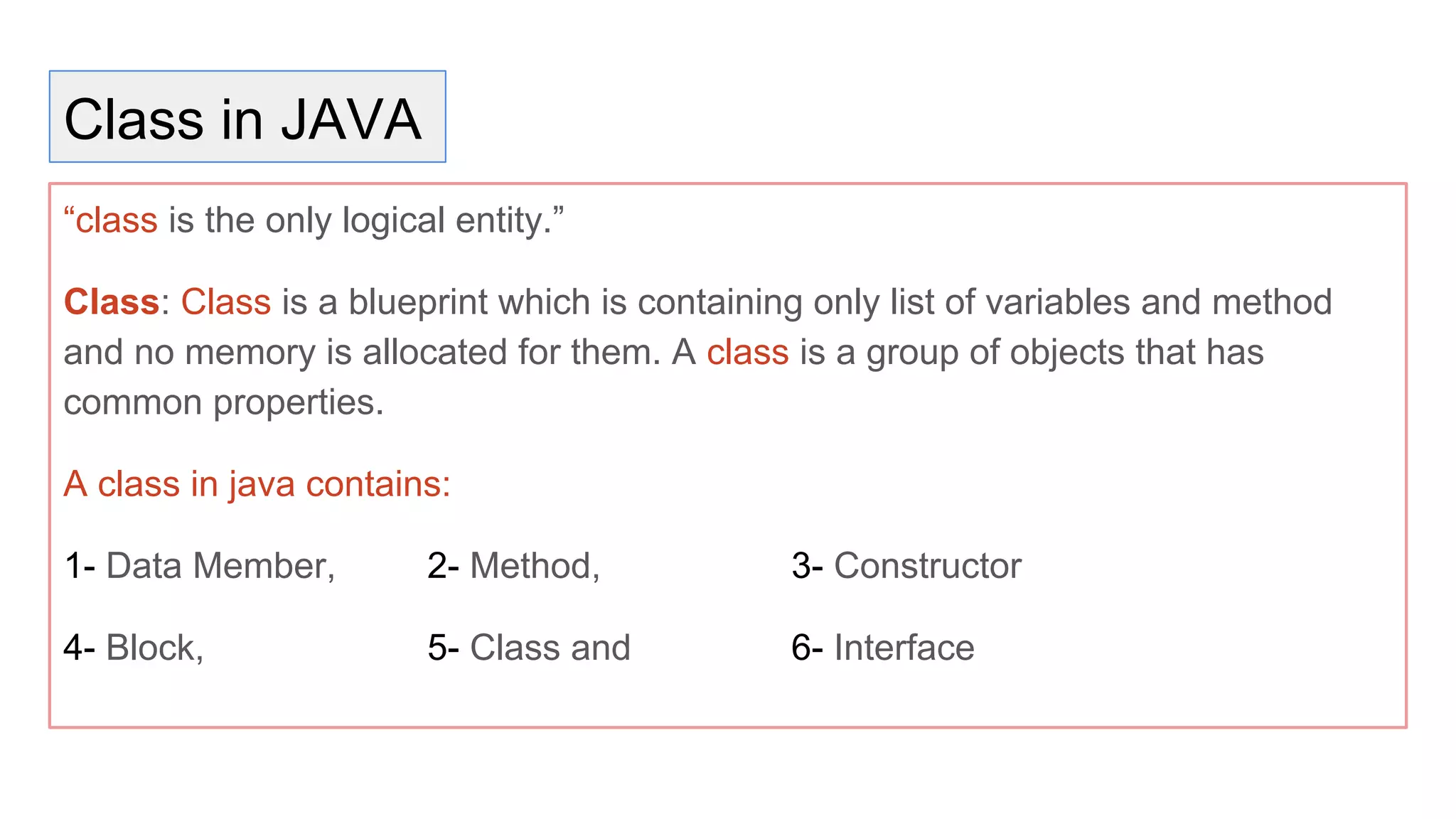
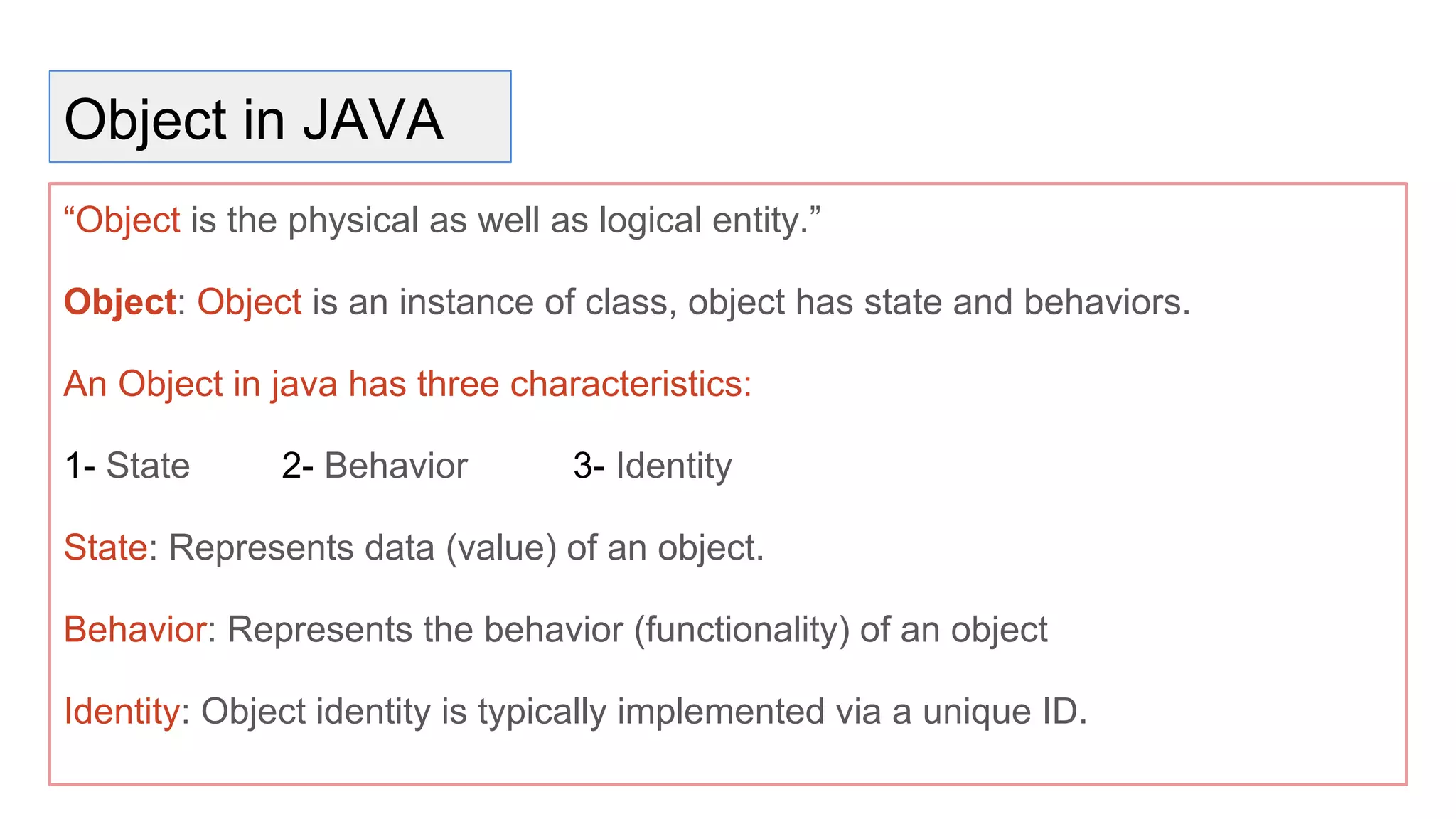
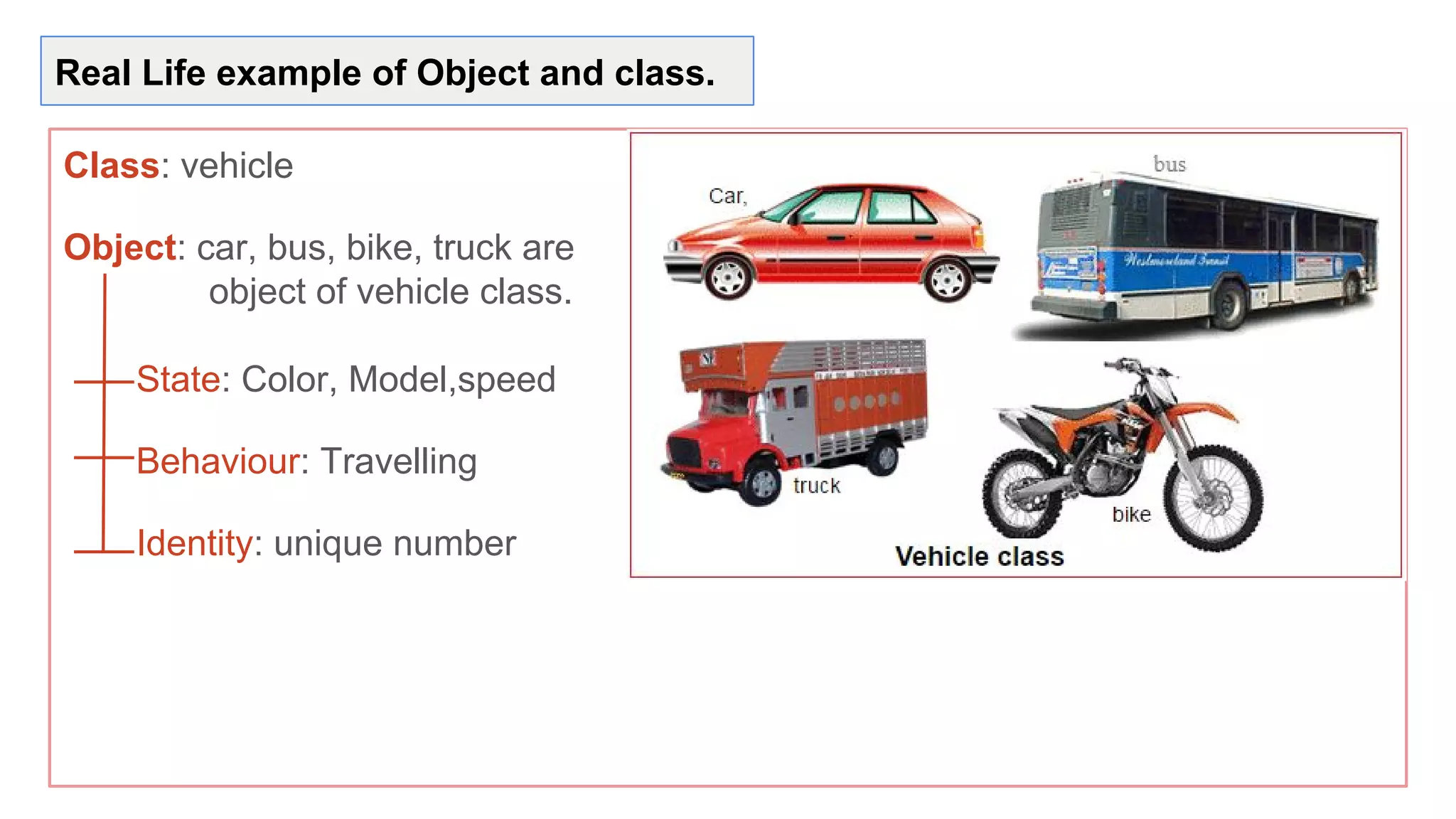
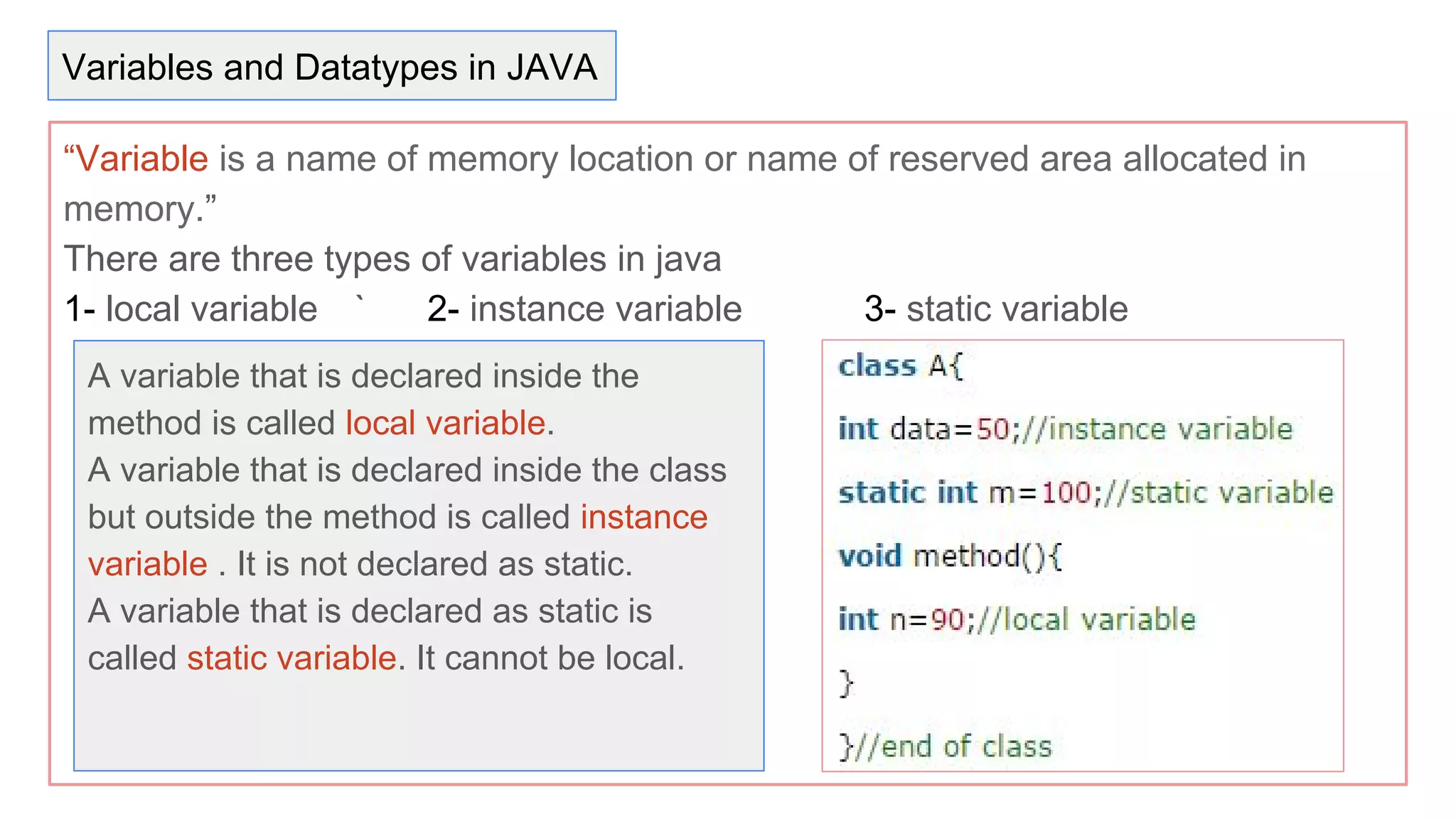
