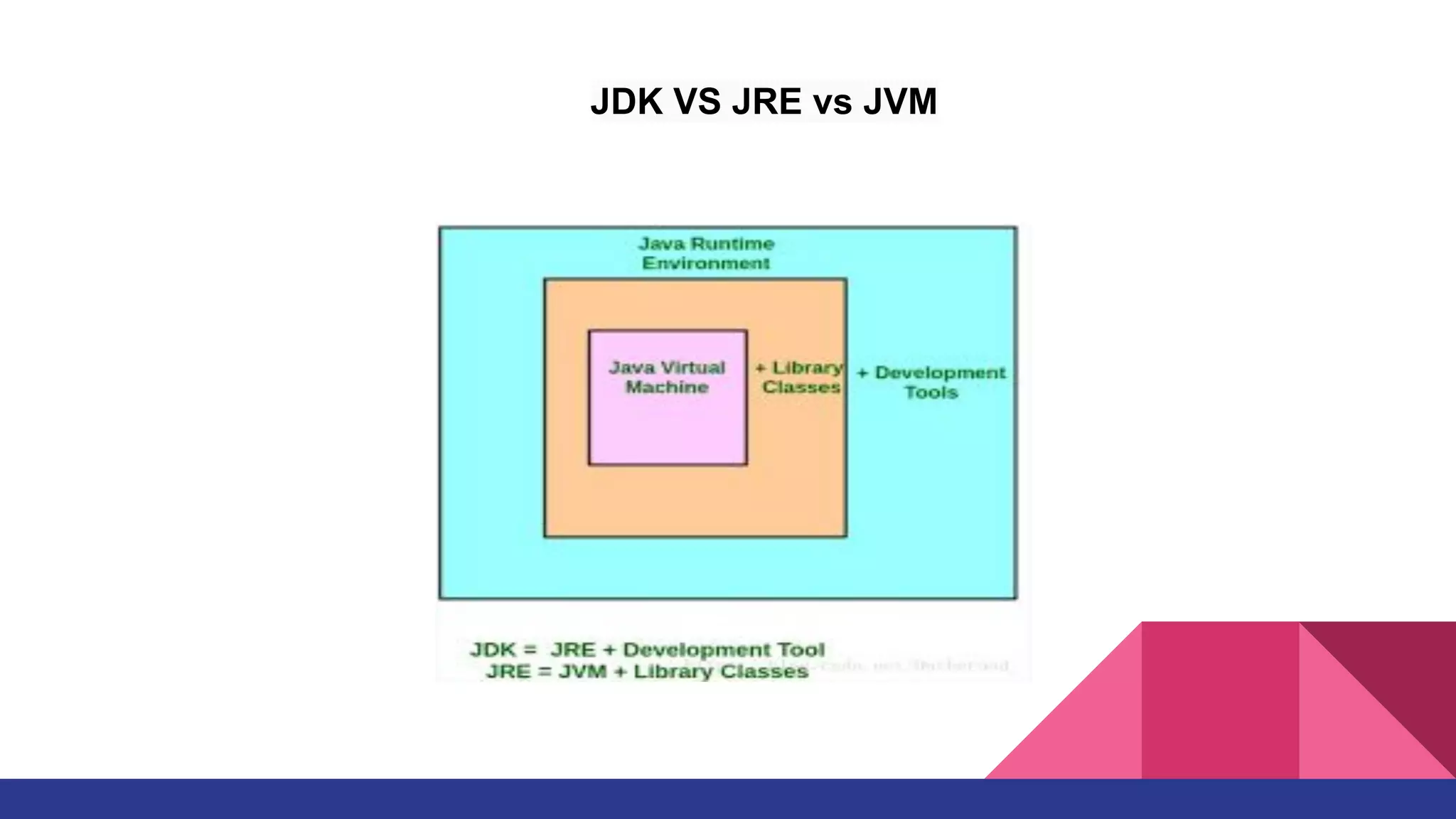
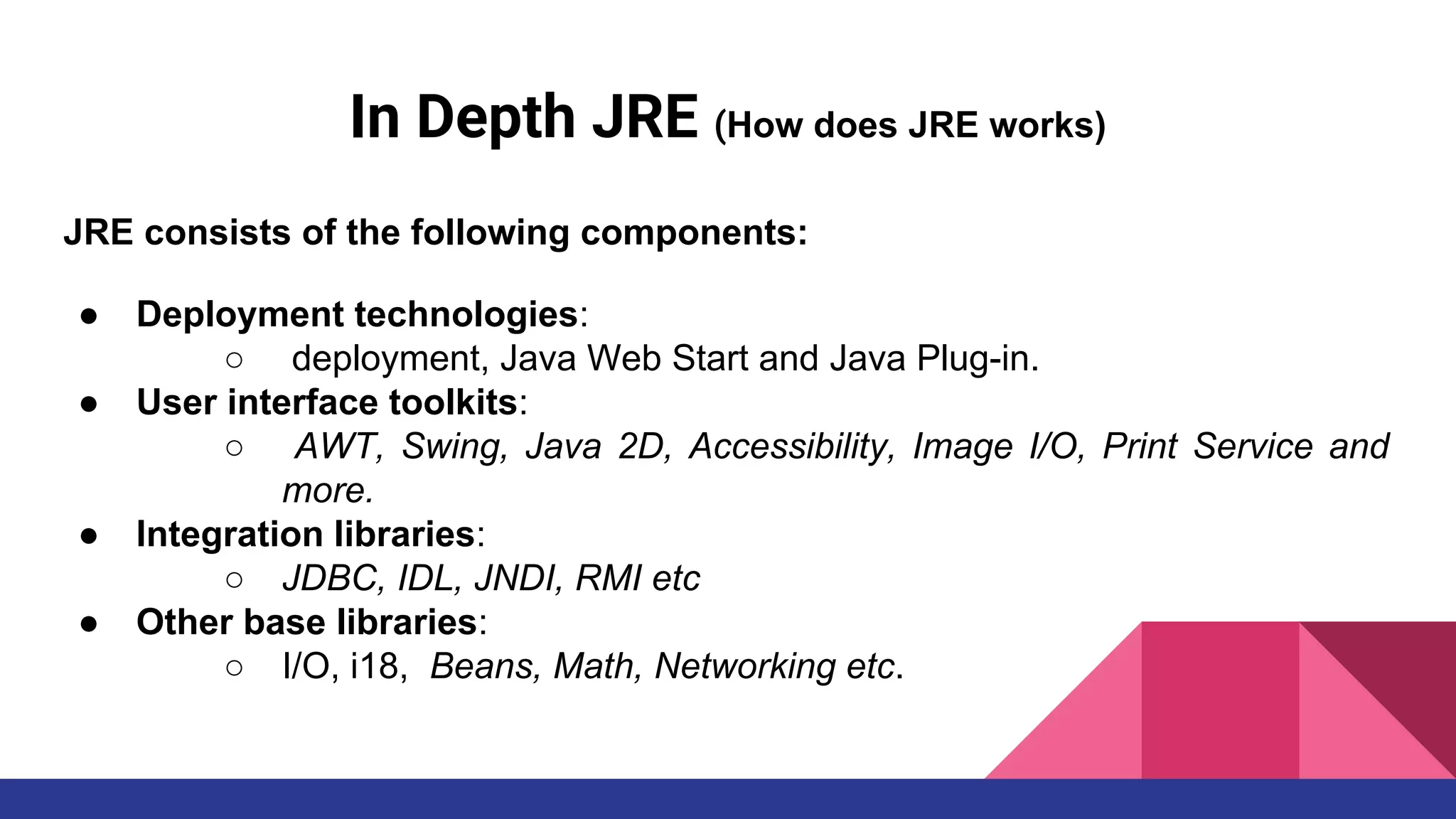
