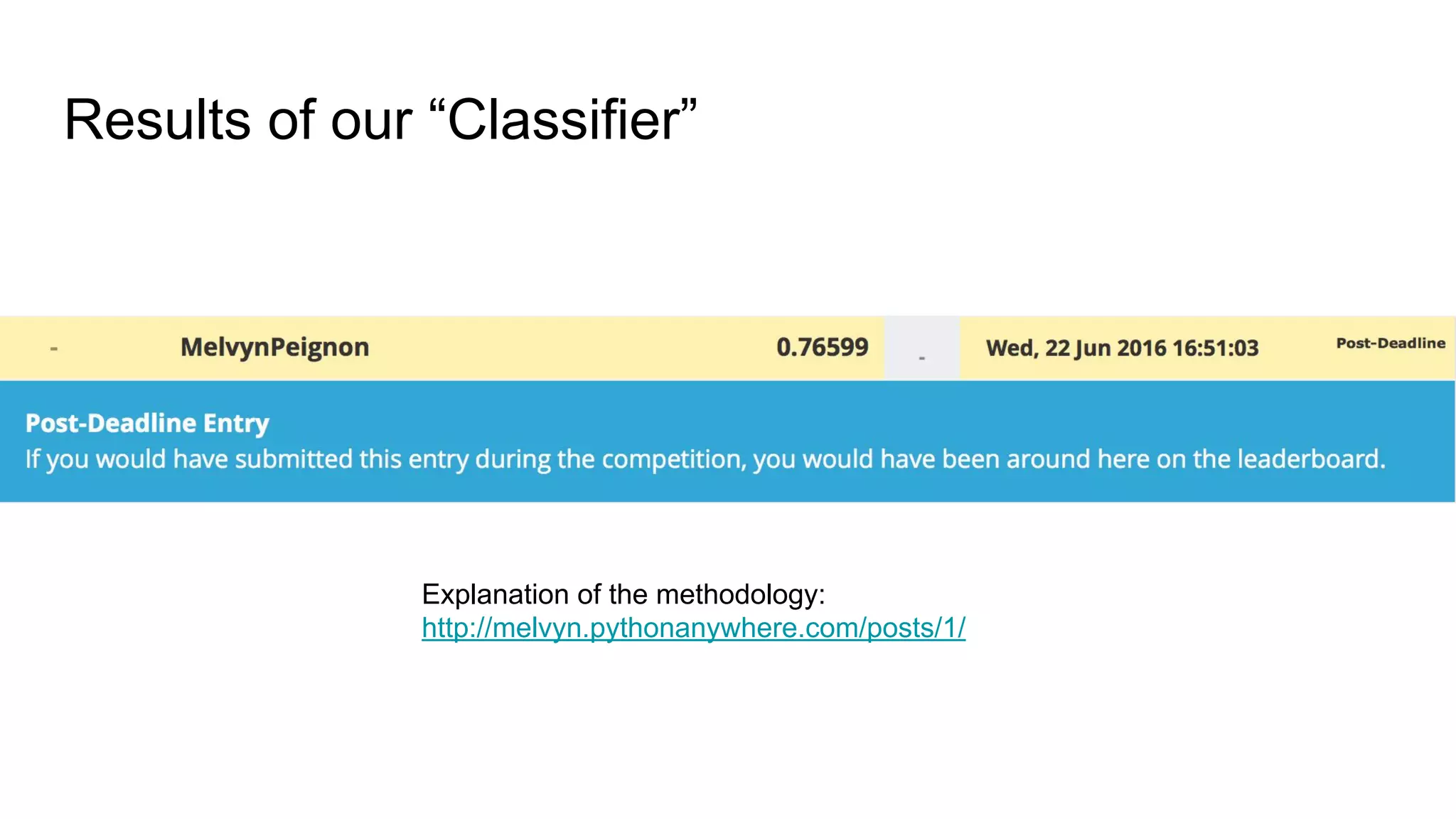
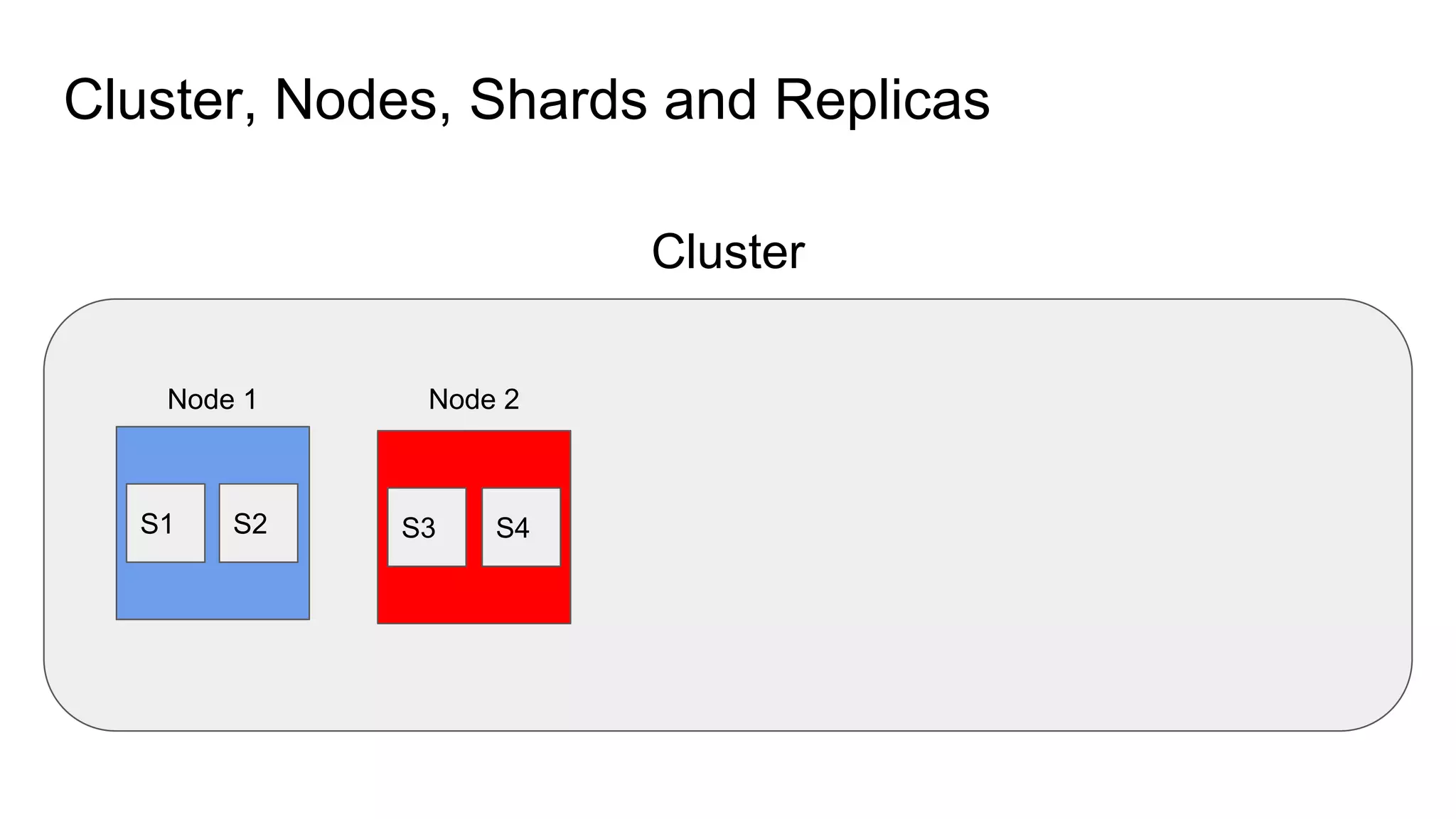
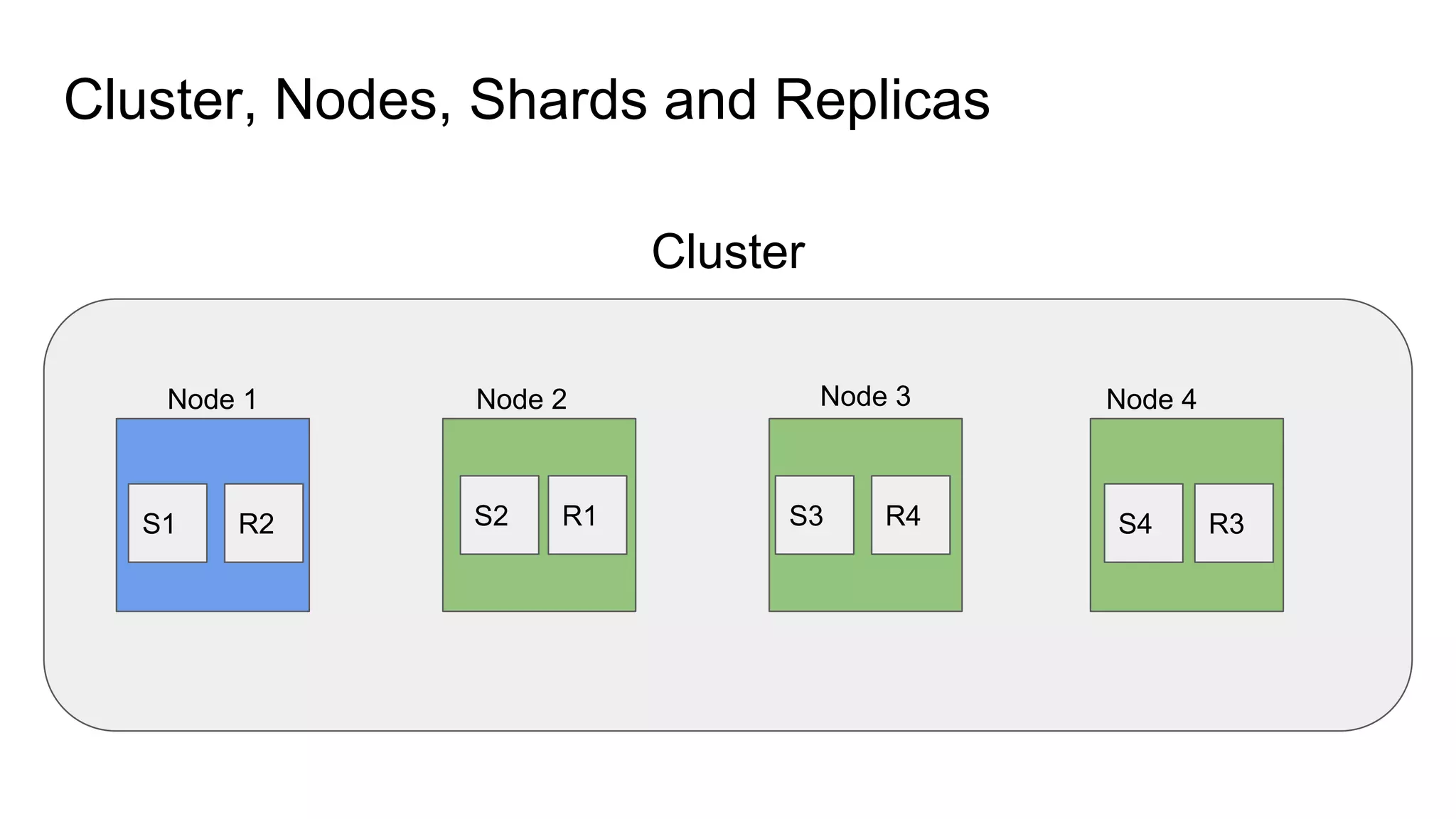
