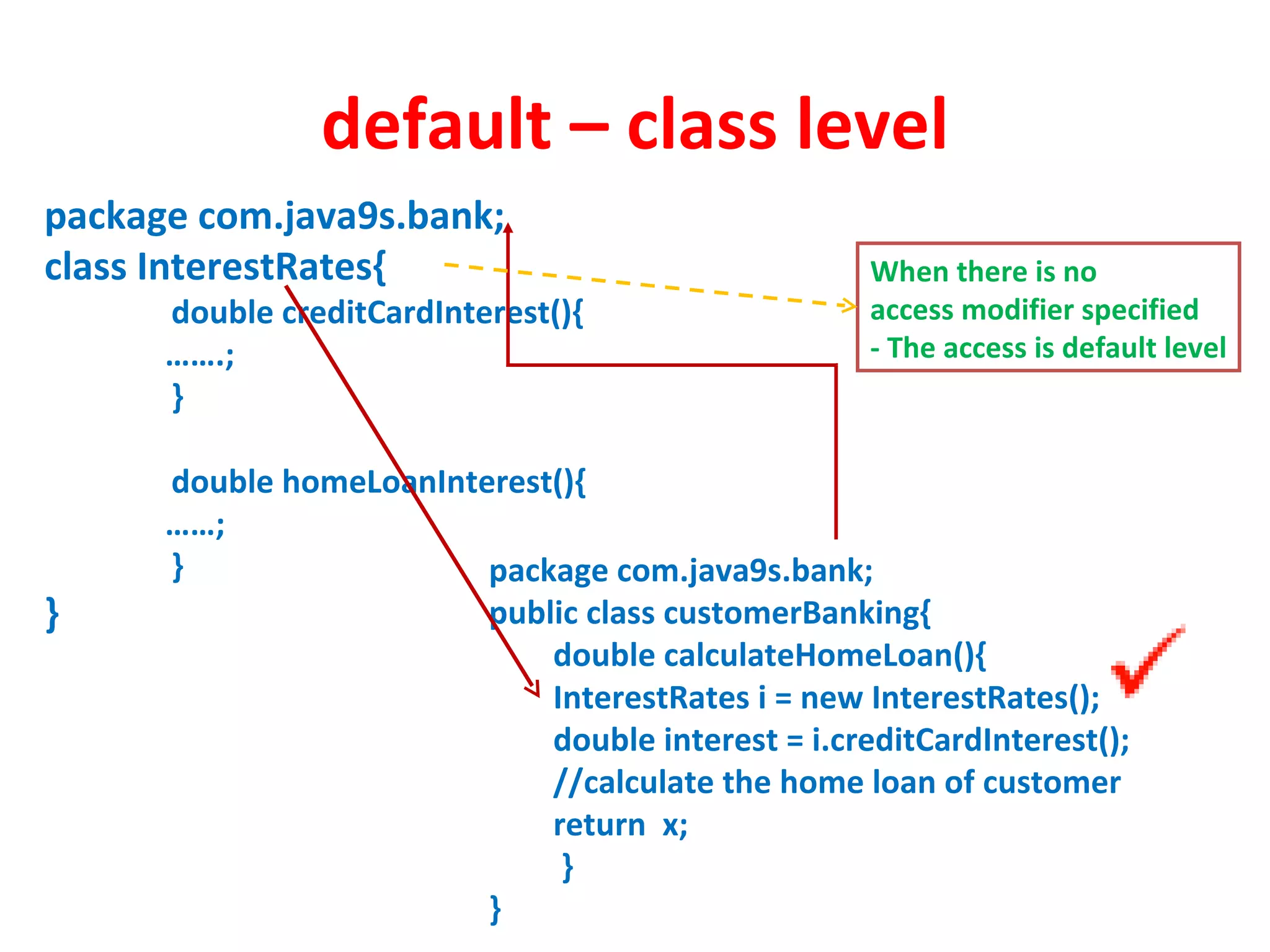
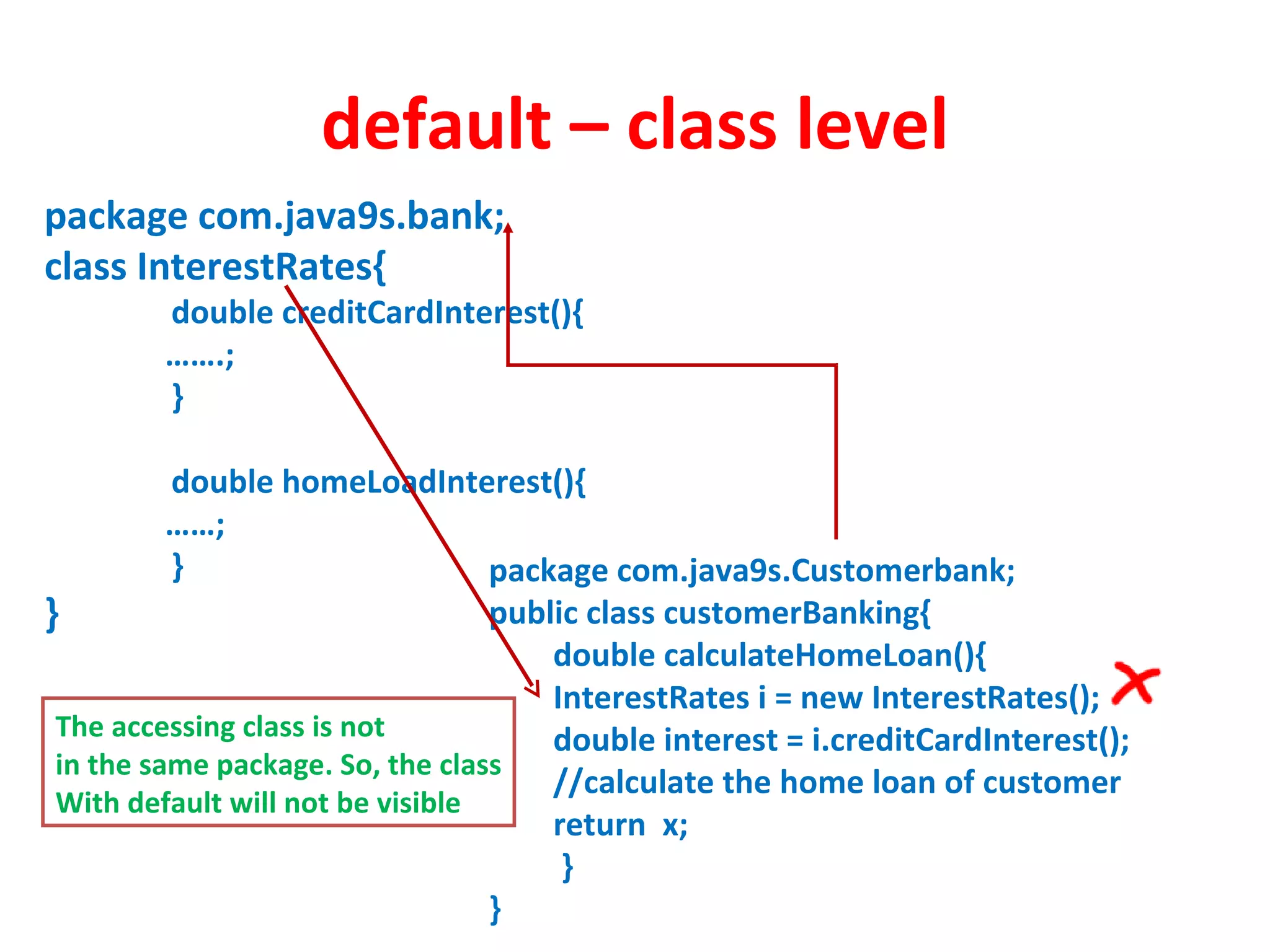
