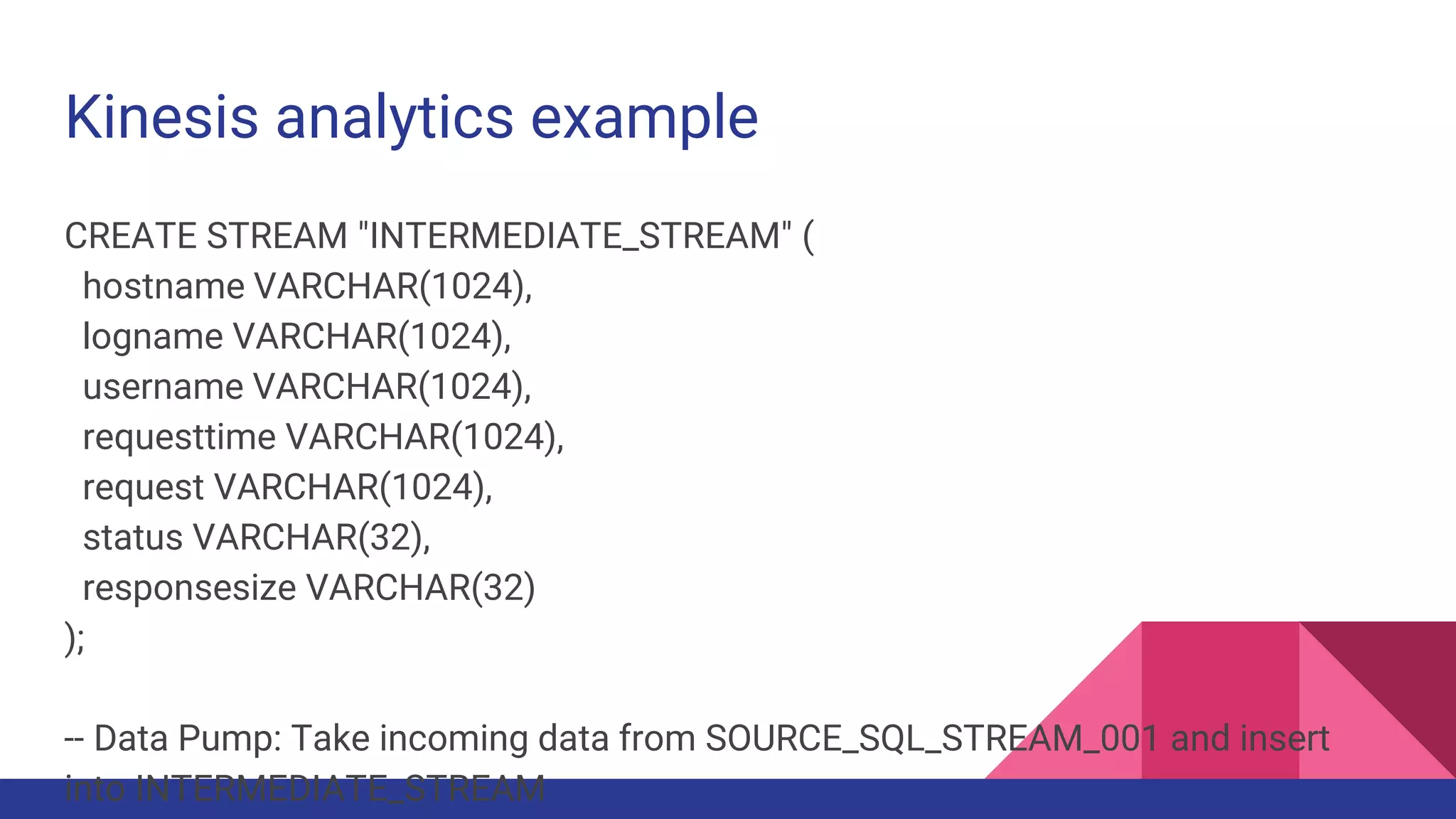
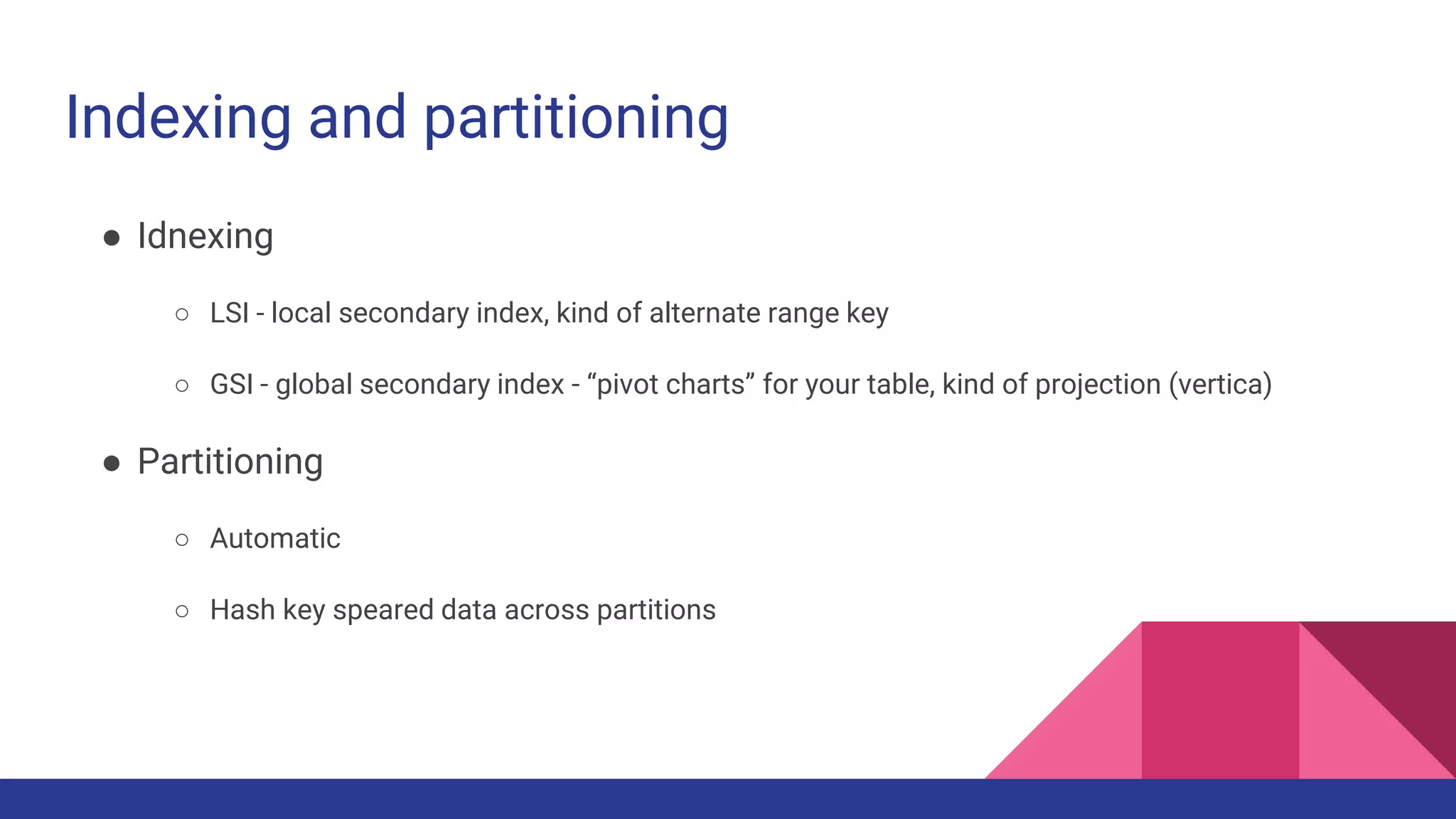
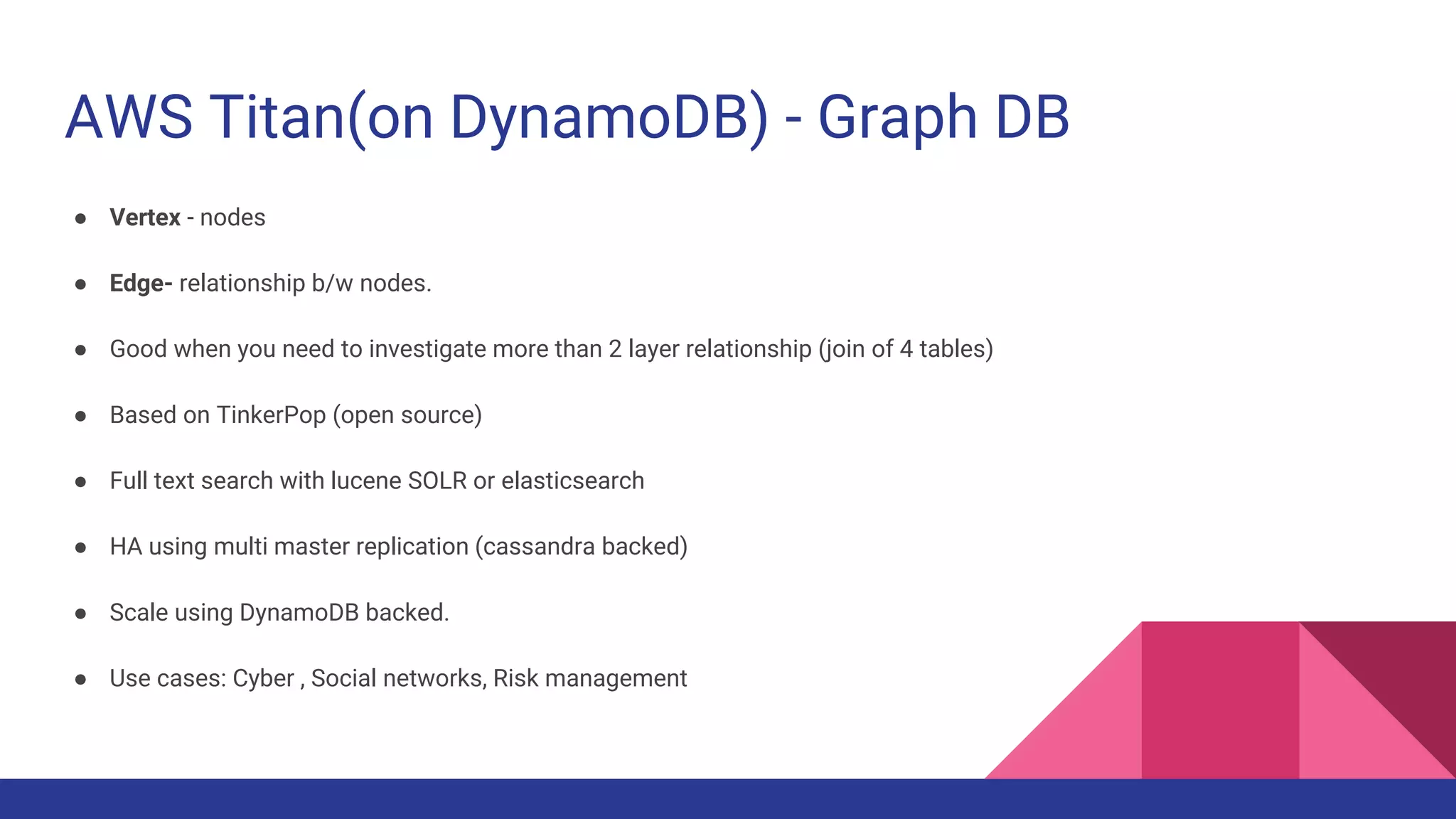
