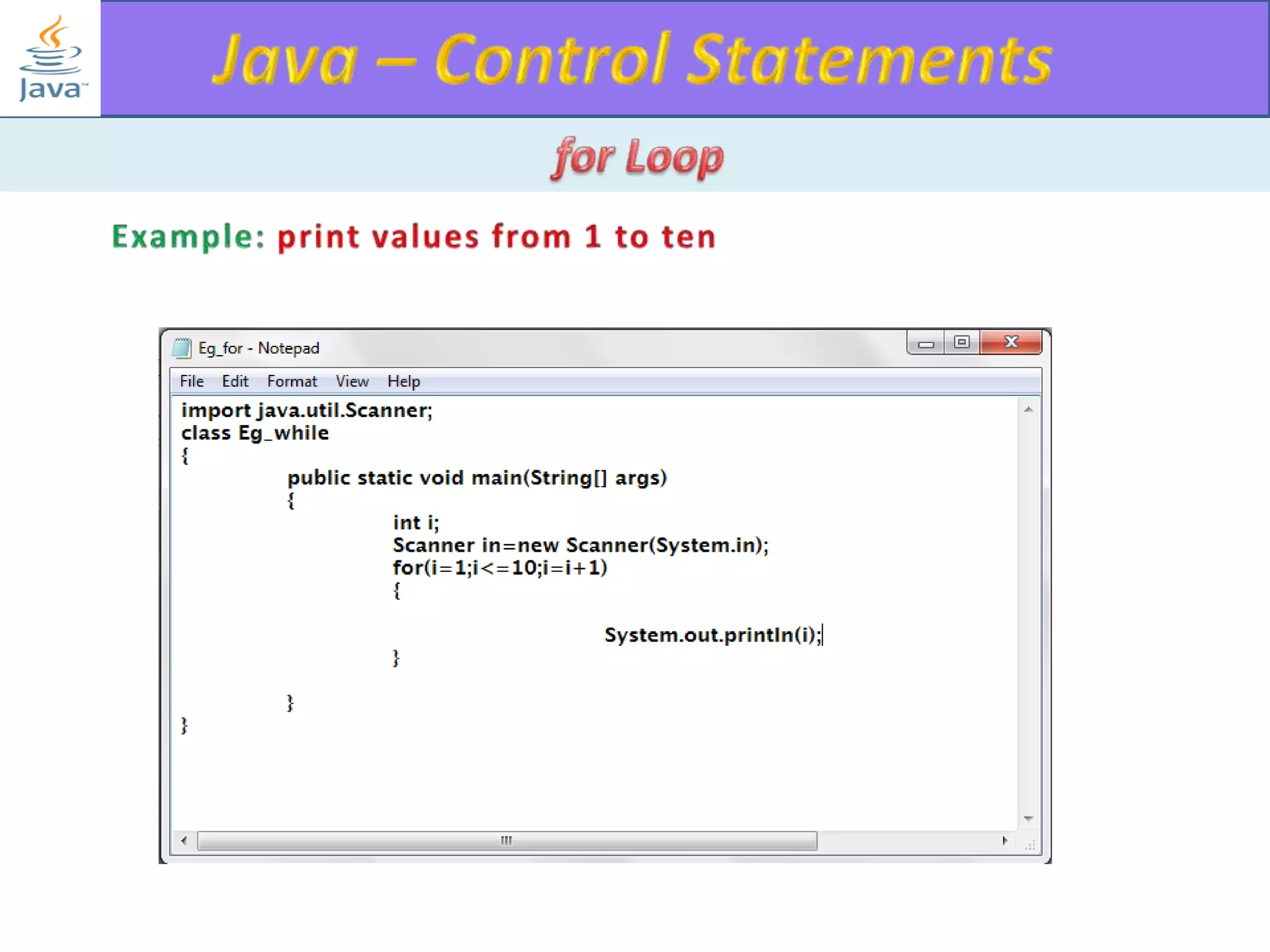
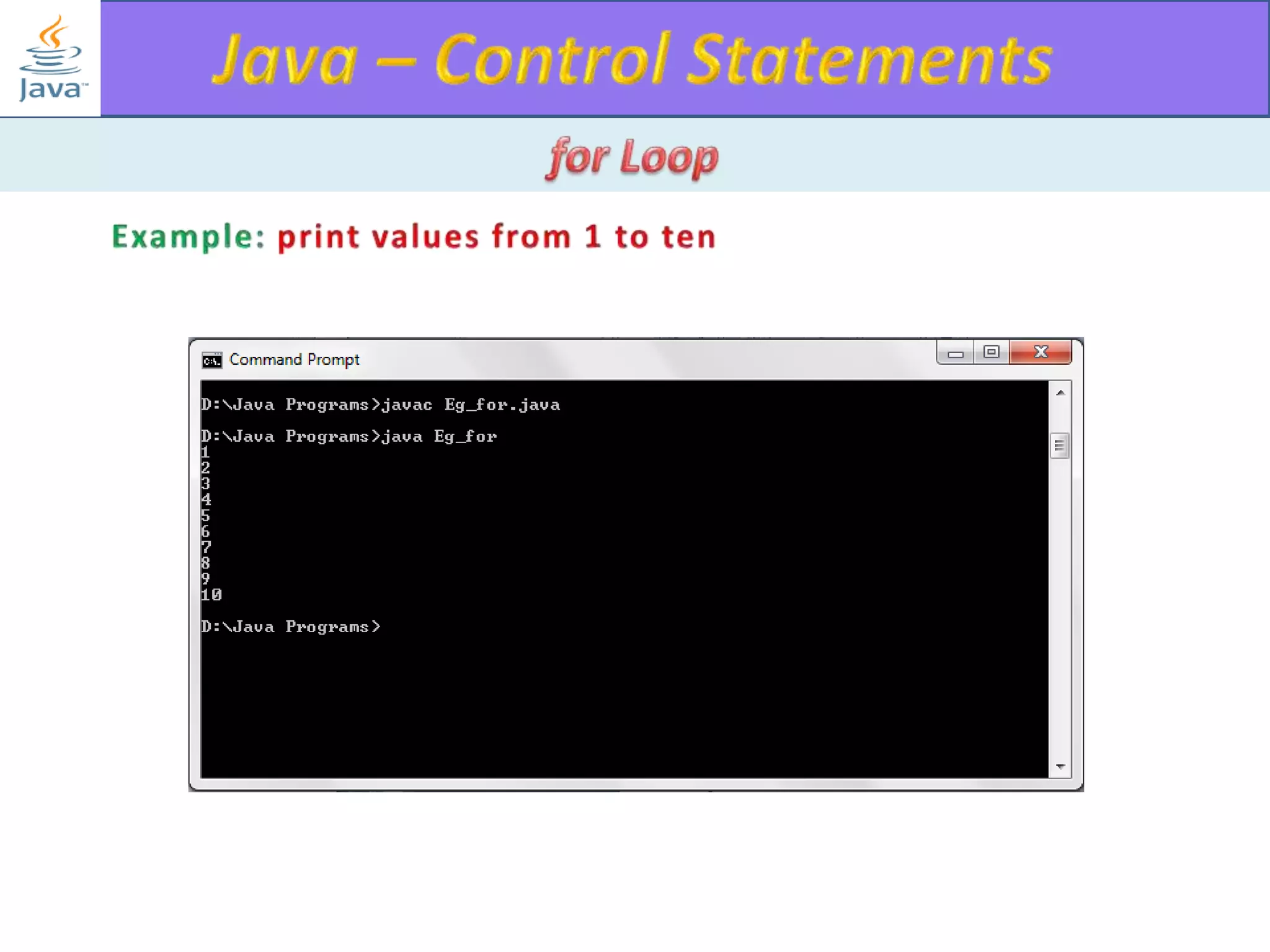
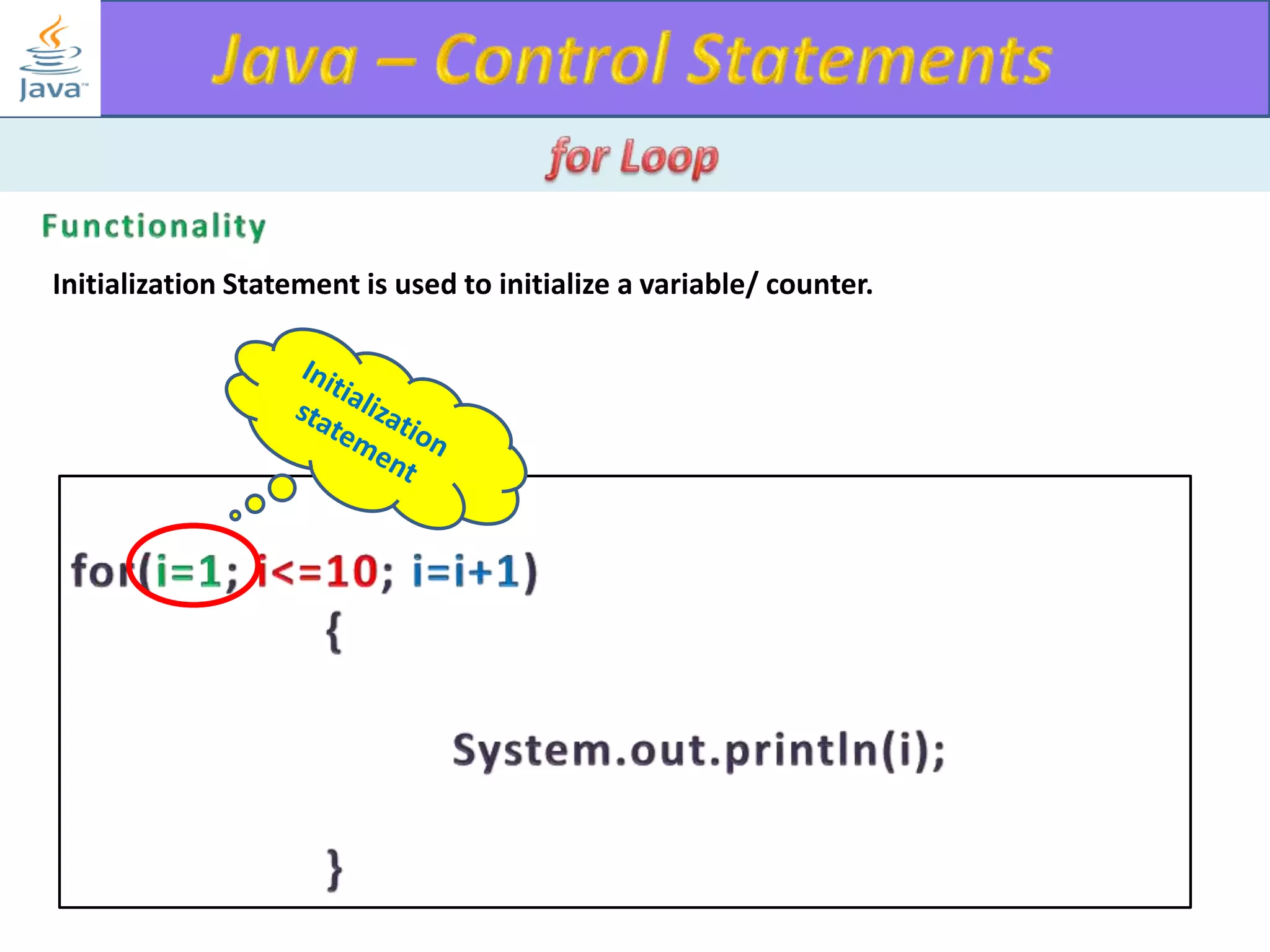
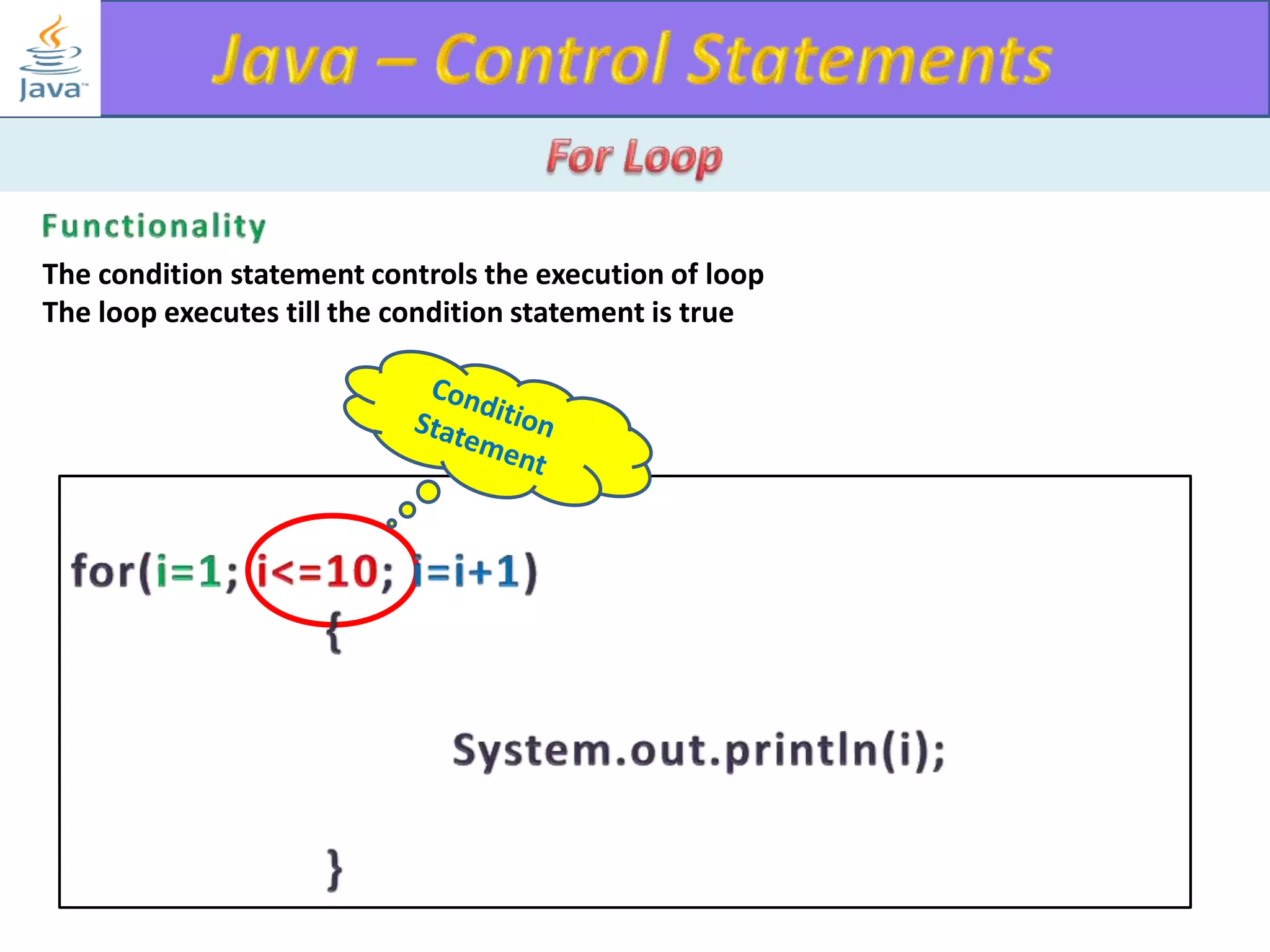
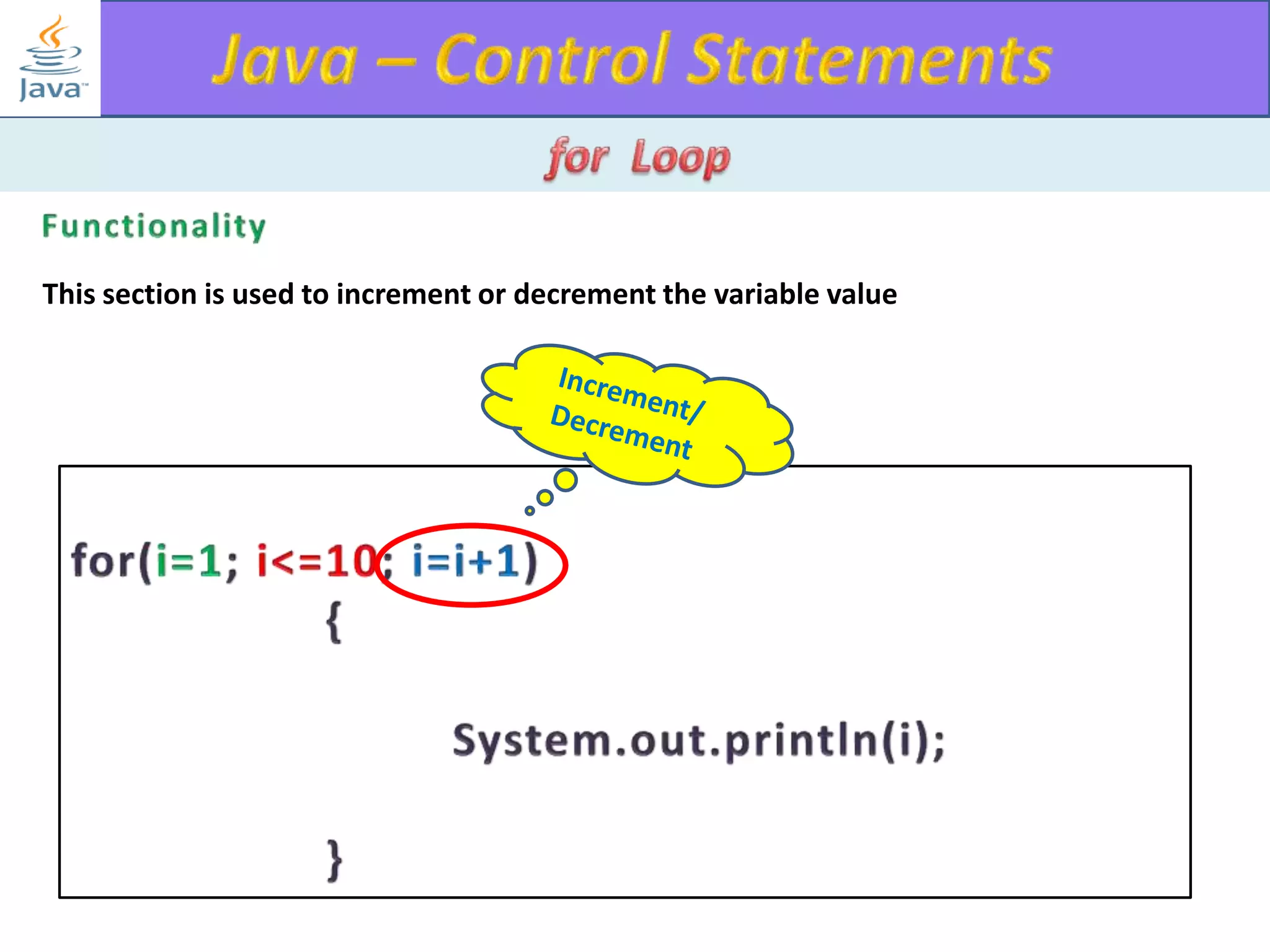
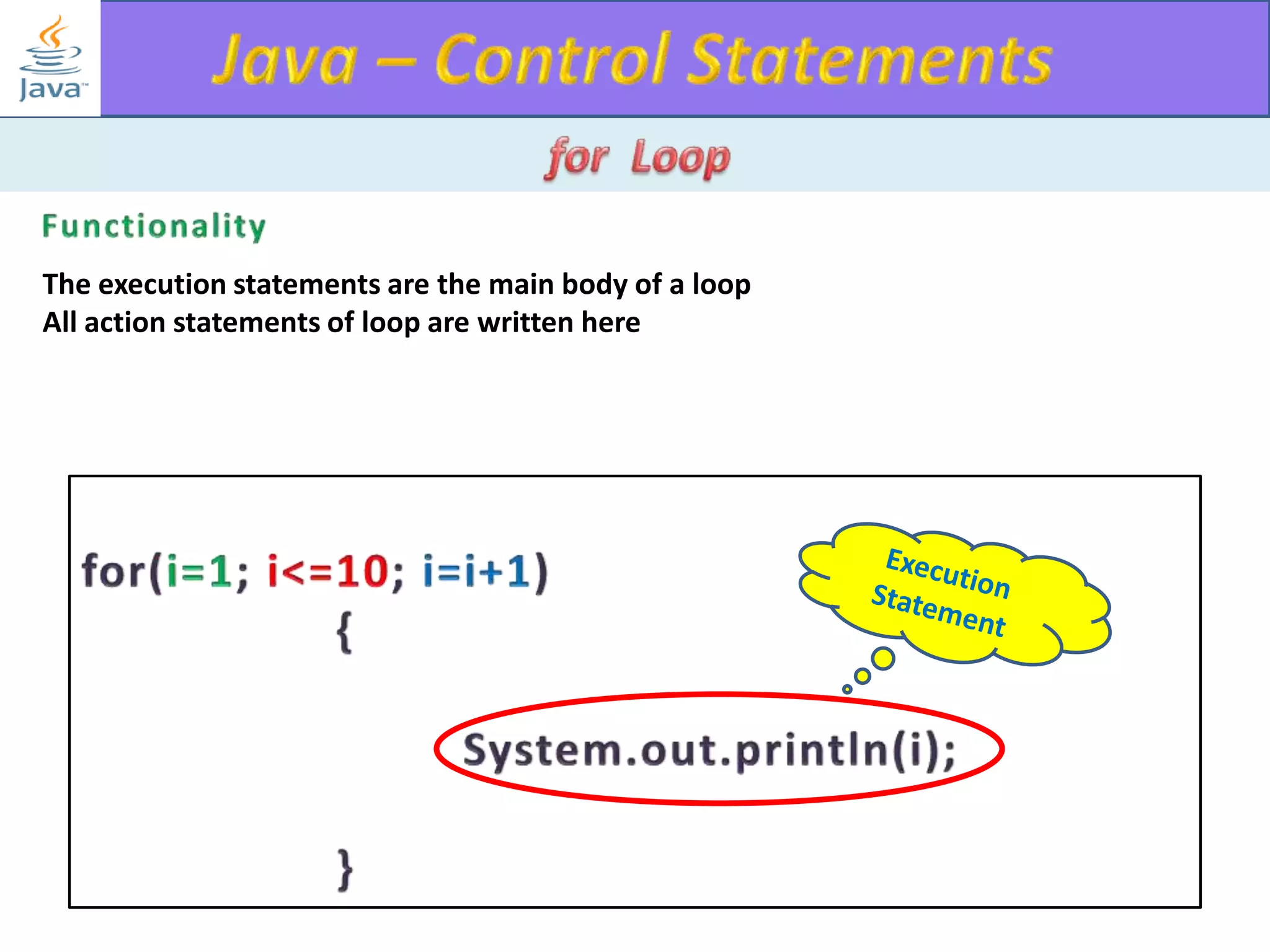
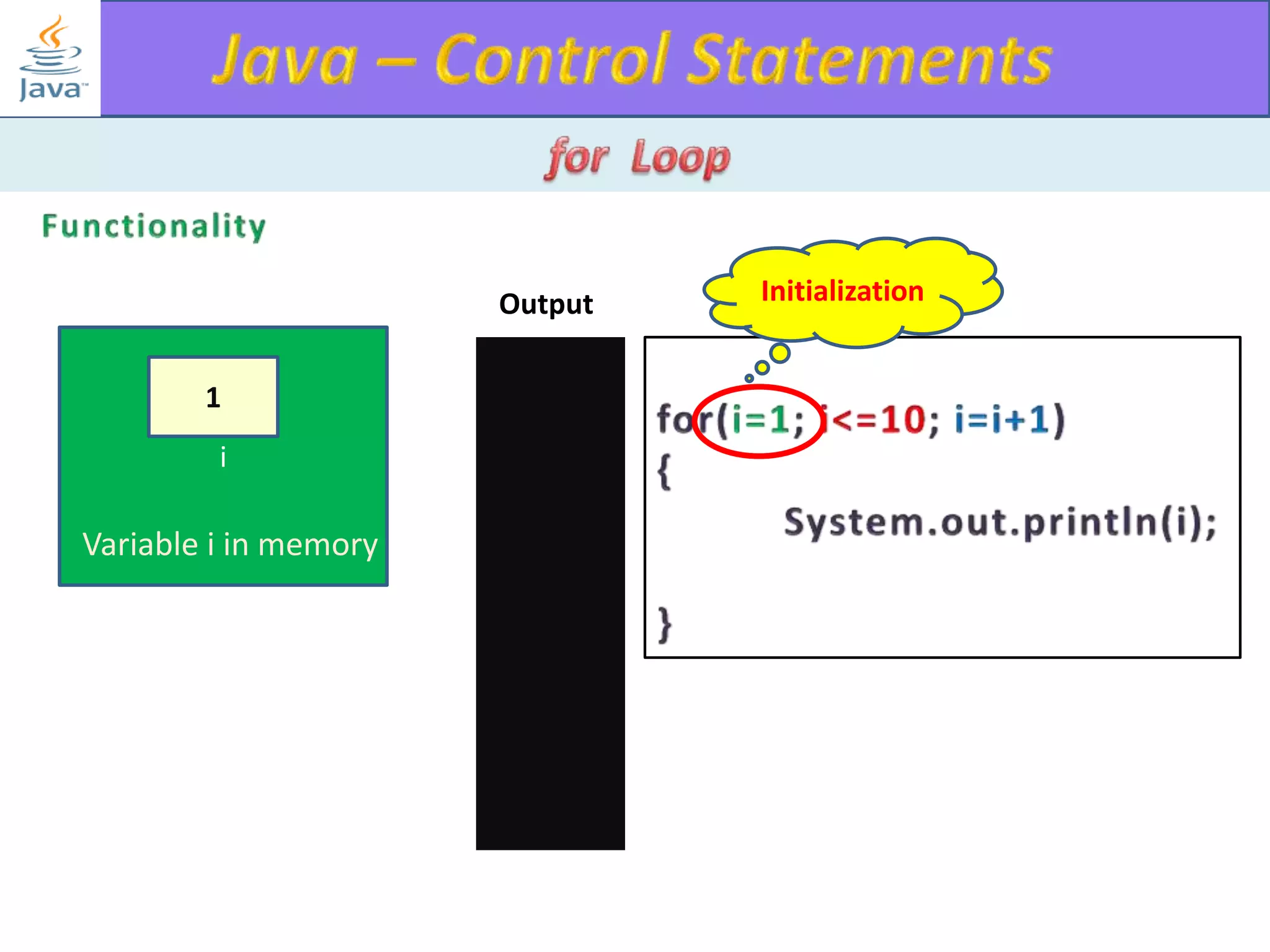
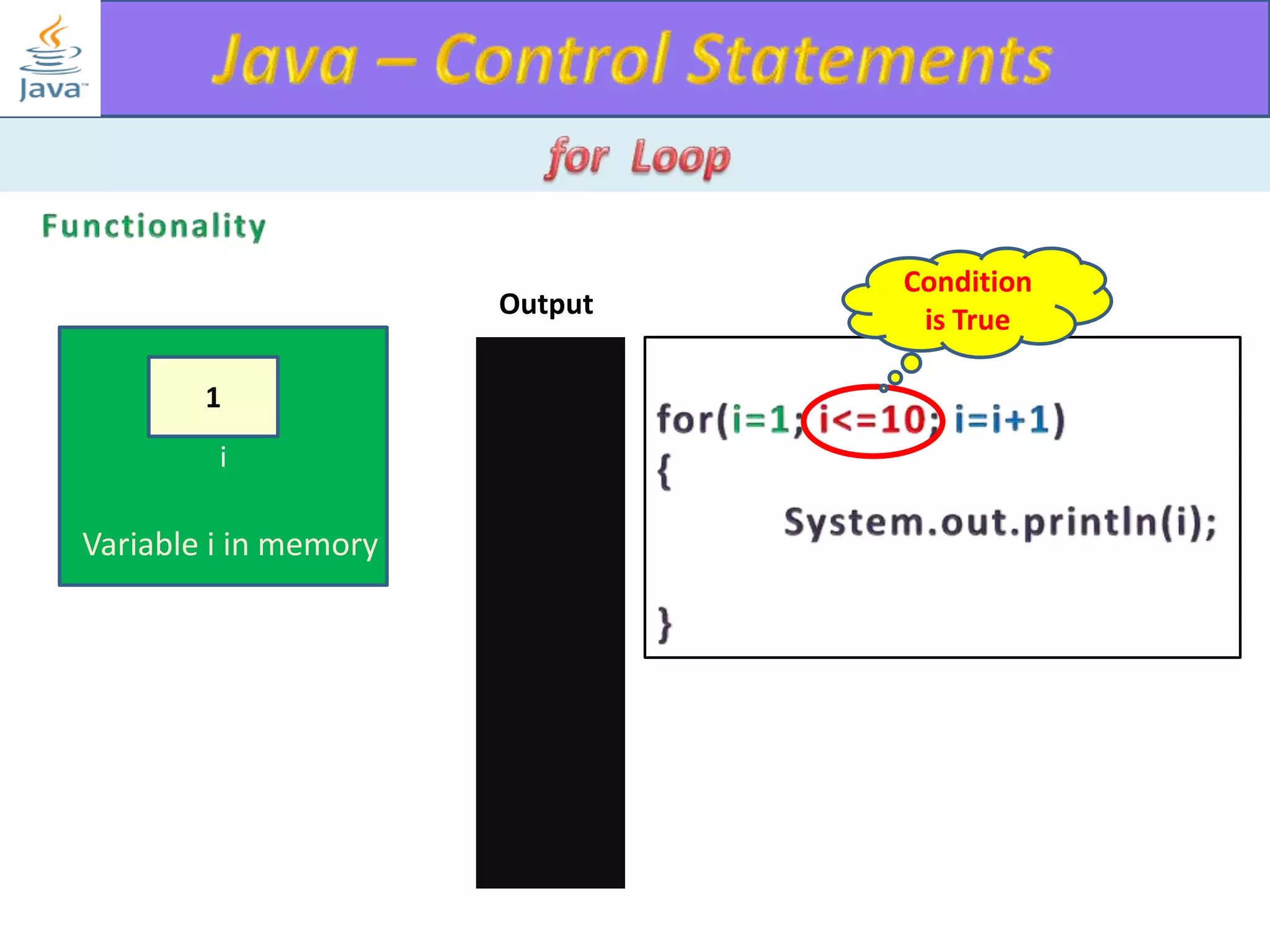
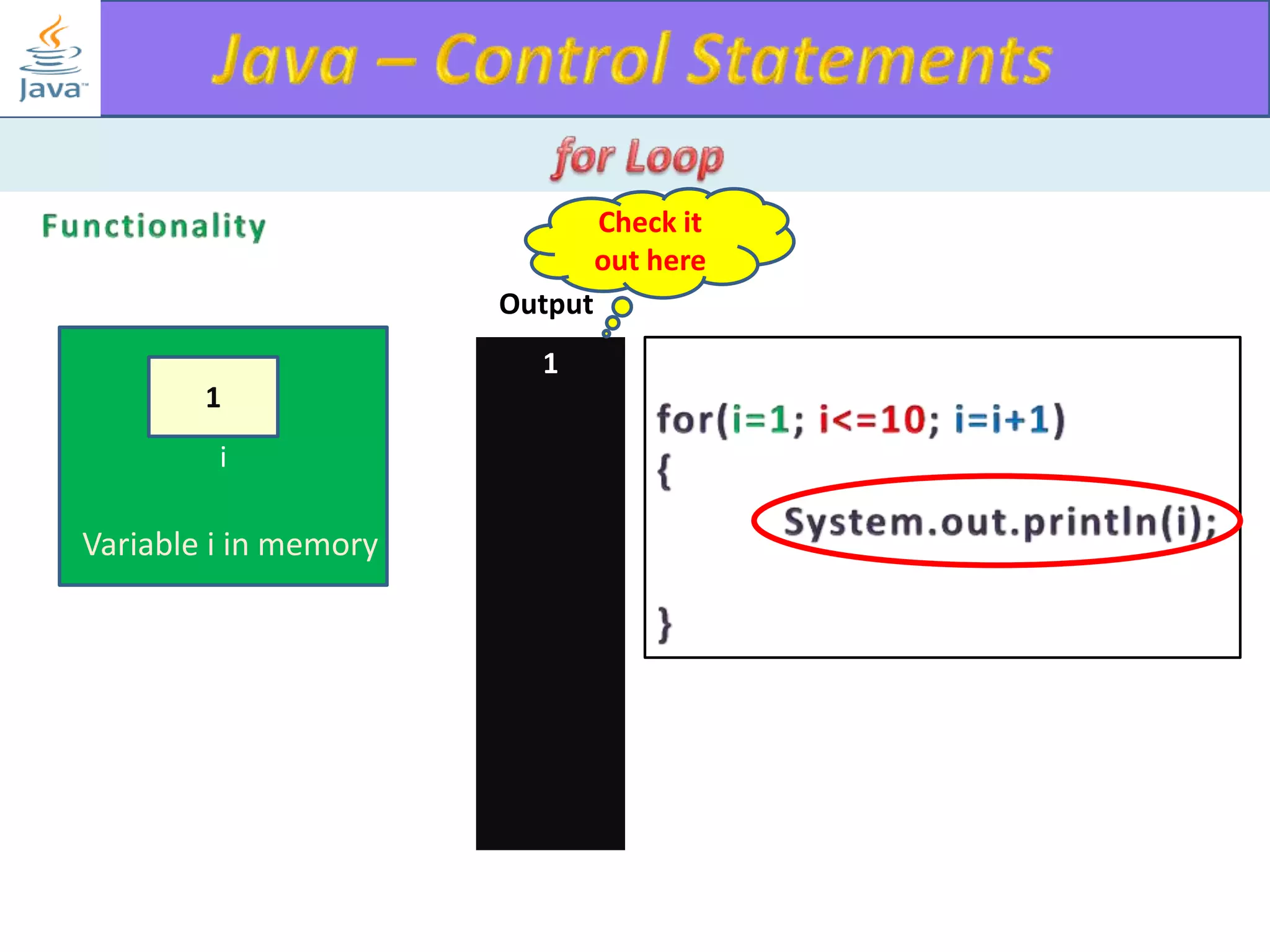
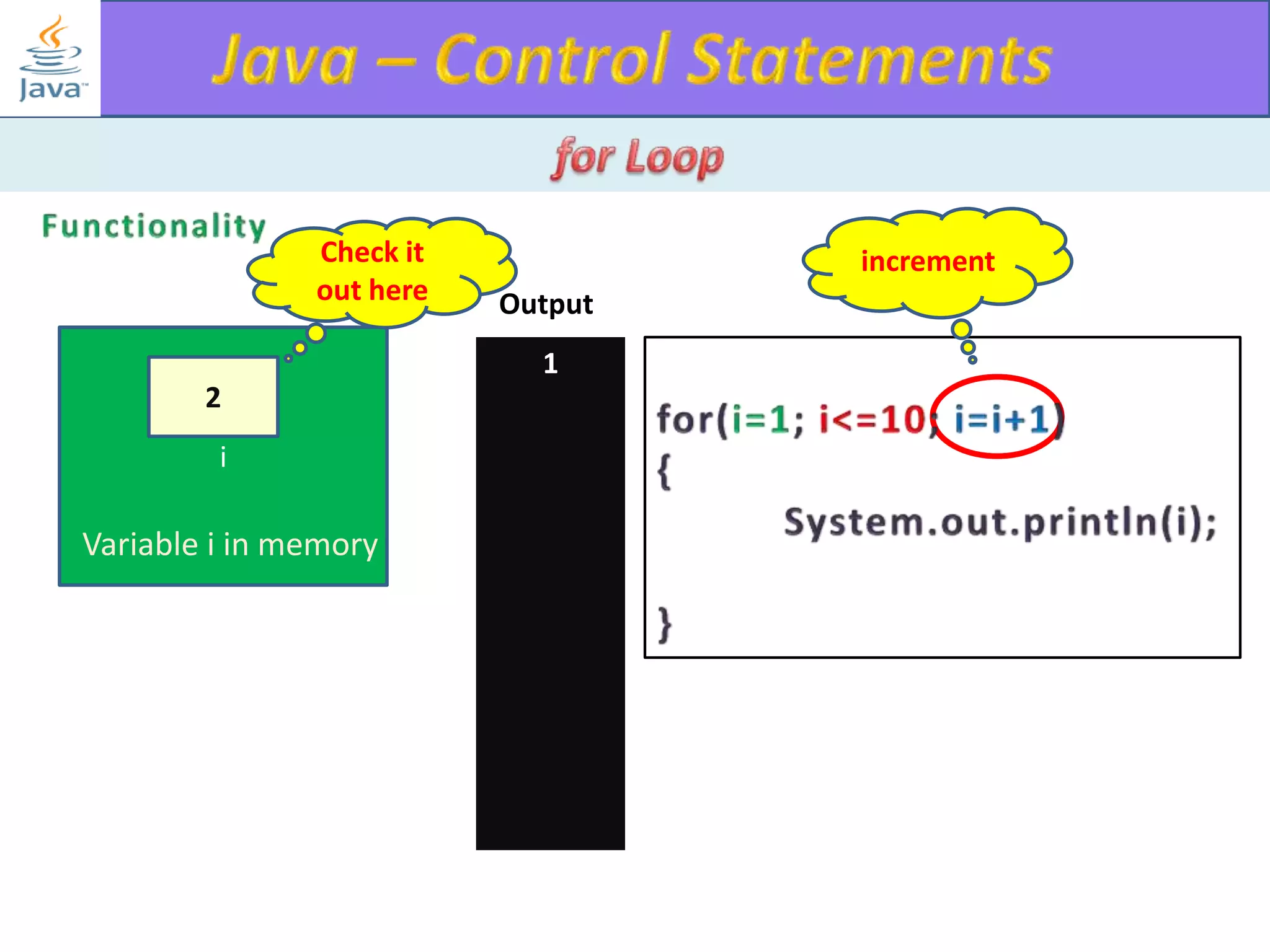
