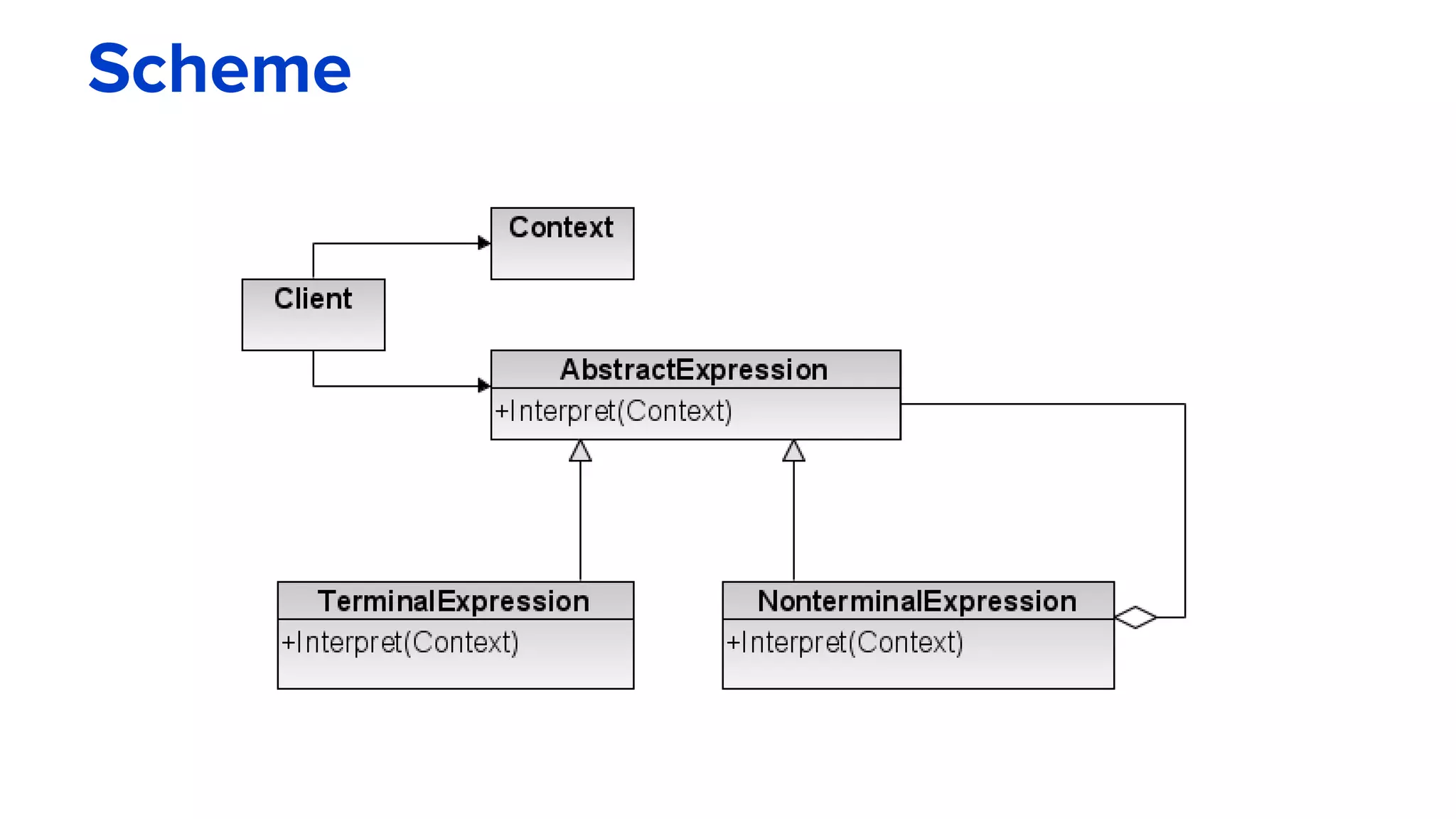
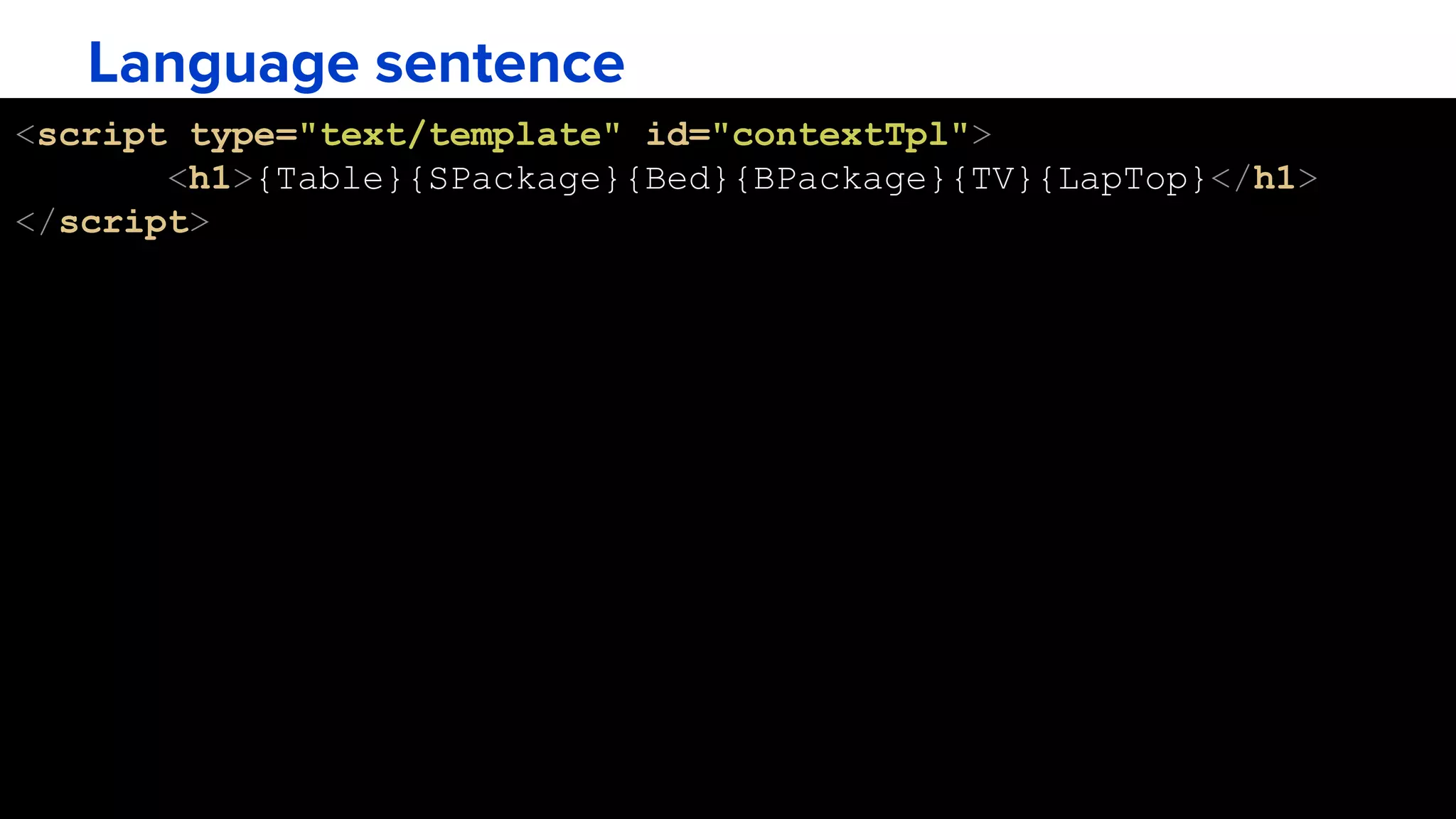
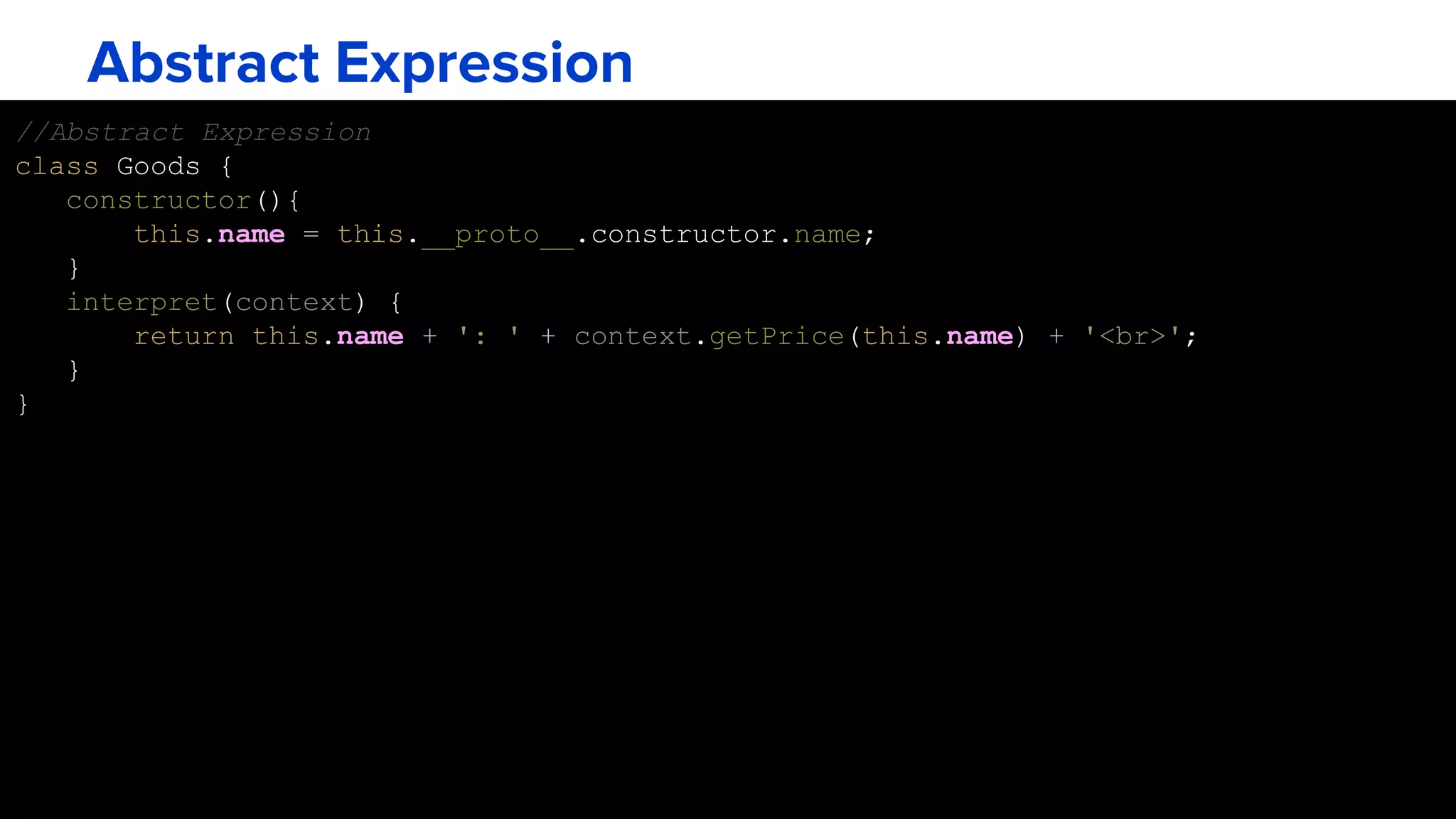
The interpreter pattern describes a way to define the grammar of a language and an interpreter that uses that representation to interpret sentences in the language. It involves creating a class for each symbol (terminal or non-terminal) in the language's grammar. Sentences can then be represented as abstract syntax trees that are easy to traverse and modify. The interpreter pattern is demonstrated through an example of interpreting a barcode grammar. A context class is used to hold pricing data and interpret terminal expression classes like products to return their price.







