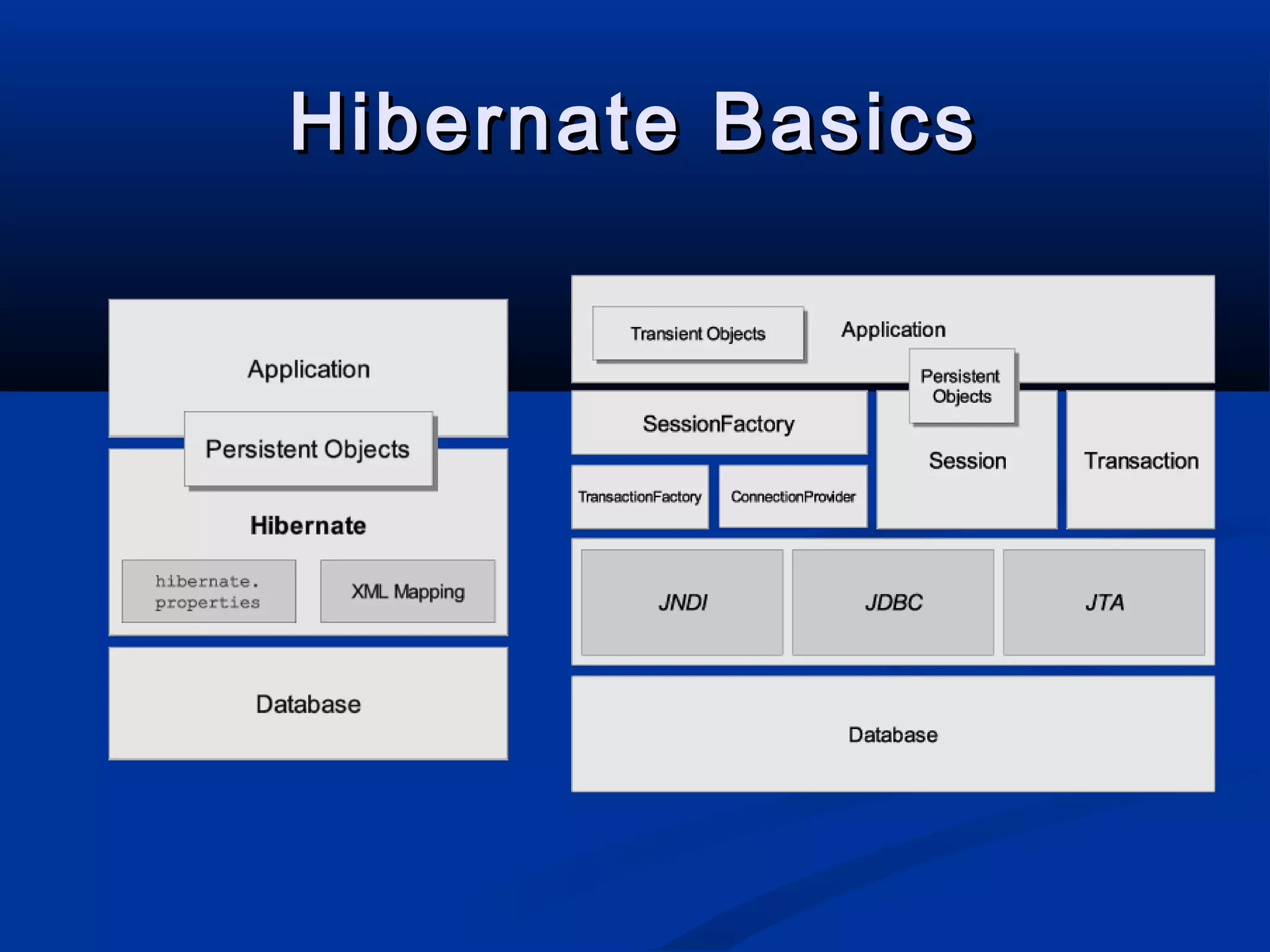
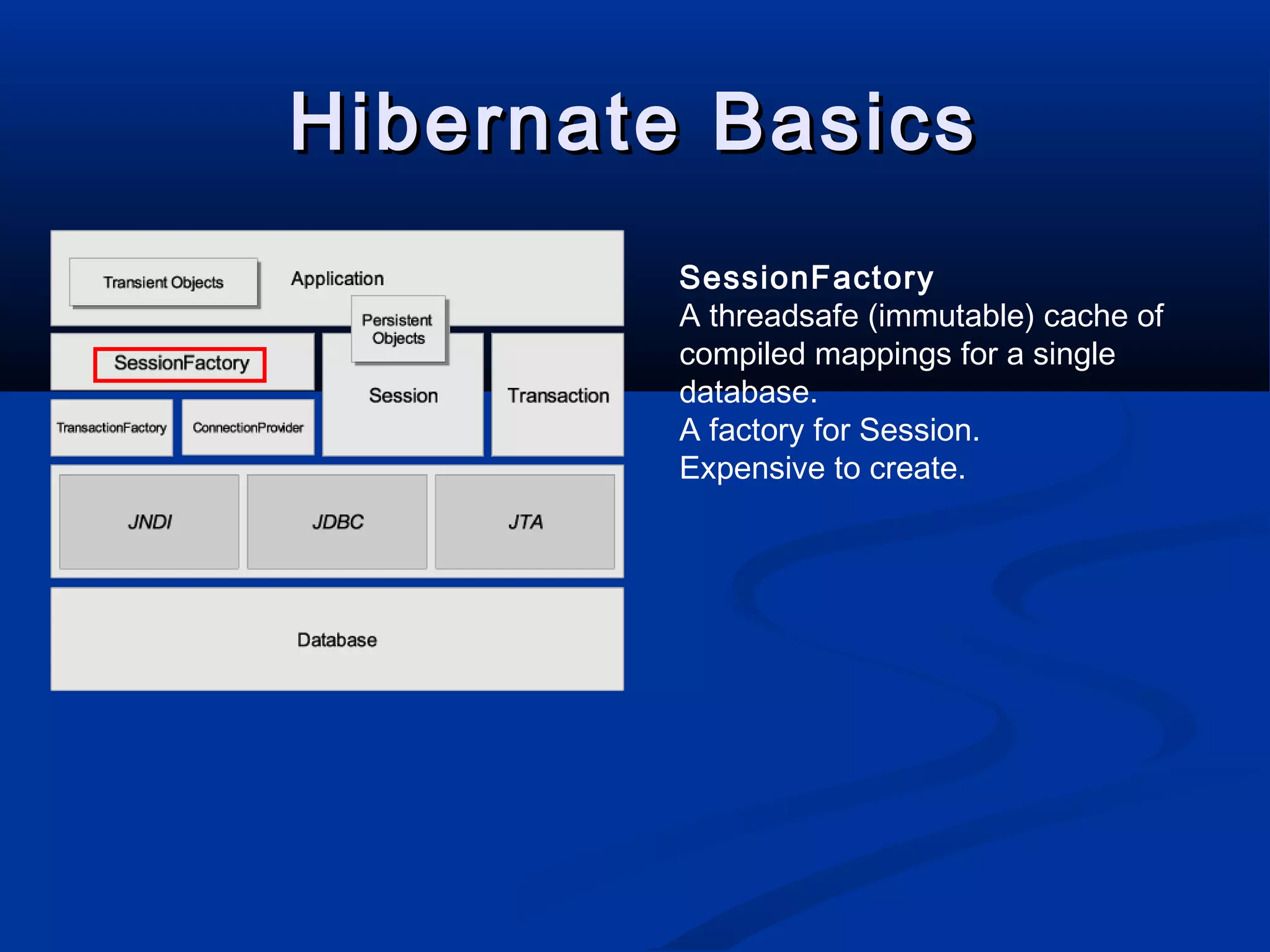