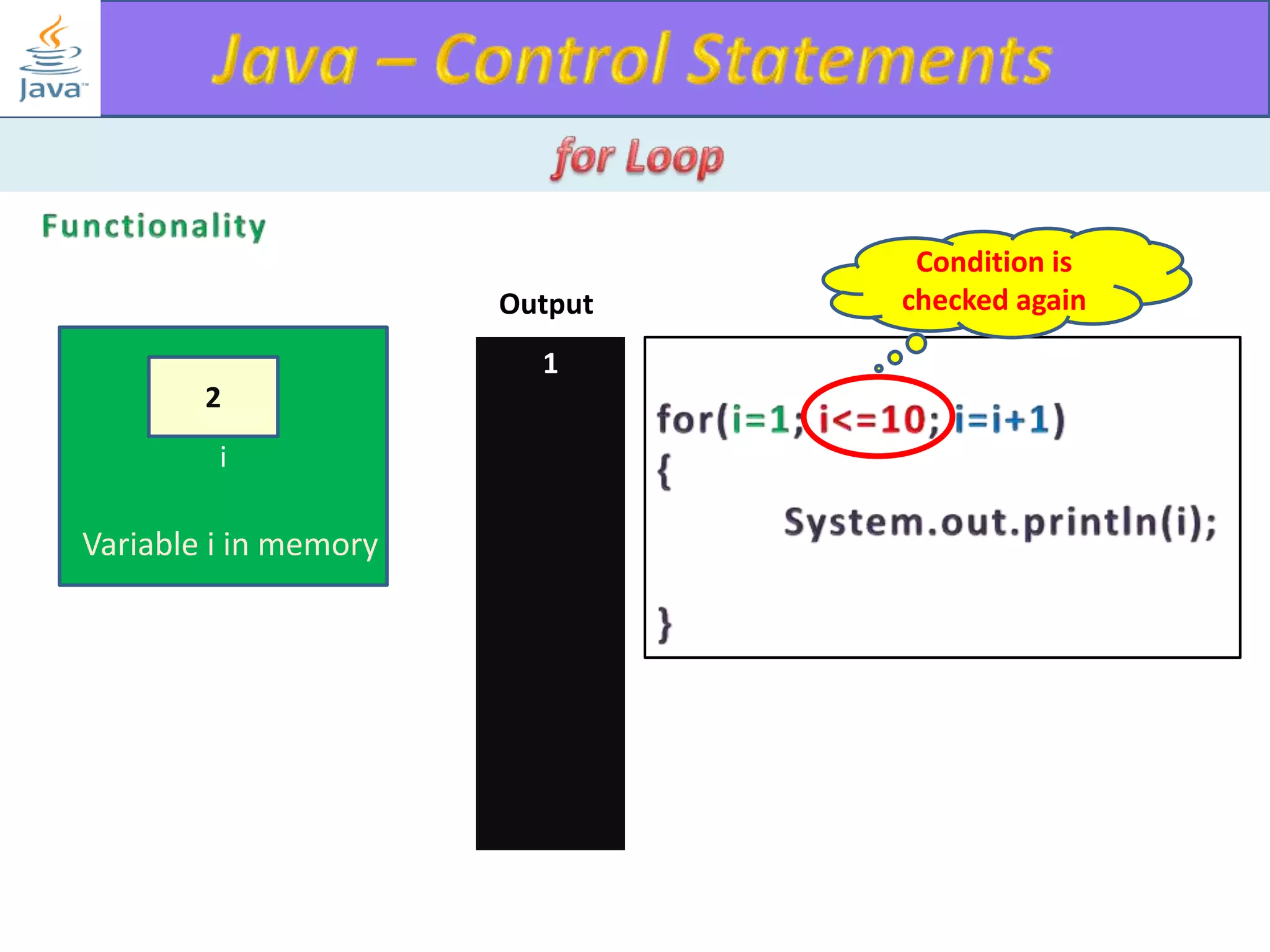
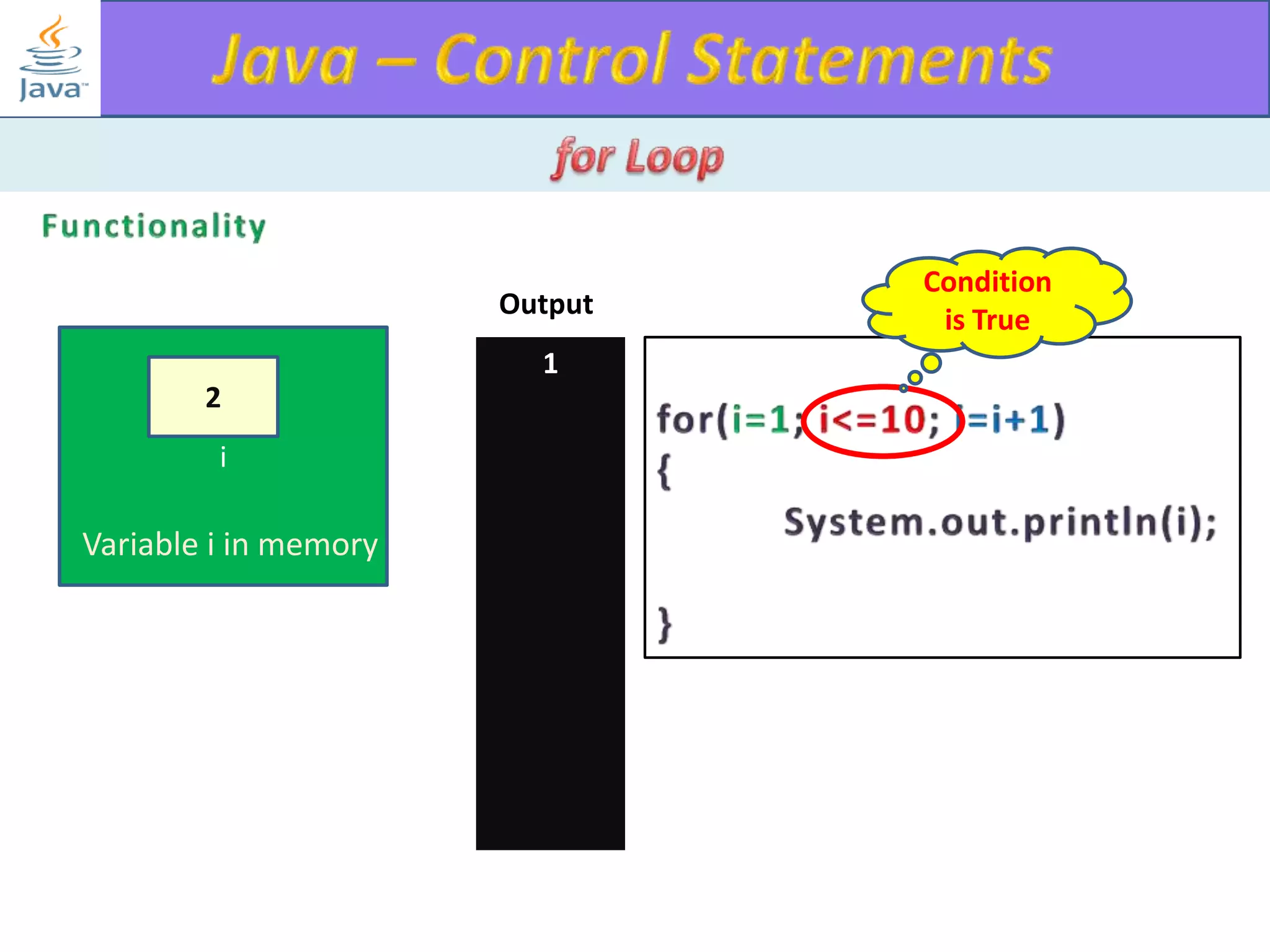
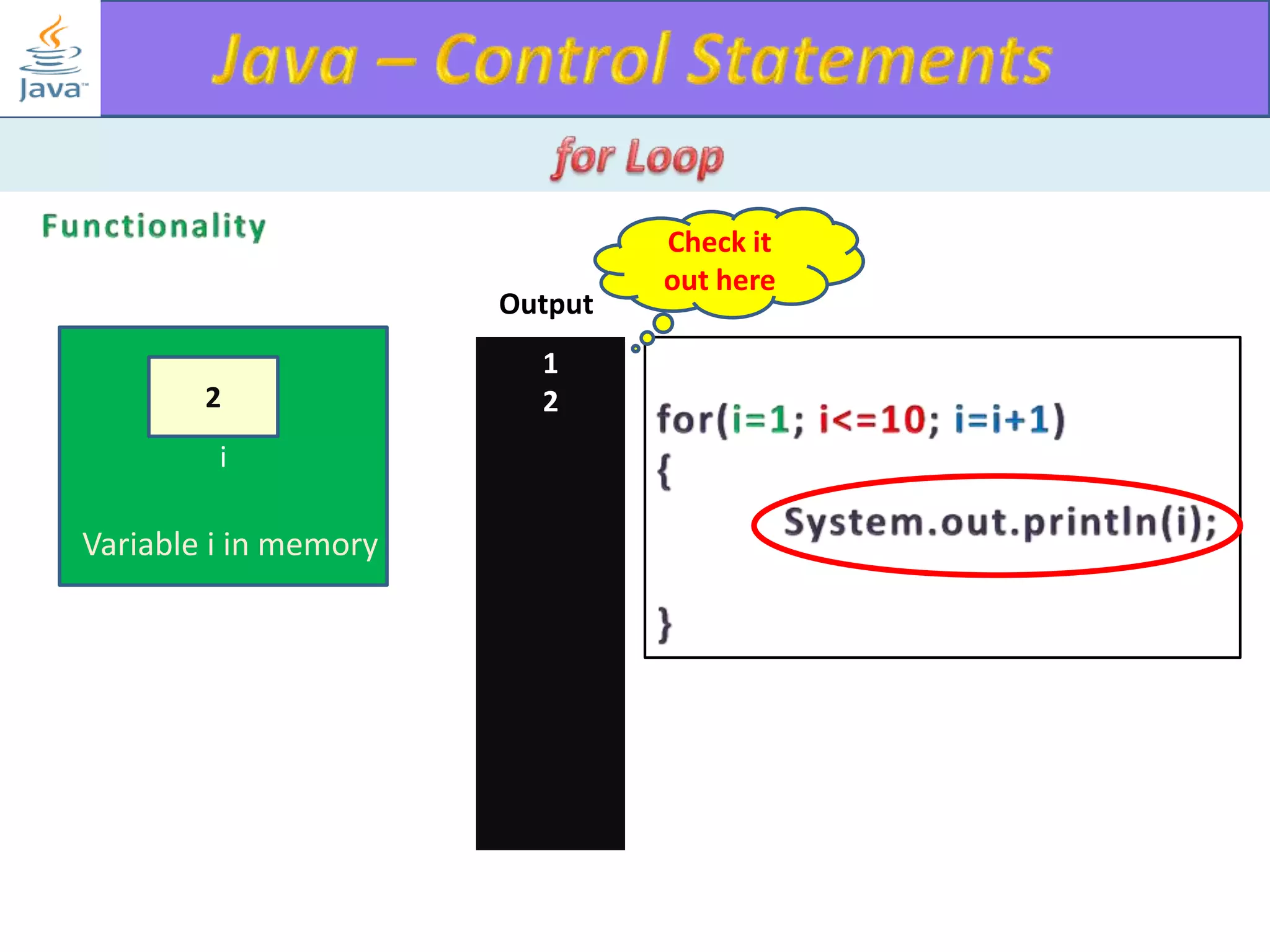
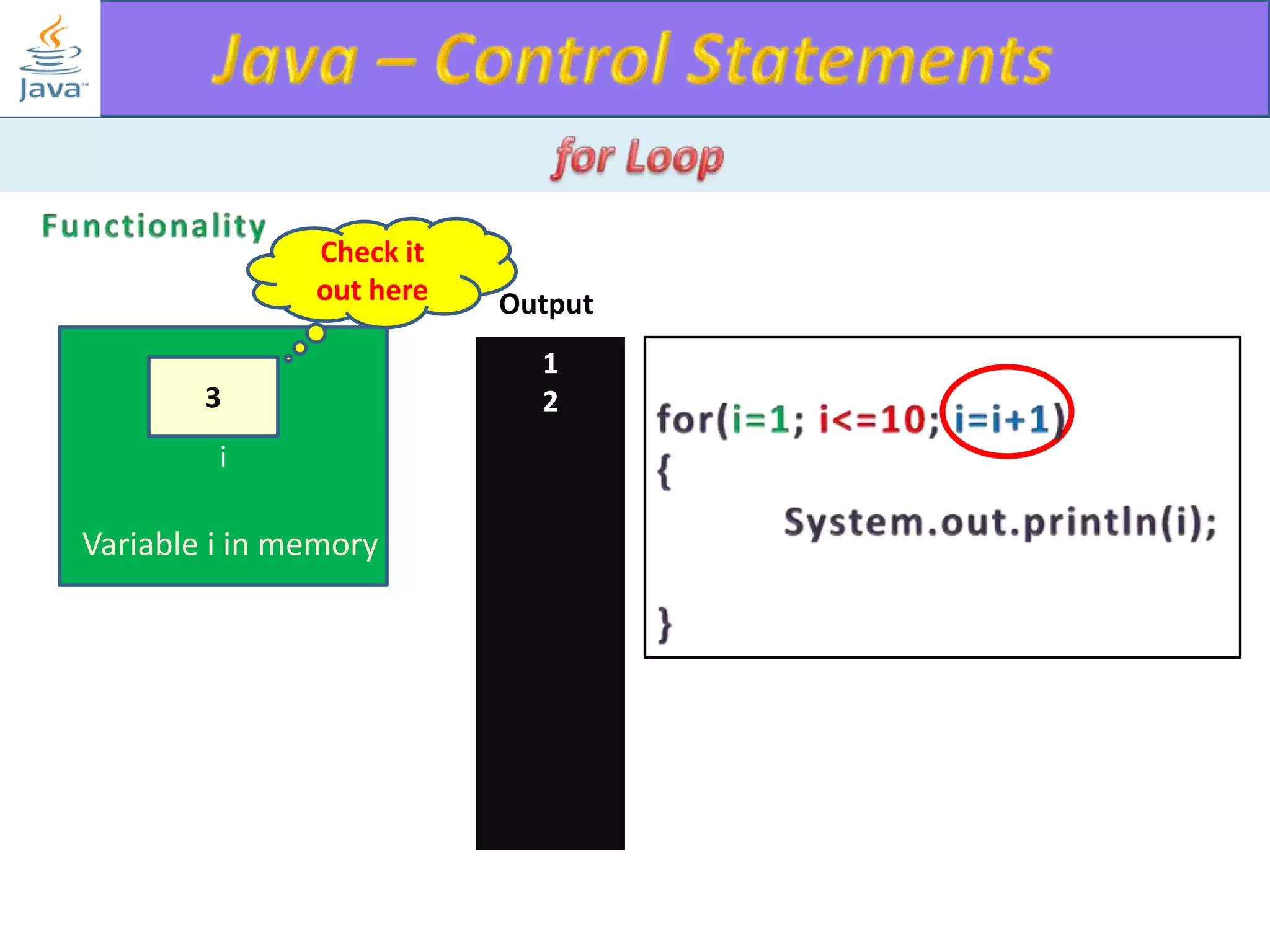
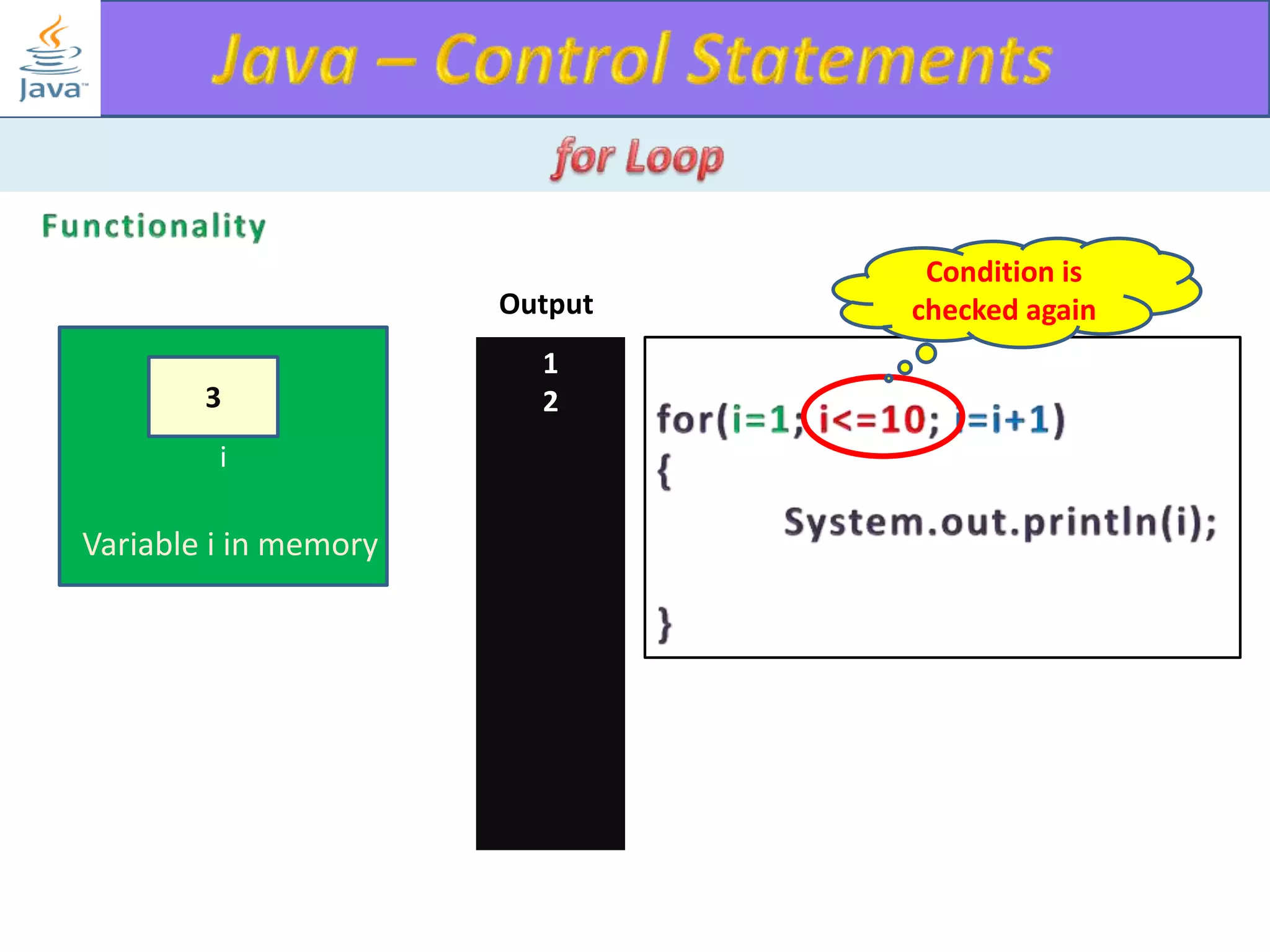
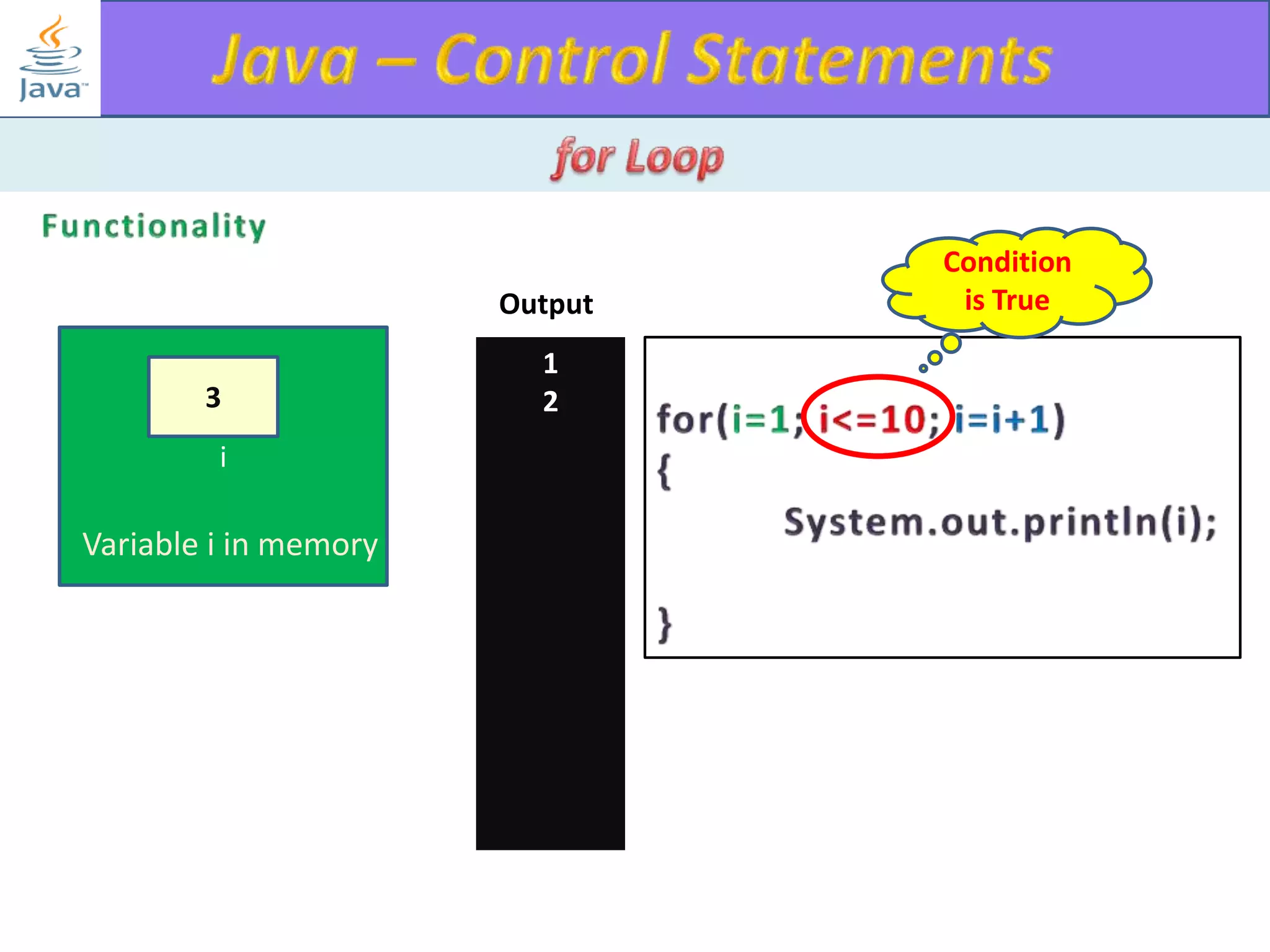
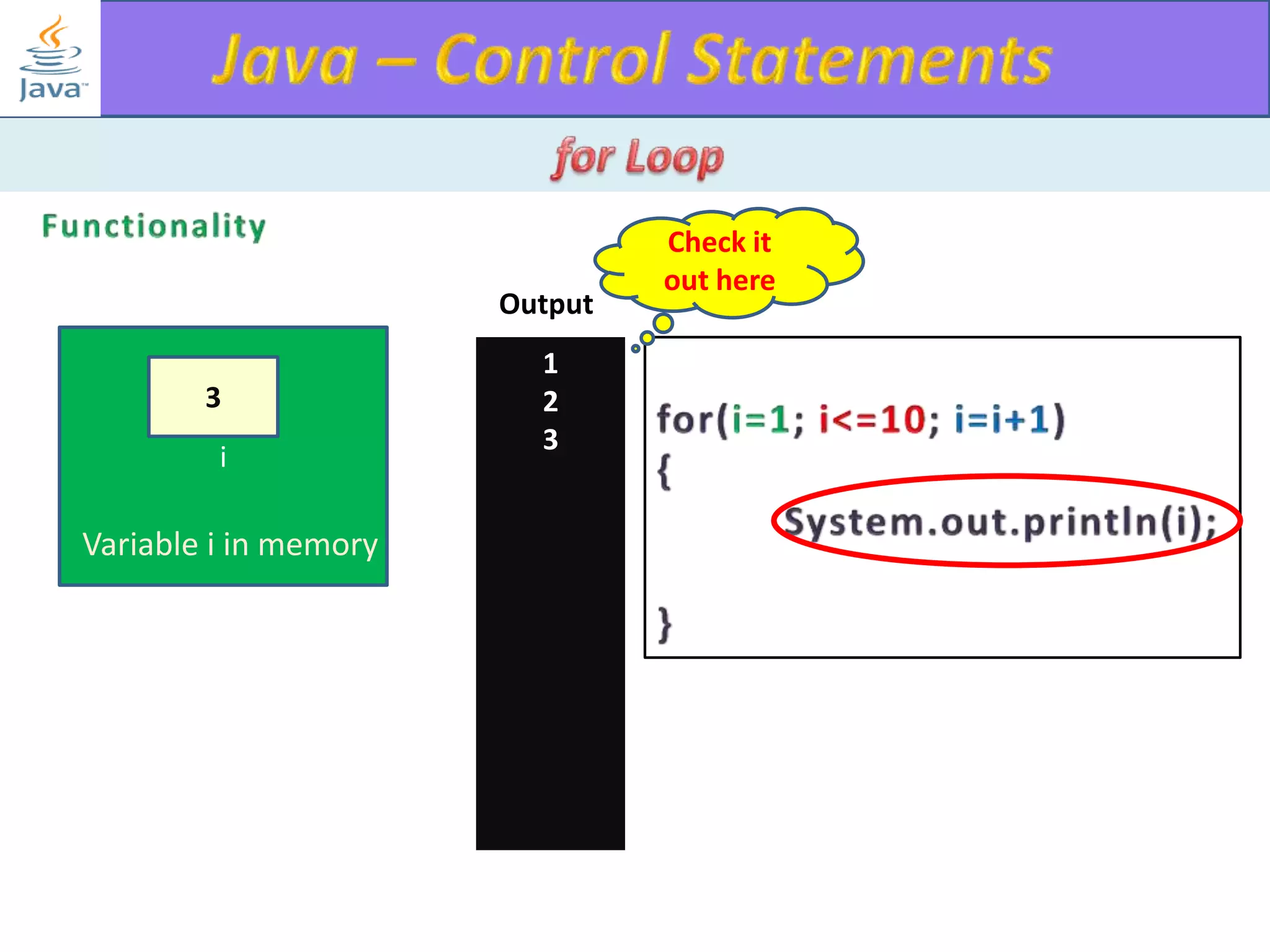
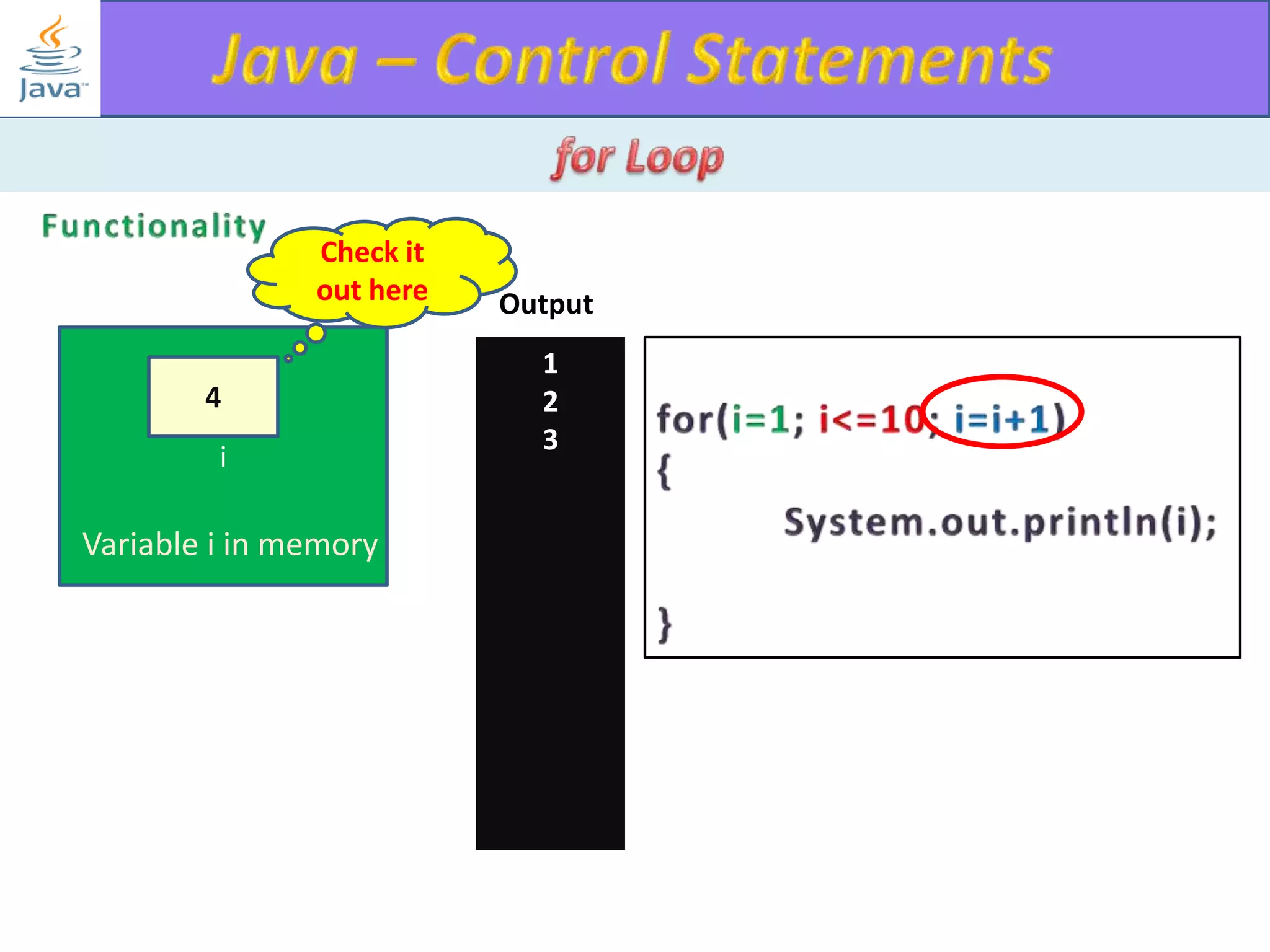
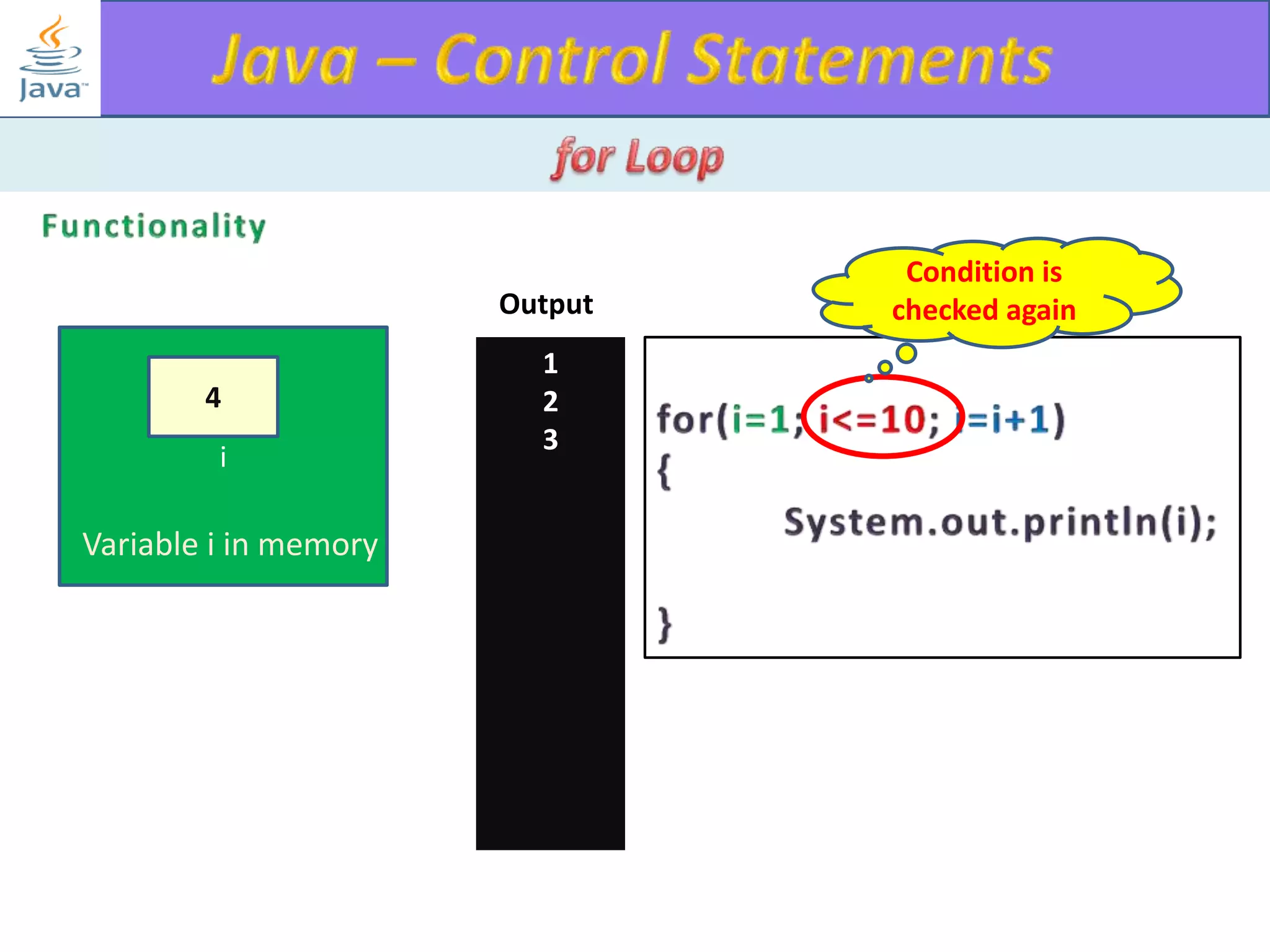
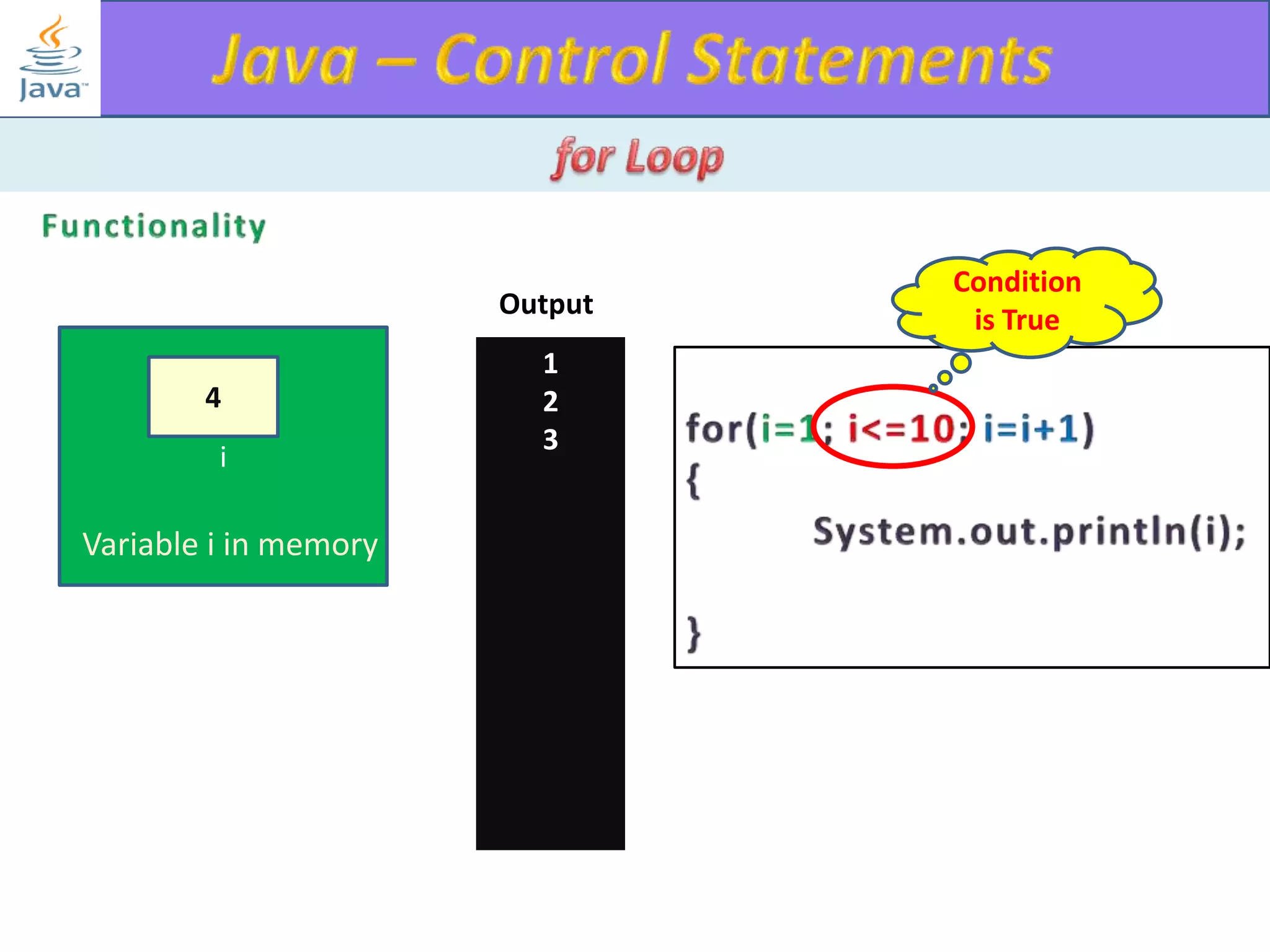