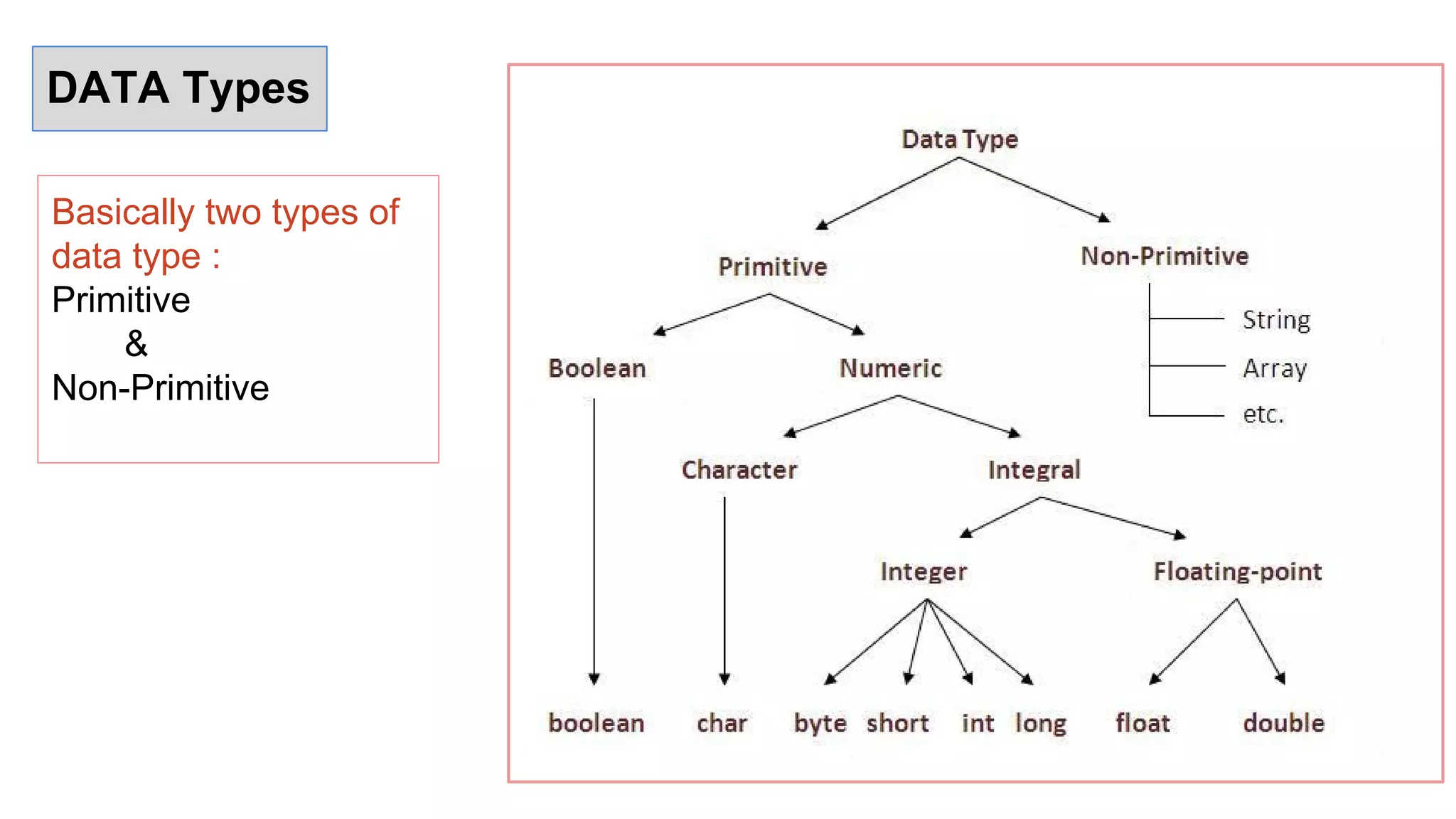
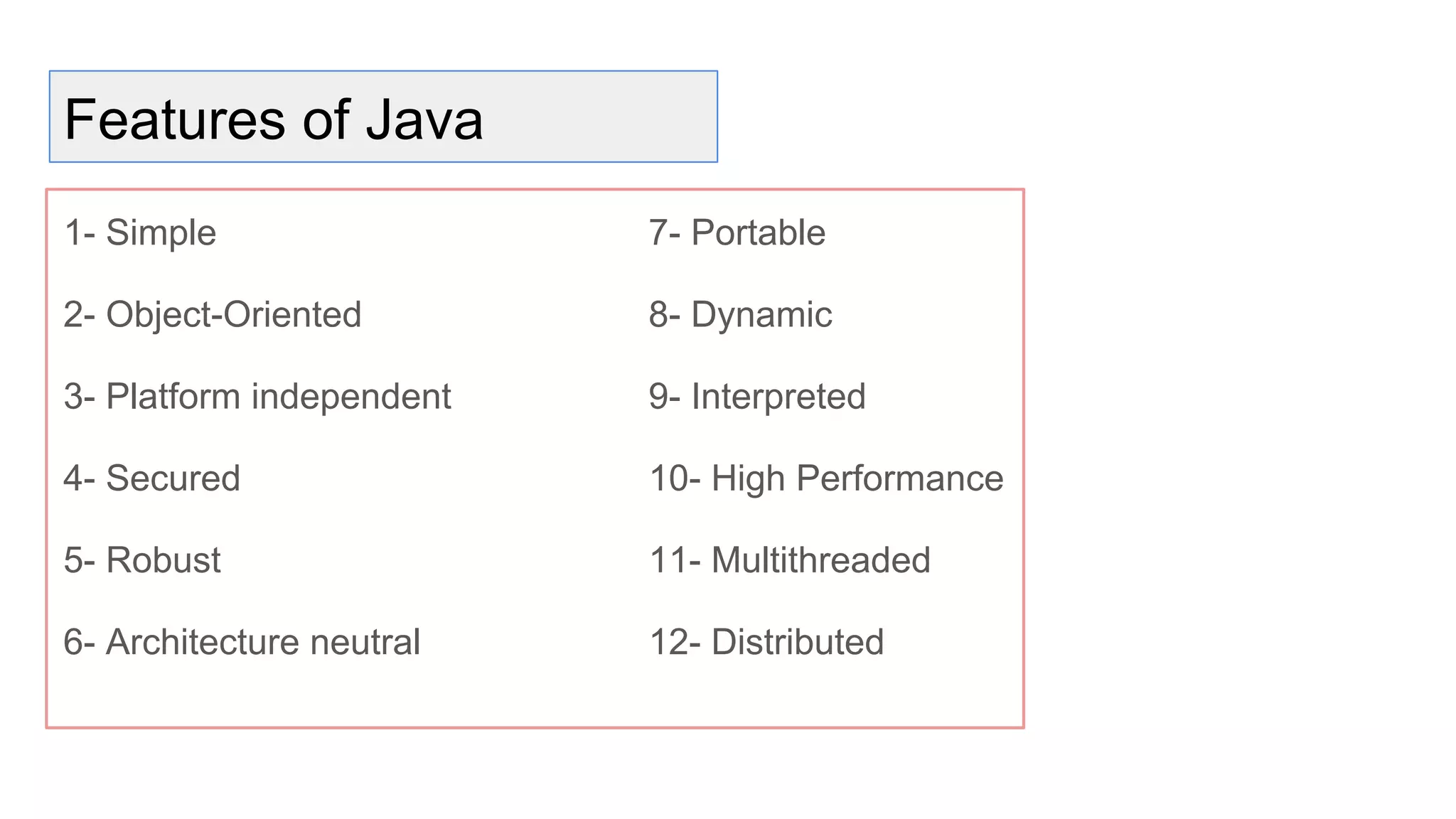
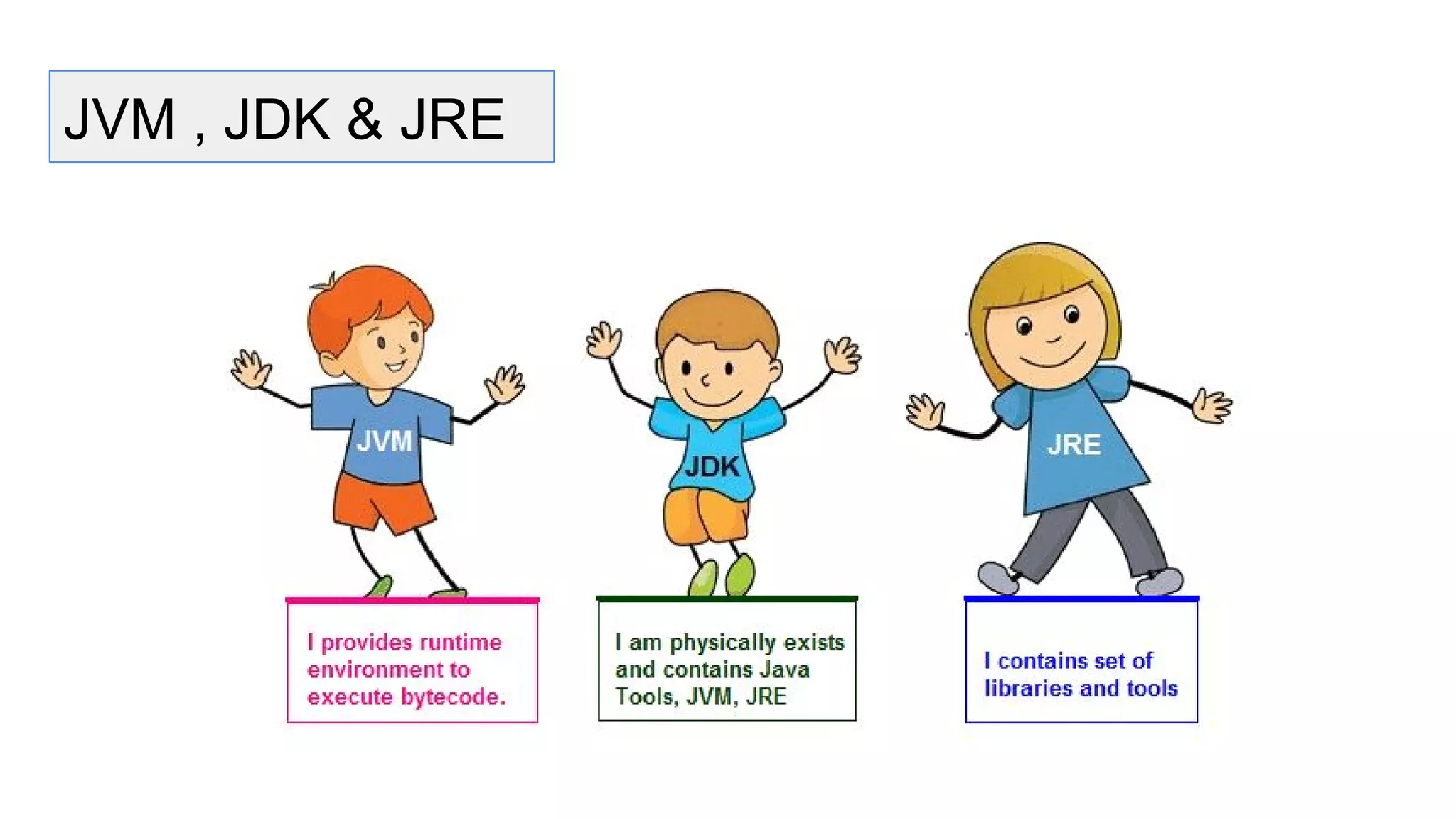
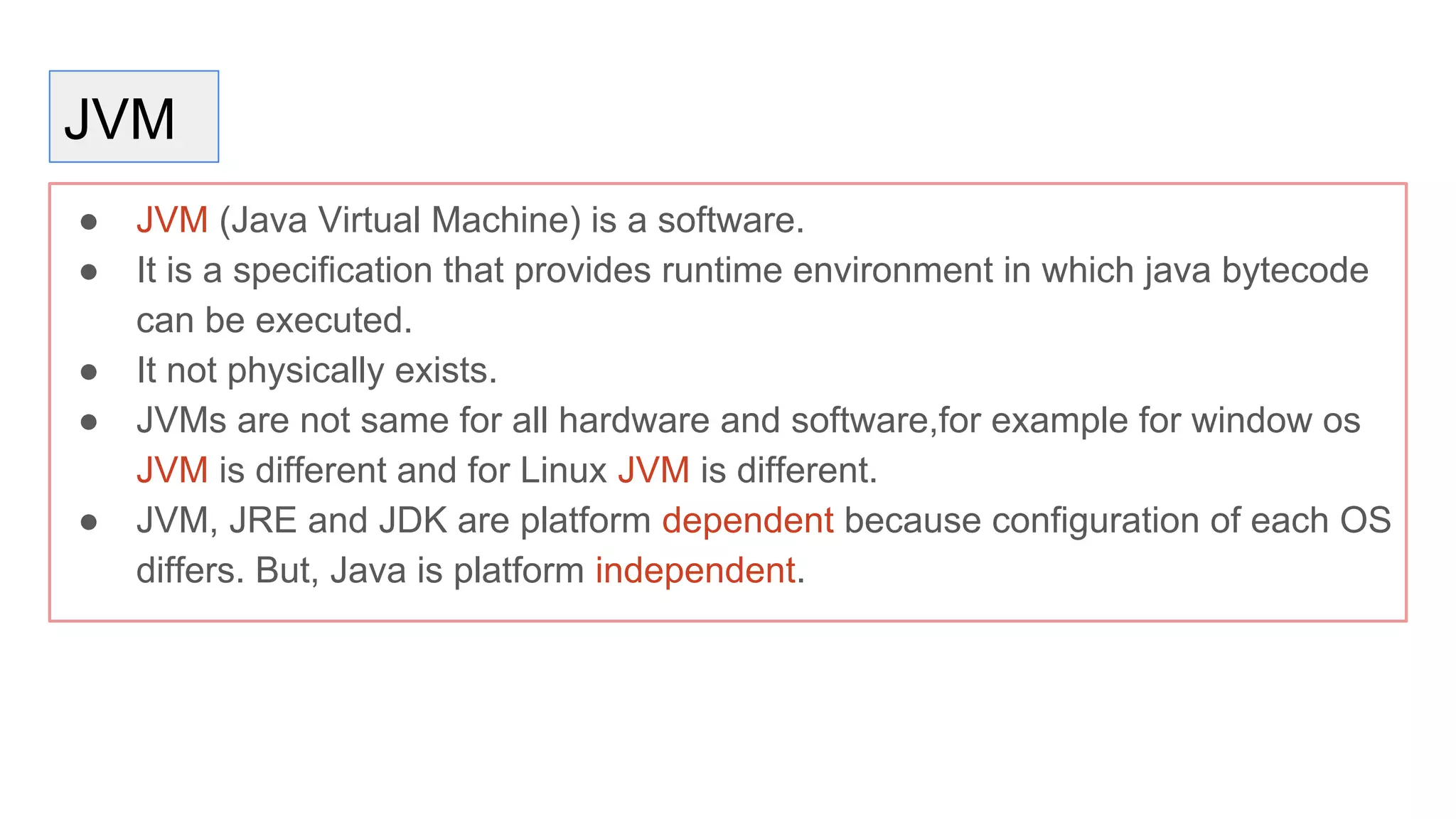
