This document provides an introduction to Java, including:
- What Java is and its key characteristics like being object-oriented, portable, secure, and multithreaded.
- The birth and growth of Java at Sun Microsystems in 1995.
- The different Java editions: Standard, Enterprise, and Micro.
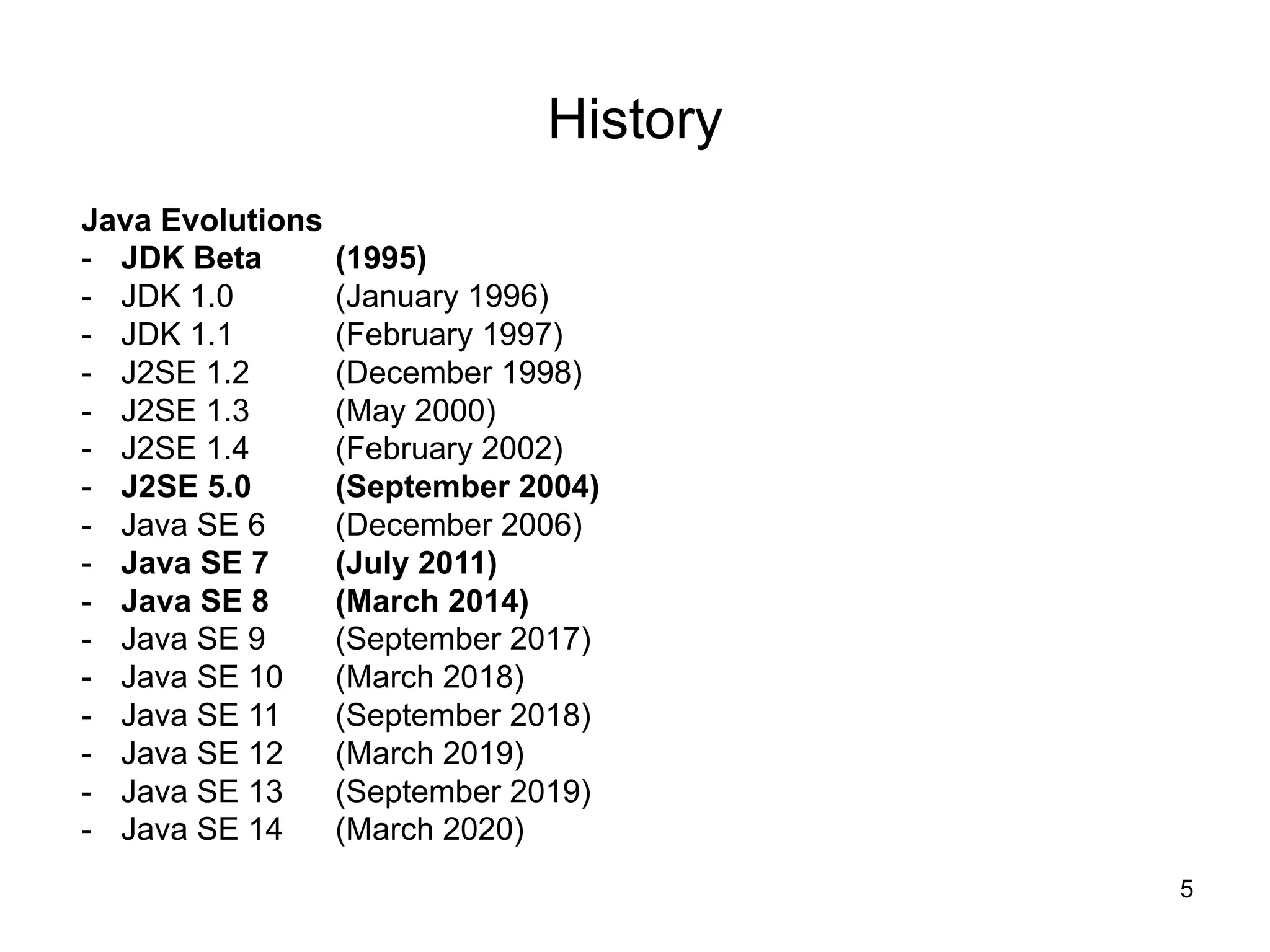
- An overview of Java's evolution through its versions from 1995 to today.
