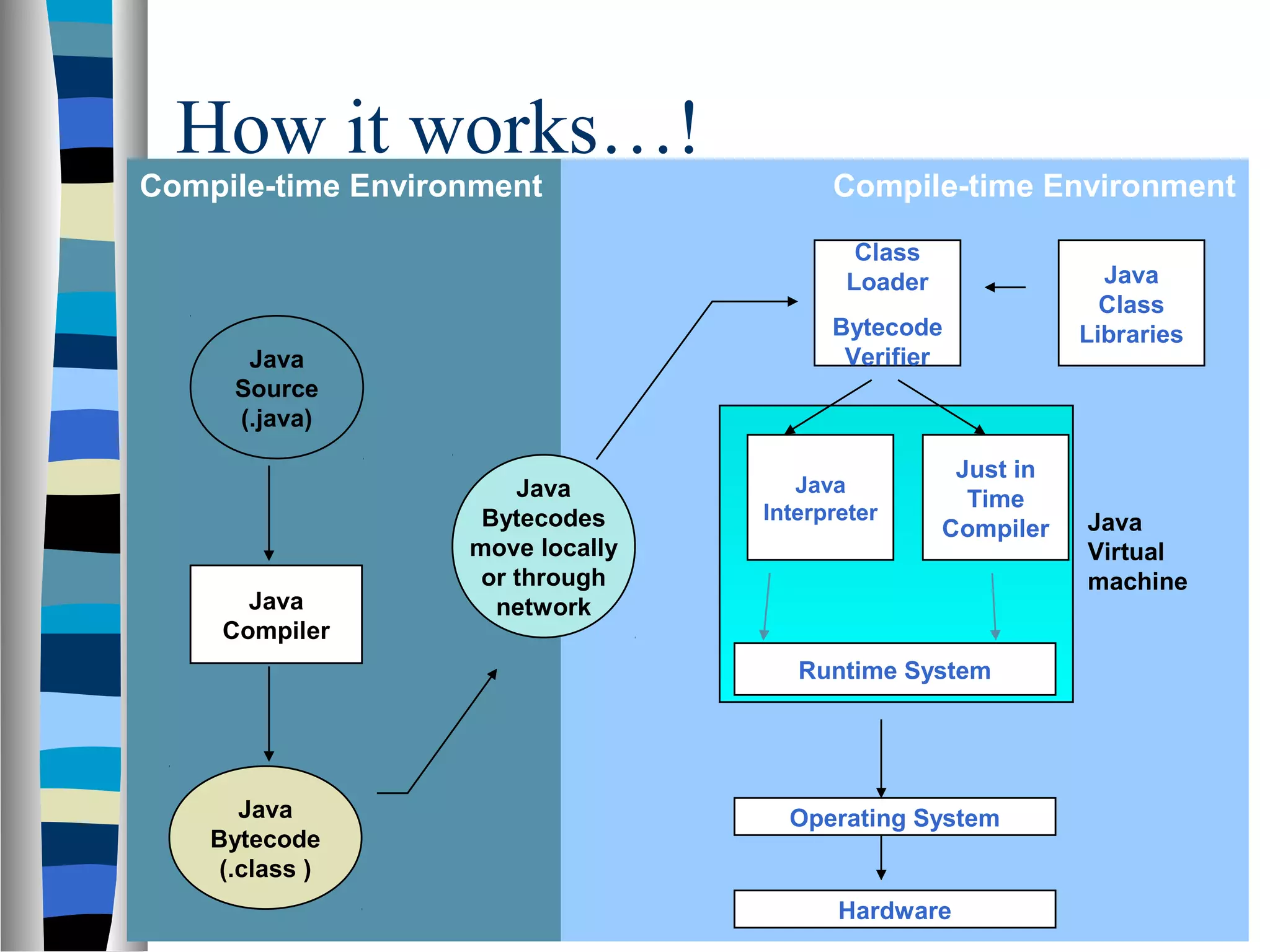
This document provides an overview of the Java programming language. It discusses key Java concepts like object-oriented programming, classes, methods, streams, and input/output. It also covers Java syntax like primitive types, variables, operators, flow control, and arrays. The document explains how Java code is compiled to bytecode and run on the Java Virtual Machine, making it platform independent.













![while loops
while(response == 1) {
System.out.print( “ID =” +
userID[n]);
n++;
response = readInt( “Enter “);
}
What is the minimum number of times the loop
is executed?
What is the maximum number of times?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javabasictutorialbysanjeeviniindia-130304060521-phpapp02/75/Java-basic-tutorial-by-sanjeevini-india-25-2048.jpg)
![do {… } while loops
do {
System.out.print( “ID =” + userID[n] );
n++;
response = readInt( “Enter ” );
}while (response == 1);
What is the minimum number of times the loop
is executed?
What is the maximum number of times?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javabasictutorialbysanjeeviniindia-130304060521-phpapp02/75/Java-basic-tutorial-by-sanjeevini-india-26-2048.jpg)
![Break
A break statement causes an exit from the
innermost containing while, do, for or
switch statement.
for ( int i = 0; i < maxID, i++ ) {
if ( userID[i] == targetID ) {
index = i;
break;
}
} // program jumps here after break](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javabasictutorialbysanjeeviniindia-130304060521-phpapp02/75/Java-basic-tutorial-by-sanjeevini-india-27-2048.jpg)
![Continue
Can only be used with while, do or for.
The continue statement causes the innermost loop to
start the next iteration immediately
for ( int i = 0; i < maxID; i++ ) {
if ( userID[i] != -1 ) continue;
System.out.print( “UserID ” + i + “ :” +
userID);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javabasictutorialbysanjeeviniindia-130304060521-phpapp02/75/Java-basic-tutorial-by-sanjeevini-india-28-2048.jpg)


