This document provides an introduction and overview of jQuery, including:
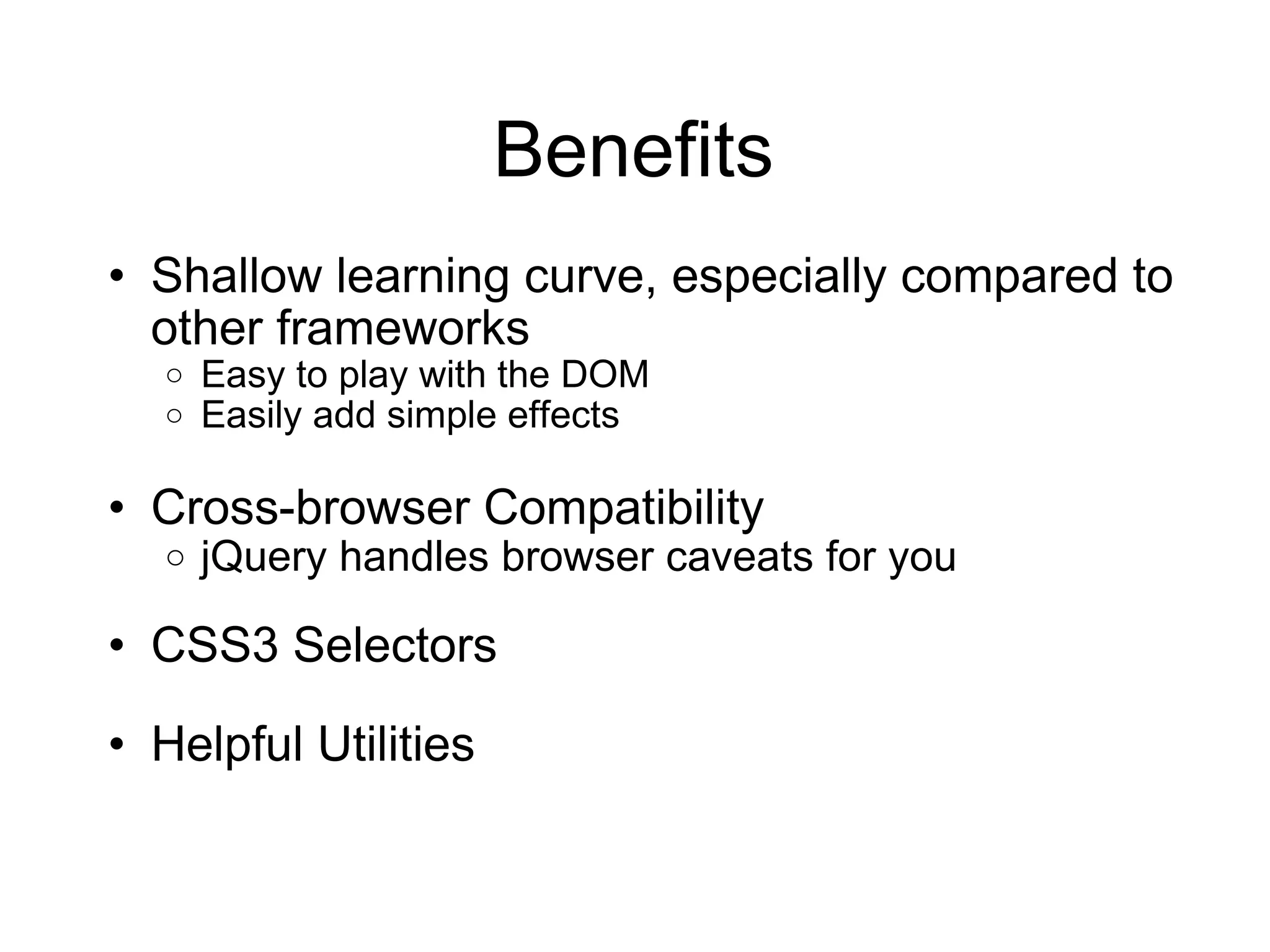
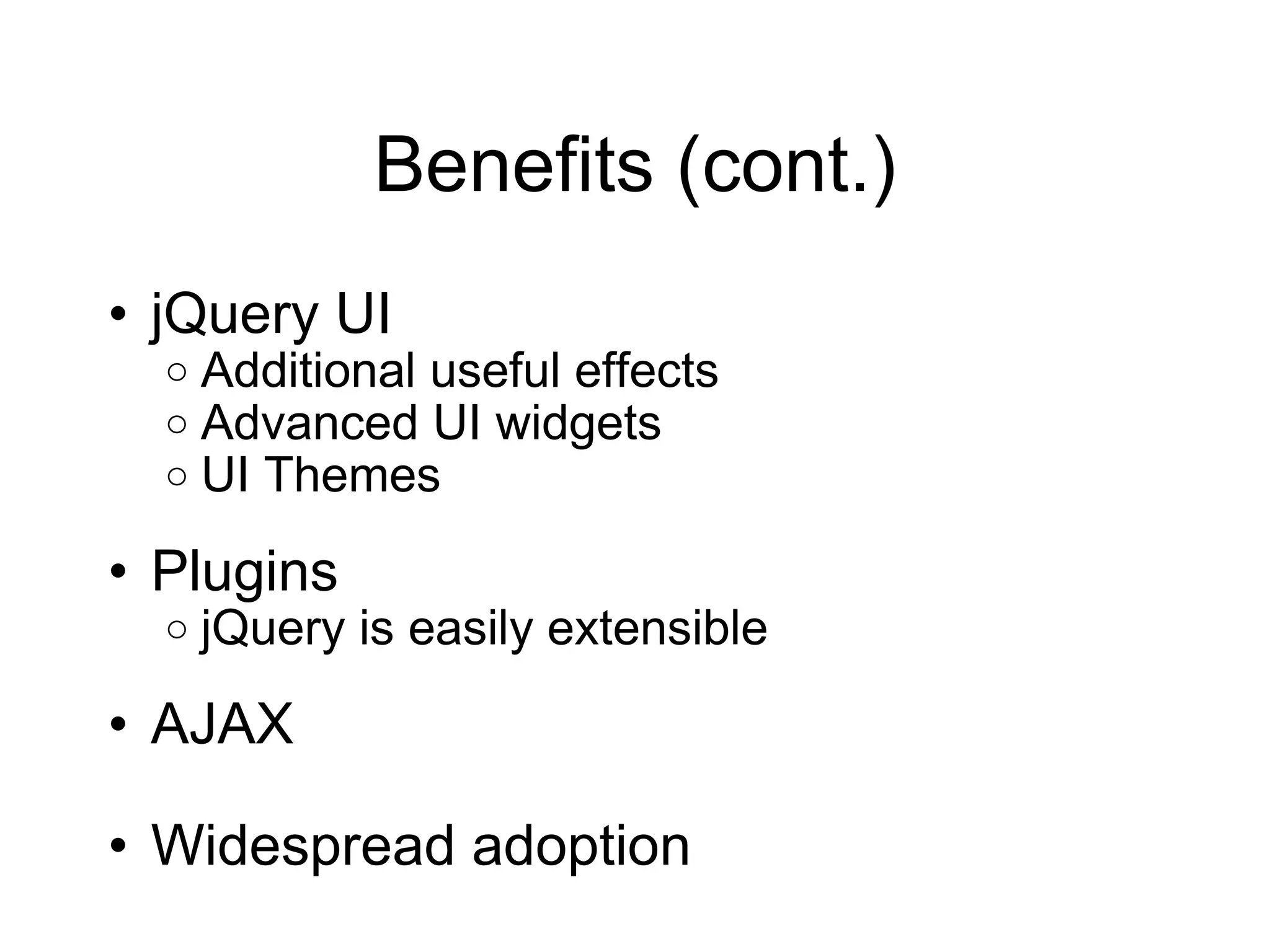
1) The benefits of jQuery such as its shallow learning curve, ease of DOM manipulation, cross-browser compatibility, and extensibility through plugins.
