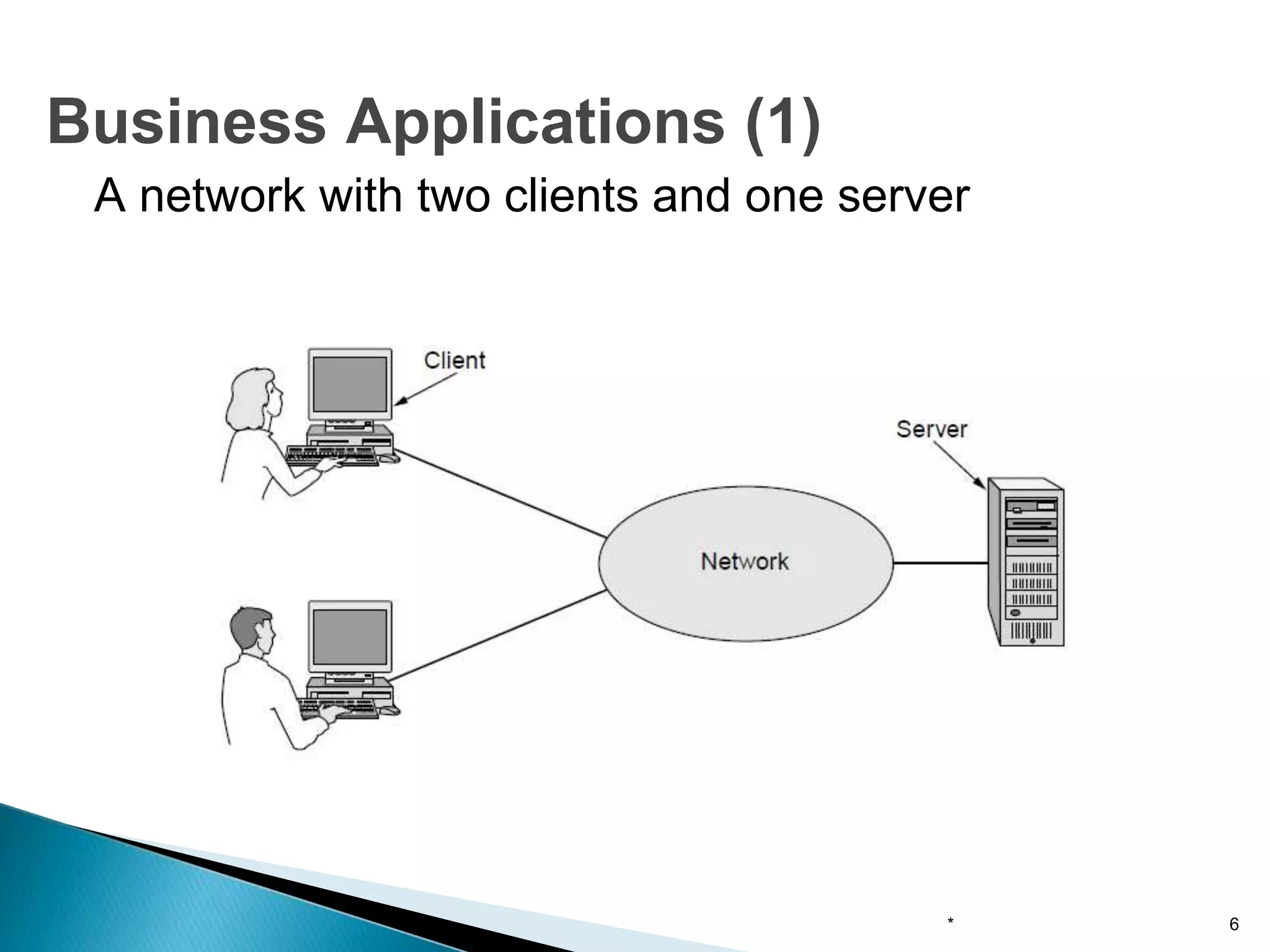
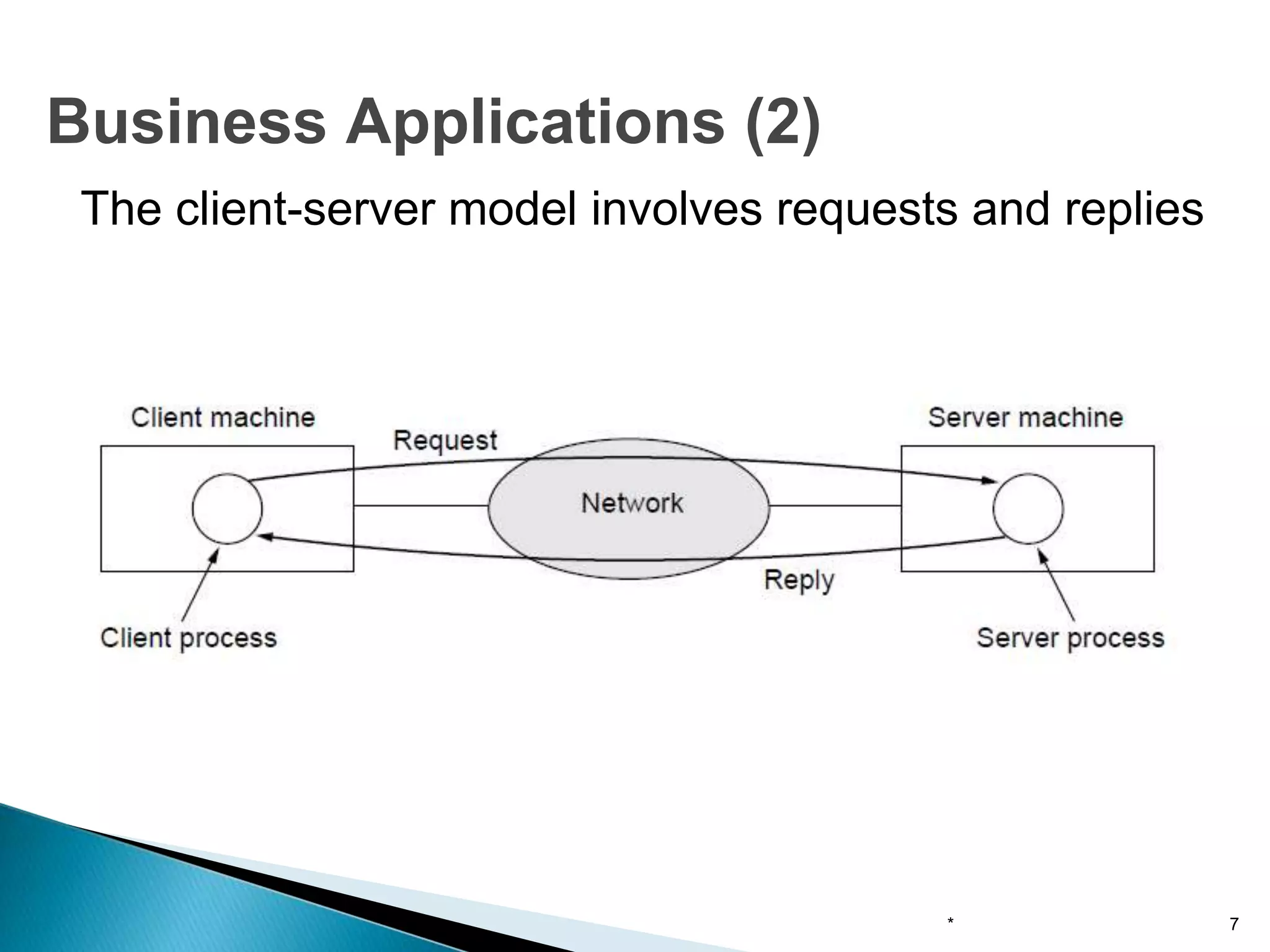
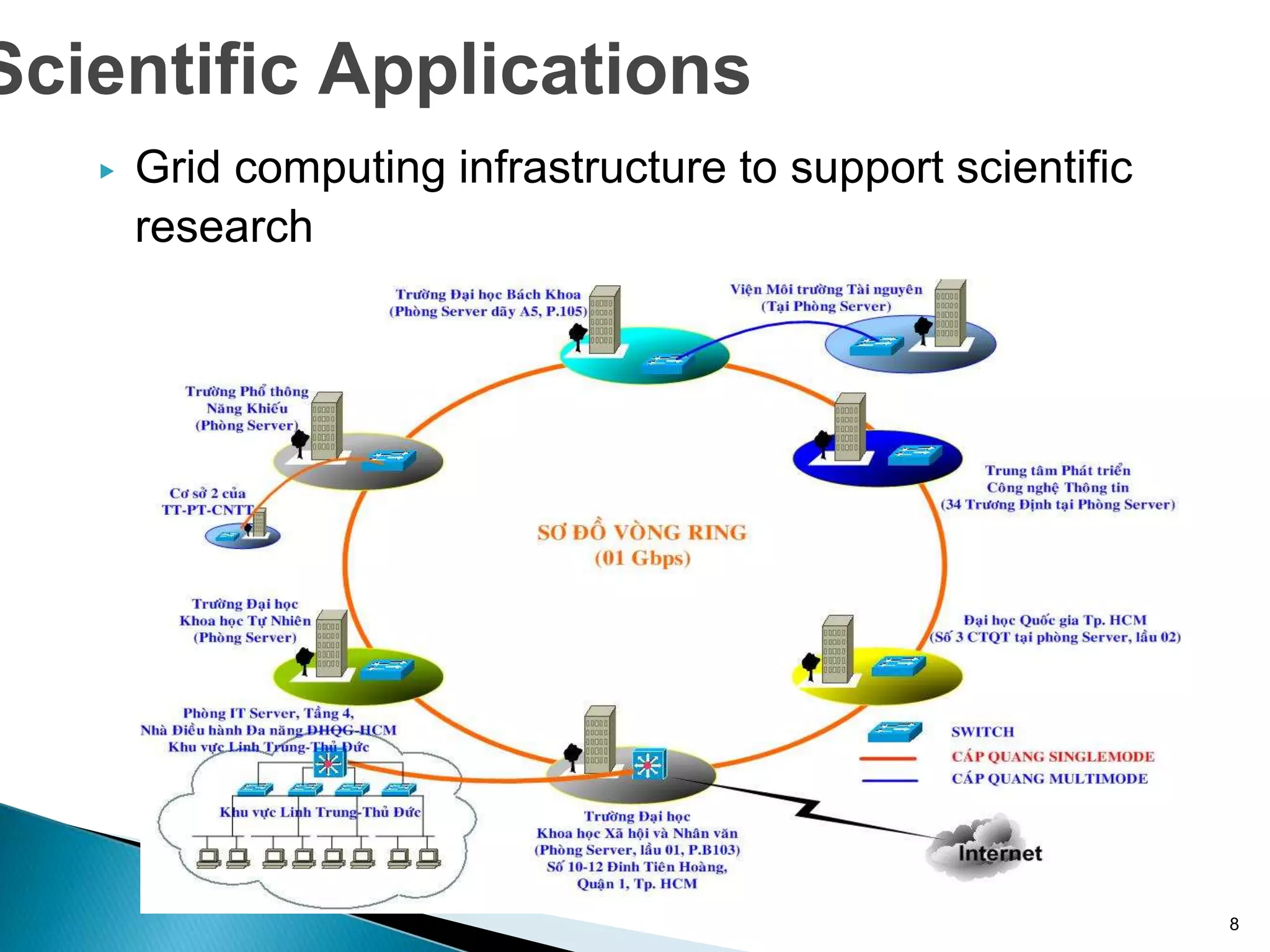
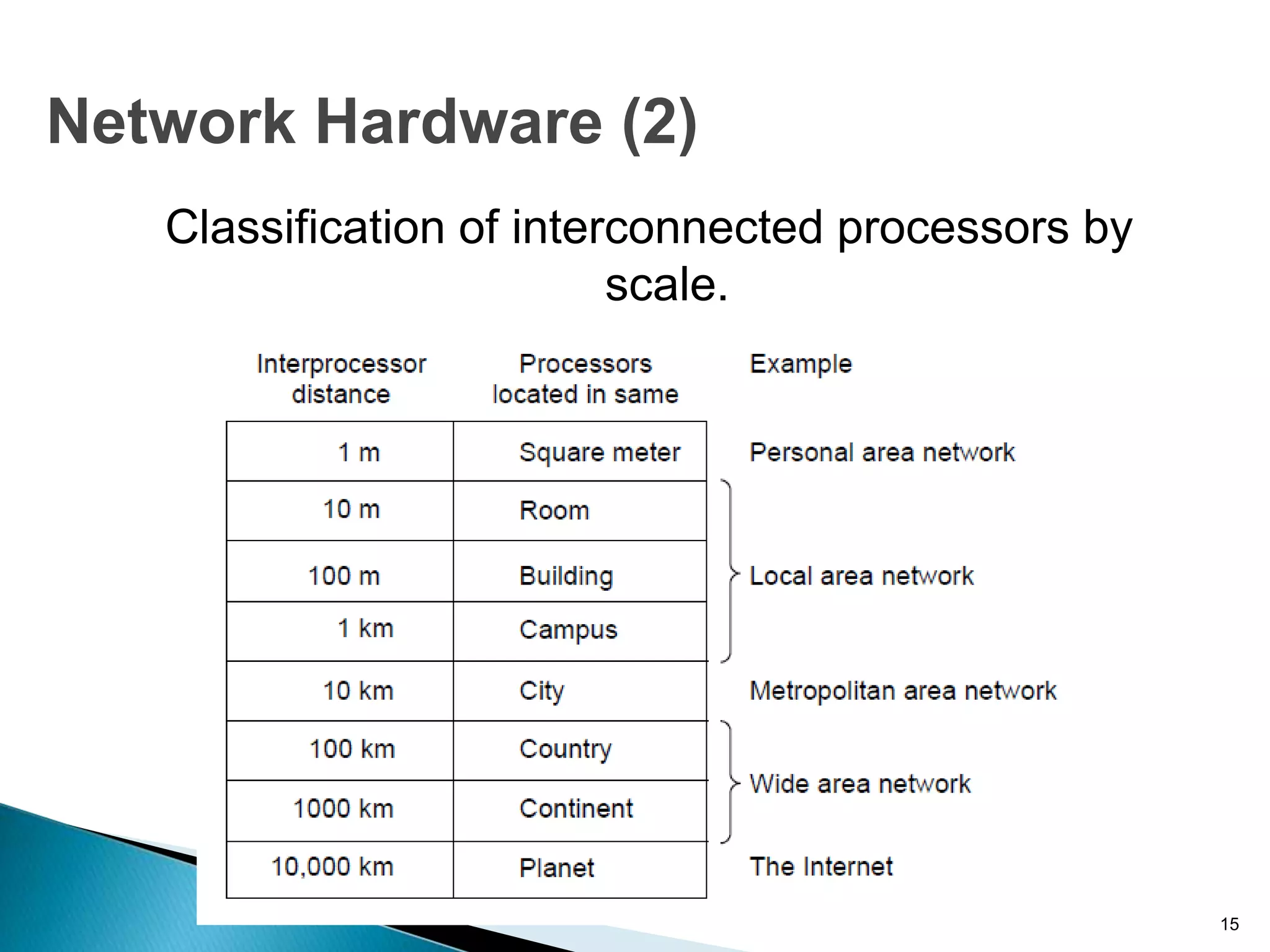