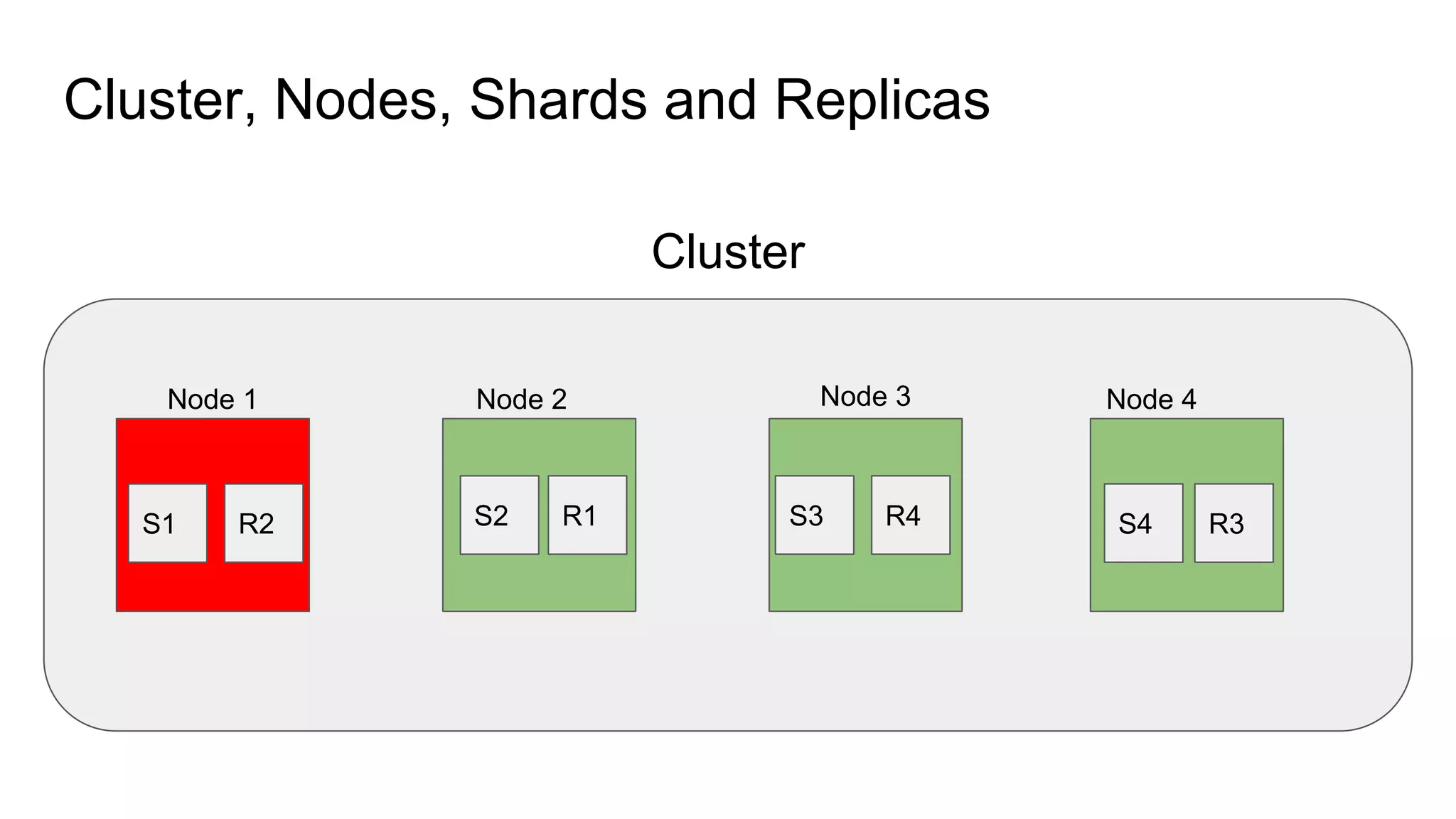
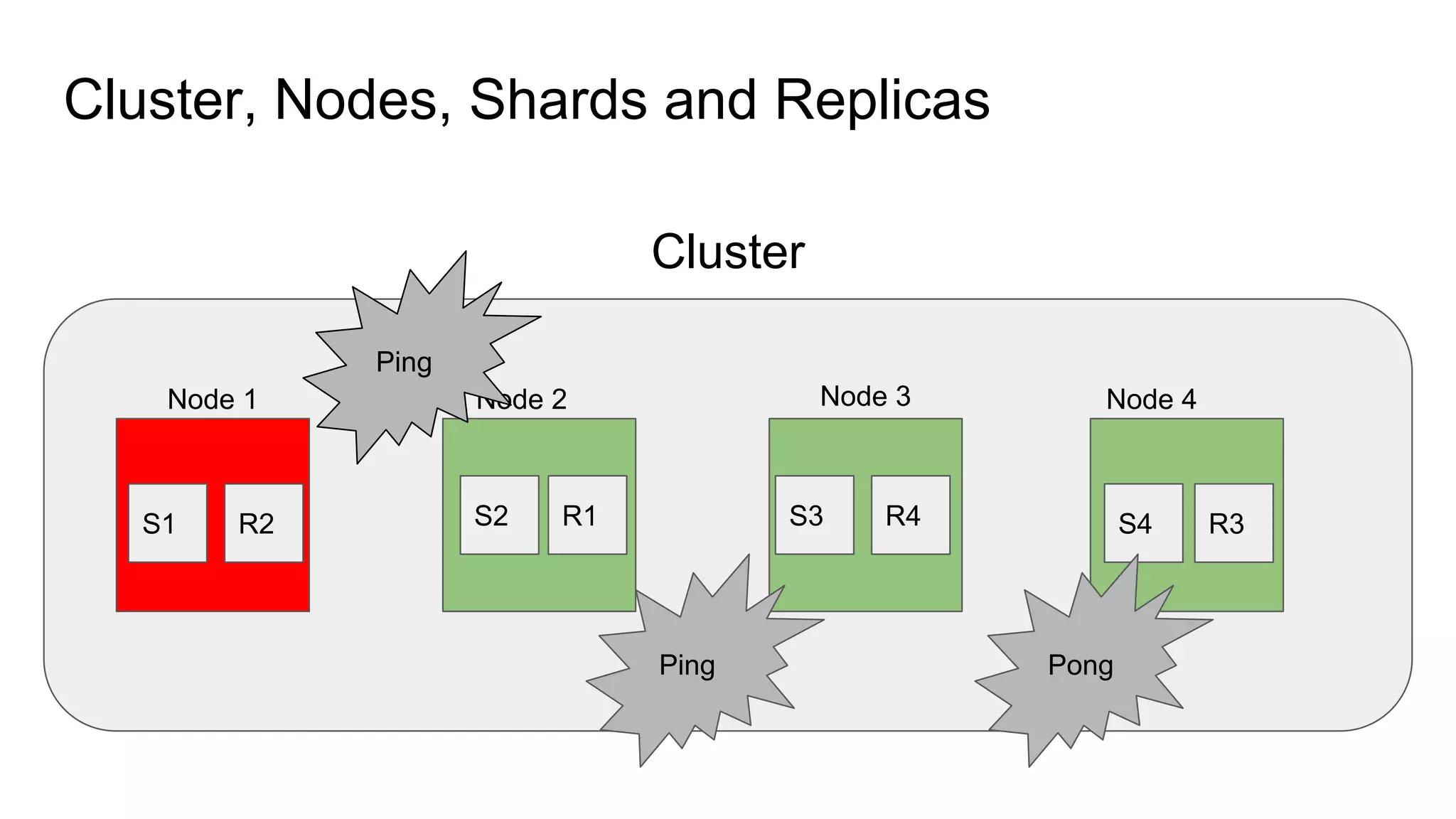
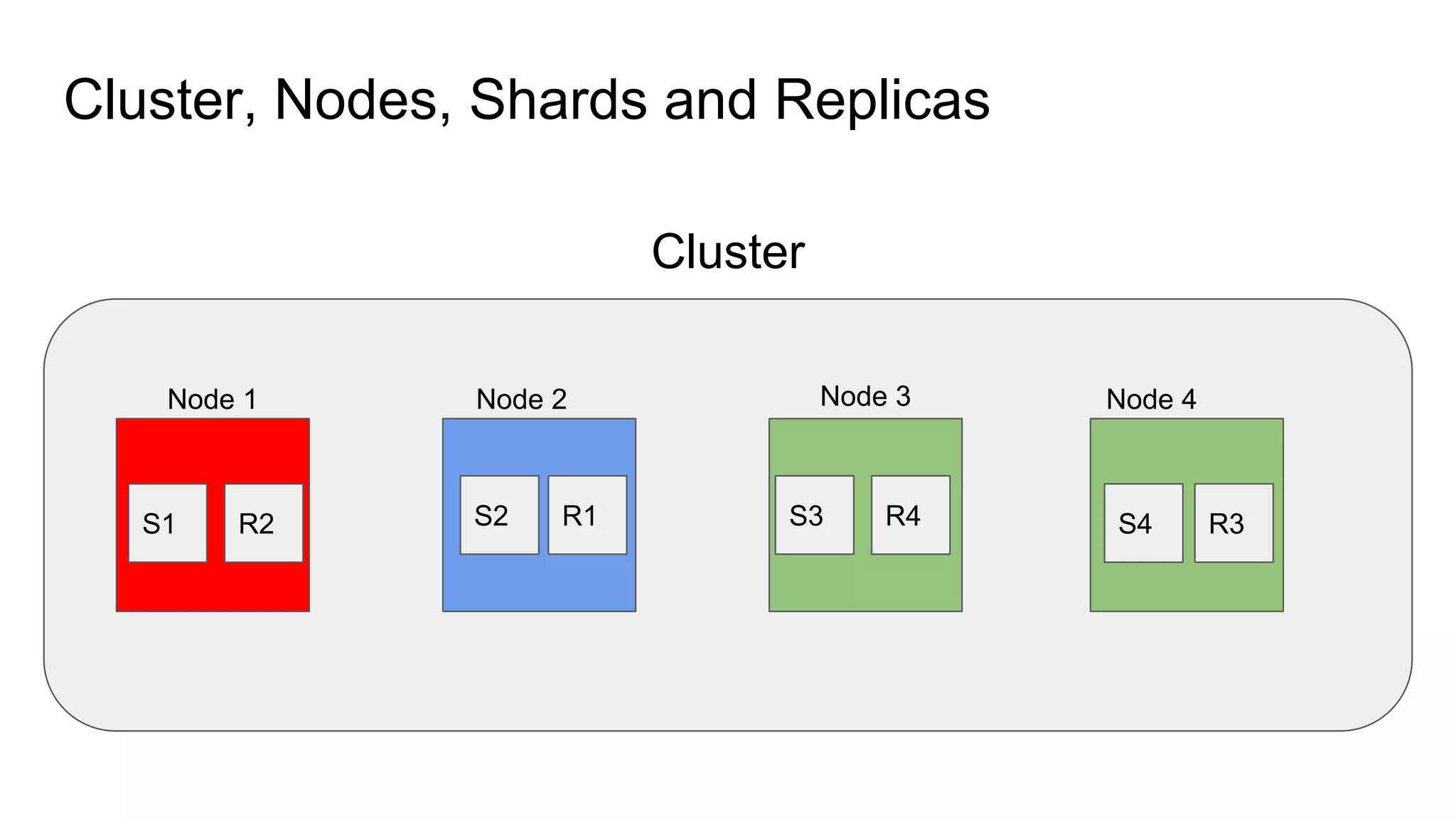