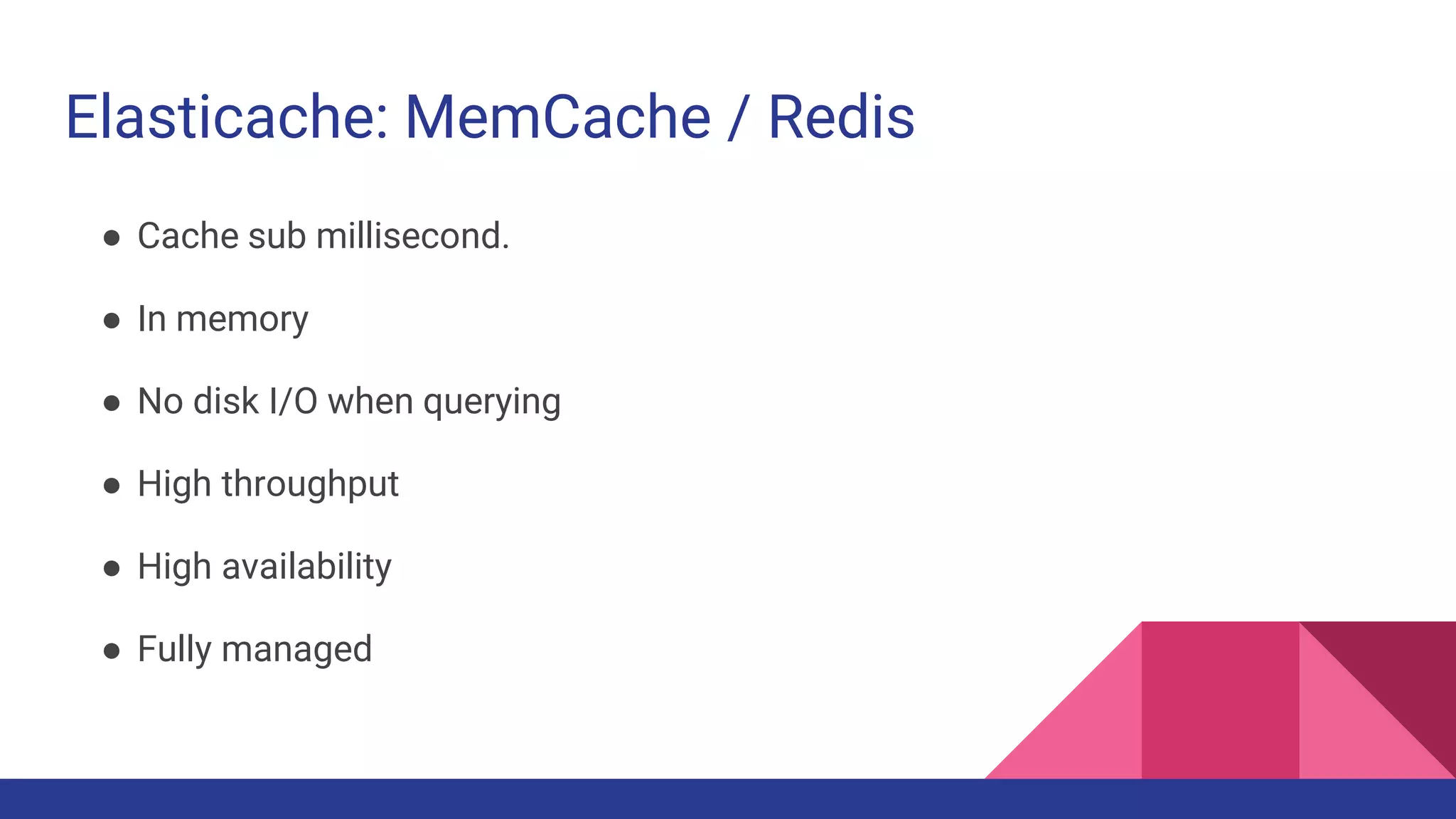
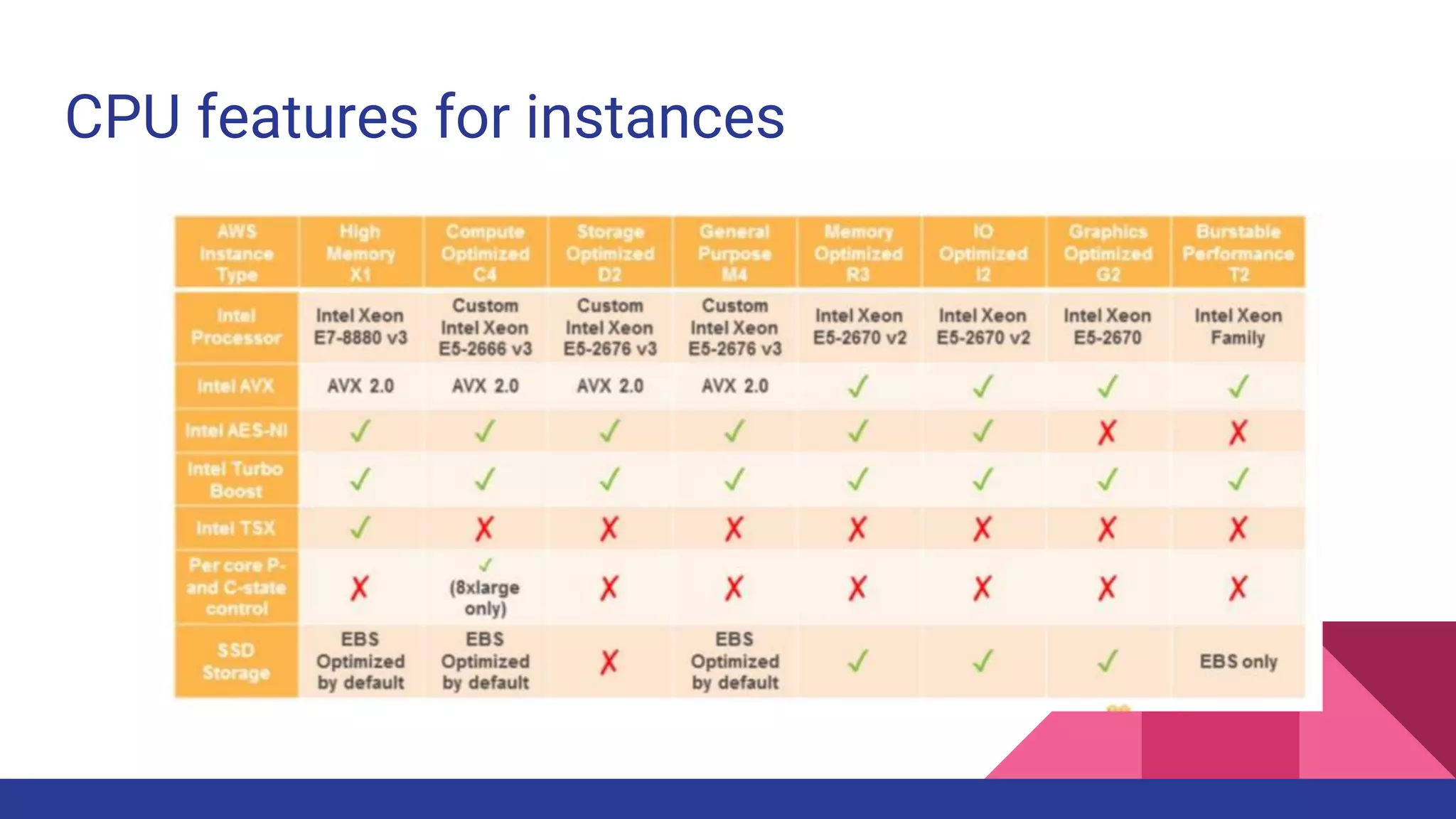
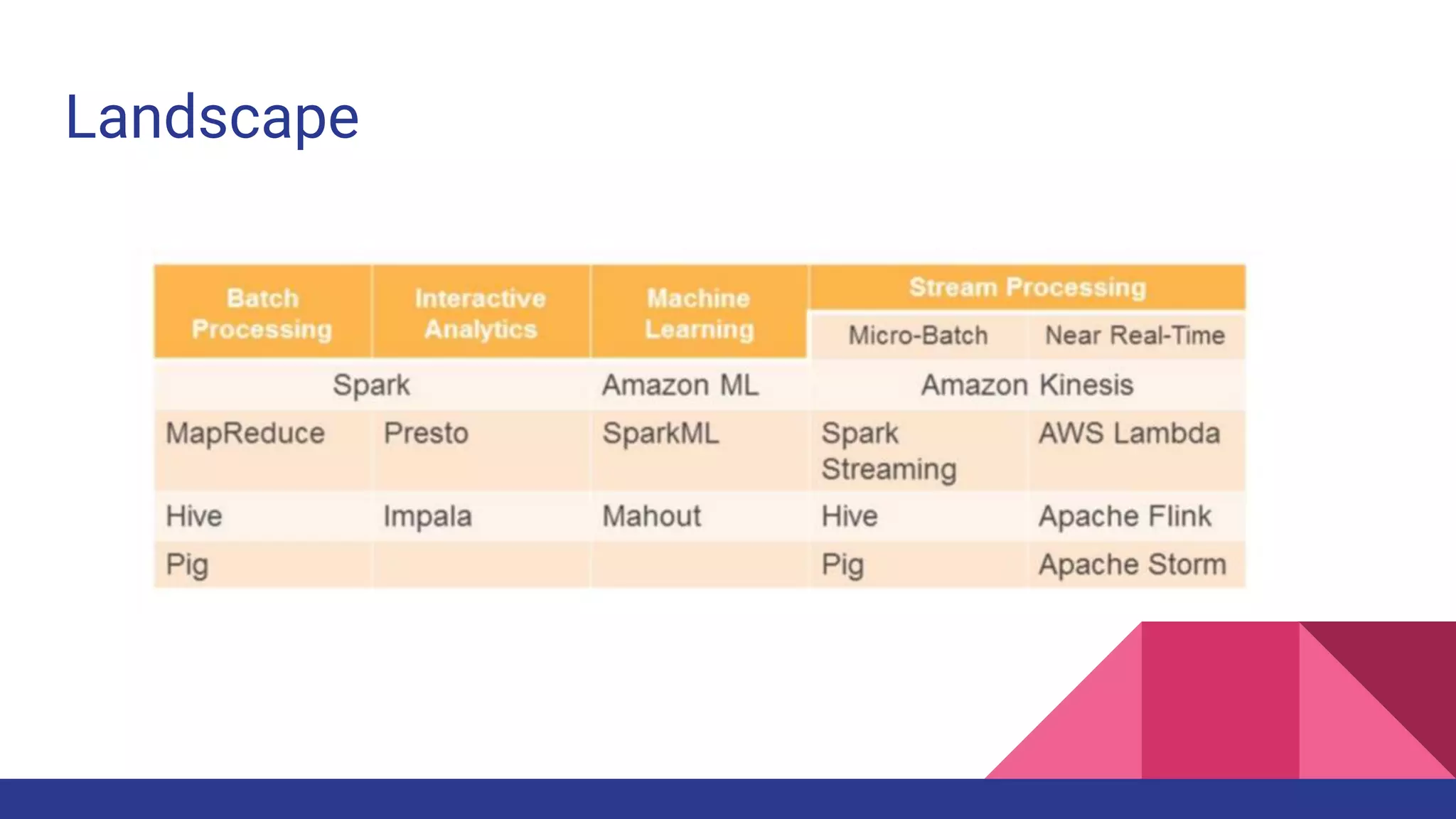
