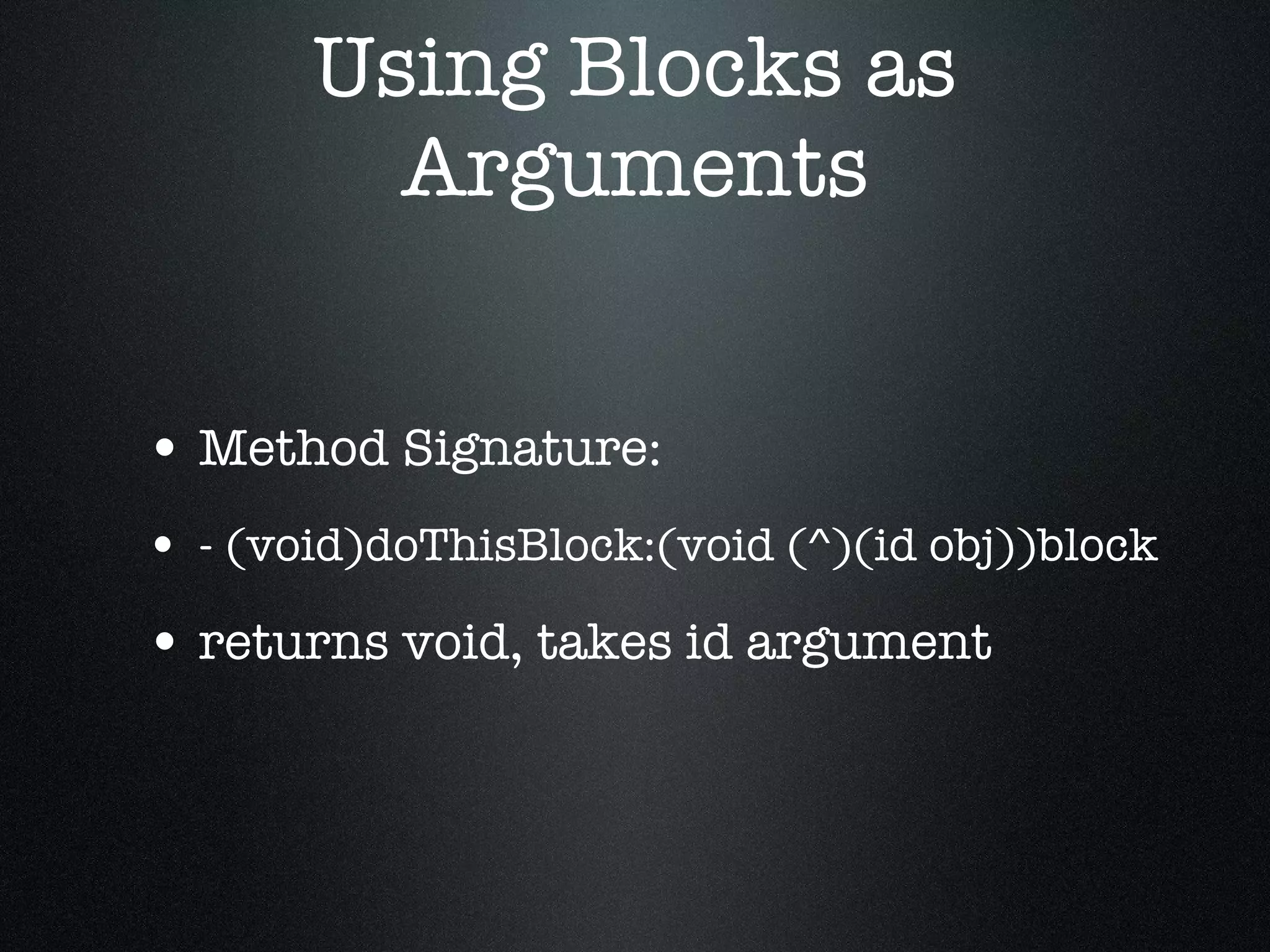
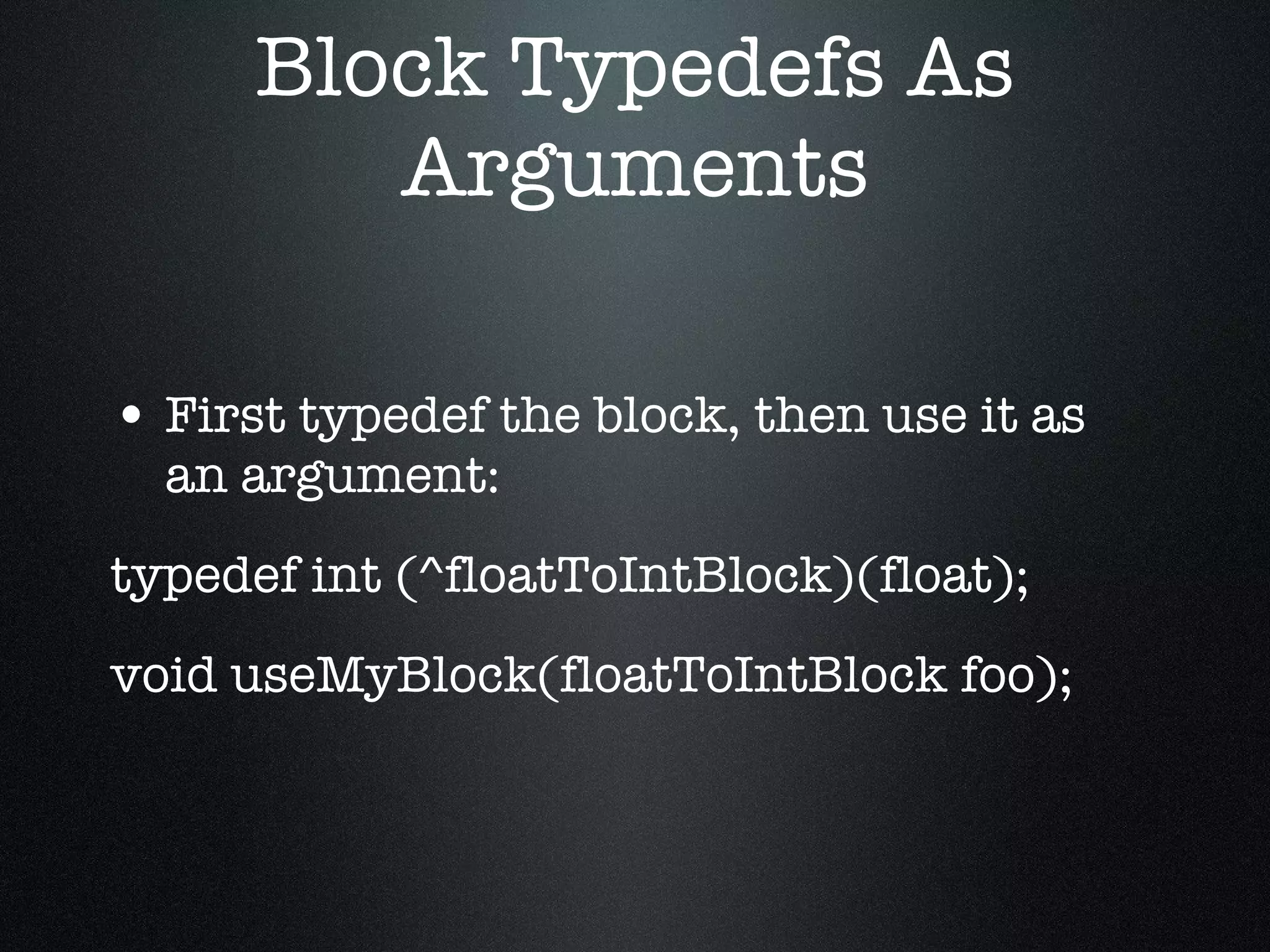
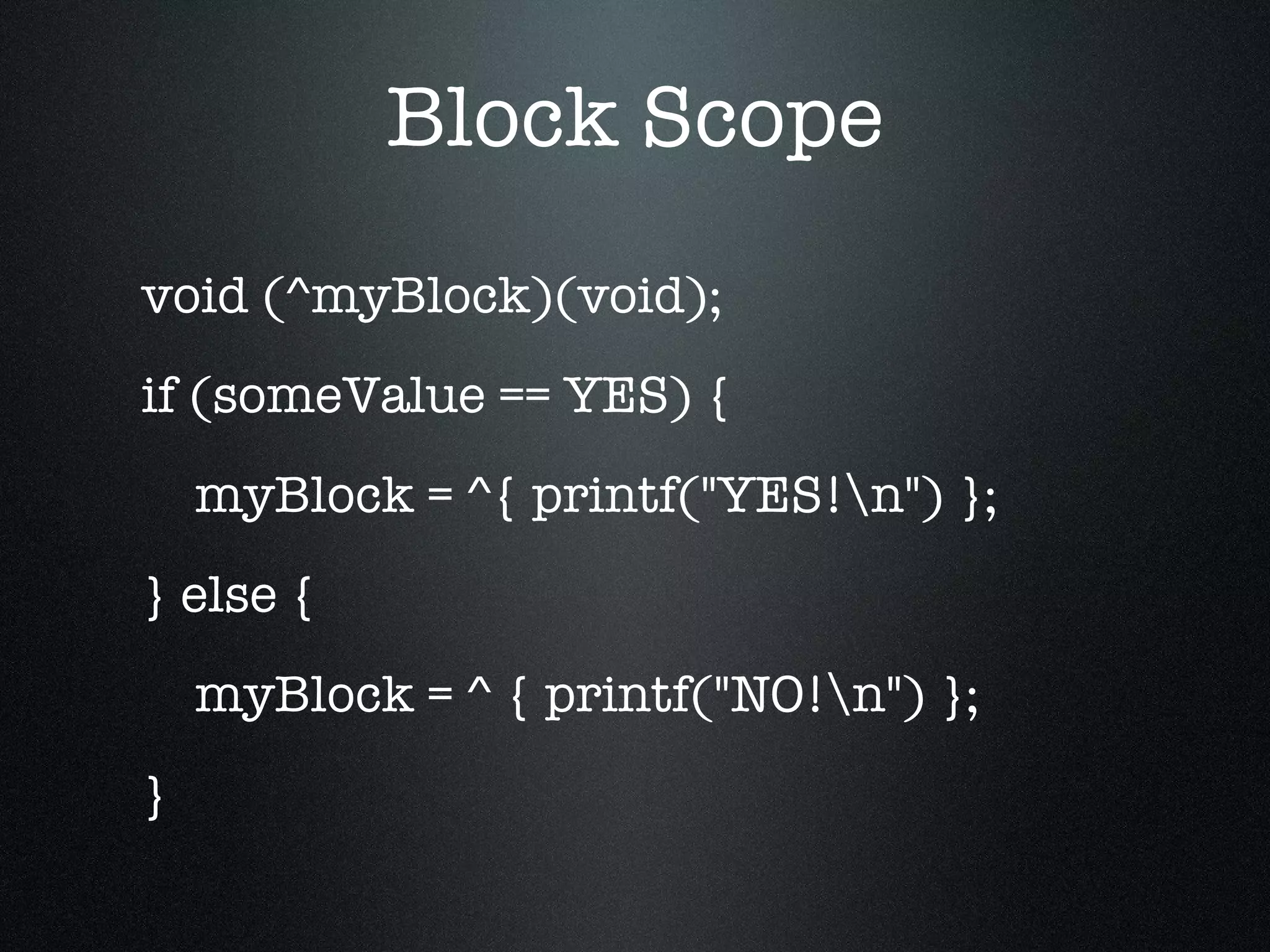
The document discusses iOS development with blocks and Grand Central Dispatch (GCD). It introduces blocks as a way to encapsulate code similar to functions but with additional features. It describes how to define, call and pass blocks. It then discusses how blocks can be used to replace callbacks, handle notifications, enable concurrent enumeration and sorting. The document concludes with an introduction to GCD, describing it as an open-source threading library that automatically optimizes threading using queues, timers and handlers.