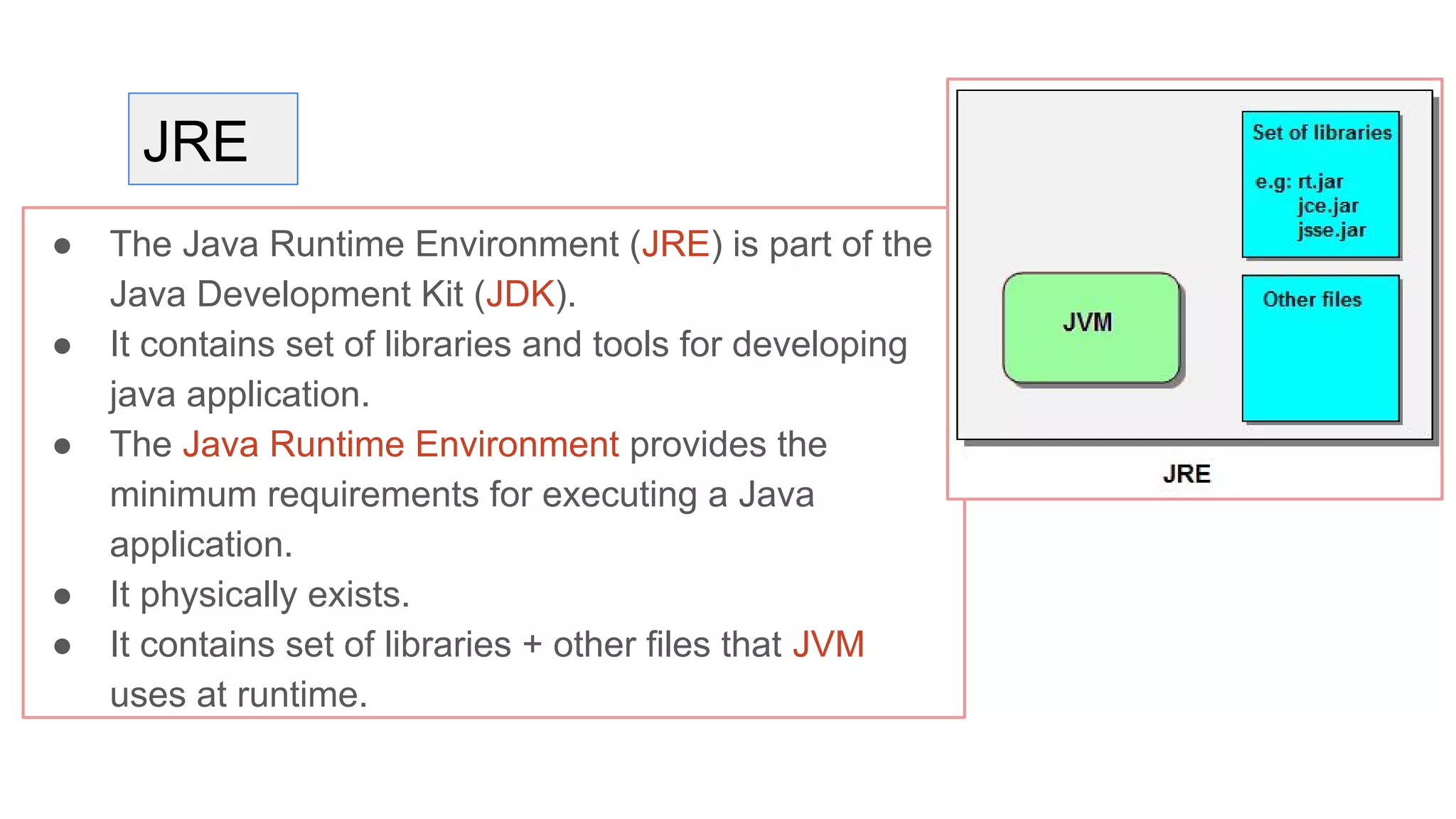
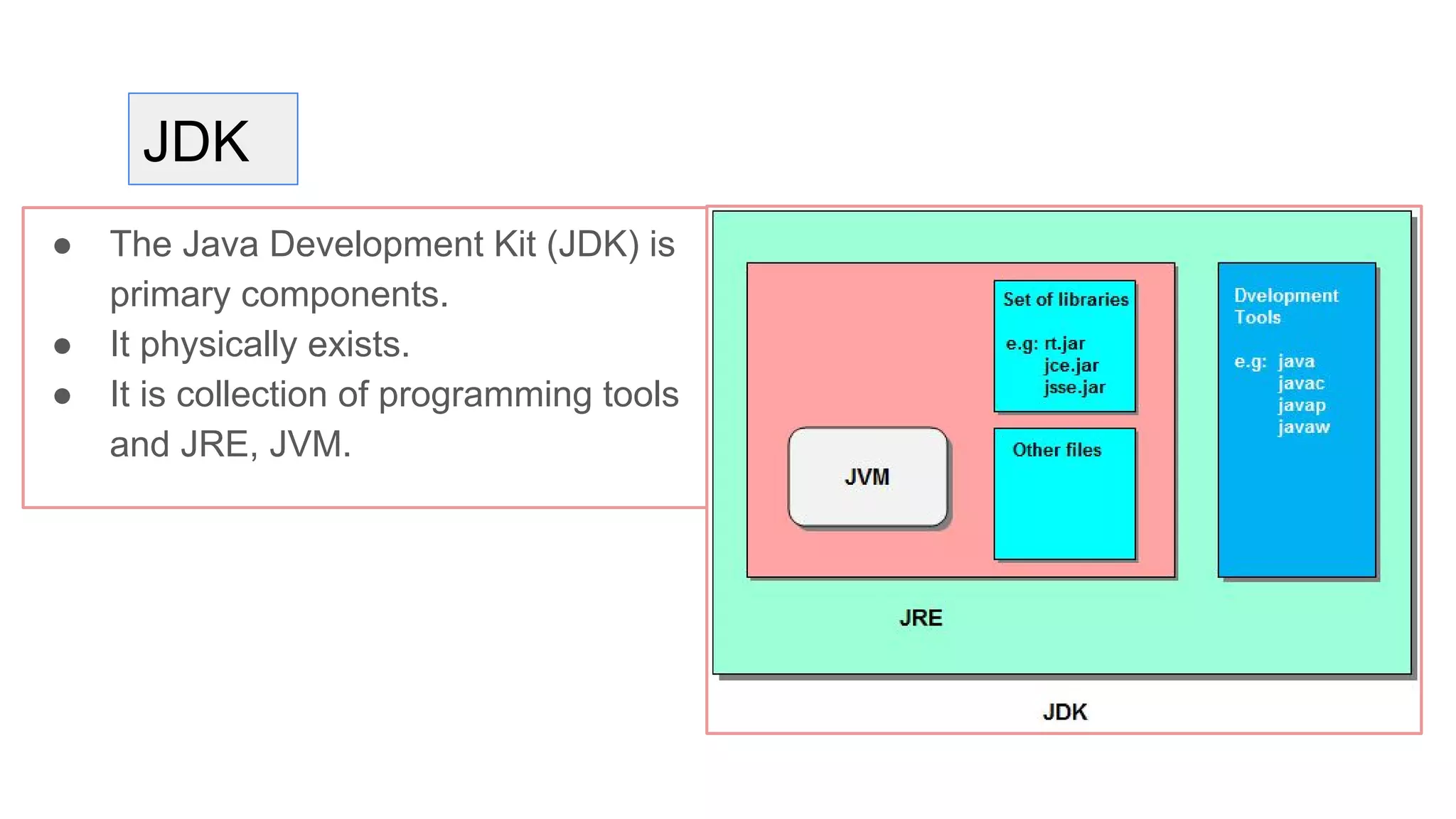
Java is an object-oriented programming language and platform. It was developed at Sun Microsystems in 1995 to be portable and high-performance. Java applications can run on many systems without recompilation because it uses a virtual machine that translates bytecode into native machine code. The key components of Java are the JVM (Java Virtual Machine), JRE (Java Runtime Environment), and JDK (Java Development Kit). The JVM executes Java bytecode, while the JRE provides libraries and tools for developing Java applications. The JDK is a superset of the JRE and includes development tools like compilers and debuggers.