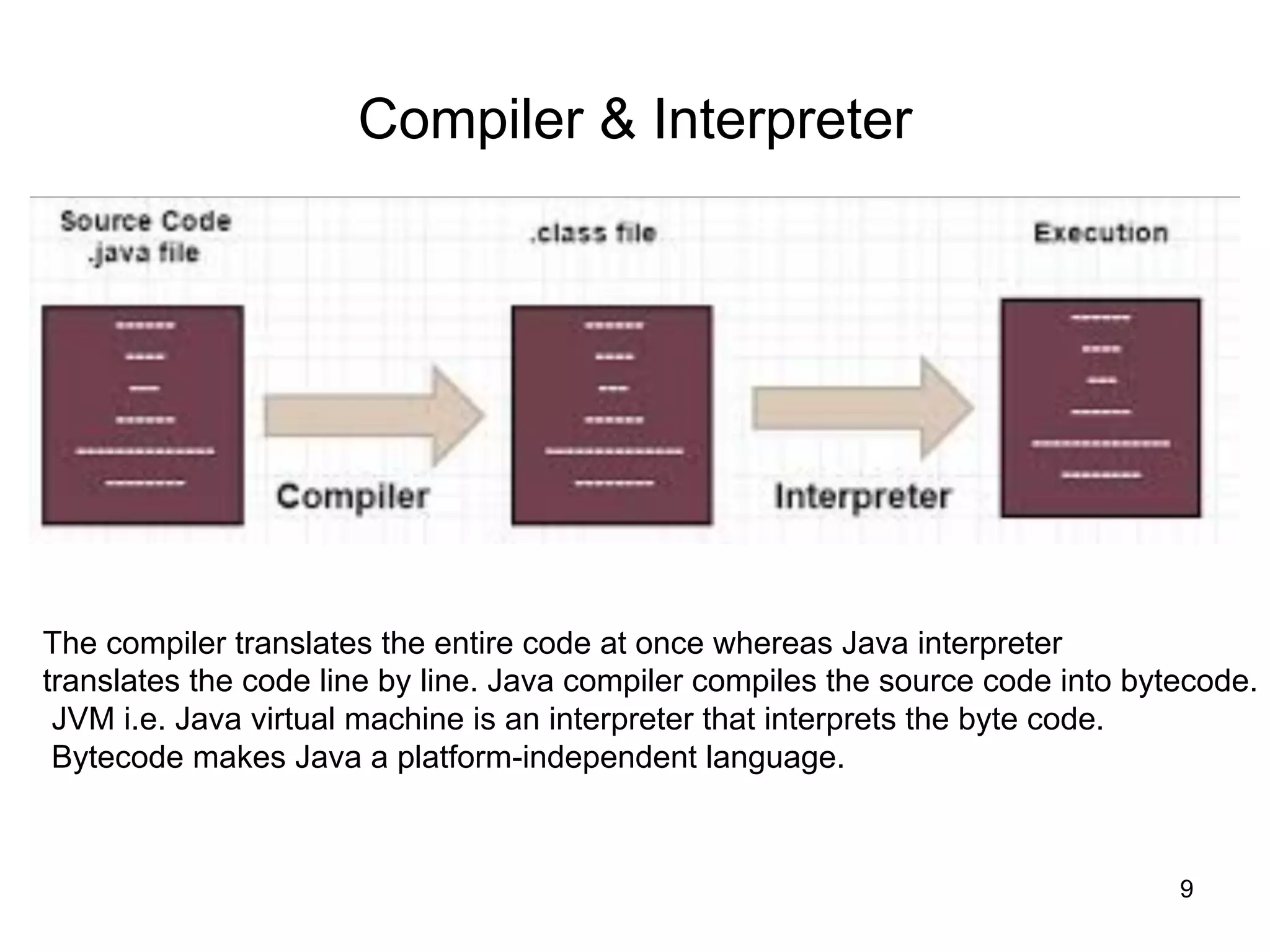
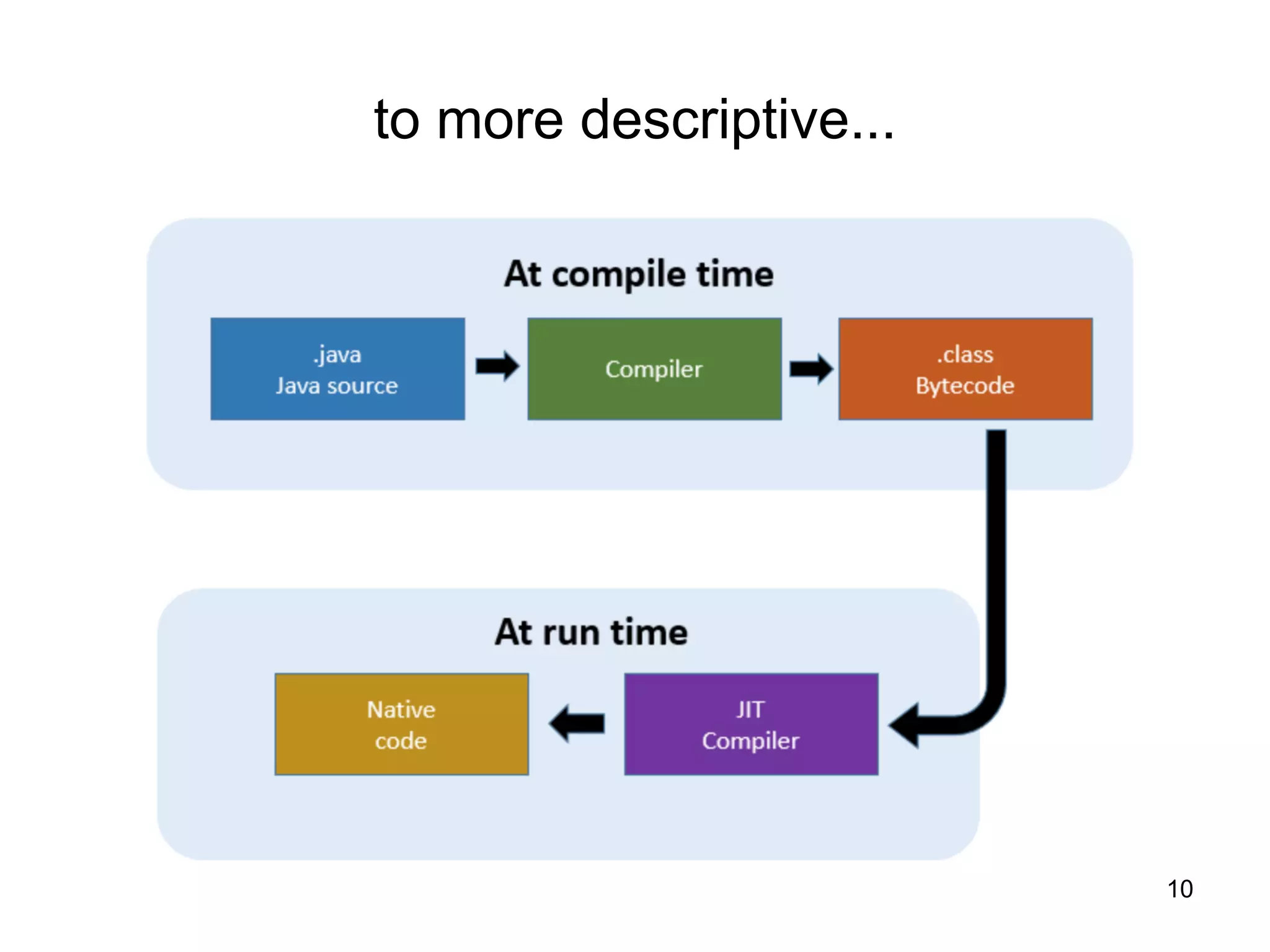