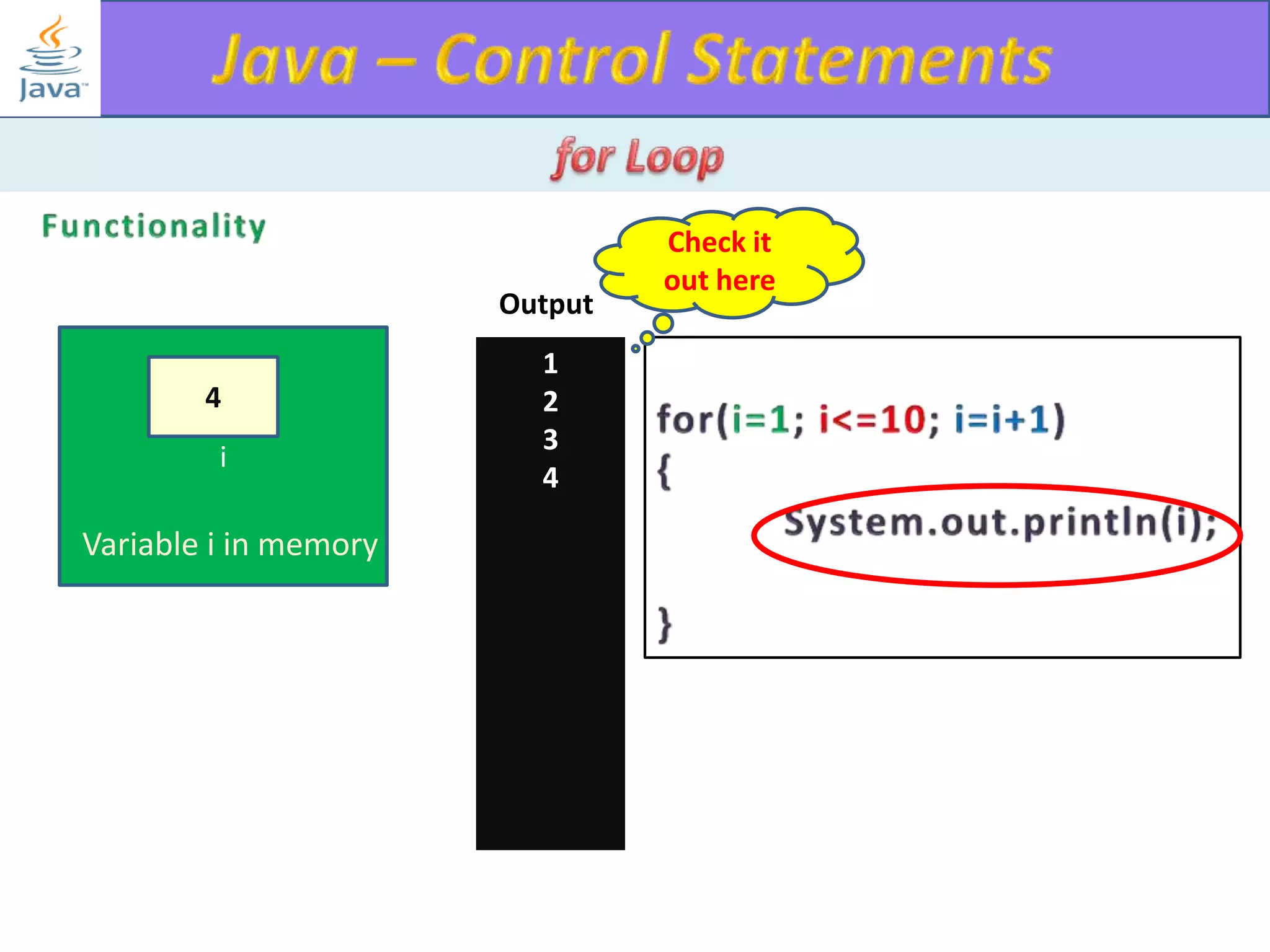
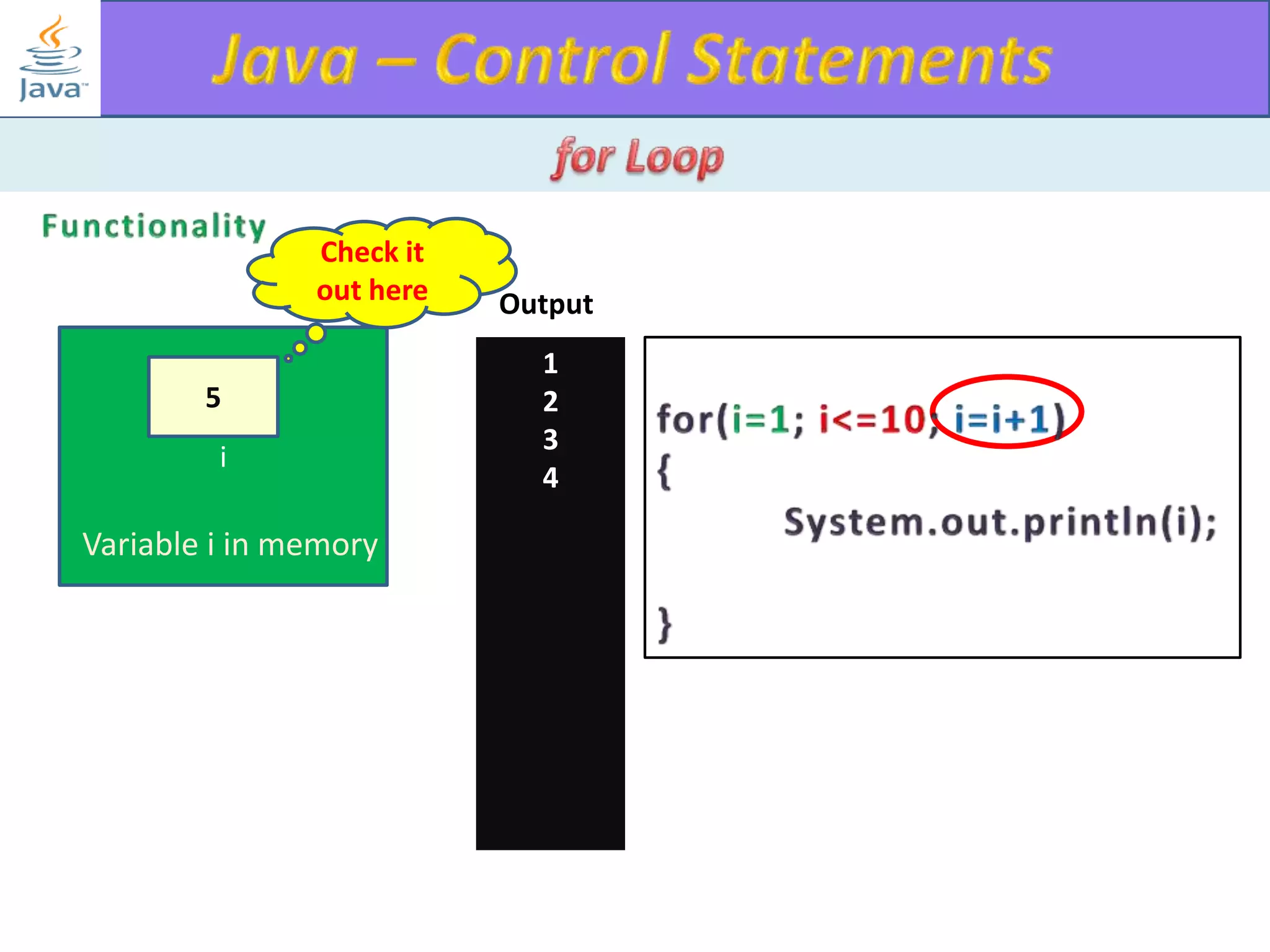
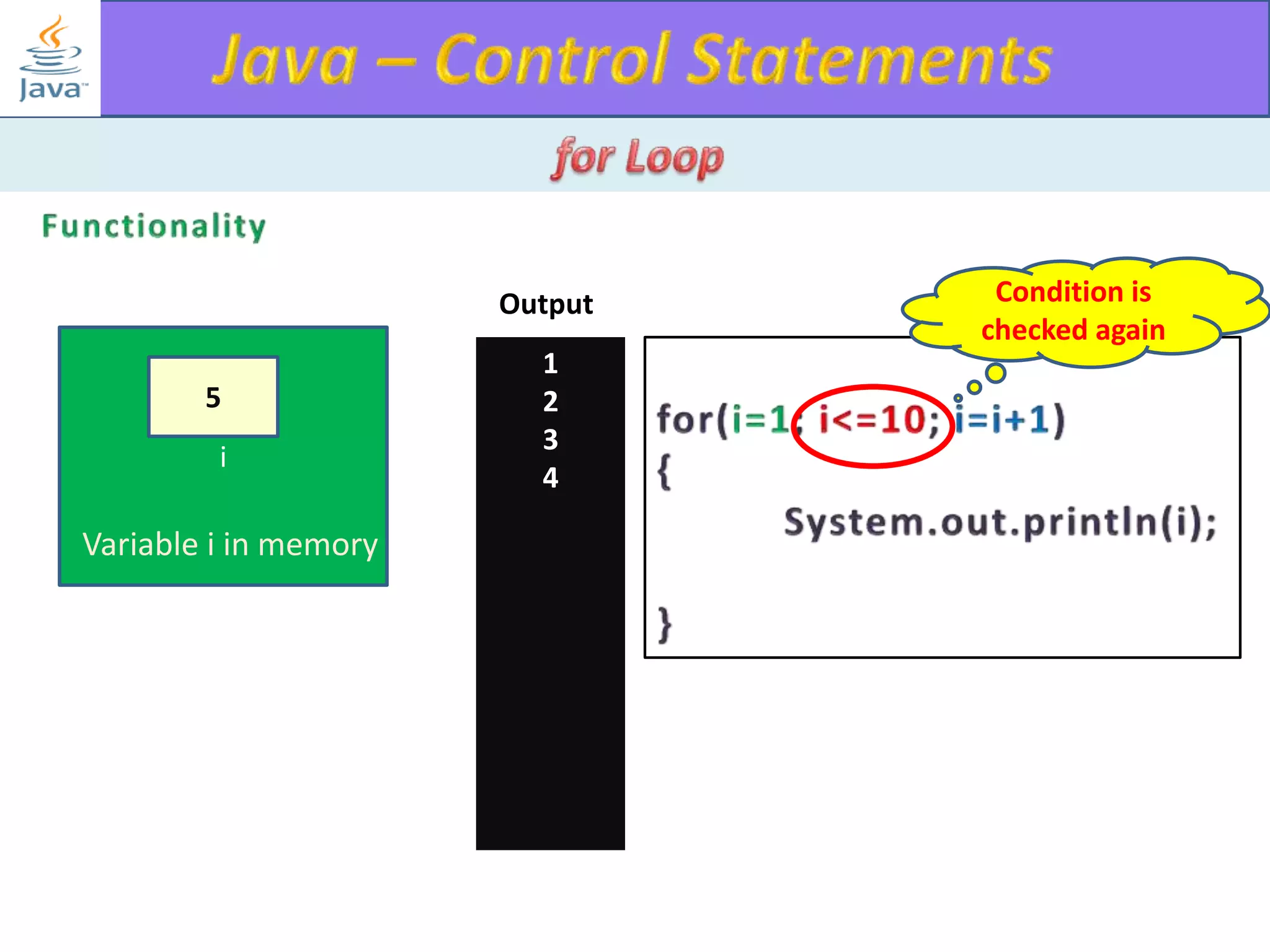
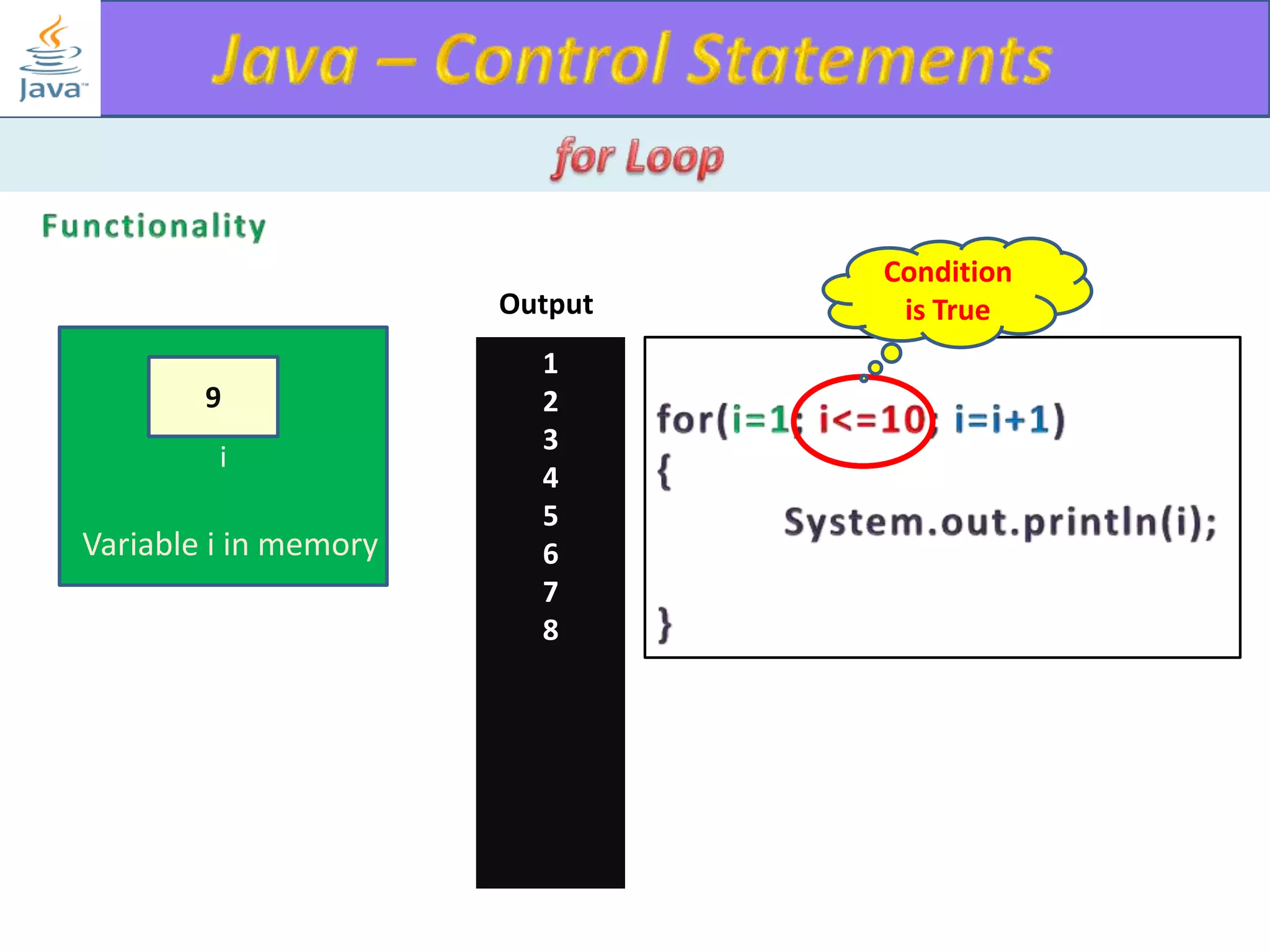
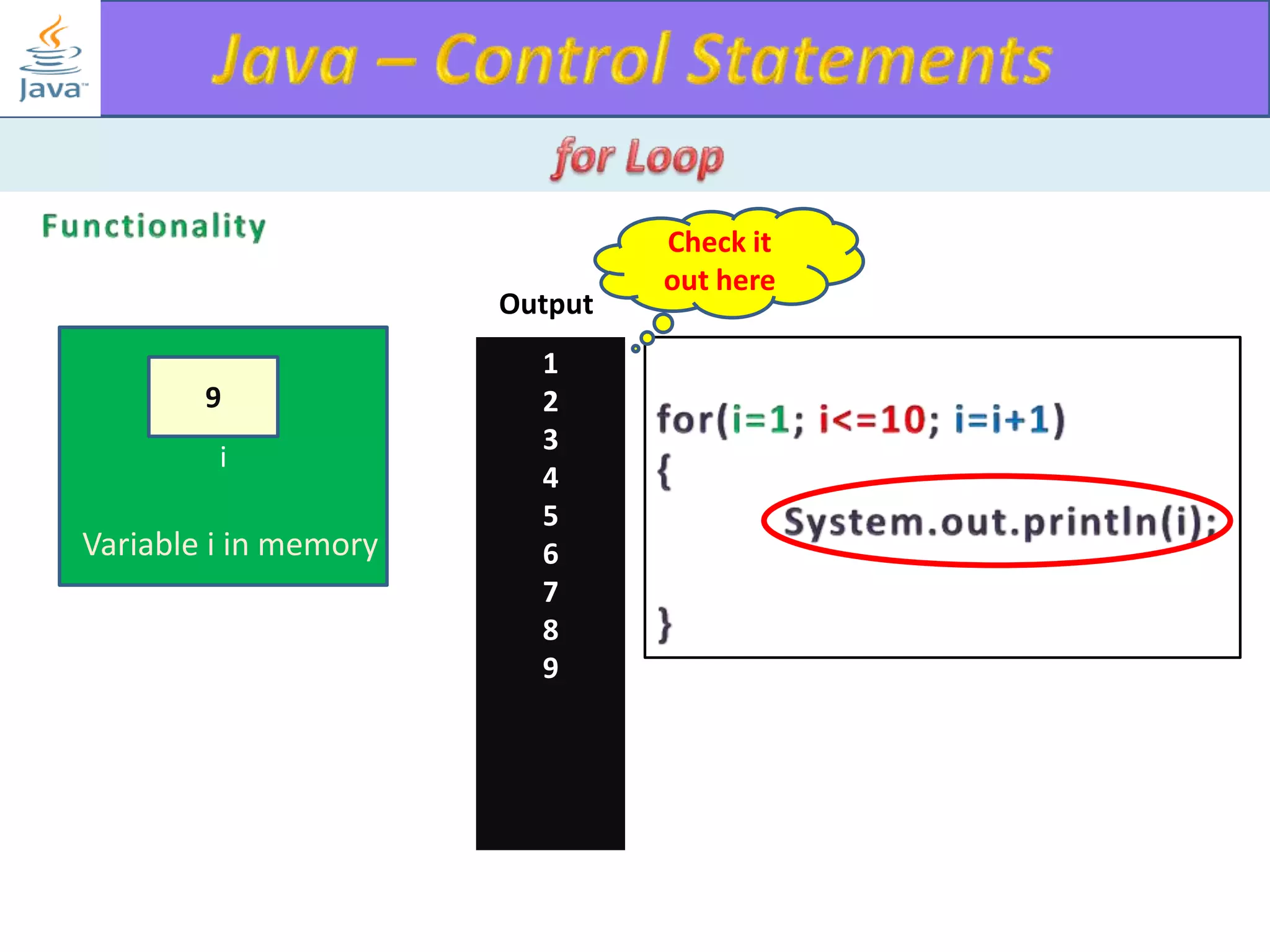
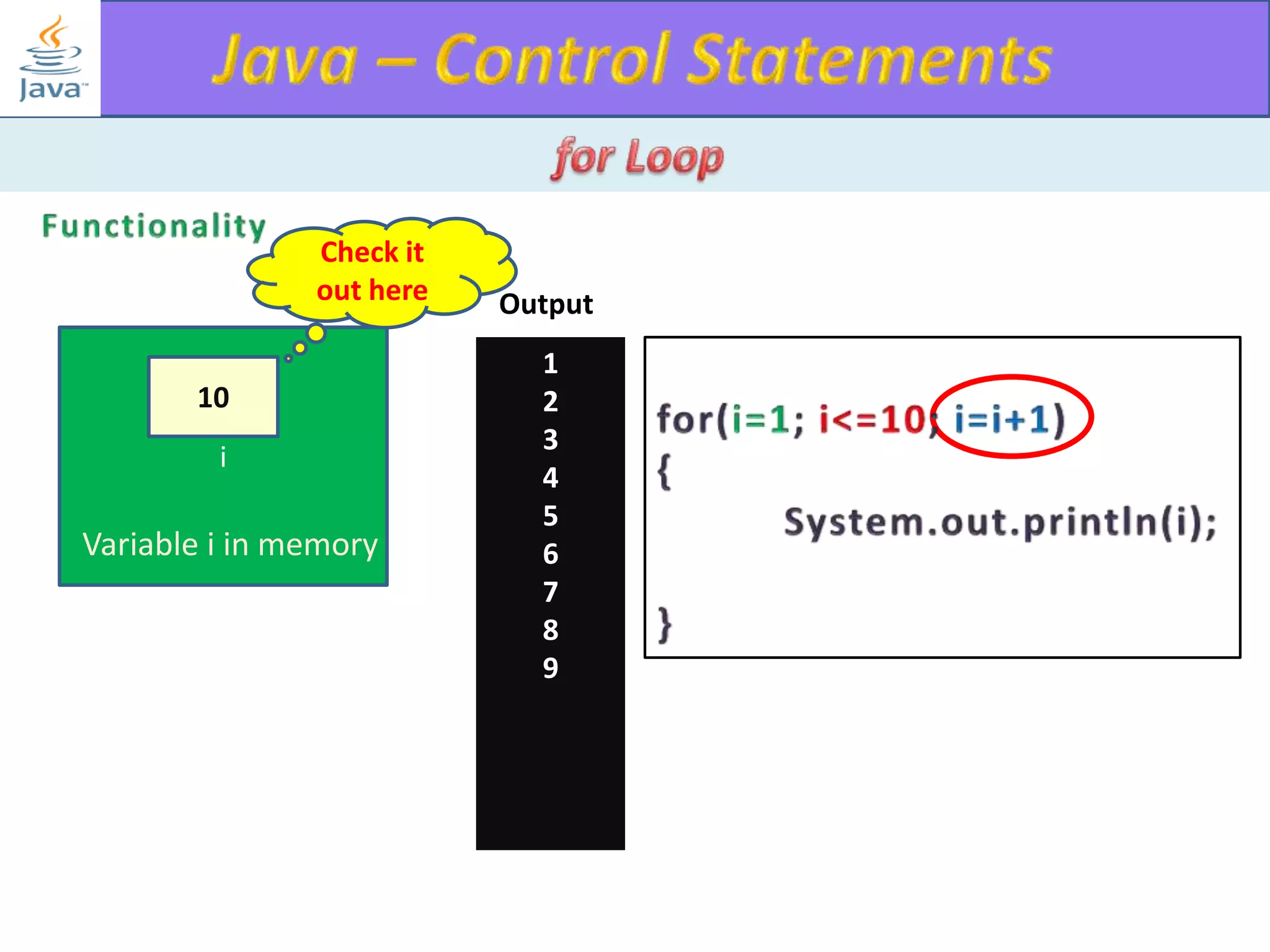
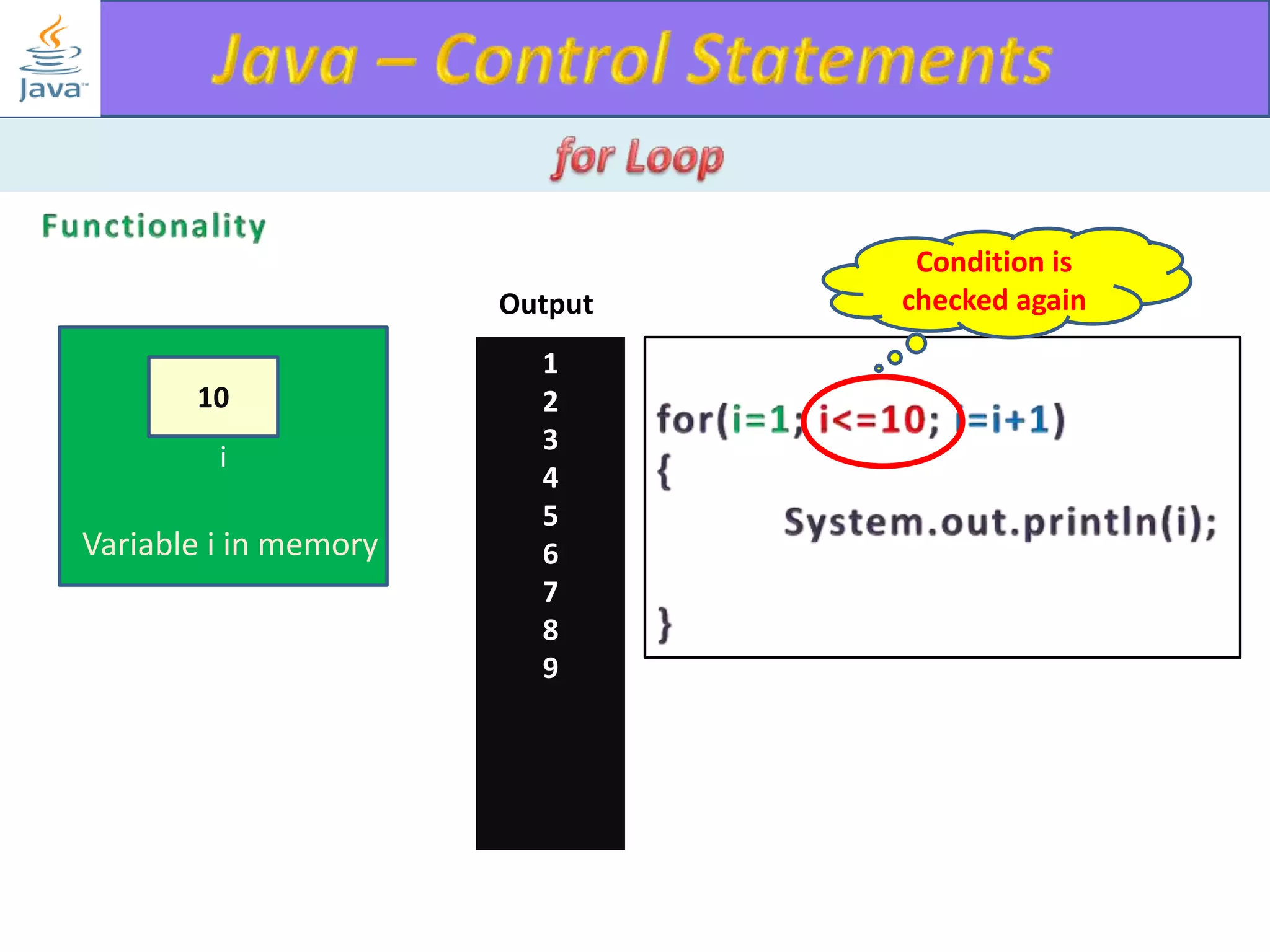
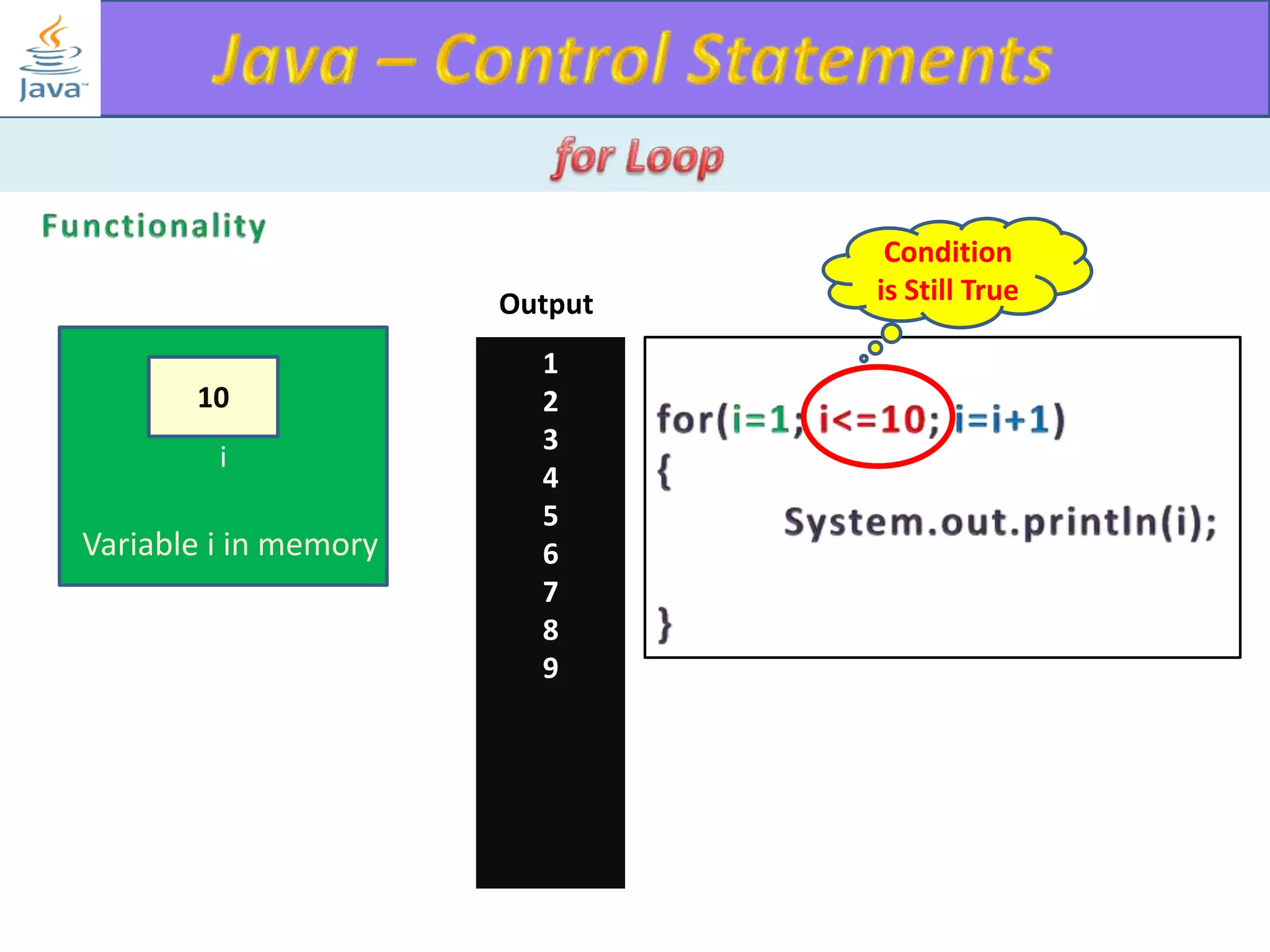
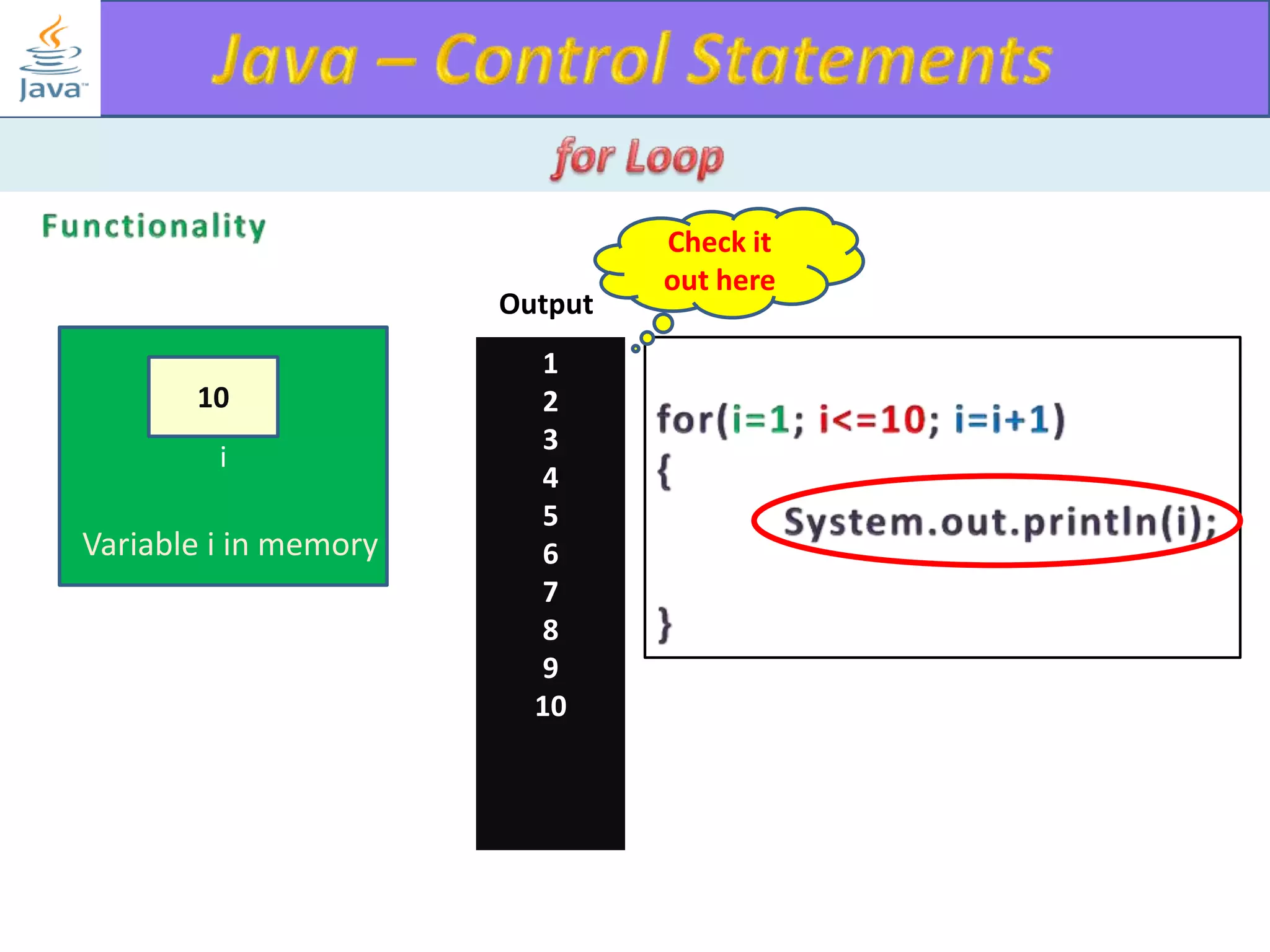
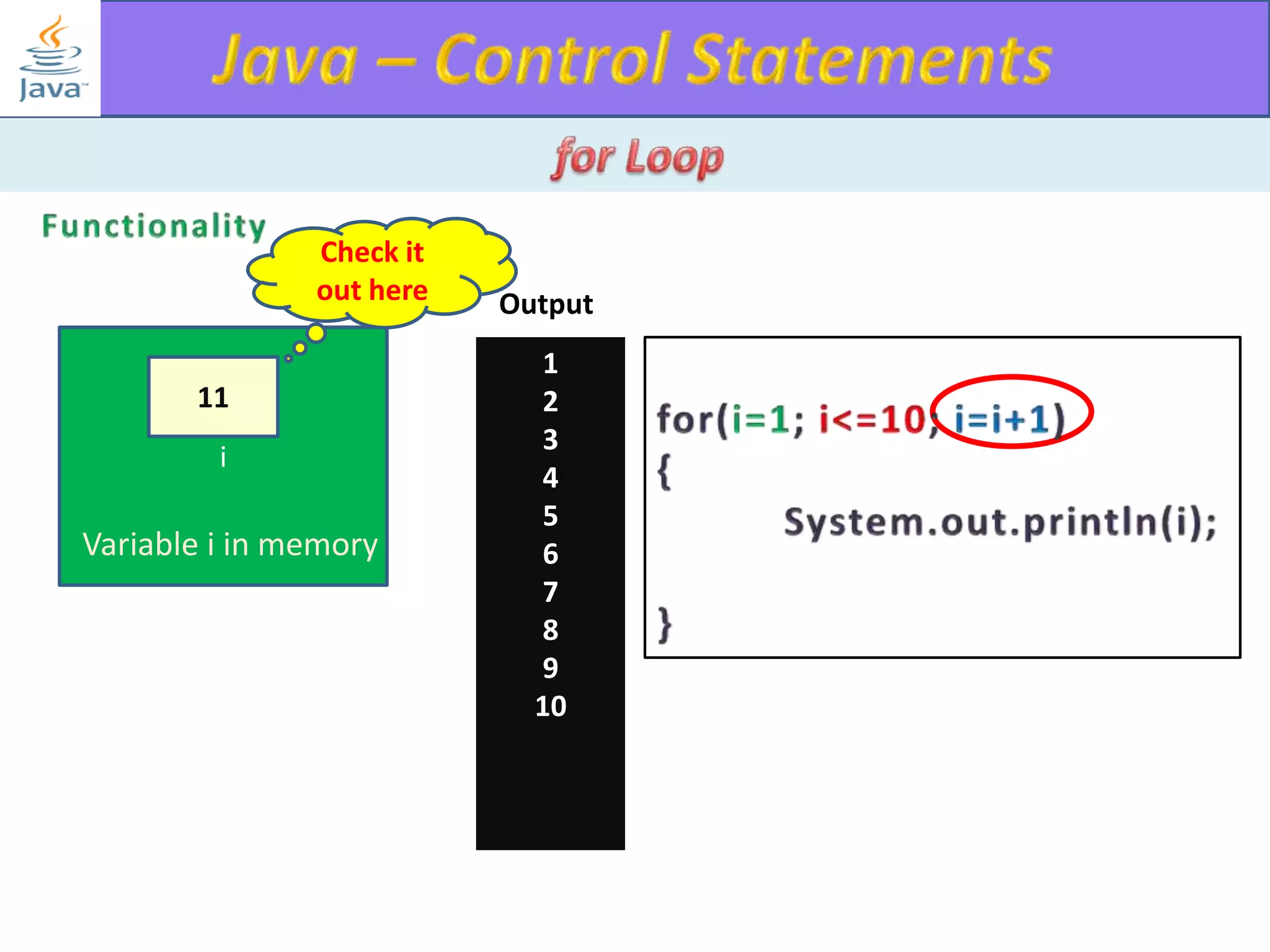