![Block Memory Management Block_copy() and Block_release() Copied onto heap Blocks are Objective-C objects! [myBlock copy]; [myBlock release];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/iosdevelopmentwithblocks-110219133331-phpapp02/75/iOS-Development-with-Blocks-15-2048.jpg)
![Block Memory Management Unlike Objective-C objects, blocks are created on the stack Block_copy() moves them to the heap Block_retain() does not . Can also call [myBlock autorelease]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/iosdevelopmentwithblocks-110219133331-phpapp02/75/iOS-Development-with-Blocks-16-2048.jpg)
![NSString *helloWorld = [[NSString alloc] initWithString:@"Hello, World!"]; void (^helloBlock)(void) = ^{ NSLog(@"%@", helloWorld); }; [helloWorld release]; helloBlock(); Blocks Retain Objects](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/iosdevelopmentwithblocks-110219133331-phpapp02/75/iOS-Development-with-Blocks-17-2048.jpg)

![Replacing Callbacks Old UIView animations: [UIView beginAnimations:@"foo" context:nil]; [UIView setAnimationDelegate:self]; [UIView setAnimationDidStopSelector:@selector(animationDidStop:finished:context:)]; Then you implement the callback](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/iosdevelopmentwithblocks-110219133331-phpapp02/75/iOS-Development-with-Blocks-20-2048.jpg)
![Replacing Callbacks - (void)animationDidStop:(NSString *)animationID finished:(NSNumber *)finished context:(void *)context { if ([animationID isEqualToString:kIDOne]) { … } else if ([animationID isEqualToString:kIDTwo]) { … } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/iosdevelopmentwithblocks-110219133331-phpapp02/75/iOS-Development-with-Blocks-21-2048.jpg)
![Replacing Callbacks New UIView Animations: [UIView animateWithDuration:0.3 animations:^{ [myView setAlpha:0.0f]; } completion:^(BOOL finished) { [self doSomething]; }];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/iosdevelopmentwithblocks-110219133331-phpapp02/75/iOS-Development-with-Blocks-22-2048.jpg)
