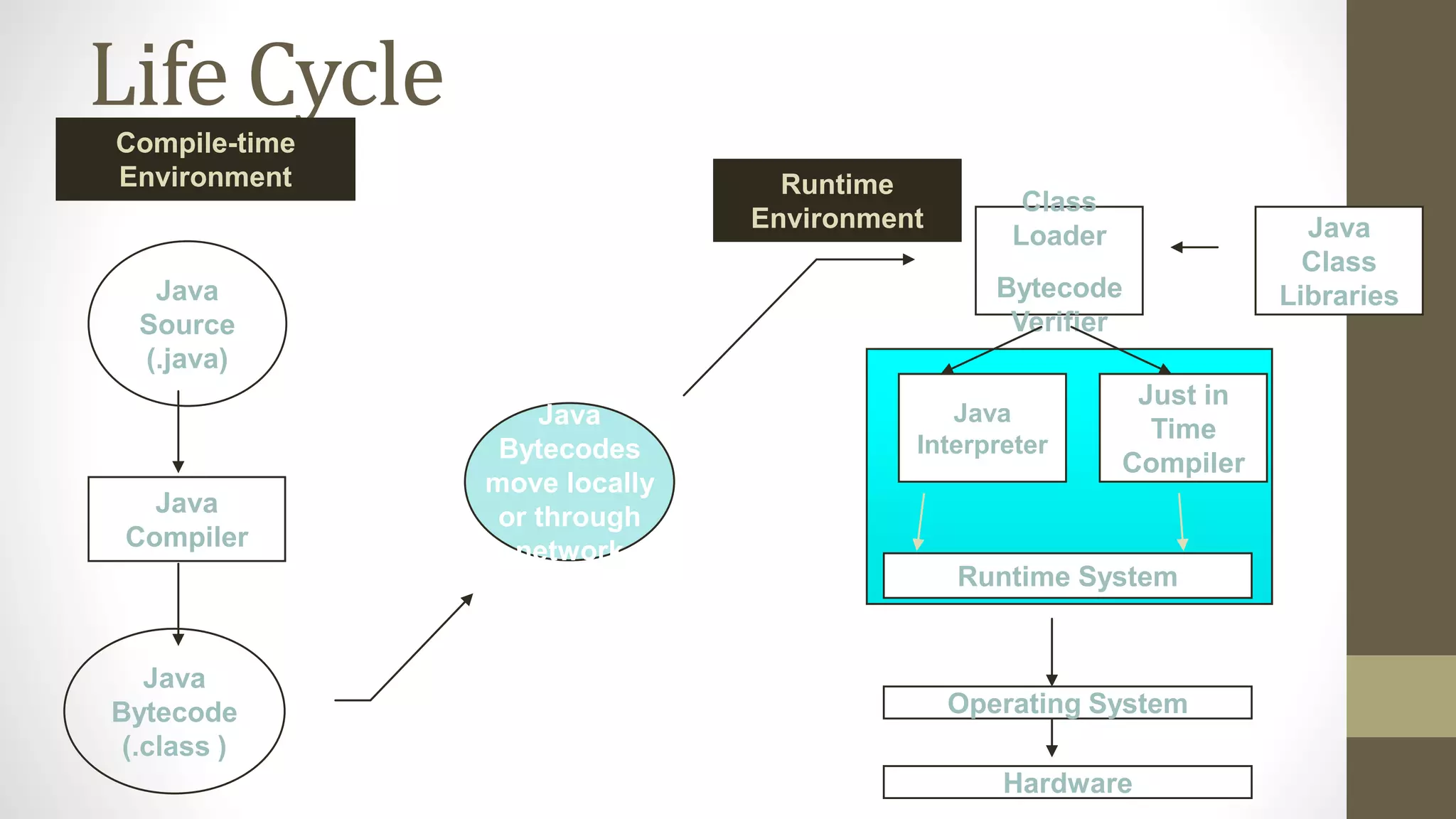
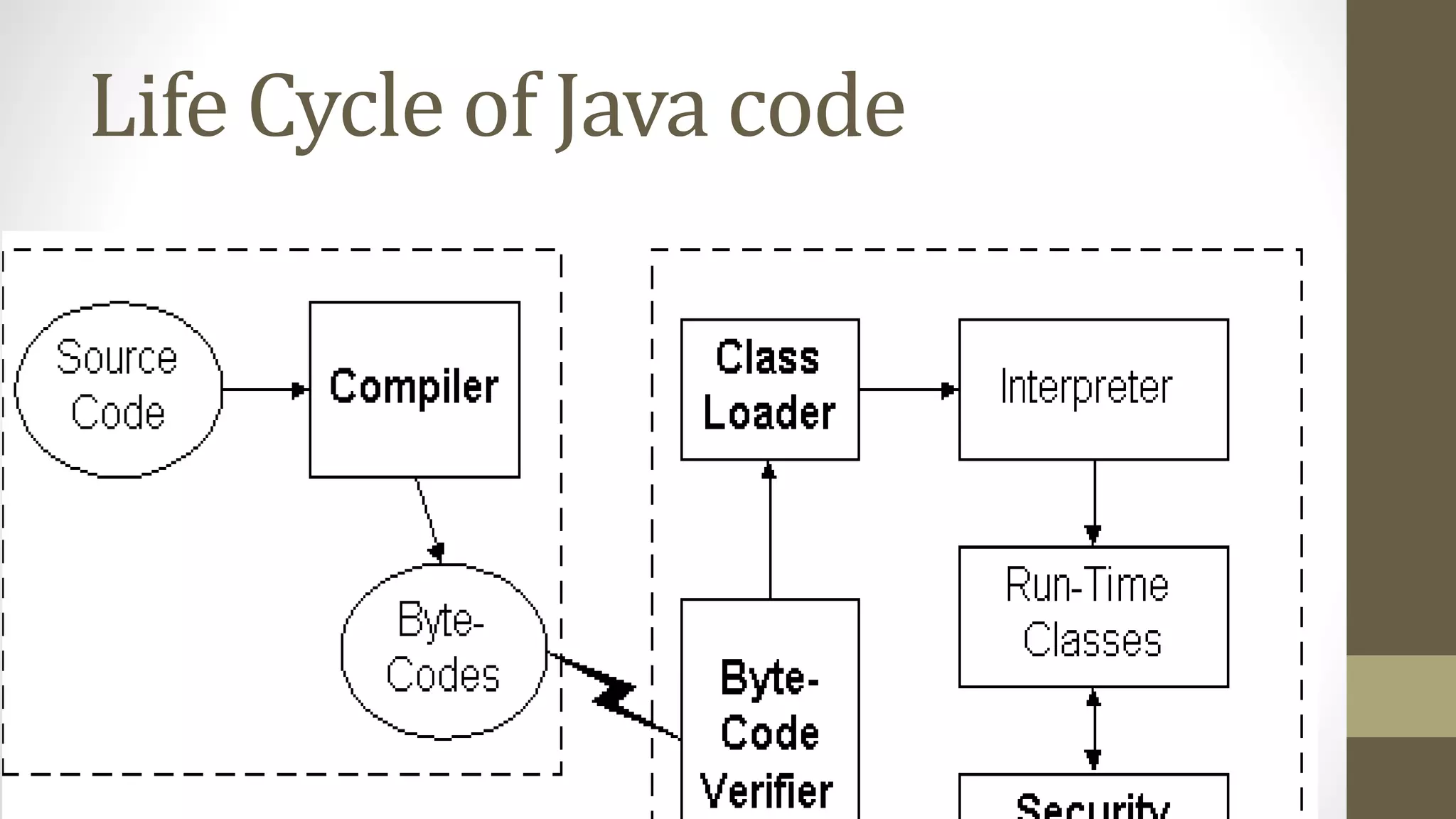
The Java SDK comes in three versions for different platforms and purposes. It includes command line compilation and execution tools like javac and java but is not an IDE. Many IDEs are available both open source and commercial that provide integrated environments for Java development. The Java code lifecycle involves compiling Java source code to bytecode, verifying and interpreting the bytecode at runtime with the help of various runtime components like the classloader and JVM.



![Hello.java
// hello.java: Hello Internet program
class Hello
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
System.out.println(“Hello Internet”);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/class2-160215070423/75/Java-Class-2-5-2048.jpg)


![• public class Comments
• {
• /* A prgm to show comments
• */
• public static void main (String args[])
• { // main is the function which is called to run a prgm
• // public access specifier
• // static no instance is required
• // String args Parameters
• System.out.println("Java has three types of Comments");
• // ; is used as terminator for every statement
• }
• }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/class2-160215070423/75/Java-Class-2-9-2048.jpg)
![• // Prgm to compare print and println
• public class Out
• {
• public static void main(String args[])
• { System.out.println("First Line"); // Next output on new line
• System.out.print("Second Line"); // Next o/p on same line
• System.out.println("Third Line");
• }
• }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/class2-160215070423/75/Java-Class-2-10-2048.jpg)
![public class Conc
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
System.out.println("Hi" + " Hello" + " How r u");
// + results in concatenation of strings
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/class2-160215070423/75/Java-Class-2-11-2048.jpg)