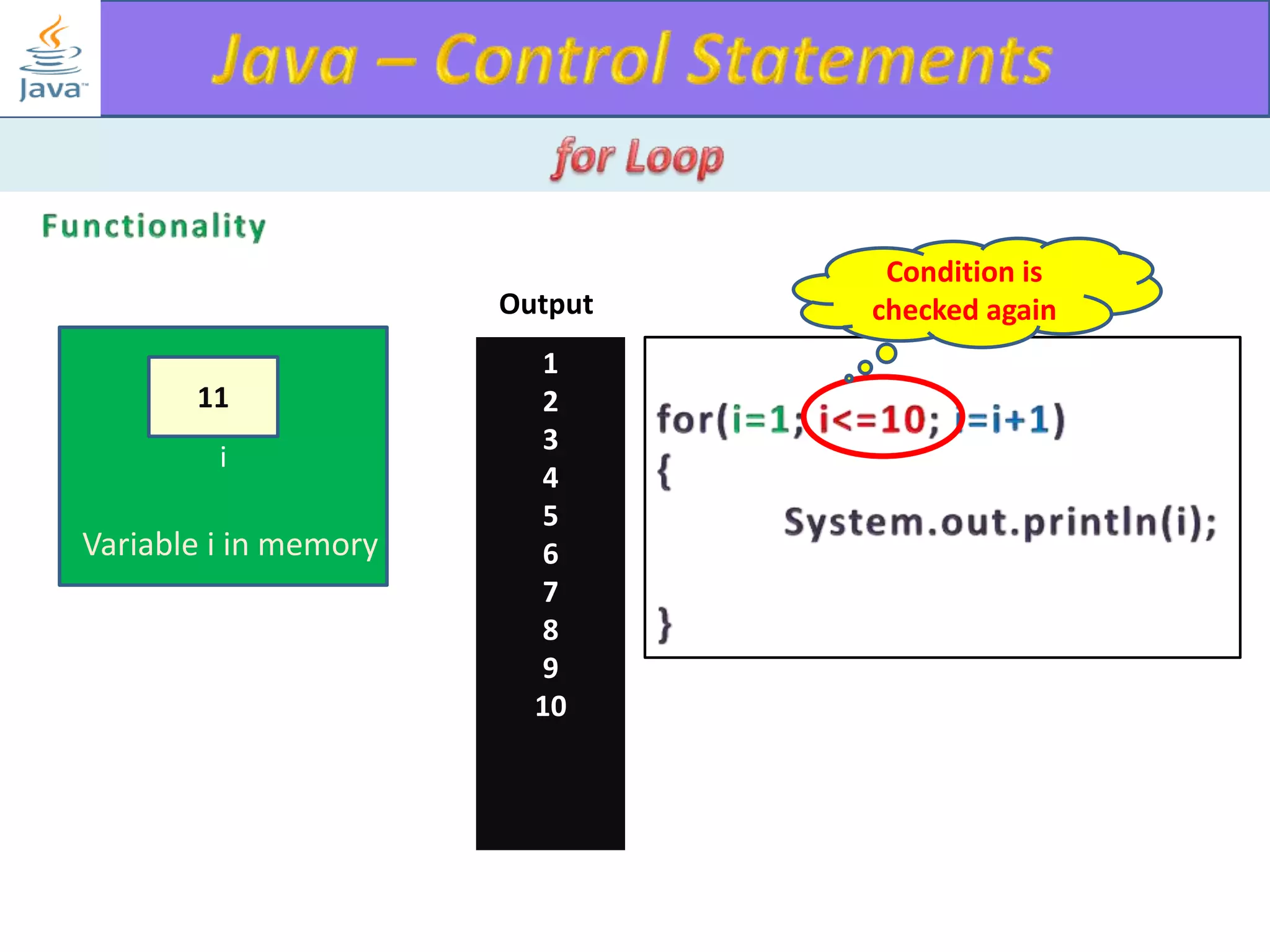
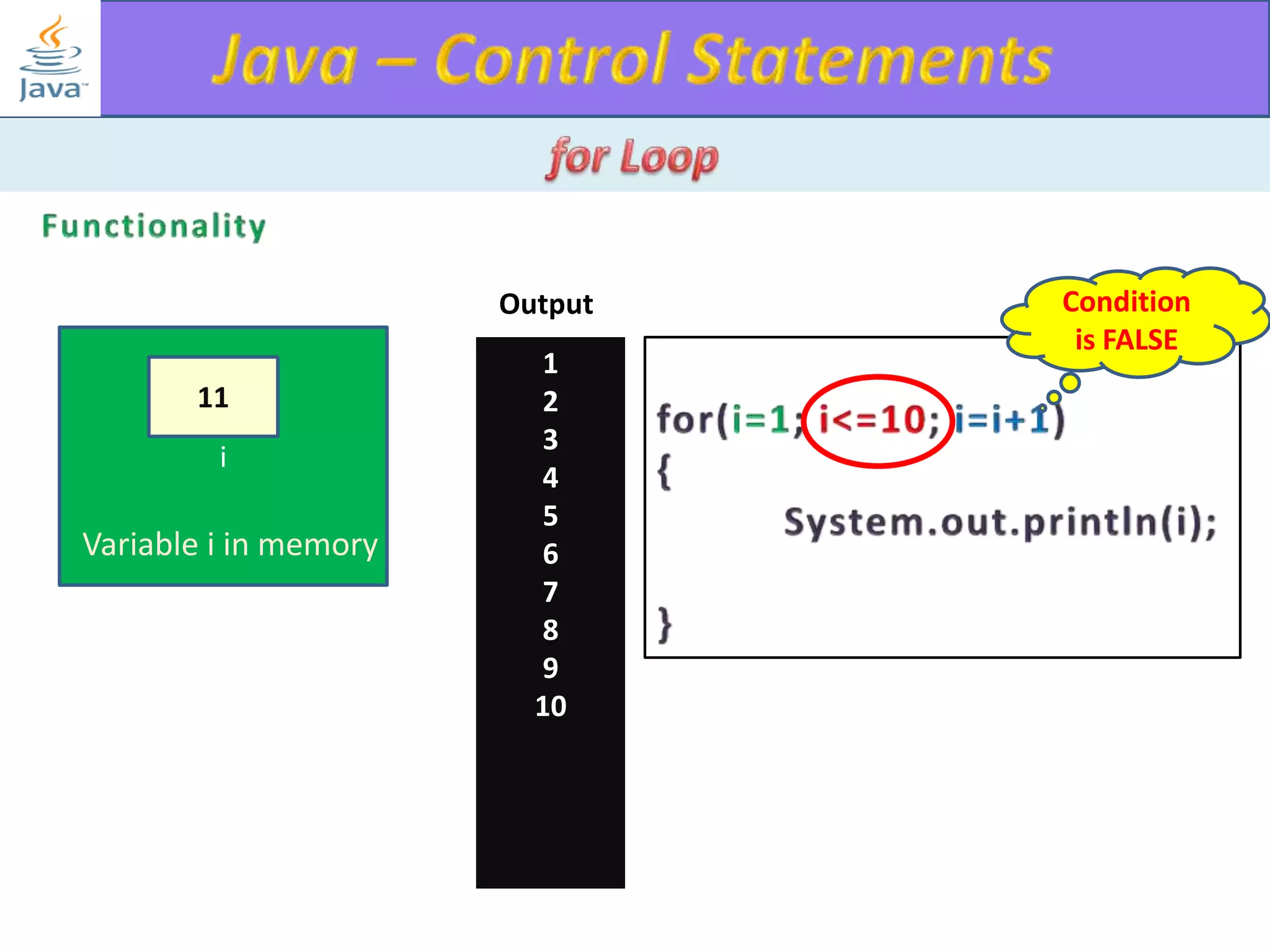
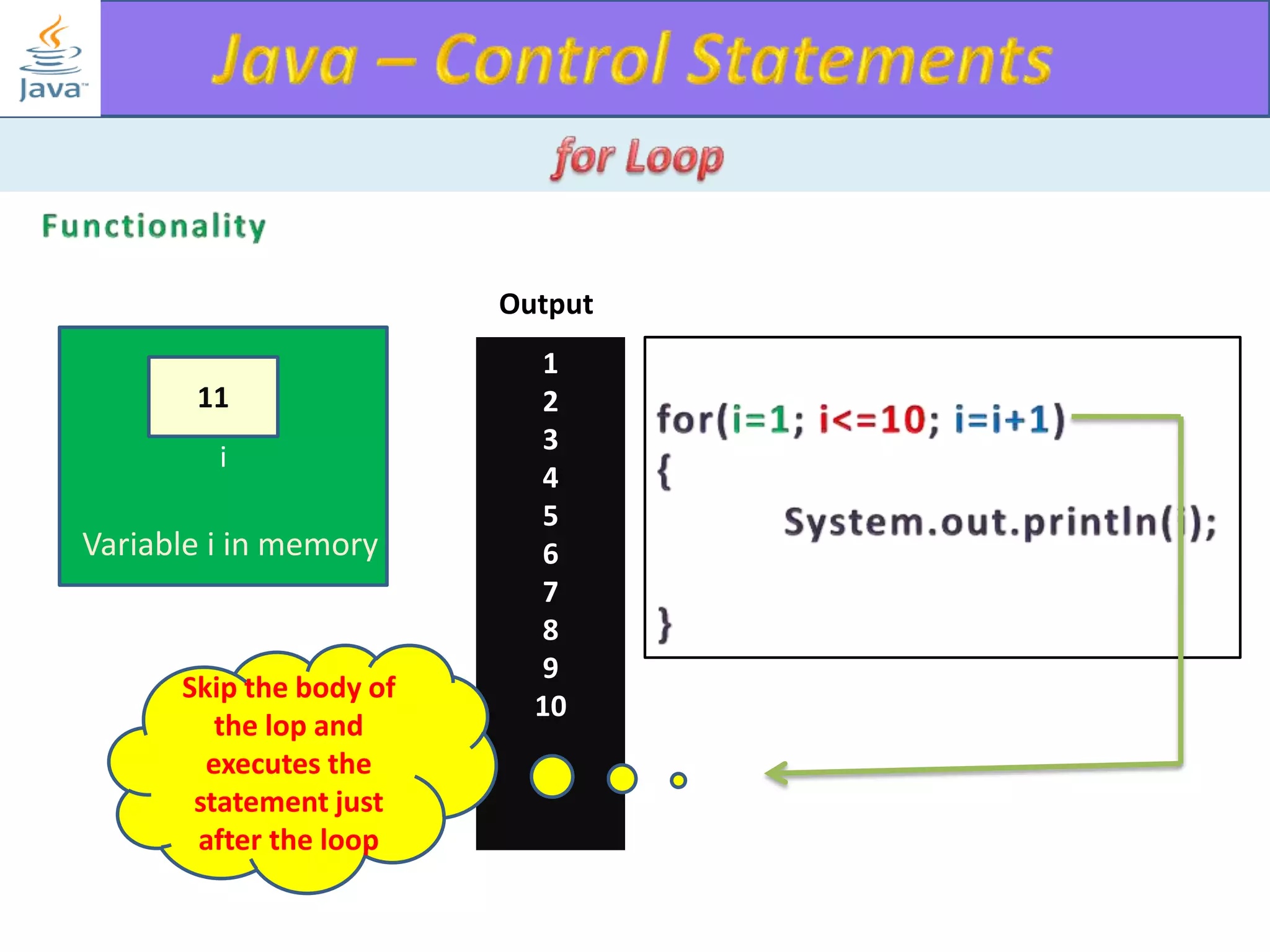
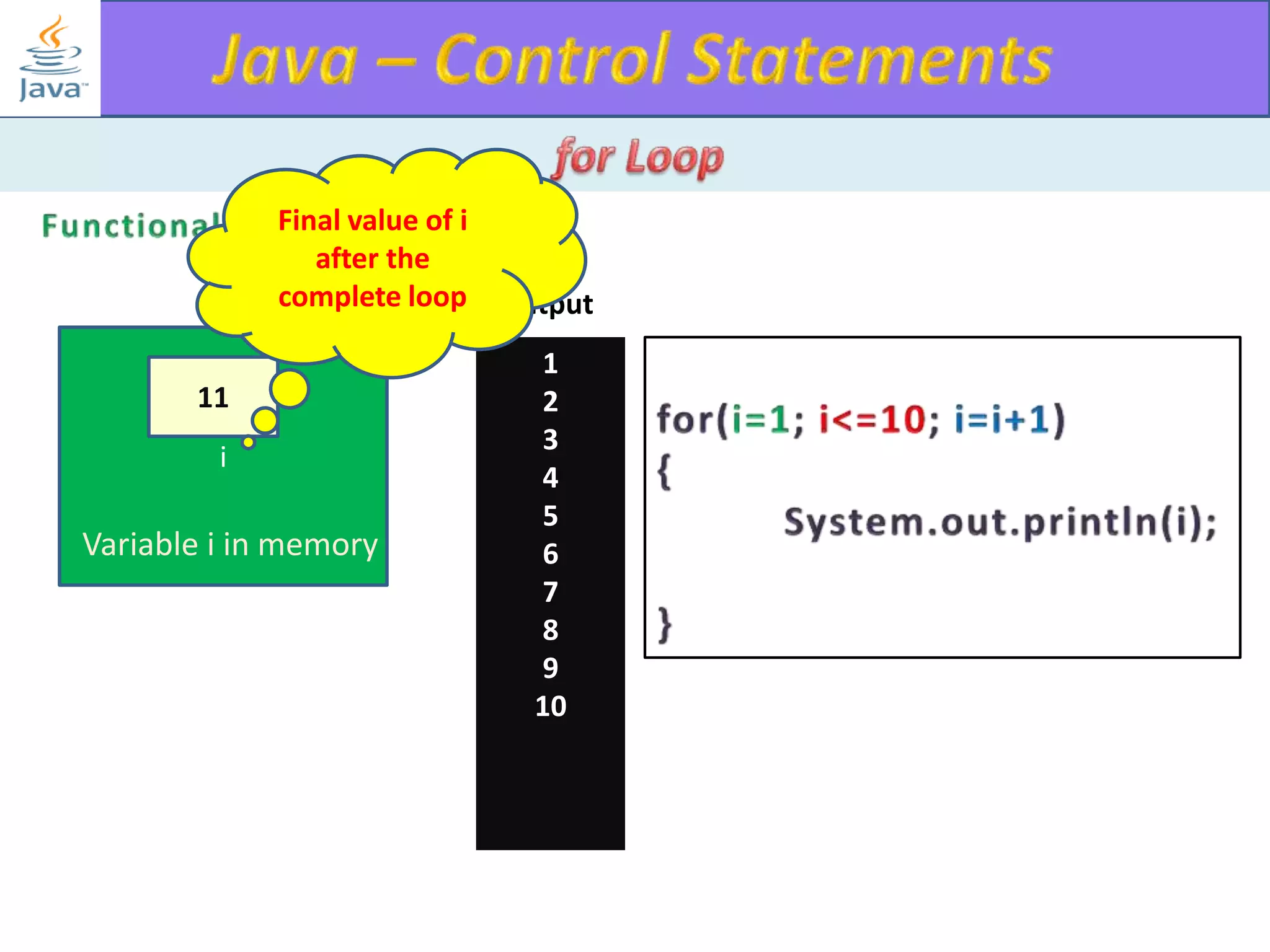
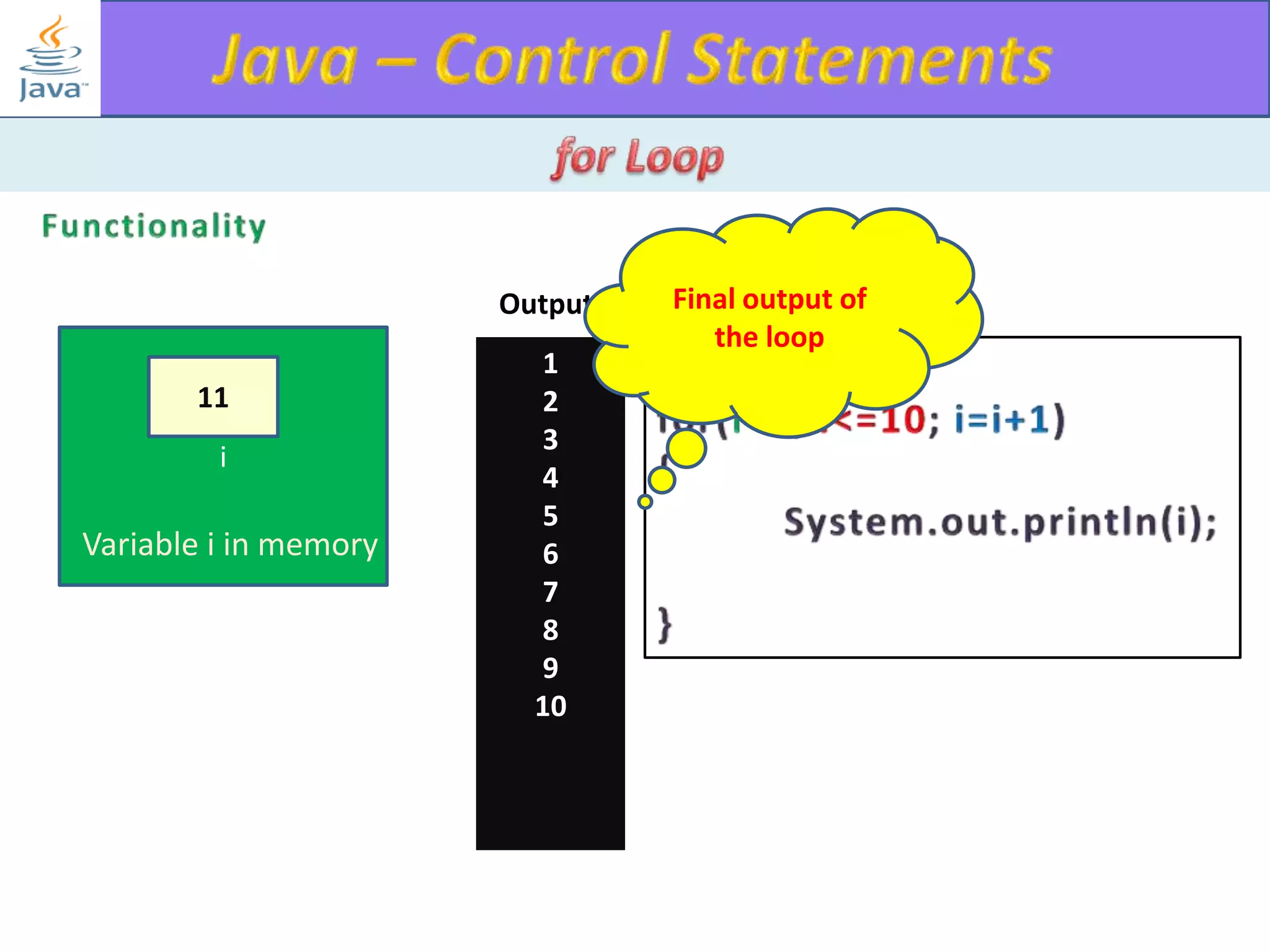
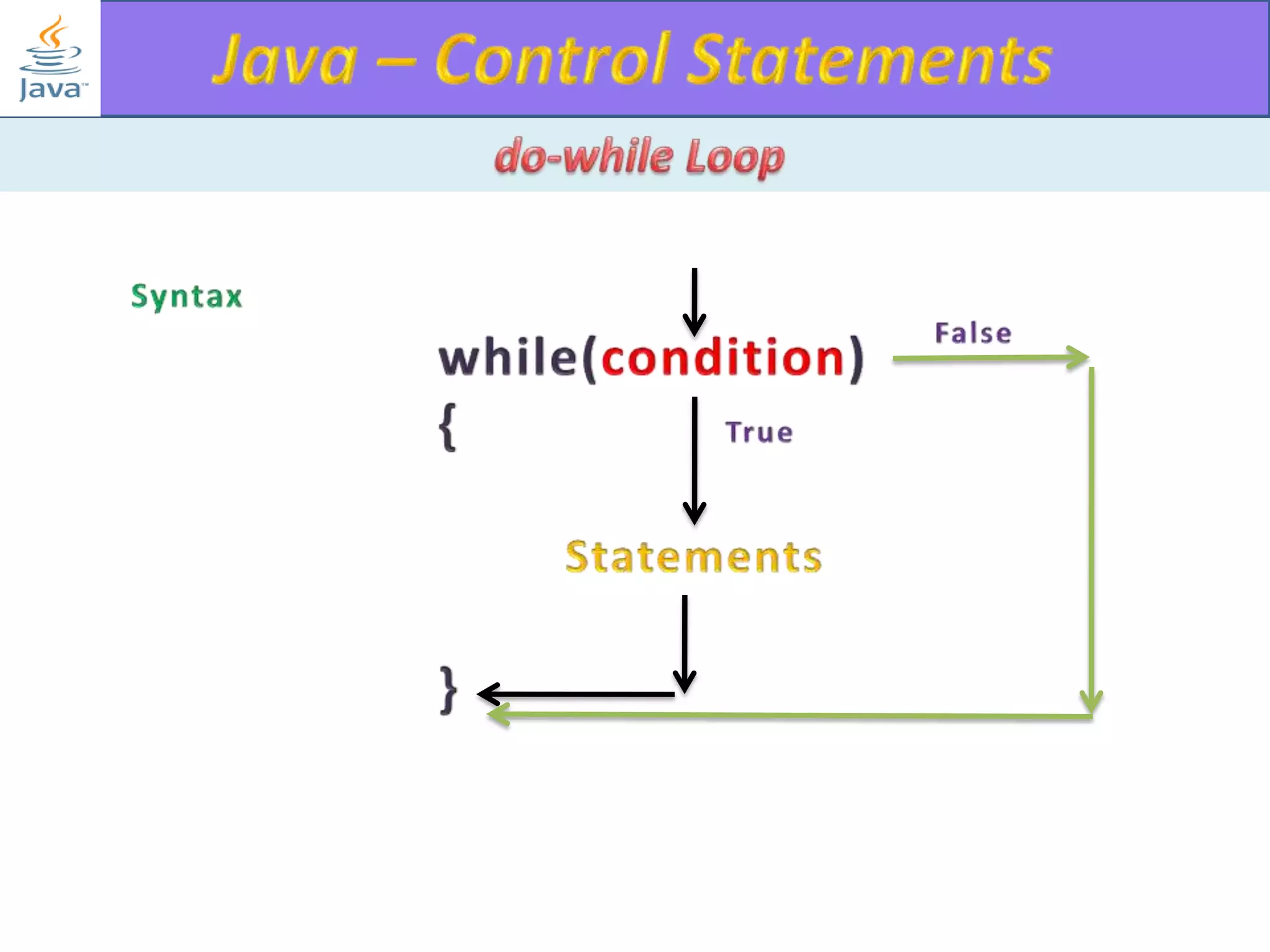
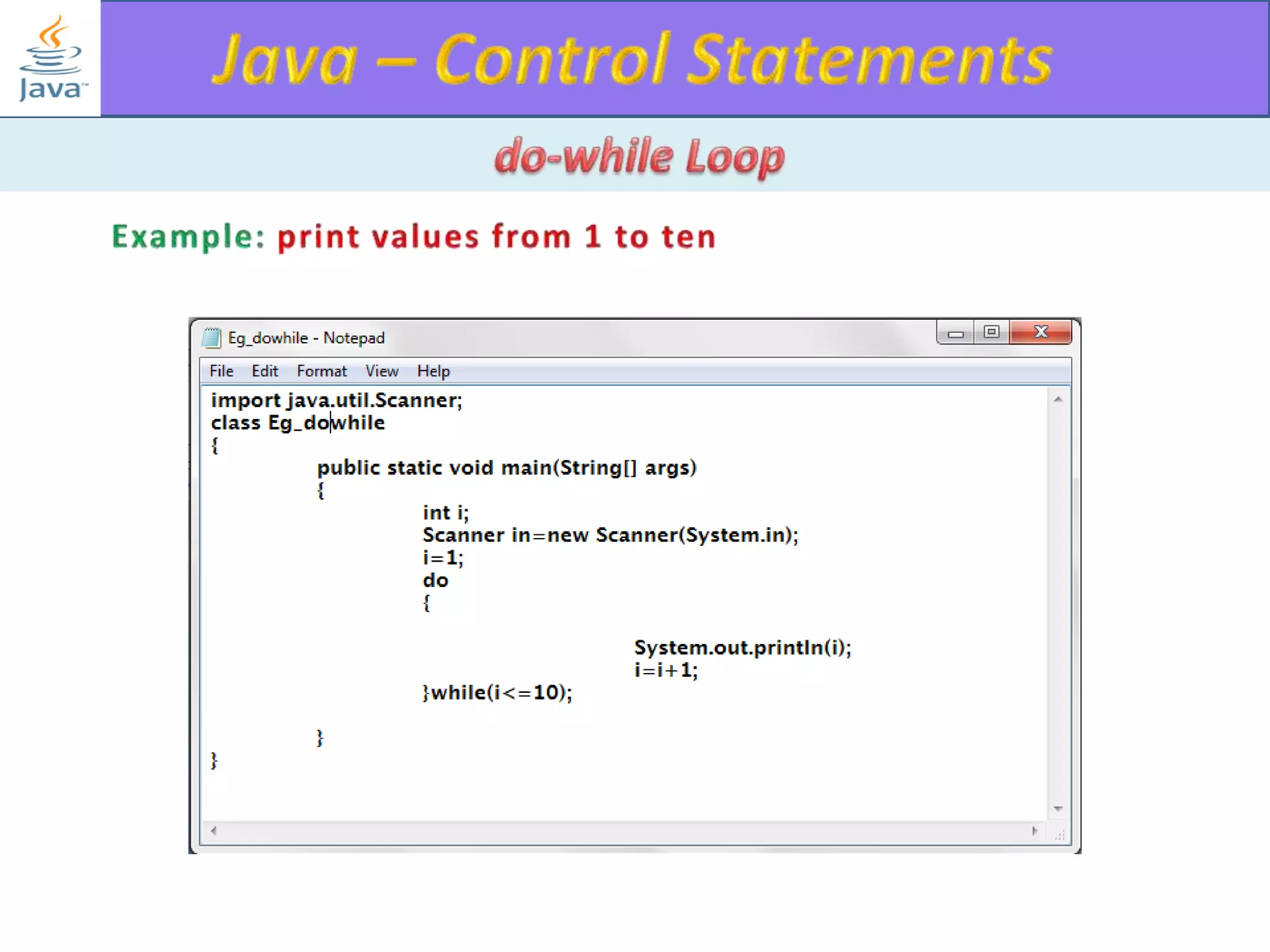
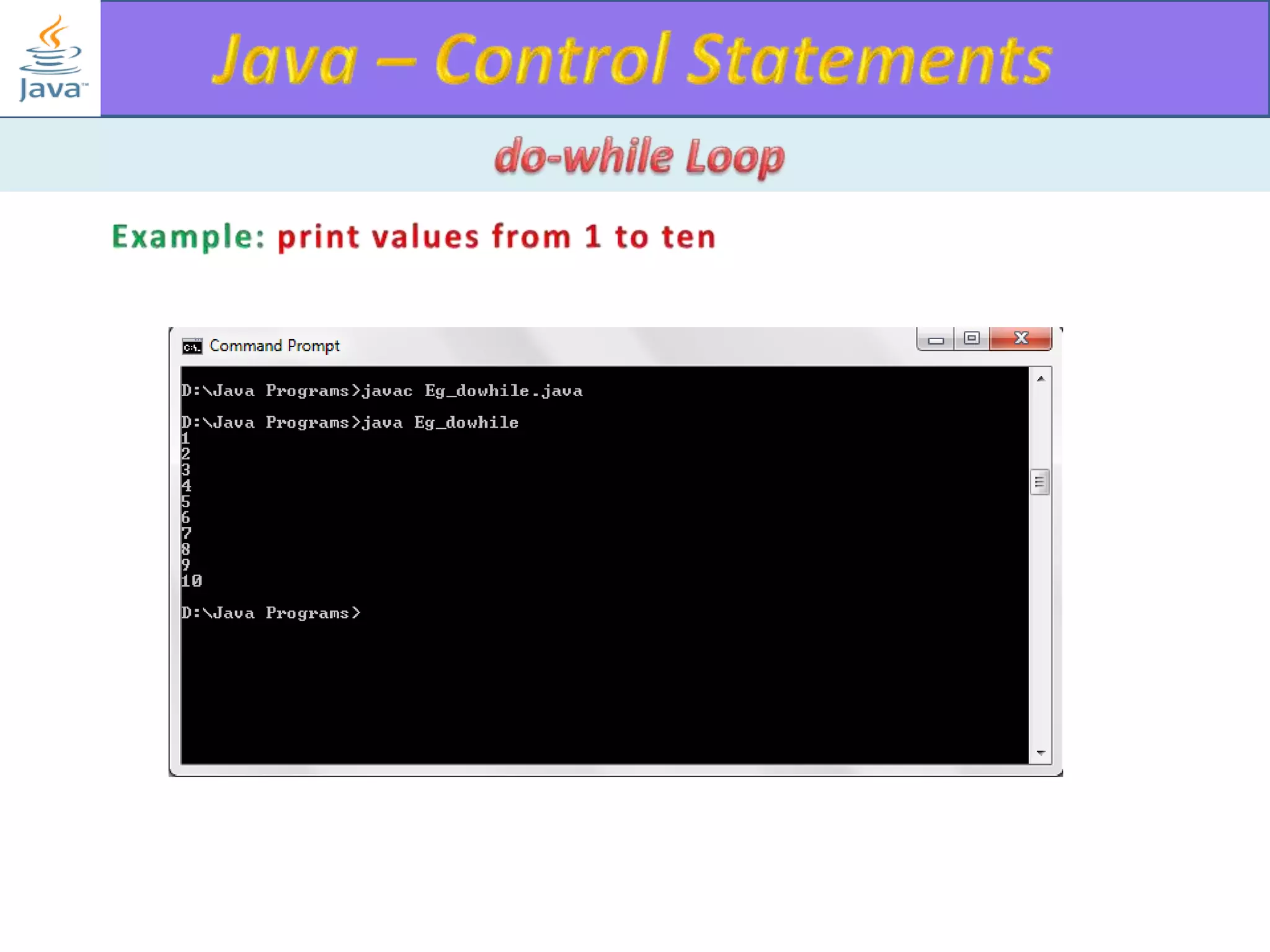
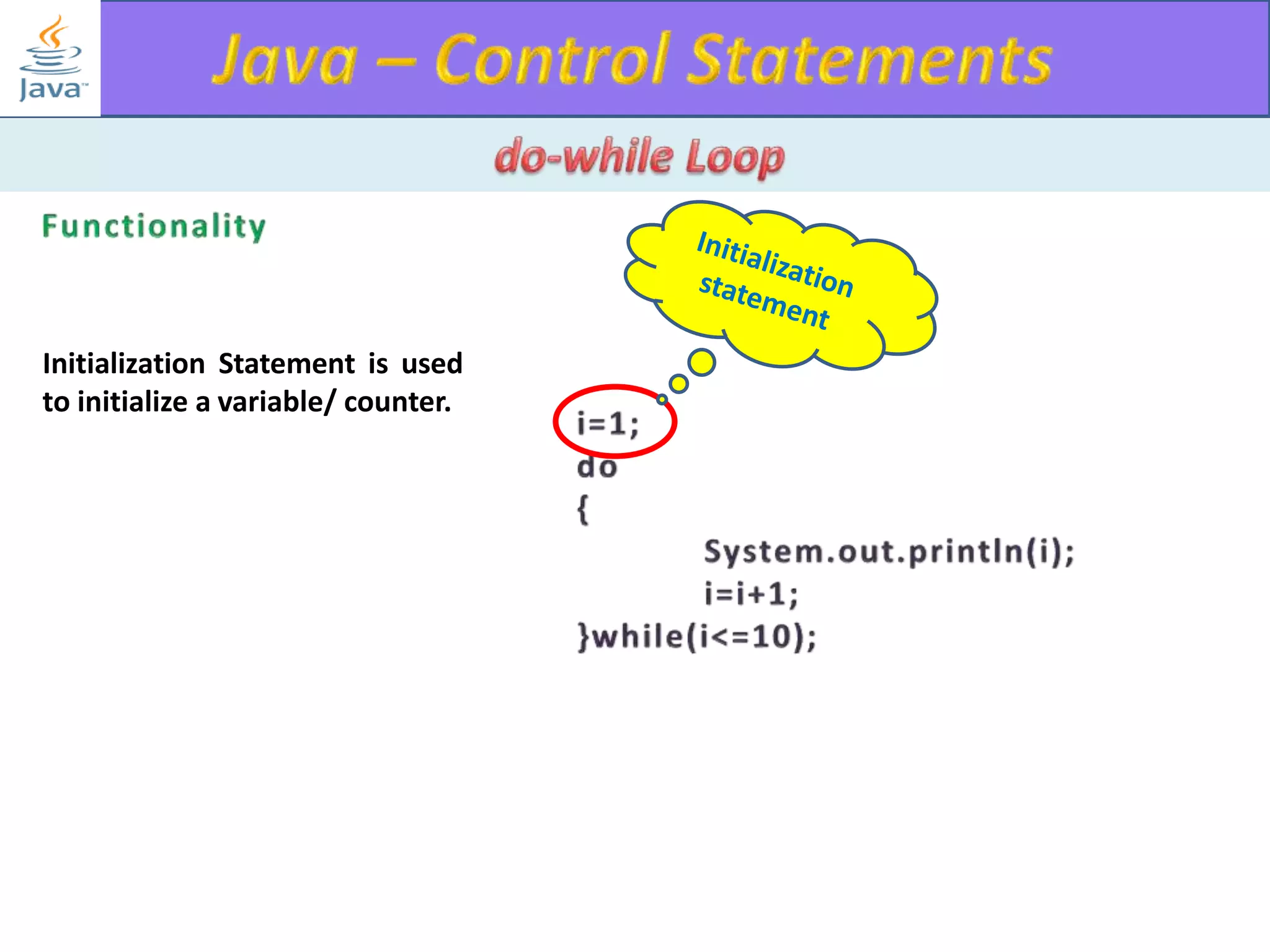
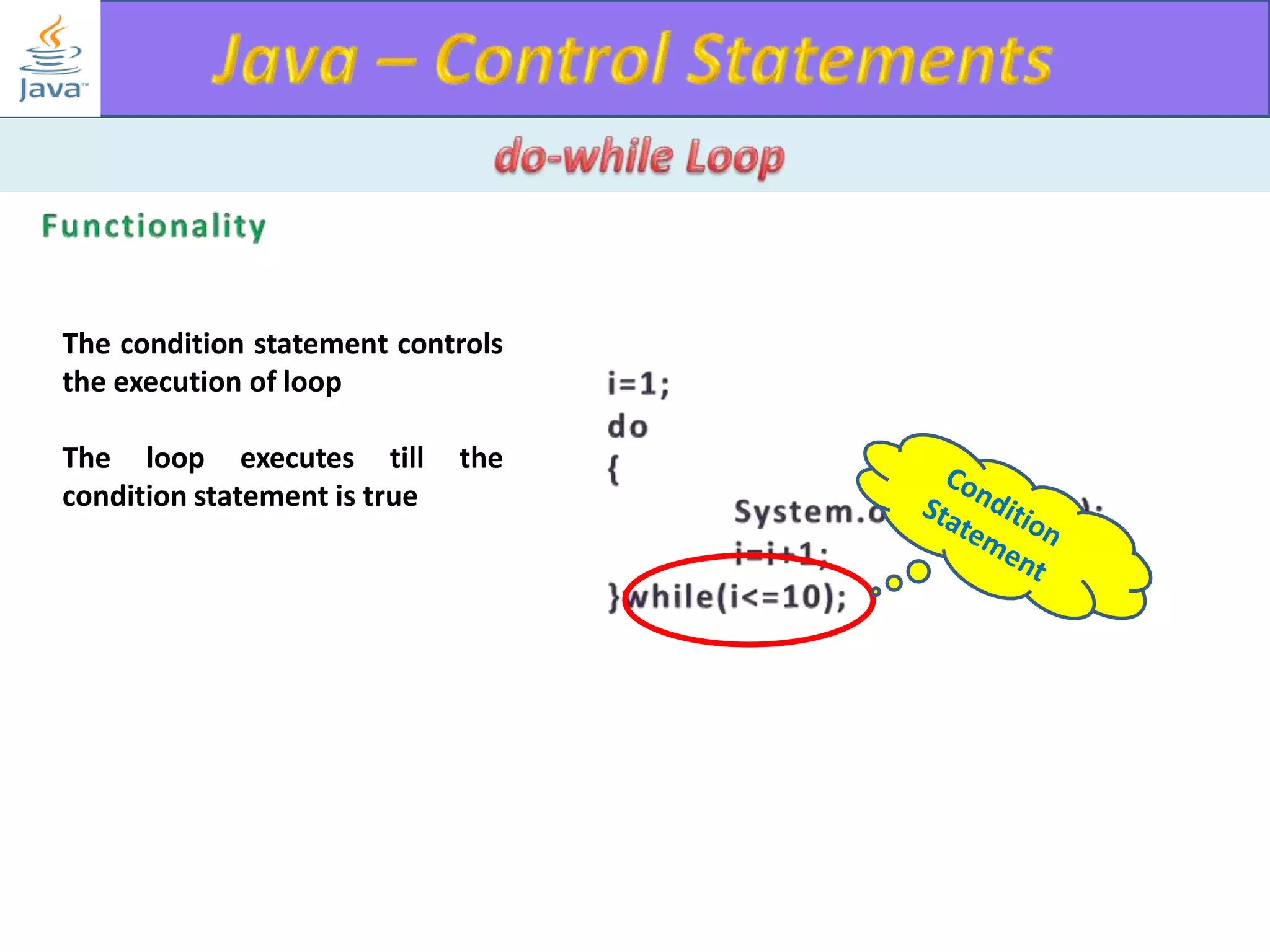
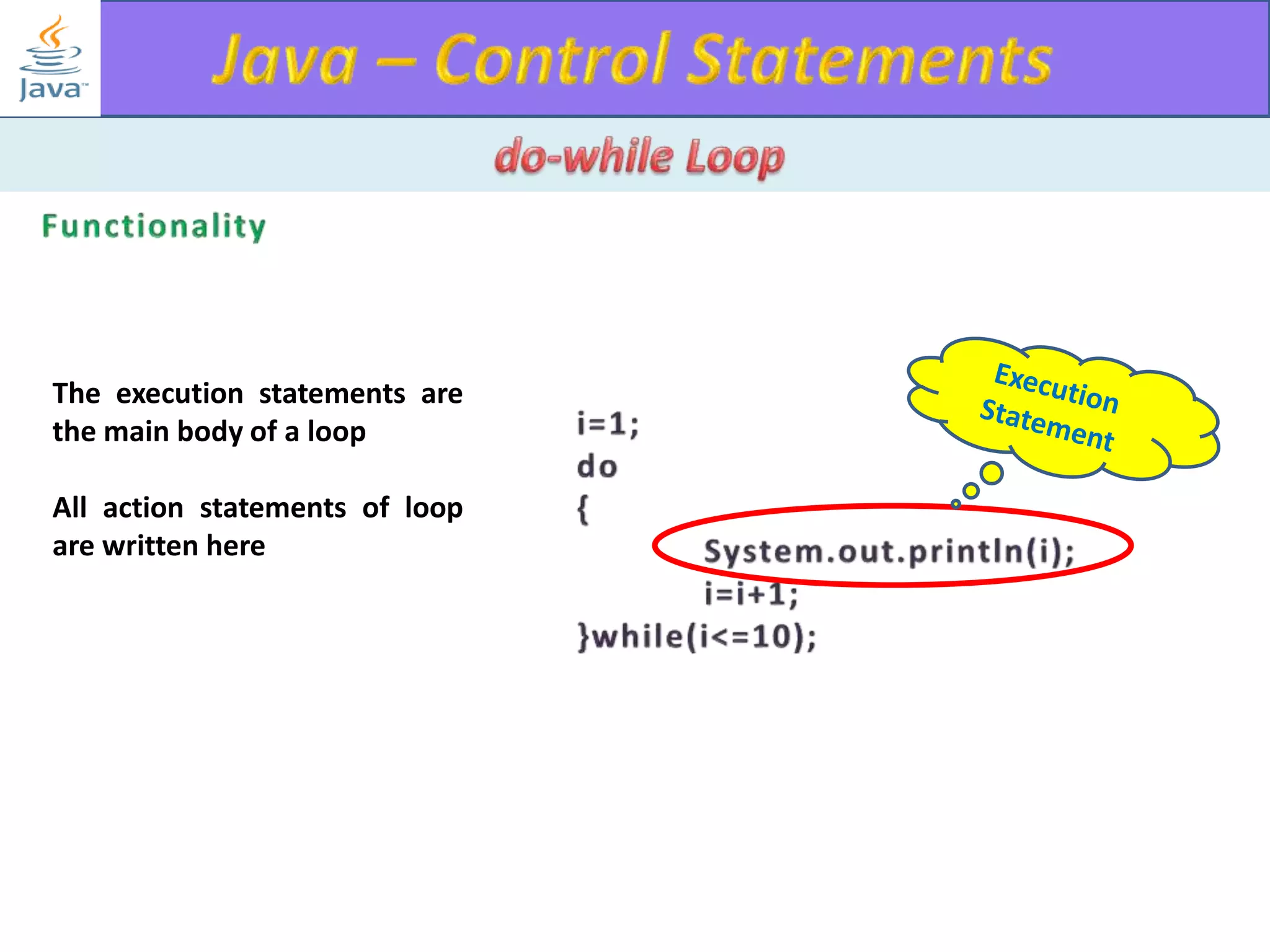
