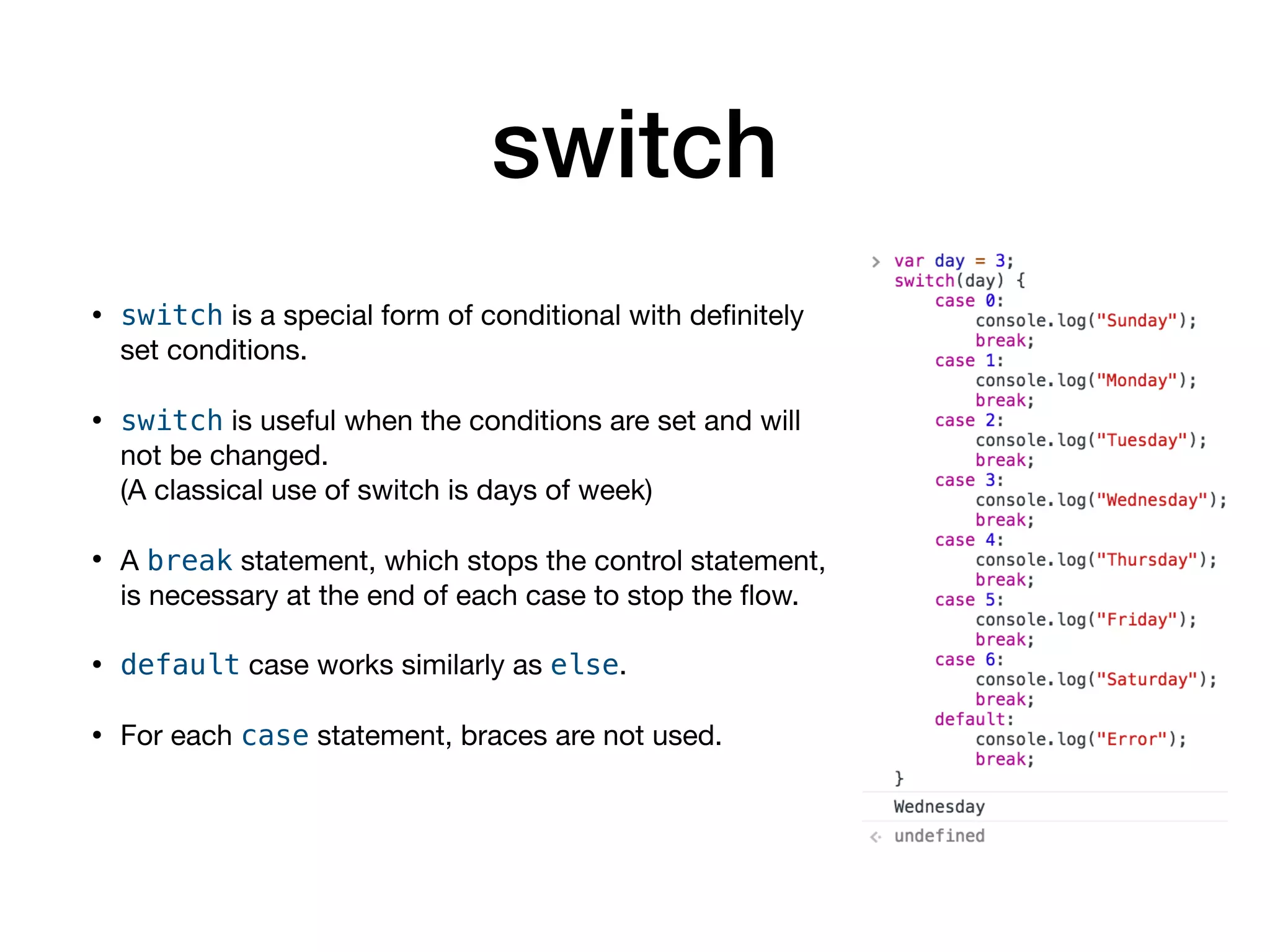
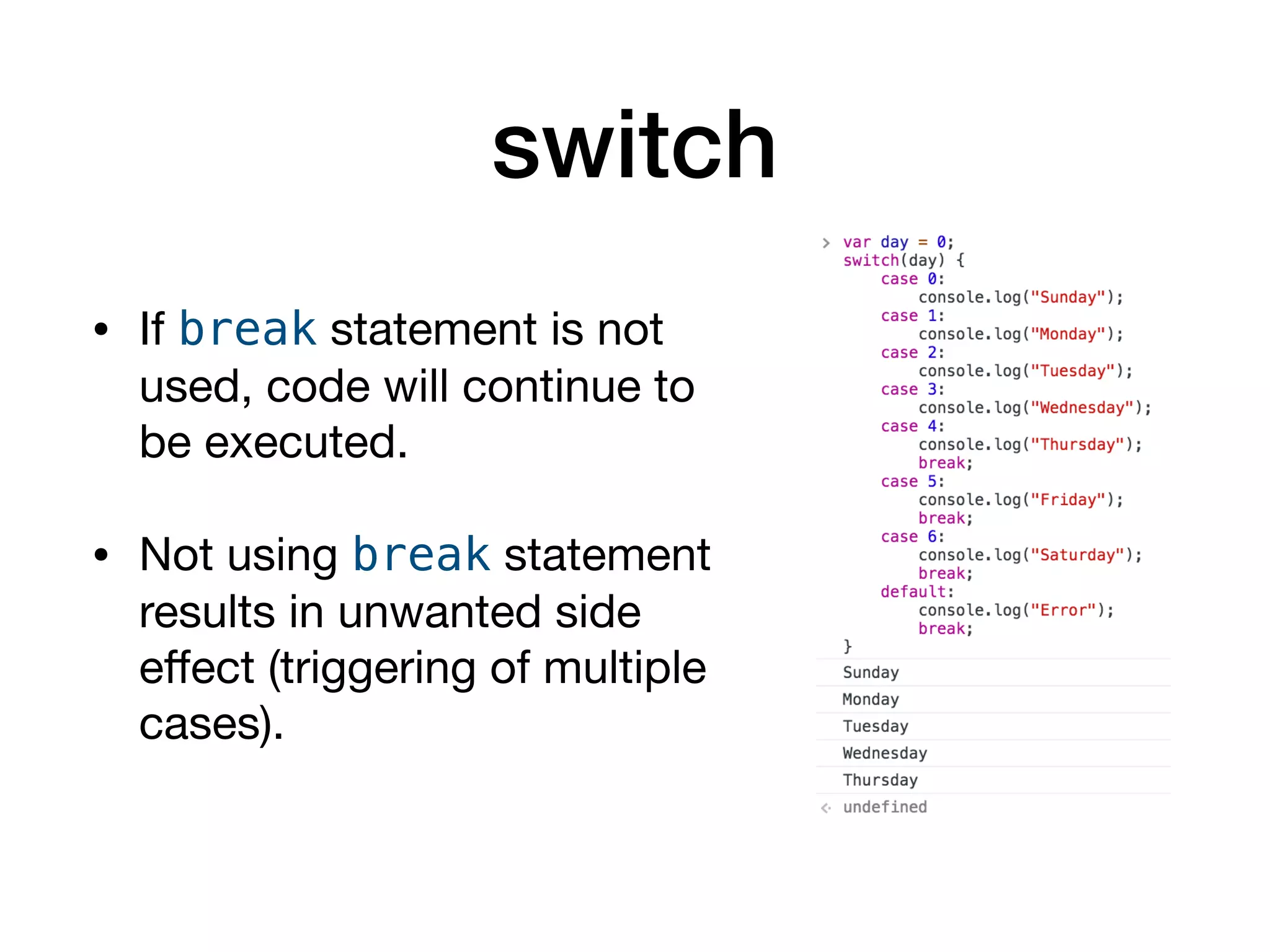
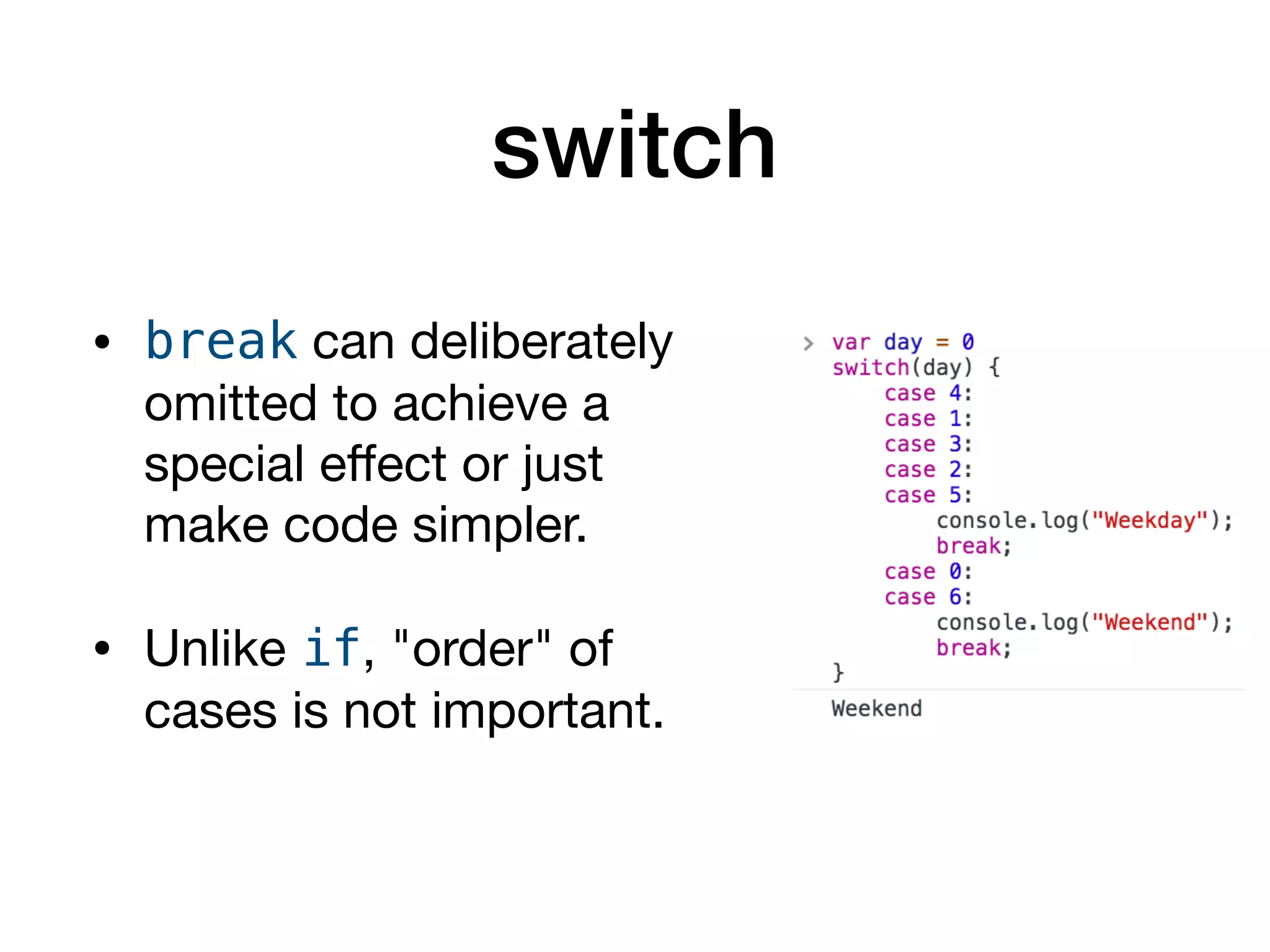
