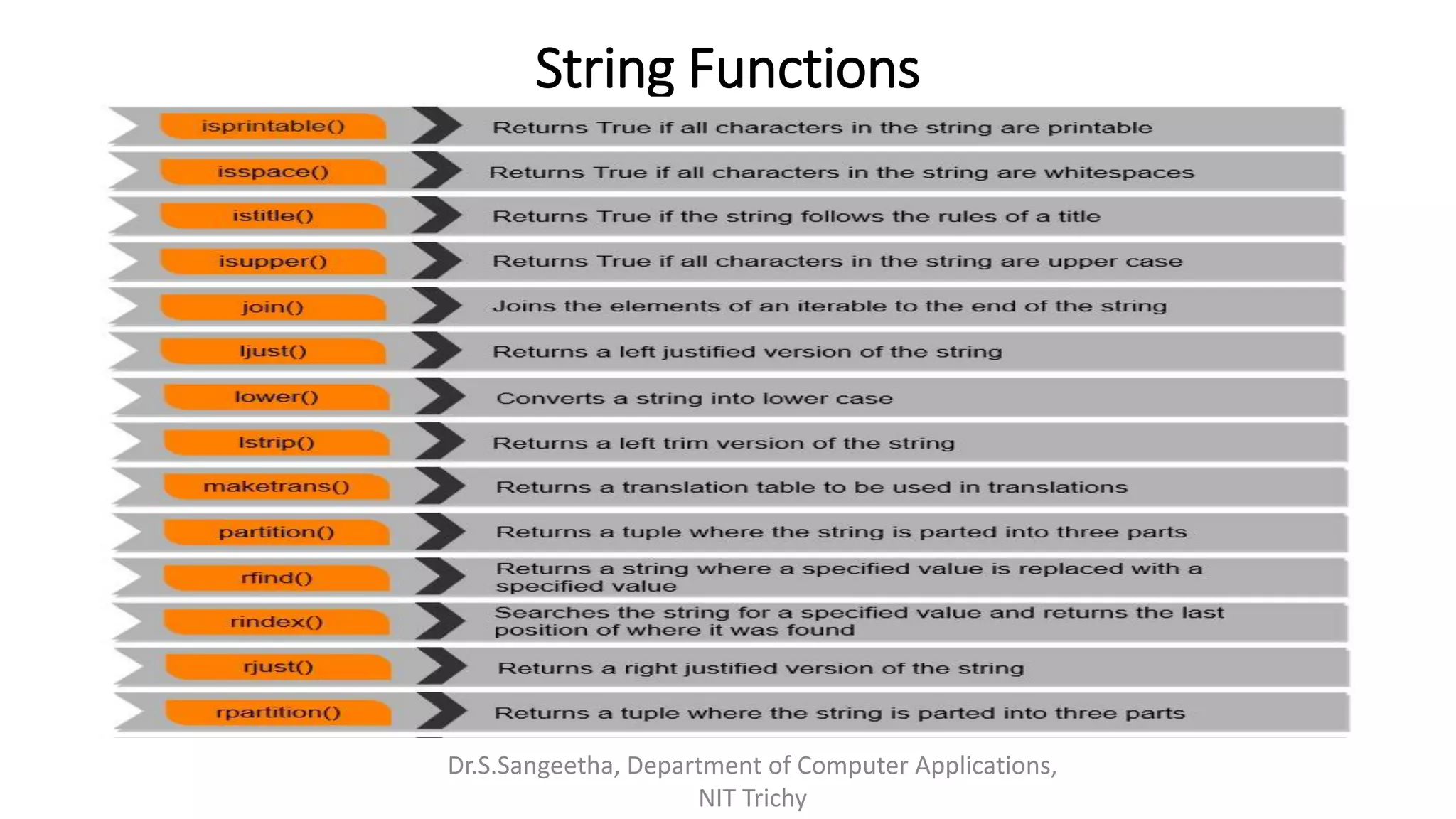
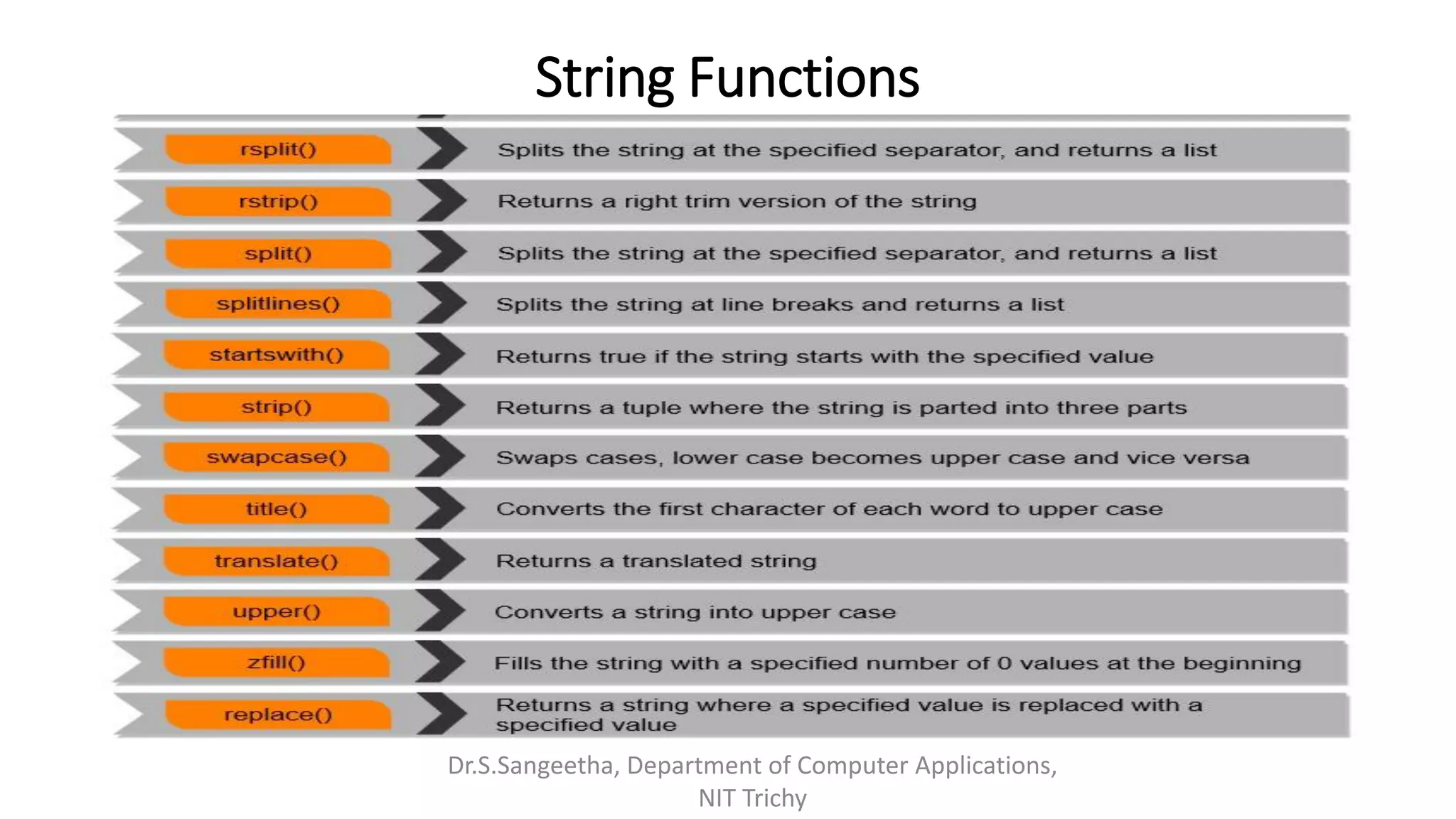
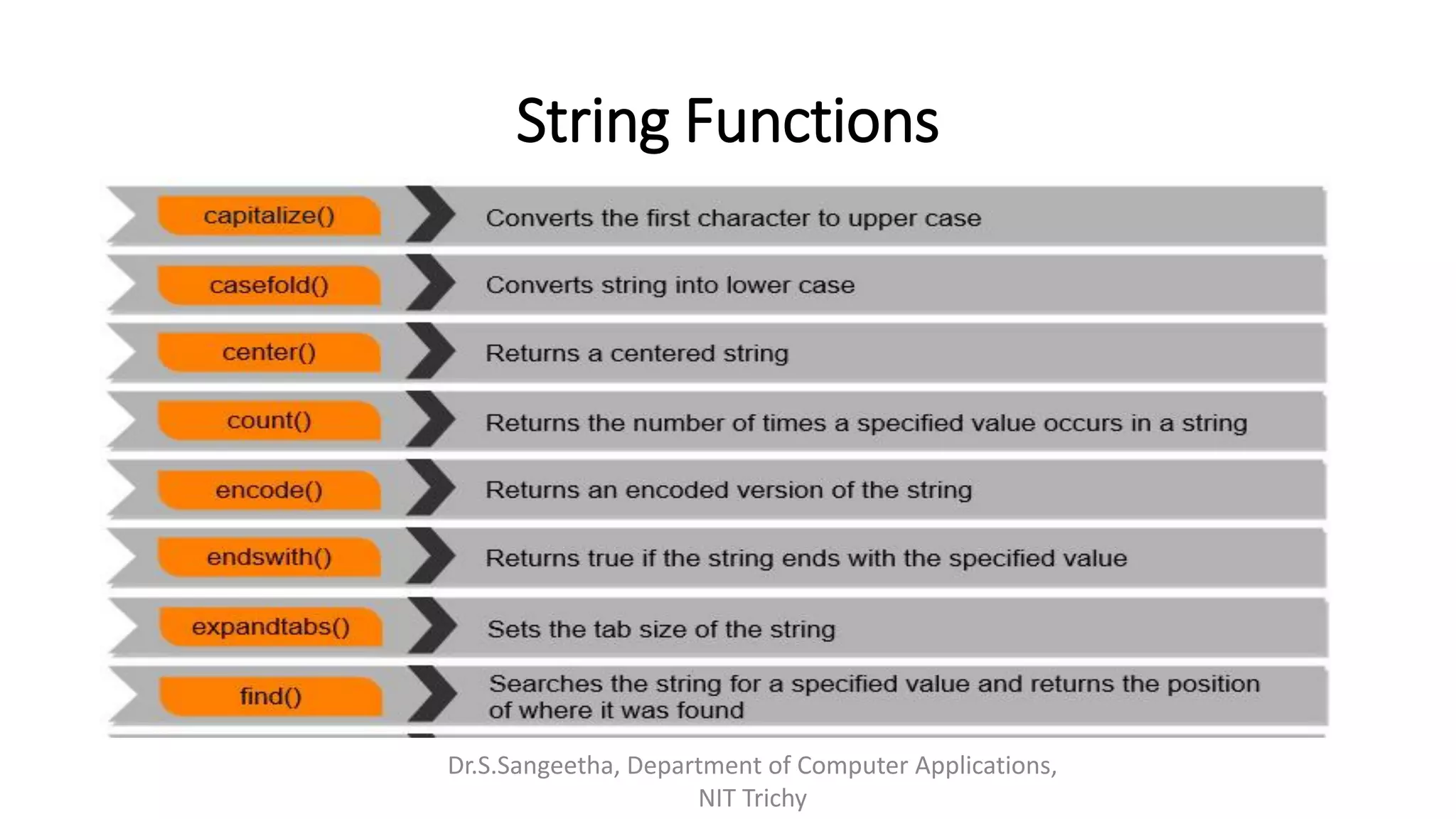
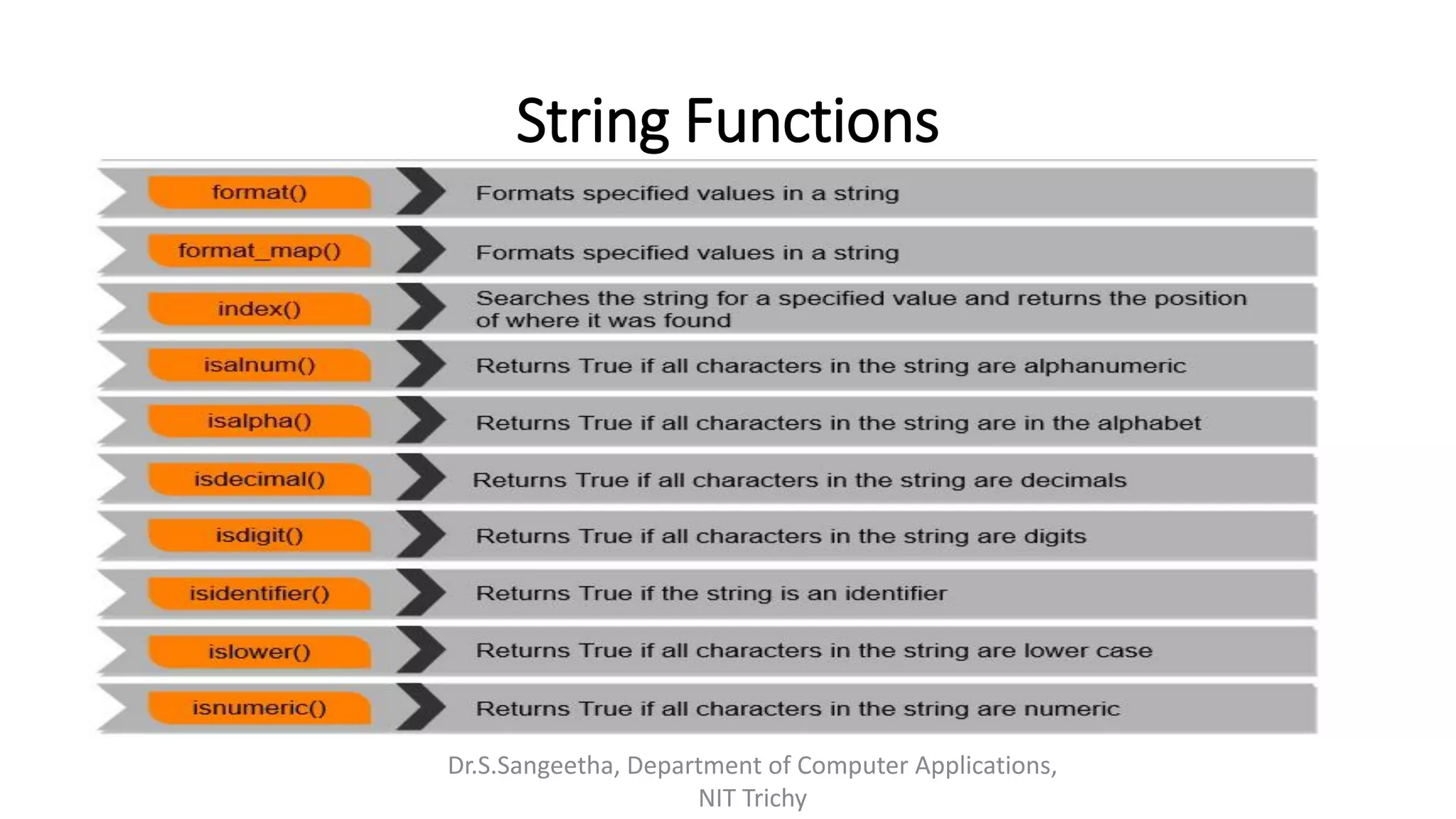