2) How to get started with jQuery by downloading the library and using basic selectors and functions.
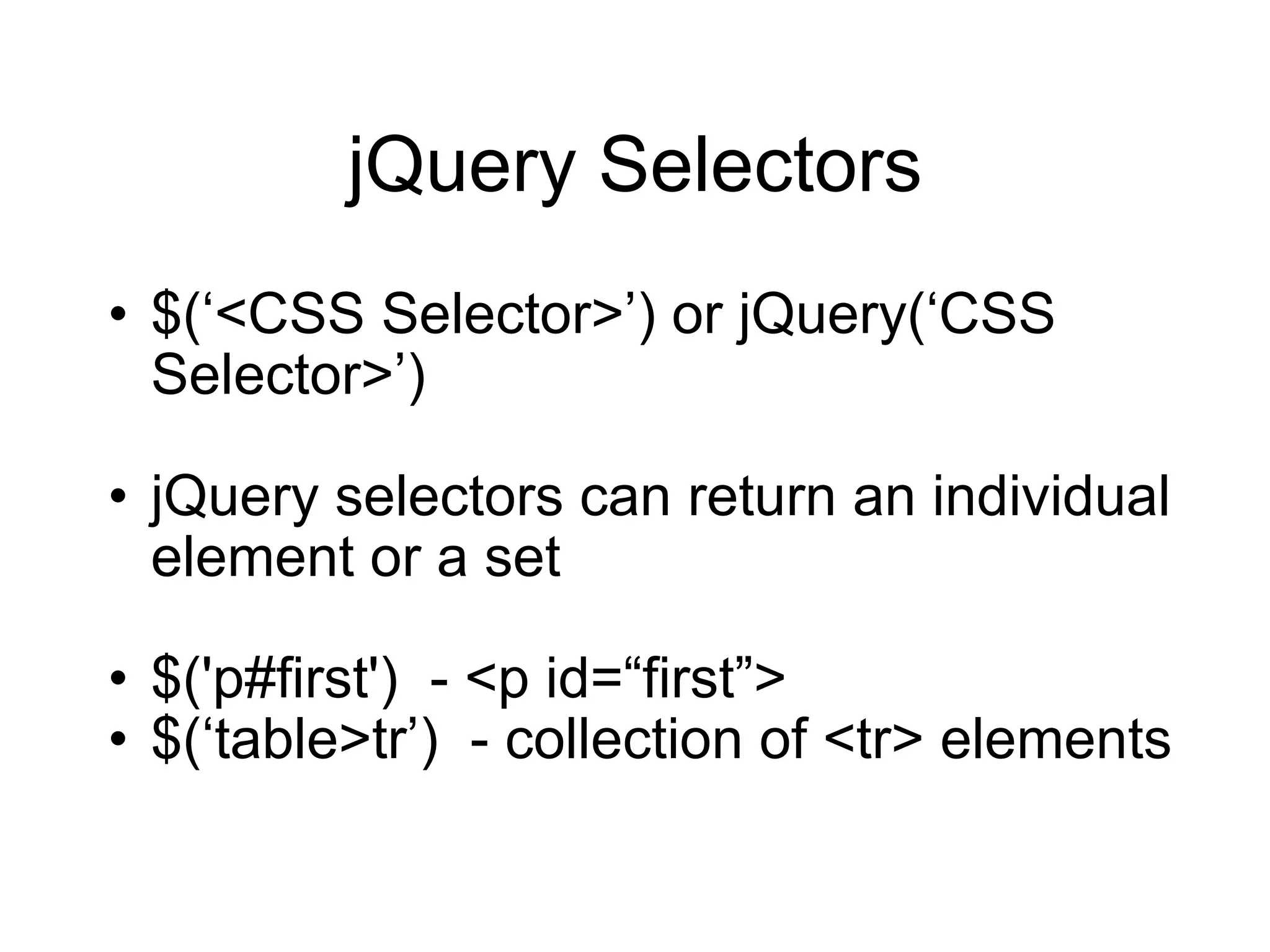
3) Examples of jQuery selectors, actions, and effects that can be used to manipulate and style page elements.