![Replacing Callbacks New UIView Animations: [UIView animateWithDuration:0.3 animations:^{ [myView setAlpha:0.0f]; } completion:^(BOOL finished) { [self doSomething]; }];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/iosdevelopmentwithblocks-110219133331-phpapp02/75/iOS-Development-with-Blocks-23-2048.jpg)
![Replacing Callbacks New UIView Animations: [UIView animateWithDuration:0.3 animations:^{ [myView setAlpha:0.0f]; } completion:^(BOOL finished) { [self doSomething]; }];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/iosdevelopmentwithblocks-110219133331-phpapp02/75/iOS-Development-with-Blocks-24-2048.jpg)
![Replacing Callbacks New UIView Animations: [UIView animateWithDuration:0.3 animations:^{ [myView setAlpha:0.0f]; } completion:^(BOOL finished) { [self doSomething]; } ];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/iosdevelopmentwithblocks-110219133331-phpapp02/75/iOS-Development-with-Blocks-25-2048.jpg)

![Notification Handlers Old Notifications: [notificationCenter addObserver:self selector:@selector(foo:) name:kMyNotification object:myObject];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/iosdevelopmentwithblocks-110219133331-phpapp02/75/iOS-Development-with-Blocks-27-2048.jpg)
![Notification Handlers Old Notifications: Userinfo Dictionaries - (void)foo:(NSNotification *)aNotification { NSDictionary *userInfo = [aNotification userInfo]; NSString *UID = [userInfo objectForKey:kIDKey]; NSNumber *value = [userInfo objectForKey:kValueKey]; }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/iosdevelopmentwithblocks-110219133331-phpapp02/75/iOS-Development-with-Blocks-28-2048.jpg)
![Notification Handlers New Notification Handlers: [notificationCenter addObserverForName:kName object:myObject queue:nil usingBlock:^(NSNotification *aNotification) { [myObject doSomething]; }]; [myObject startLongTask];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/iosdevelopmentwithblocks-110219133331-phpapp02/75/iOS-Development-with-Blocks-29-2048.jpg)