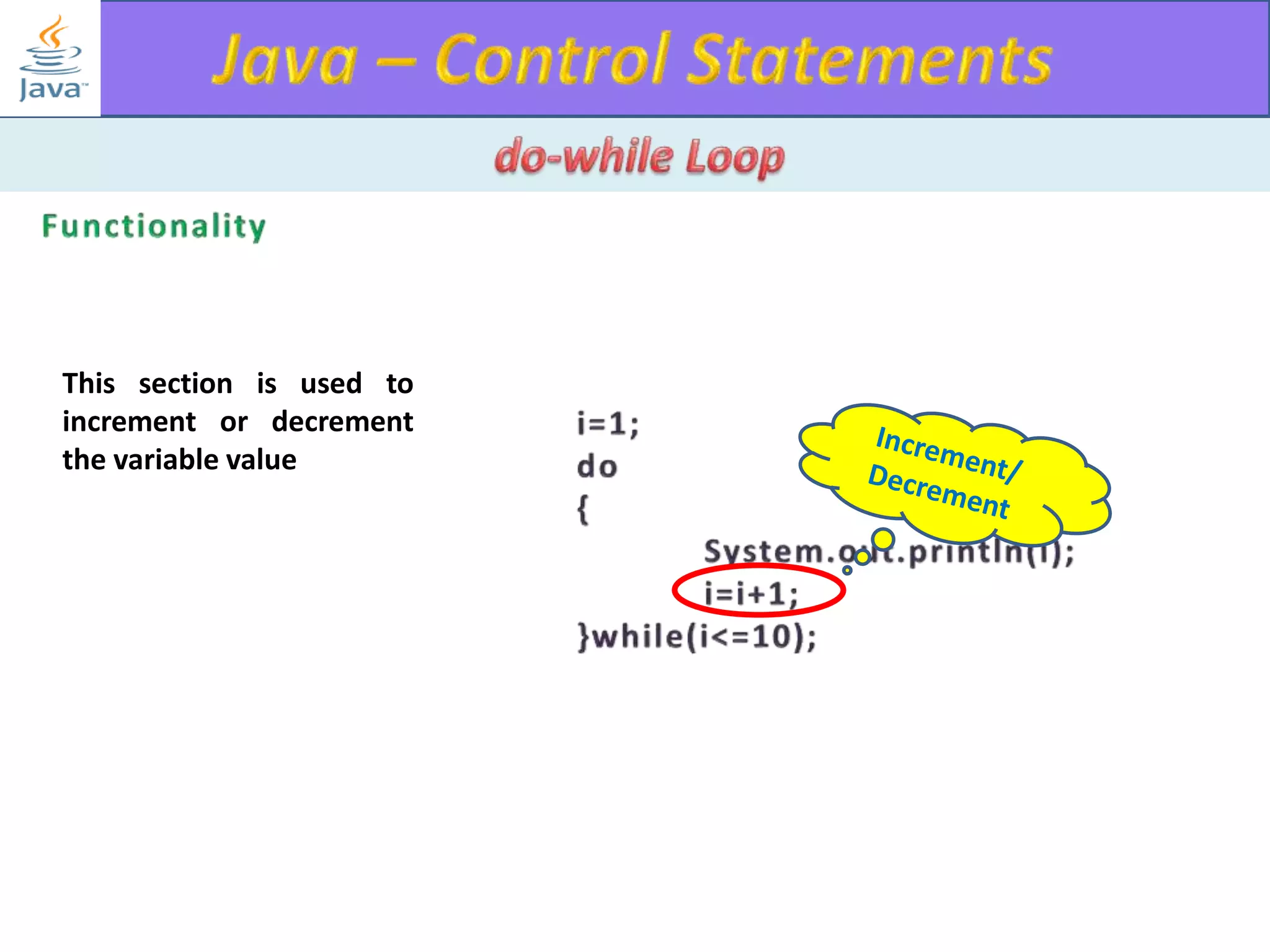
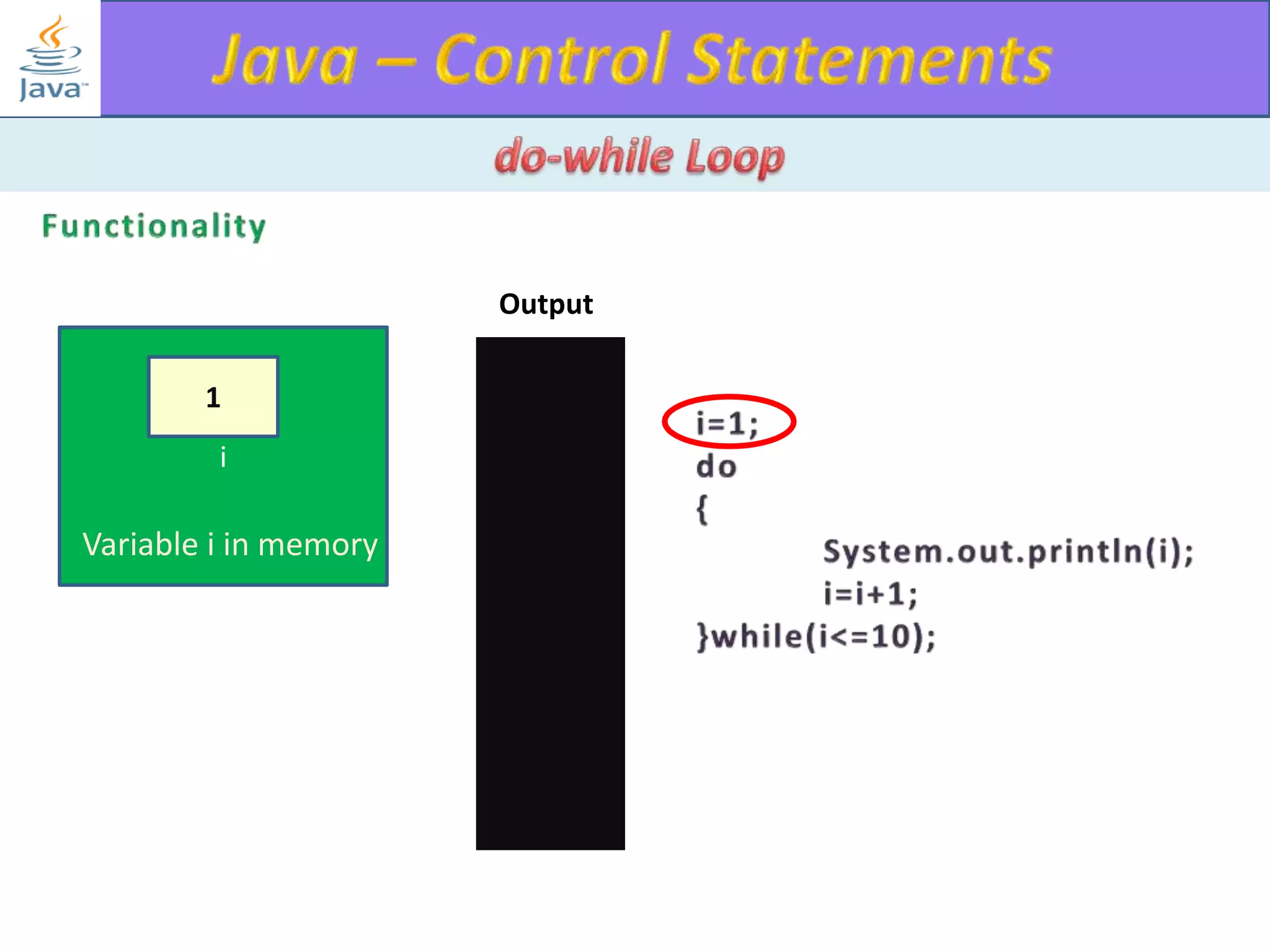
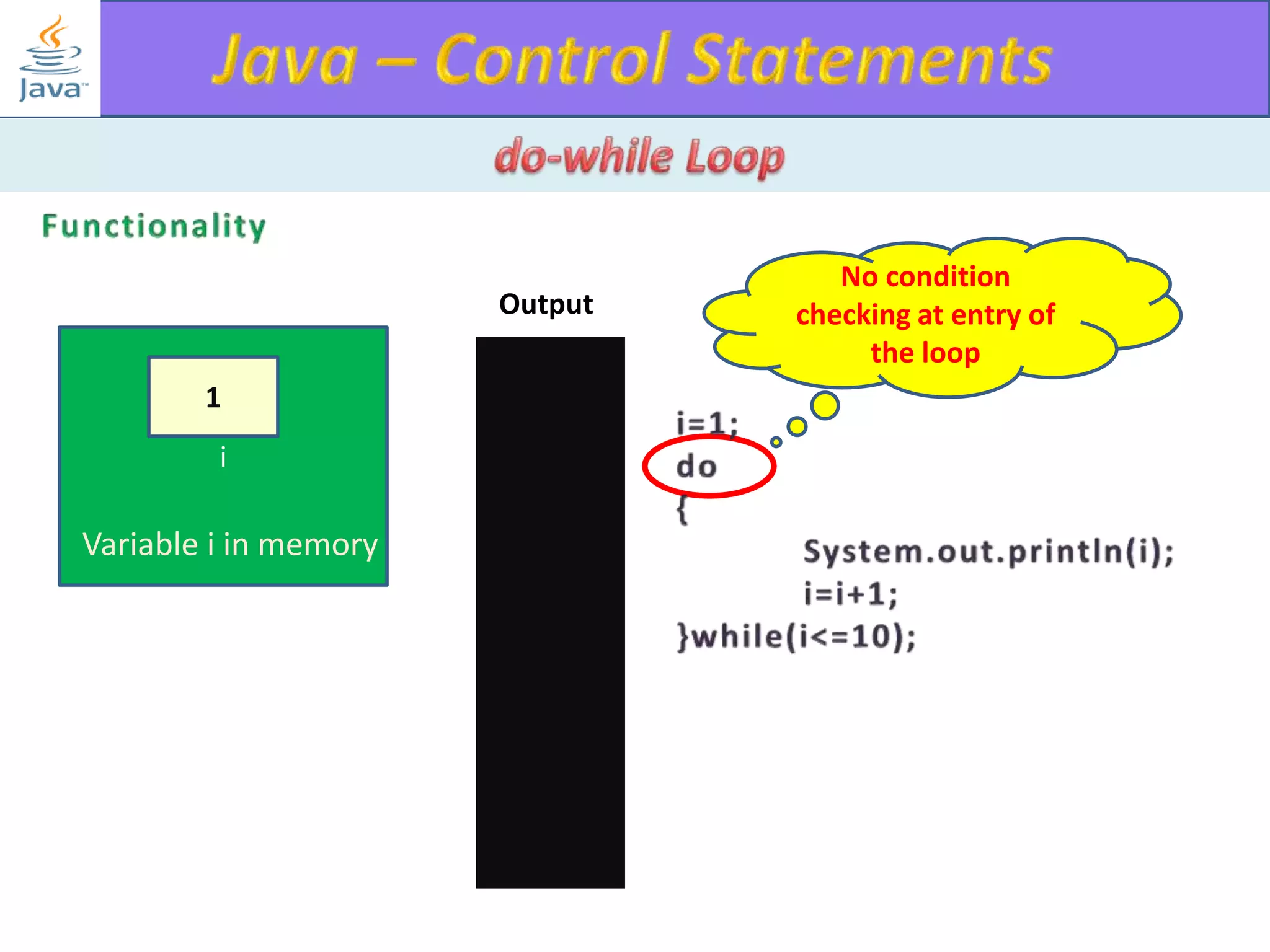
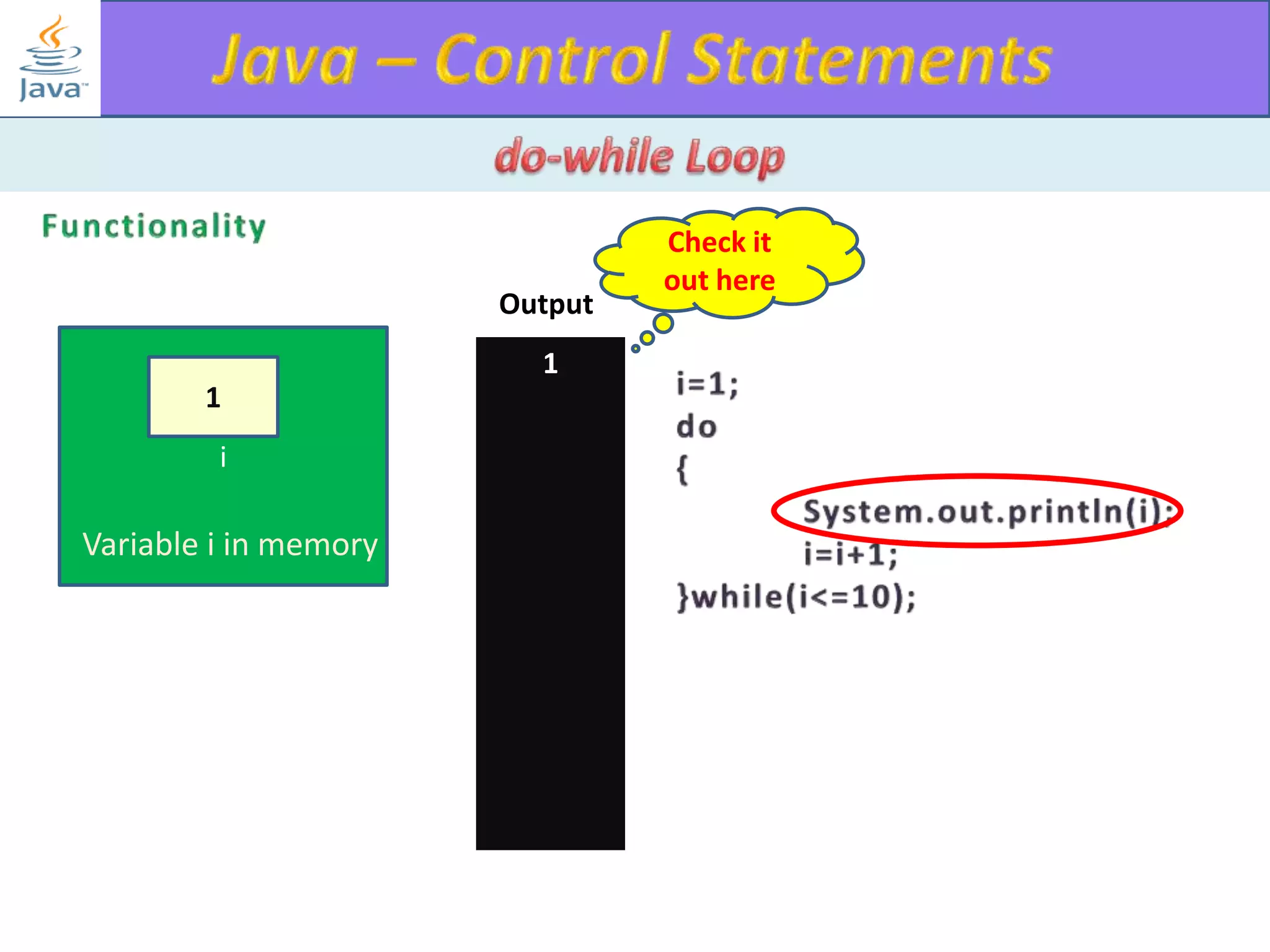
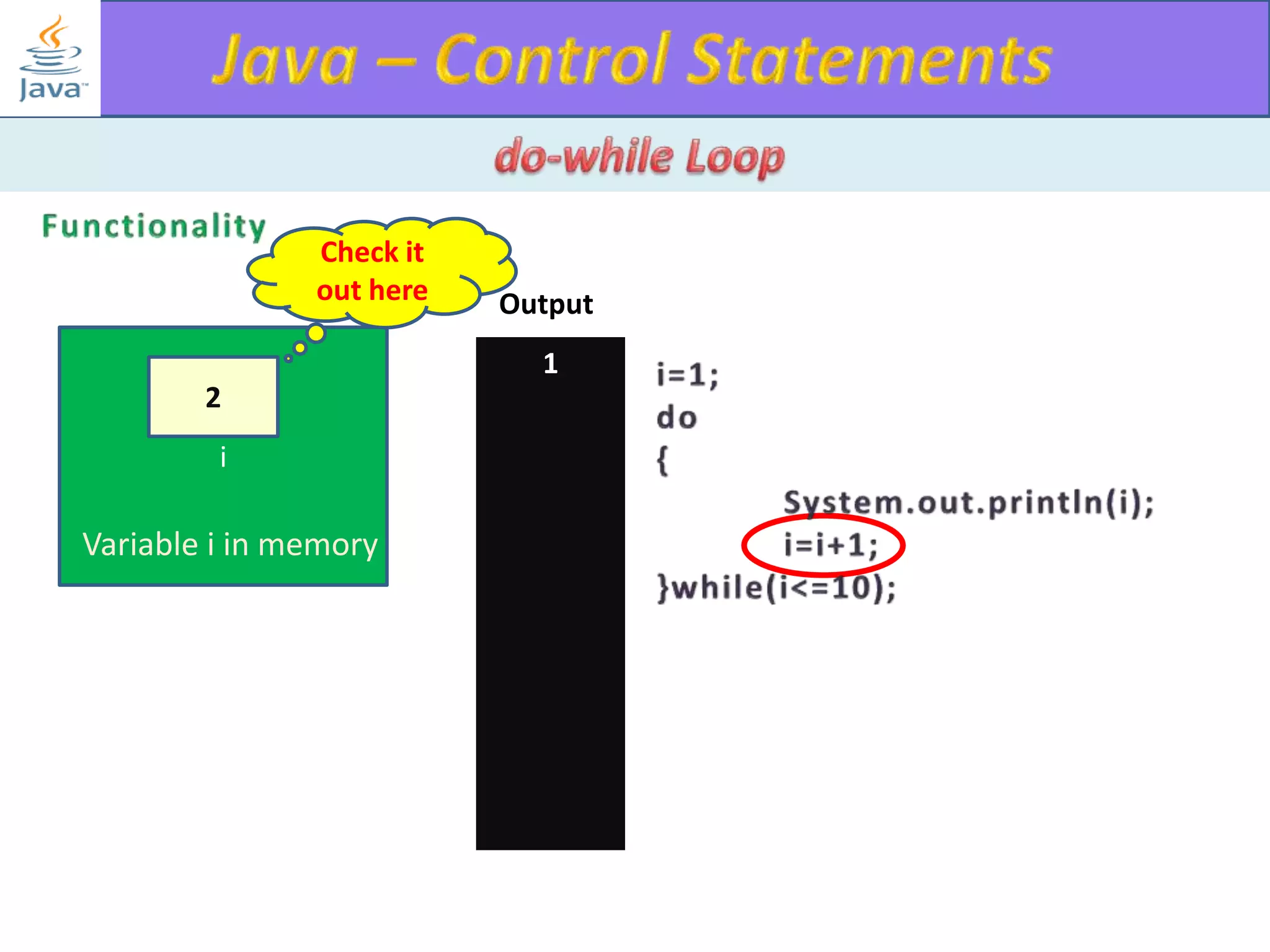
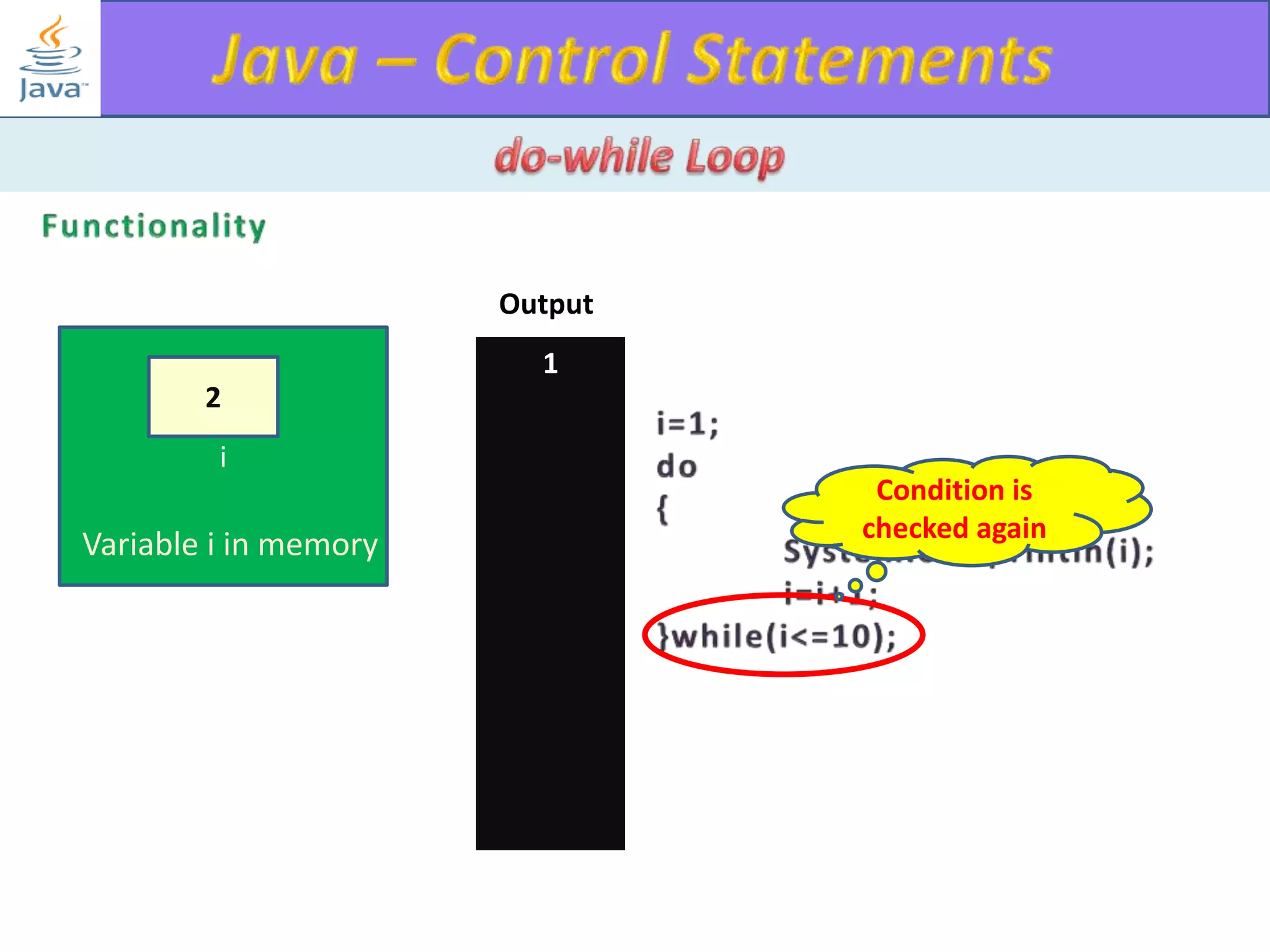
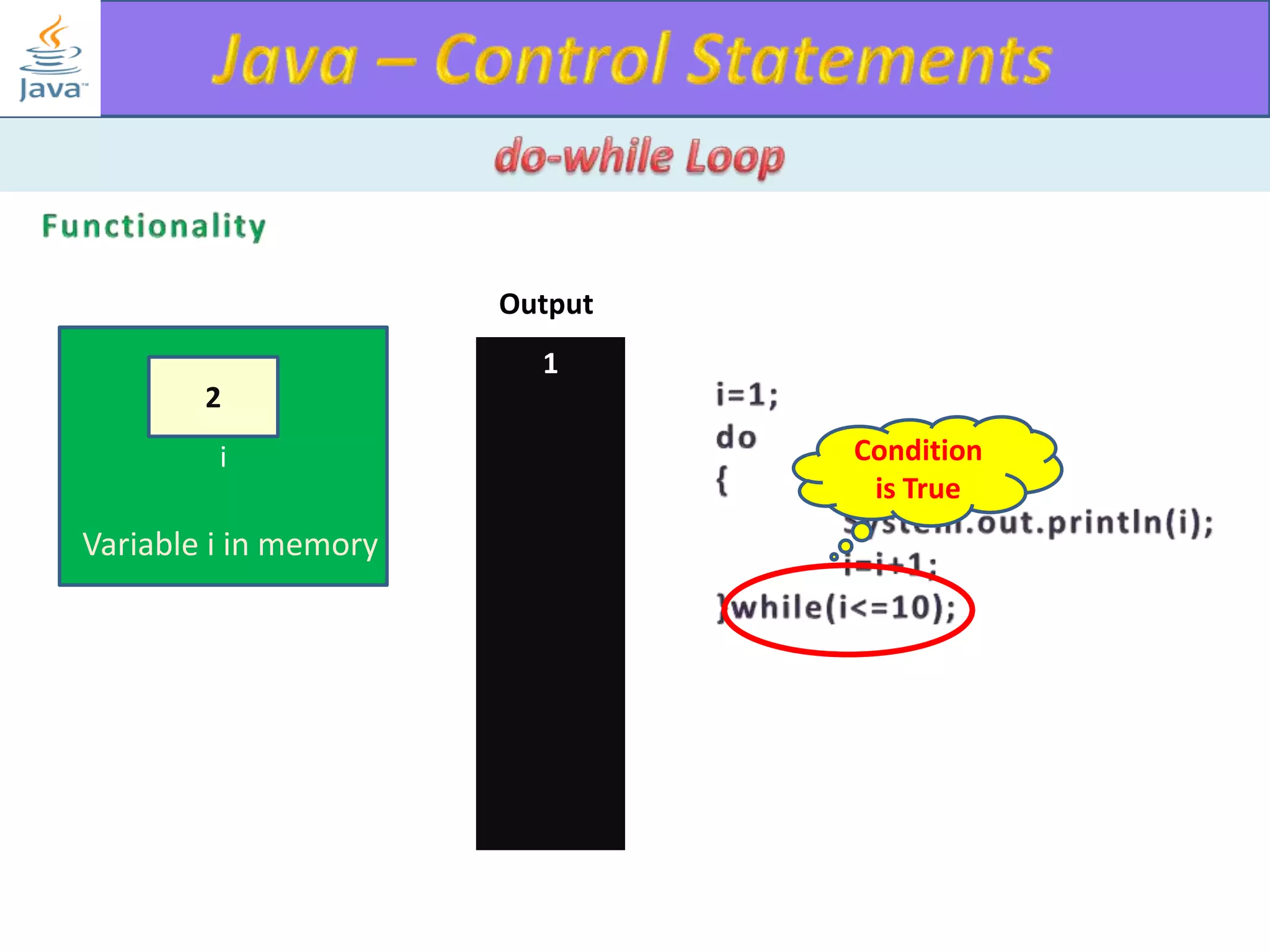
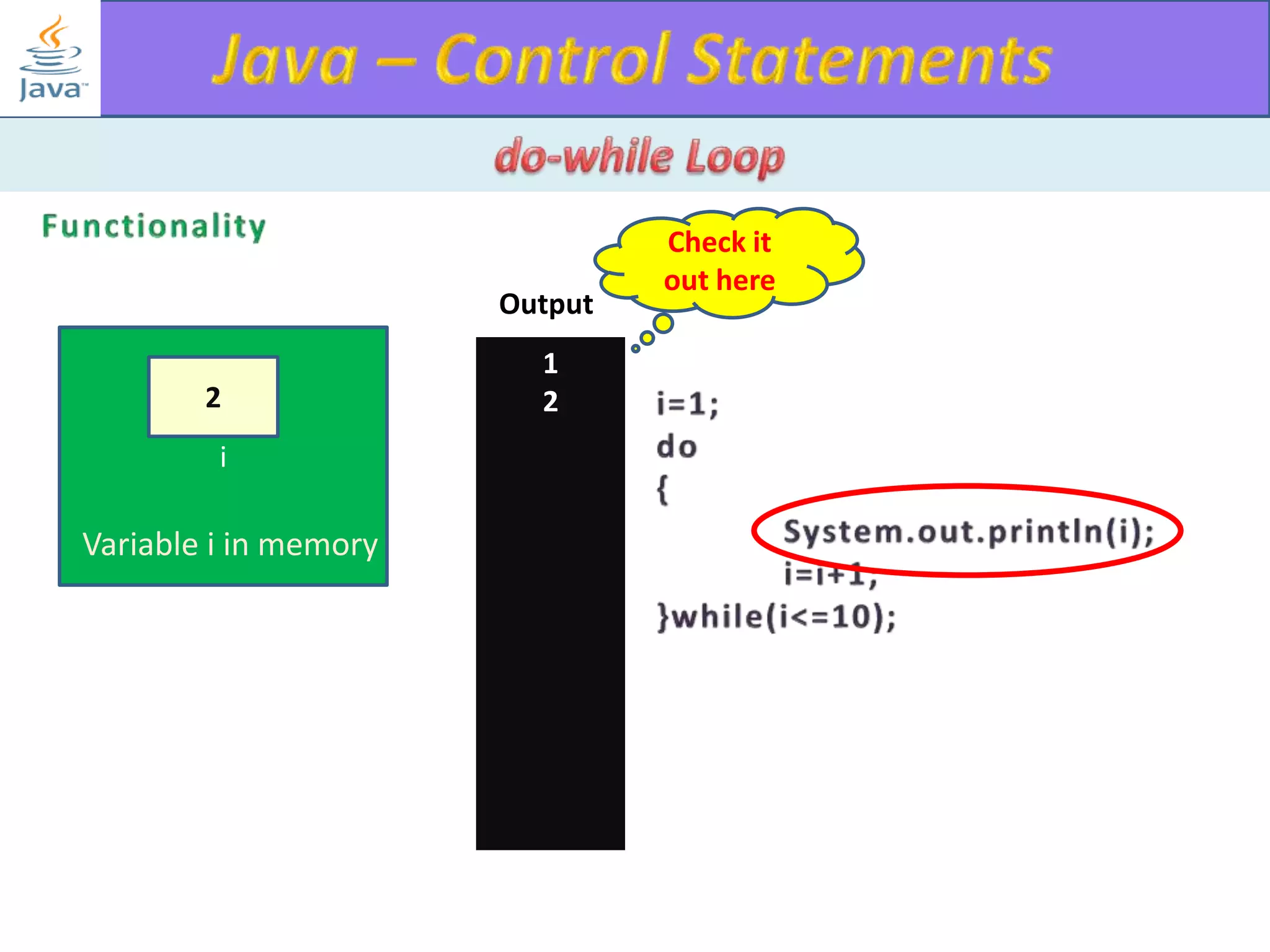
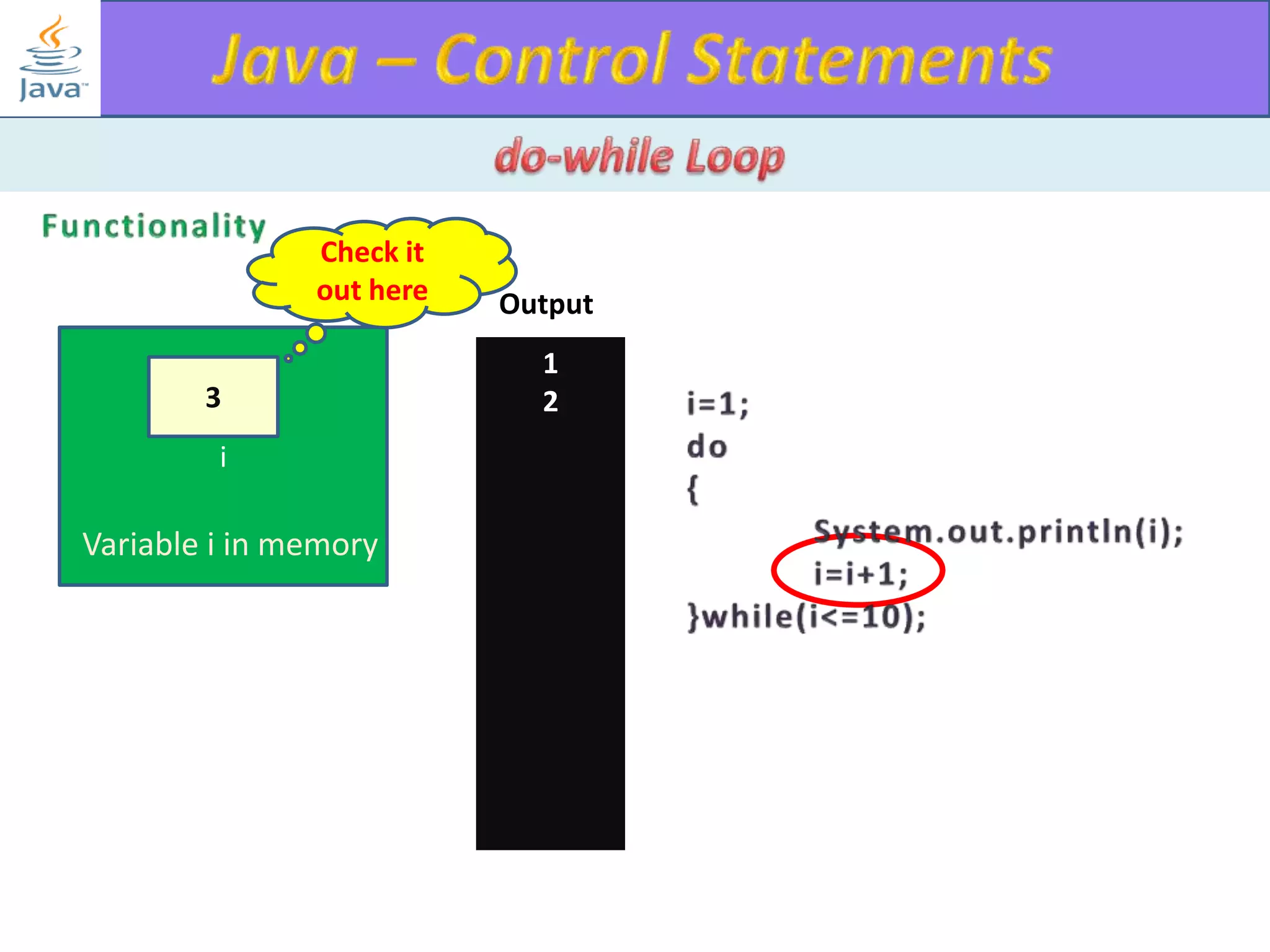
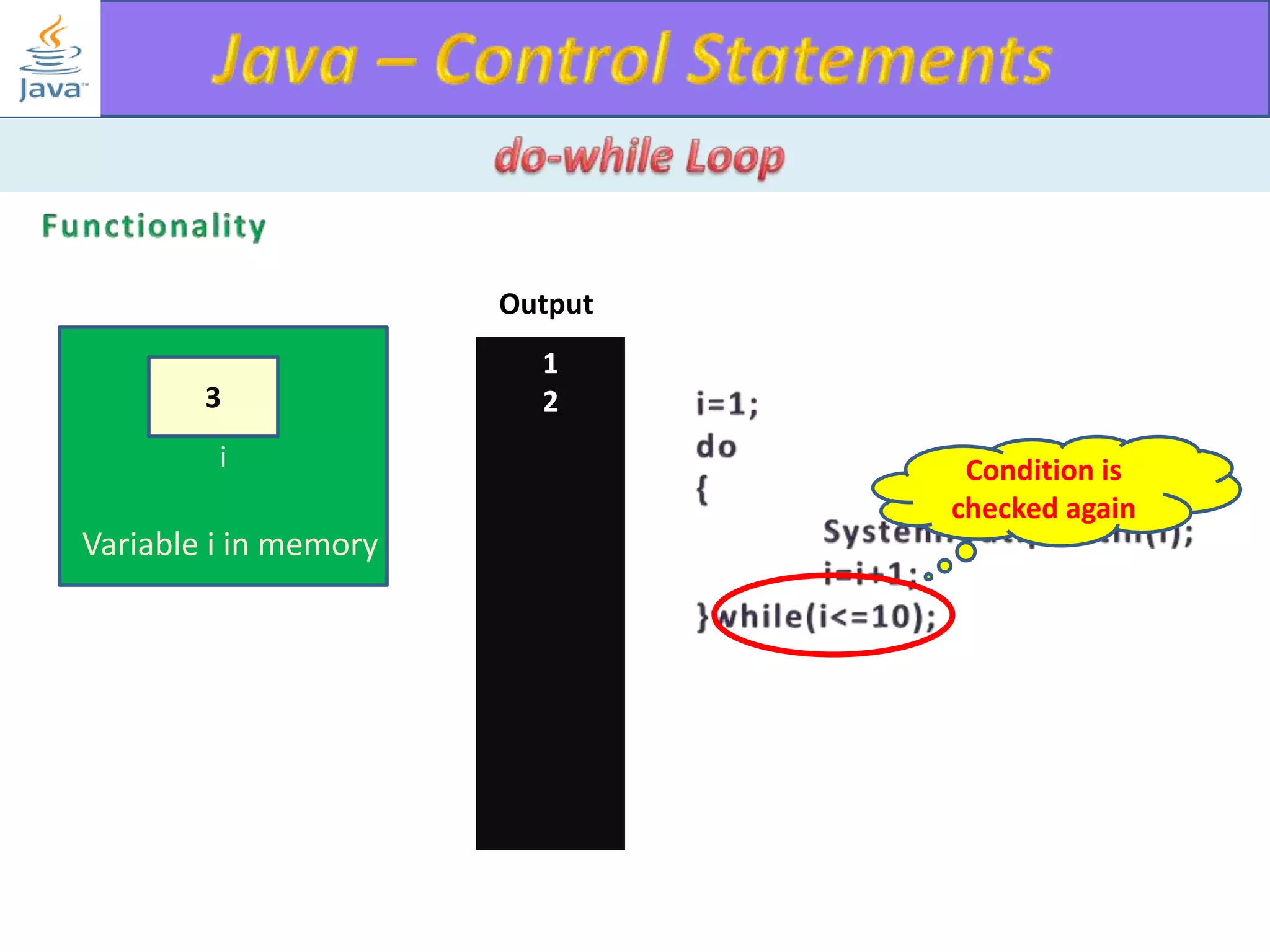