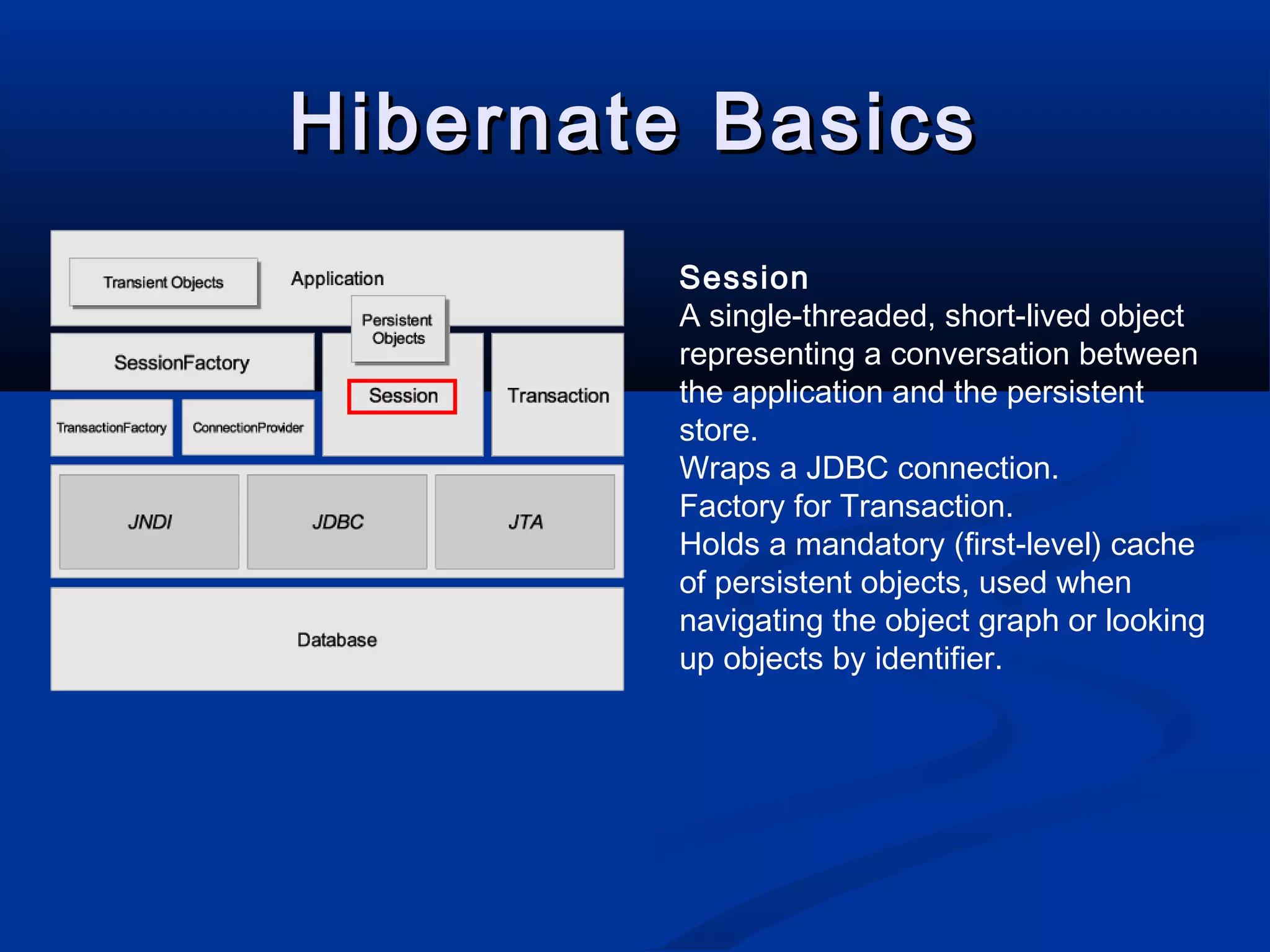
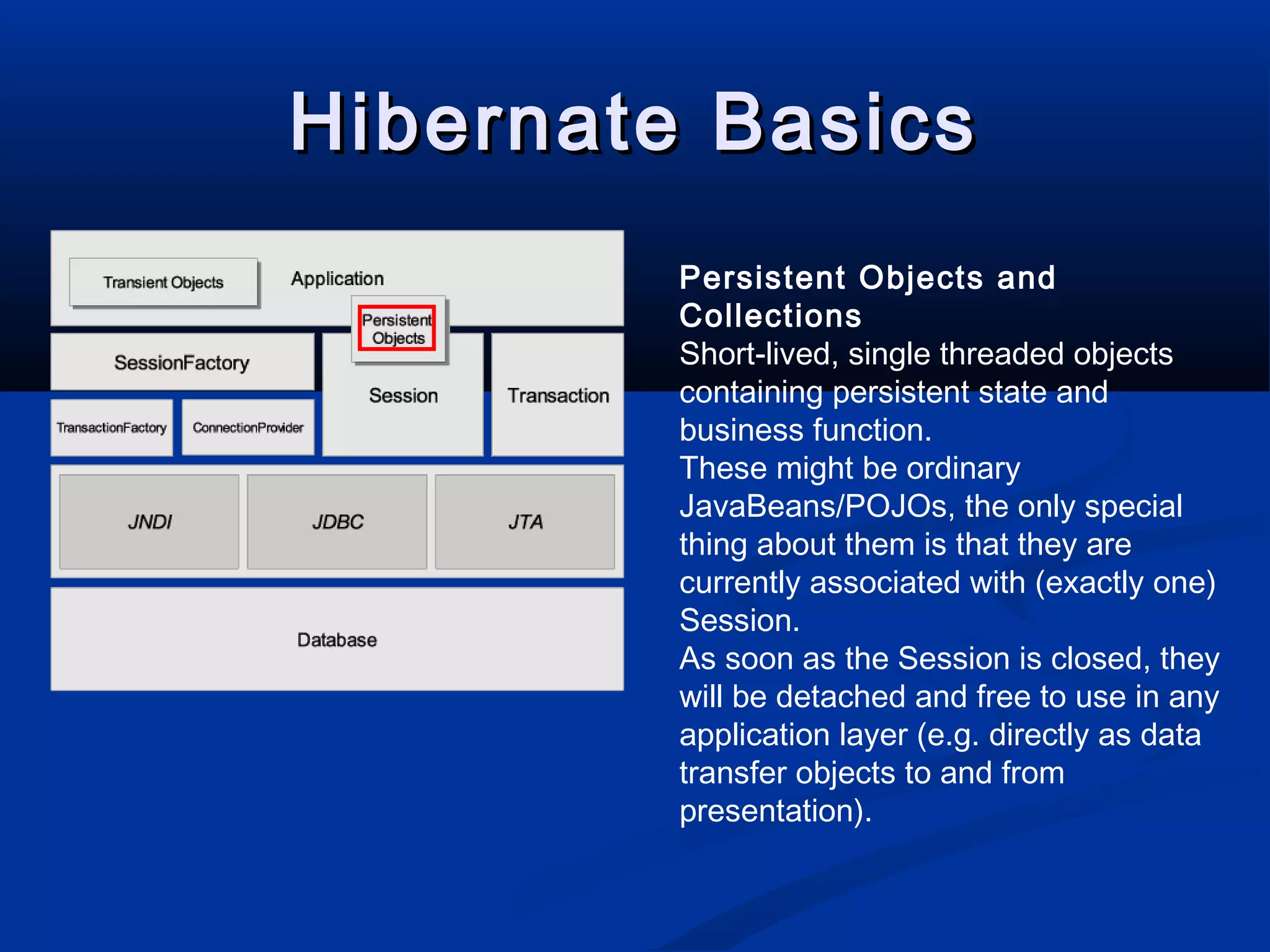
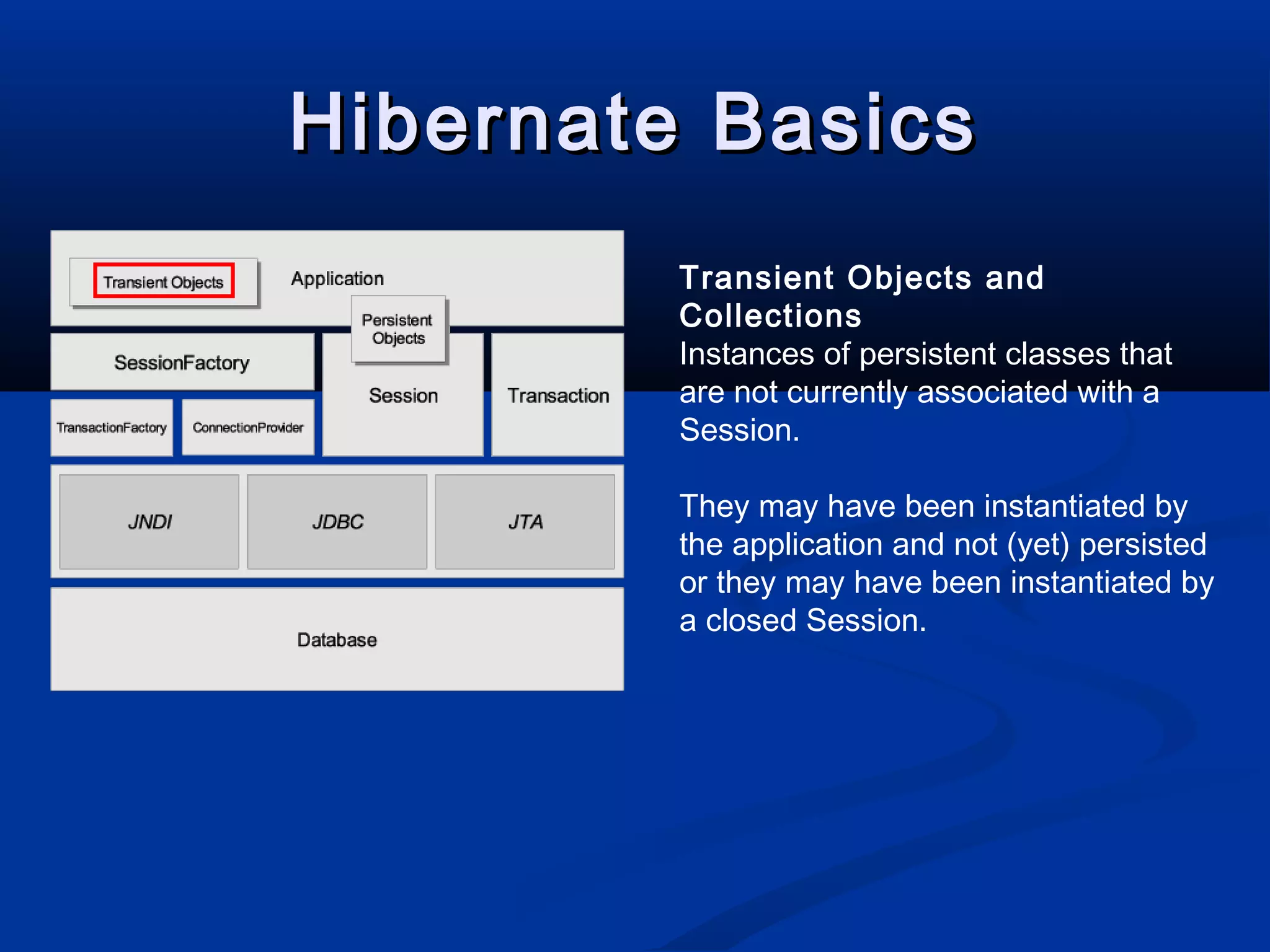