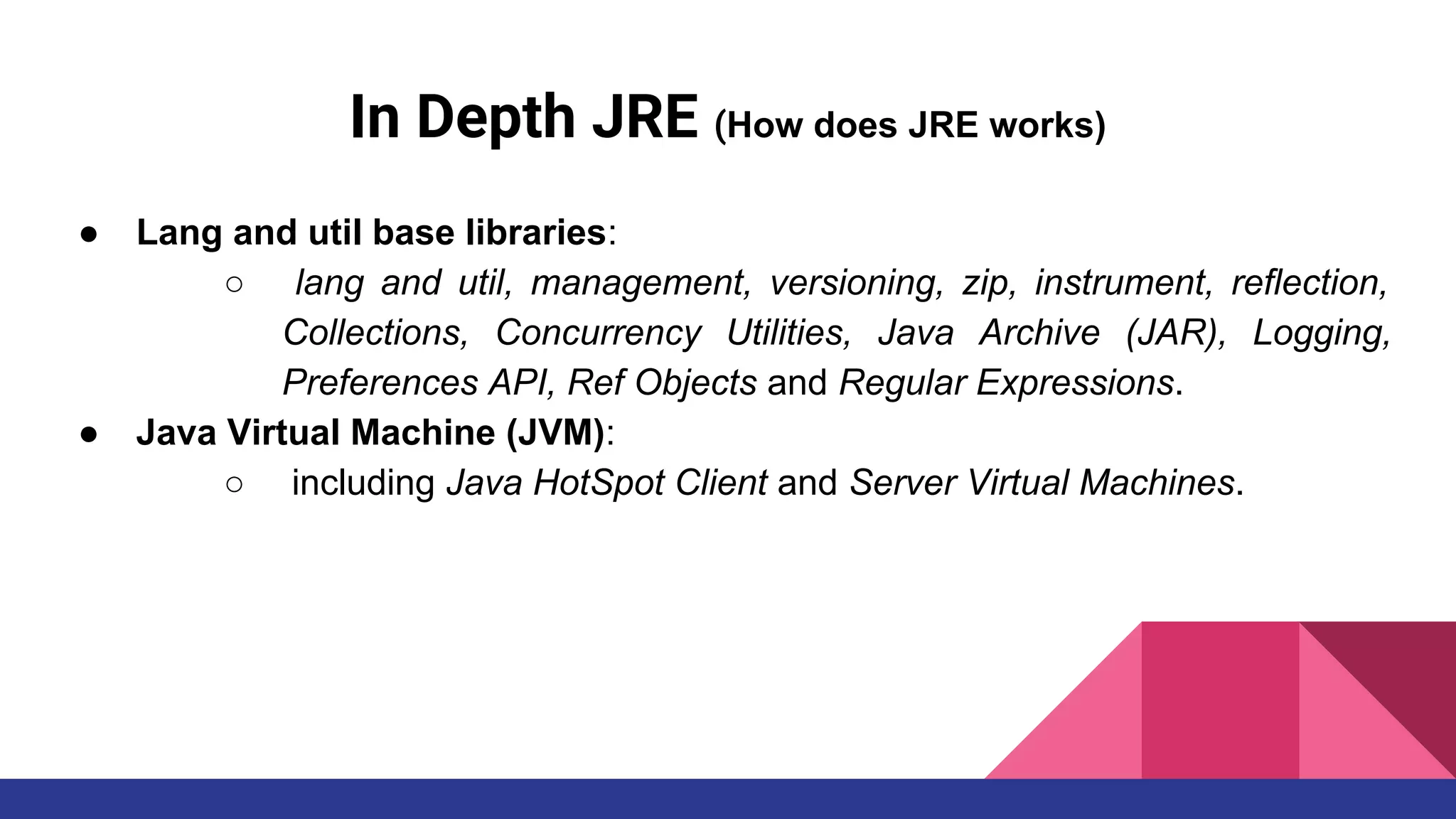
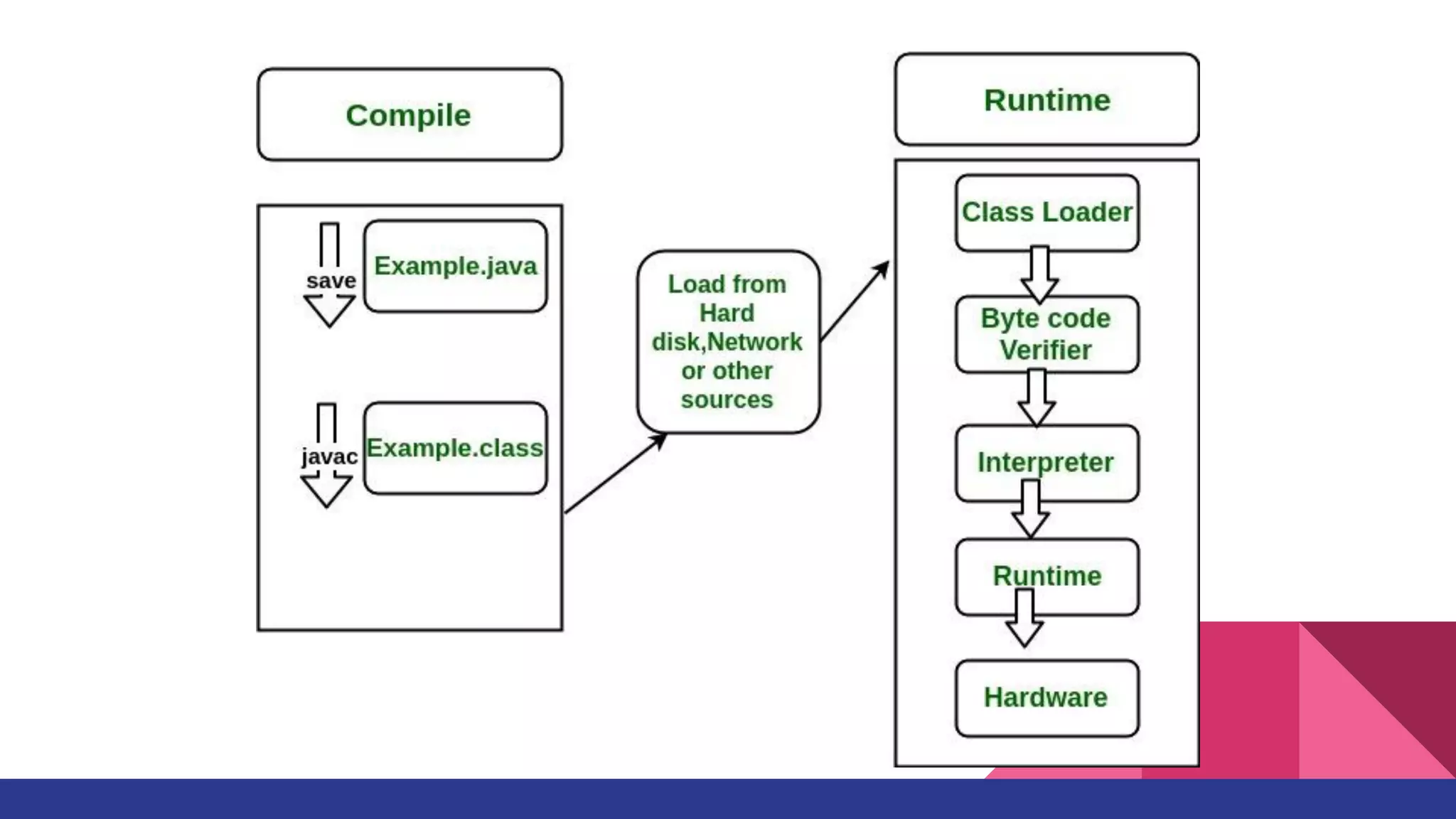