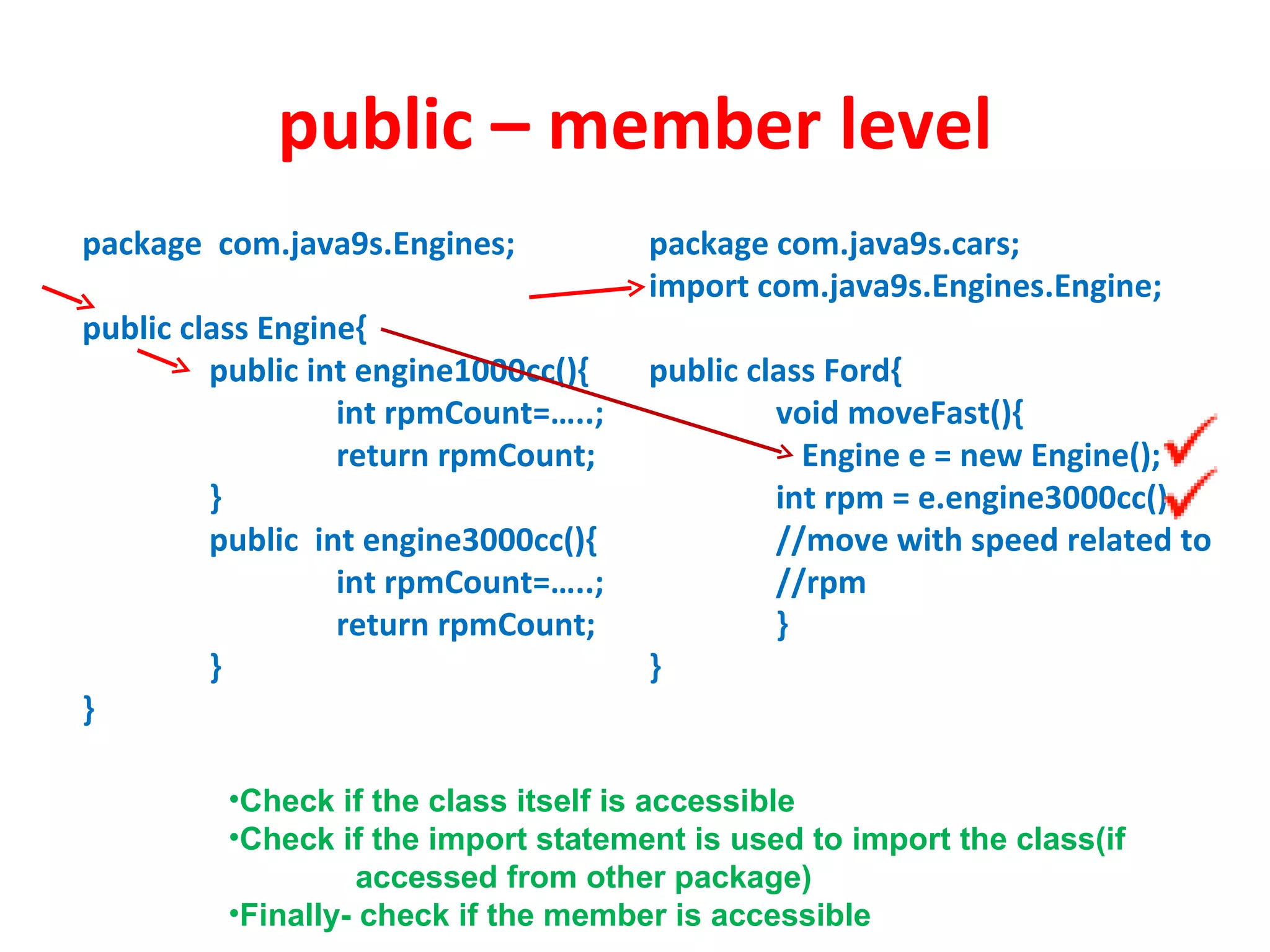
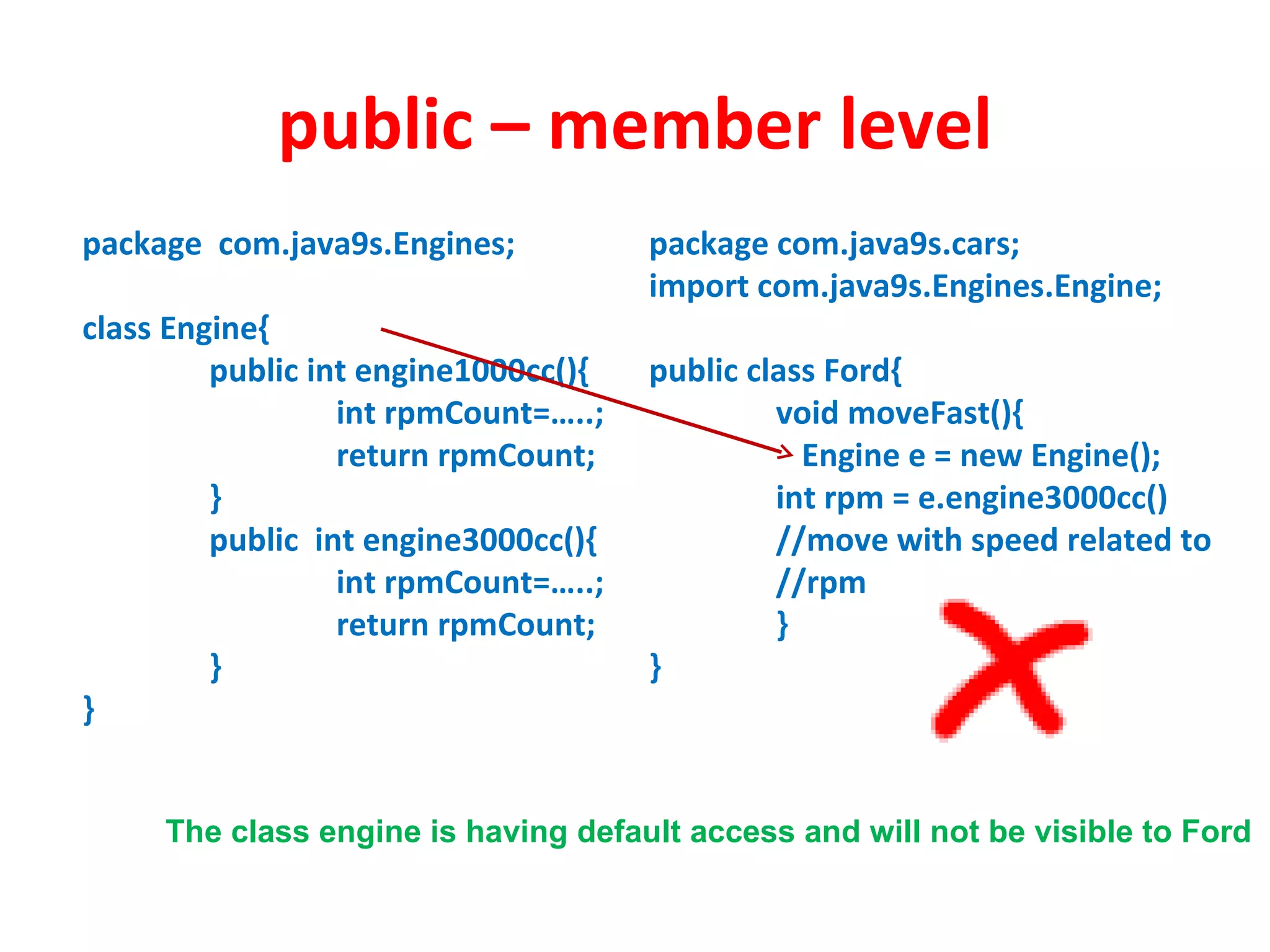
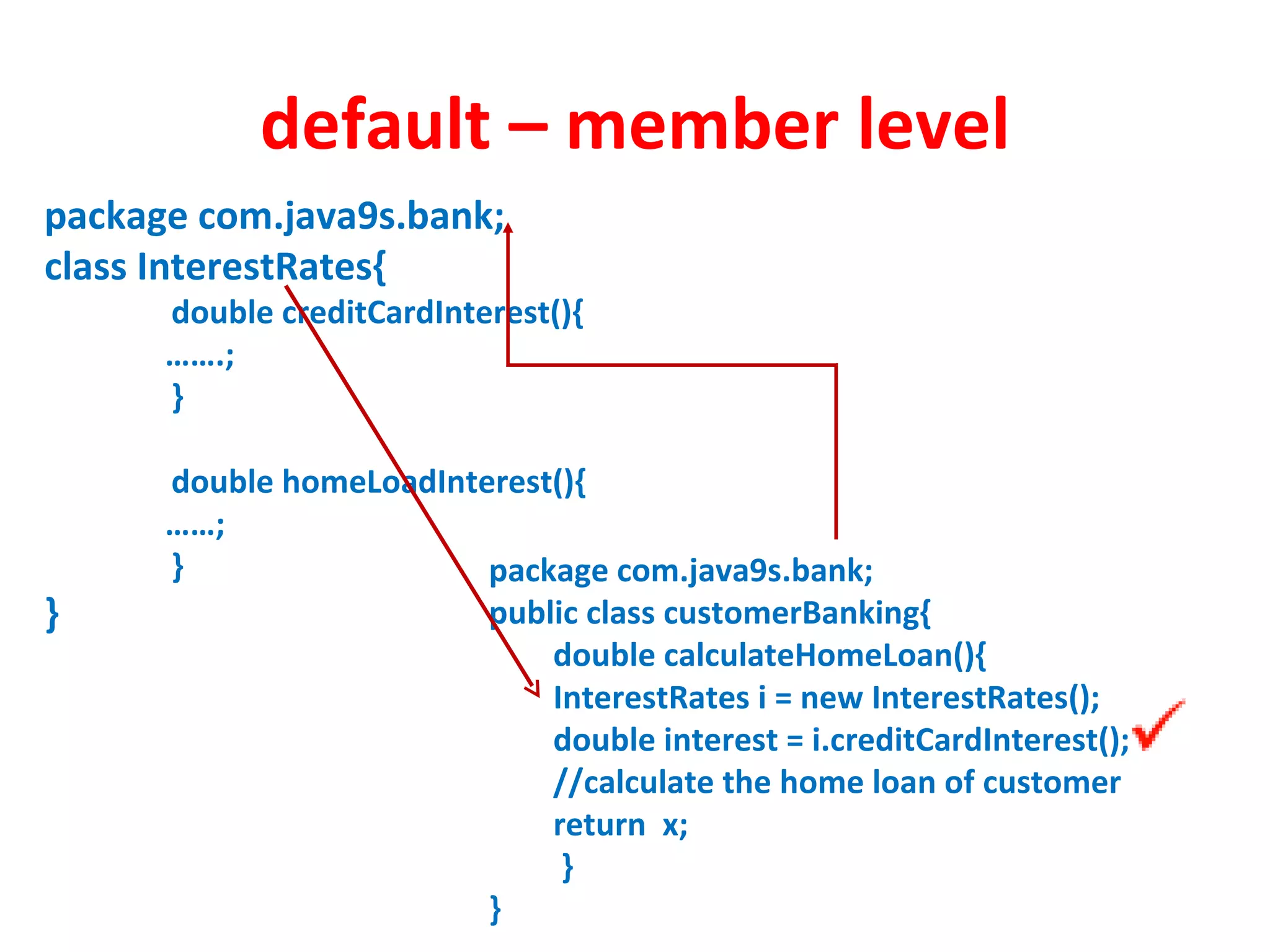