![Nonterminal Expressions
//Non-Terminal Expresions
class SPackage extends Goods {
constructor() {
super();
this.itemsList = [].slice.call(arguments);
}
add(item) {
this.itemsList.push(item);
}
interpret(context) {
let output = '';
this.itemsList.forEach((exp)=> {
output += exp.interpret(context);
});
return output;
}
}
class BPackage extends SPackage {}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vig3chcq0ewlav9lgnla-signature-a31d1e72b850c4e2e2ea400188a02faf6983d6d381033acff9938b18ce1ef3b2-poli-160322094409/75/Interpreter-Design-Pattern-in-Javascript-12-2048.jpg)
![Context
class PriceContext {
constructor(bed, table, tv, laptop, sPackage, bPackage) {
this.bed = bed;
this.table = table;
this.tv = tv;
this.laptop = laptop;
this.spackage = sPackage;
this.bpackage = bPackage;
this.prices = {};
}
setPrice(prices) {
for(let key in prices) {
if(!prices.hasOwnProperty(key)) continue;
this.prices[key] = prices[key];
}
}
getPrice(name) {
return this.prices[name];
}
interpret(expName){
return
this[expName].interpret(this);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vig3chcq0ewlav9lgnla-signature-a31d1e72b850c4e2e2ea400188a02faf6983d6d381033acff9938b18ce1ef3b2-poli-160322094409/75/Interpreter-Design-Pattern-in-Javascript-13-2048.jpg)