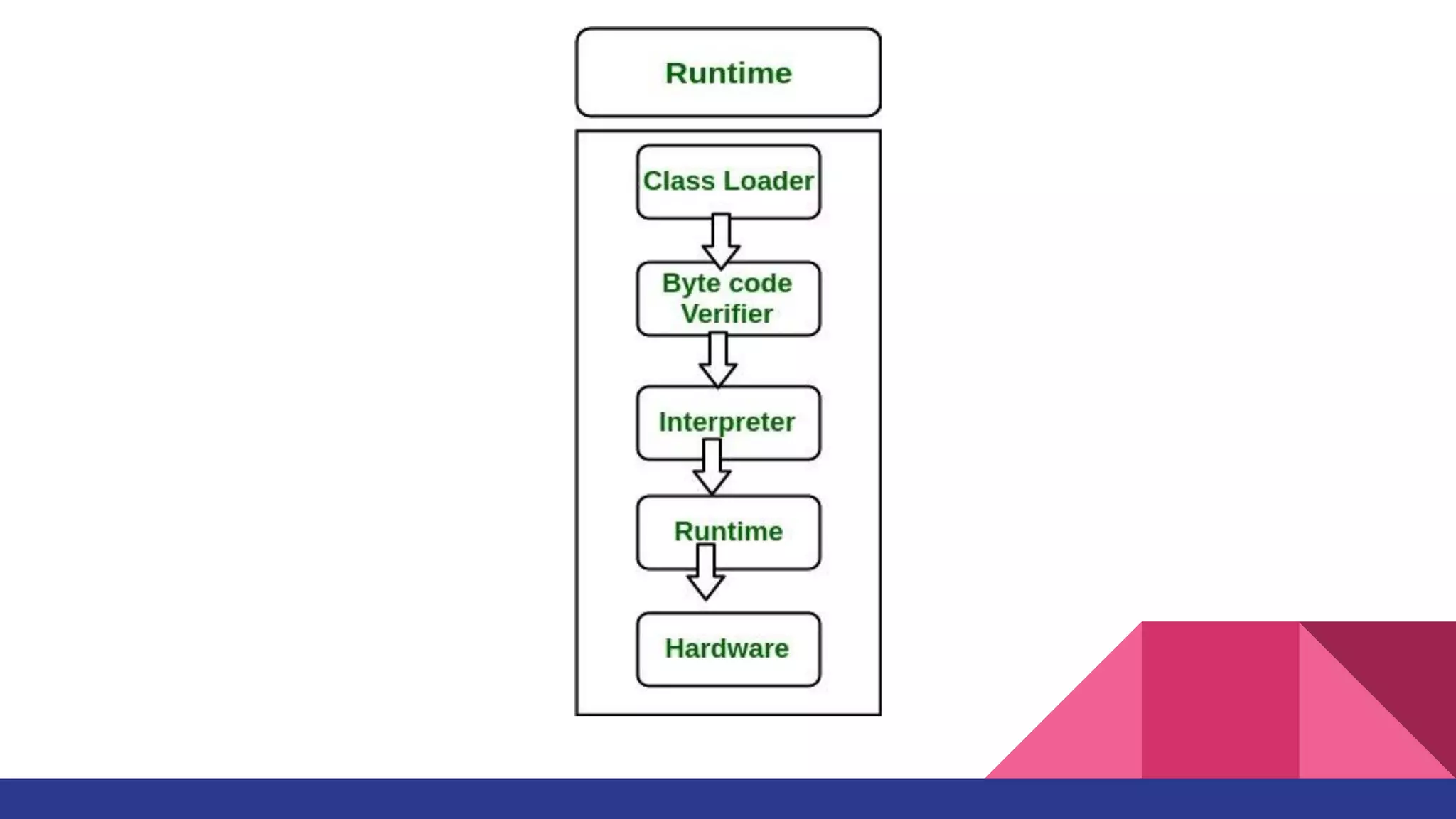
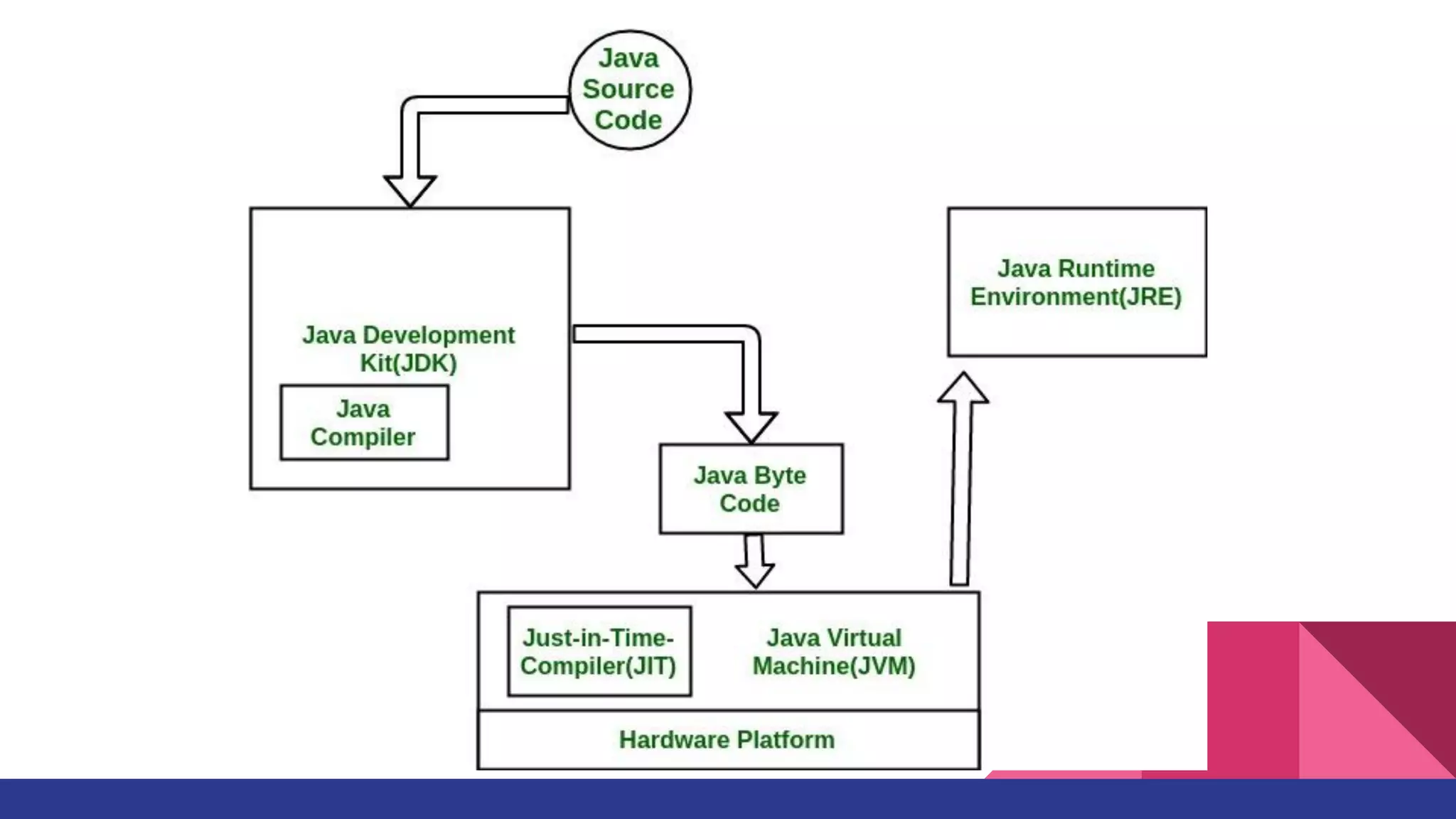
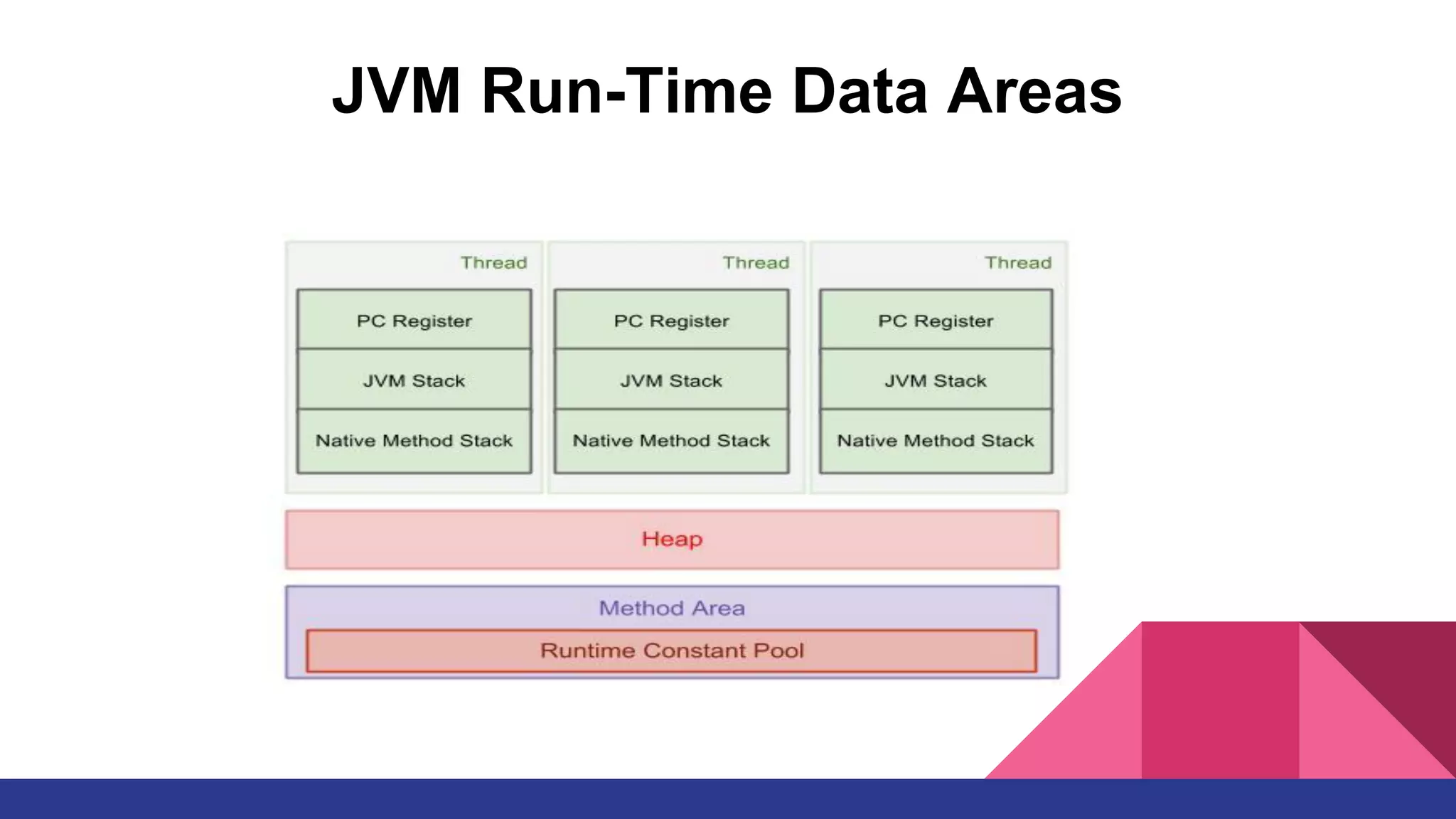
