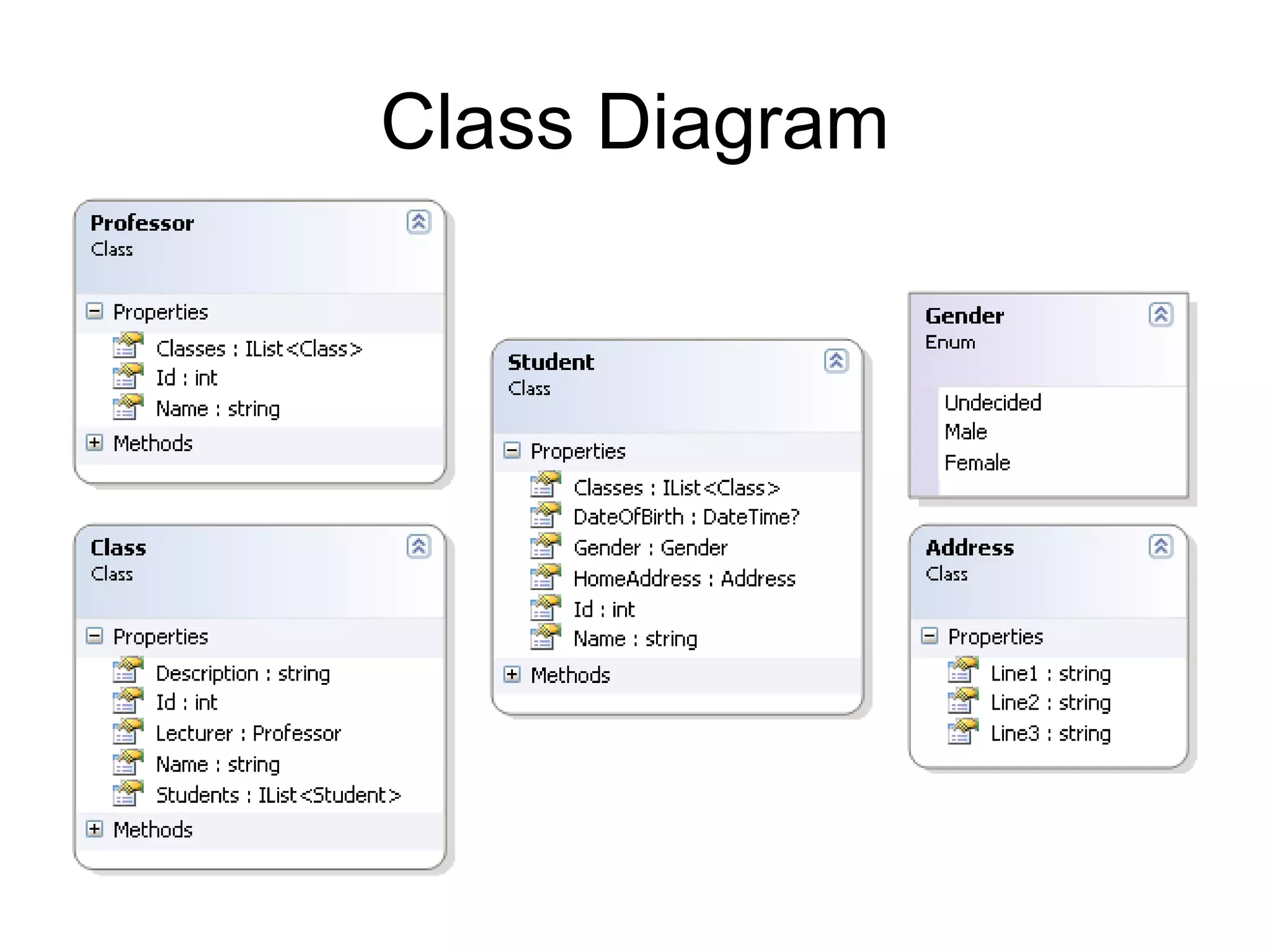
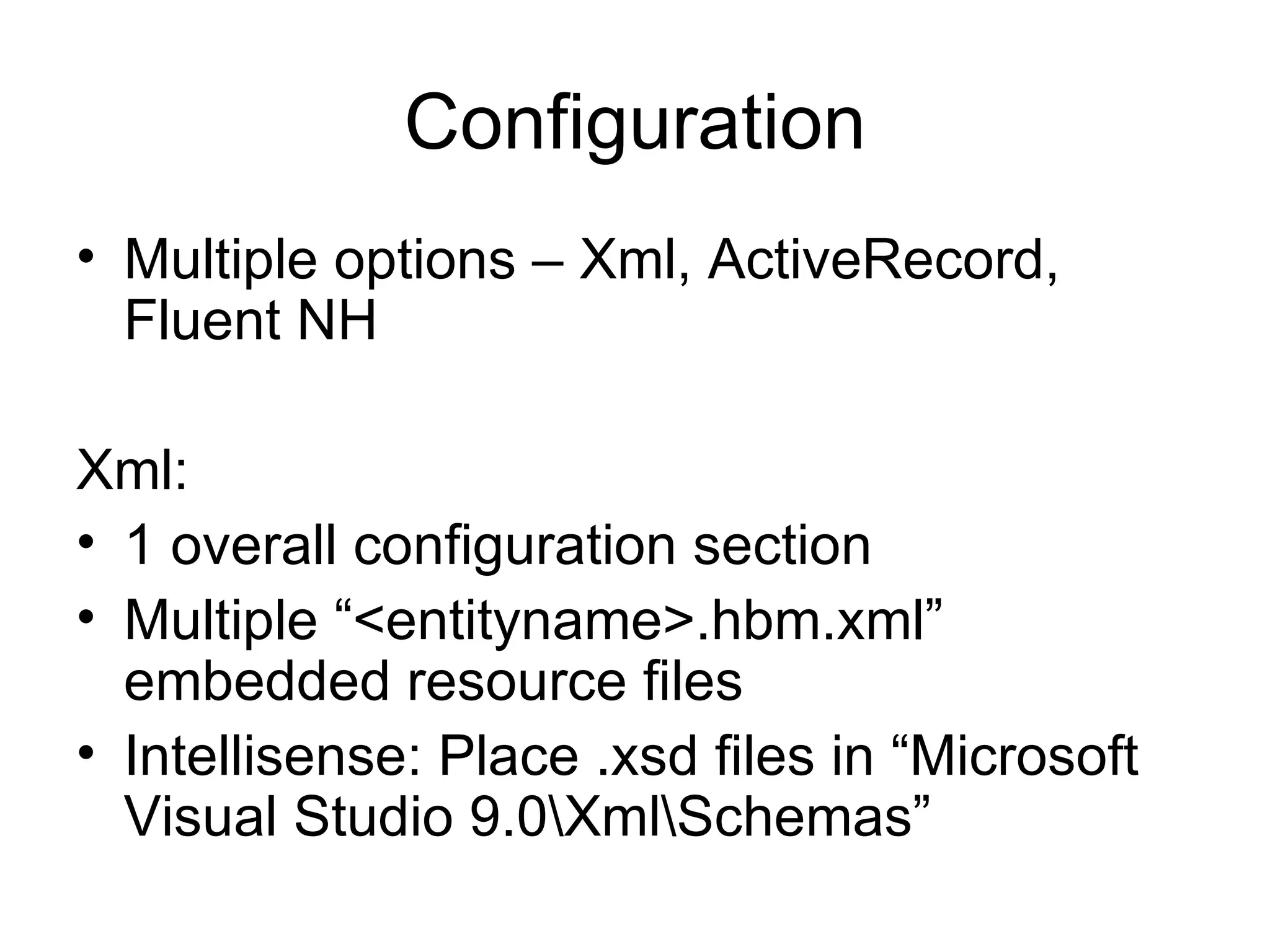
NHibernate is an object-relational mapper that maps plain old CLR objects (POCOs) to database tables. It is based on Hibernate and provides a stable, database agnostic way to generate SQL at runtime. NHibernate configurations can be defined using XML, attributes or code-first fluent APIs. Sessions represent a lightweight transaction and identity mapping unit of work with the database. Entities are mapped to tables through properties, identifiers and relationships such as one-to-many, many-to-many and inheritance. Queries can be performed using the criteria API, HQL, LINQ or future queries to optimize performance. Caching at the session and query levels improves efficiency. NHibernate reduces