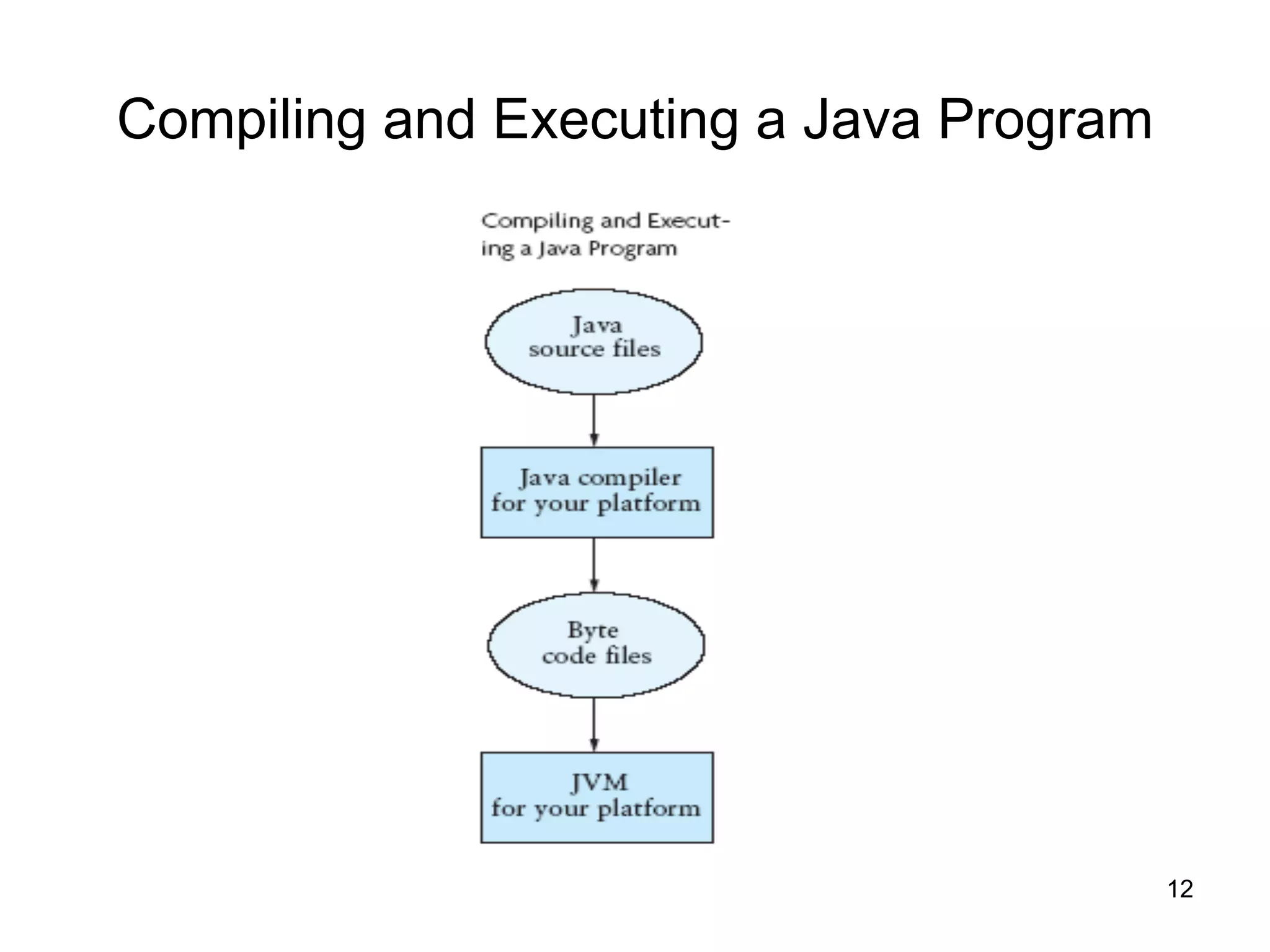
- Descriptions of important Java concepts like the JDK, JRE, JVM, compilation vs interpretation, and garbage collection.