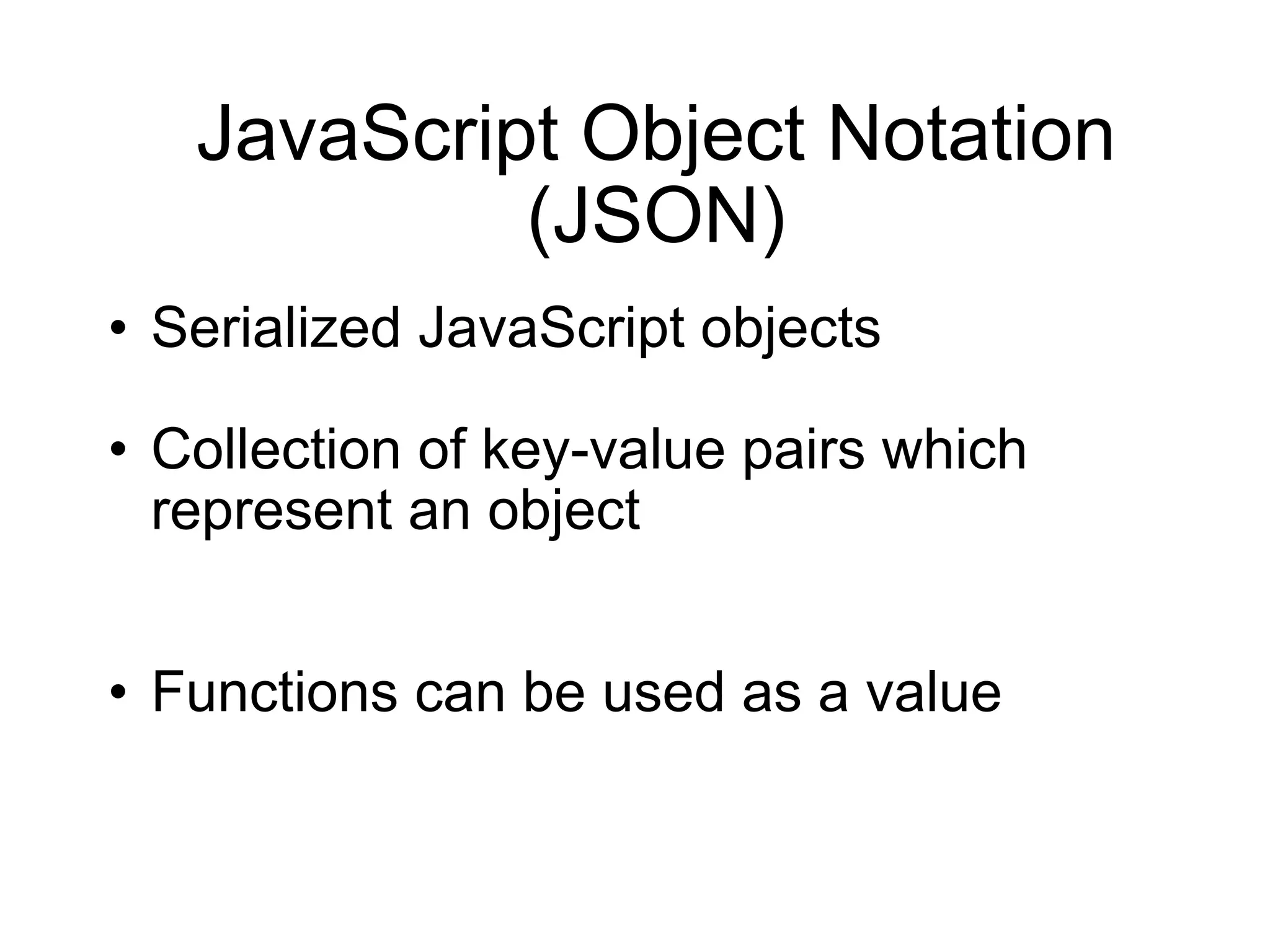
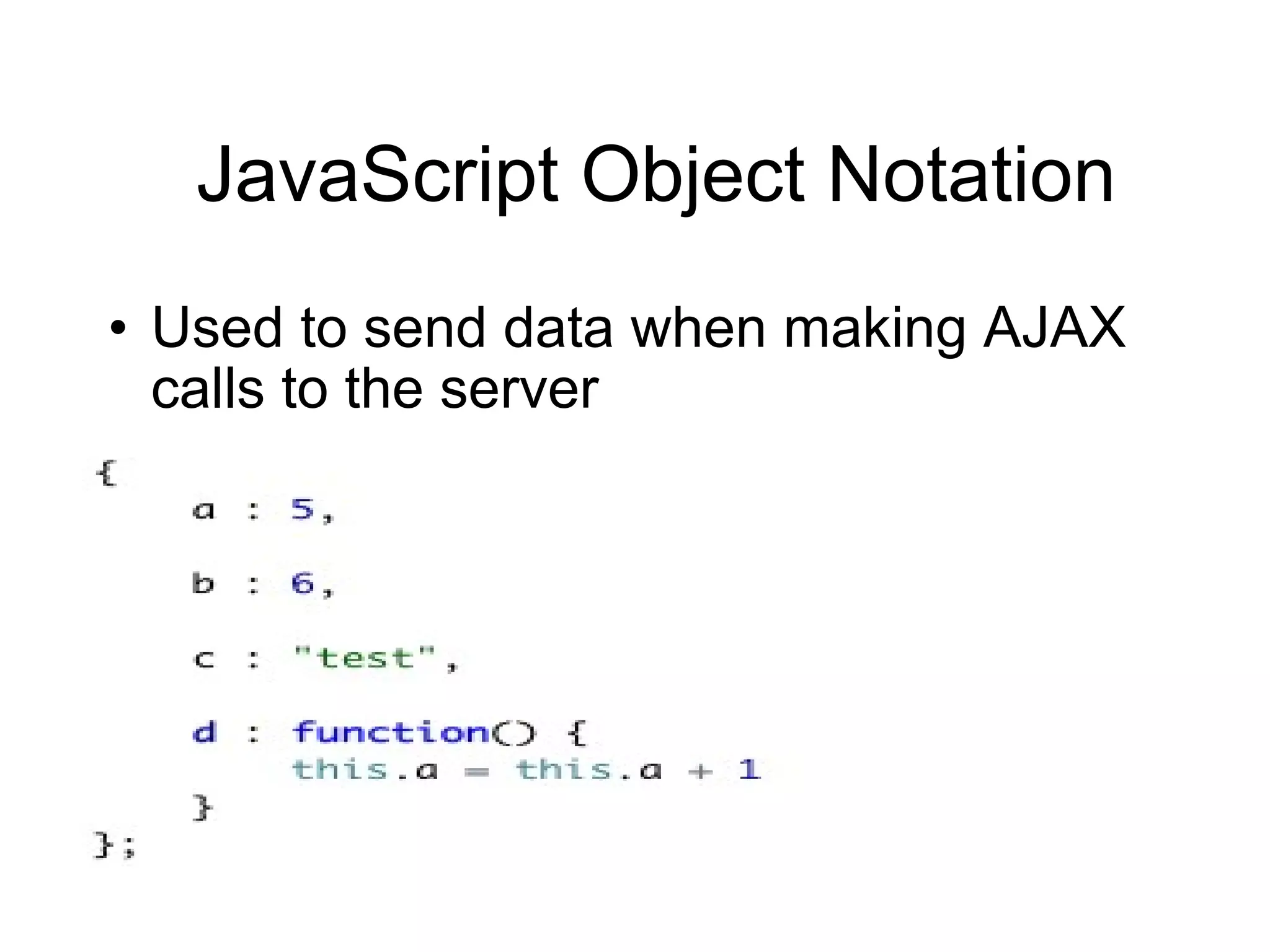
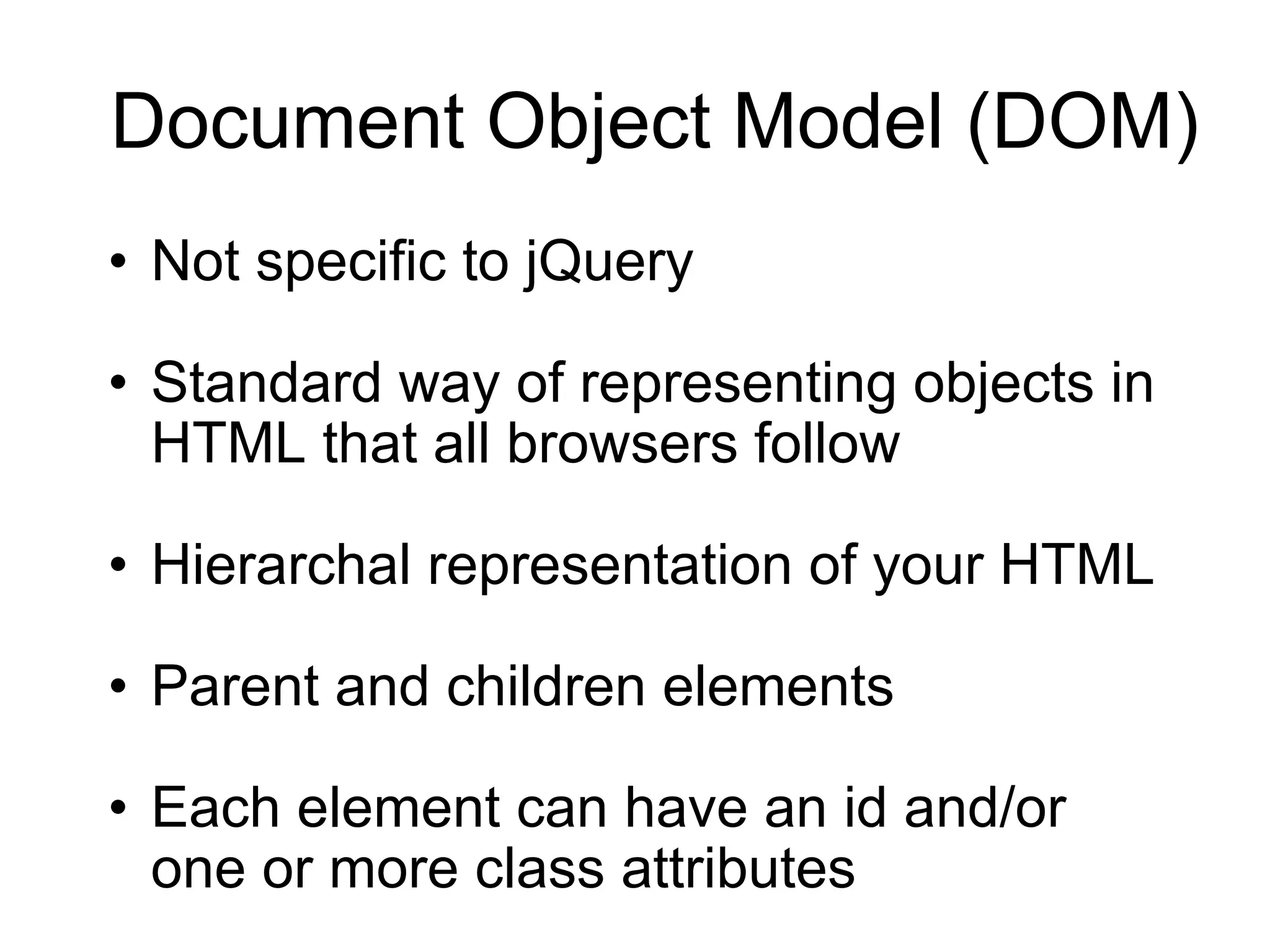