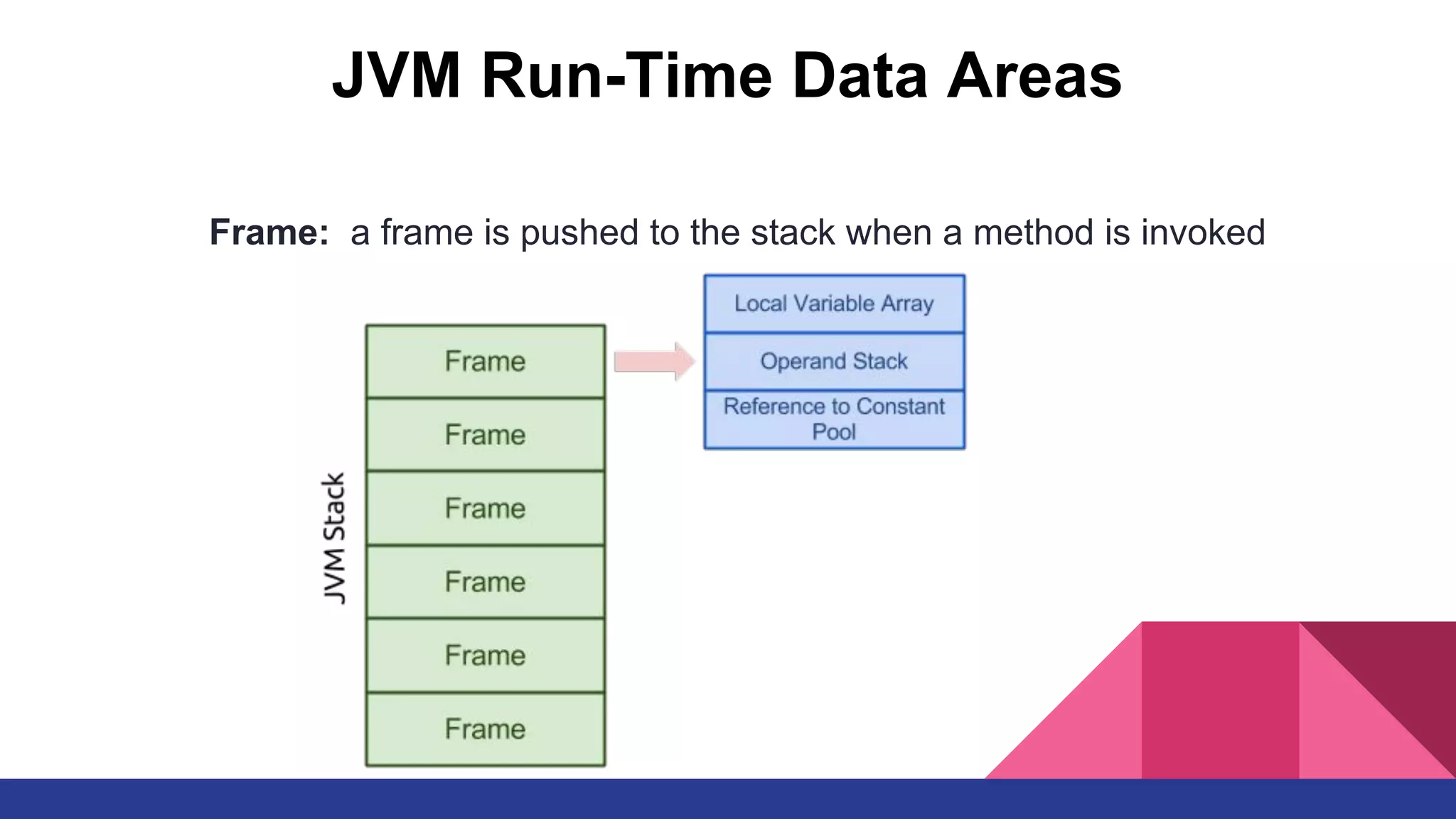
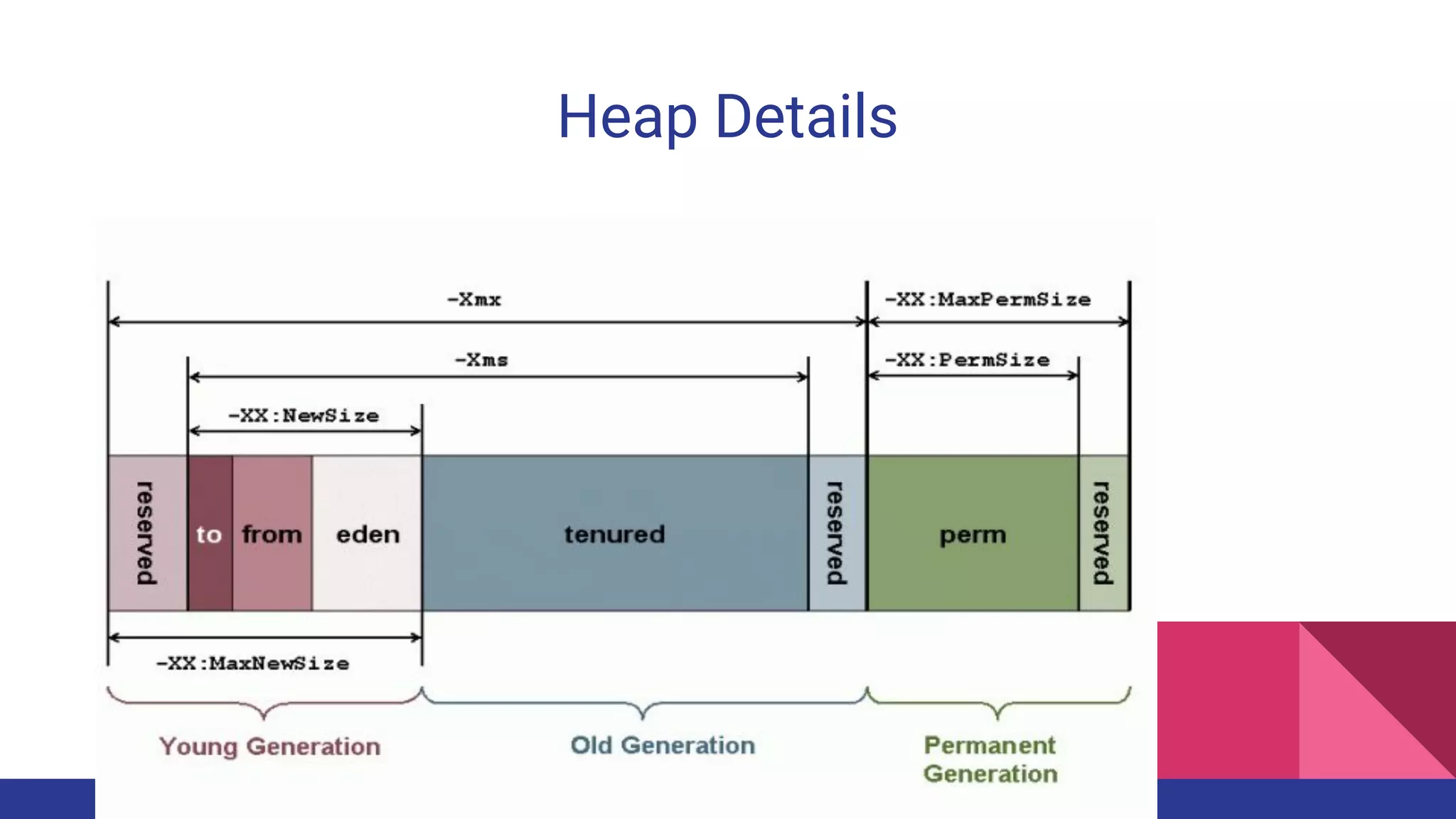
The document discusses topics related to Java memory areas including the differences between JDK, JRE, and JVM. It then covers runtime data areas like the heap, method area, and threads' stacks. The heap stores objects and arrays and is shared among all threads while each thread has its own stack. The method area contains class metadata that is also shared.