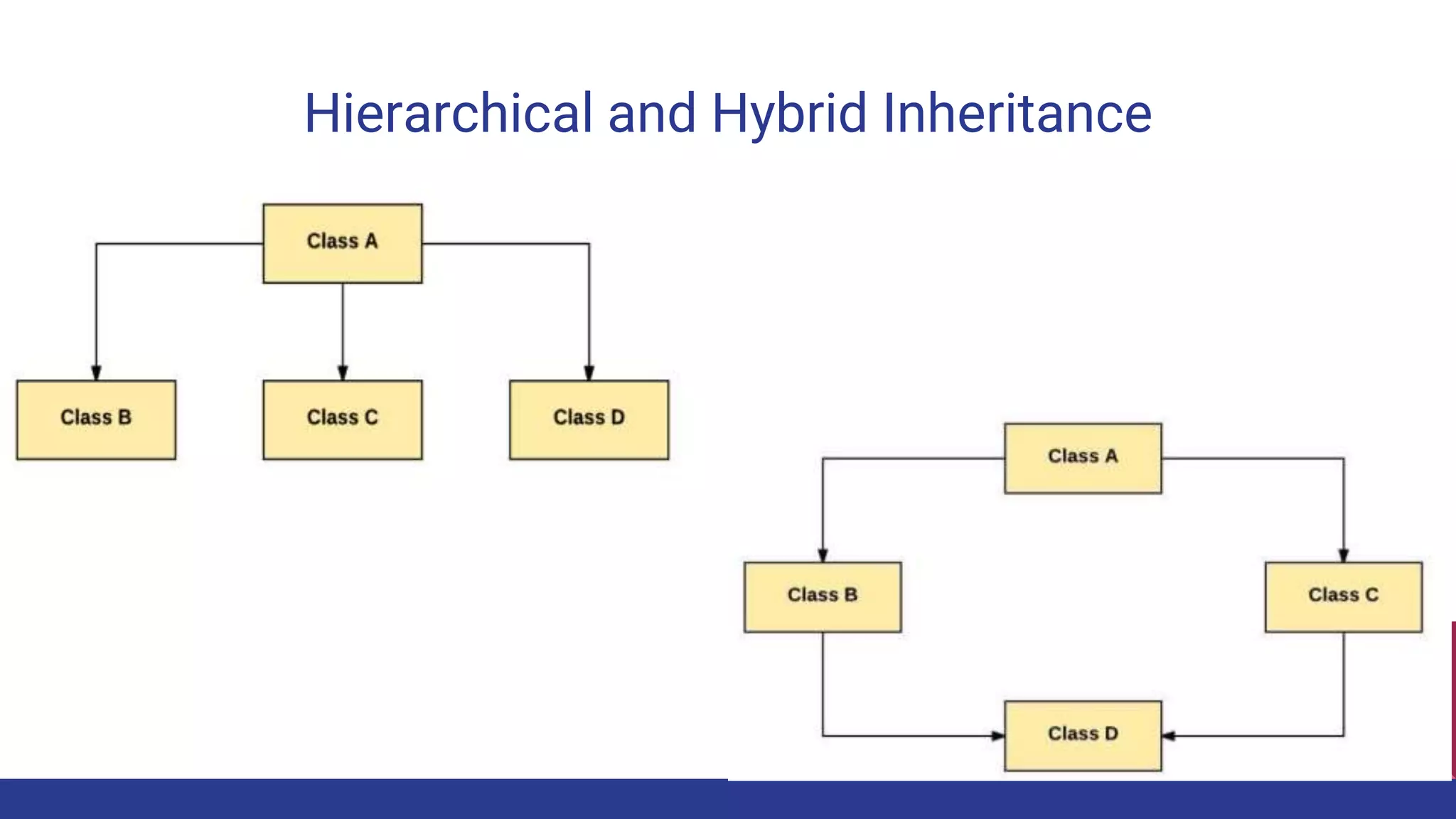
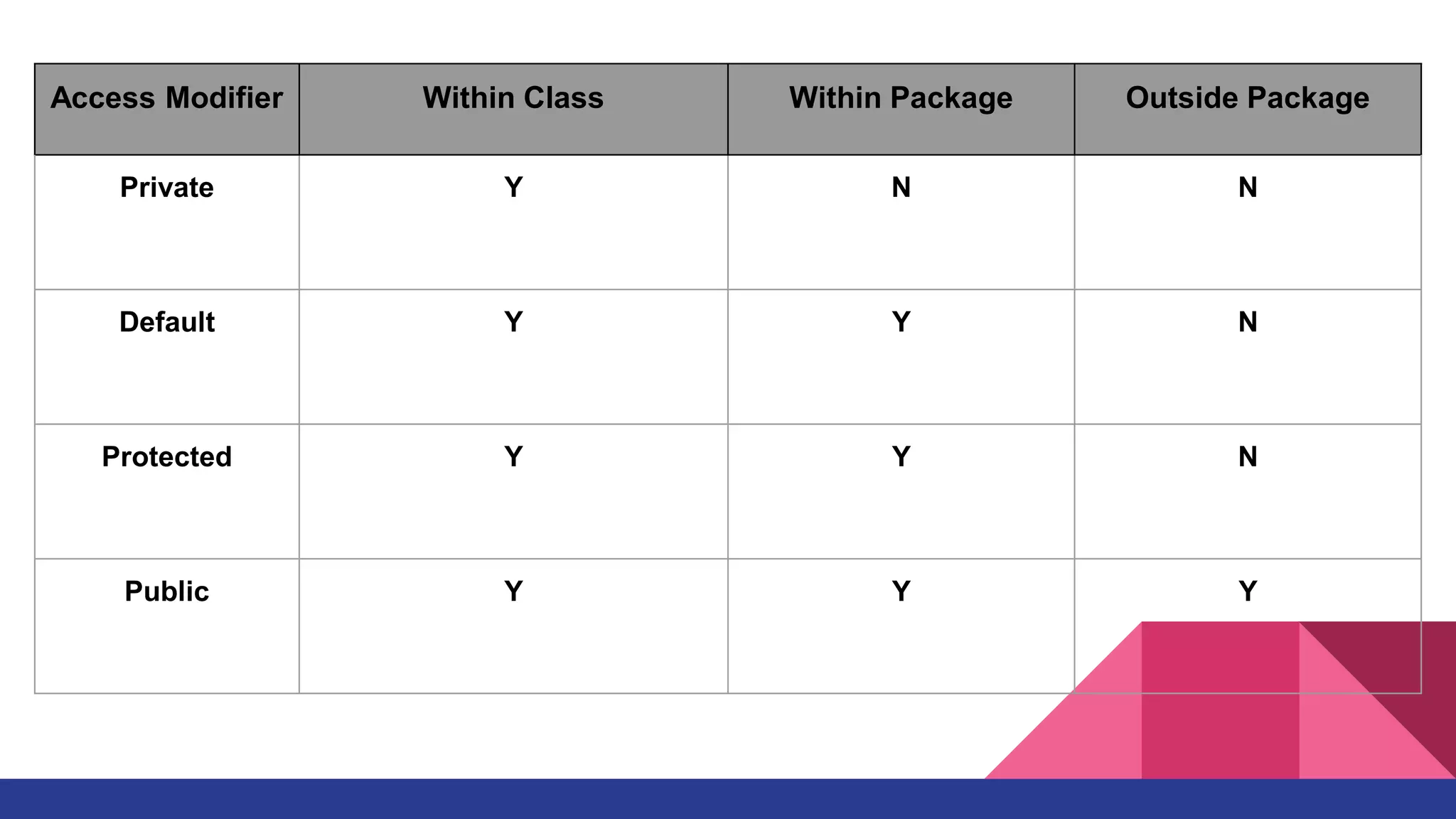
The document discusses Java inheritance and polymorphism, explaining how child classes inherit attributes and methods from parent classes. It outlines various types of inheritance (single, multiple, multilevel, hierarchical, and hybrid) and two forms of polymorphism (compile-time and run-time). Additionally, it covers method overloading and access modifiers that determine the accessibility of class members.