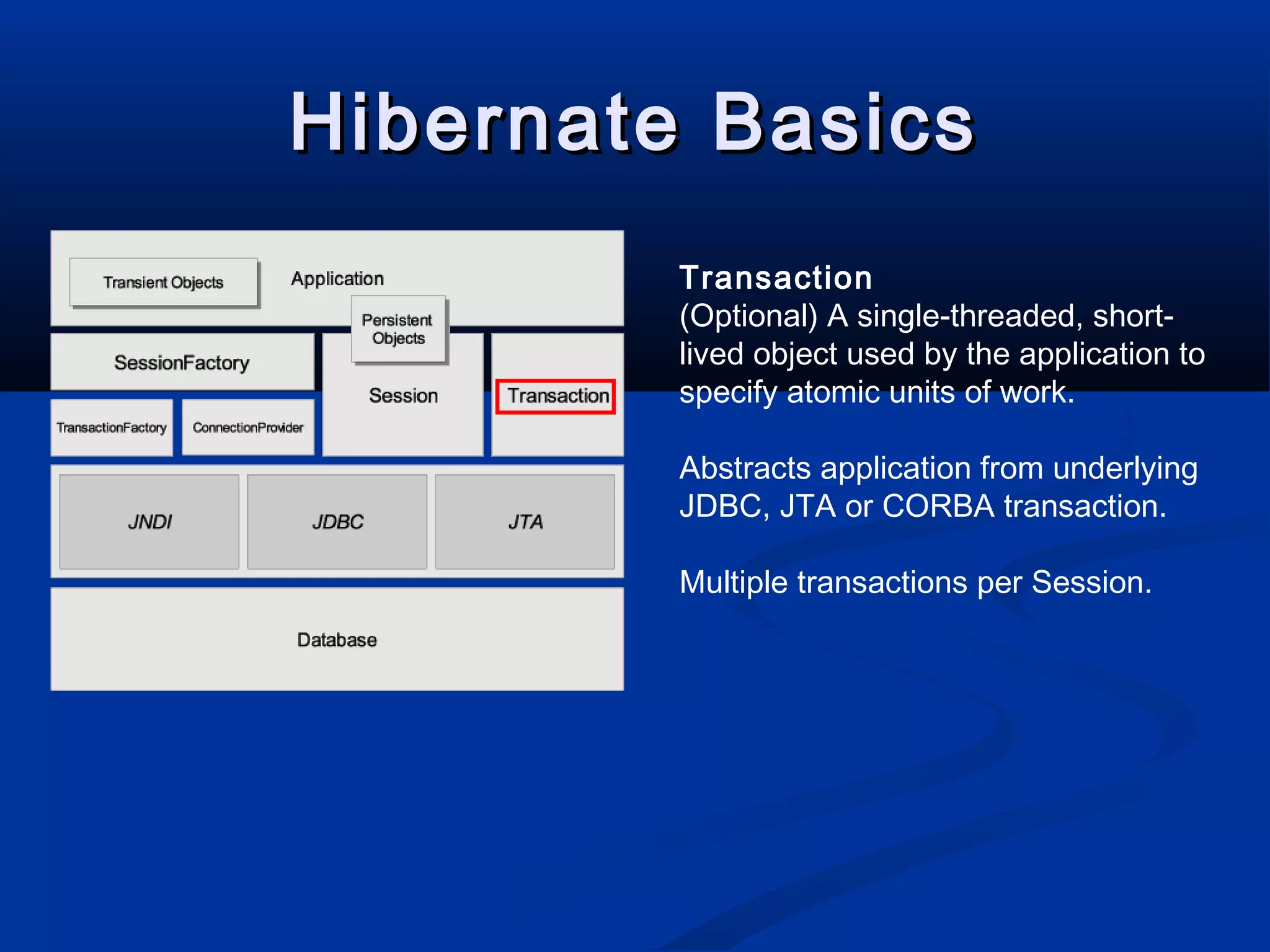
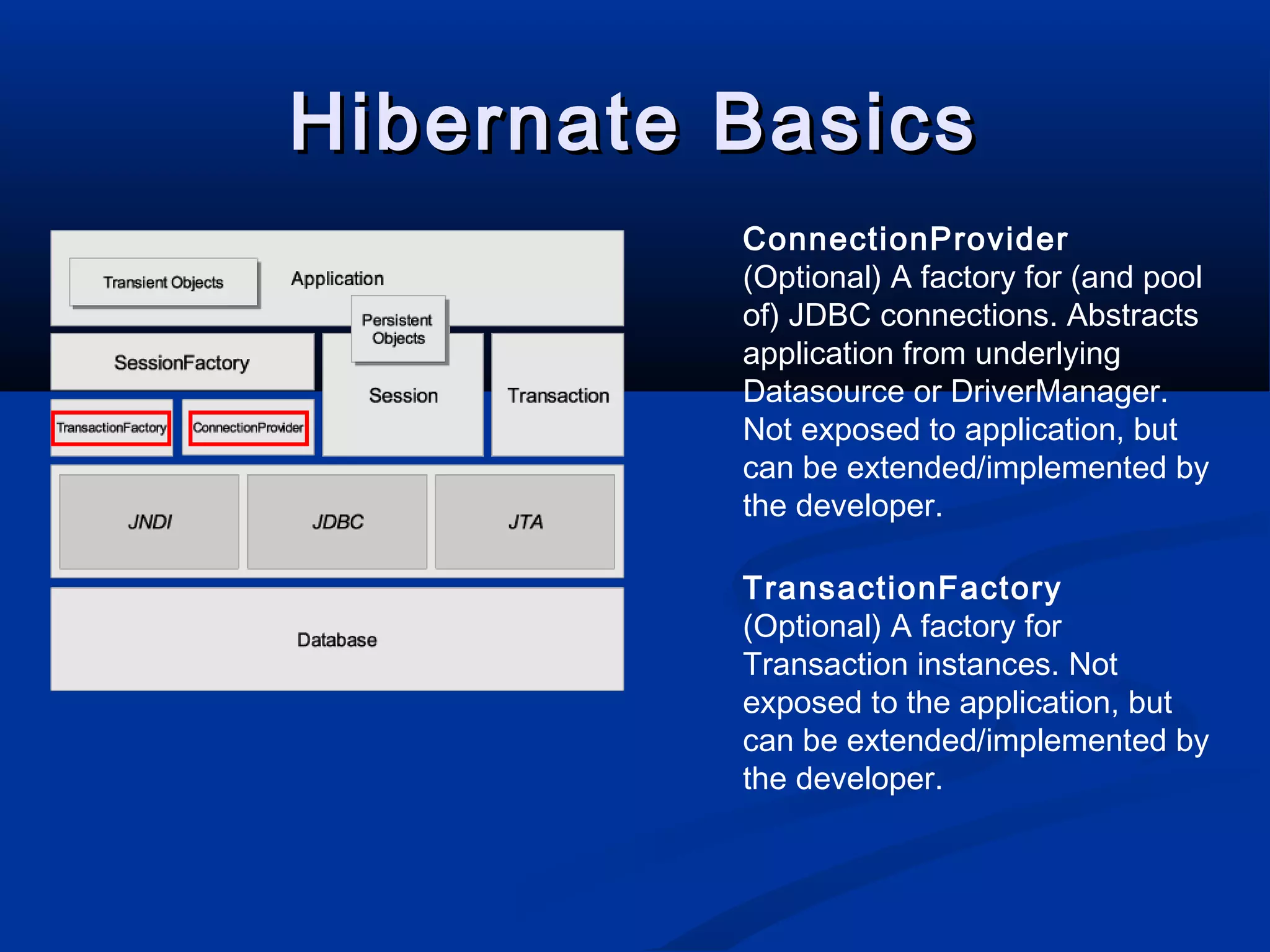