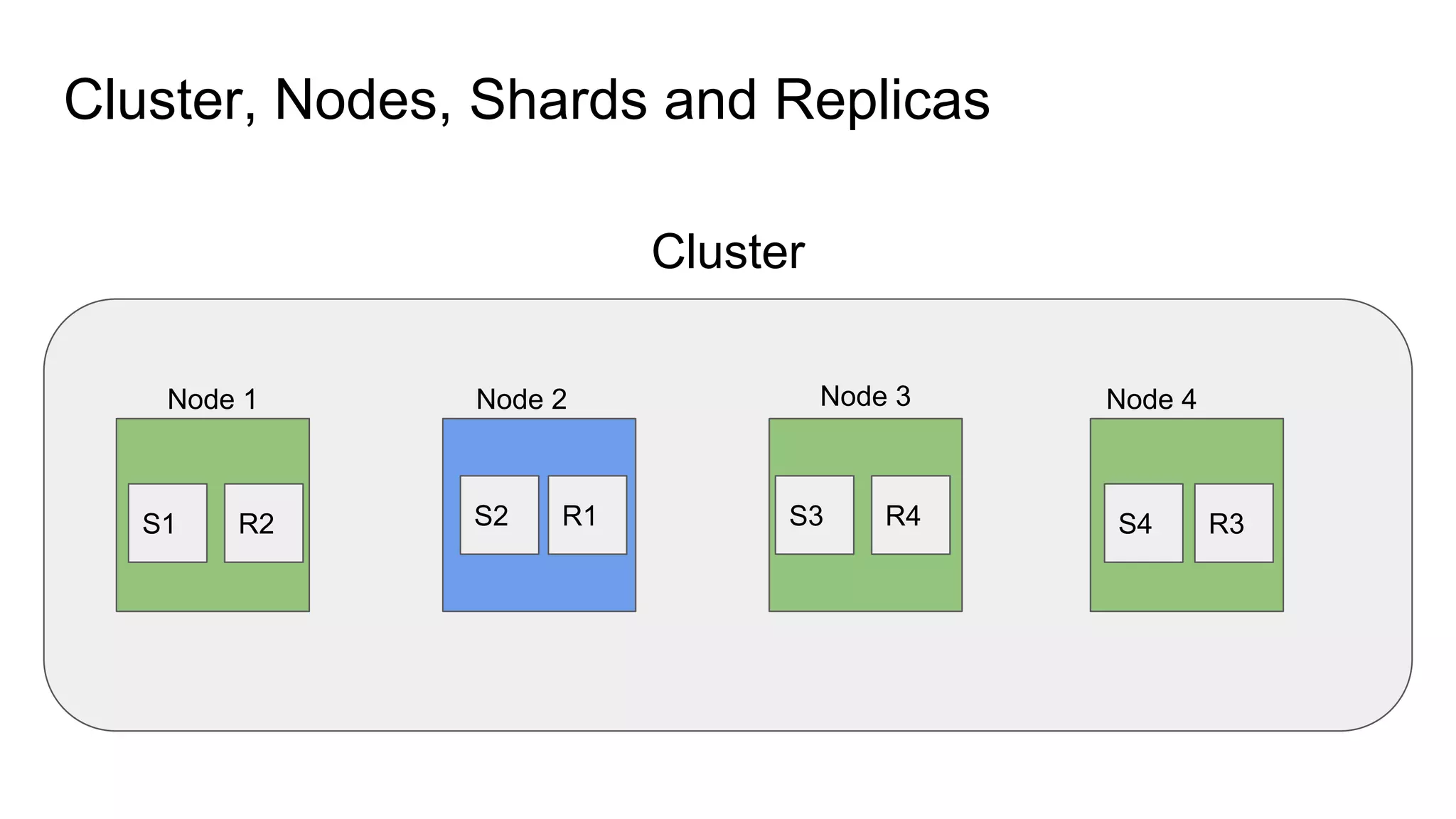
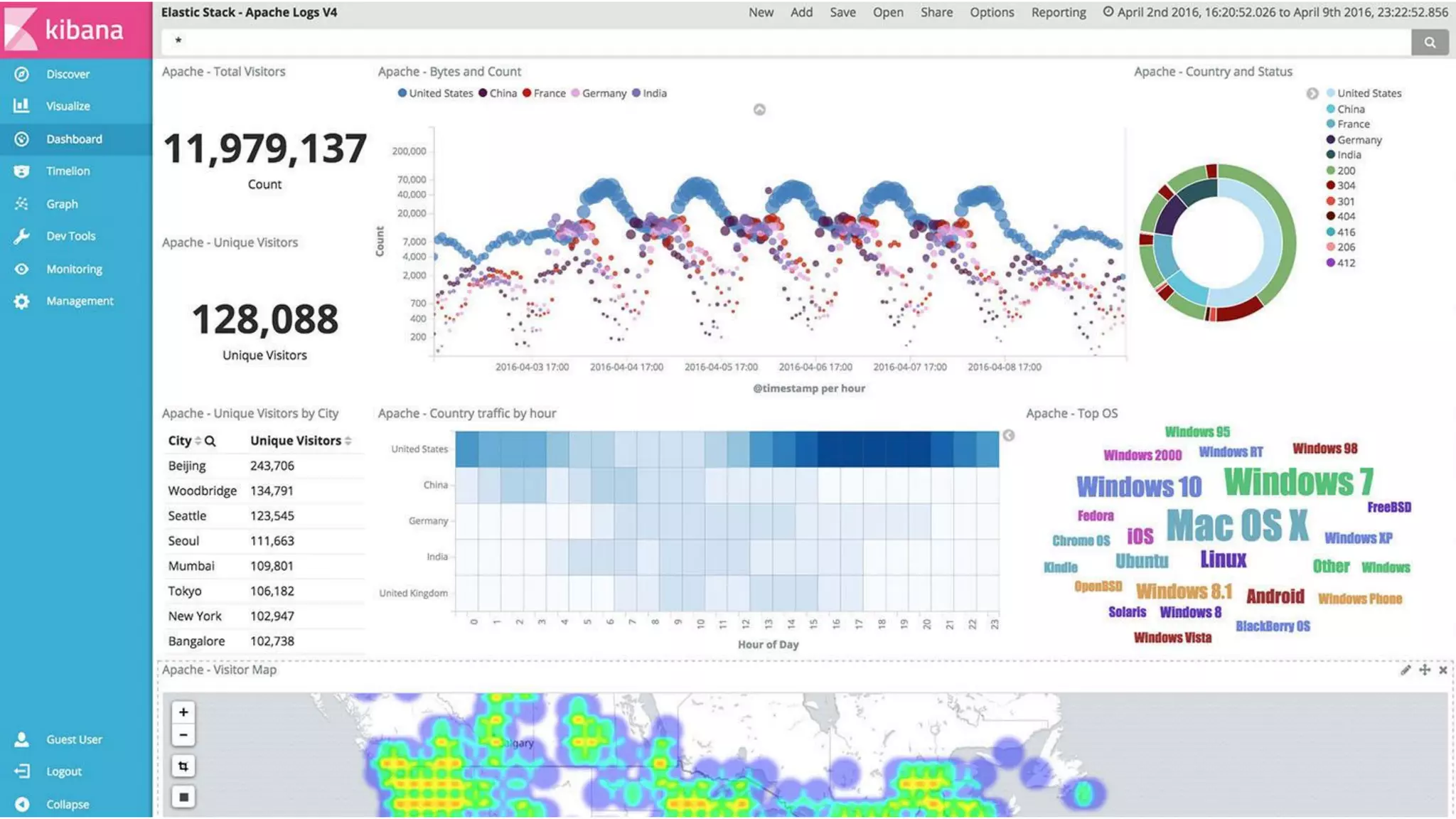
The document provides an introduction to Elasticsearch, its architecture, and associated tools like Kibana and Logstash. It covers key concepts such as indices, documents, clustering, and relevance models, while also discussing practical advice for using Elasticsearch effectively. Additionally, a demonstration using Kibana and insights into the company's revenue model are included.