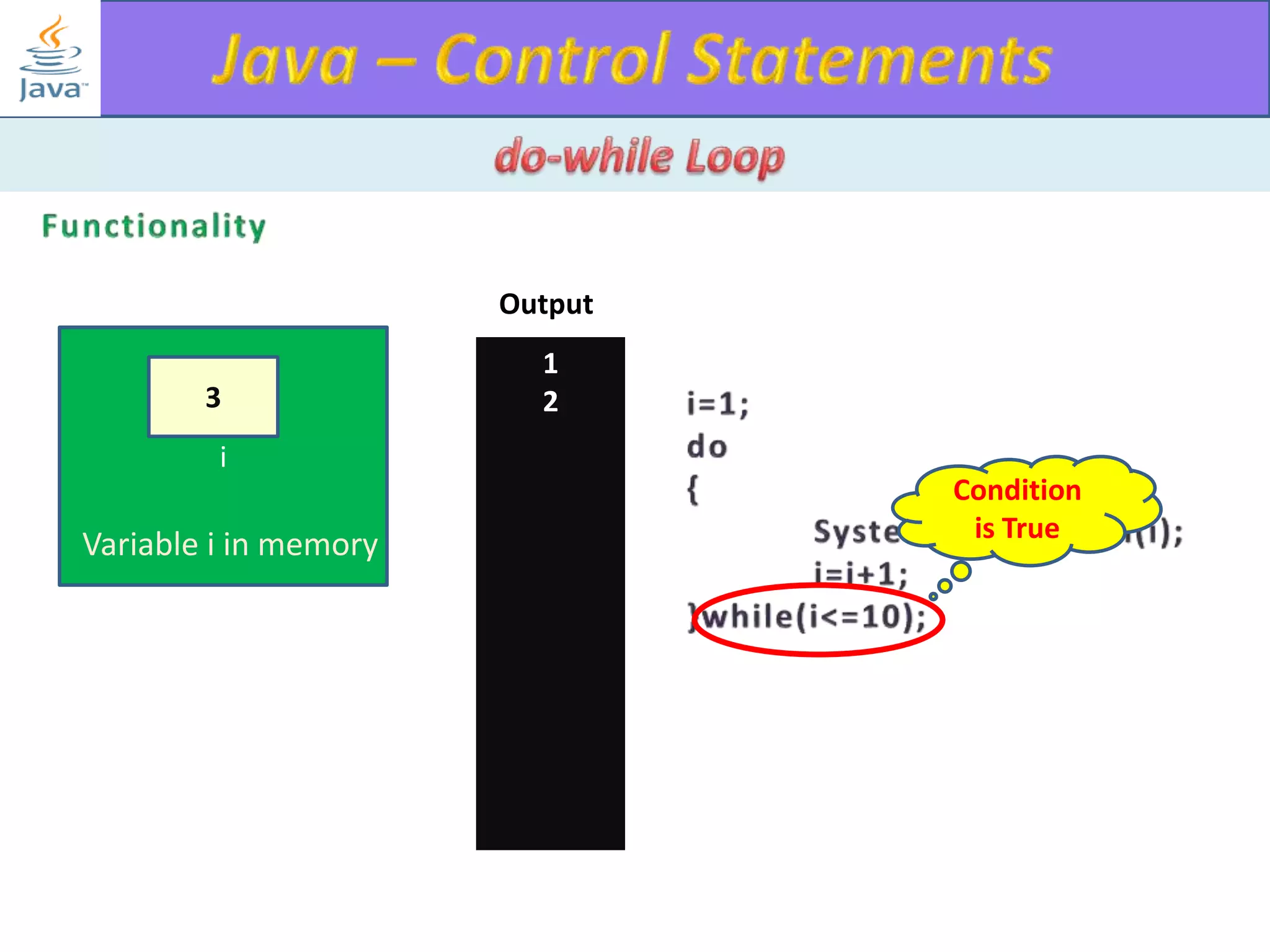
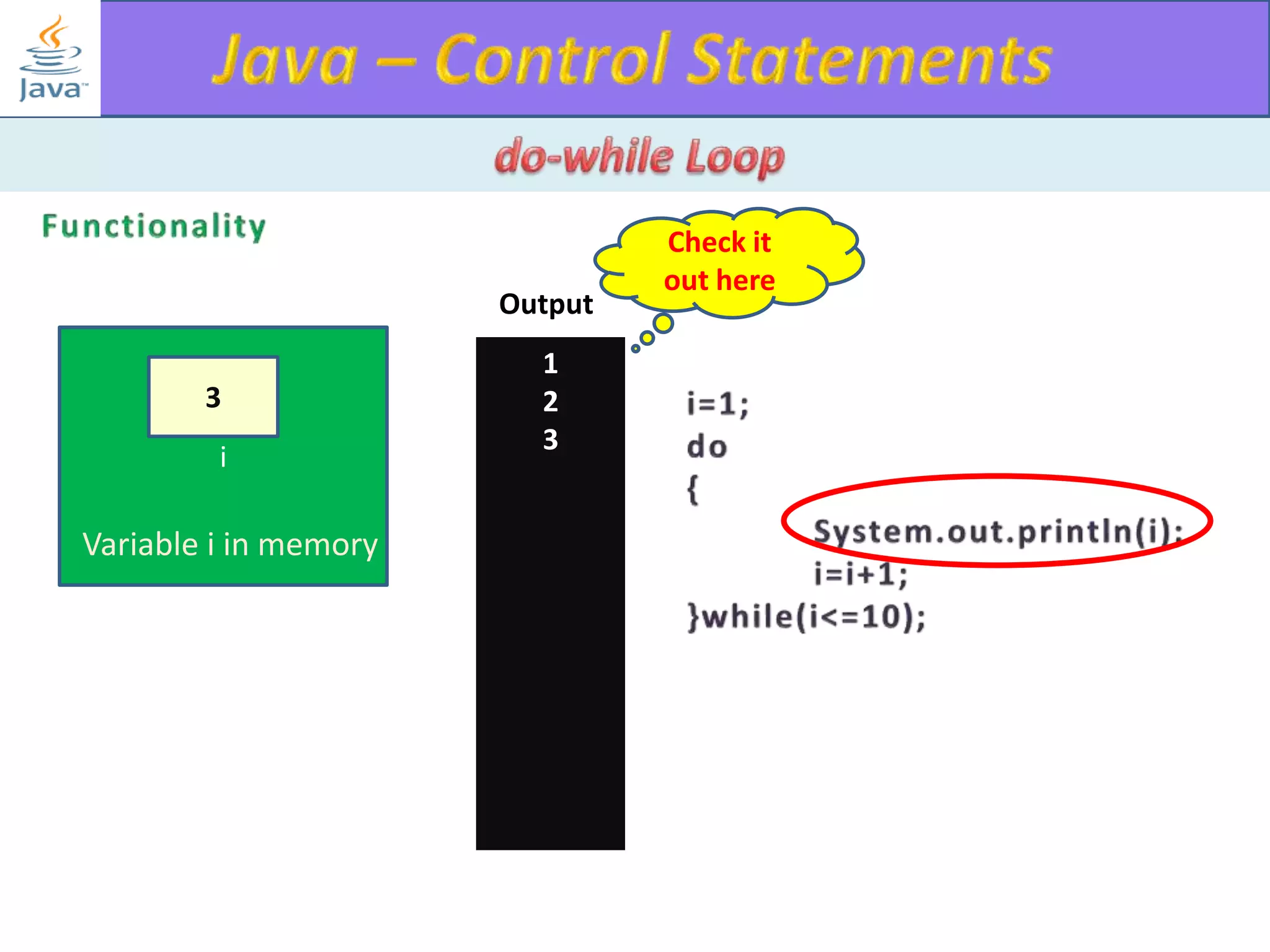
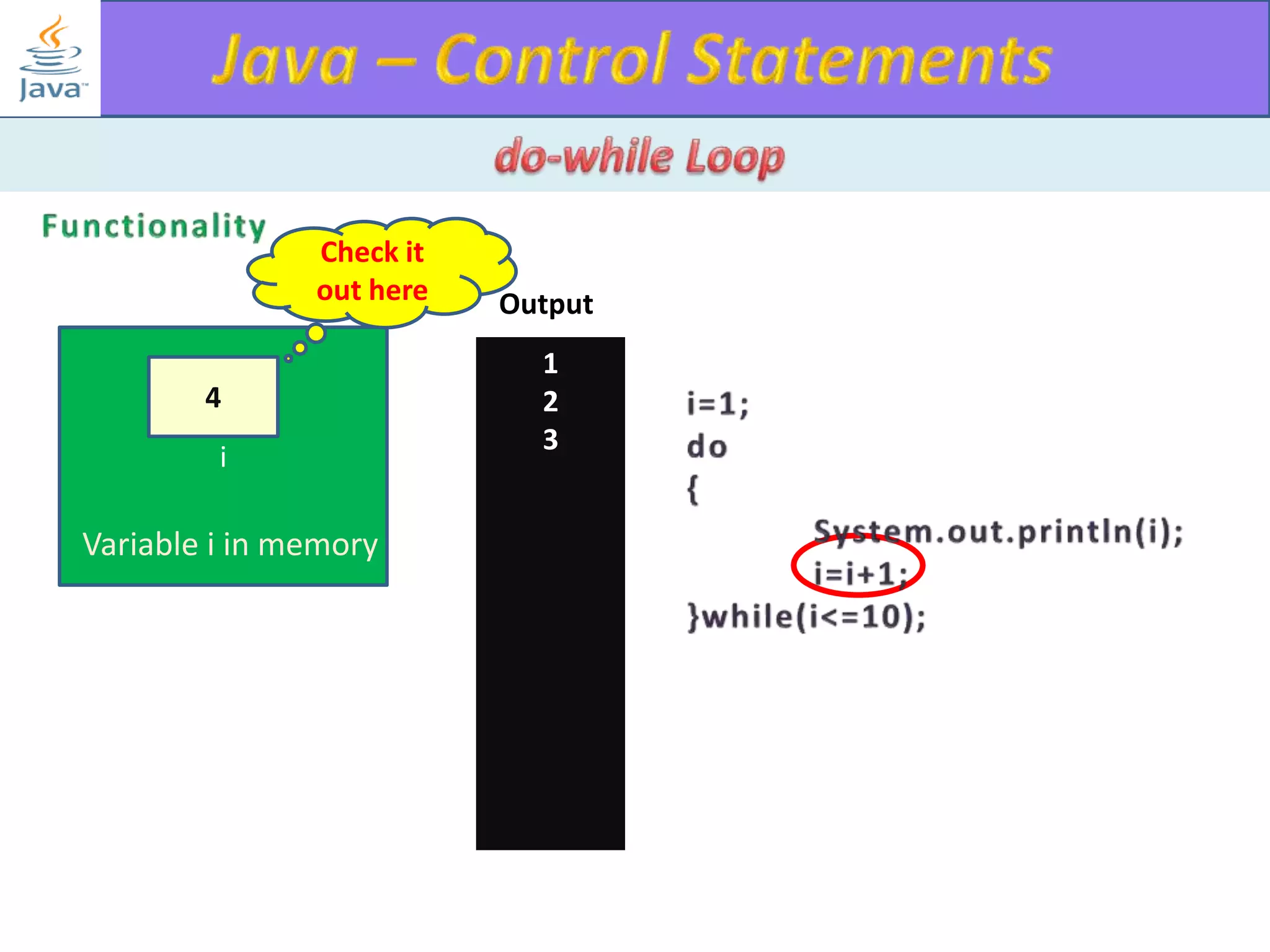
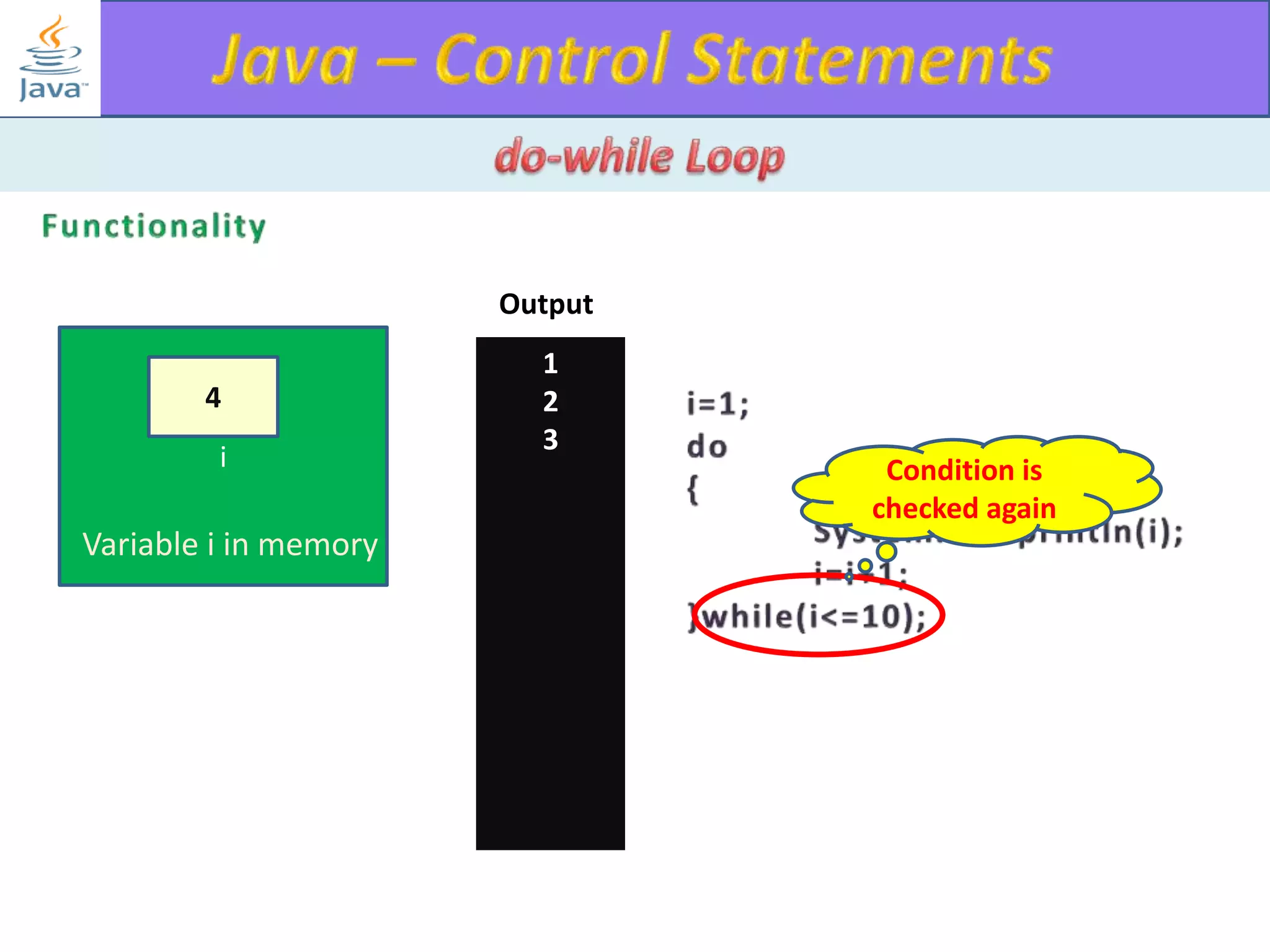
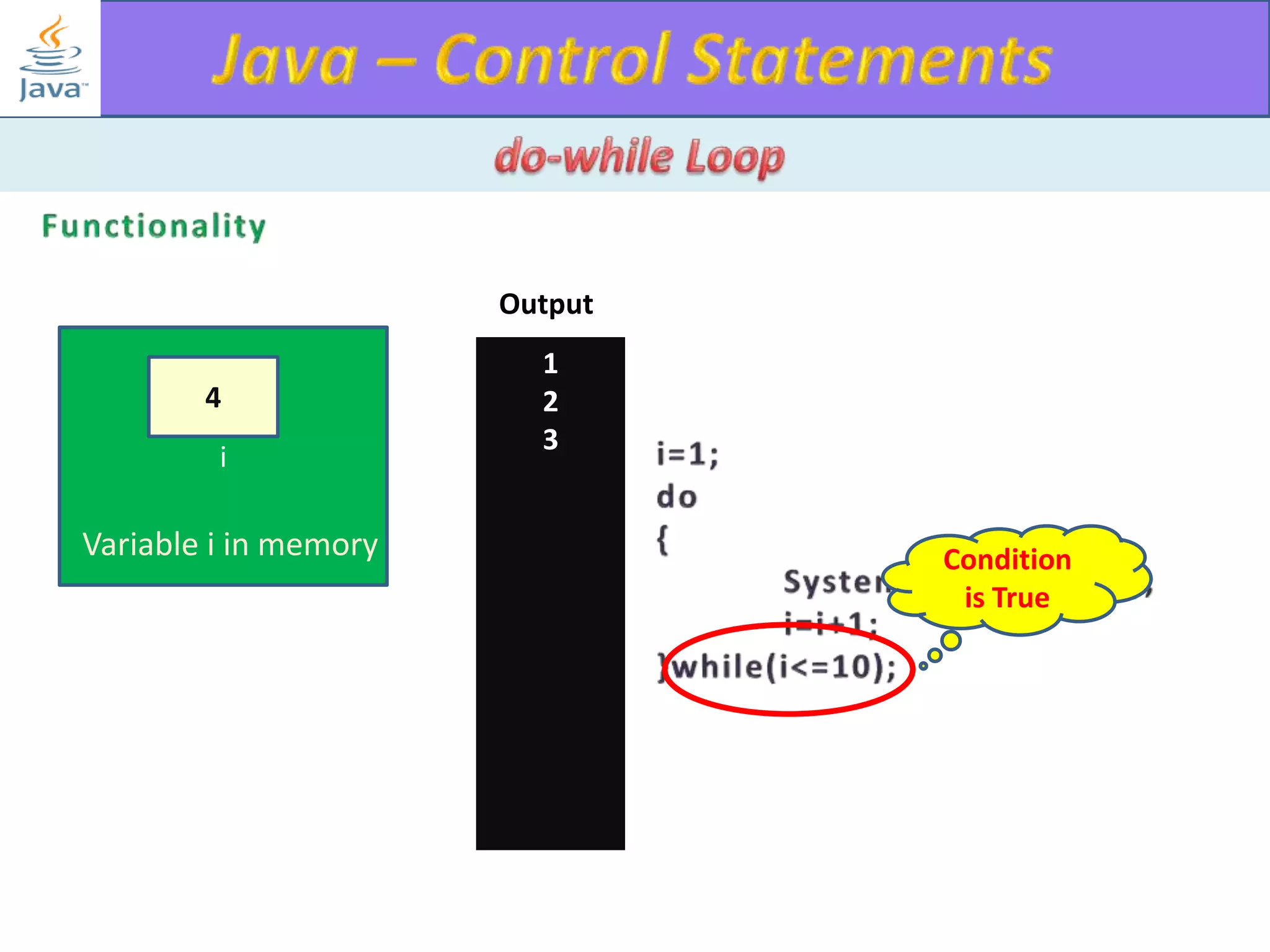
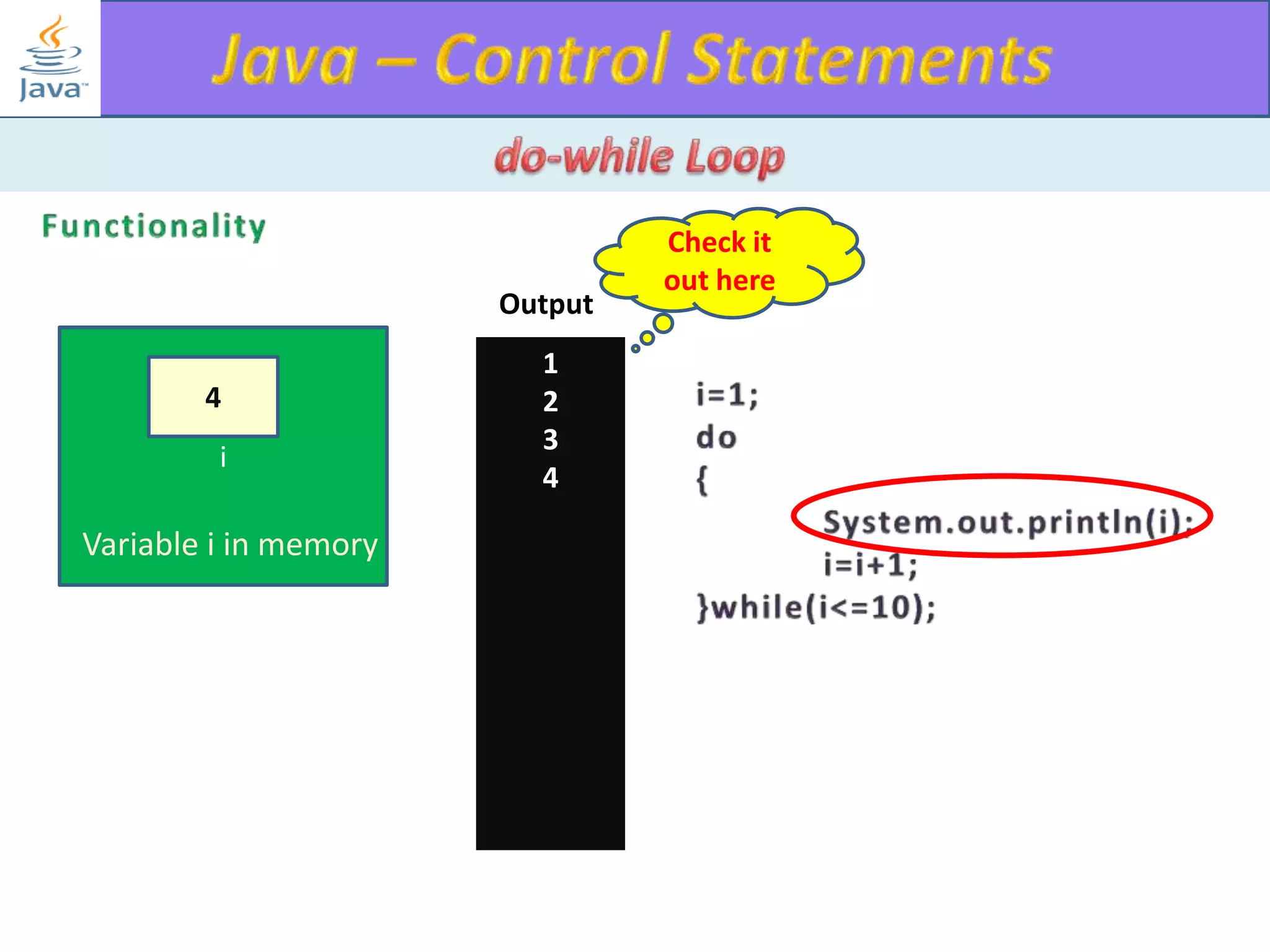
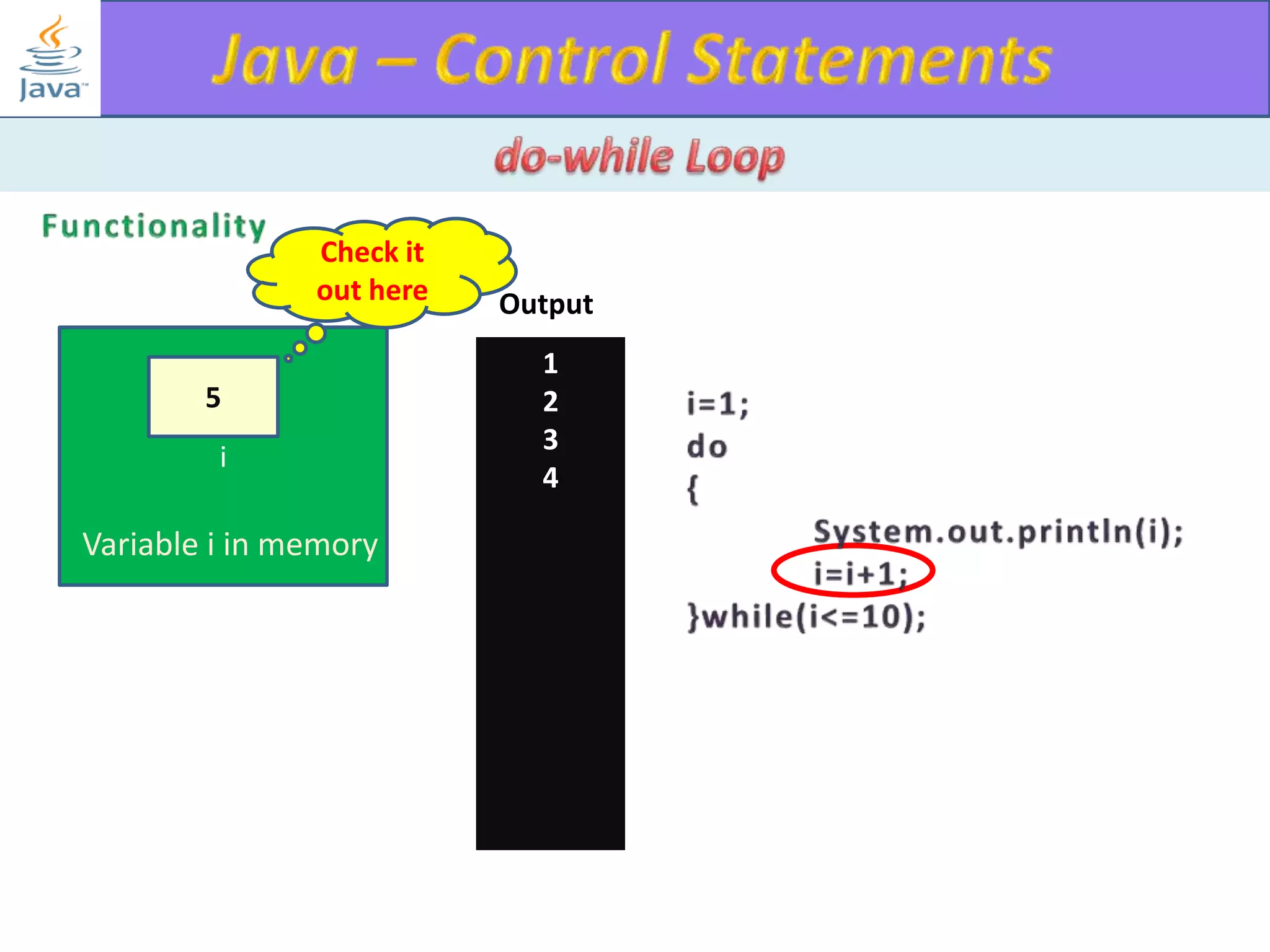
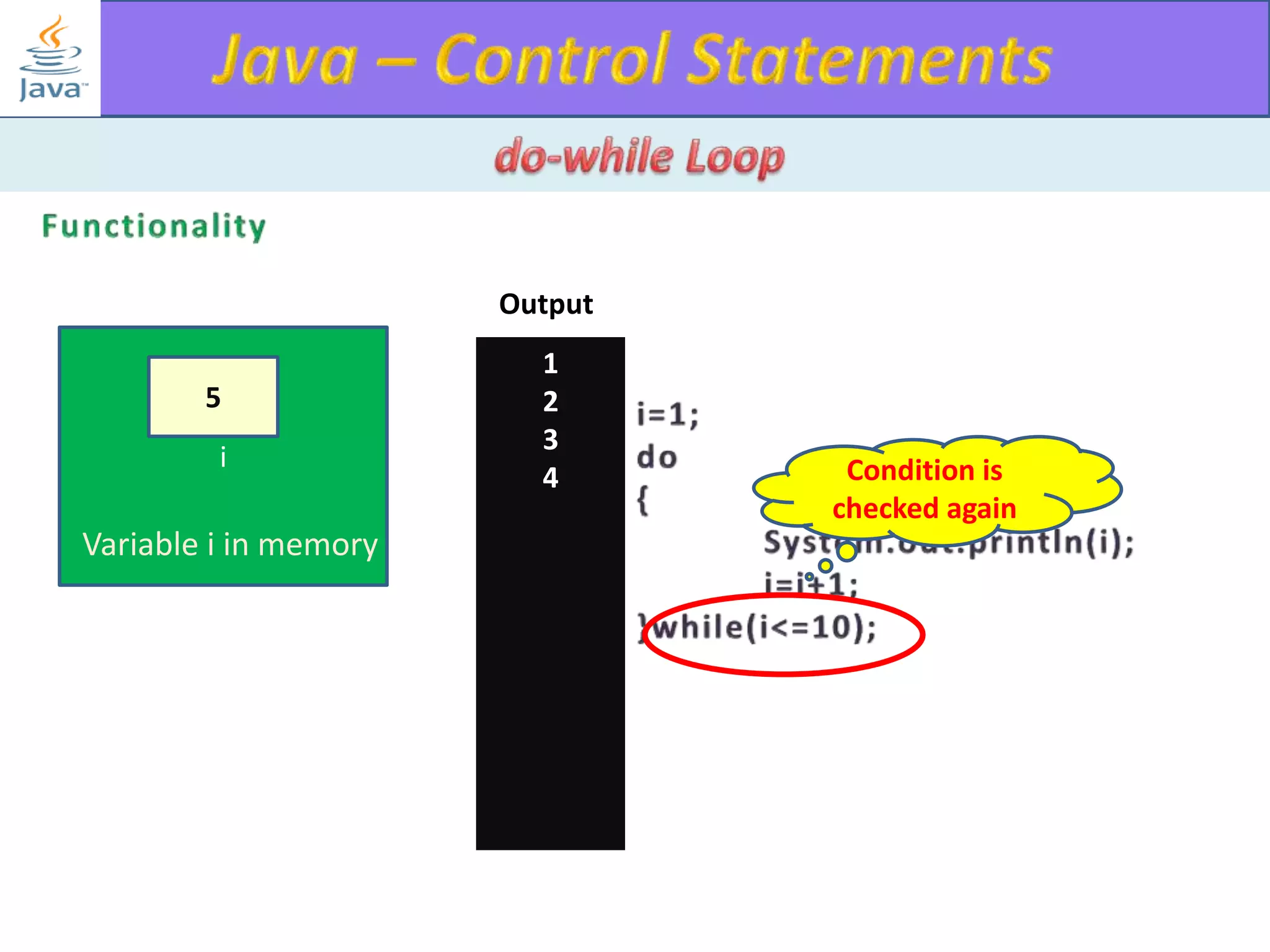
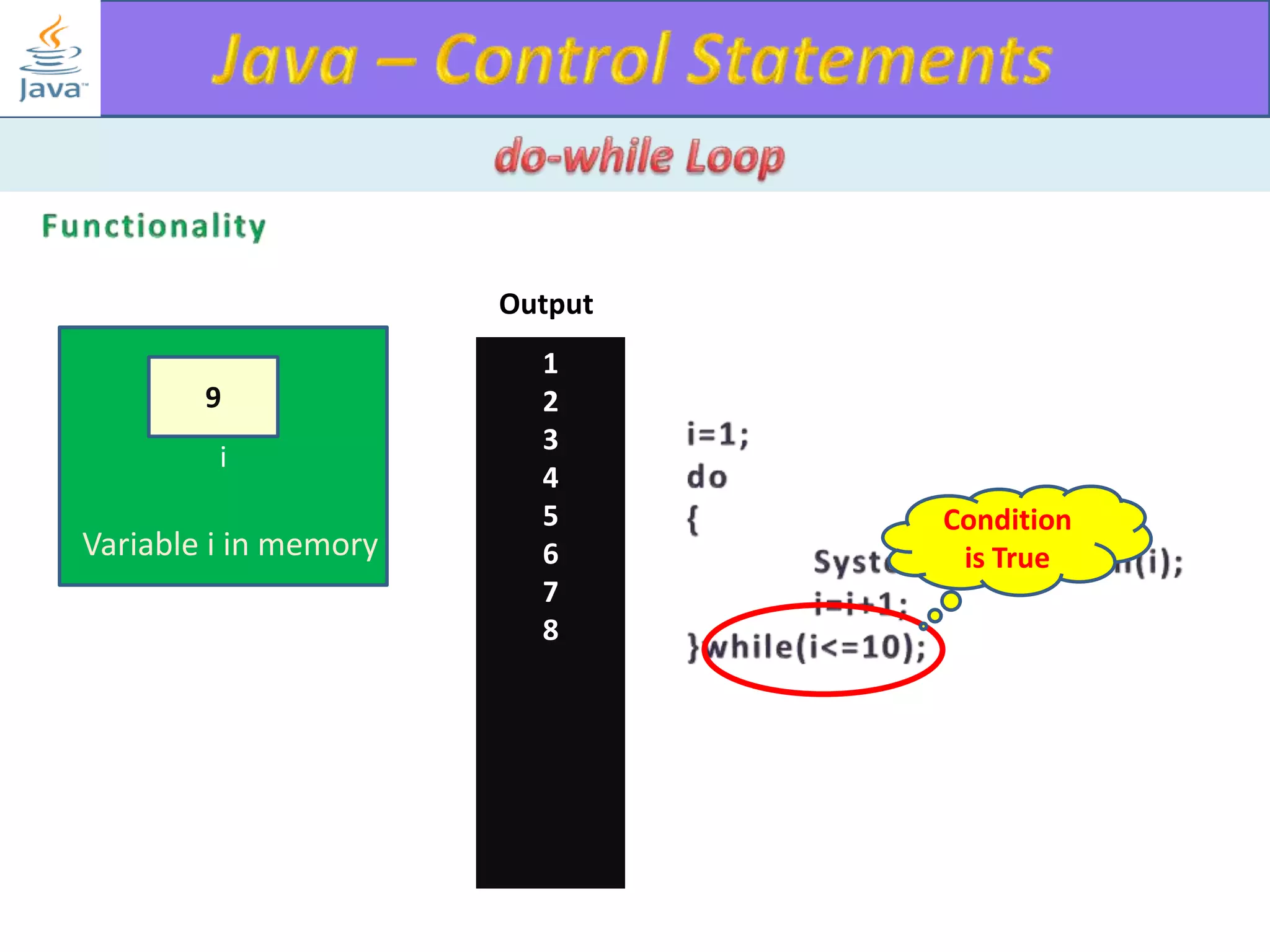
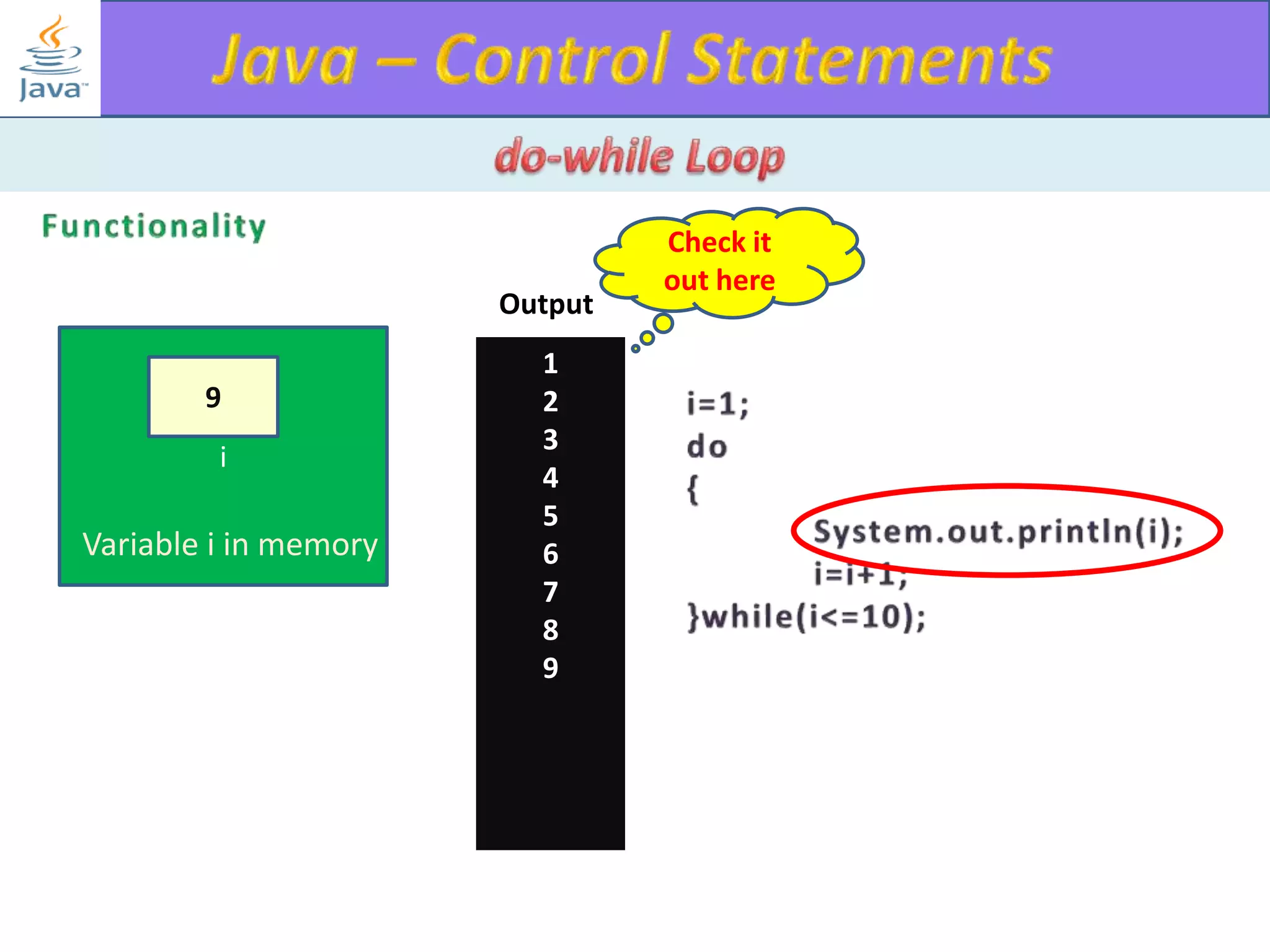