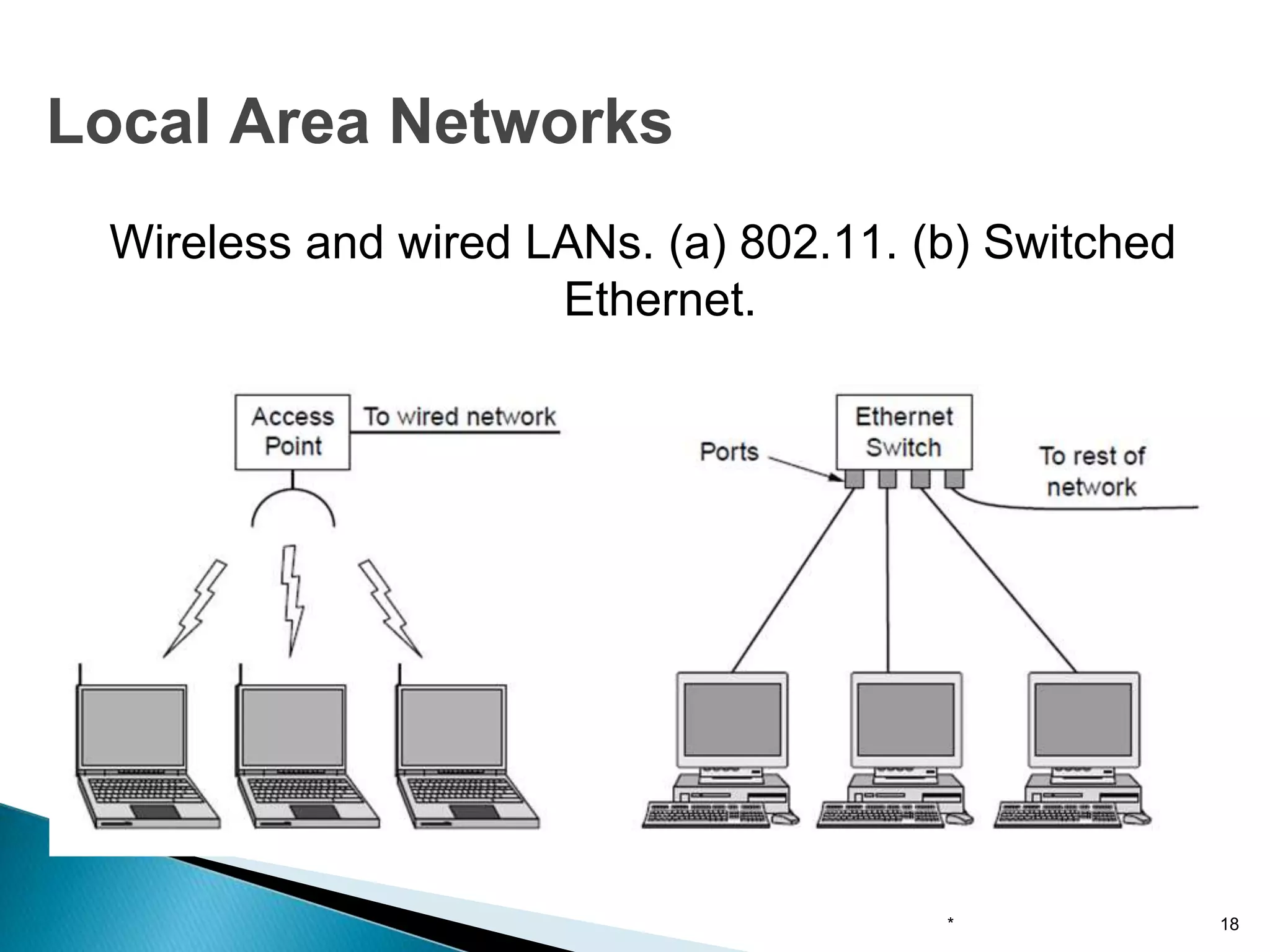
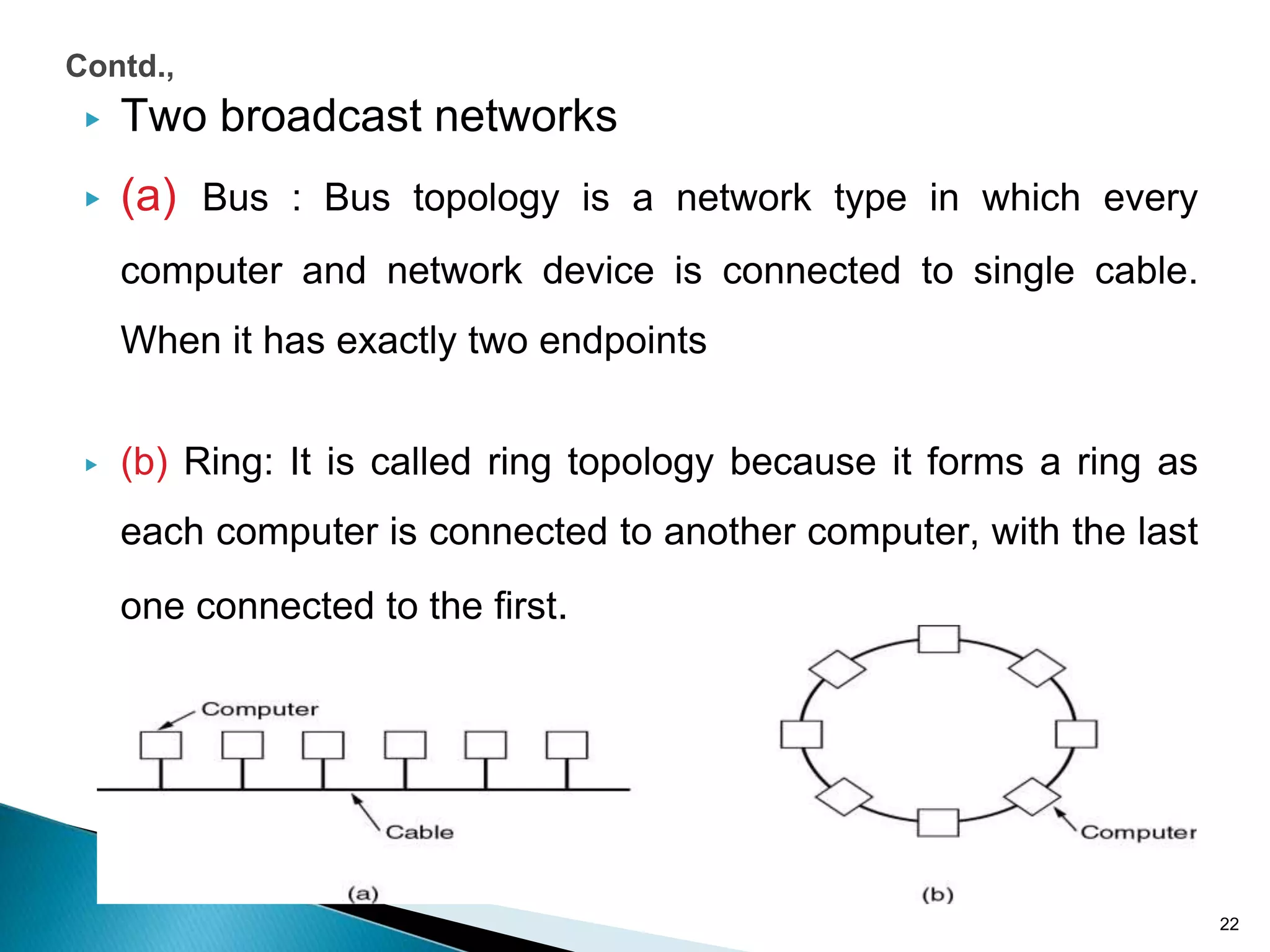
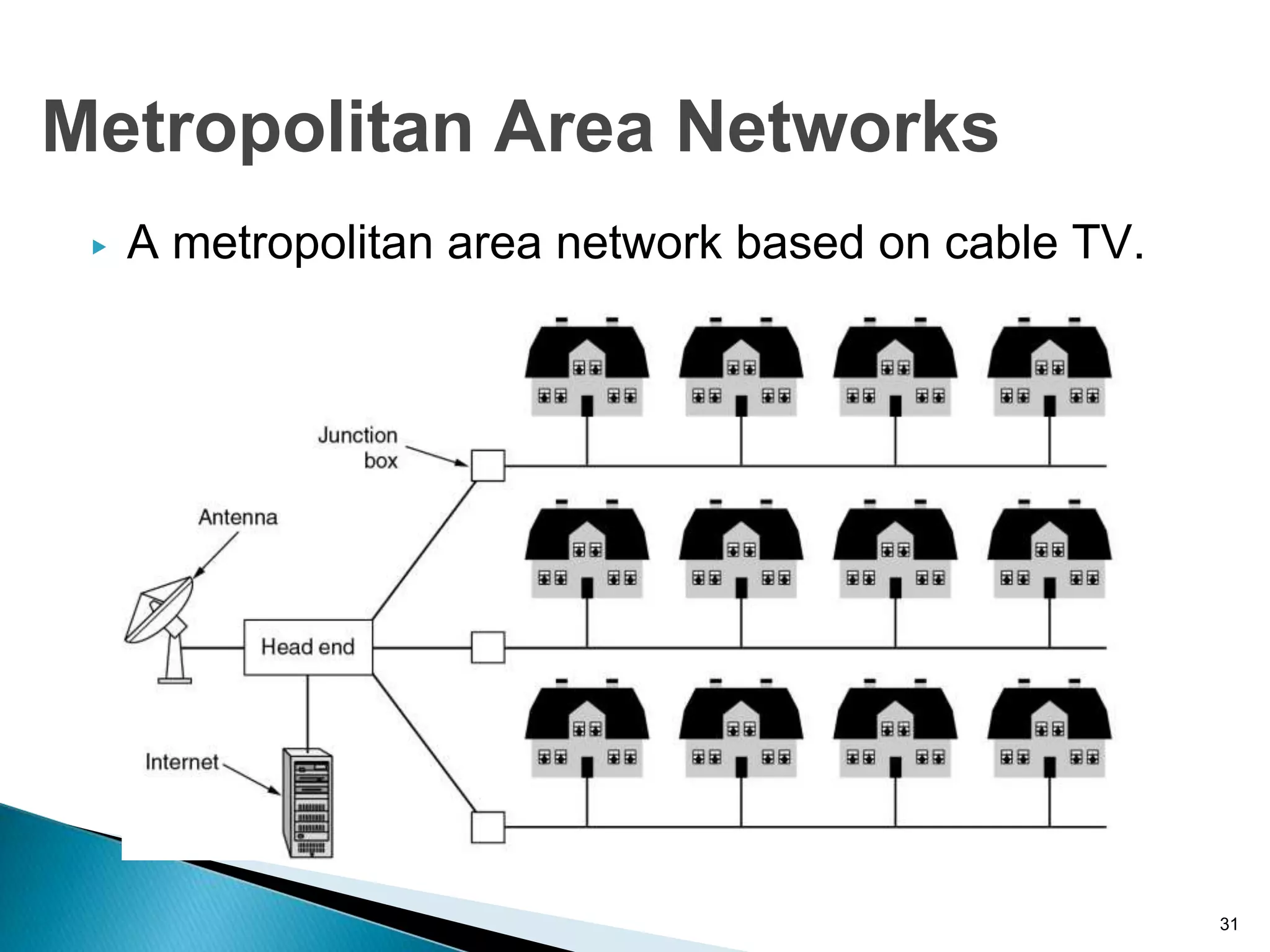
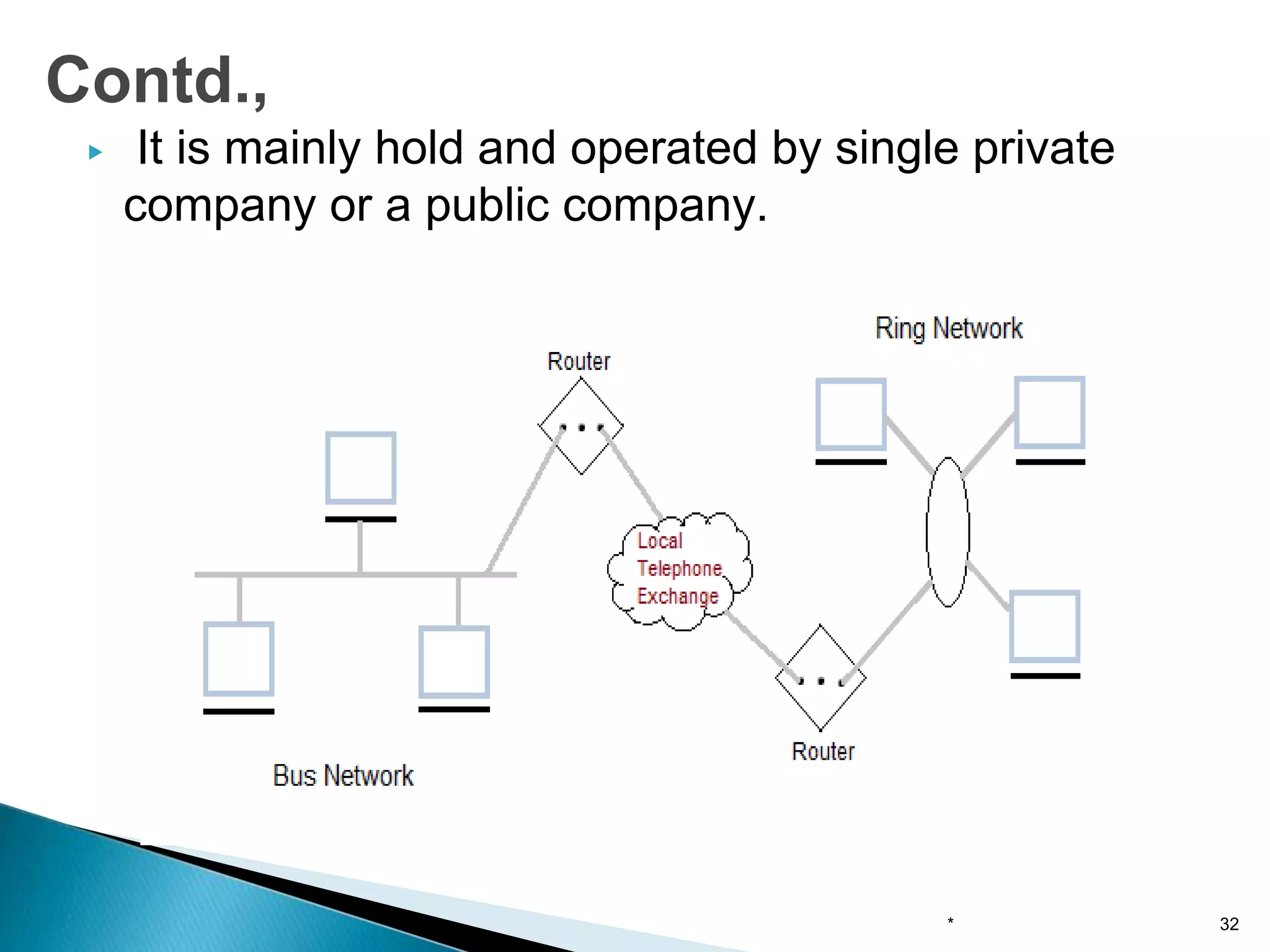