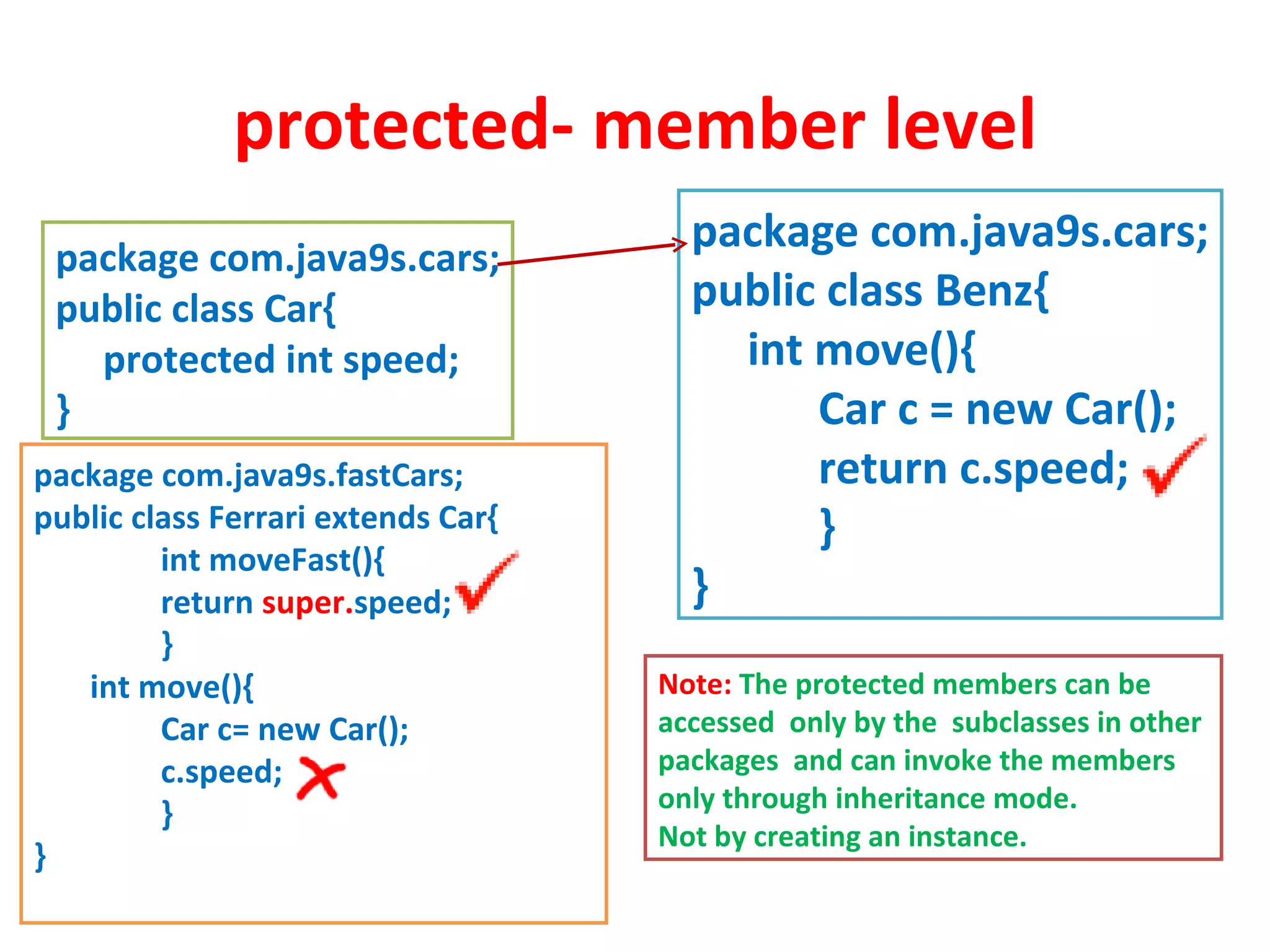
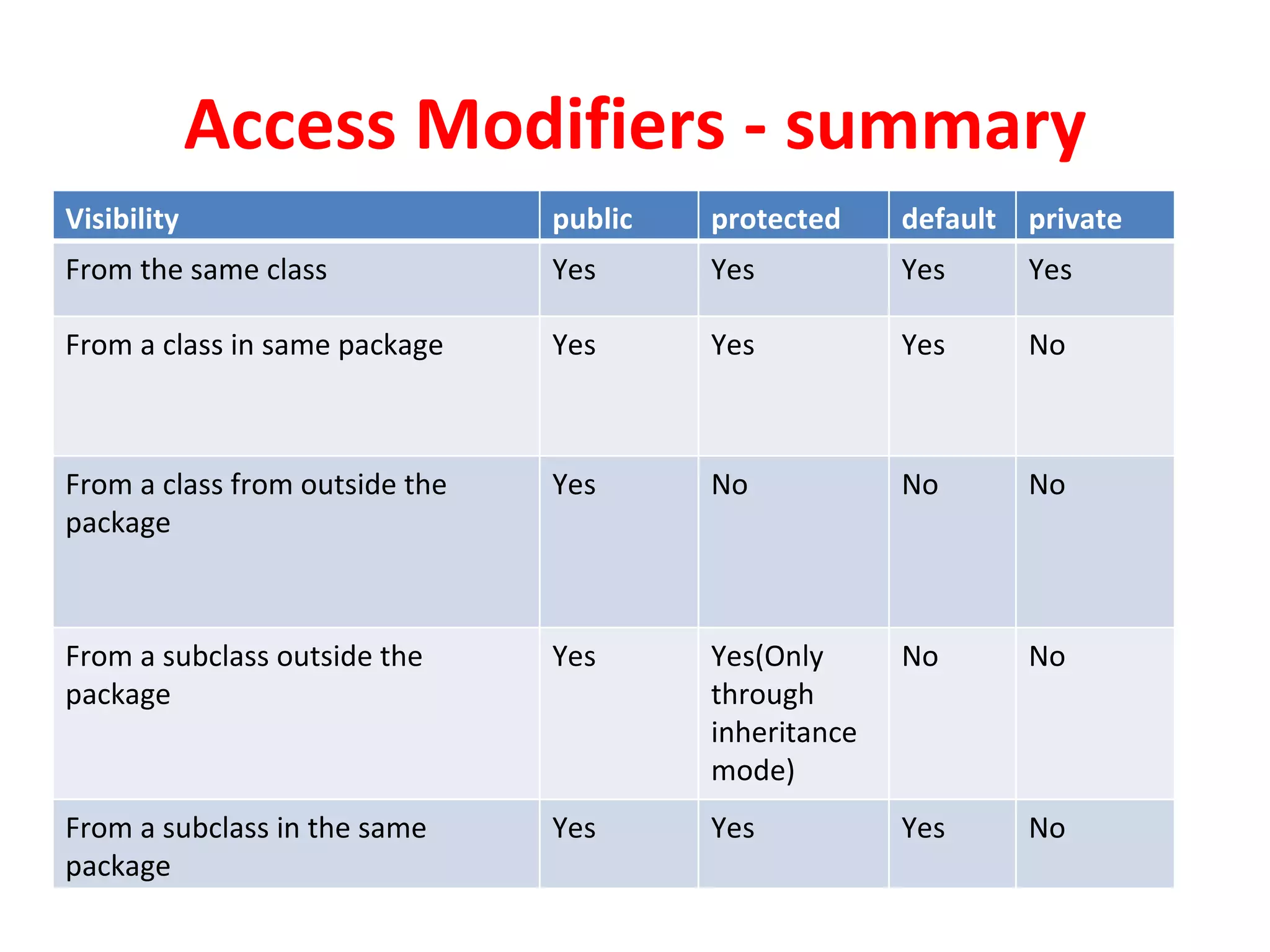