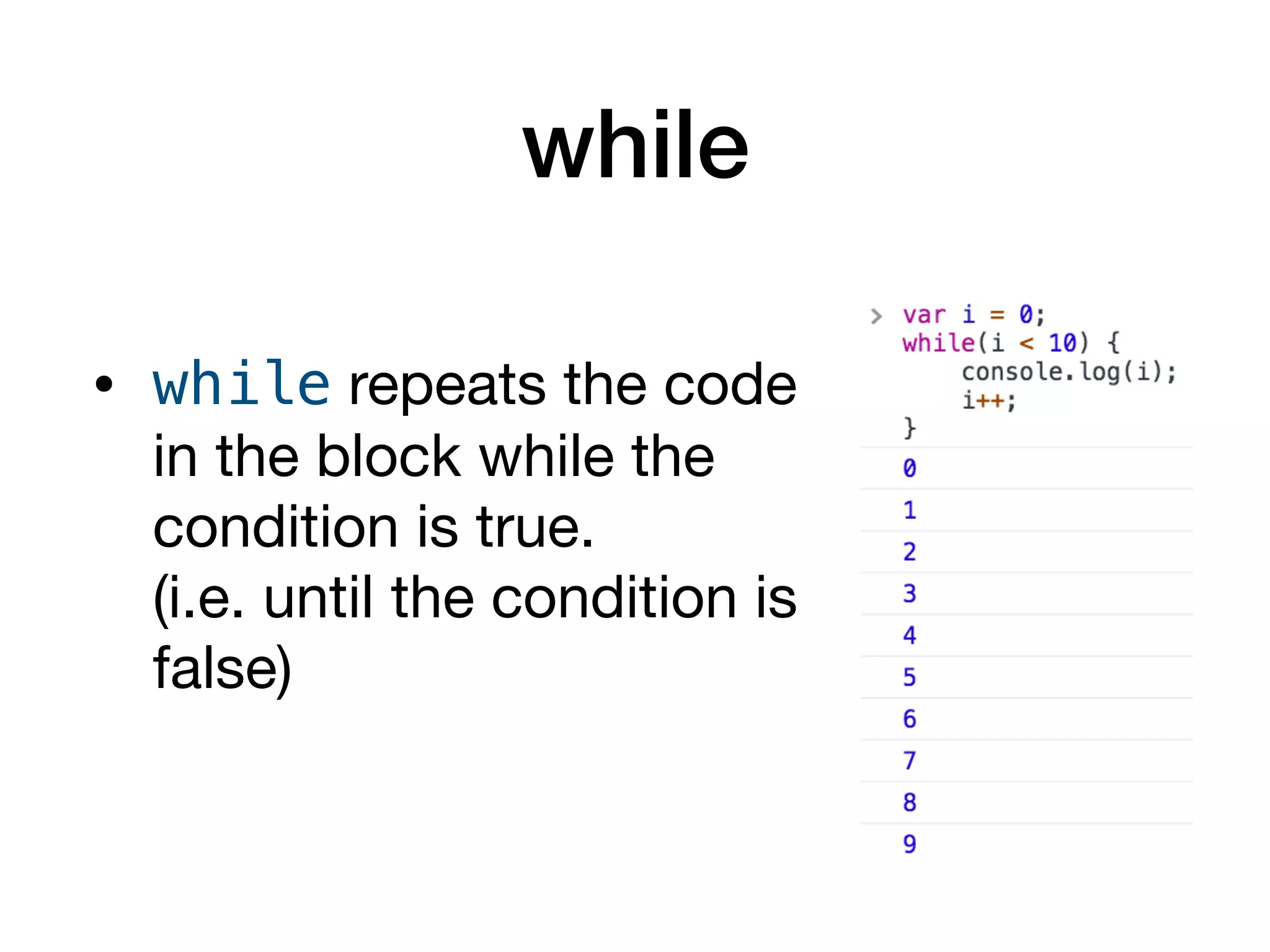
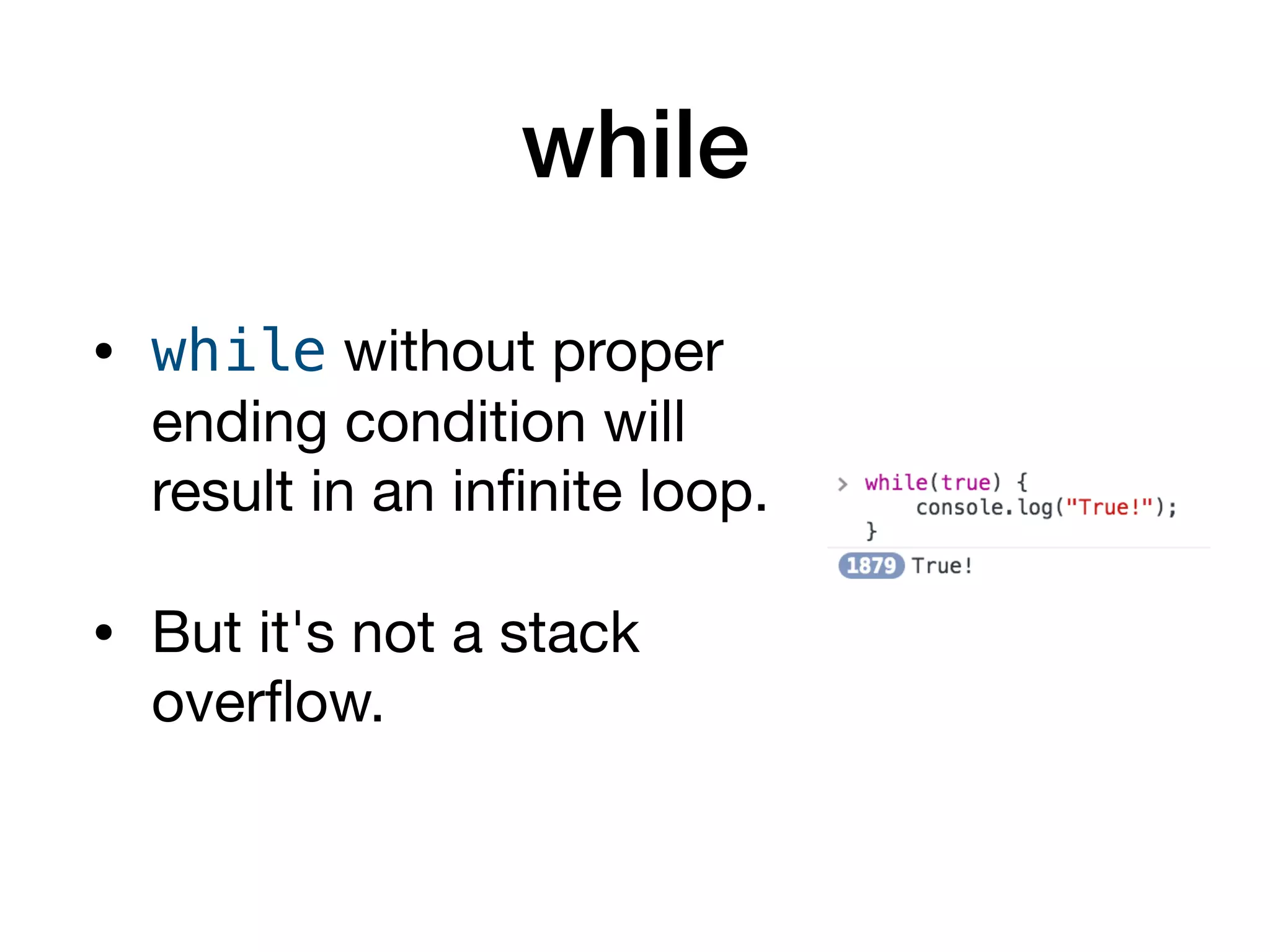