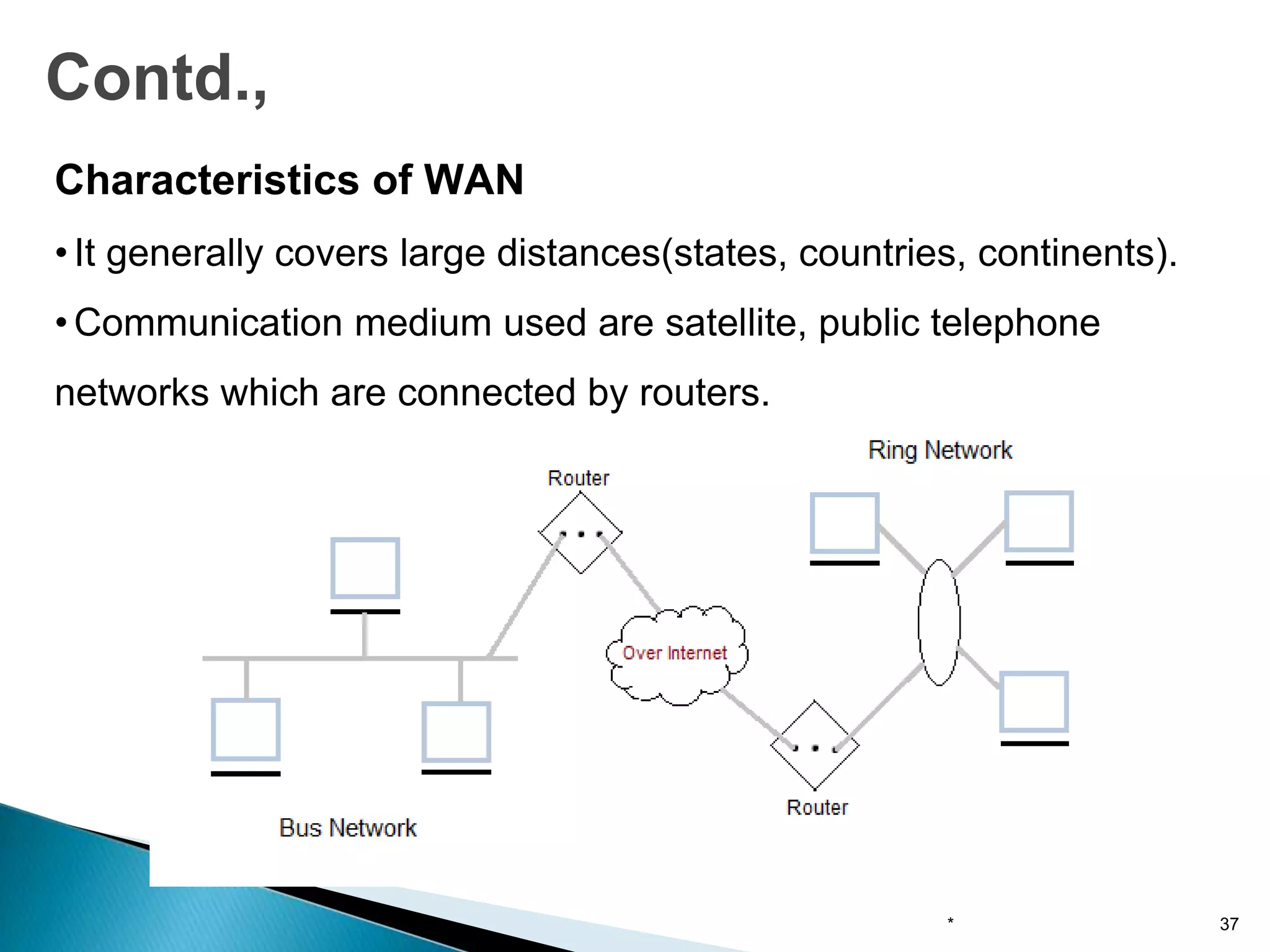
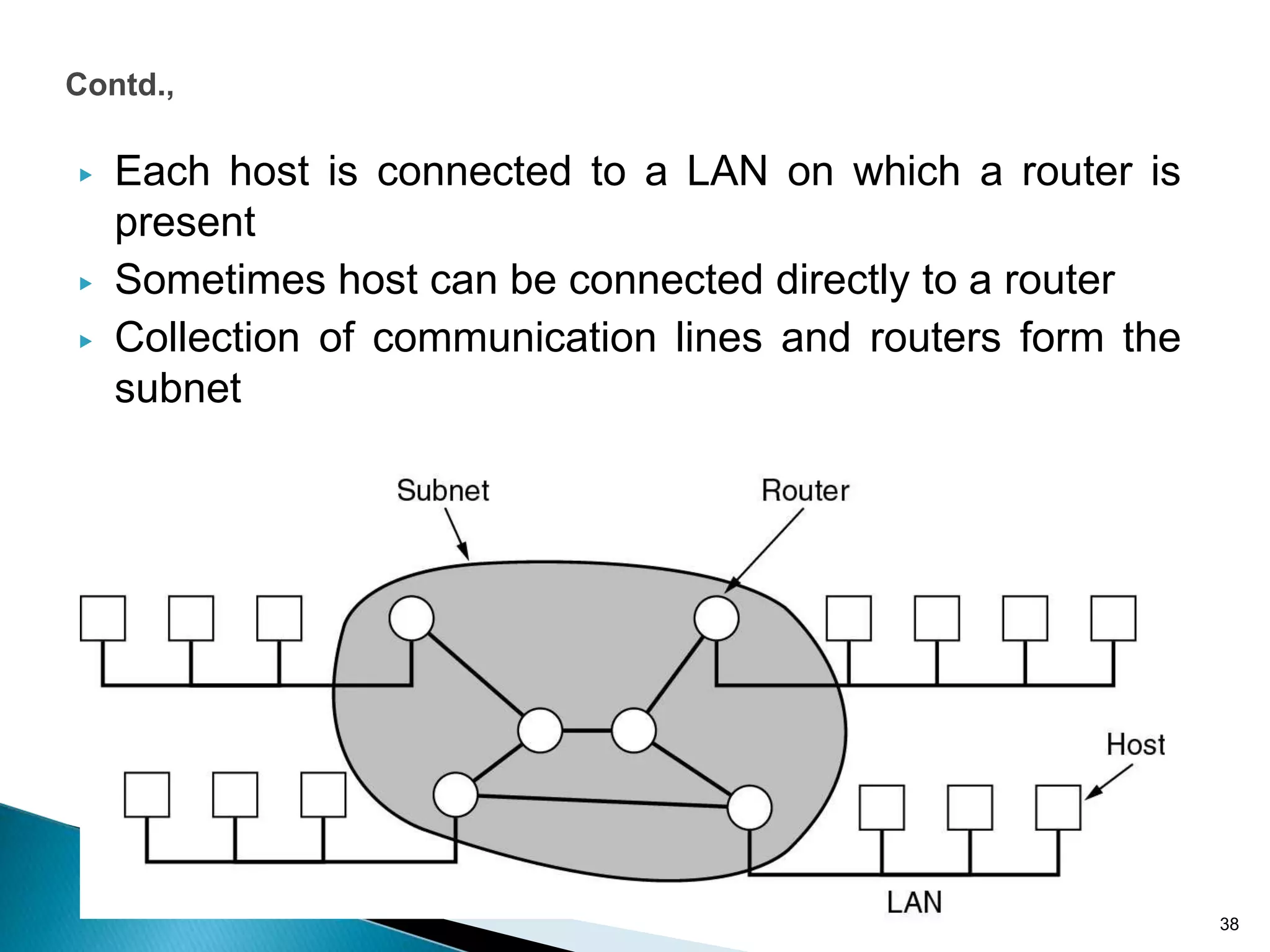
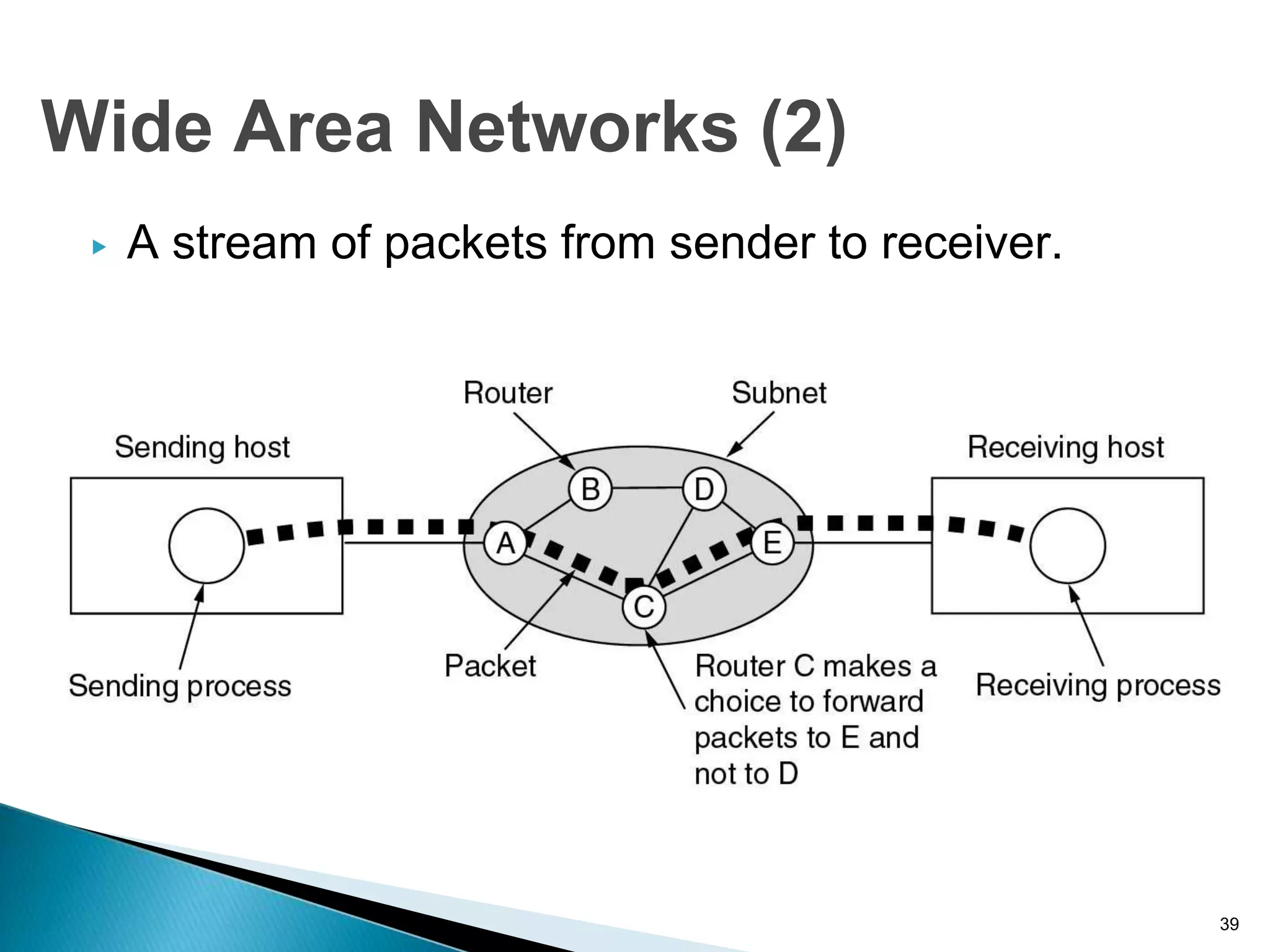
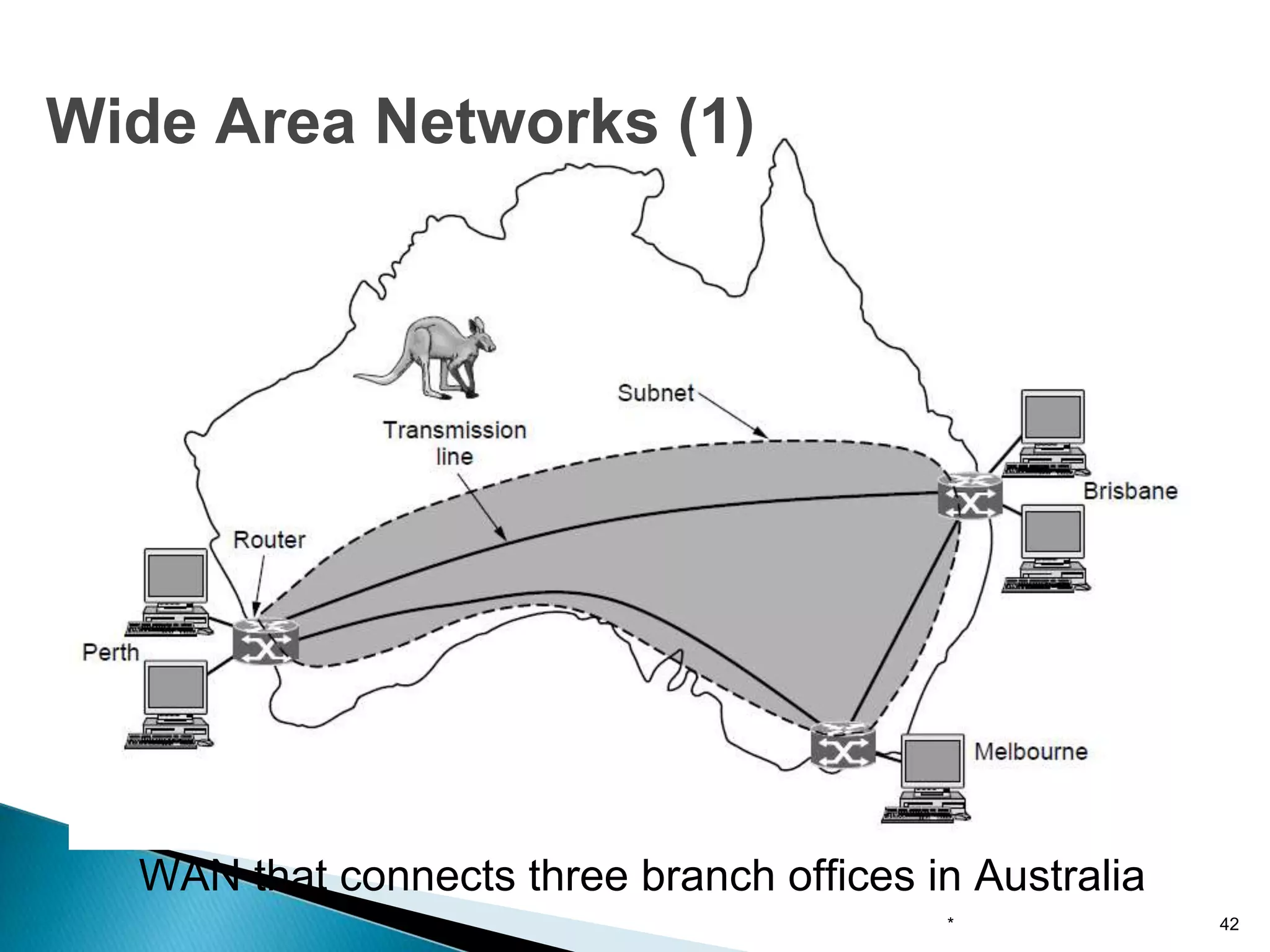