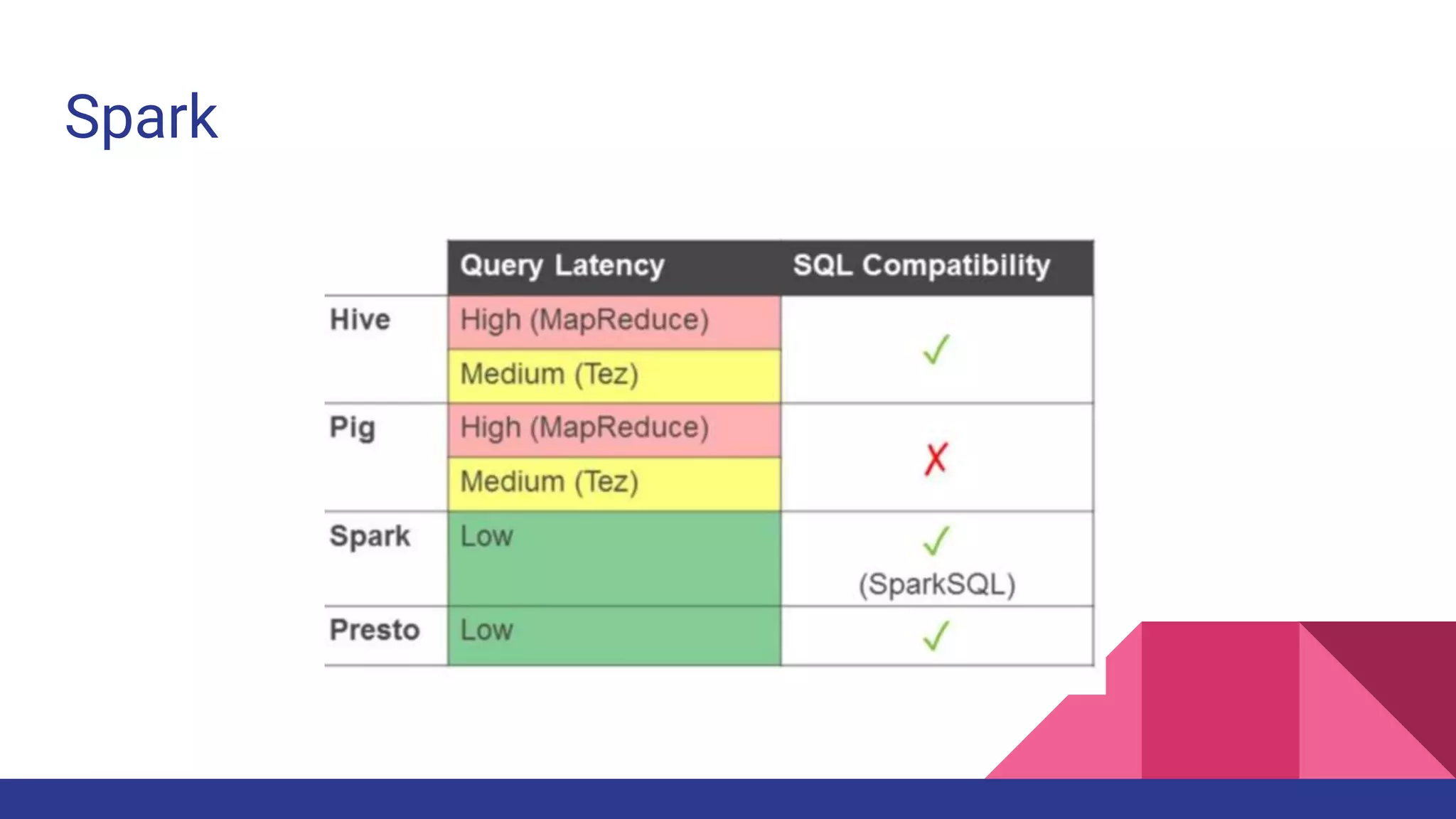
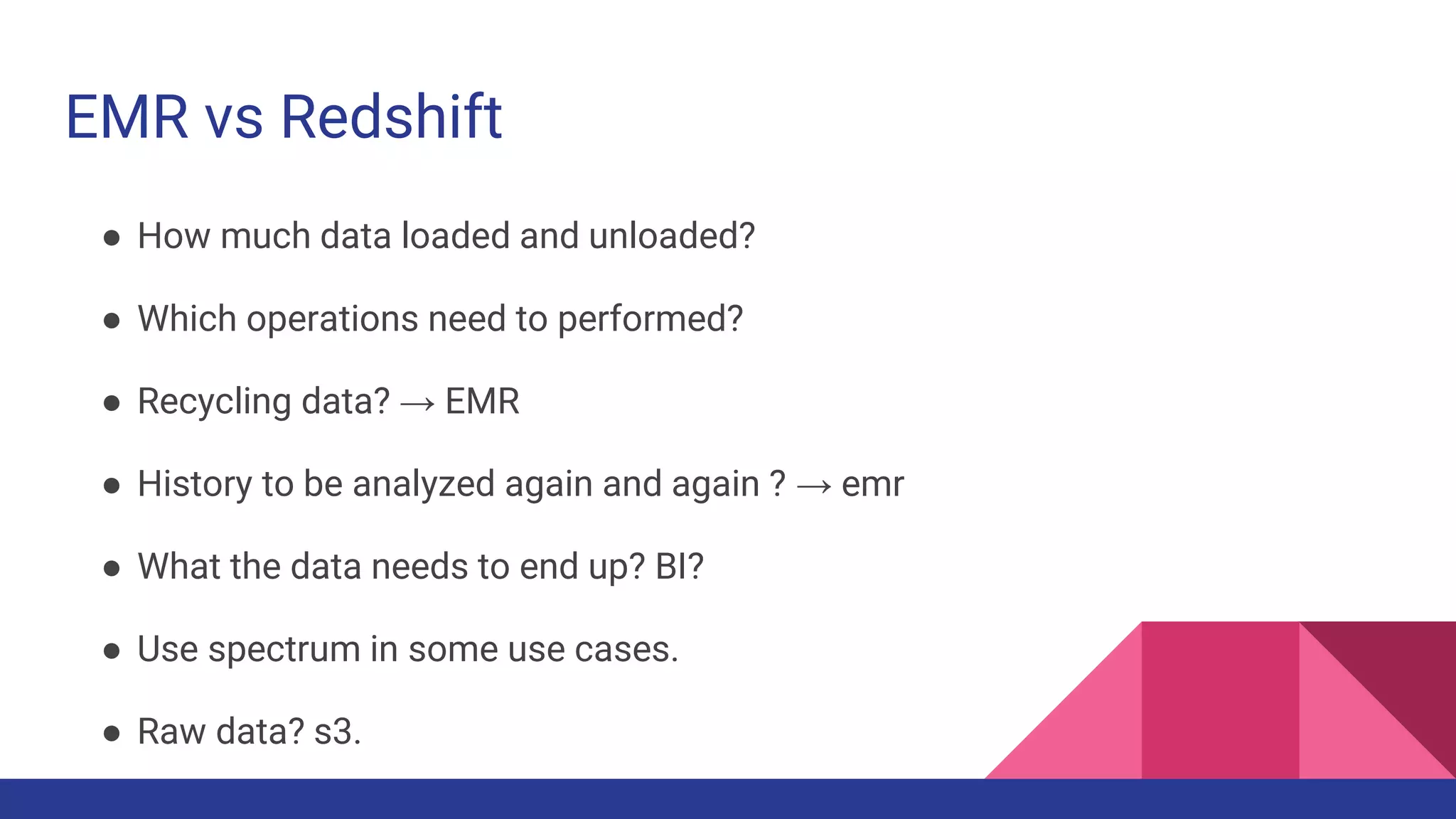
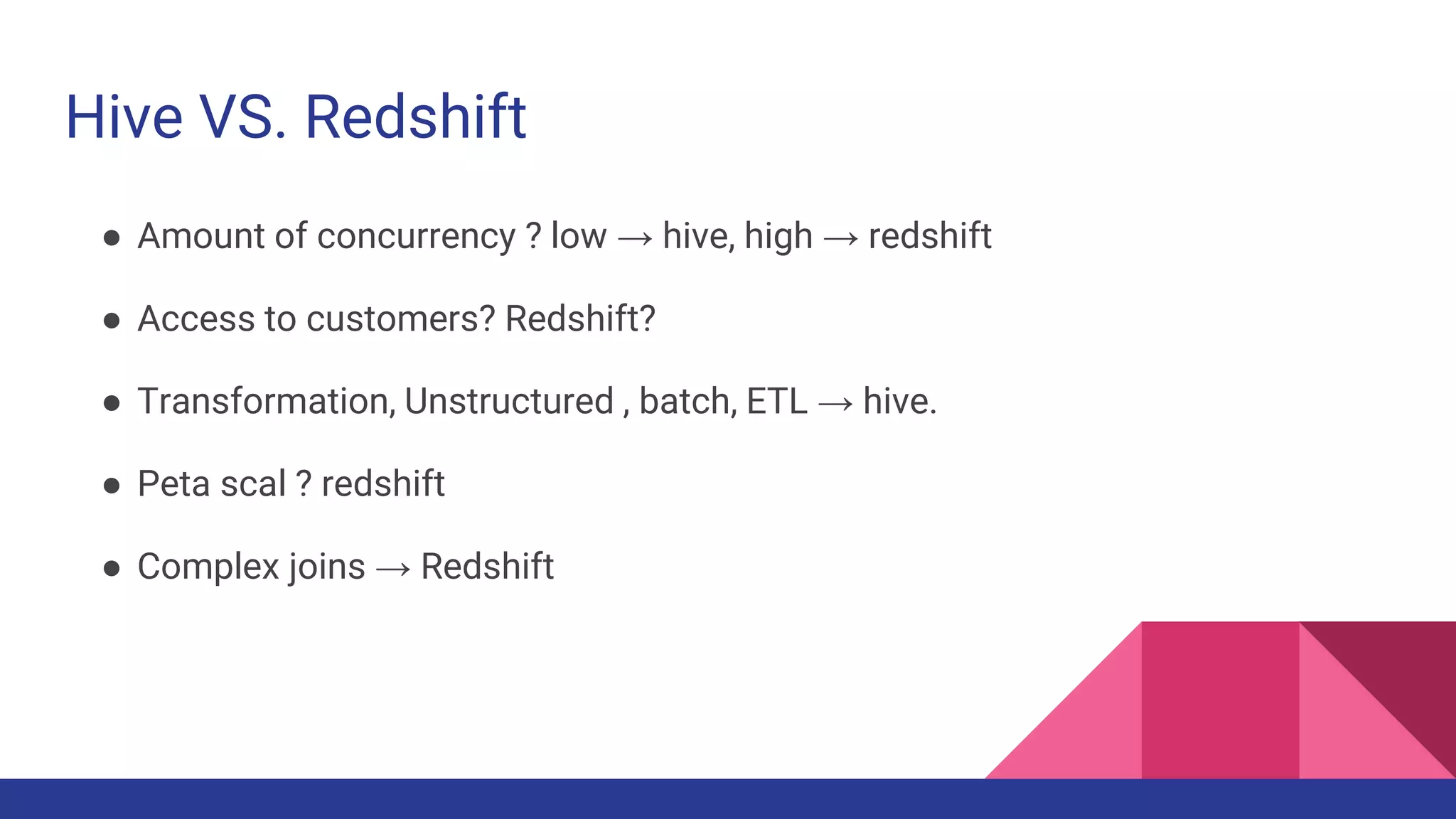
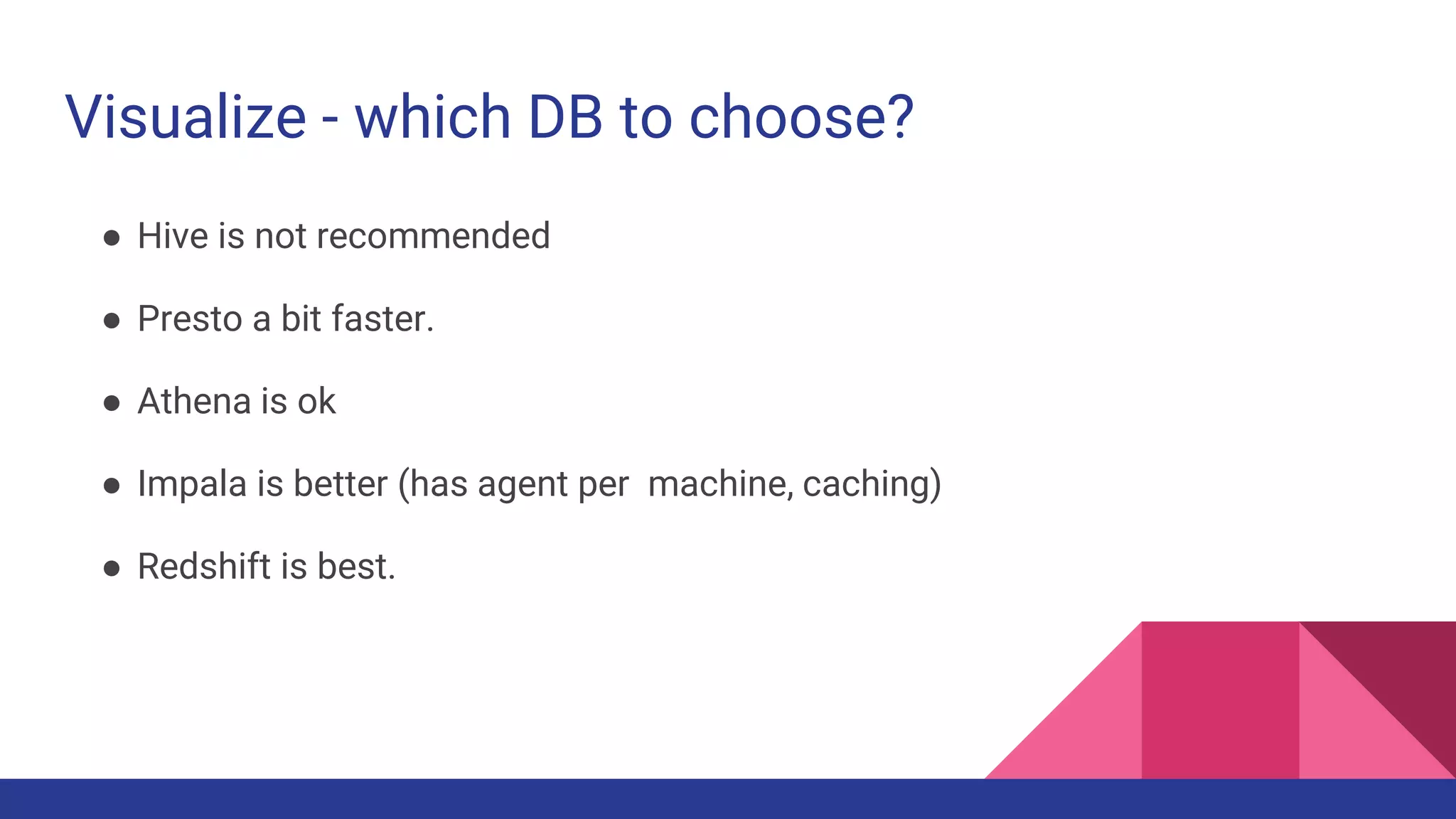
