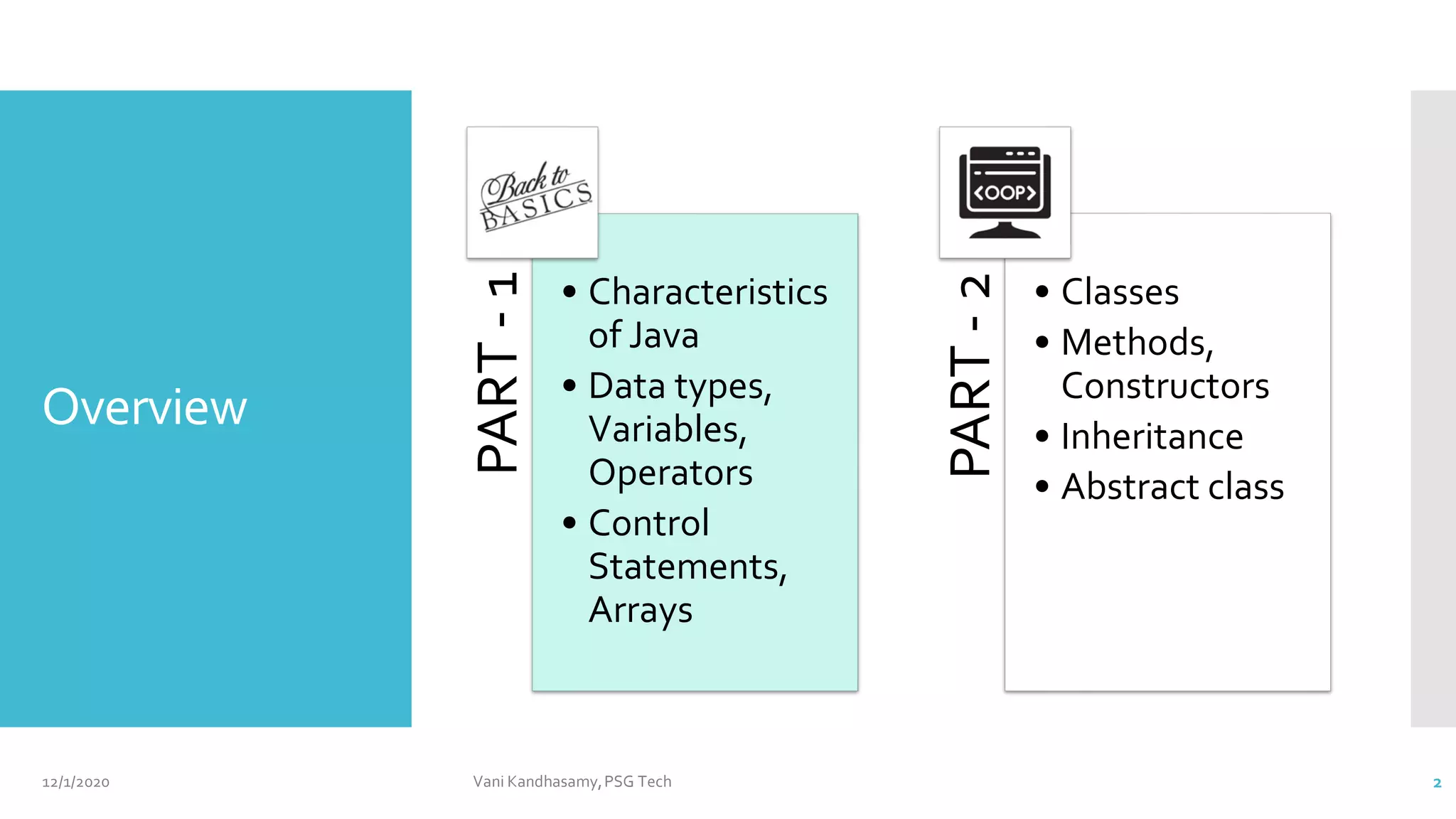
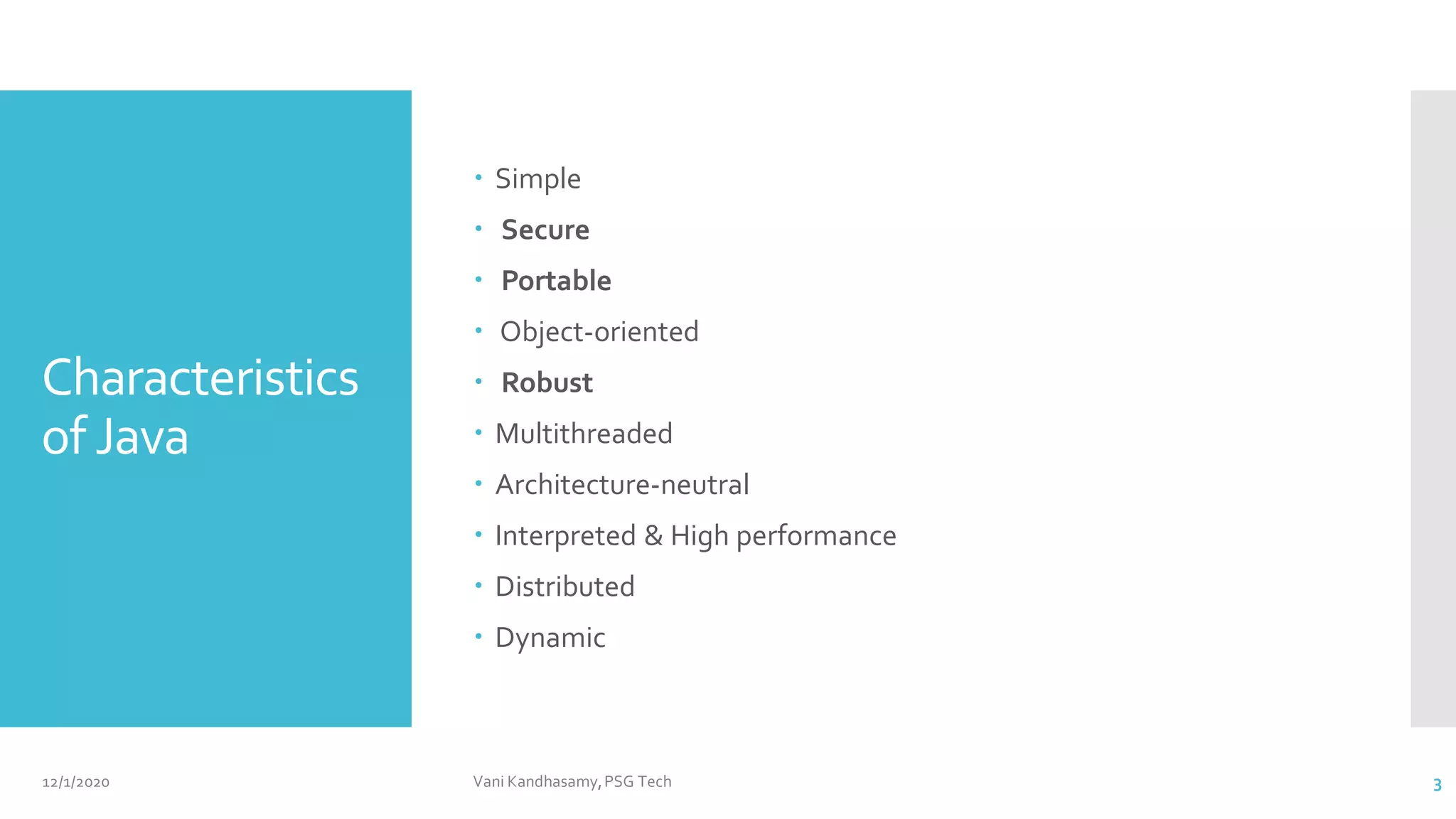
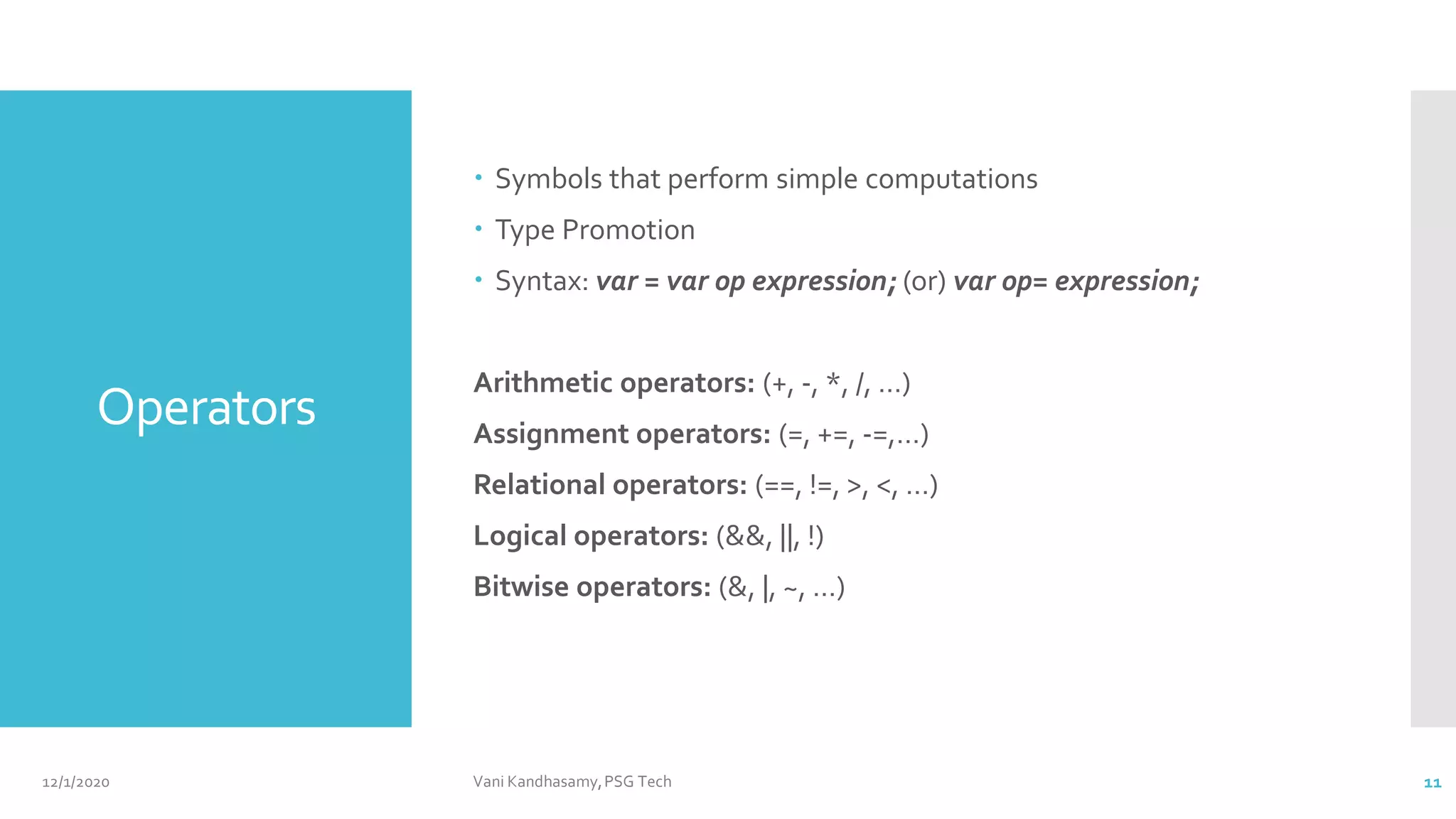
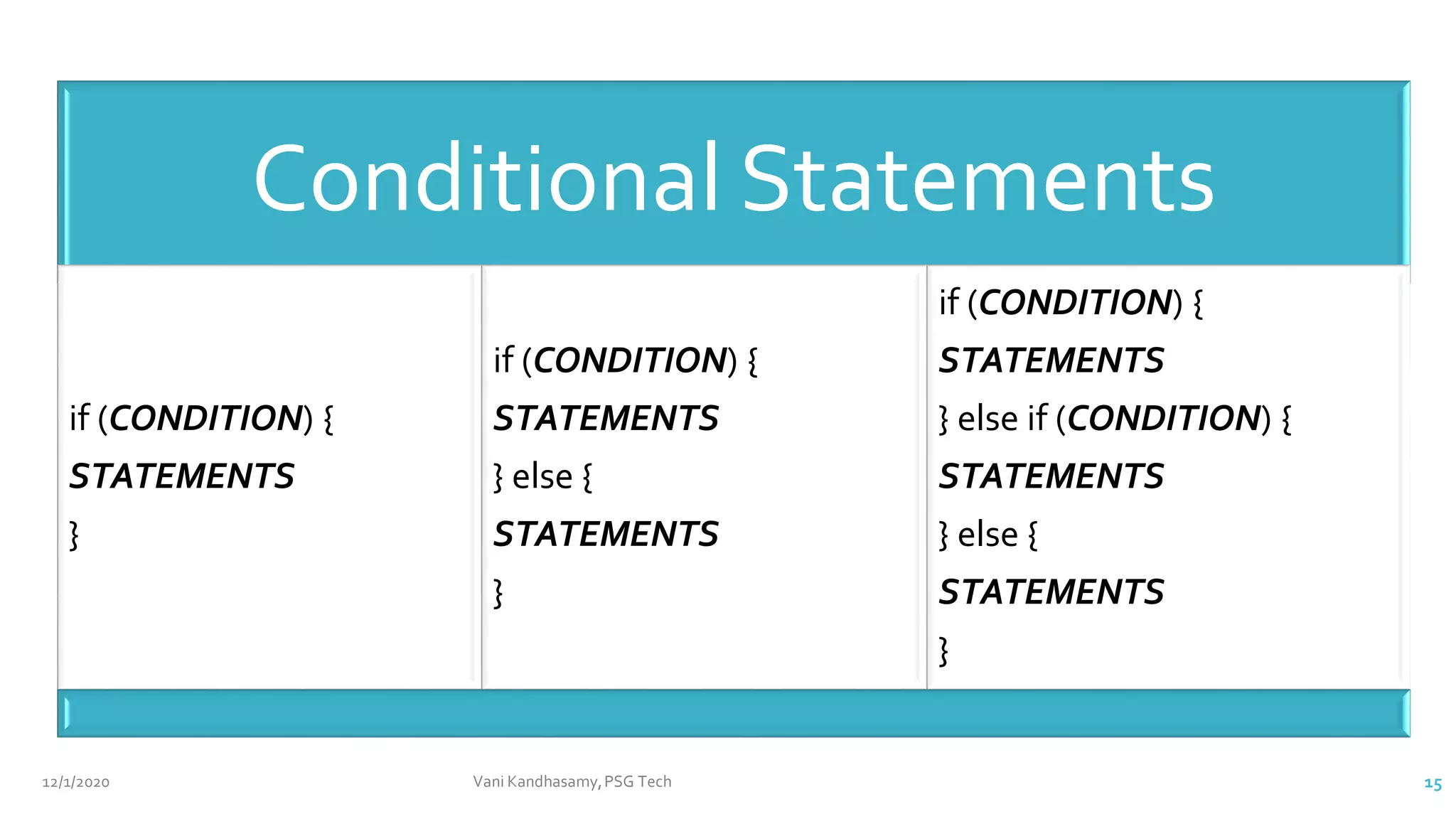