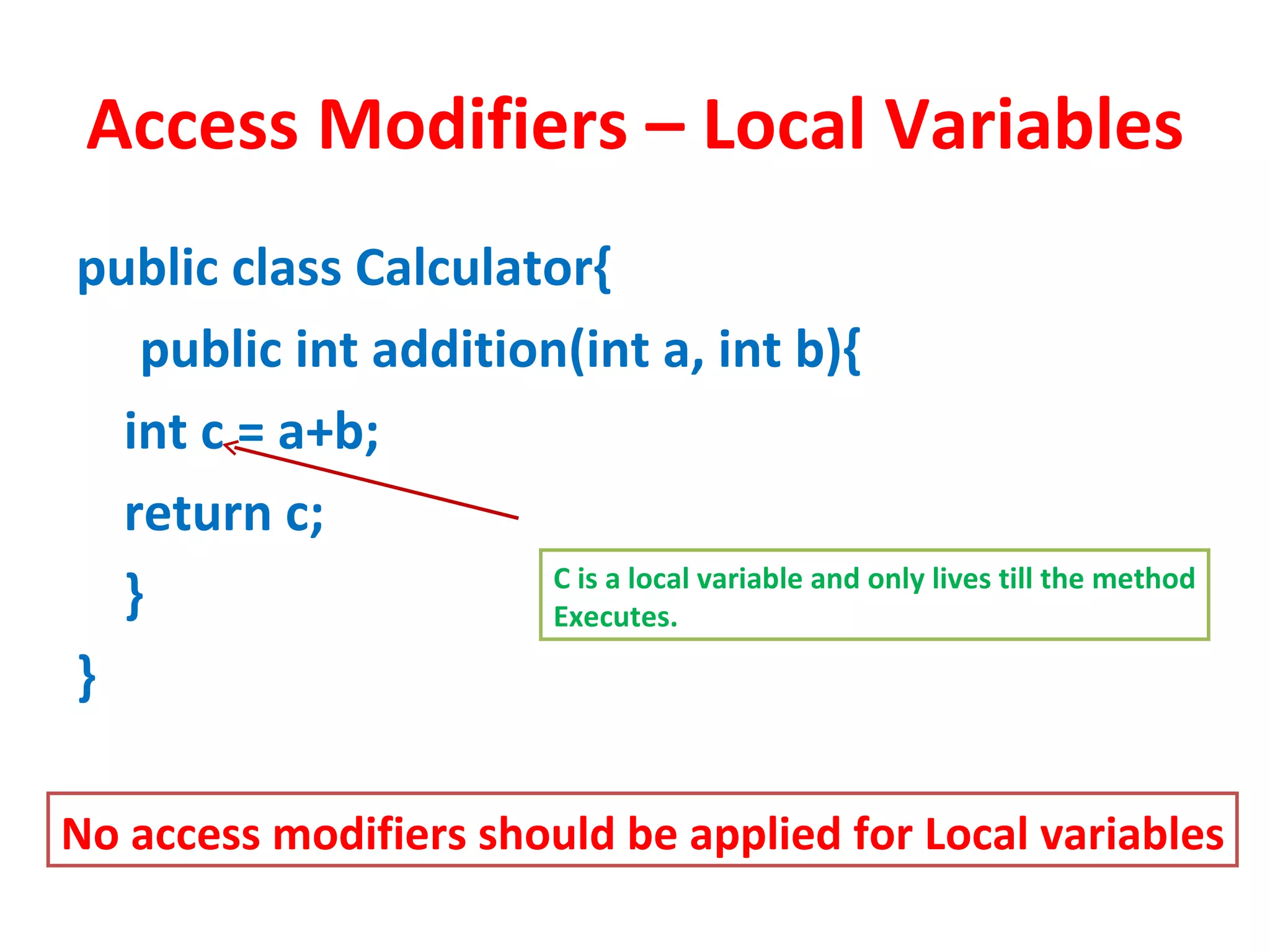
Access modifiers determine the visibility and accessibility of classes, methods, and variables in Java. The four main access modifiers are public, protected, default, and private. Public members are visible everywhere, protected requires inheritance, default is for the same package, and private is only within the class. Access modifiers help implement encapsulation by hiding data and controlling access at the class and member level.