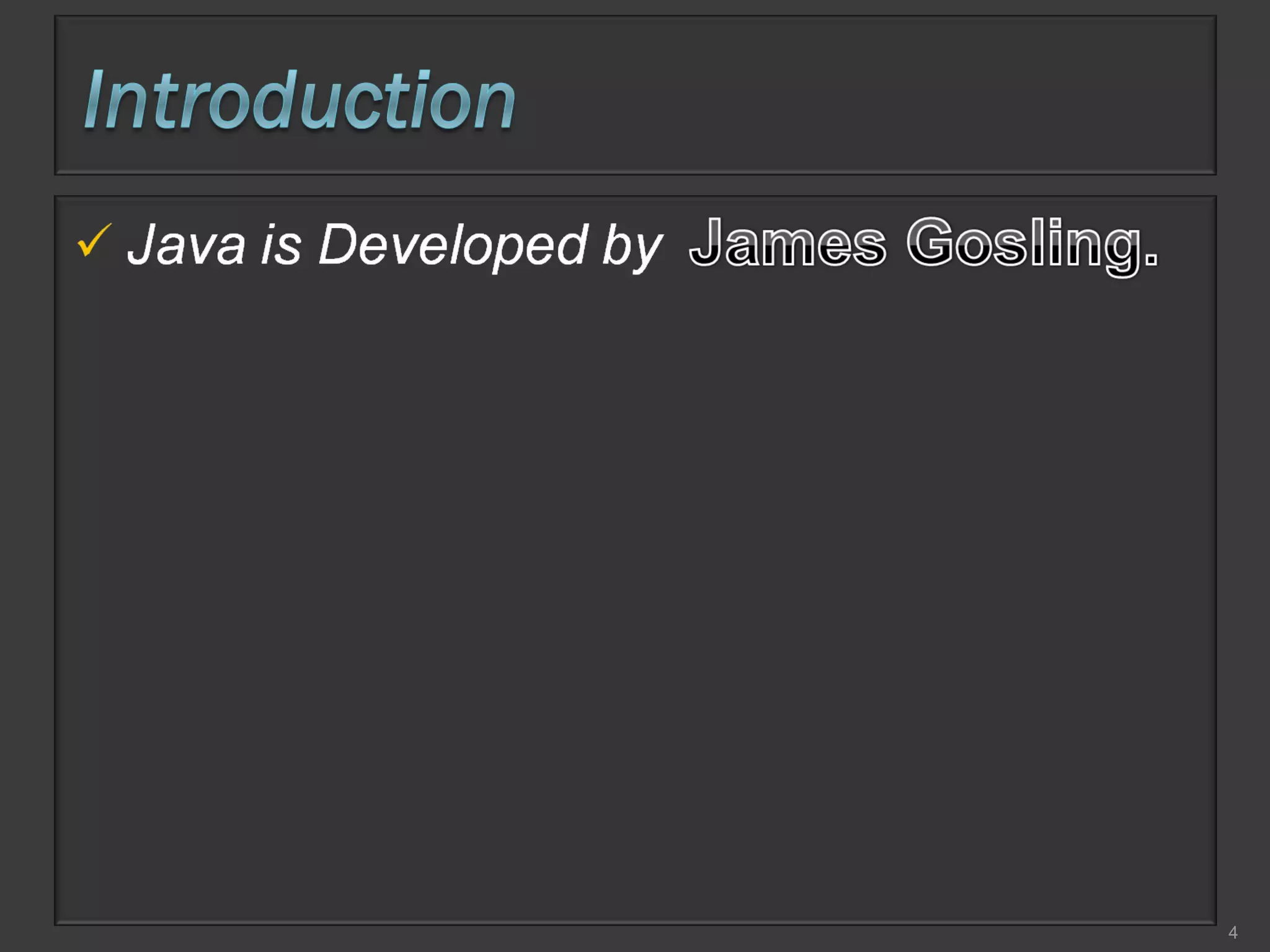
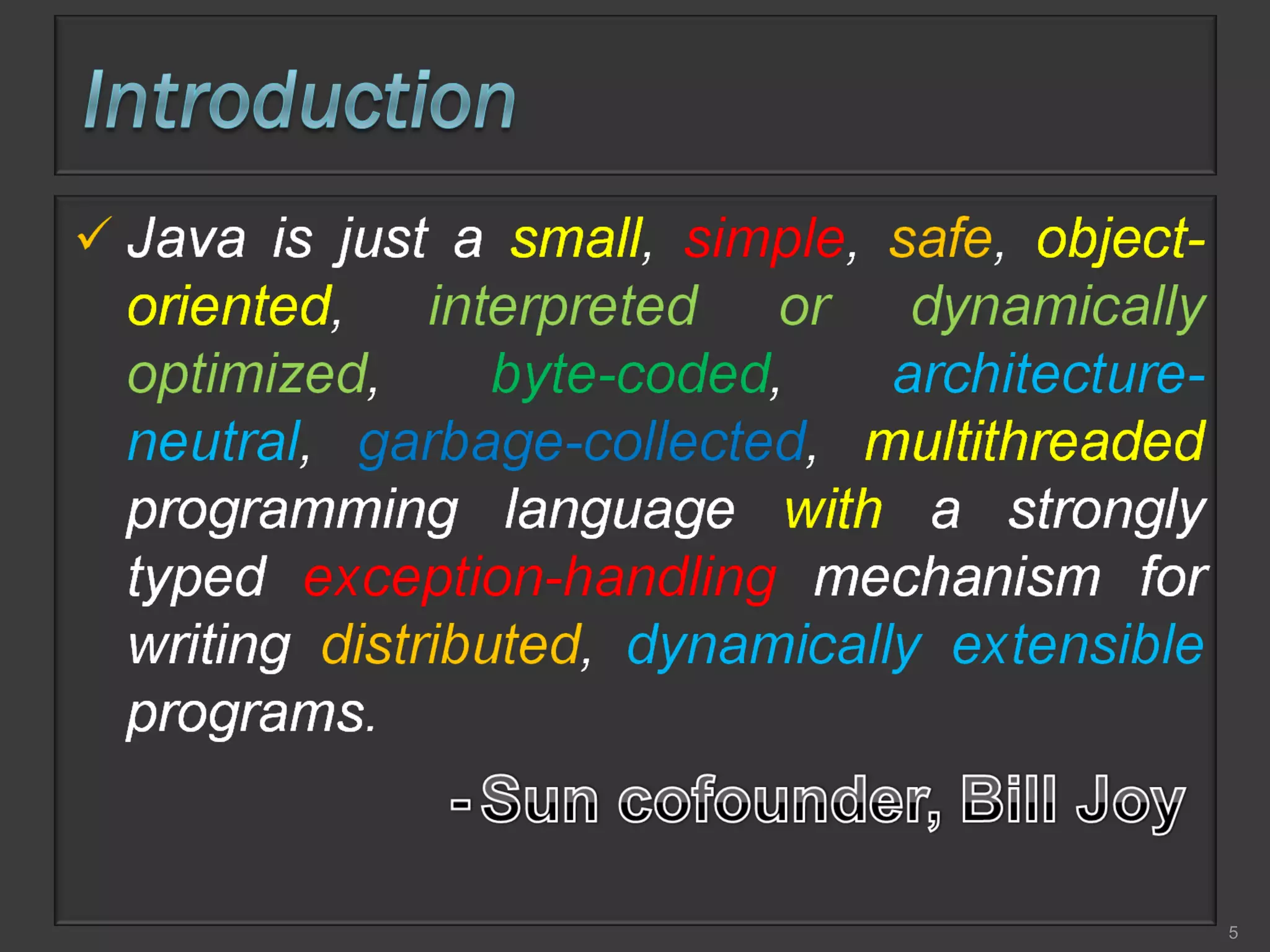
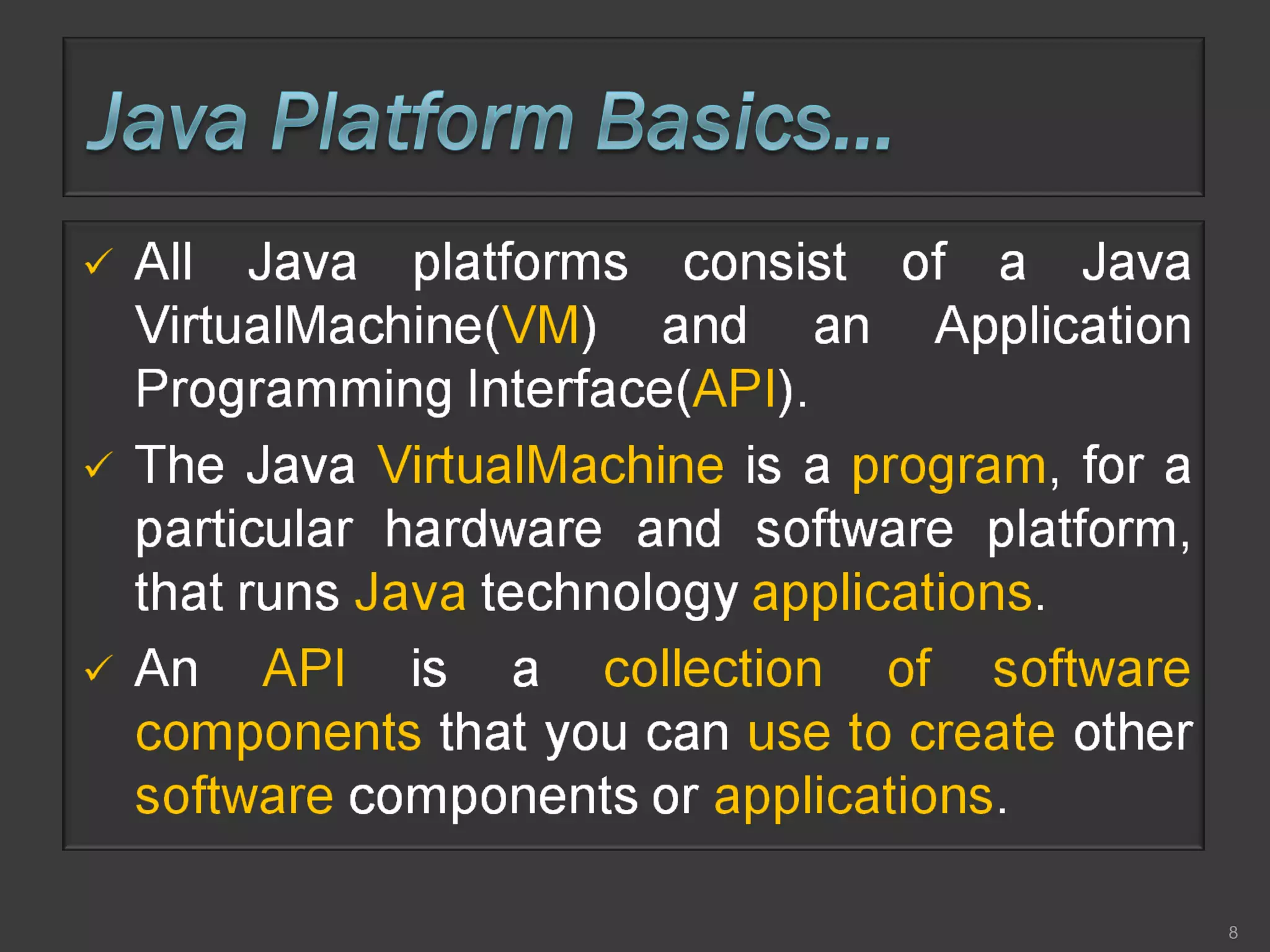
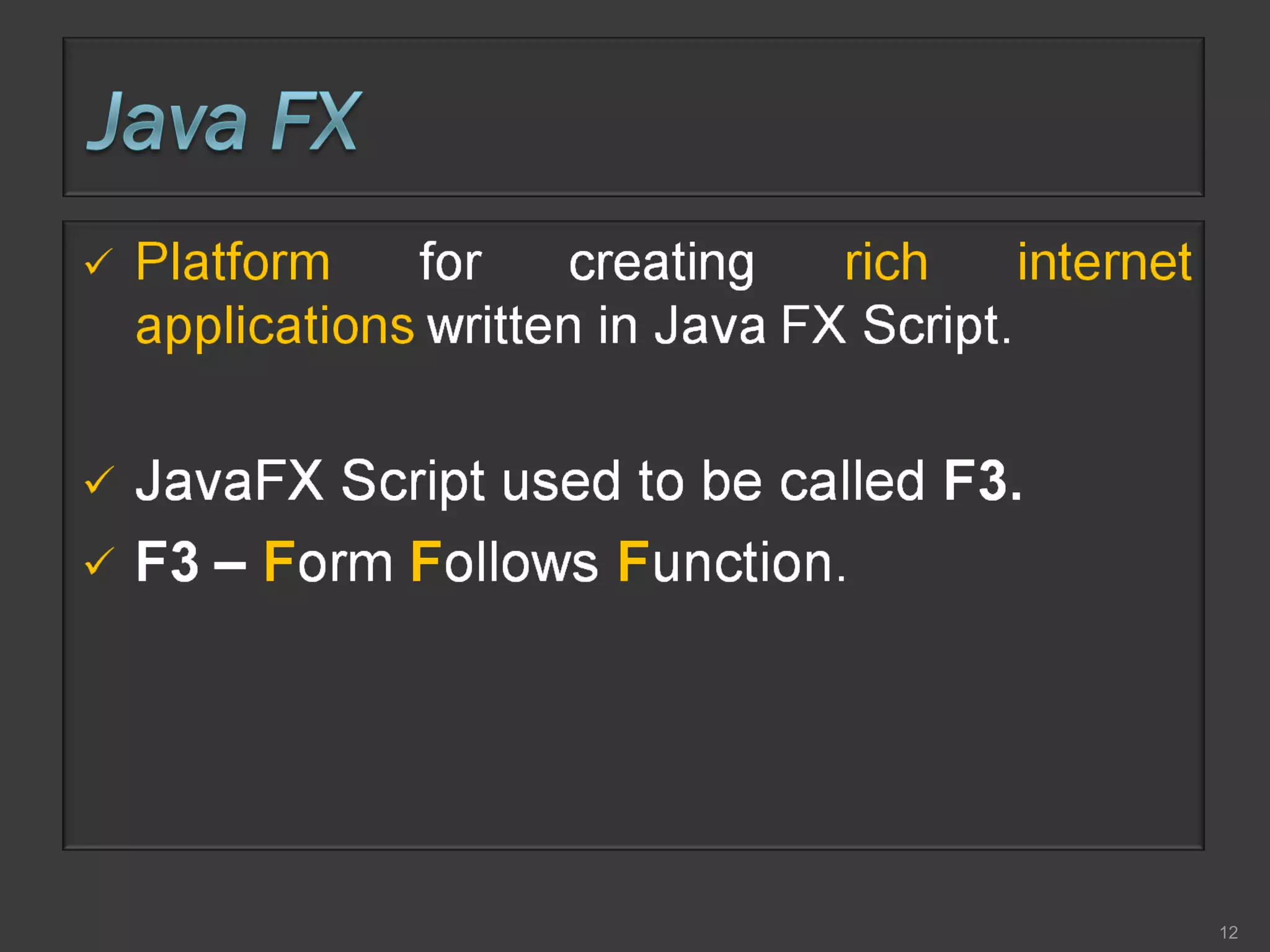