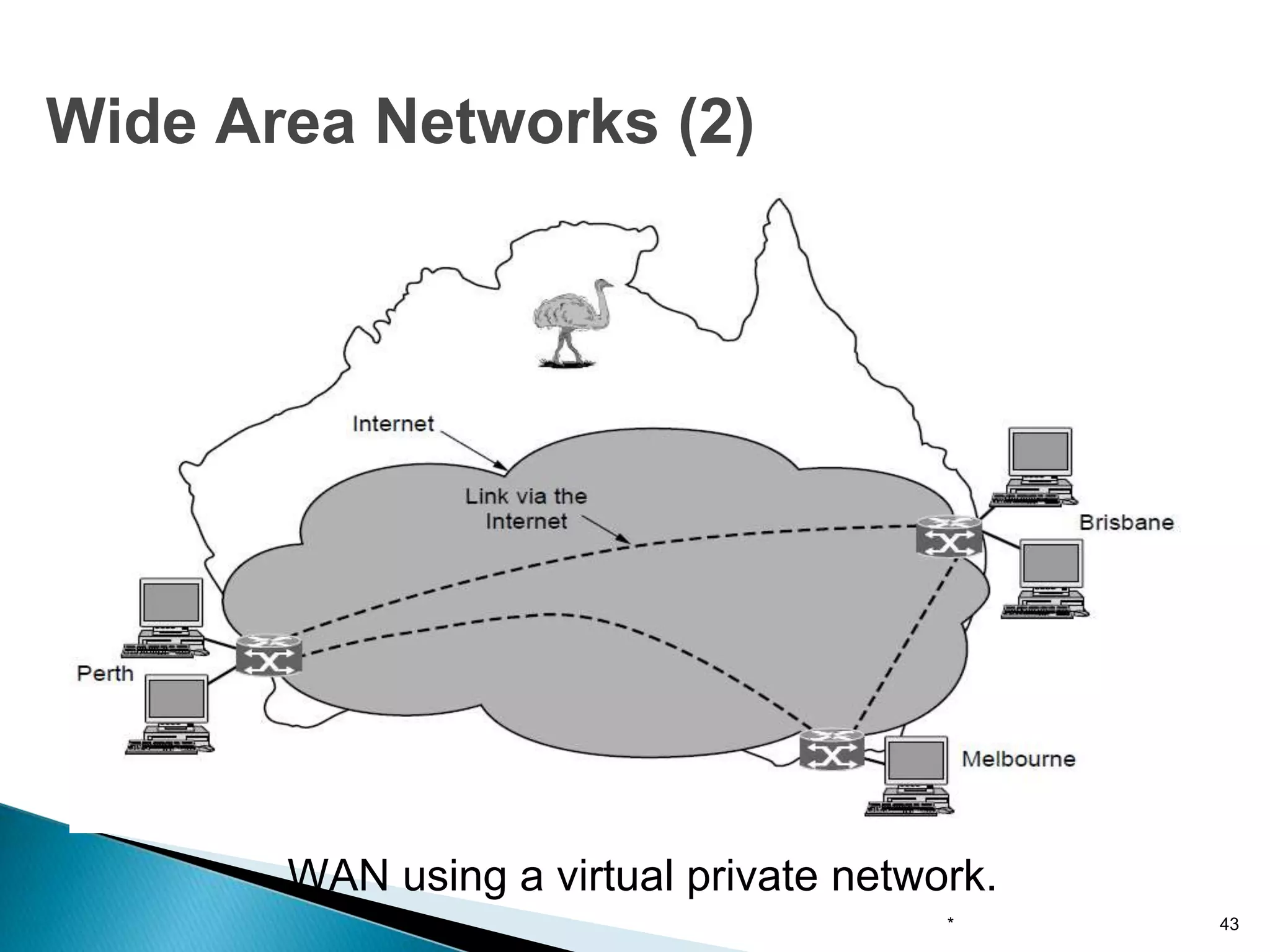
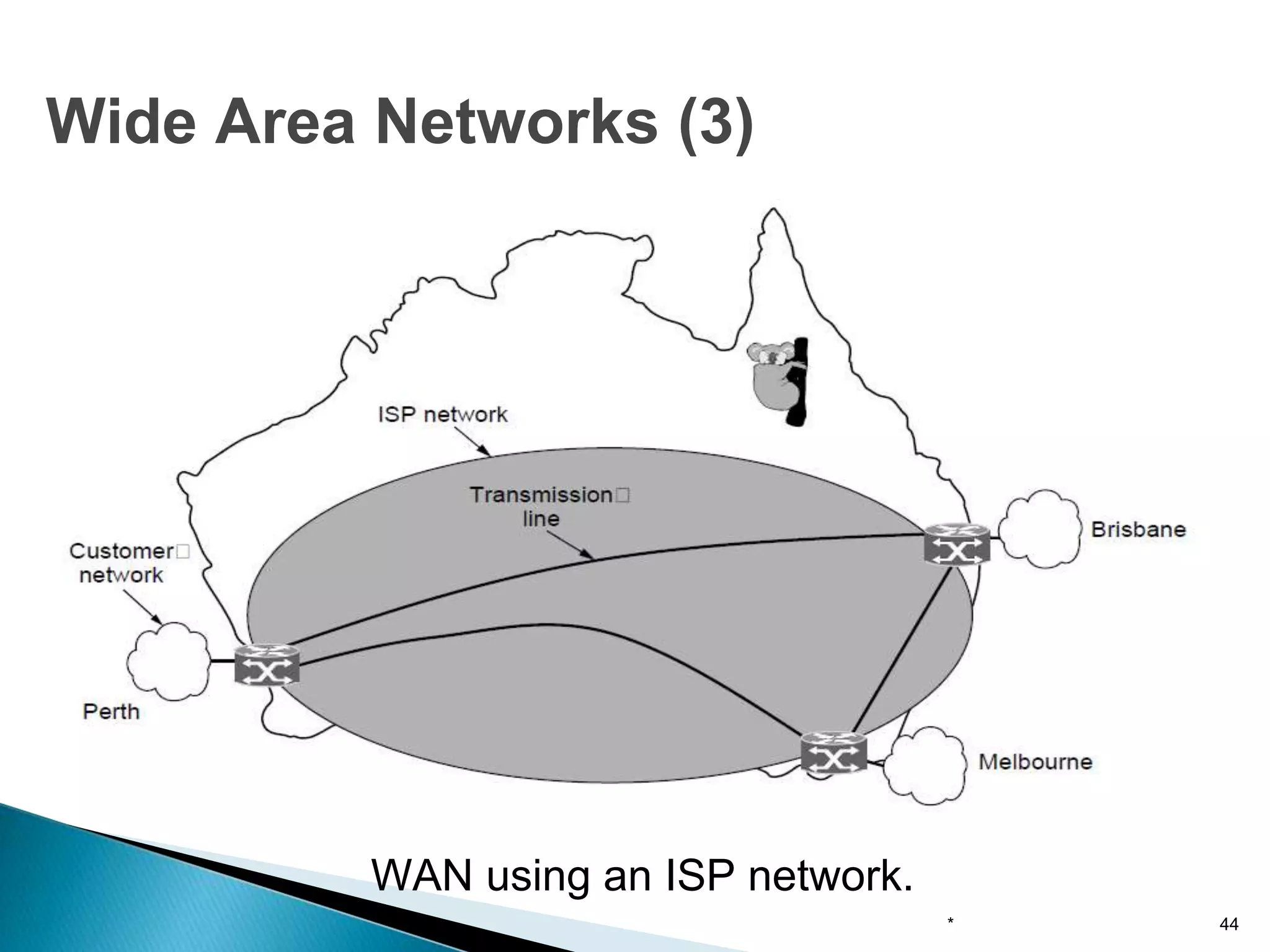
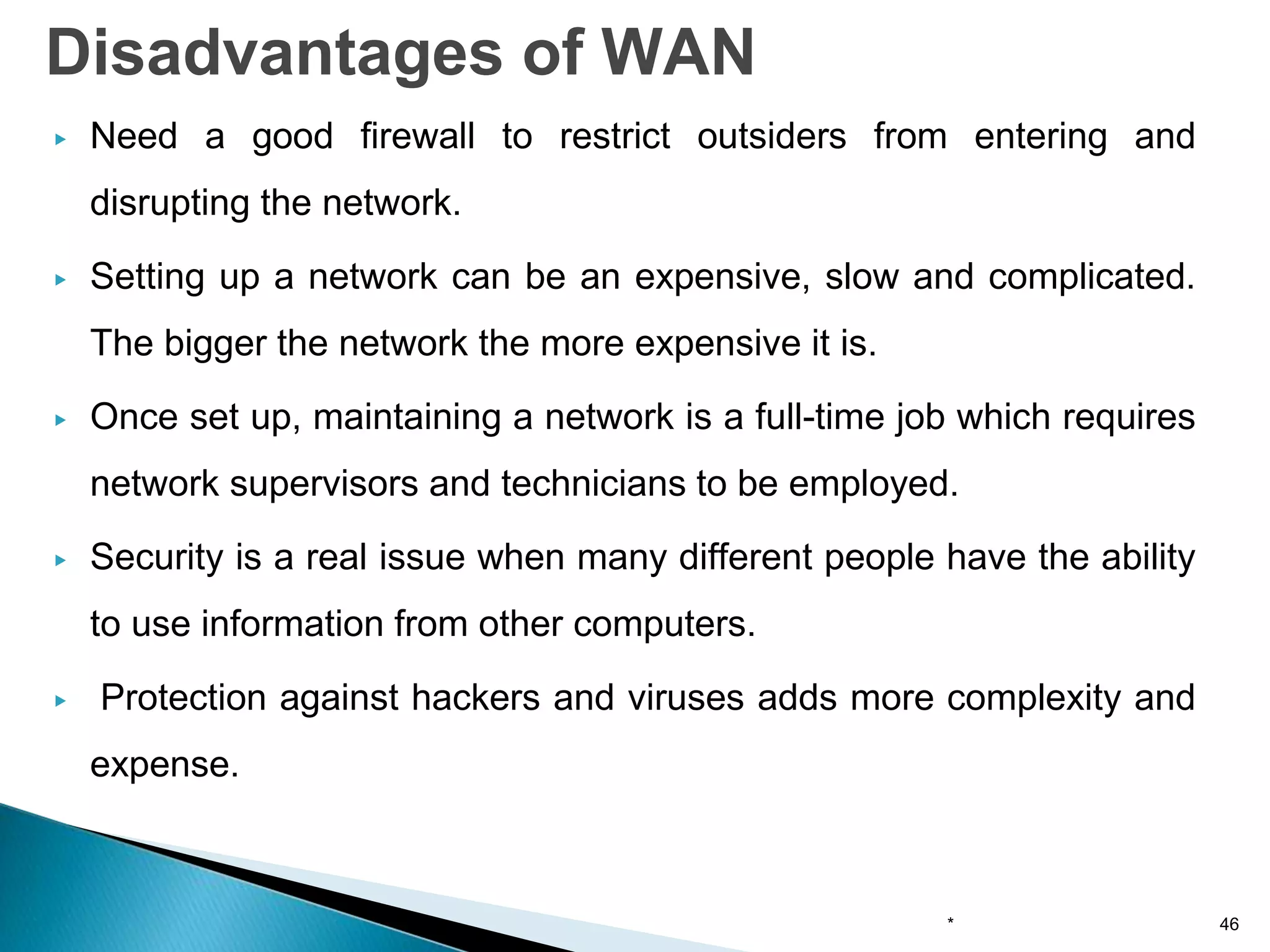
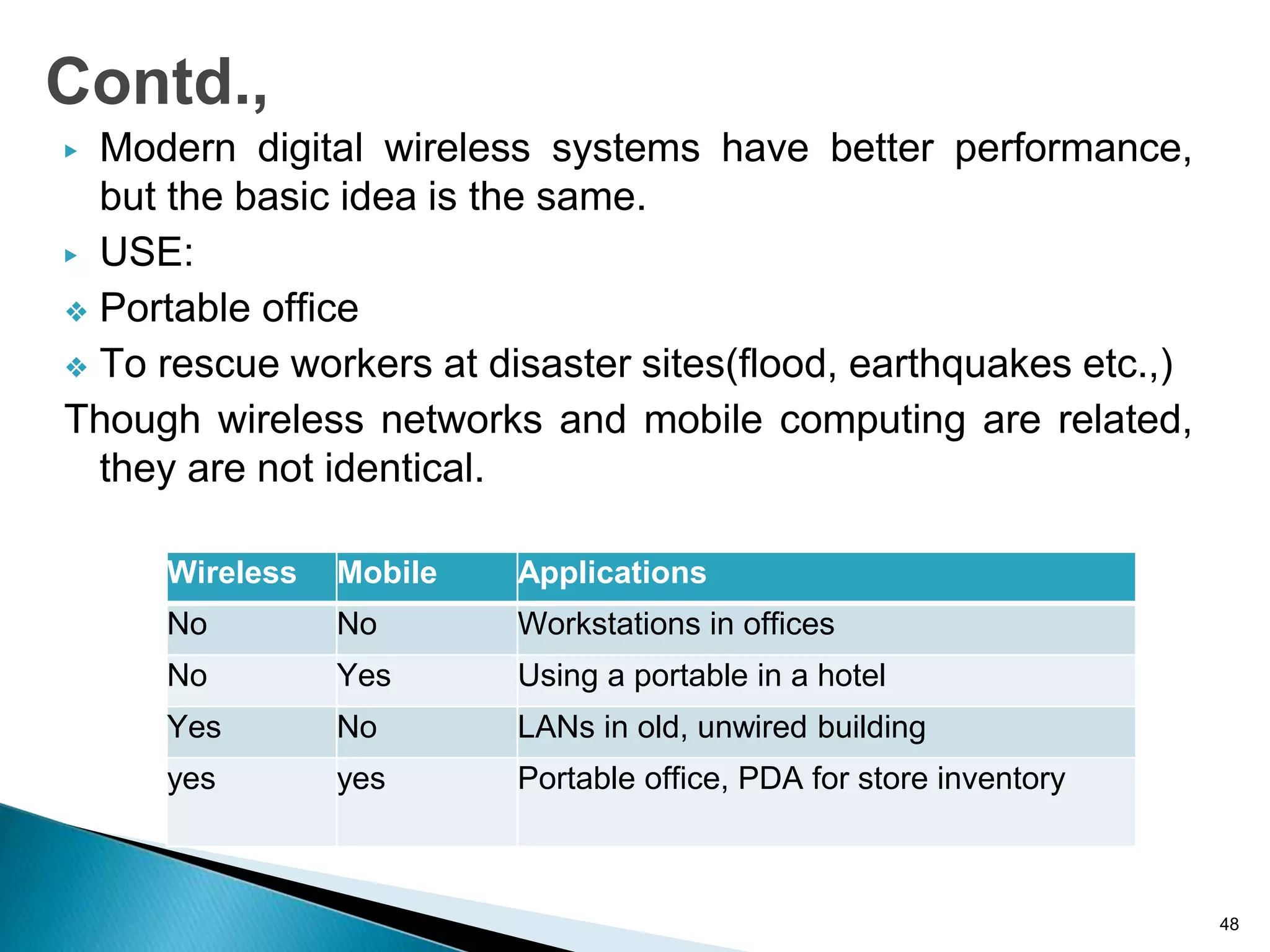