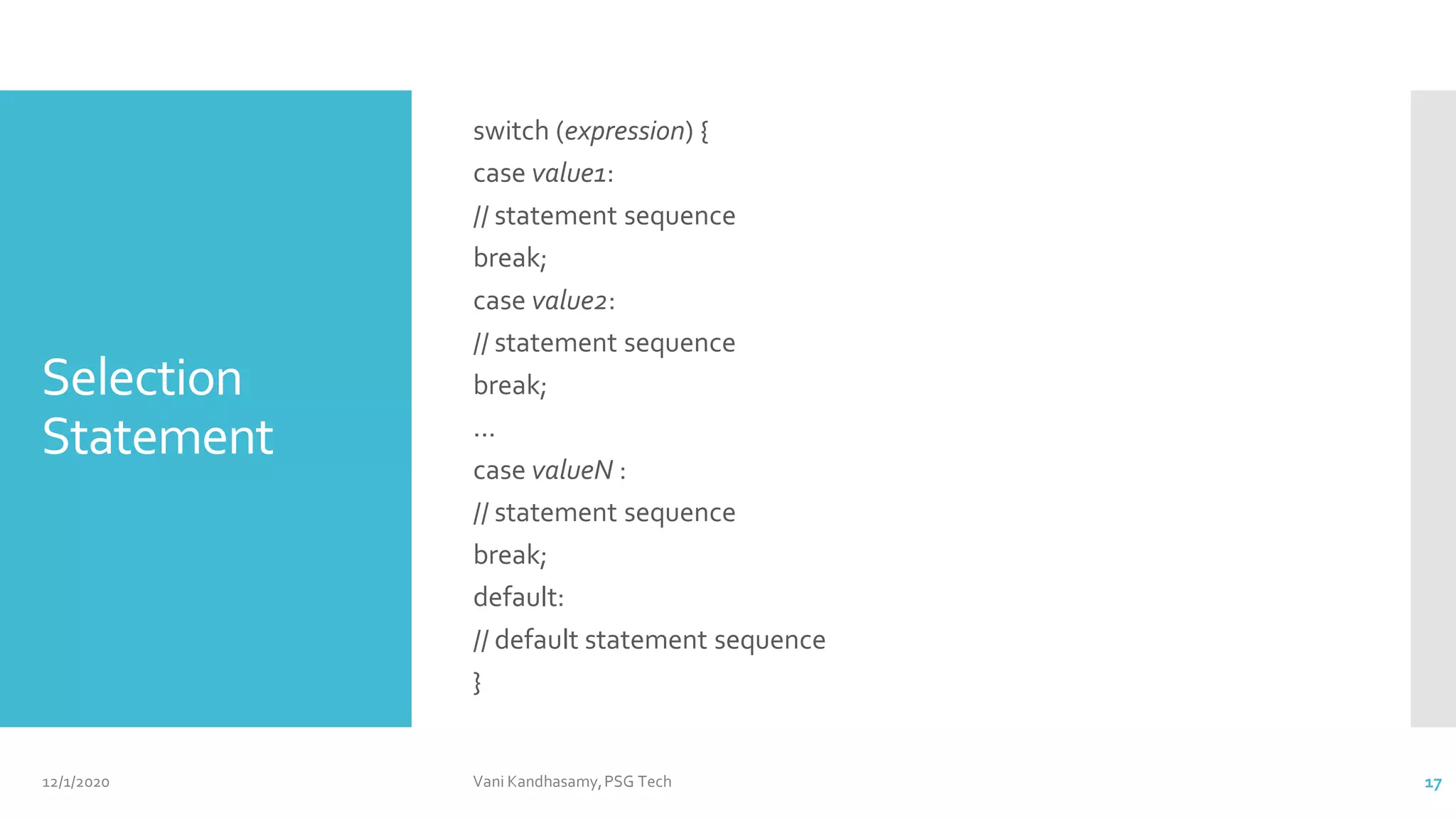
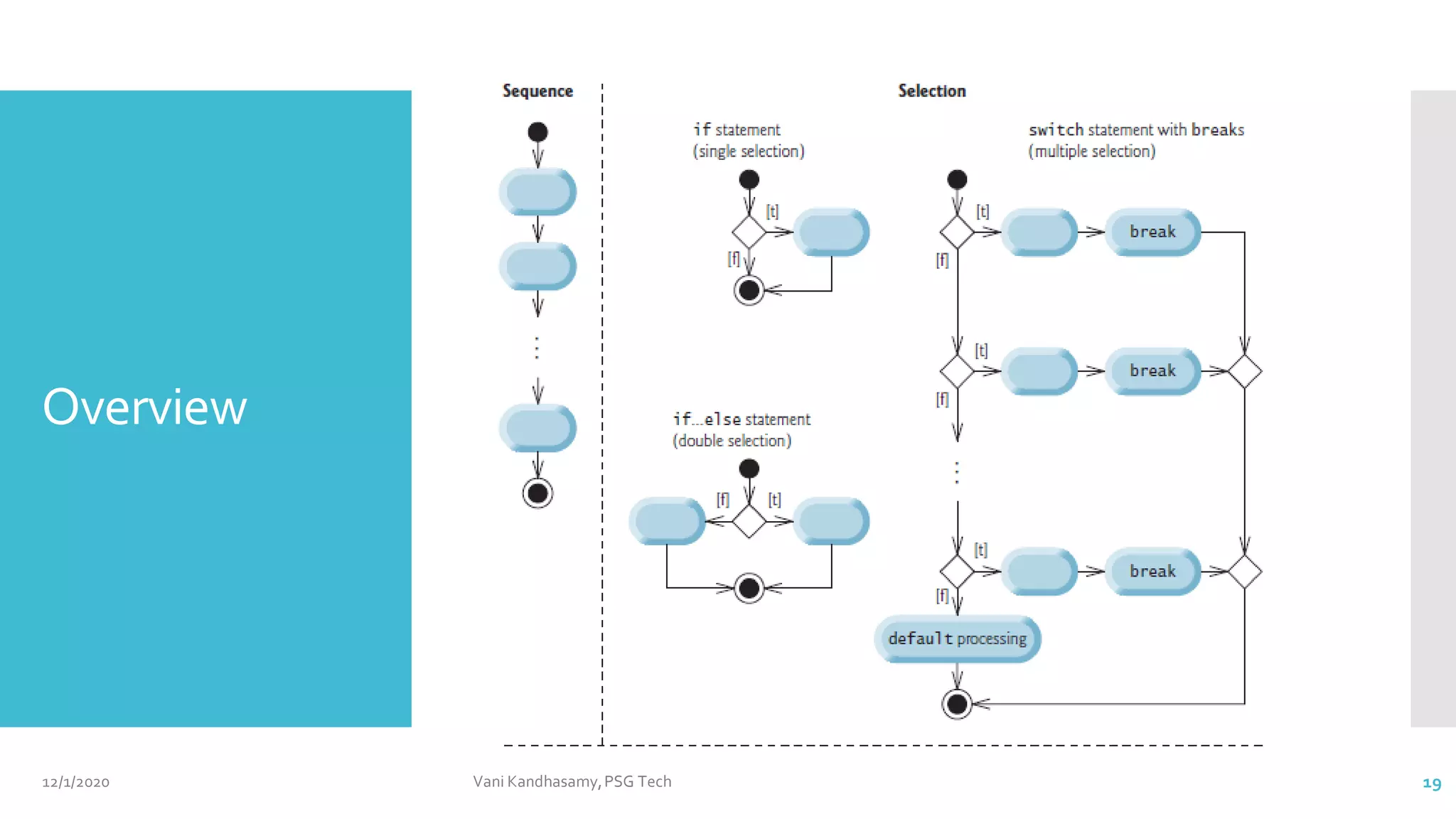
This document provides an overview of key concepts in Java programming, including characteristics of the language, data types, variables, operators, control statements, and arrays. It features example code snippets to illustrate these concepts, such as classes, methods, and the use of various types of operators. Additionally, it includes references for further reading and practical exercises to reinforce learning.