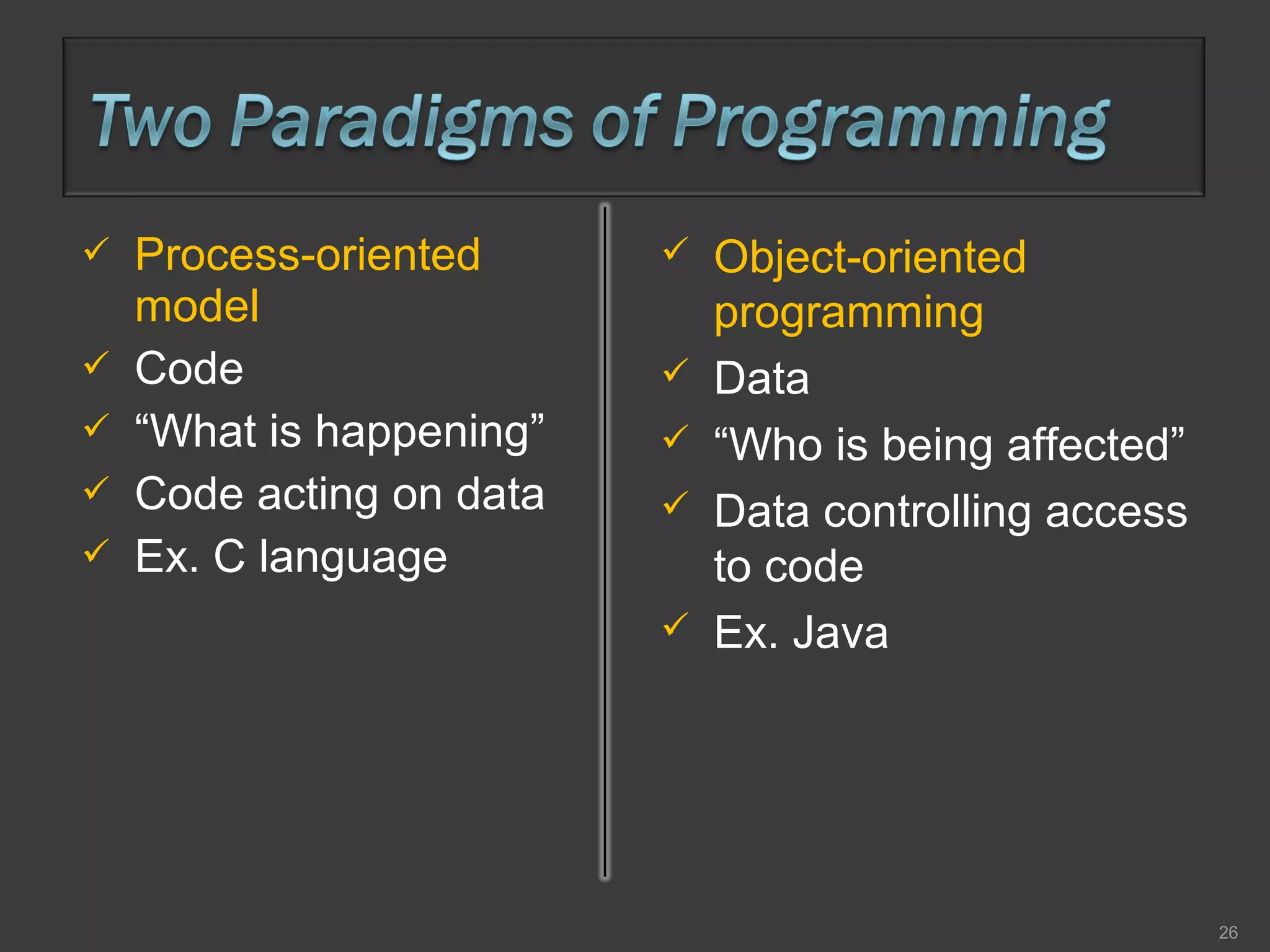
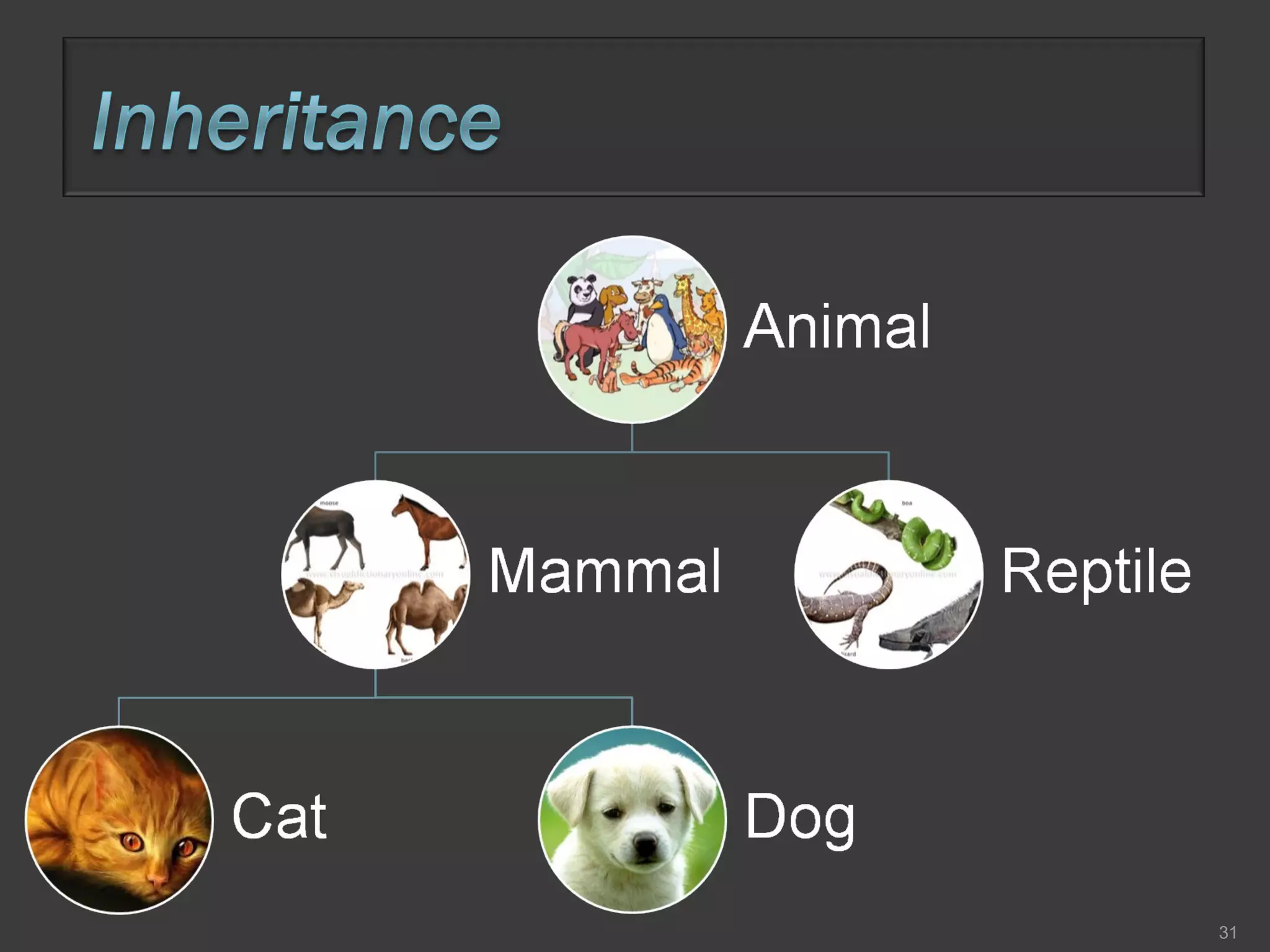
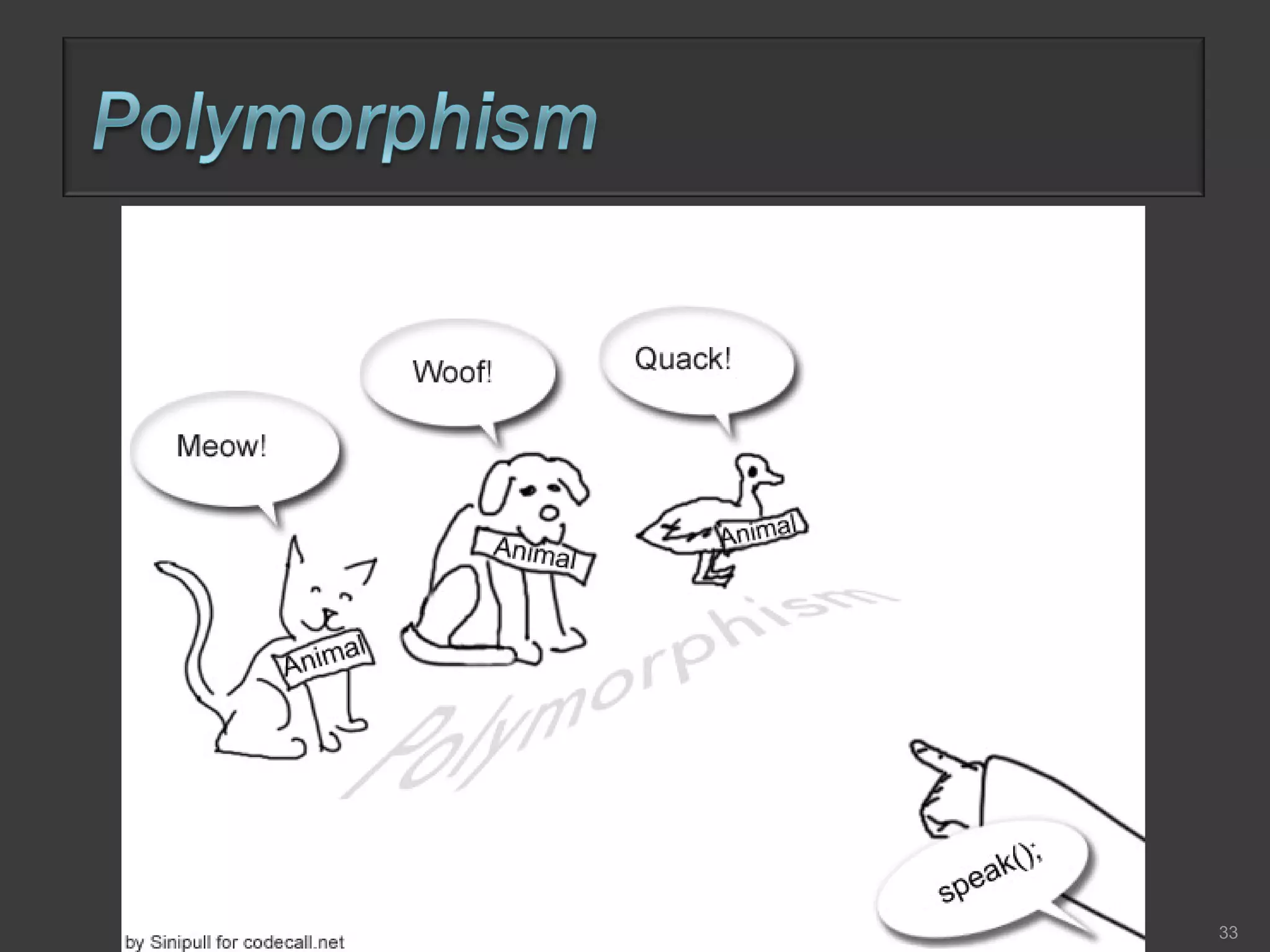