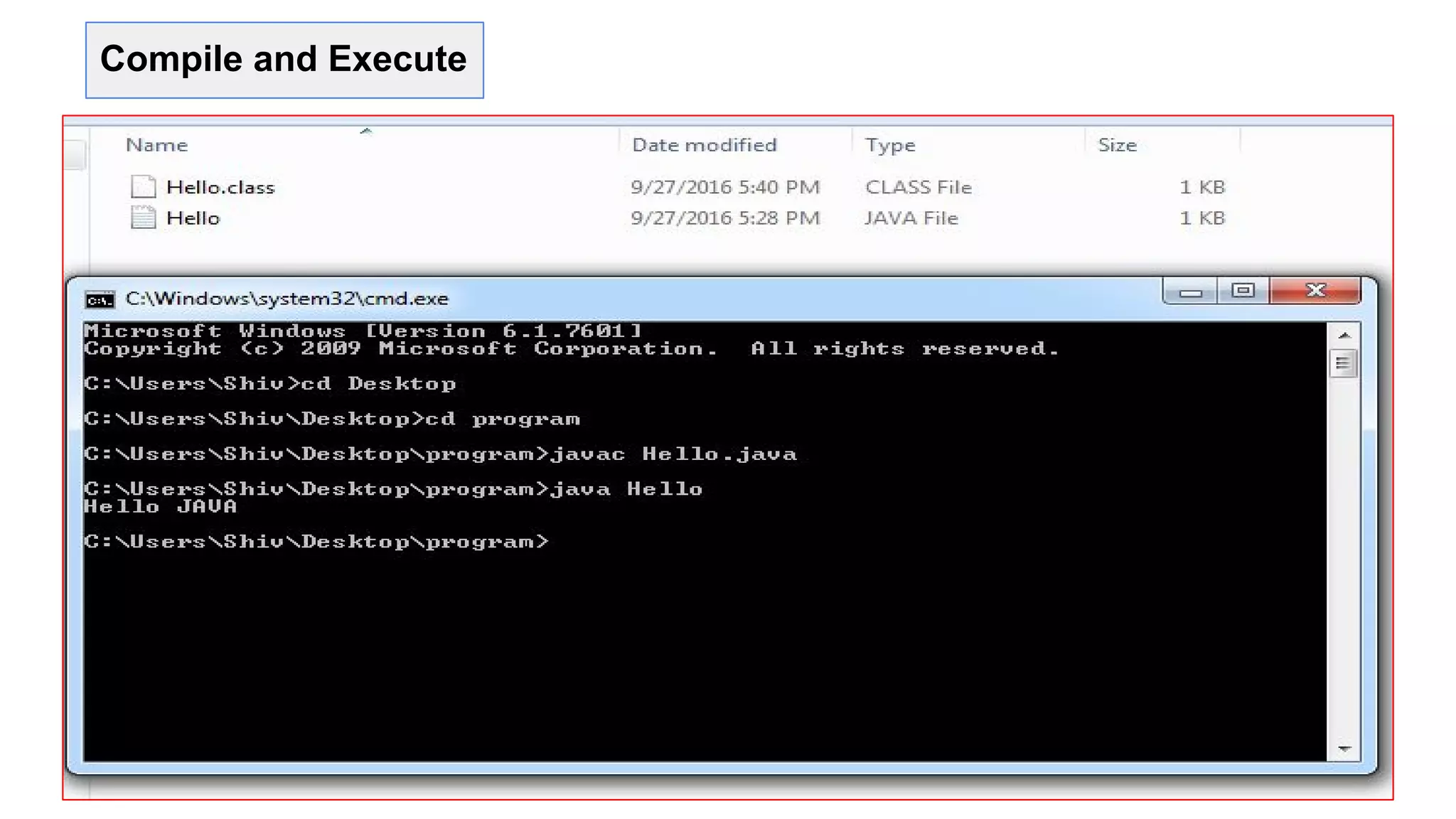
![First Program “Hello World”
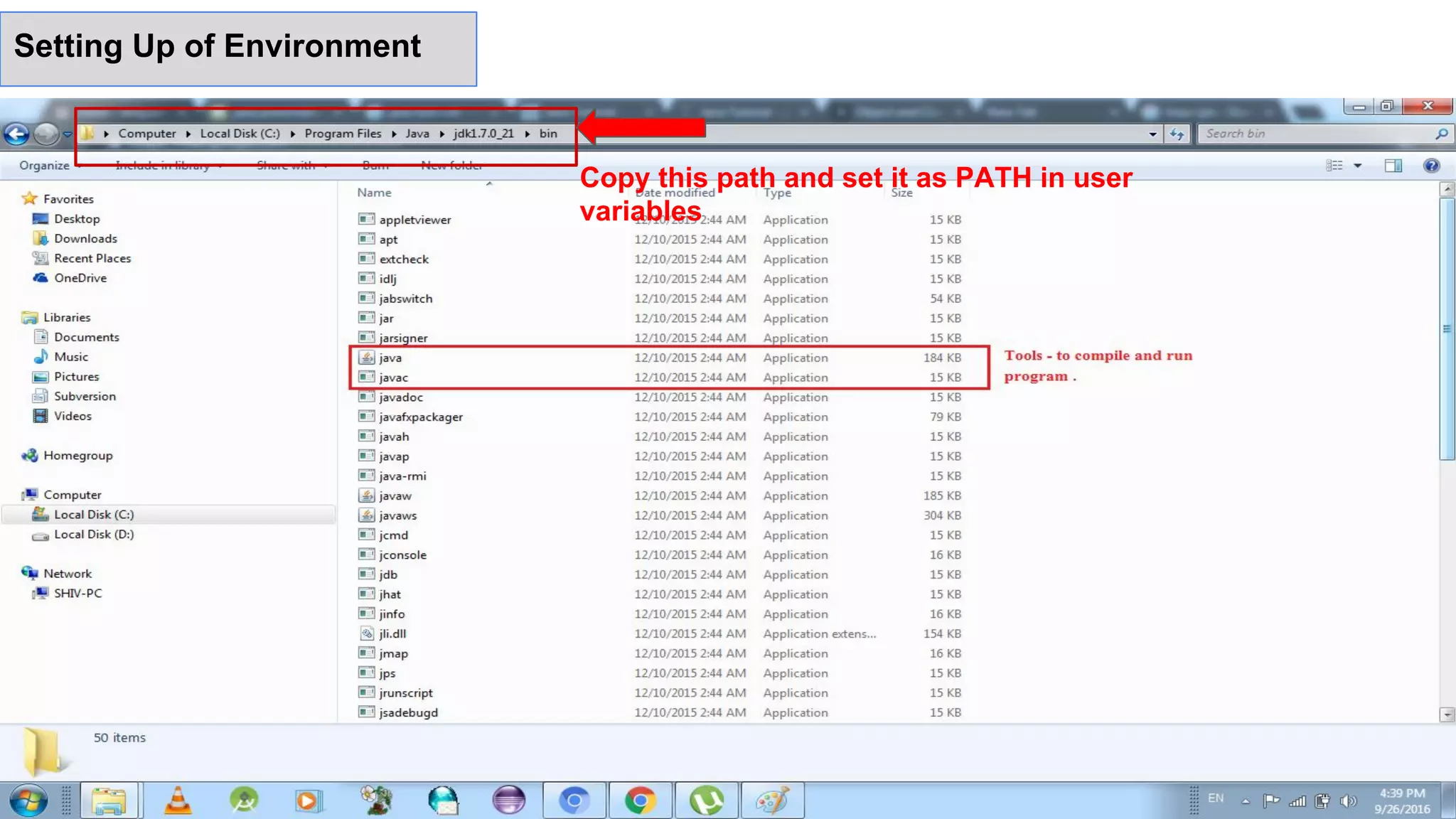
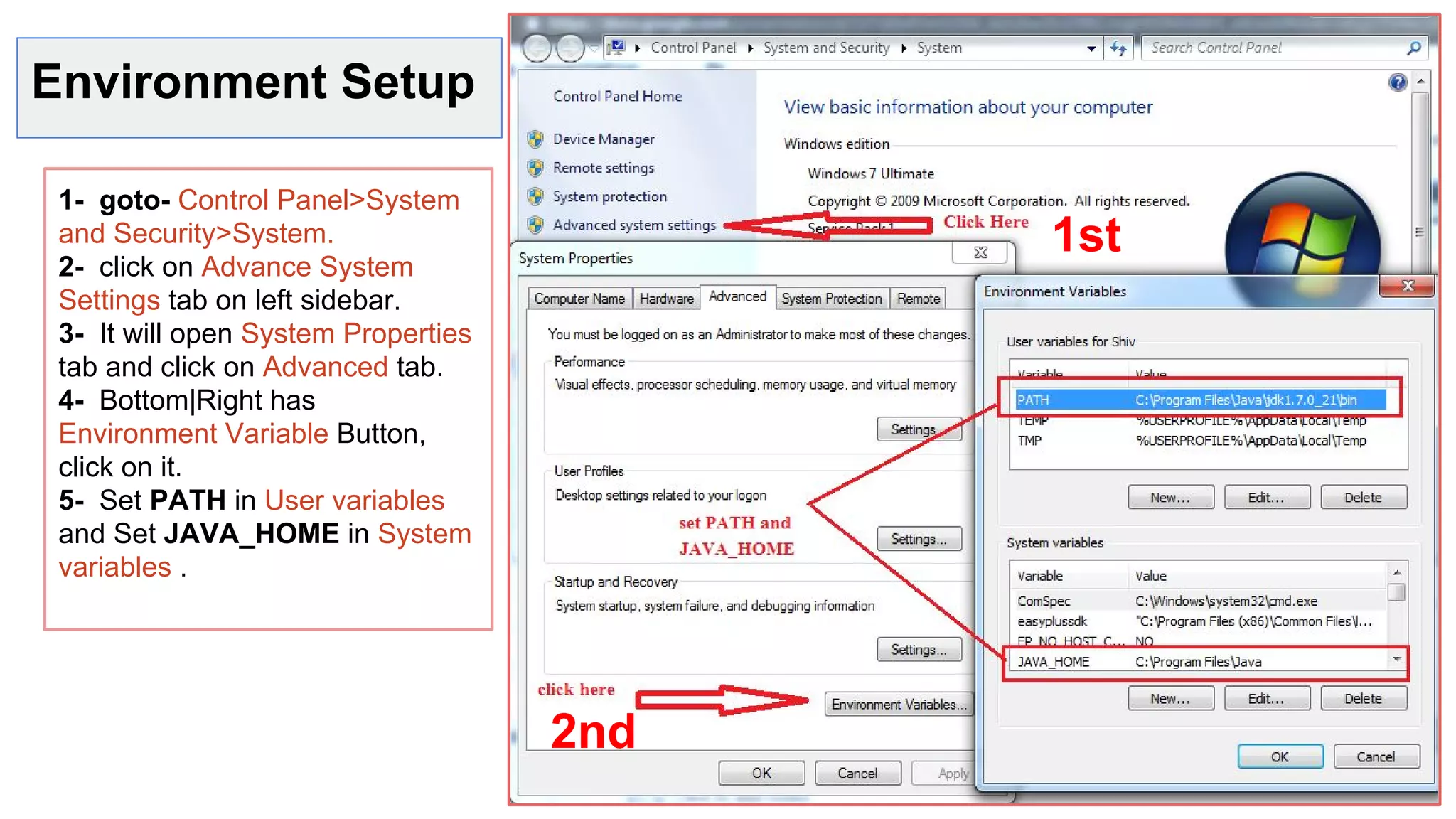
1- open text editor and write first program
2- Save it as Hello.java
3- Open command prompt or terminal .
4- Go to the file and to compile code write
“javac Hello.java” command.
5- to run “java Hello”.
class Hello {
public static void main (String args[])
{
System.out.println("Hello JAVA");
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javapresentation-161212014423/75/Java-presentation-13-2048.jpg)