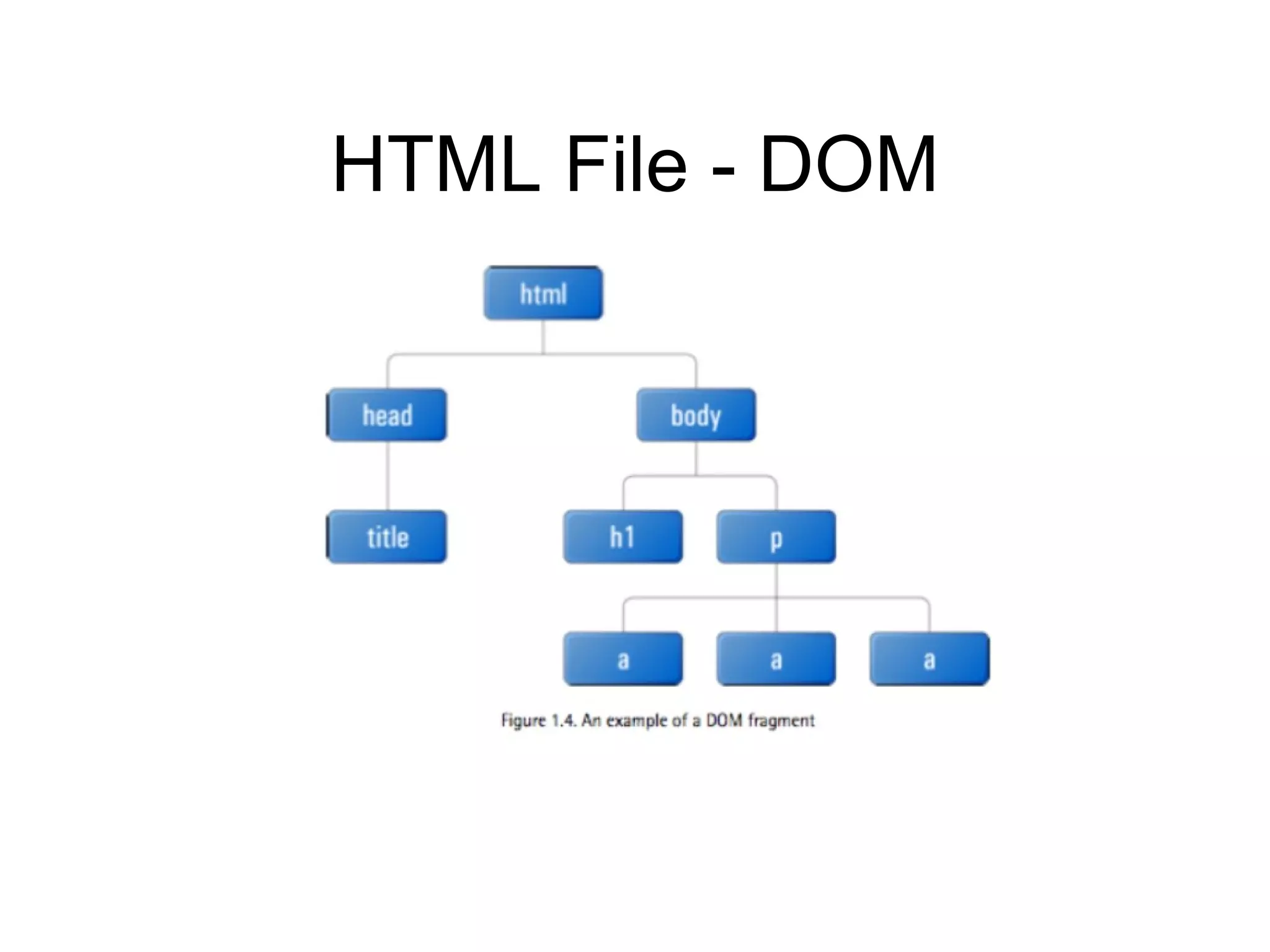
4) Important jQuery concepts like the DOM, CSS selectors, JSON, and using events like "ready" and "click" to execute code.











![CSS Selectors Bare words selects HTML tags span <span> Can filter on attributes within HTML tags input[type = ‘button’] <input type=“button” />](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introtojquery-110314204402-phpapp02/75/Intro-to-jQuery-18-2048.jpg)