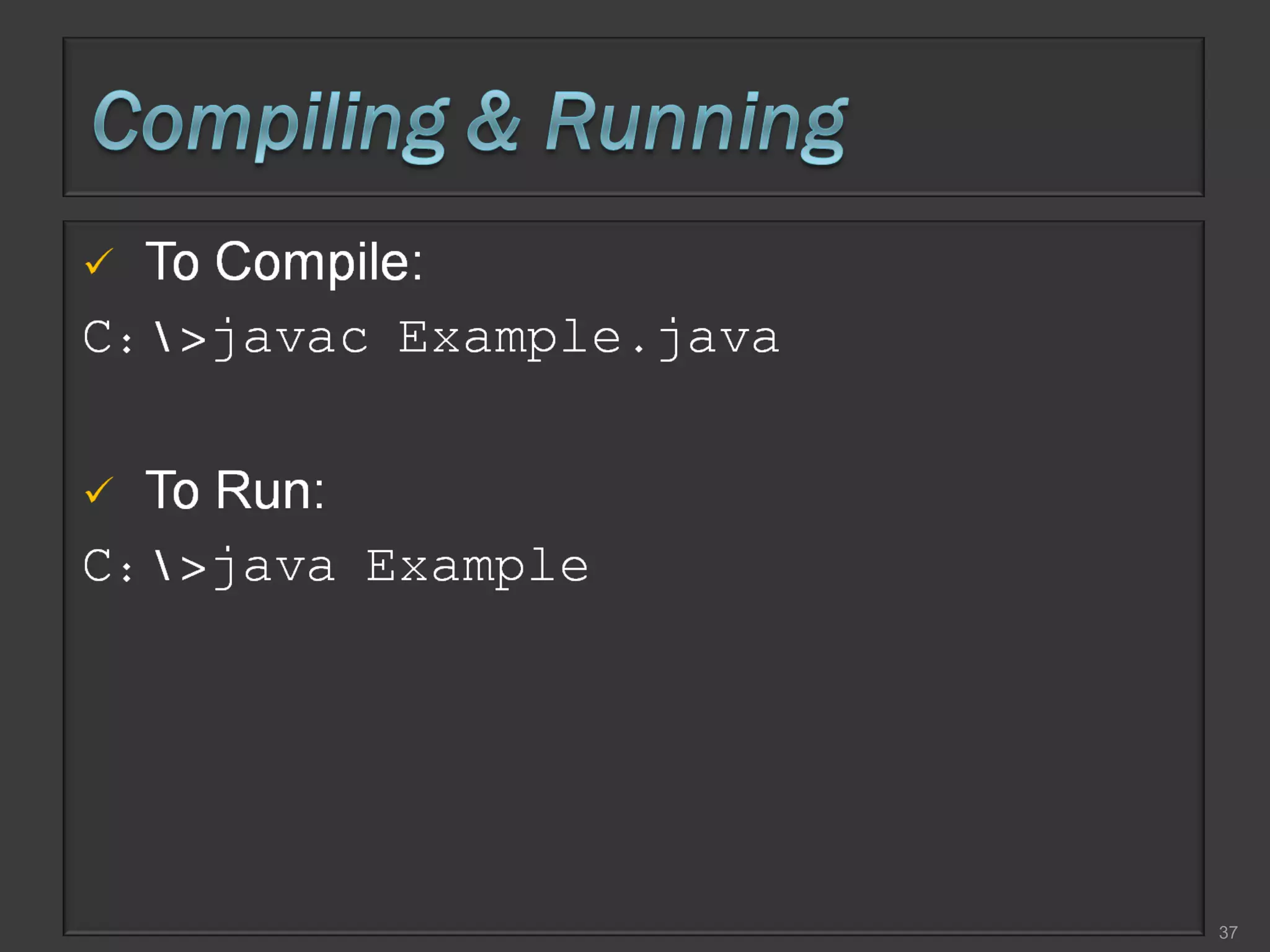
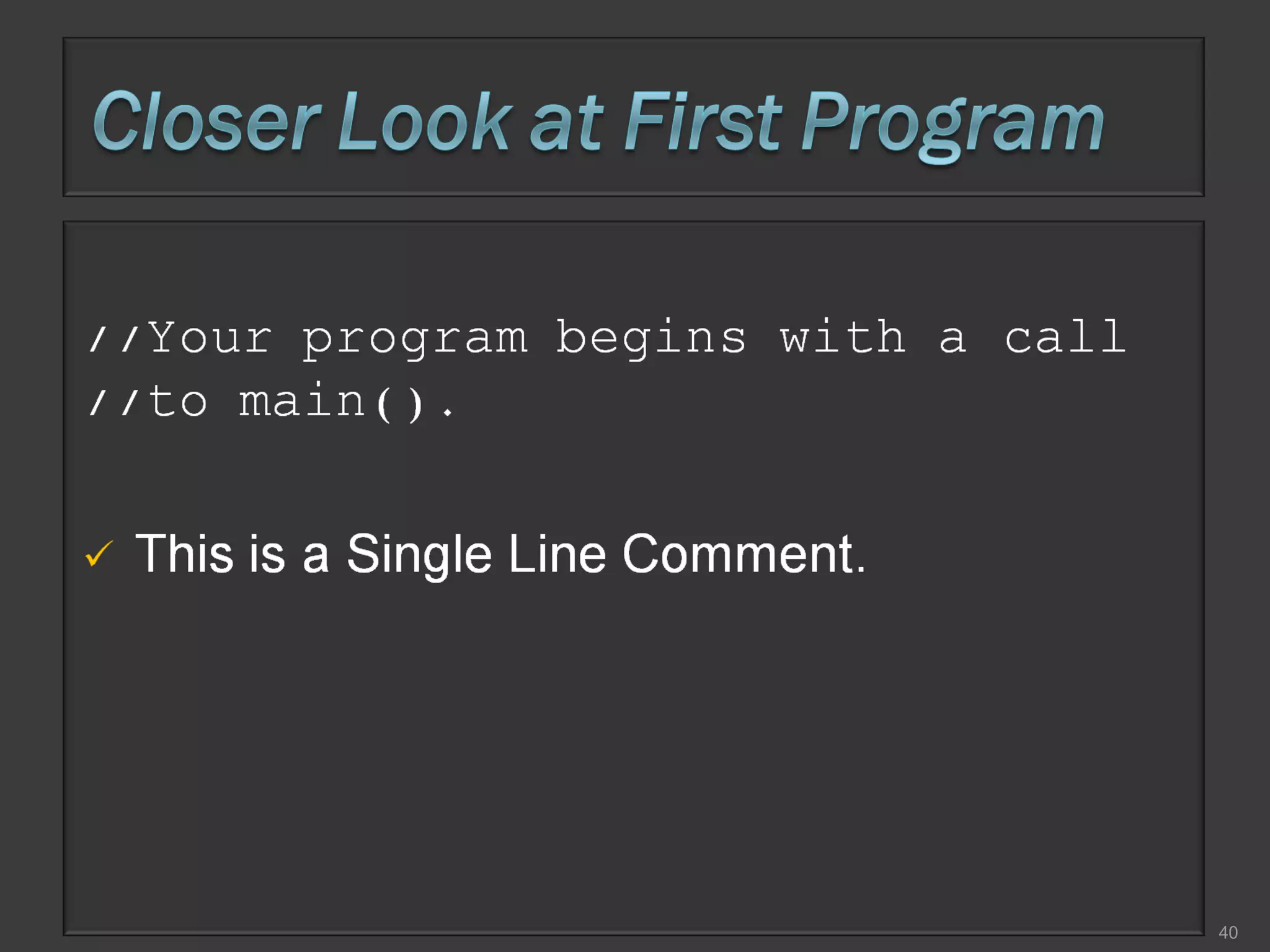
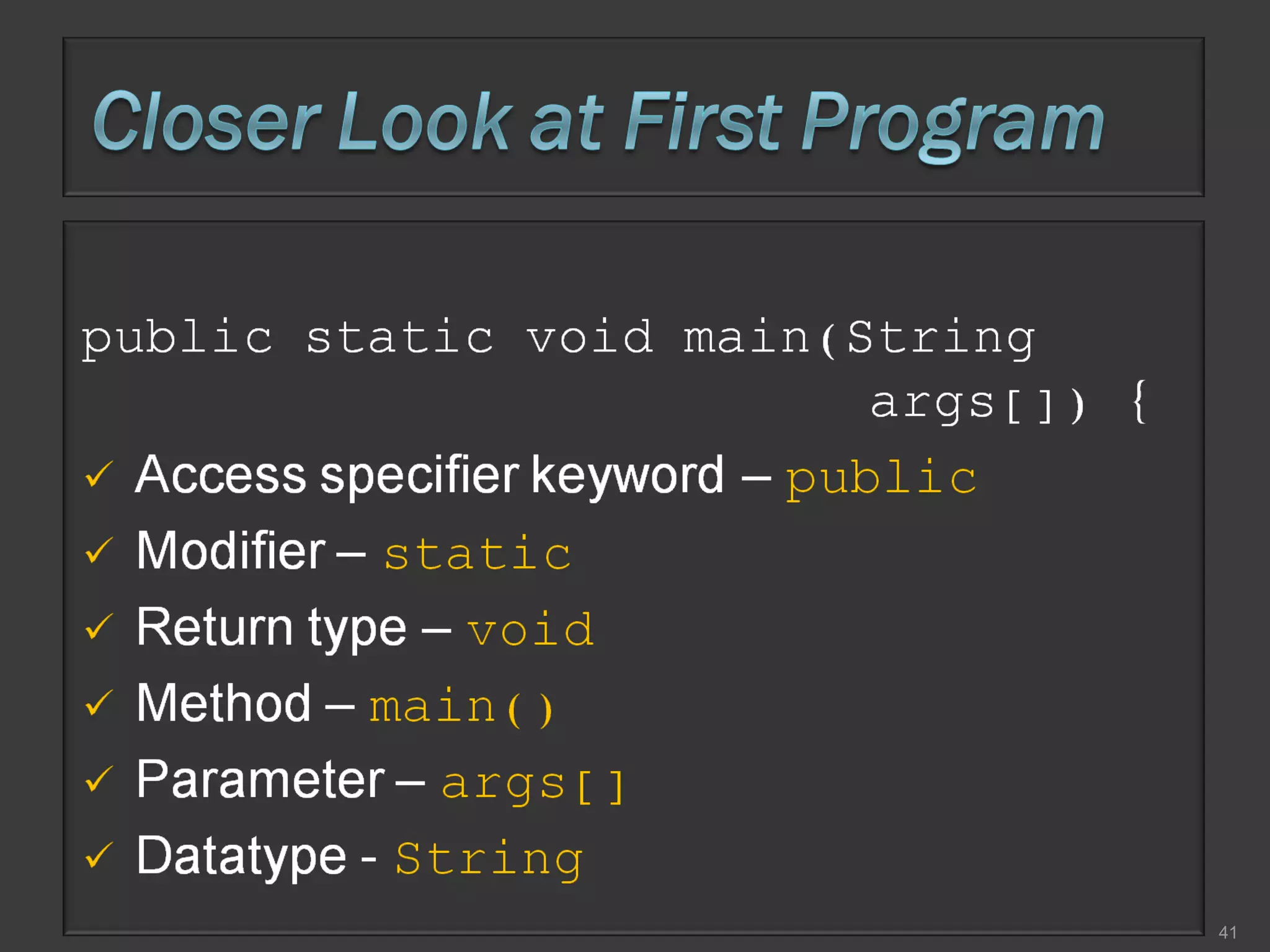
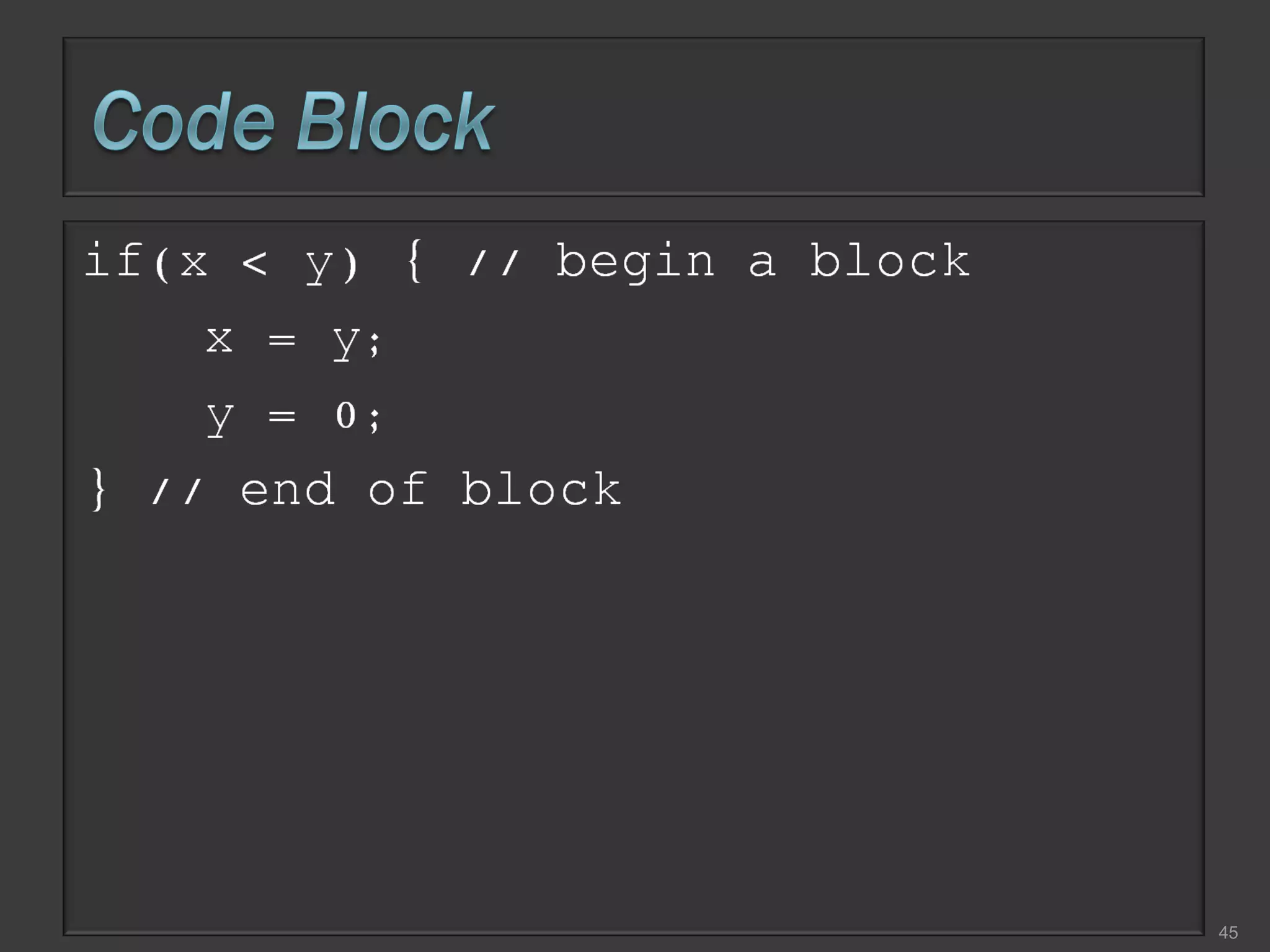