![Declaring Arrays
int myArray[];
declares myArray to be an array of integers
myArray = new int[8];
sets up 8 integer-sized spaces in memory,
labelled myArray[0] to myArray[7]
int myArray[] = new int[8];
combines the two statements in one line](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javabasictutorialbysanjeeviniindia-130304060521-phpapp02/75/Java-basic-tutorial-by-sanjeevini-india-31-2048.jpg)
![Assigning Values
refer to the array elements by index to store values in
them.
myArray[0] = 3;
myArray[1] = 6;
myArray[2] = 3; ...
can create and initialise in one step:
int myArray[] = {3, 6, 3, 1, 6, 3, 4, 1};](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javabasictutorialbysanjeeviniindia-130304060521-phpapp02/75/Java-basic-tutorial-by-sanjeevini-india-32-2048.jpg)
![Iterating Through Arrays
for loops are useful when dealing with arrays:
for (int i = 0; i <
myArray.length; i++) {
myArray[i] = getsomevalue();
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javabasictutorialbysanjeeviniindia-130304060521-phpapp02/75/Java-basic-tutorial-by-sanjeevini-india-33-2048.jpg)

![Declaring the Array
1. Declare the array
private Student studentList[];
– this declares studentList
2 .Create the array
studentList = new Student[10];
– this sets up 10 spaces in memory that can
hold references to Student objects
3. Create Student objects and add them to the
array: studentList[0] = new
Student("Cathy", "Computing");](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javabasictutorialbysanjeeviniindia-130304060521-phpapp02/75/Java-basic-tutorial-by-sanjeevini-india-35-2048.jpg)




![Method Signatures
A method signature specifies:
– The name of the method.
– The type and name of each parameter.
– The type of the value (or object) returned by the method.
– The checked exceptions thrown by the method.
– Various method modifiers.
– modifiers type name ( parameter list ) [throws exceptions ]
public float convertCelsius (float tCelsius ) {}
public boolean setUserInfo ( int i, int j, String name ) throws
IndexOutOfBoundsException {}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javabasictutorialbysanjeeviniindia-130304060521-phpapp02/75/Java-basic-tutorial-by-sanjeevini-india-41-2048.jpg)







![Display File Contents
import java.io.*;
public class FileToOut1 {
public static void main(String args[]) {
try {
FileInputStream infile = new FileInputStream("testfile.txt");
byte buffer[] = new byte[50];
int nBytesRead;
do {
nBytesRead = infile.read(buffer);
System.out.write(buffer, 0, nBytesRead);
} while (nBytesRead == buffer.length);
}
catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
System.err.println("File not found");
}
catch (IOException e) { System.err.println("Read failed"); }
}
} 49](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javabasictutorialbysanjeeviniindia-130304060521-phpapp02/75/Java-basic-tutorial-by-sanjeevini-india-49-2048.jpg)

![Writing data to a file using Filters
import java.io.*;
public class GenerateData {
public static void main(String args[]) {
try {
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("stuff.dat");
DataOutputStream dos = new DataOutputStream(fos);
dos.writeInt(2);
dos.writeDouble(2.7182818284590451);
dos.writeDouble(3.1415926535);
dos.close(); fos.close();
}
catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
System.err.println("File not found");
}
catch (IOException e) {
System.err.println("Read or write failed");
}
} 51
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javabasictutorialbysanjeeviniindia-130304060521-phpapp02/75/Java-basic-tutorial-by-sanjeevini-india-51-2048.jpg)
![Reading data from a file using filters
import java.io.*;
public class ReadData {
public static void main(String args[]) {
try {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("stuff.dat");
DataInputStream dis = new DataInputStream(fis);
int n = dis.readInt();
System.out.println(n);
for( int i = 0; i < n; i++ ) { System.out.println(dis.readDouble());
}
dis.close(); fis.close();
}
catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
System.err.println("File not found");
}
catch (IOException e) { System.err.println("Read or write failed");
}
} 52
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javabasictutorialbysanjeeviniindia-130304060521-phpapp02/75/Java-basic-tutorial-by-sanjeevini-india-52-2048.jpg)

![Write an object to a file
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
public class WriteDate {
public WriteDate () {
Date d = new Date();
try {
FileOutputStream f = new FileOutputStream("date.ser");
ObjectOutputStream s = new ObjectOutputStream (f);
s.writeObject (d);
s.close ();
}
catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
public static void main (String args[]) {
new WriteDate ();
}
} 54](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javabasictutorialbysanjeeviniindia-130304060521-phpapp02/75/Java-basic-tutorial-by-sanjeevini-india-54-2048.jpg)
![Read an object from a file
import java.util.*;
public class ReadDate {
public ReadDate () {
Date d = null;
ObjectInputStream s = null;
try { FileInputStream f = new FileInputStream ("date.ser");
s = new ObjectInputStream (f);
} catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
try { d = (Date)s.readObject (); }
catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
catch (InvalidClassException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
catch (StreamCorruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
catch (OptionalDataException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
System.out.println ("Date serialized at: "+ d);
}
public static void main (String args[]) { new ReadDate (); } 55
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javabasictutorialbysanjeeviniindia-130304060521-phpapp02/75/Java-basic-tutorial-by-sanjeevini-india-55-2048.jpg)