![The analyzer
{“a”: [id_0], “walk”: [id_0], “in”: [id_0], “the”: [id_0], “wood”: [id_0]}
Standard Analyzer](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductionto-170630104647/75/Introduction-to-elasticsearch-24-2048.jpg)
![The analyzer
{“a”: [id_0, id_1], “walk”: [id_0], “in”: [id_0], “the”: [id_0],
“wood”: [id_0], “probability”:[id_1], “complete”:[id_1],
“guide”:[id_1]}
Standard Analyzer](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductionto-170630104647/75/Introduction-to-elasticsearch-25-2048.jpg)
![The analyzer
{“a”: [id_0, id_1], “walk”: [id_0], “in”: [id_0],
“the”: [id_0], “wood”: [id_0], “probability”:[id_1],
“complete”:[id_1], “guide”:[id_1]}
[id_0, id_1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductionto-170630104647/75/Introduction-to-elasticsearch-26-2048.jpg)
![The analyzer
{“a”: [id_0, id_1], “walk”: [id_0], “in”: [id_0],
“the”: [id_0], “wood”: [id_0],
“probability”:[id_1], “complete”:[id_1],
“guide”:[id_1]}
[]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductionto-170630104647/75/Introduction-to-elasticsearch-27-2048.jpg)
![The english analyzer
English Analyzer
{“walk”: [id_0], “wood”: [id_0]}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductionto-170630104647/75/Introduction-to-elasticsearch-28-2048.jpg)
![The english analyzer
{ “walk”: [id_0], “wood”: [id_0]}
[]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductionto-170630104647/75/Introduction-to-elasticsearch-29-2048.jpg)


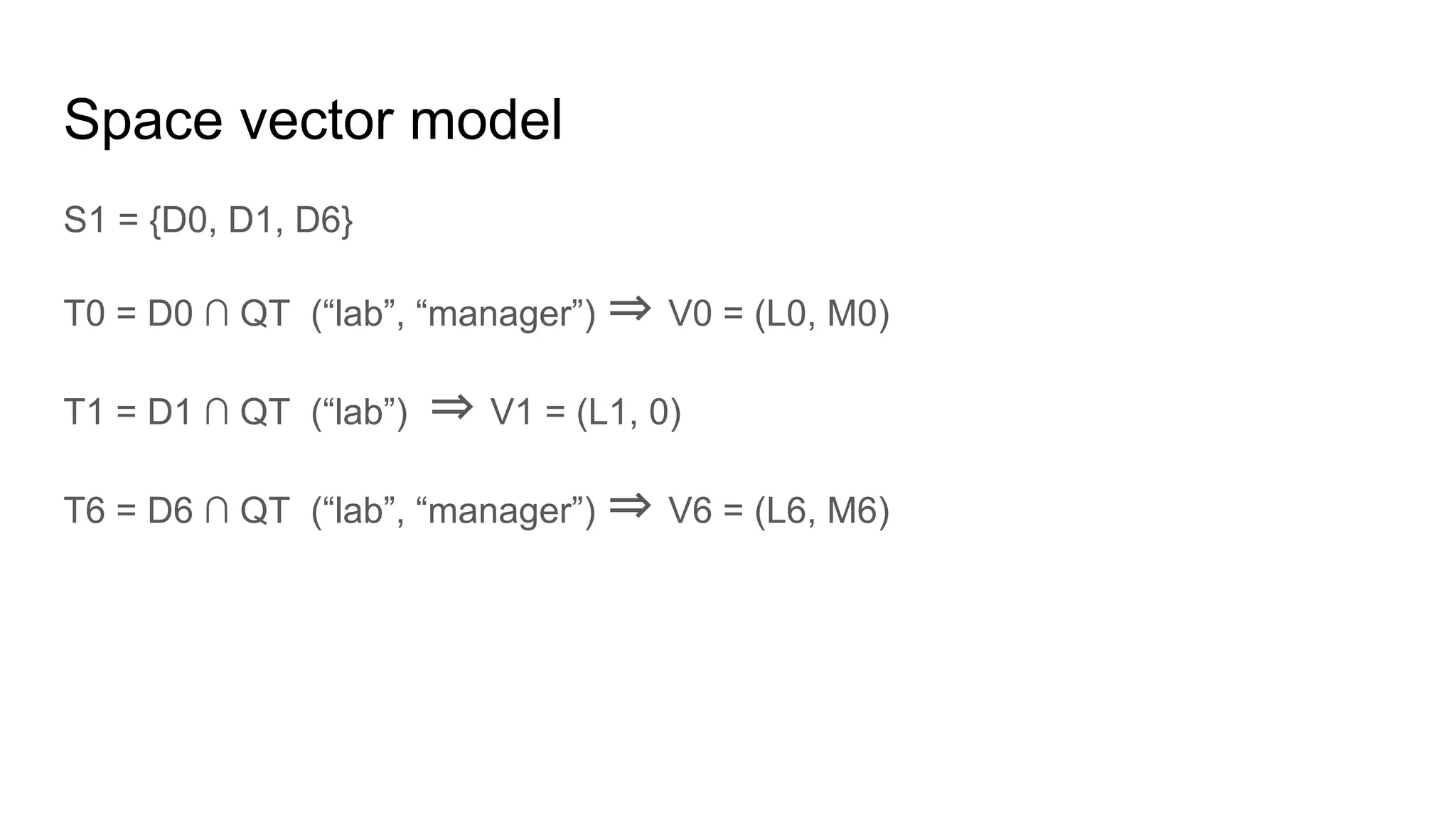
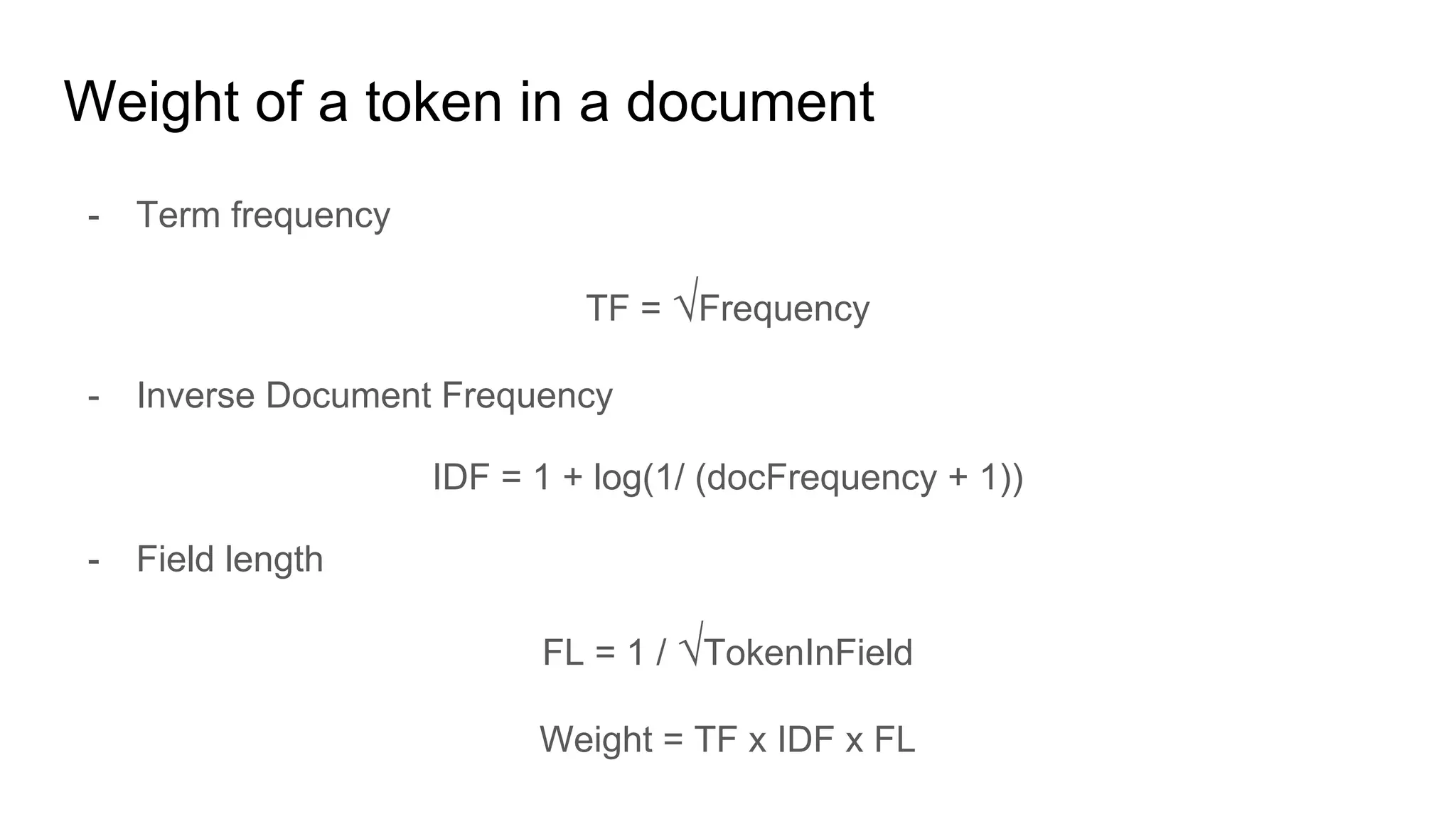
![Relevance
Vq = [1, 1.47]
V0 = [0.81, 0.85]
V1 = [0.37, 0]
V6 = [0.8, 1.2]
Relevance(Vq, Vx) = cos(Vq, Vx) =
(Vq . Vx) / (॥Vq॥.॥Vx॥)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductionto-170630104647/75/Introduction-to-elasticsearch-34-2048.jpg)