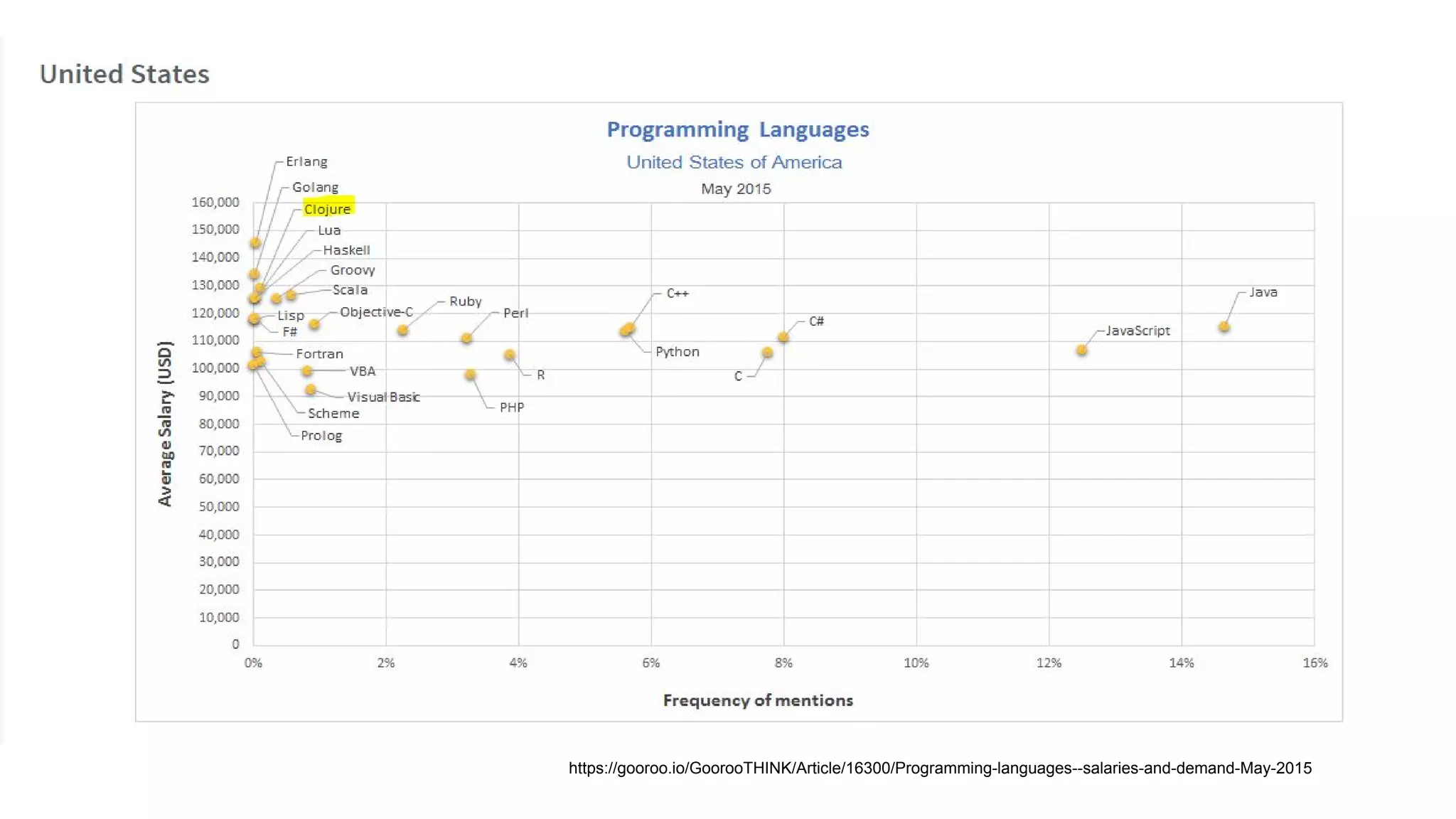
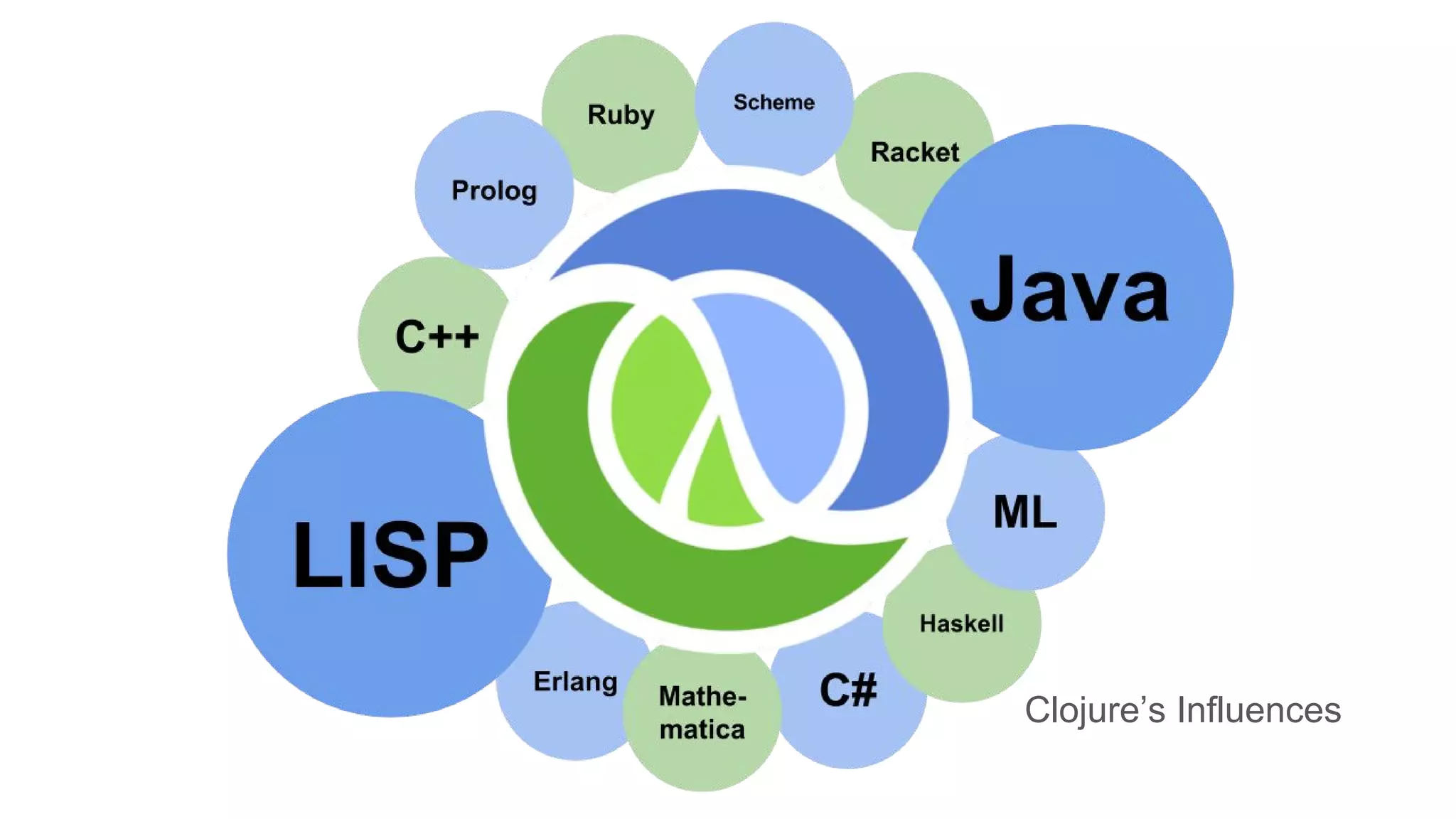
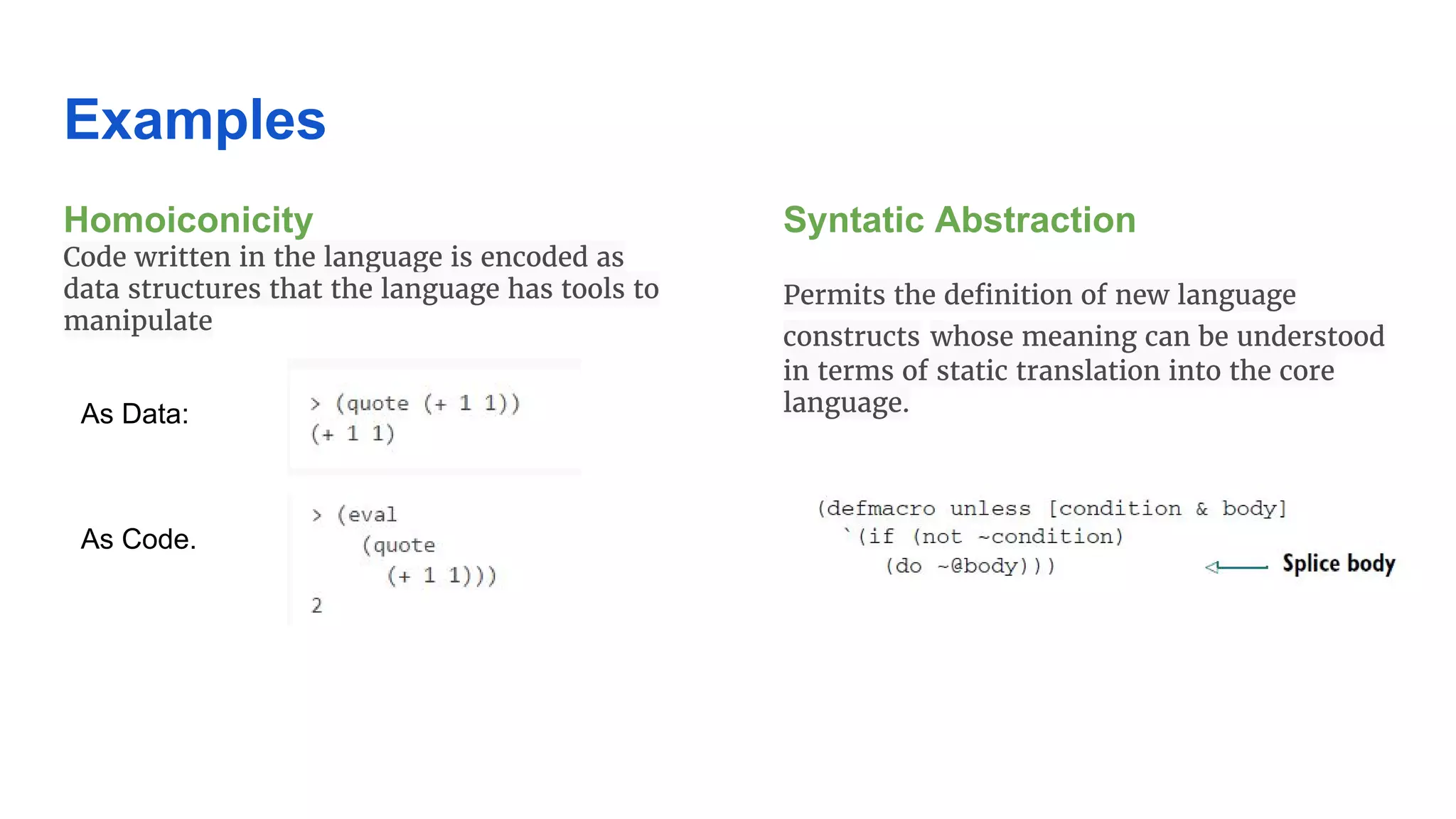
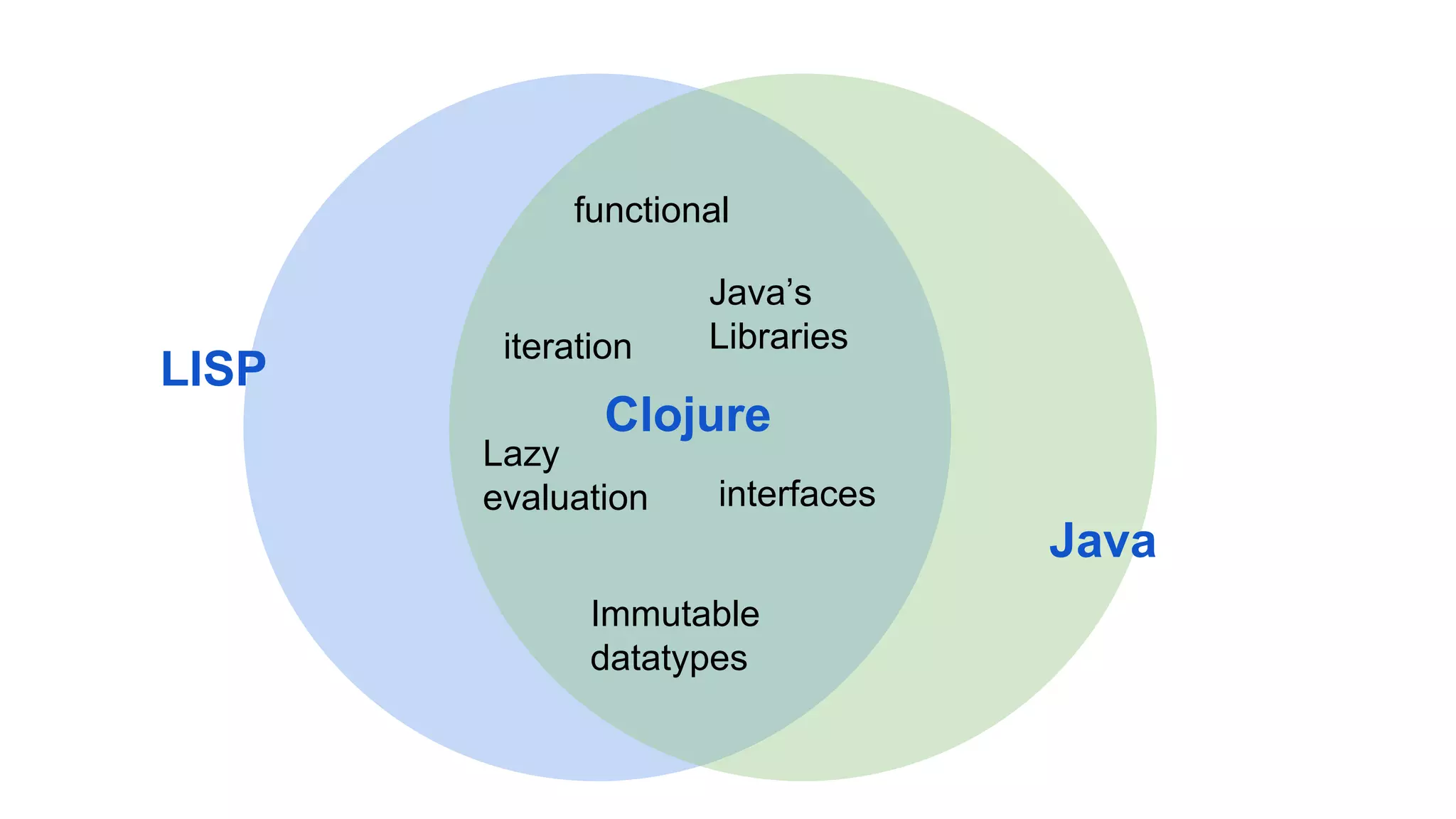
Clojure is a general-purpose, functional programming language that runs on the Java Virtual Machine and emphasizes simplicity and concurrency. It was created by Rich Hickey and is known for its immutable data structures, code-as-data (homoiconicity), and interoperability with Java libraries. Clojure is used in industries by companies like CapitalOne, Amazon, and Facebook, and its developers report high satisfaction levels.








![Truthiness
What is truthy?
● true
● 1
● (= 1 1)
● 0
● “False”
● []
● Literally any value but false or nil
What is falsey?
● false
● nil
● (= 3 1)
Nil Punning: Handling Clojure’s
empty sequences that are Truthy