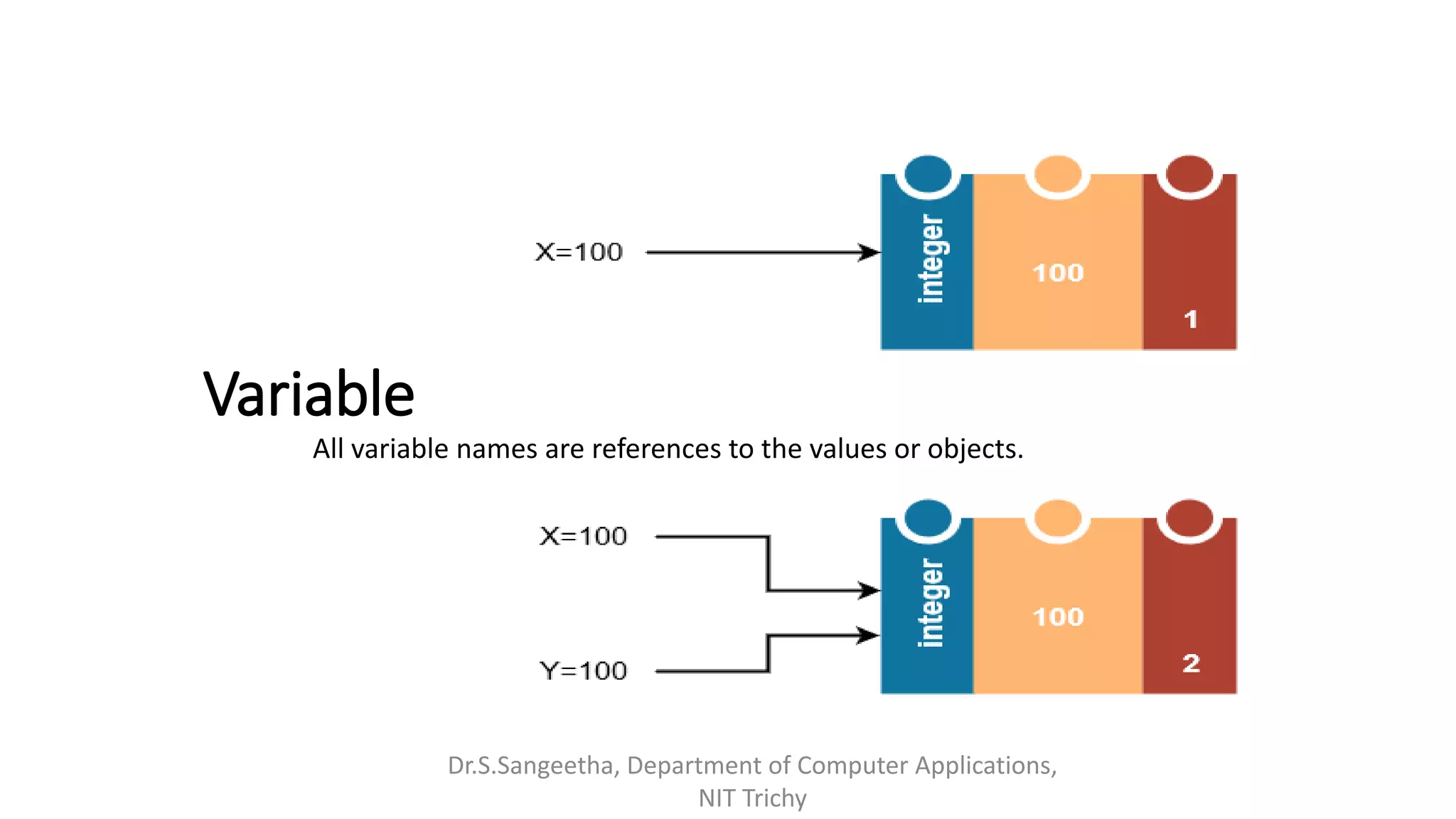
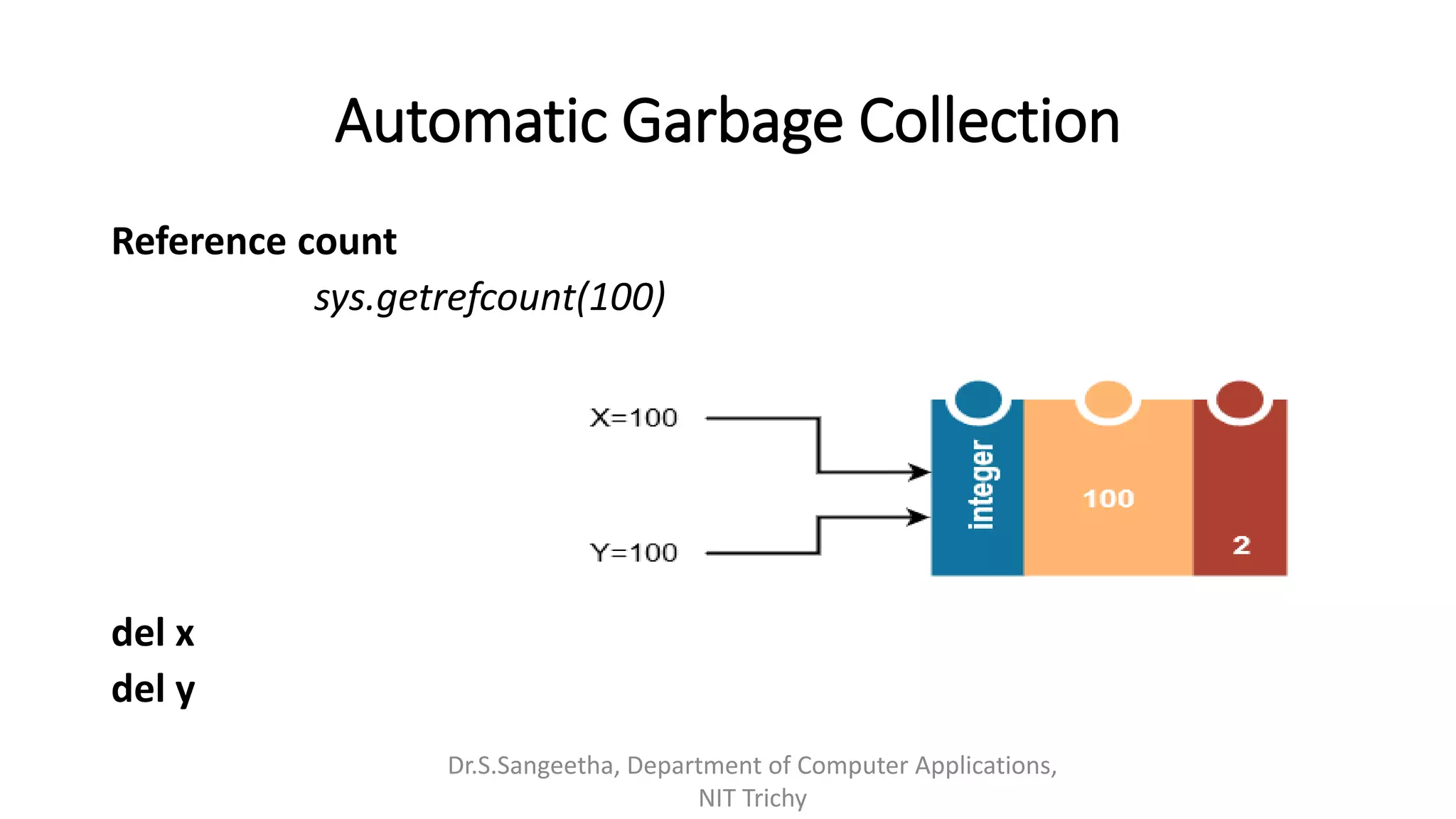
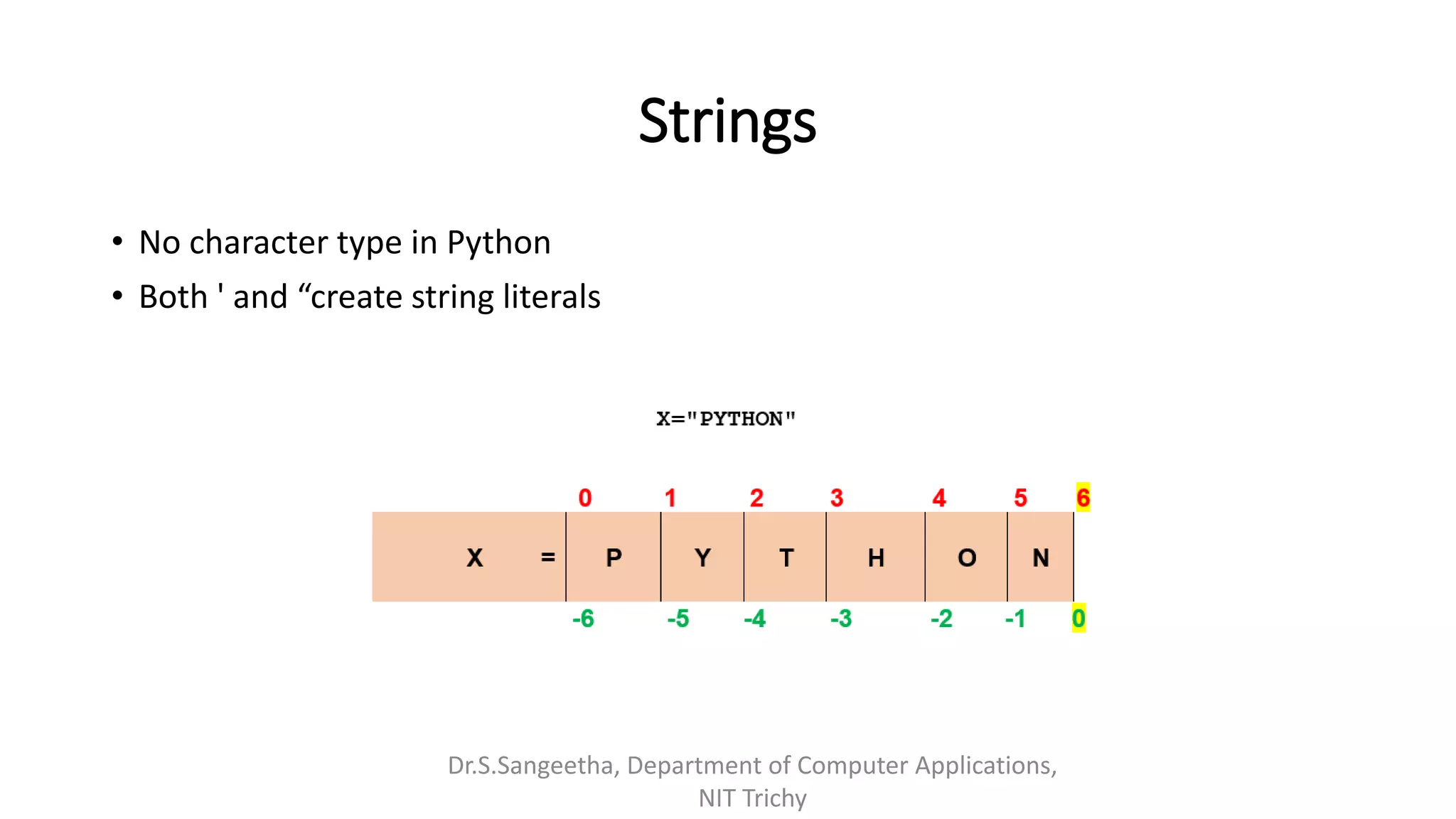