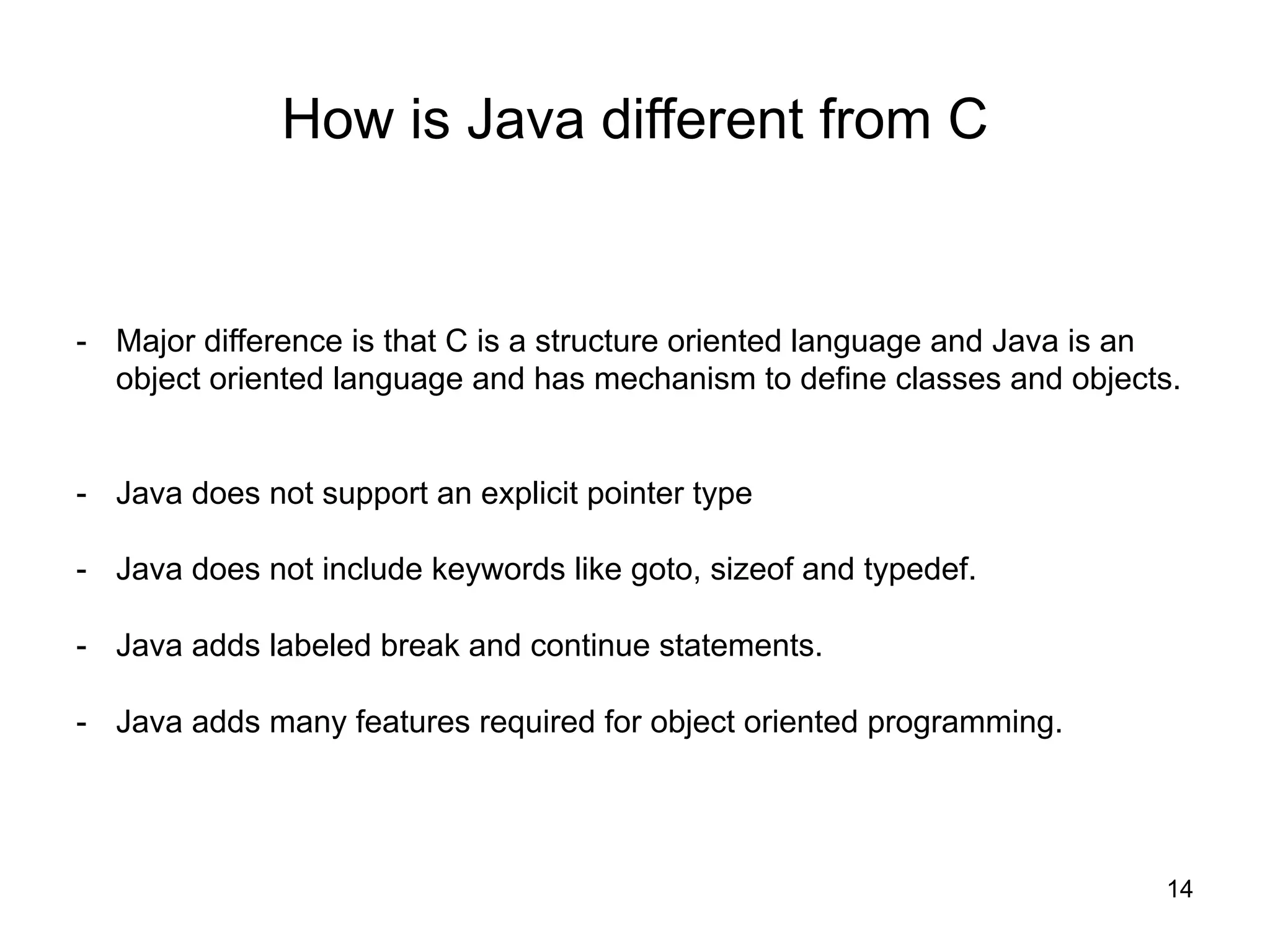
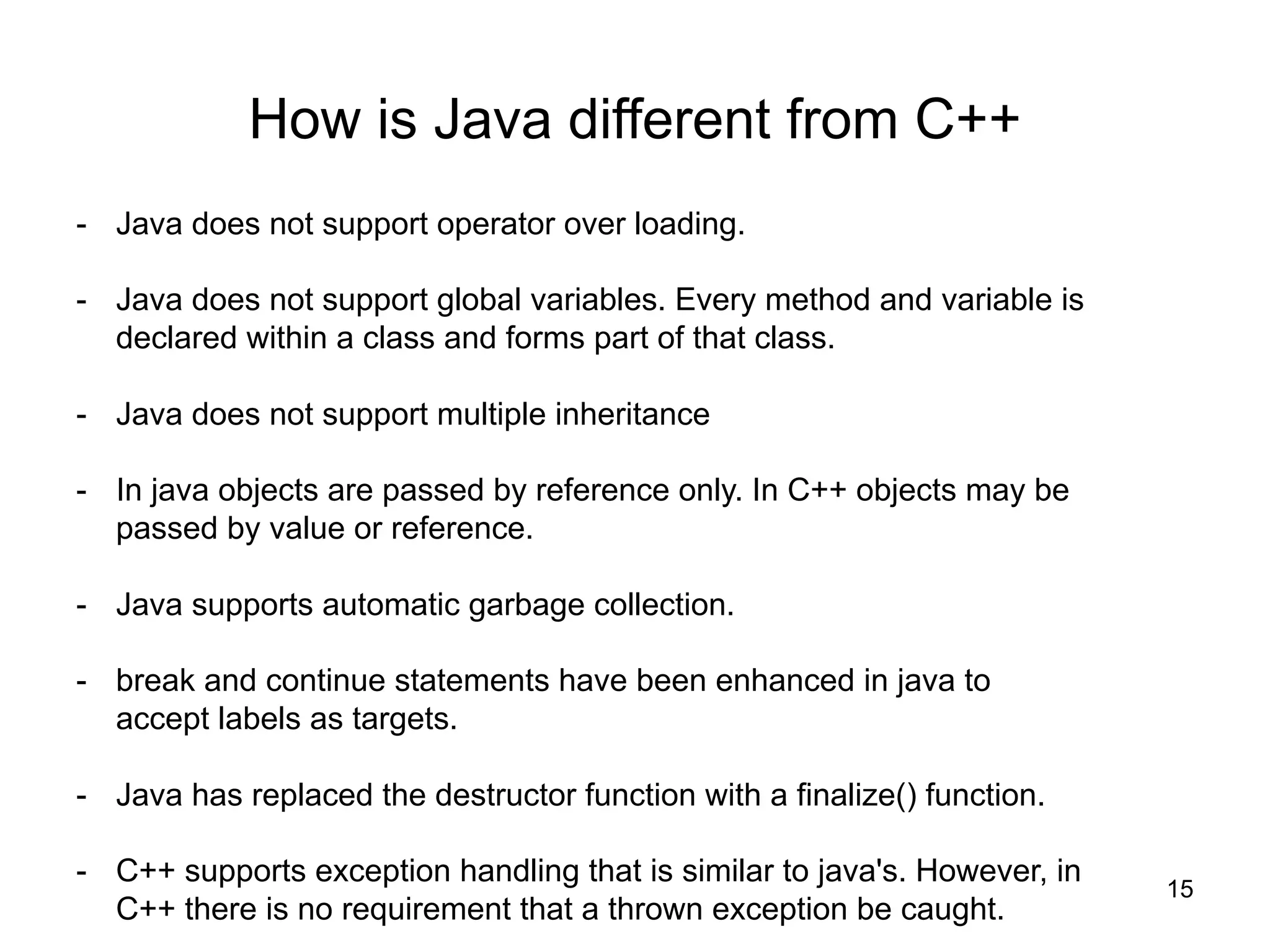
- How Java differs from C/C++ in its design as an object-oriented language.
- The importance of Java being a portable, platform-independent language demanded by the growth of