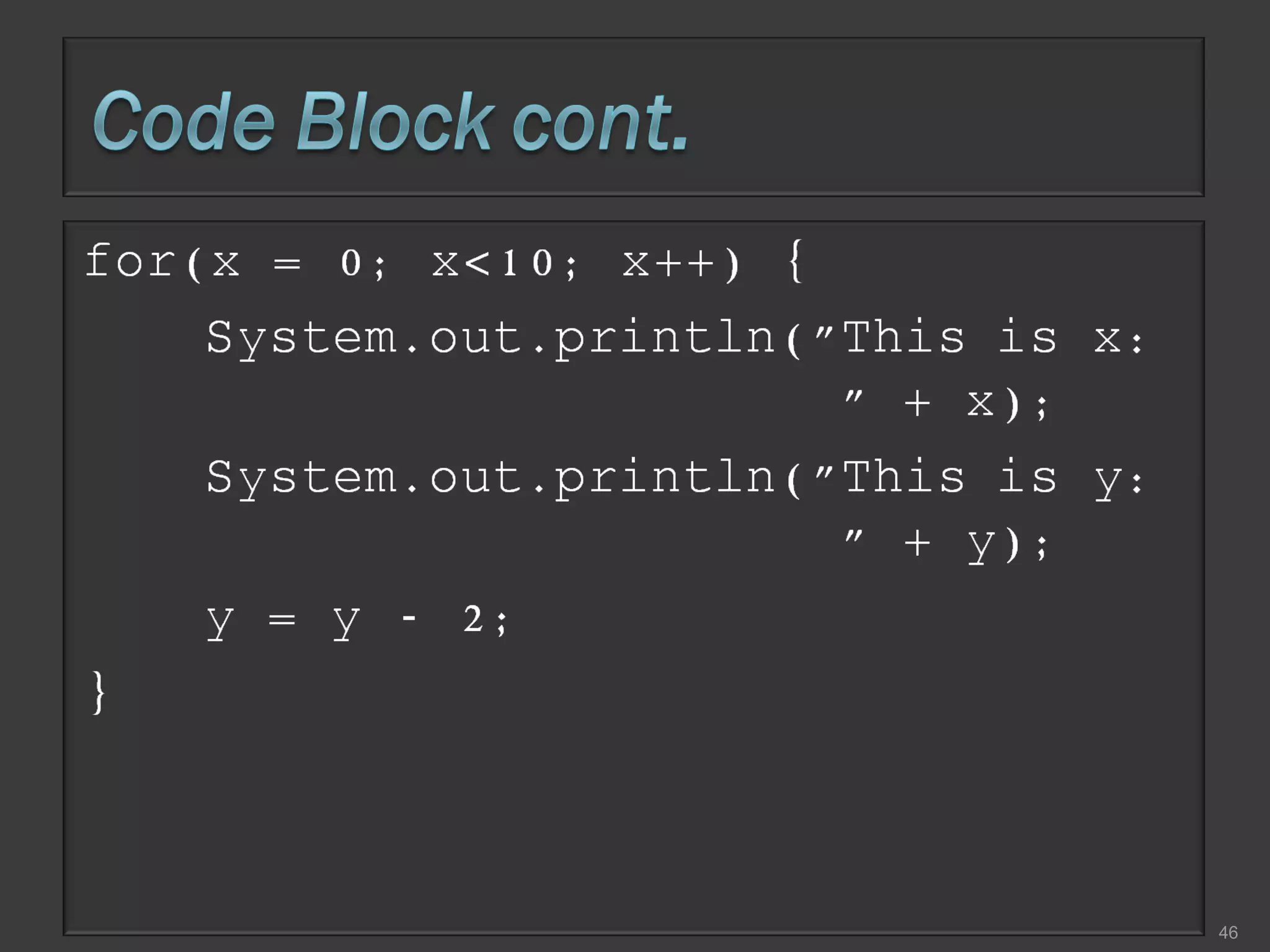
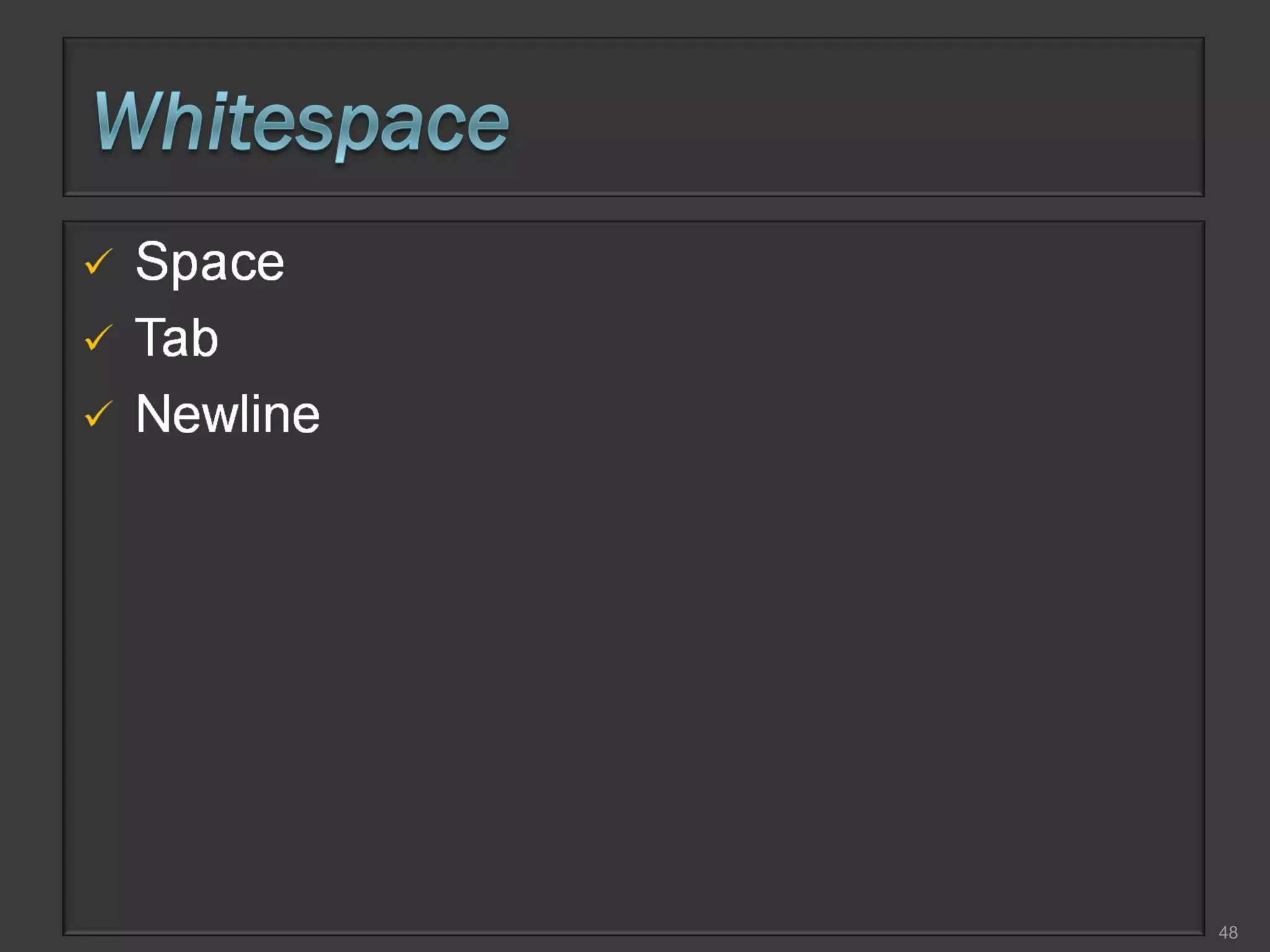
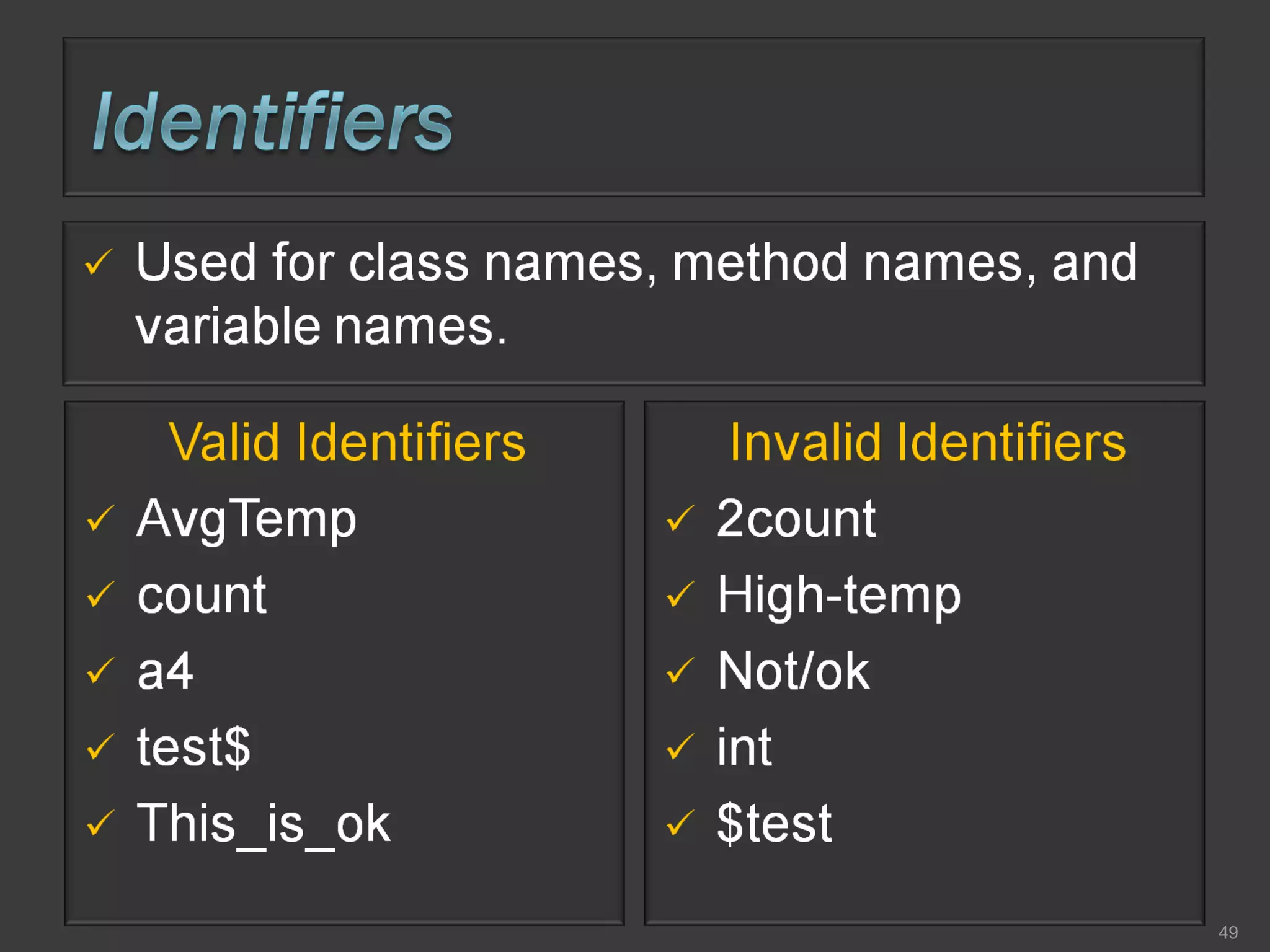
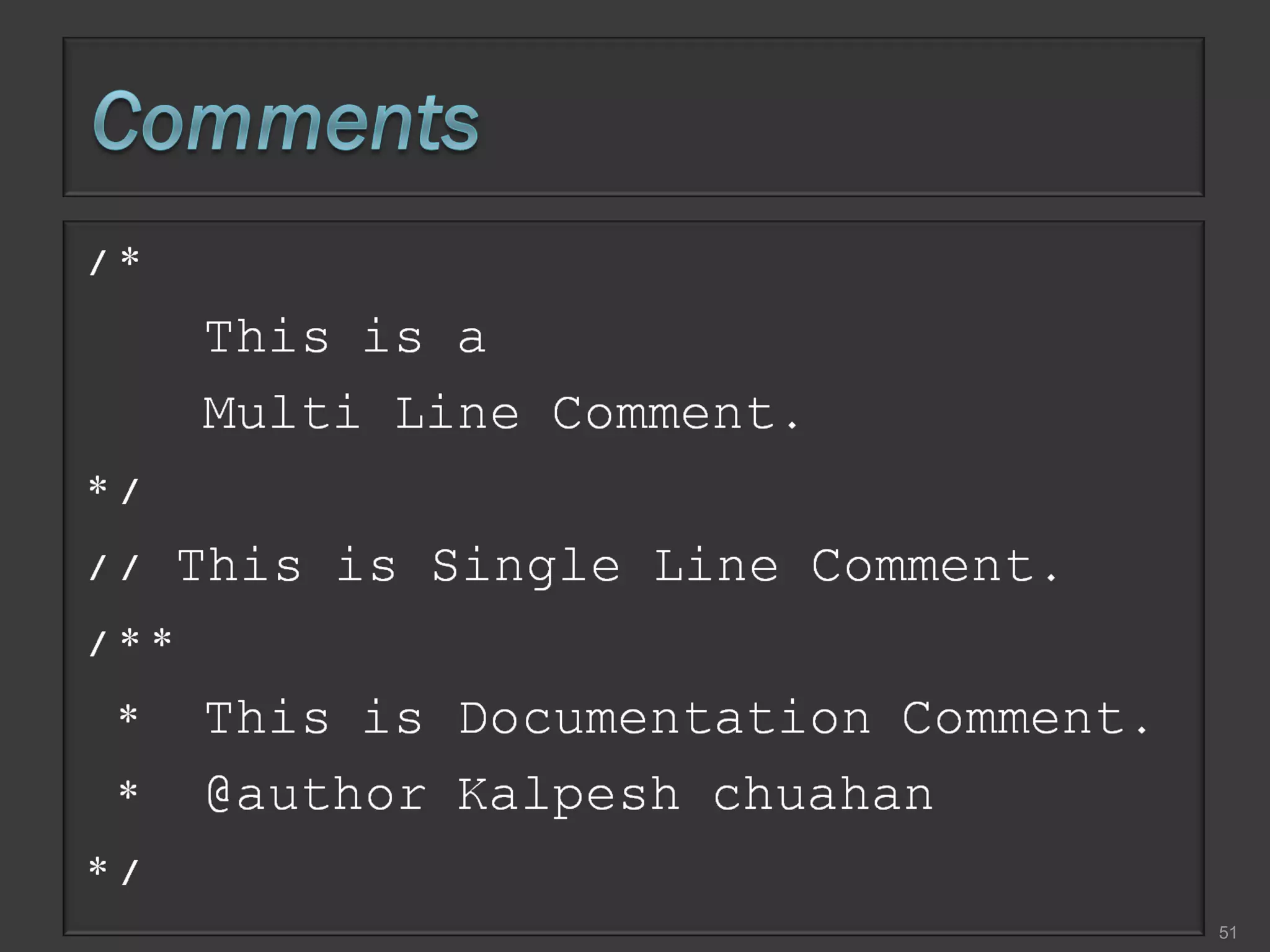