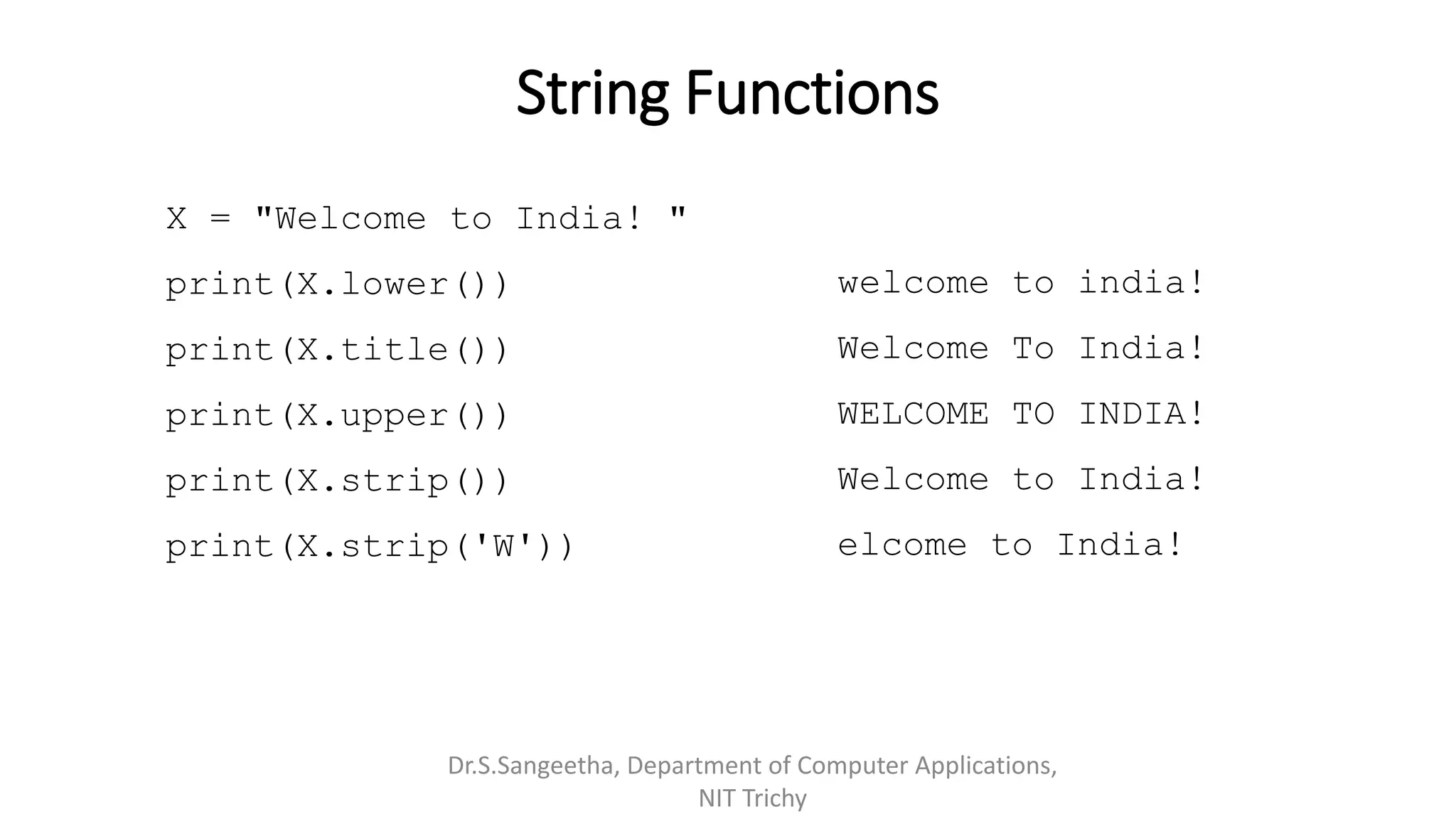
This document provides an introduction and overview of Python programming presented by Dr. S. Sangeetha from the Department of Computer Applications at the National Institute of Technology in Tiruchirappalli, India. It discusses Python's history and features, working environments like Anaconda and Conda, data types, operators, objects, variables and garbage collection, strings, formatting, and basics of writing Python programs.