![12/1/2020 Vani Kandhasamy,PSG Tech 7
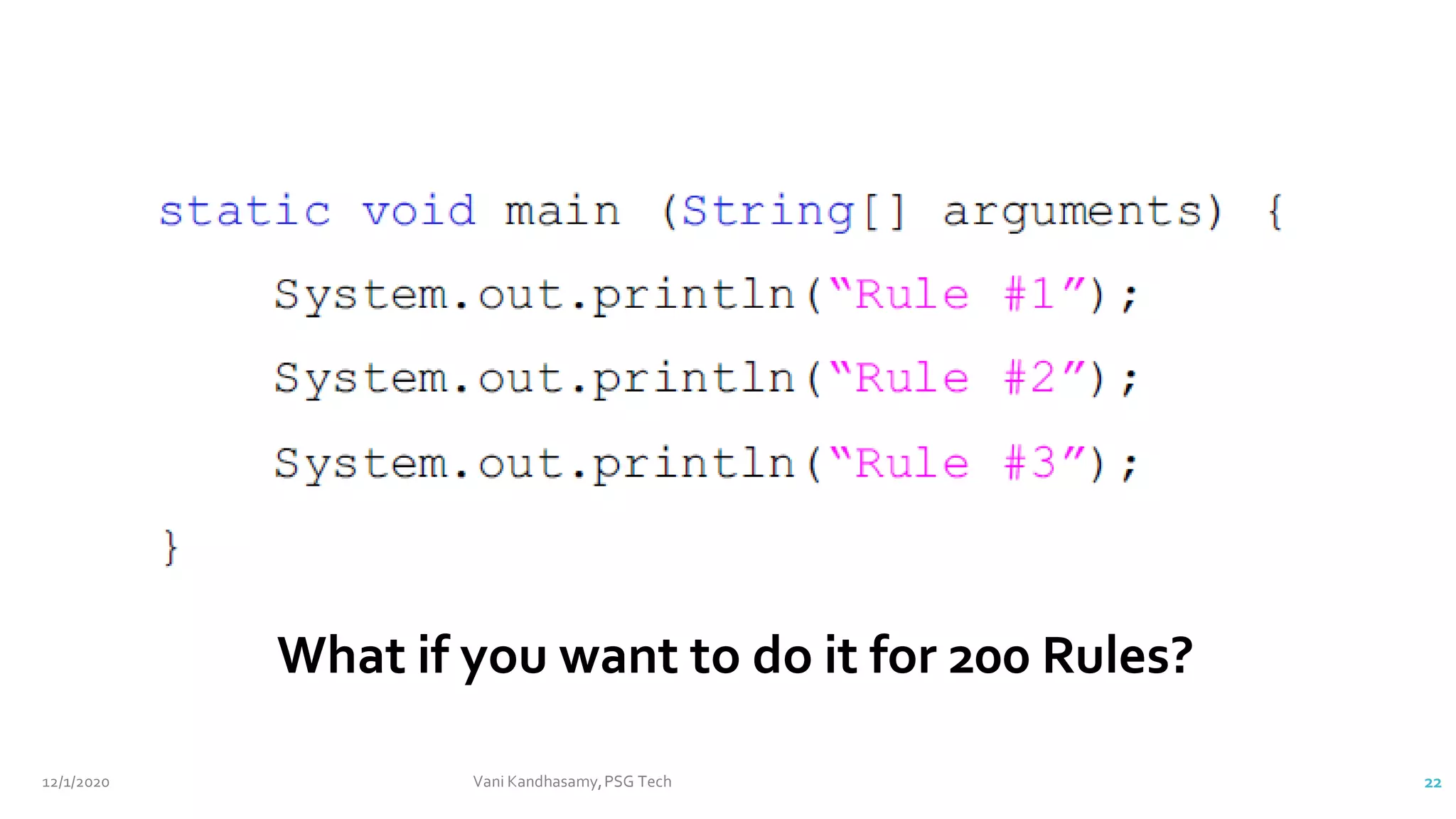
public class Example1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int myInt = 9;
double myDouble = myInt; // Automatic casting: int to double
System.out.println(myInt); // Outputs 9
System.out.println(myDouble); // Outputs 9.0
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit2a-210512071152/75/Java-Basics-Part1-7-2048.jpg)

![12/1/2020 Vani Kandhasamy,PSG Tech 9
class Example2 {
public static void printSquare(int x){
System.out.println("printSquare x = " + x);
x = x * x;
System.out.println("printSquare x = " + x);
}
public static void main(String[] arguments){
int x = 5;
System.out.println("main x = " + x);
printSquare(x);
System.out.println("main x = " + x);
}
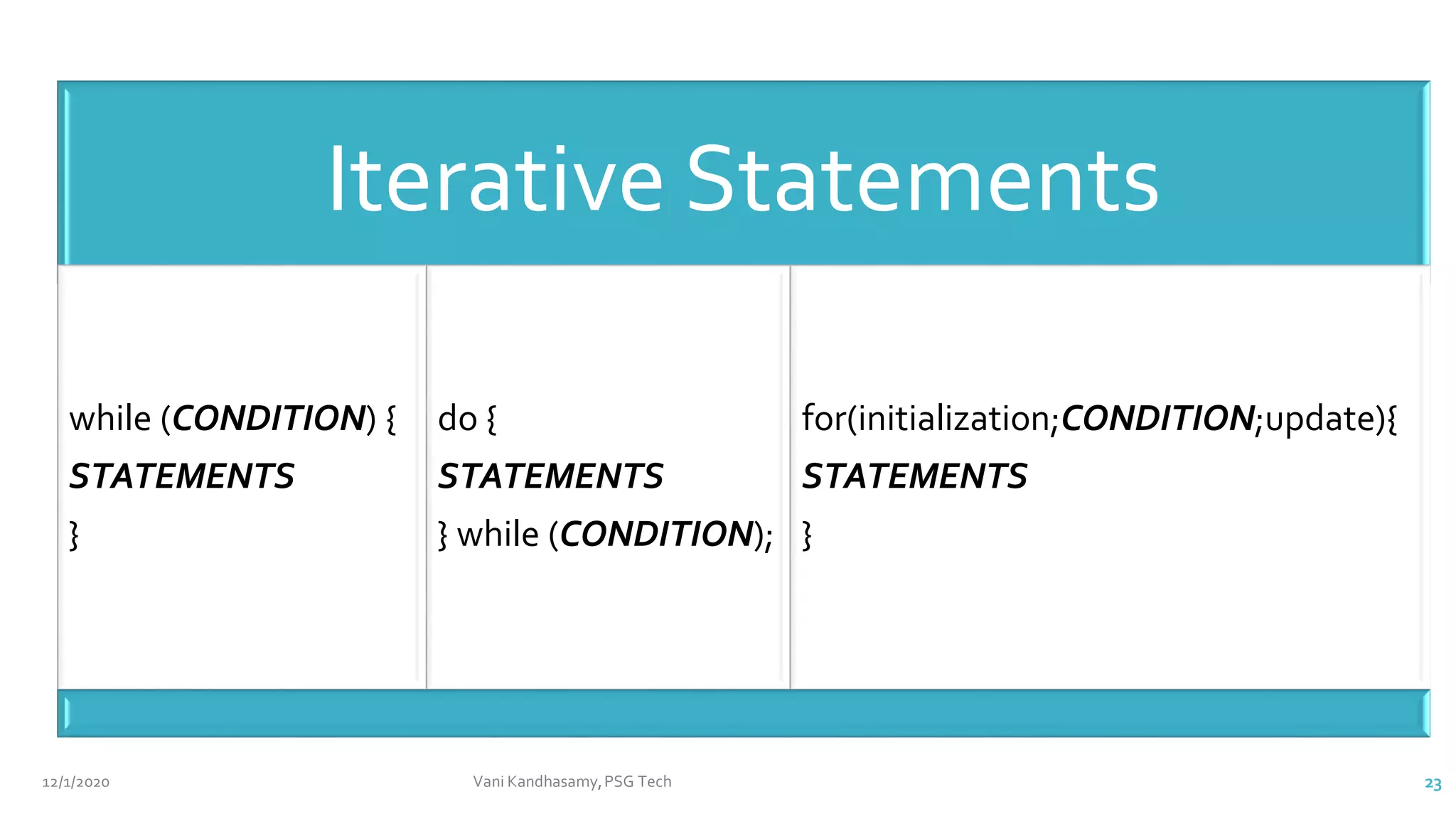
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit2a-210512071152/75/Java-Basics-Part1-9-2048.jpg)

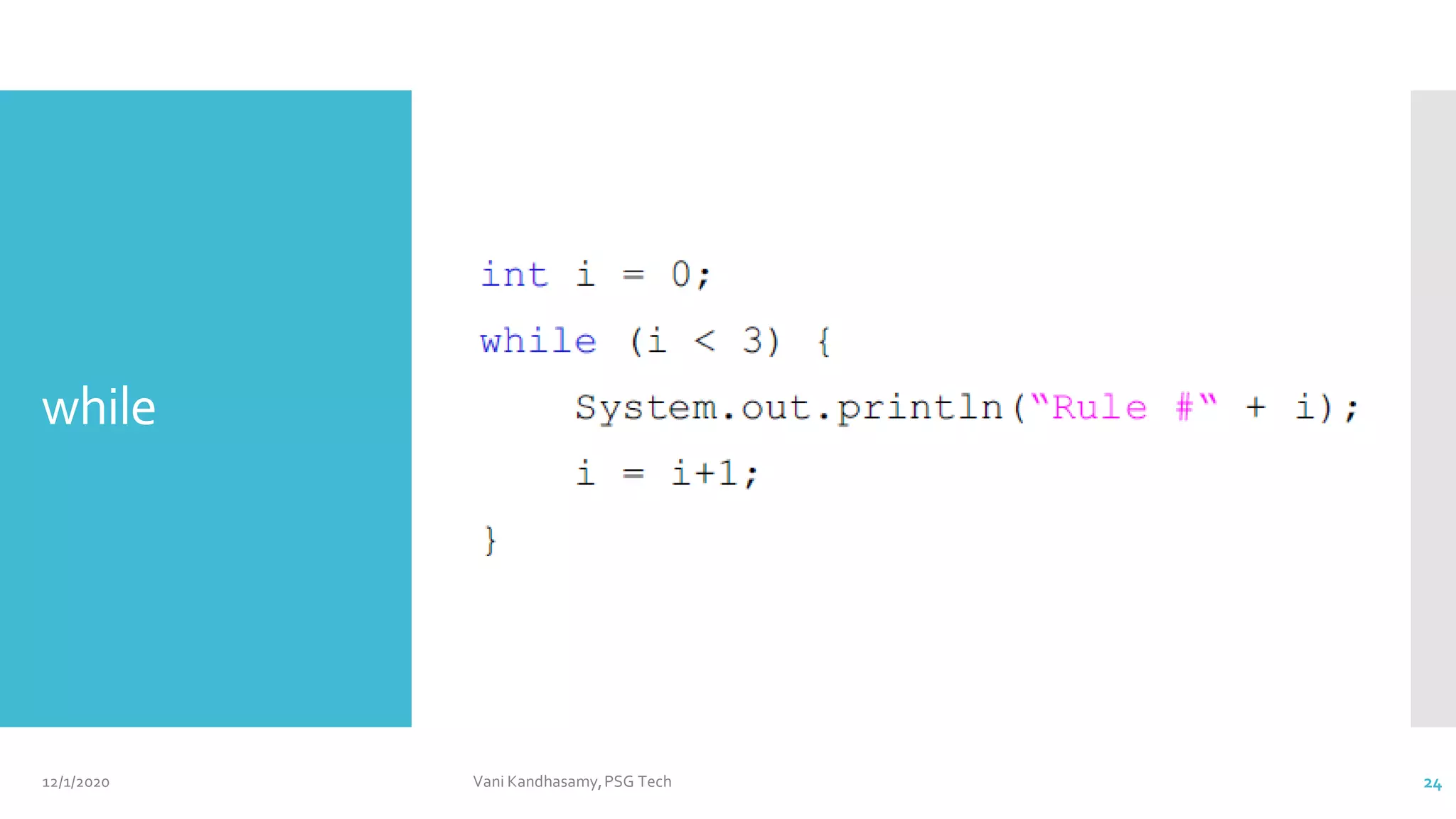
![12/1/2020 Vani Kandhasamy,PSG Tech 12
class Example3 {
public static void main(String args[]) {
byte b = 42;
char c = 'a';
short s = 1024;
int i = 50000;
float f = 5.67f;
double d = .1234;
double result = (f * b) + (i / c) - (d * s);