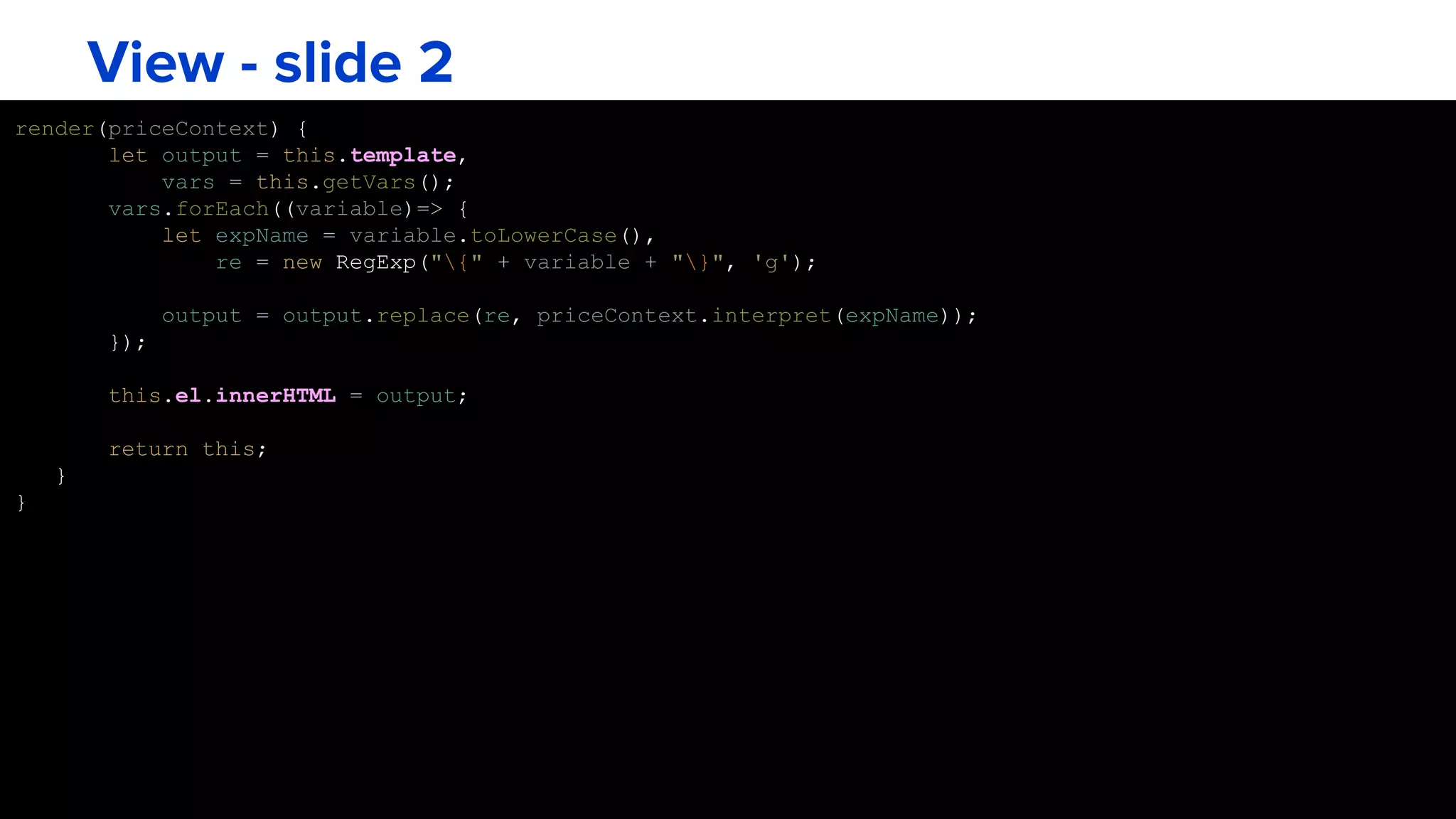
![View - slide 1
class View {
constructor(el, tplId) {
this.el = el;
this._vars = {};
this.setTemplate(tplId);
}
setTemplate(tplId) {
this.template = document.getElementById(tplId).innerHTML.replace(/s/g, '');
}
getVars() {
let regex = /{(.*?)}/g,
matches, expressions = [];
while (matches = regex.exec(this.template)) {
expressions.push(matches[1]);
}
return expressions;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vig3chcq0ewlav9lgnla-signature-a31d1e72b850c4e2e2ea400188a02faf6983d6d381033acff9938b18ce1ef3b2-poli-160322094409/75/Interpreter-Design-Pattern-in-Javascript-14-2048.jpg)