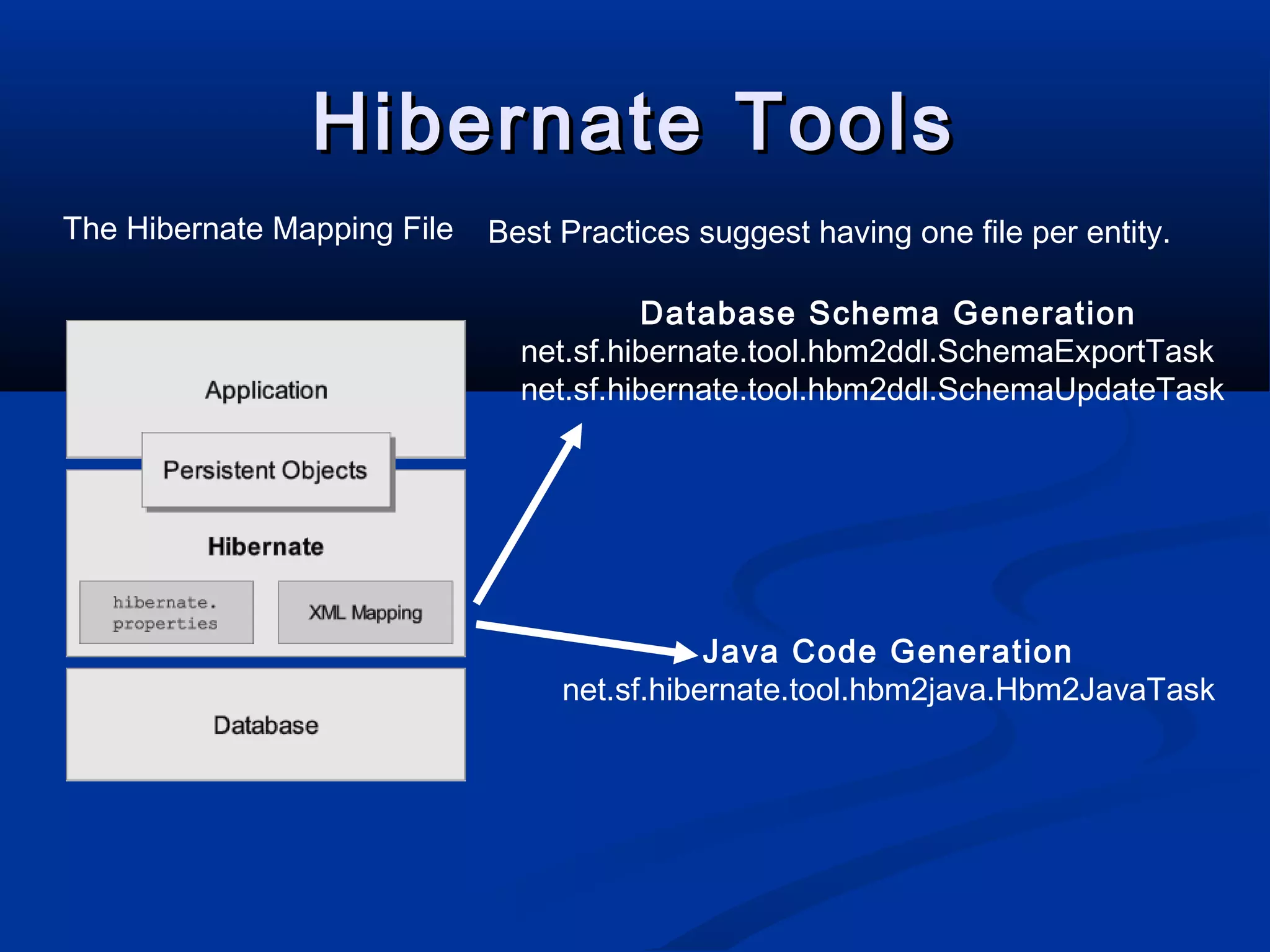
The document provides an introduction to Hibernate, a Java-based object/relational mapping tool that facilitates the integration of relational databases with Java applications. It covers various aspects including session management, persistent objects, transaction handling, Hibernate tools, and configuration settings. Additionally, the document outlines a case study focusing on a music database schema along with mapping file structures and relationships.