![Why it is Slow?
1) Dynamically typed Language
2) Interpreted code is always slower
Takes more instructions in order to implement actual machine instruction
3) GIL (Global Interpreter Lock)
➢Allows only one thread to hold the control of python Interpreter
➢Bottleneck in CPU bound multi-threaded code [Even in multi thread architecture
with more than CPU core]
➢Prevents CPU bound threads from executing parallel
Dr.S.Sangeetha, Department of Computer Applications,
NIT Trichy](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductionandstrings-200916171305/75/Introduction-to-Python-Objects-and-Strings-9-2048.jpg)

![Operators
() {}[] Tuple, List, Dictionary, set display
f (….), x [ :], X.attr Function calls, slicing, Attribute reference
** Exponentiation - Right to left associativity
x, -x Bitwise Not, Negative
*, /, //,% Multiplication, division, floor division,
Modulo division
+ - Additive
<< >> Shift
& Bitwise AND
Bitwise XOR
| Bitwise OR
in, not in, is, is not <, <=, >, >=, <>, !=, == Membership, Comparison/relational
not Boolean NOT
and Boolean AND
or Boolean OR
lambda Lambda expressions](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductionandstrings-200916171305/75/Introduction-to-Python-Objects-and-Strings-13-2048.jpg)





![String Slicing
print(X[0:2])
print(X[4:6])
print(X[1:3])
print(X[:3])
print(X[4:])
print(X[1:5:2]) #step size as 3rd parameter
print(X[4::-2])
PY
ON
YT
PYT
ON
YH
OTP
print(X[::-1]) # NOHTYP
Dr.S.Sangeetha, Department of Computer Applications, NIT Trichy](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductionandstrings-200916171305/75/Introduction-to-Python-Objects-and-Strings-24-2048.jpg)

![Immutability
>>> x="In India"
>>> id(x)
64787744
>>> x=x+' We have'
>>> x
'In India We have'
>>> id(x)
64763184
>>> y="India"
>>> id(y)
64799392
>>> y[2]="o"