Every[thing] is "true" all the time, unless it is nil or false.
—Brian Goetz,
The Joy of Clojure](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cs571clojurepresentation-161103161113/75/Introductory-Clojure-Presentation-13-2048.jpg)


![Functions
First Class
Created on demand
Stored in a data structure
Passed as an argument
Returned as a value
Higher-Order
Takes one or more function args
Returns function as result
Pure Functions
ALWAYS return same result
No observable side effects
(defn
[arg1 arg2]
(;function code
))
def or defn?
● Both bind a symbol or name
● def is only evaluated once
● defn is evaluated every time it is called](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cs571clojurepresentation-161103161113/75/Introductory-Clojure-Presentation-19-2048.jpg)

![Quick Comparison
Haskell:
average numbers = (fold (+) (numbers) ) / (length(numbers))
Clojure:
(defn average [numbers] (/ (reduce + numbers) (count numbers)))](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cs571clojurepresentation-161103161113/75/Introductory-Clojure-Presentation-21-2048.jpg)
![Quick Comparison
Haskell:
fact x = if x == 0 then 1 else x * fact(x-1)
Clojure:
(defn factorial [n] (if (= n 0) 1 (* n (factorial (dec n)))))](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cs571clojurepresentation-161103161113/75/Introductory-Clojure-Presentation-22-2048.jpg)


![Higher-Order Functions
Map
>(map * [1 2 3 4] [5 6 7 8])
(5 12 21 32)
Reduce
>(reduce max [0 -3 10 48])
48
Comp
((comp str - +) 4 5) is equivalent to
(str ( - ( + 4 5)))
Partial
(defn add10 (partial + 10))
>(add10 3)
13
>(add10 3 4 8)
25](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cs571clojurepresentation-161103161113/75/Introductory-Clojure-Presentation-25-2048.jpg)
![Anonymous Functions
Fn
>(map (fn [x] (* x x)) (range 1 10))
(1 4 9 16 25 36 49 64 81)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cs571clojurepresentation-161103161113/75/Introductory-Clojure-Presentation-26-2048.jpg)
![Macros
(defmacro infix
[infixed]
(list (second infixed)
(first infixed)
(last infixed)))
>(1 + 2)
error
>(infix (1 + 2))
3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cs571clojurepresentation-161103161113/75/Introductory-Clojure-Presentation-27-2048.jpg)
![Java Interop
Accessing member functions
>(.toUpperCase "fred")
"FRED"
>(Math/pow 2 4)
16
( proxy [class-and-interfaces] [args]
fs+)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cs571clojurepresentation-161103161113/75/Introductory-Clojure-Presentation-28-2048.jpg)