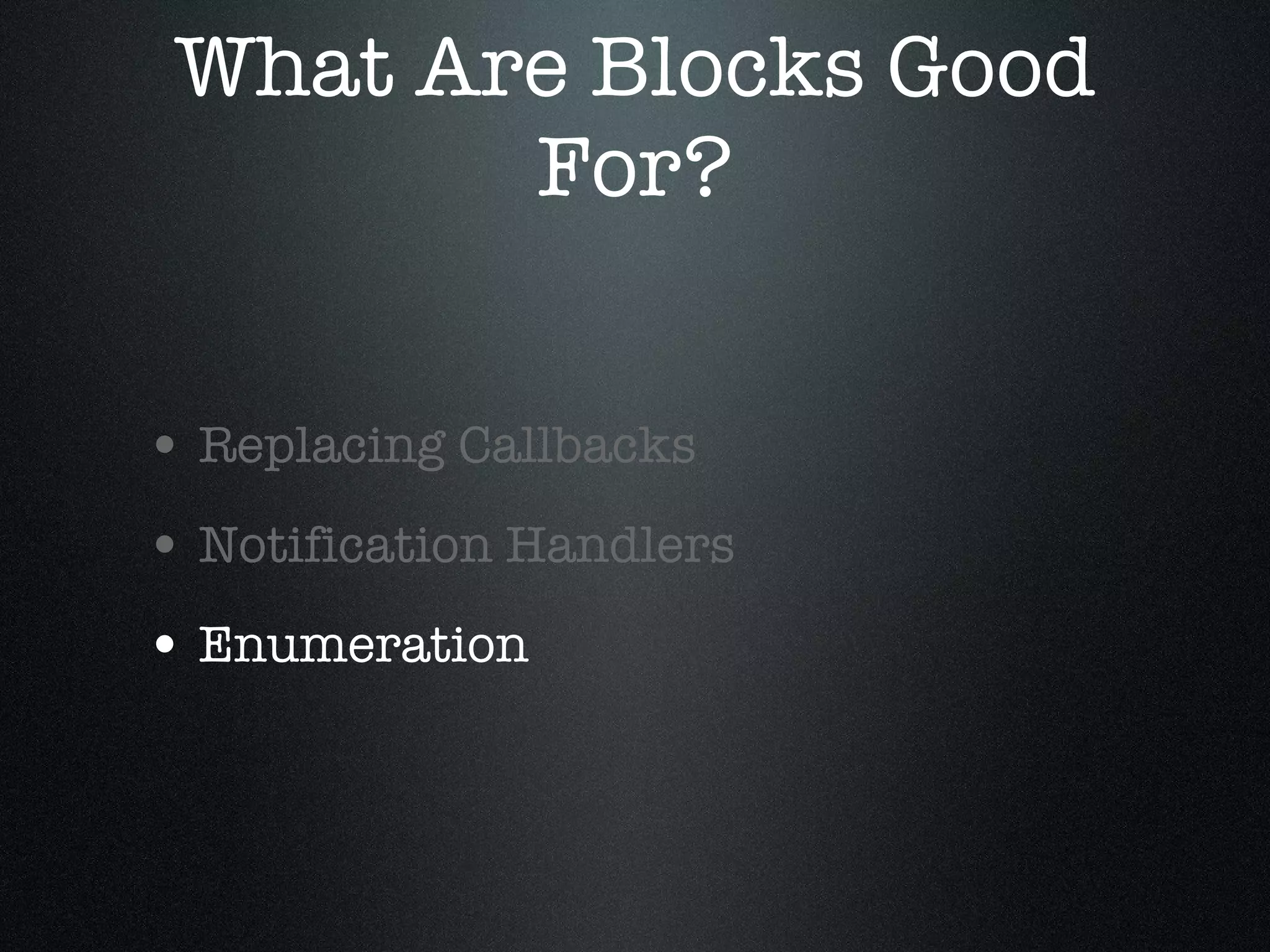
![Enumeration Basic Enumeration for (int i = 0; i < [myArray count]; i++) { id obj = [myArray objectAtIndex:i]; [obj doSomething]; }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/iosdevelopmentwithblocks-110219133331-phpapp02/75/iOS-Development-with-Blocks-31-2048.jpg)
![Enumeration But… for (int i = 0; i < [myArray count]; i++) { id obj = [myArray objectAtIndex:i]; [obj doSomething]; for (int j = 0; j < [obj count]; j++) { // Very interesting code here. } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/iosdevelopmentwithblocks-110219133331-phpapp02/75/iOS-Development-with-Blocks-32-2048.jpg)
![Enumeration NSEnumerator NSArray *anArray = // ... ; NSEnumerator *enumerator = [anArray objectEnumerator]; id object; while ((object = [enumerator nextObject])) { // do something with object... }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/iosdevelopmentwithblocks-110219133331-phpapp02/75/iOS-Development-with-Blocks-33-2048.jpg)
![Enumeration Fast Enumeration (10.5+) for (id obj in myArray) { [obj doSomething]; }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/iosdevelopmentwithblocks-110219133331-phpapp02/75/iOS-Development-with-Blocks-34-2048.jpg)
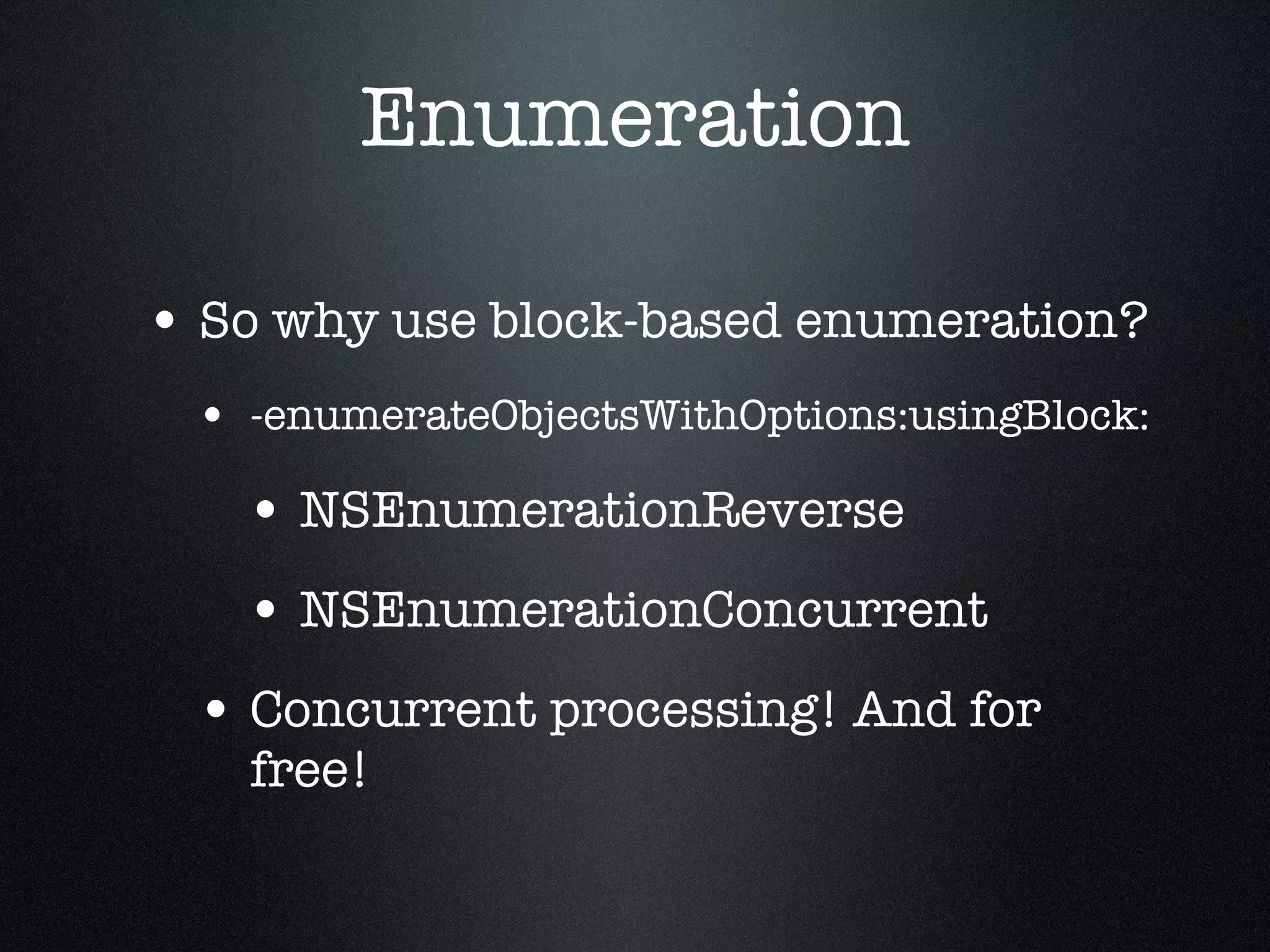
![Enumeration Block-based enumeration [myArray enumerateObjectsUsingBlock: ^(id obj, NSUInteger idx, BOOL *stop) { [obj doSomething]; }];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/iosdevelopmentwithblocks-110219133331-phpapp02/75/iOS-Development-with-Blocks-35-2048.jpg)





![Simple GCD dispatch_queue_t queue = dispatch_get_global_queue(DISPATCH_QUEUE_PRIORITY_HIGH, 0ul); dispatch_async(queue, ^{ [self performLongTask]; }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/iosdevelopmentwithblocks-110219133331-phpapp02/75/iOS-Development-with-Blocks-45-2048.jpg)