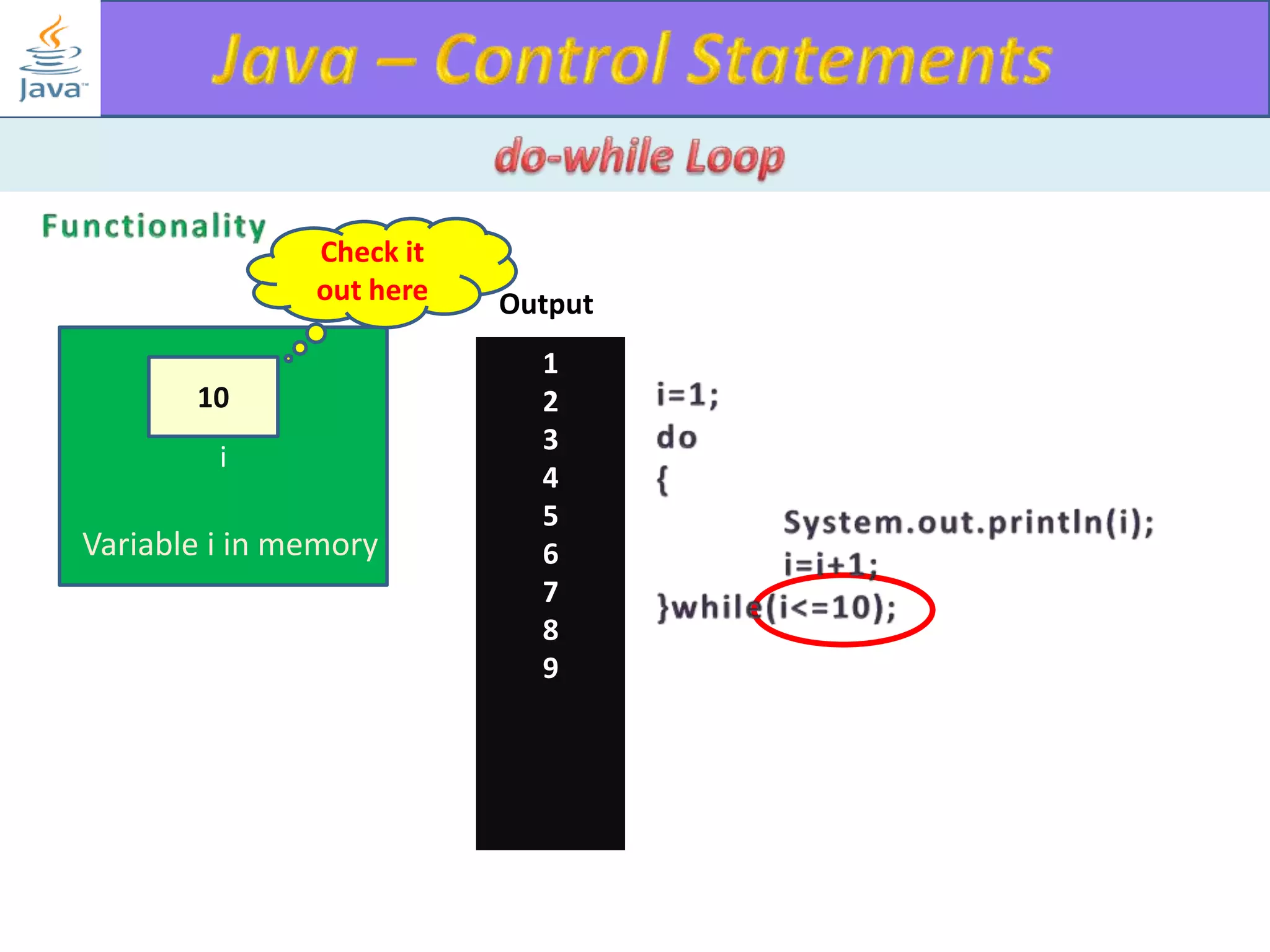
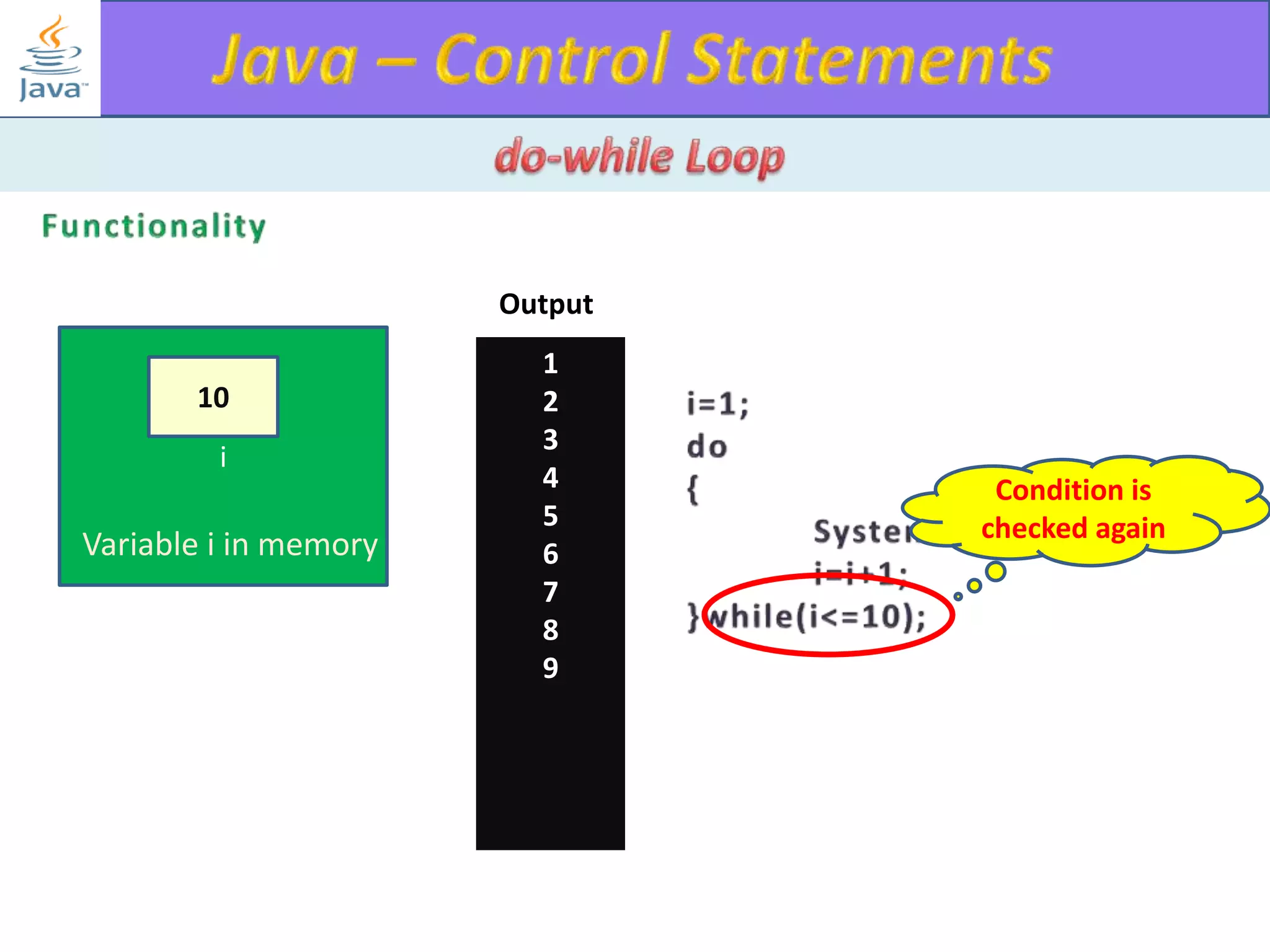
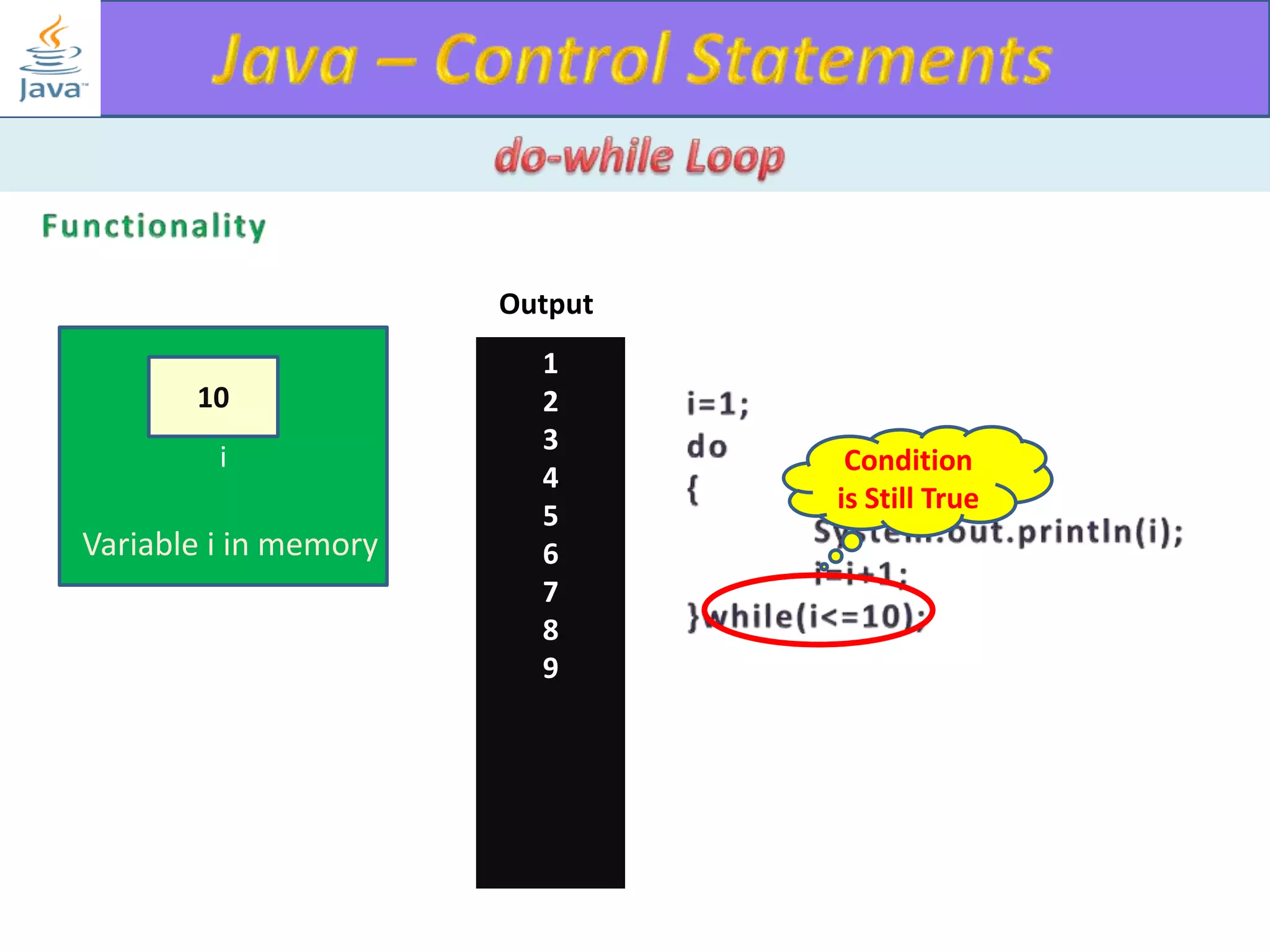
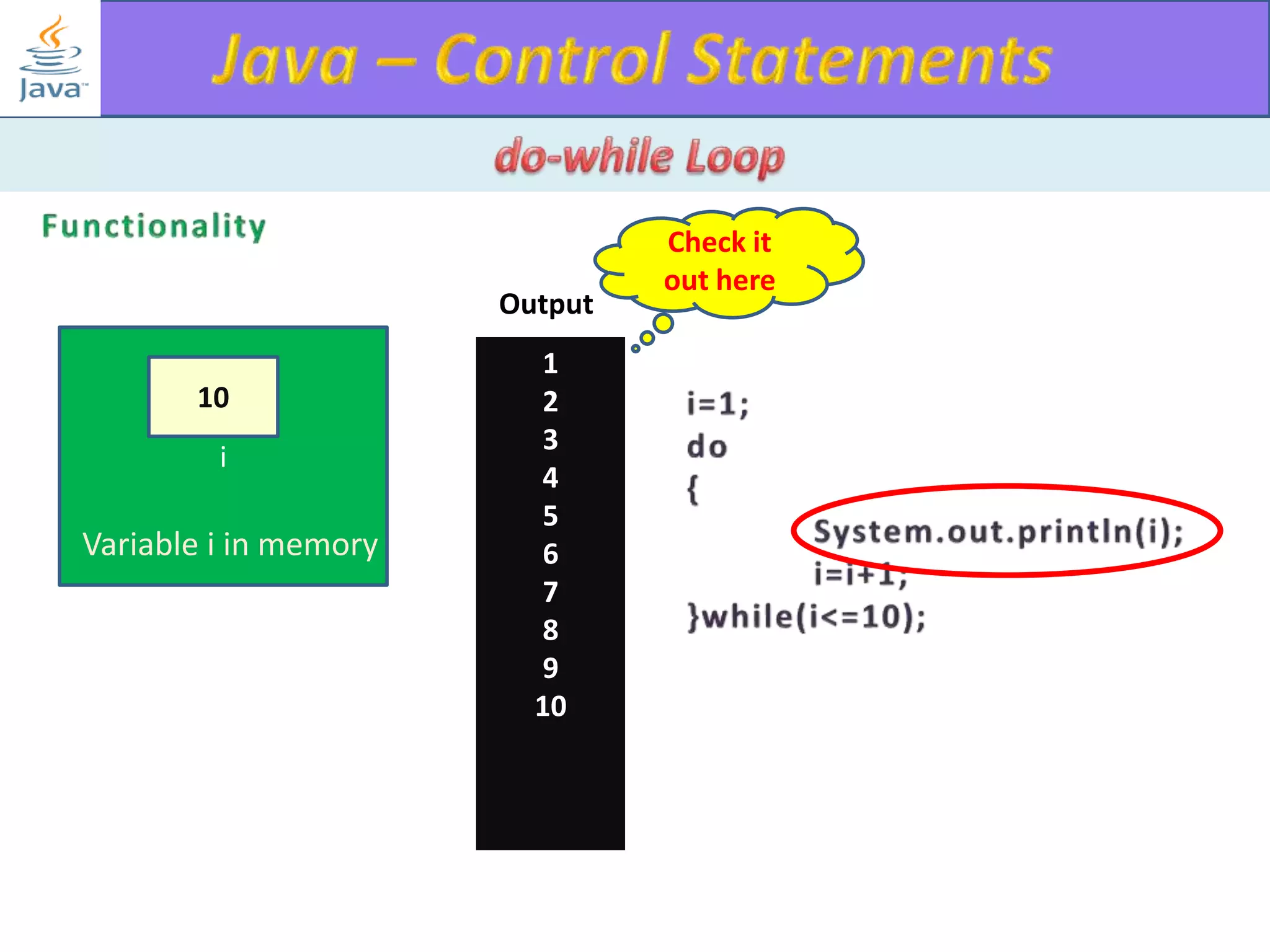
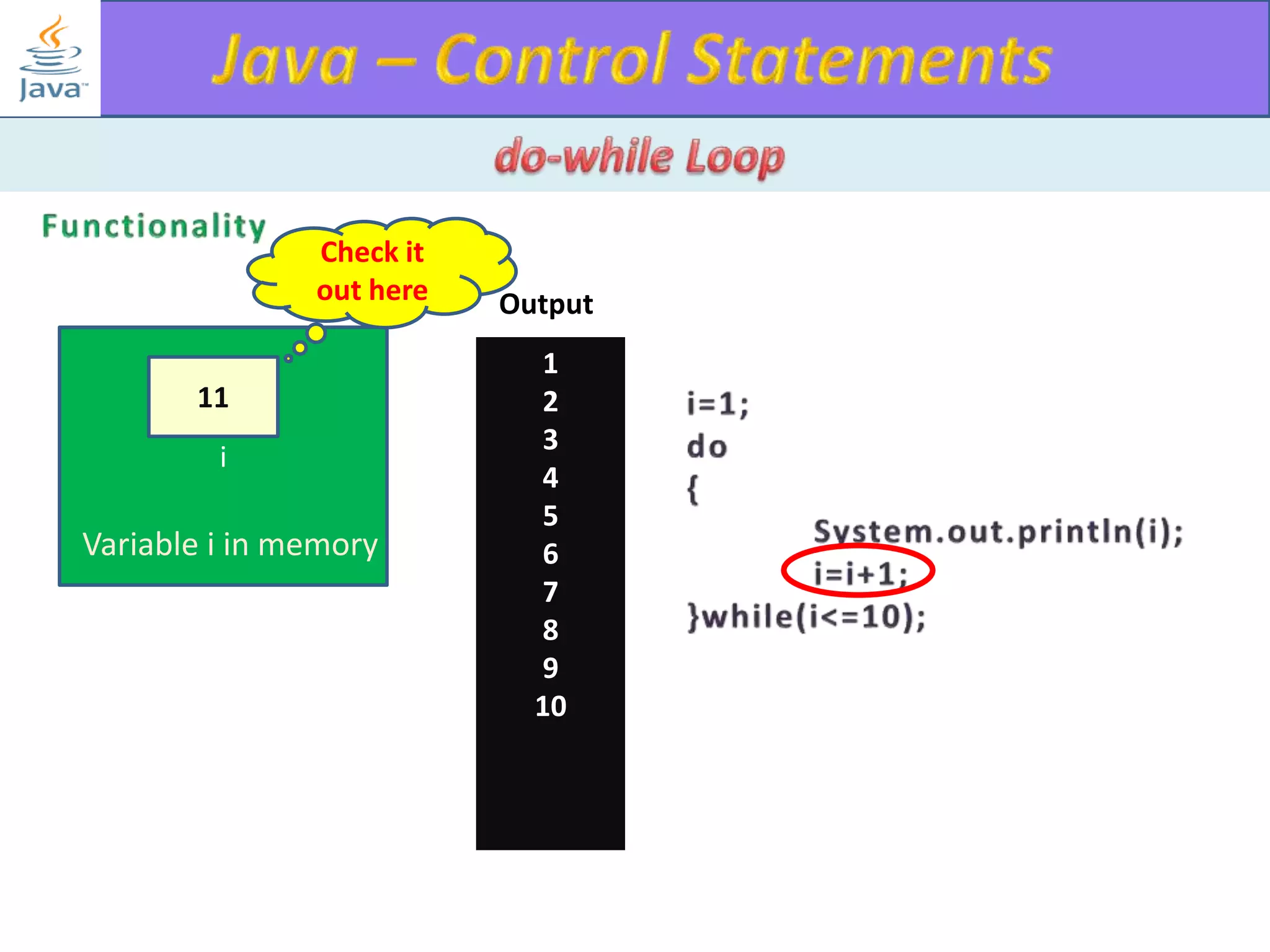
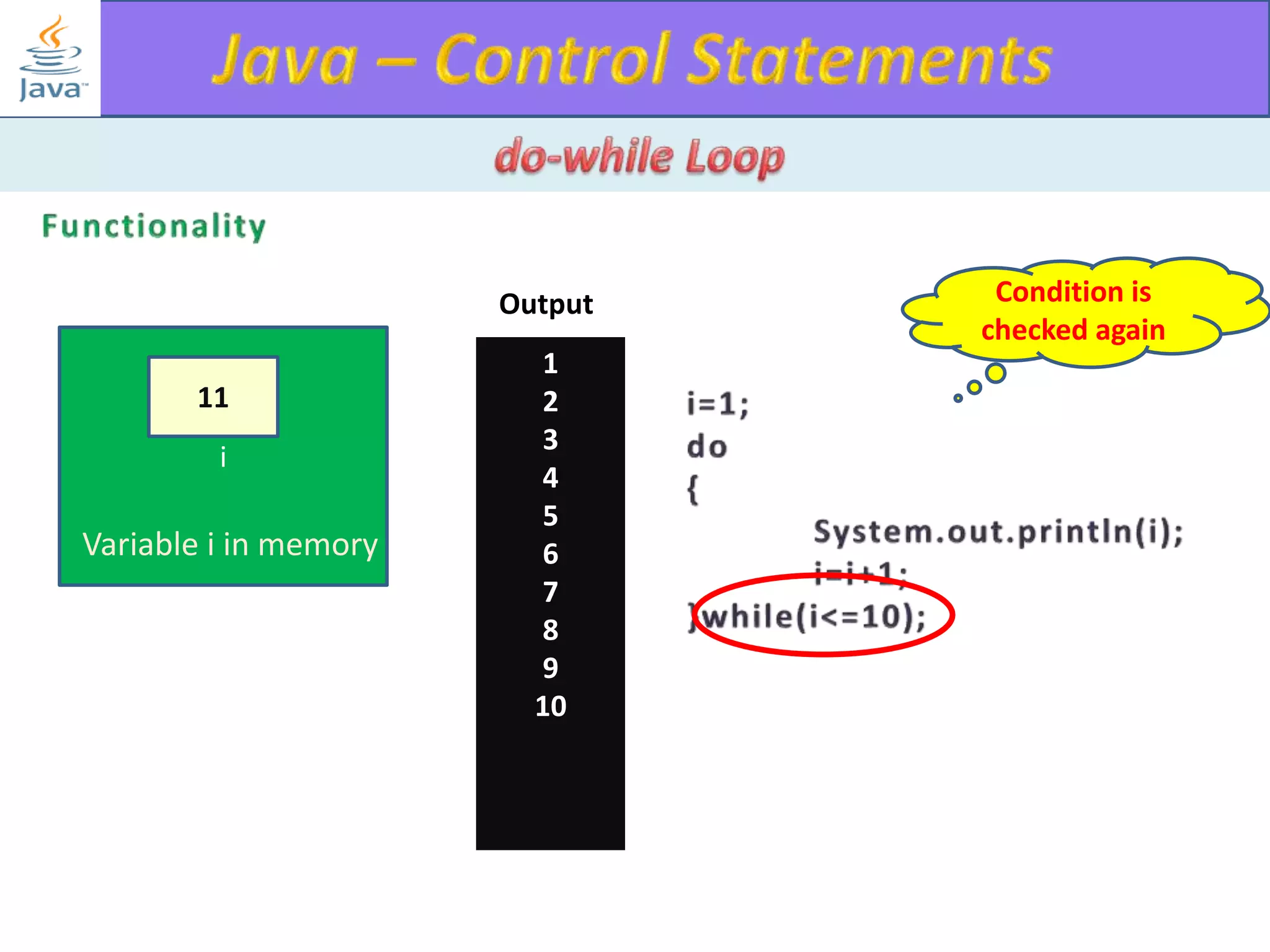
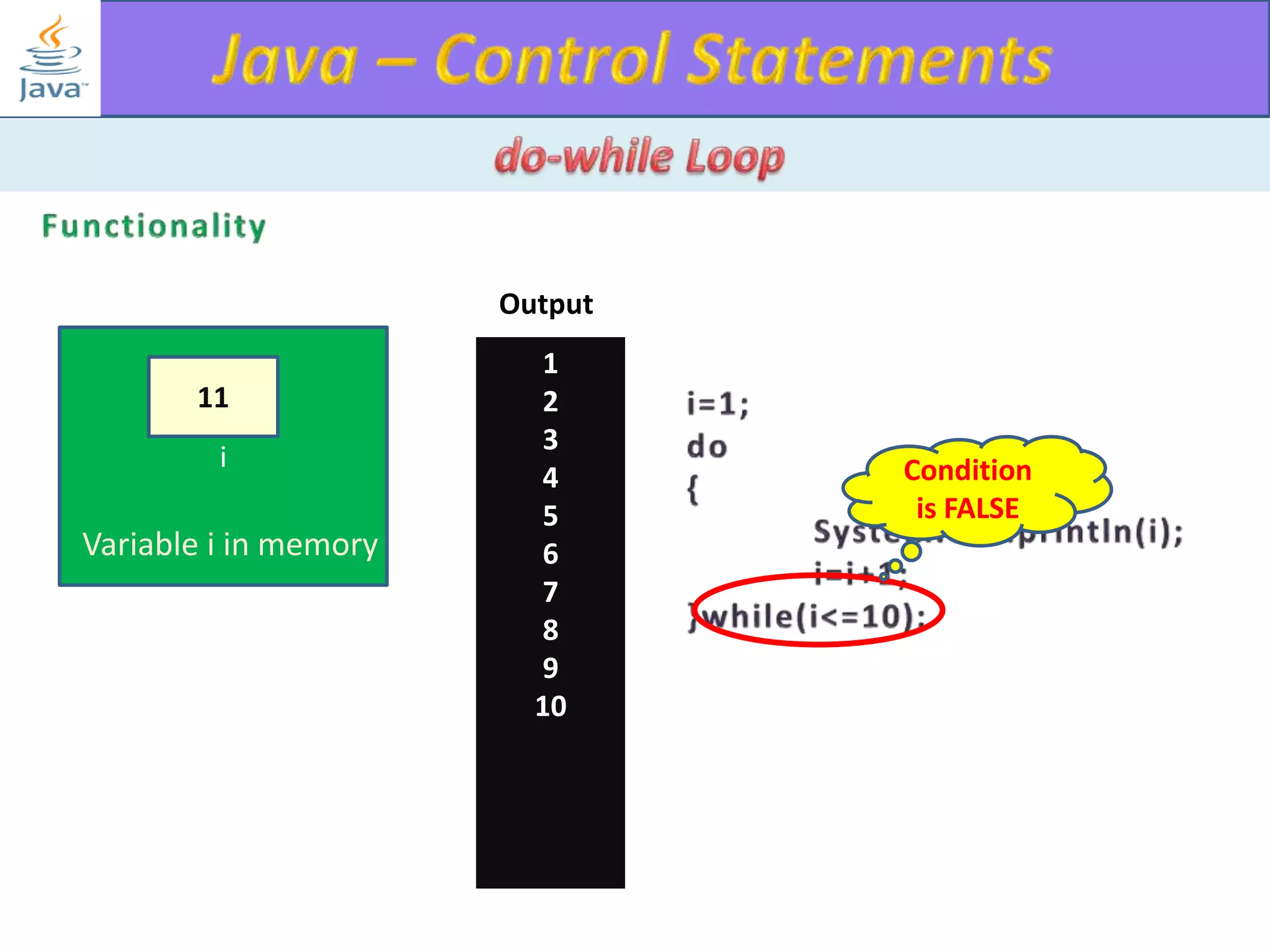
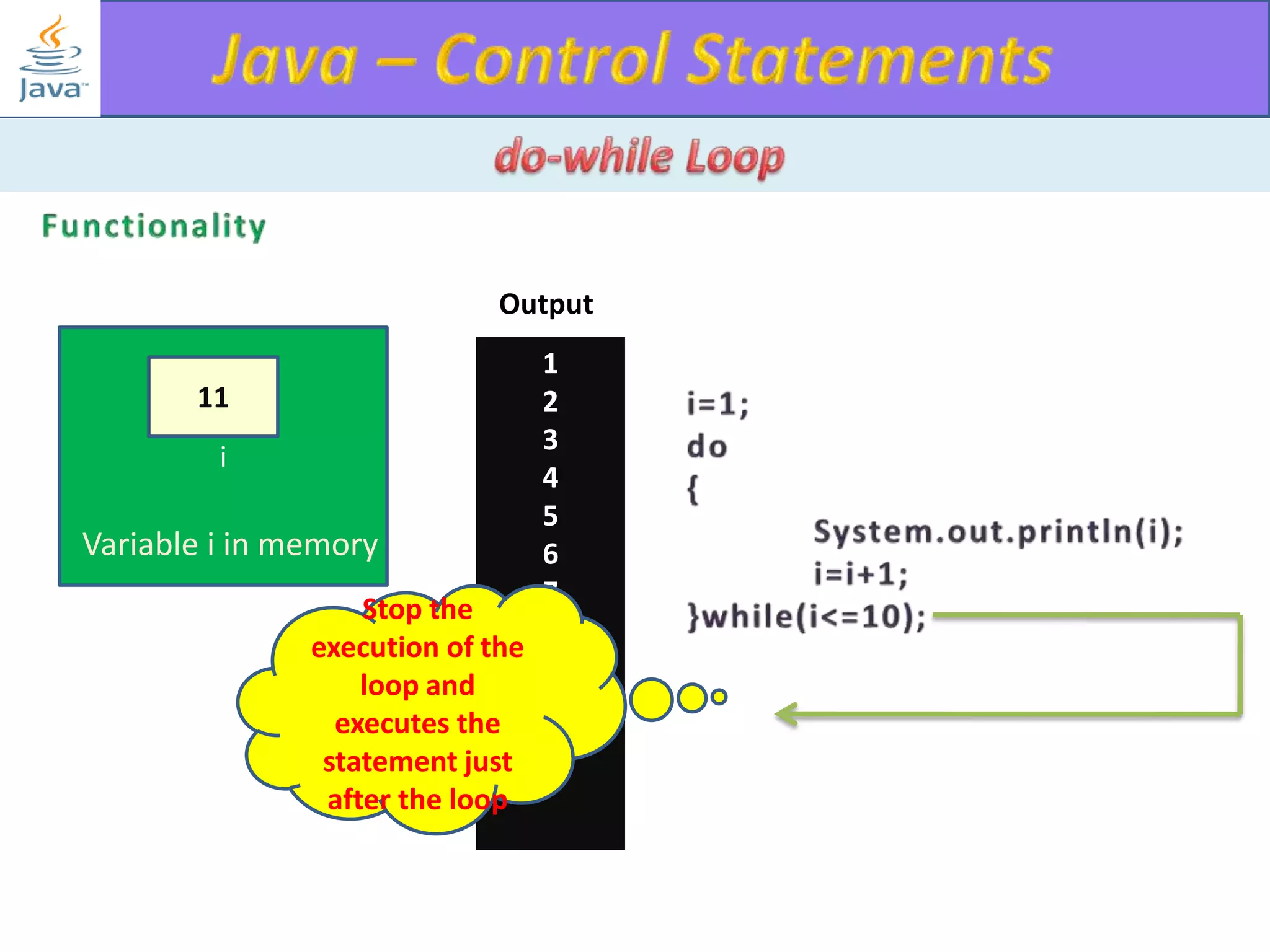
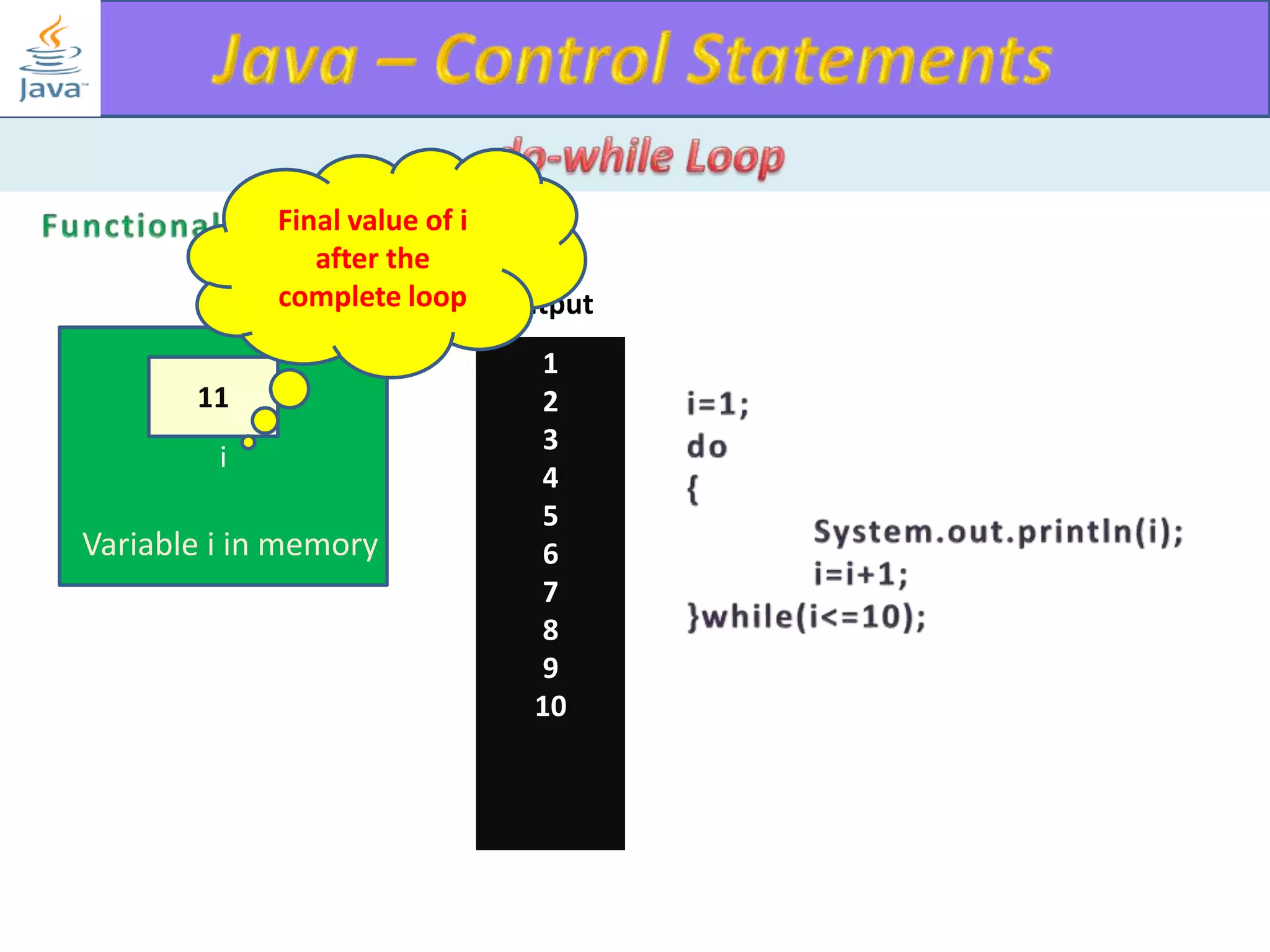
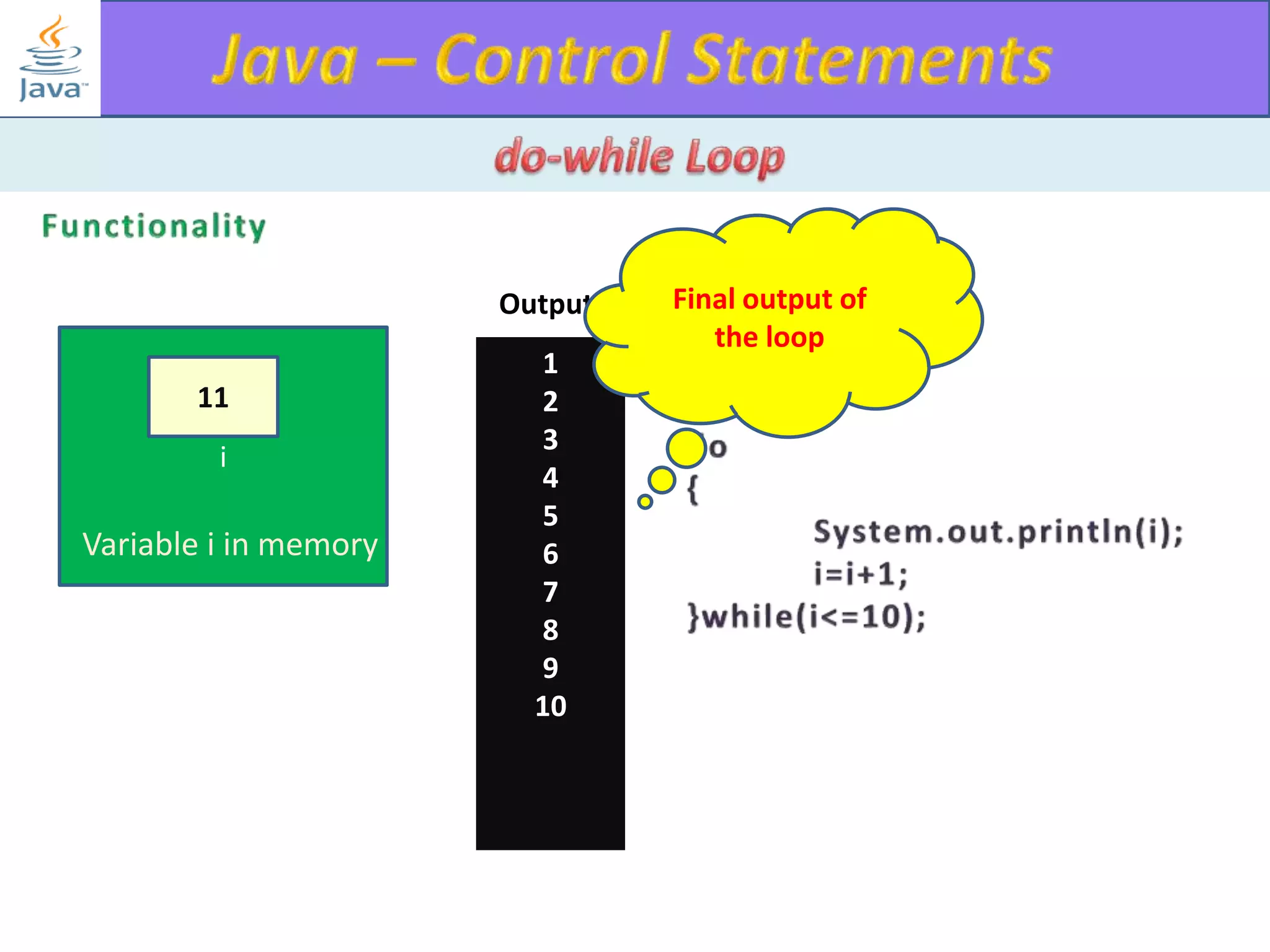
The document discusses different types of loops in programming languages. It explains the basic components of a loop - initialization, condition checking, execution, and increment/decrement. It provides examples of for, while, do-while, and entry-controlled vs exit-controlled loops. The key aspects of loops including initialization, condition, body, and increment/decrement are visualized through flow charts and output.