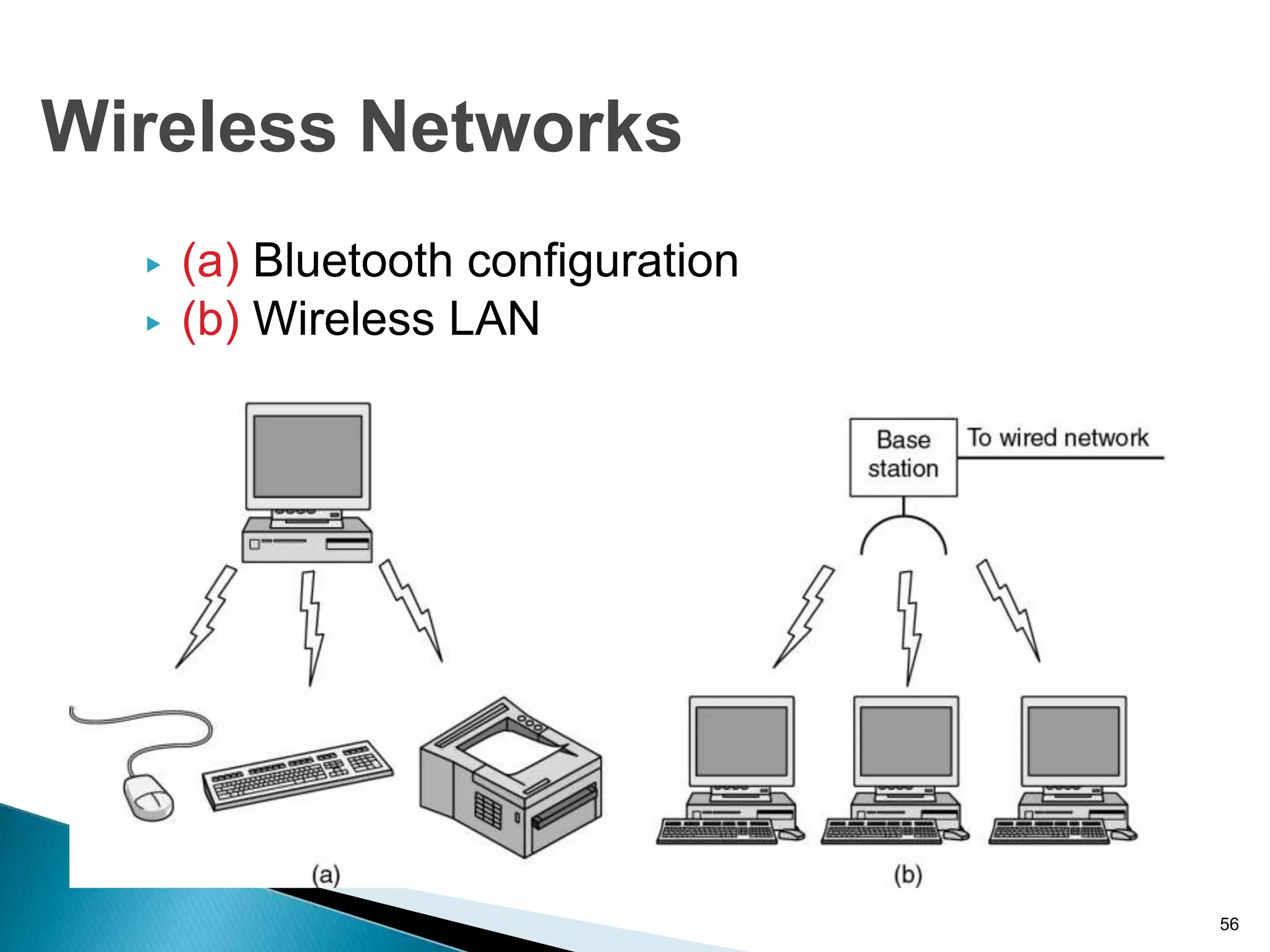
Computer networks allow for information sharing between people or groups. A computer network facilitates information sharing between computers that are interconnected using various transmission technologies like copper wire or fiber optics. There are several types of computer networks including local area networks (LANs), metropolitan area networks (MANs), and wide area networks (WANs) which differ in size, transmission medium, and distance covered. LANs connect computers within a single building or campus while WANs connect computers across large distances like cities, states or countries.