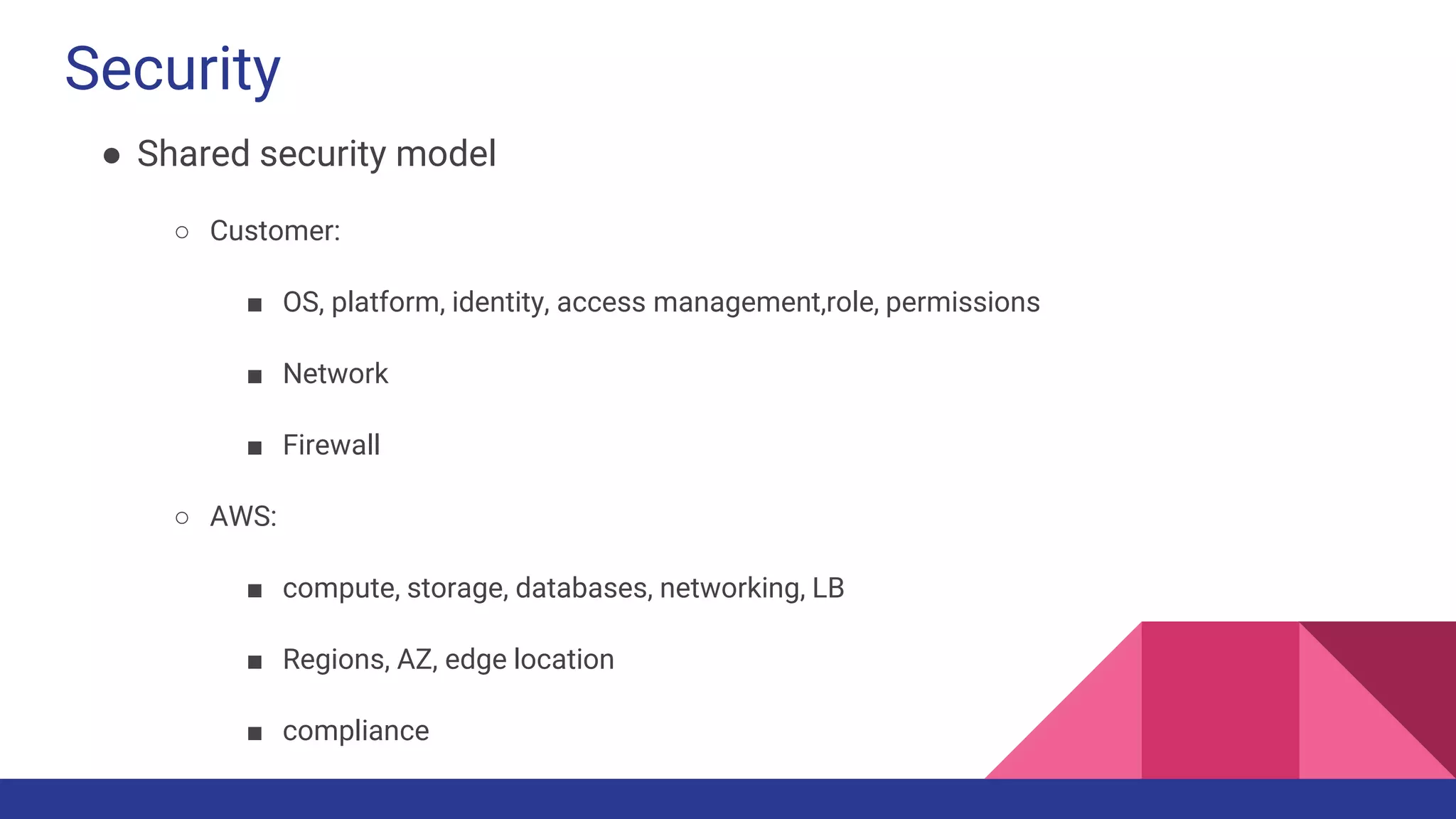
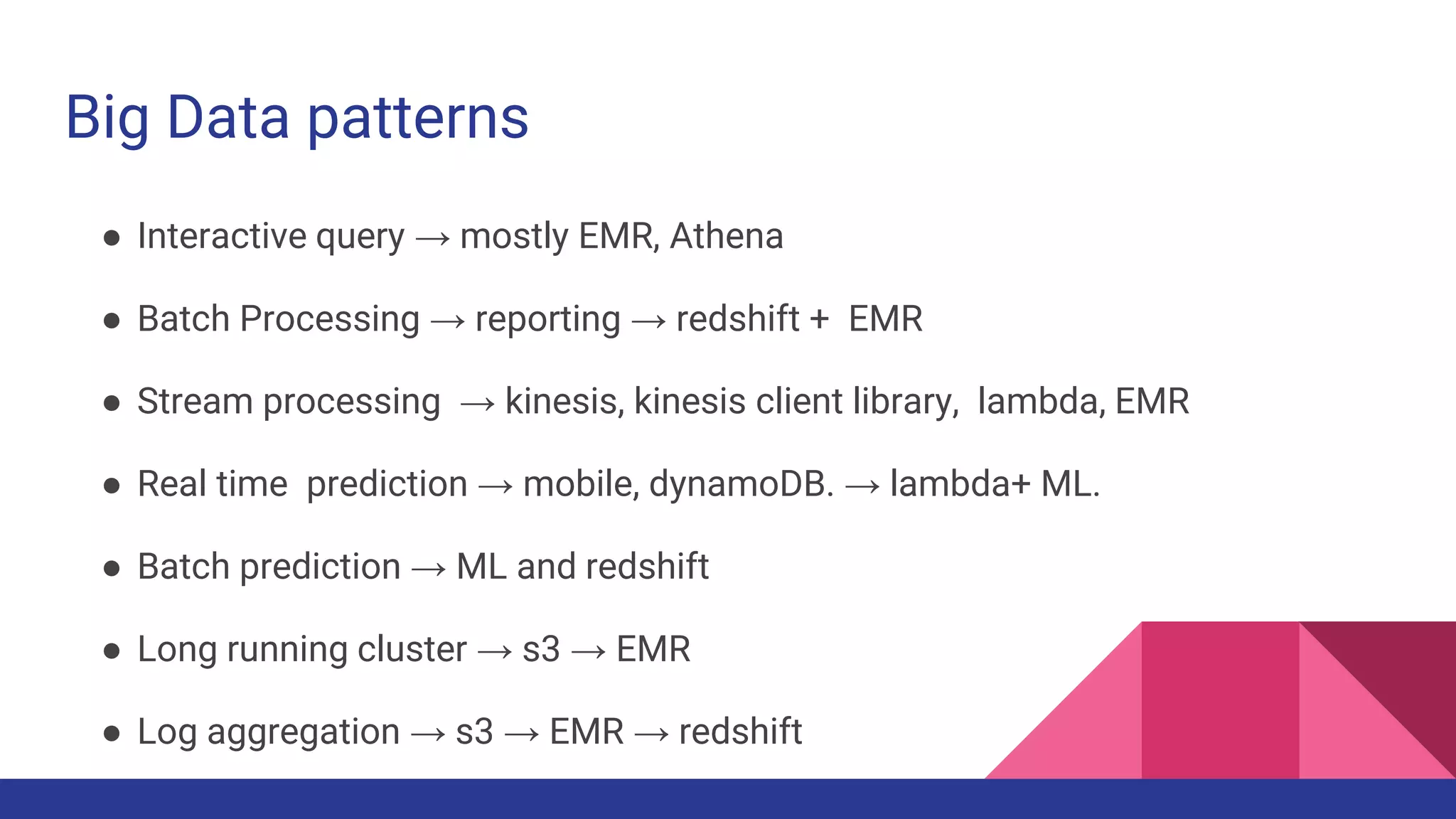
The document provides a comprehensive overview of AWS big data services, including the architecture of data storage, processing, and visualization solutions such as EMR, Redshift, DynamoDB, Kinesis, and associated tools. It covers key concepts such as ingestion types, technology recommendations, best practices, security measures, cost optimization, and various service comparisons for big data analytics and manipulation. Additionally, it discusses the roles of libraries and frameworks like Spark, Hive, and others in facilitating data operations in the AWS environment.