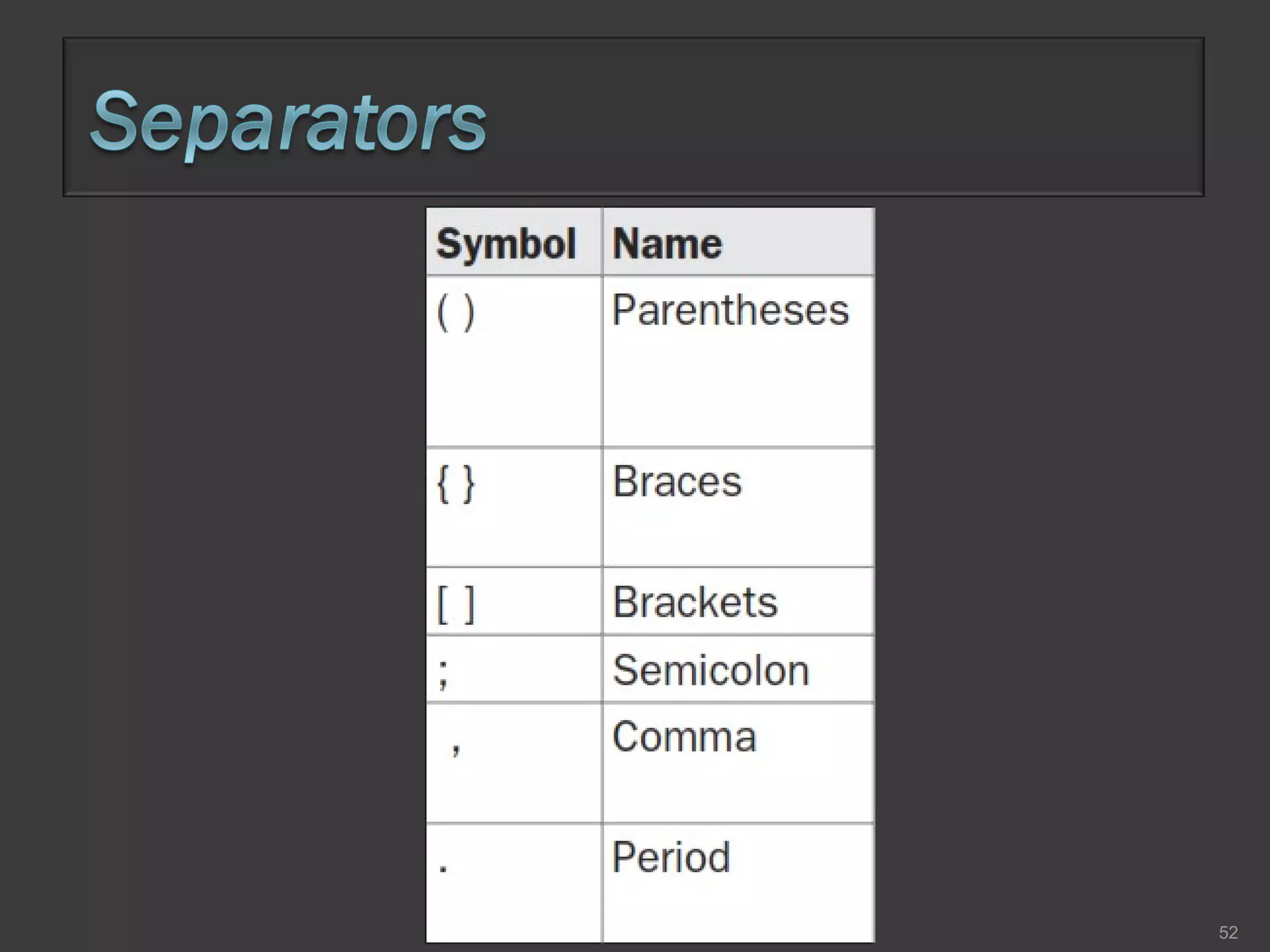
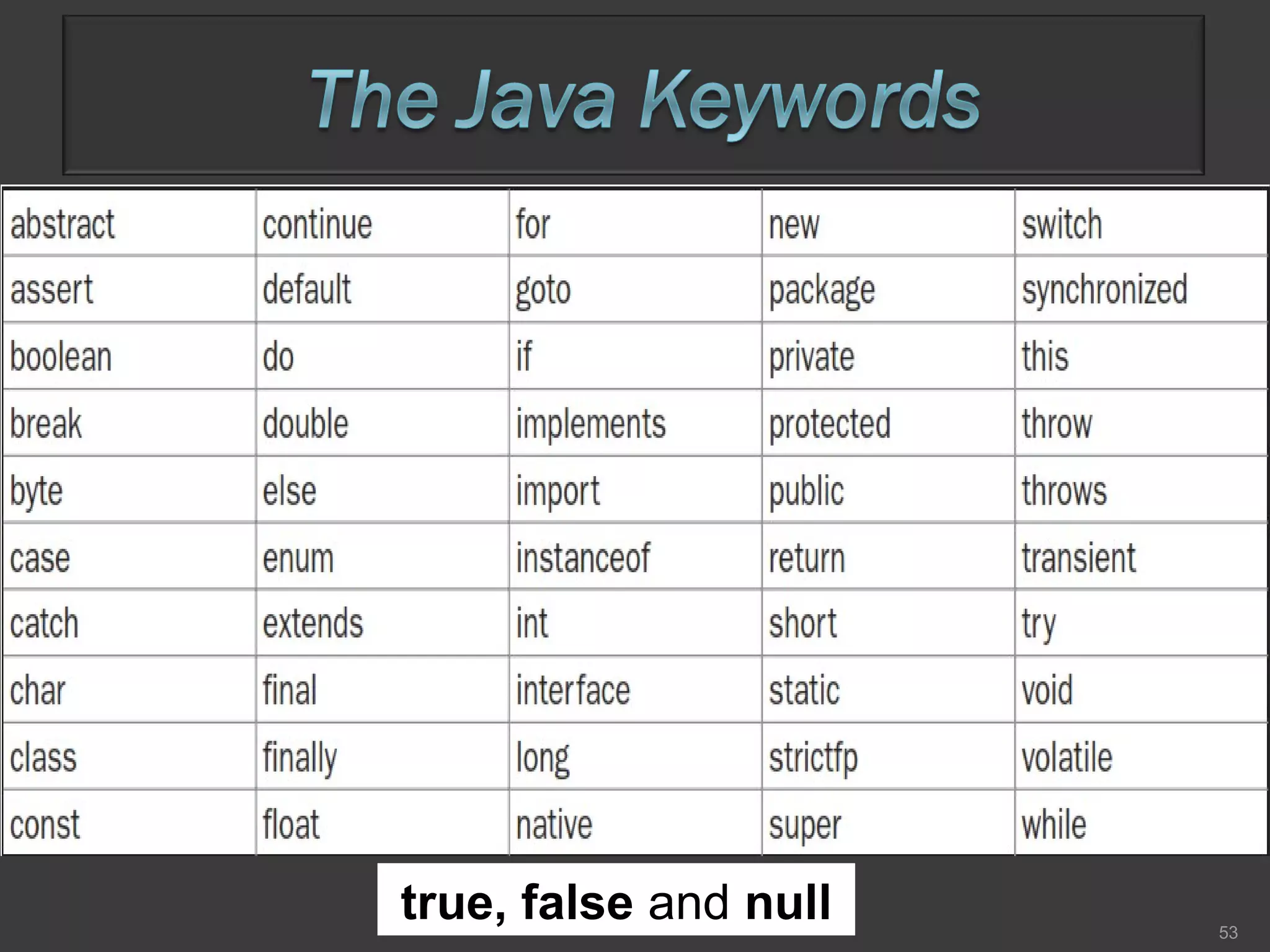
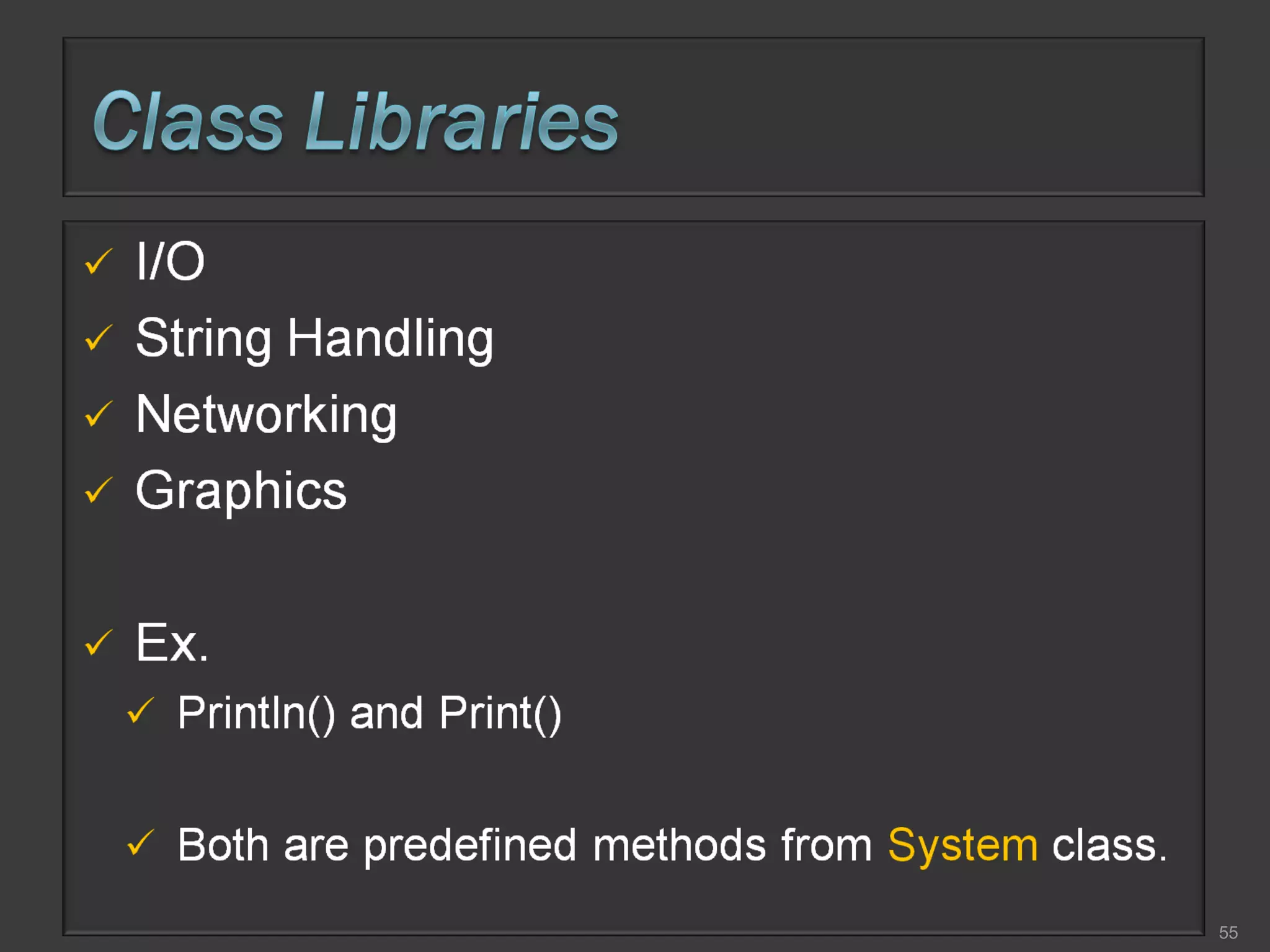
This document compares process-oriented programming and object-oriented programming. Process-oriented programming focuses on code and how it acts on data, with an example given of C language. Object-oriented programming focuses on modeling real world objects and data, and controlling access to code via objects and their properties, with an example given of Java. The document also notes that object-oriented programming uses true, false and null values.