TypeError: 'str'
object does not
support item
assignment
Dr.S.Sangeetha, Department of Computer Applications, NIT
Trichy](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductionandstrings-200916171305/75/Introduction-to-Python-Objects-and-Strings-26-2048.jpg)

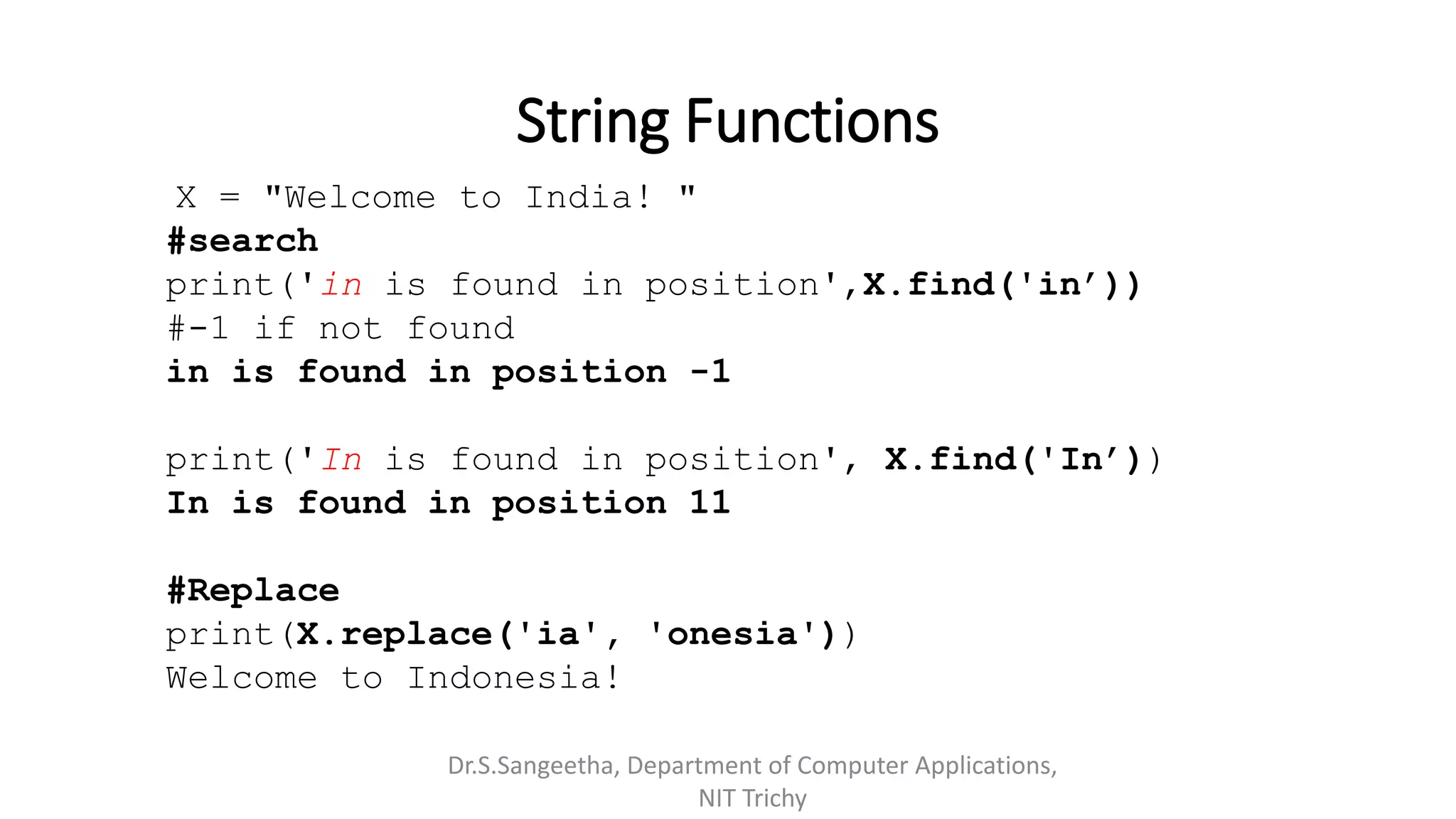
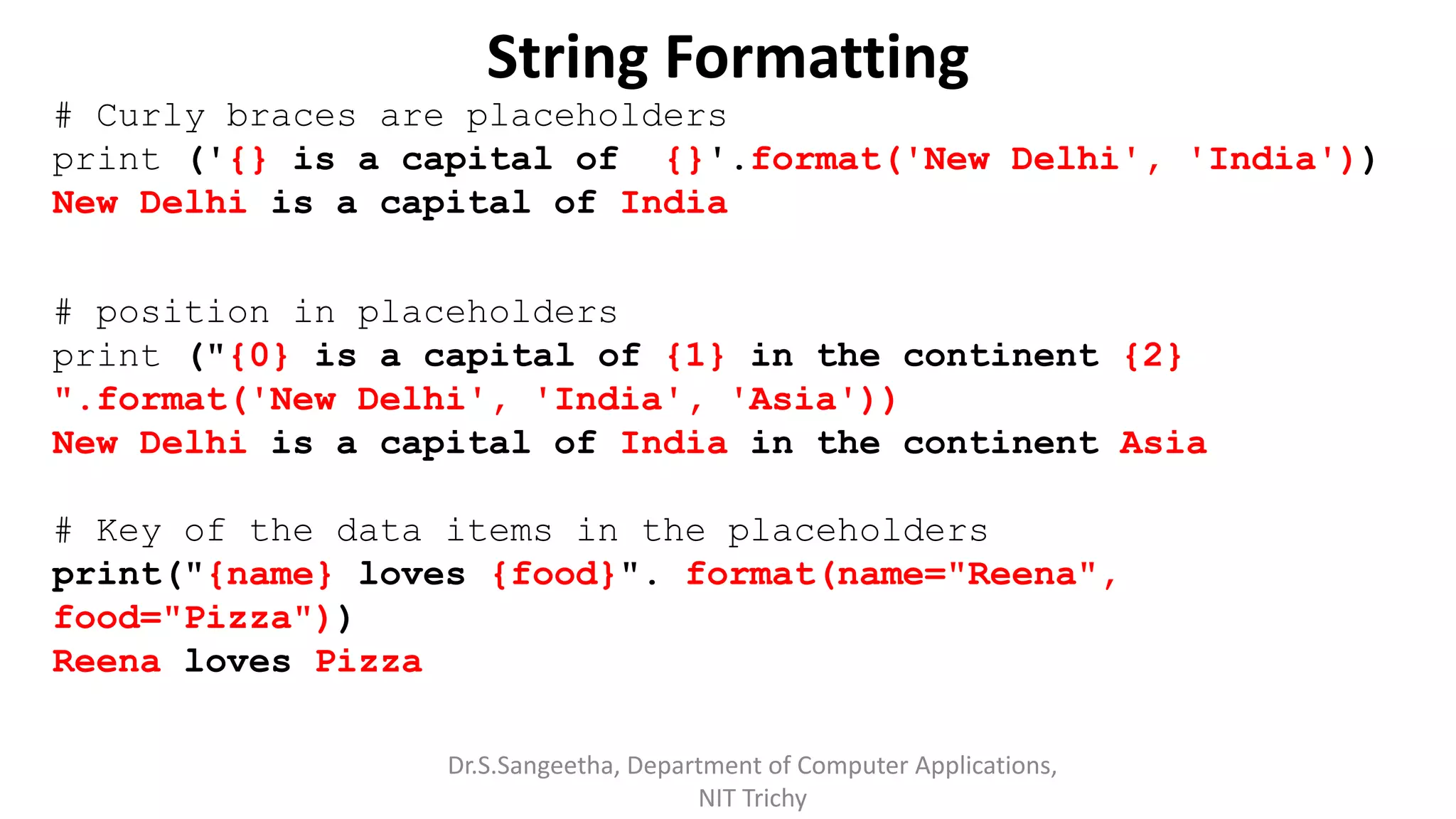
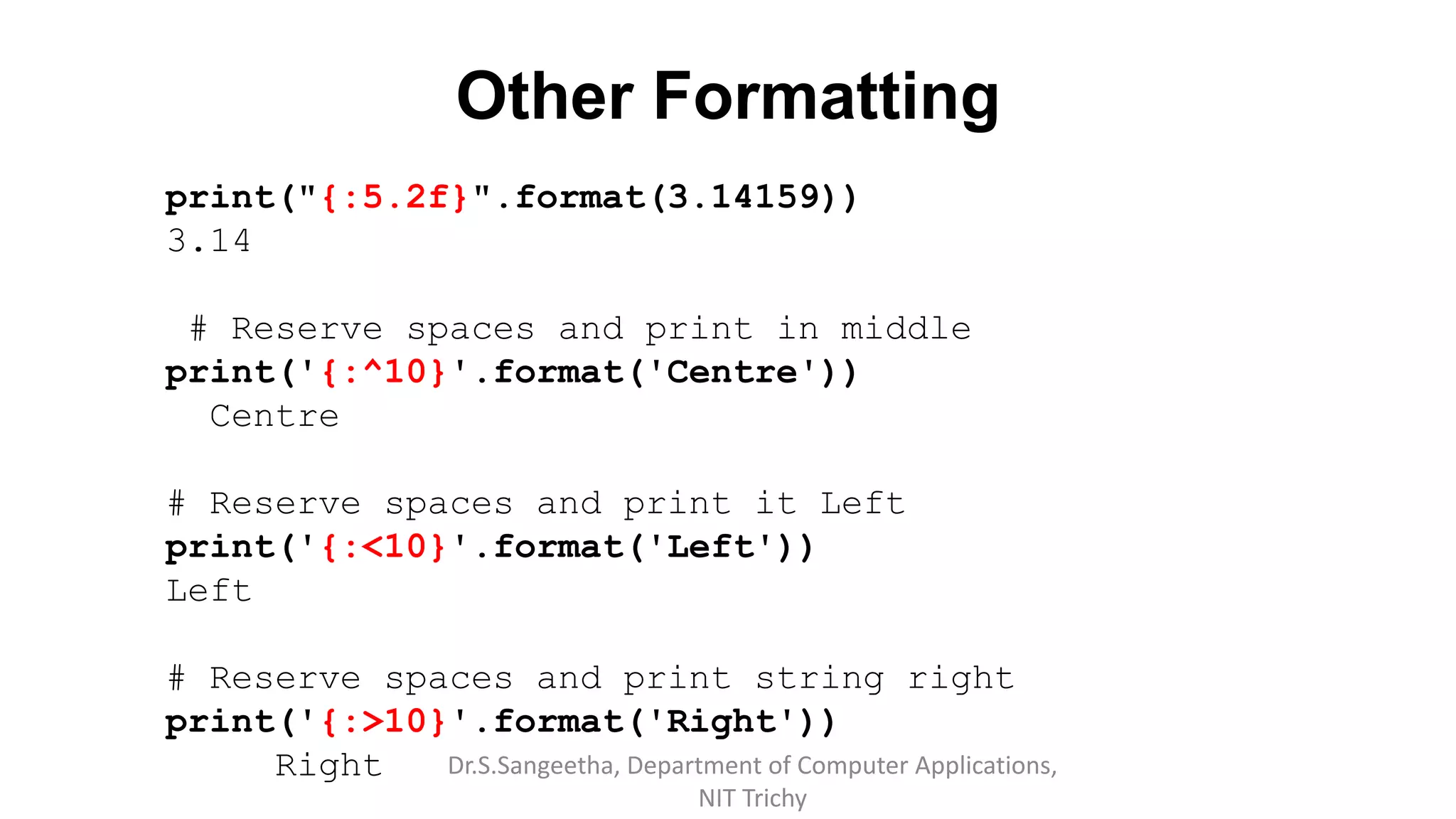
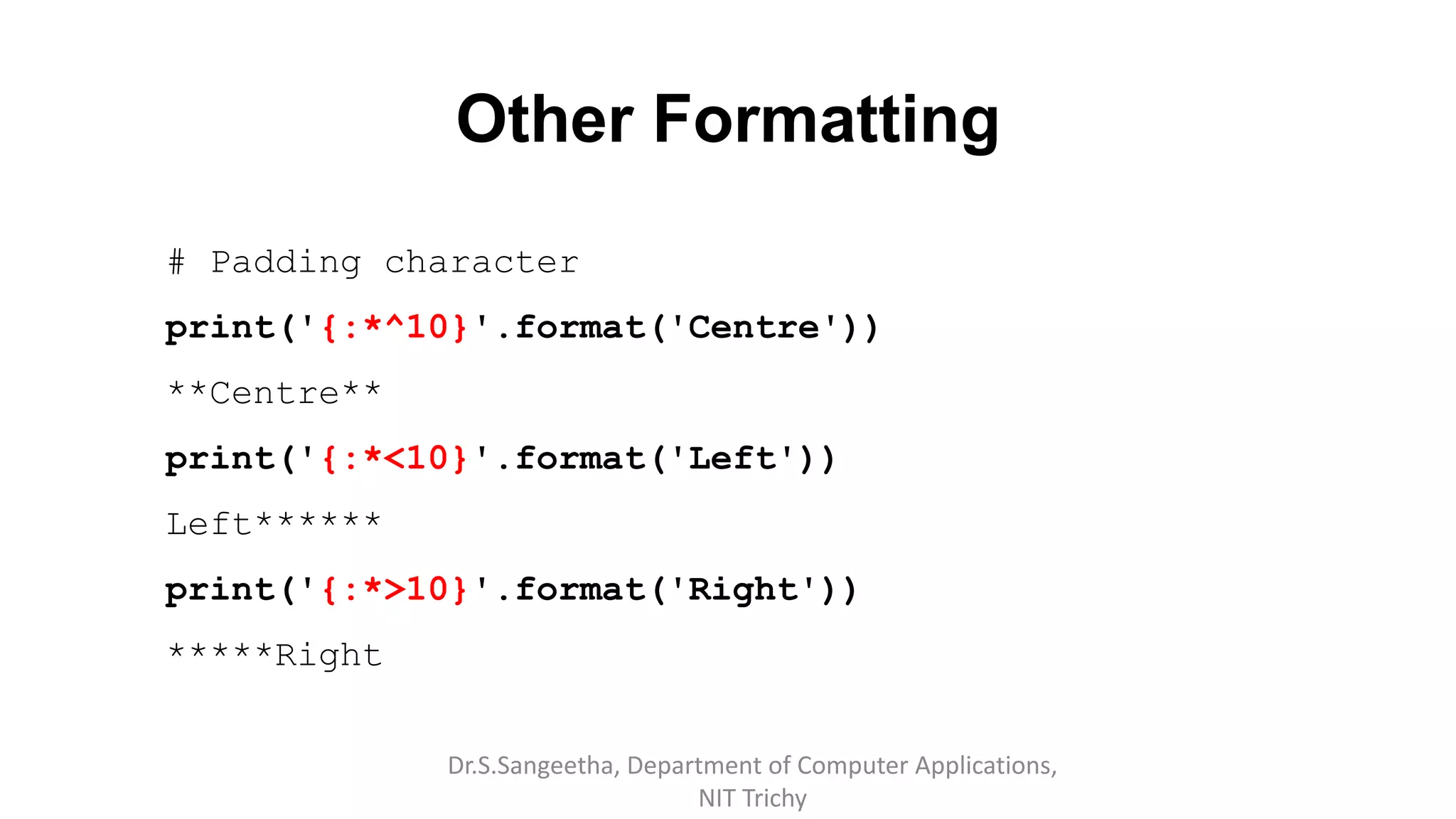
![String Formatting
# index in the placeholders
Fruits = ['Apple', 'Orange’, 'Guava']
print("{f[0]} is good compared to {f[1]}".format(f=Fruits))
Apple is good compared to Orange
# Evaluated expressions to strings
print ("Square of {} is {}".format (8, 8 ** 2))
Square of 8 is 64
Dr.S.Sangeetha, Department of Computer Applications,
NIT Trichy](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductionandstrings-200916171305/75/Introduction-to-Python-Objects-and-Strings-31-2048.jpg)