System.out.println((f * b) + " + " + (i / c) + " - " + (d * s));
System.out.println("result = " + result);
}
}
Output:
238.14 + 515 - 126.3616
result = 626.7784146484375](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit2a-210512071152/75/Java-Basics-Part1-12-2048.jpg)


![12/1/2020 Vani Kandhasamy,PSG Tech 16
public class Example5 {
public static void main(String args[]) {
int month = 4; // April
String season;
if(month == 12 || month == 1 || month == 2)
season = "Winter";
else if(month == 3 || month == 4 || month == 5)
season = "Spring";
else if(month == 6 || month == 7 || month == 8)
season = "Summer";
else if(month == 9 || month == 10 || month == 11)
season = "Autumn";
else
season = "Bogus Month";
System.out.println("April is in the " + season + ".");
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit2a-210512071152/75/Java-Basics-Part1-16-2048.jpg)
![12/1/2020 Vani Kandhasamy,PSG Tech 18
public class Example6 {
public static void main(String args[]) {
String str = "two";
switch(str) {
case "one":
System.out.println("one");
break;
case "two":
System.out.println("two");
break;
case "three":
System.out.println("three");
break;
default:
System.out.println("no match");
break;
}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit2a-210512071152/75/Java-Basics-Part1-18-2048.jpg)


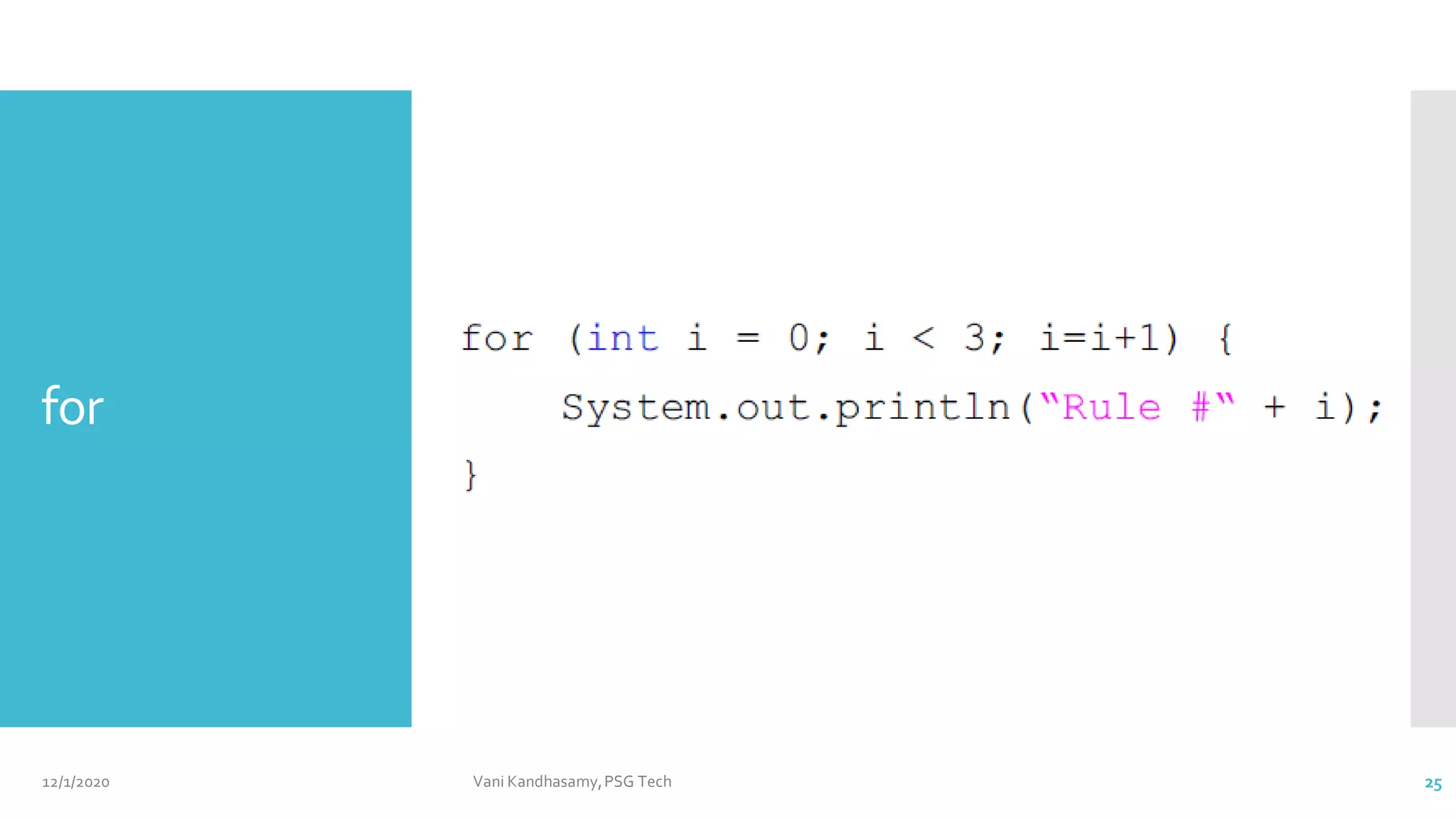
![12/1/2020 Vani Kandhasamy,PSG Tech 28
public class Example8 {
public static void main(String args[]) {
int a, b;
for(a=1, b=4; a<b; a++, b--) {
System.out.println("a = " + a);
System.out.println("b = " + b);
}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit2a-210512071152/75/Java-Basics-Part1-28-2048.jpg)

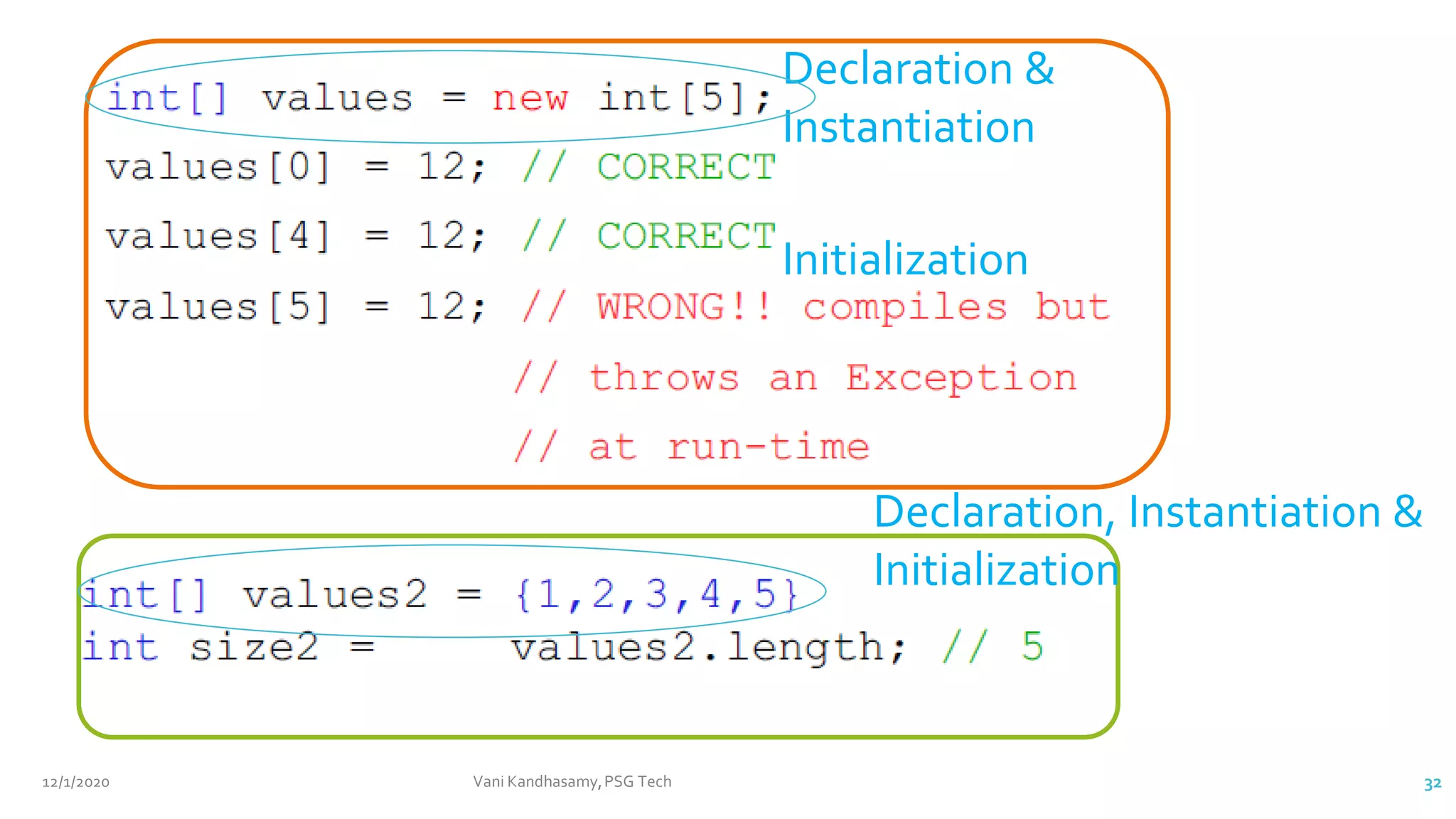
![Arrays
Syntax: type var_name[ ] = new type [size];
type[ ] var_name;
Example:
double values[ ] = new double [10]
The index starts at zero and ends at length-1
12/1/2020 Vani Kandhasamy,PSG Tech 31](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit2a-210512071152/75/Java-Basics-Part1-31-2048.jpg)
![12/1/2020 Vani Kandhasamy,PSG Tech 36
public class Example7 {
public static void main(String args[]) {
int nums[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10 };
int sum = 0;
for(int x =0; x<nums.length; x++){
System.out.println("Value is: " + x);
sum += nums[x];
}
System.out.println("Summation: " + sum);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit2a-210512071152/75/Java-Basics-Part1-33-2048.jpg)
![12/1/2020 Vani Kandhasamy,PSG Tech 37
public class Example7 {
public static void main(String args[]) {
int nums[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10 };
int sum = 0;
// use for-each style for to display and sum the values
for(int x : nums) {
System.out.println("Value is: " + x);
sum += x;
}
System.out.println("Summation: " + sum);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit2a-210512071152/75/Java-Basics-Part1-34-2048.jpg)

![Multi-
dimensional
Array
12/1/2020 Vani Kandhasamy,PSG Tech 39
int twoD[][] = new int [4][5]
int[][] twoD= new int [4][5]
int []twoD[] = new int [4][5]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit2a-210512071152/75/Java-Basics-Part1-36-2048.jpg)
![12/1/2020 Vani Kandhasamy,PSG Tech 40
public class Example9 {
public static void main(String args[]) {
int twoD[][]= new int[4][5];
int i, j, k = 0;
for(i=0; i<4; i++)
for(j=0; j<5; j++) {
twoD[i][j] = k;
k++;
}
for(i=0; i<4; i++) {
for(j=0; j<5; j++)
System.out.print(twoD[i][j] + " ");
System.out.println();
}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit2a-210512071152/75/Java-Basics-Part1-37-2048.jpg)