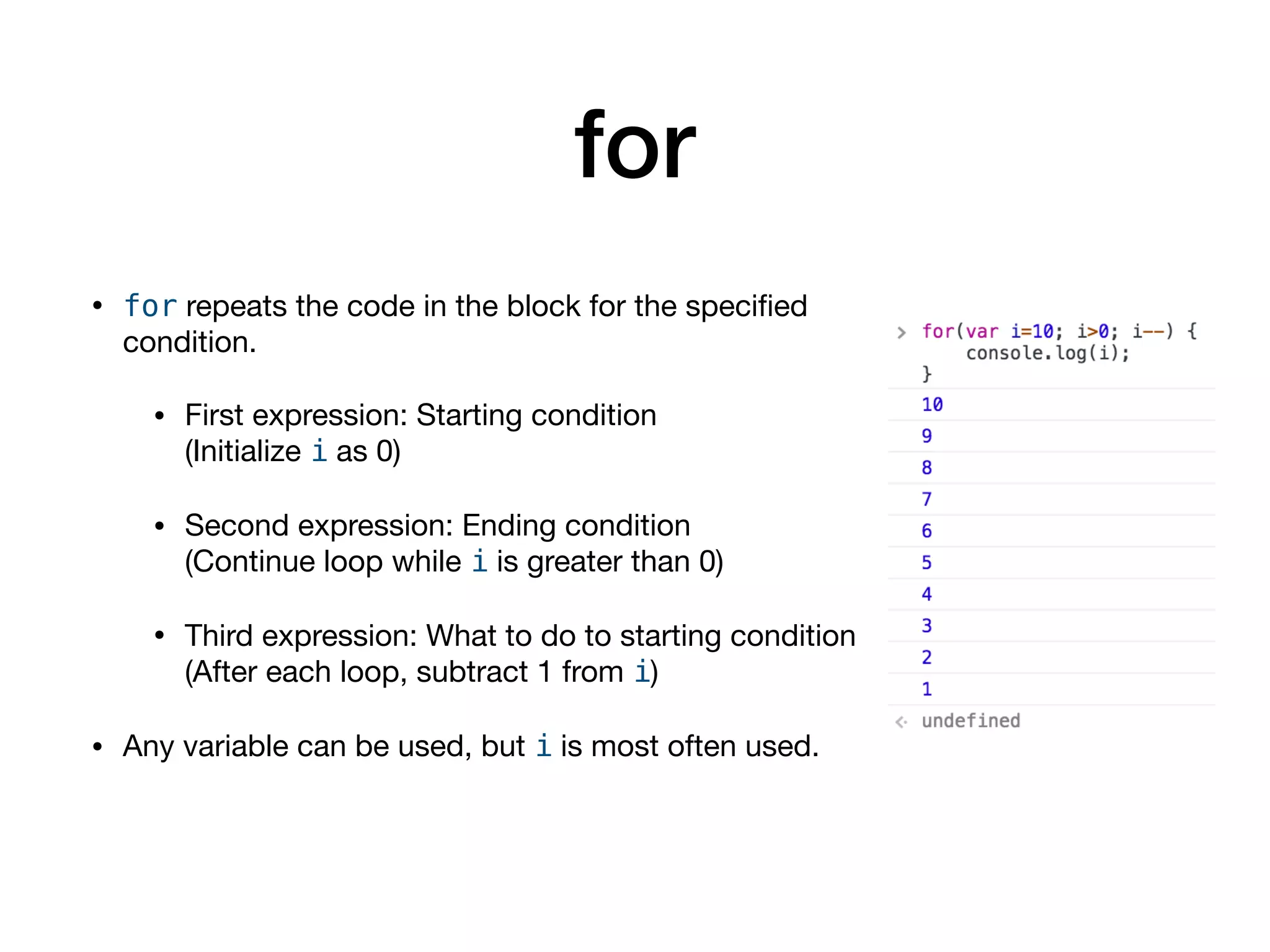
This document serves as an introduction to programming with JavaScript, focusing on control statements such as conditionals and loops. It explains how control flow can be altered using structures like 'if...else', 'switch', and 'try...catch', alongside common error types in programming. The document also outlines different looping methods like 'while', 'do...while', and 'for', emphasizing proper usage to avoid errors.