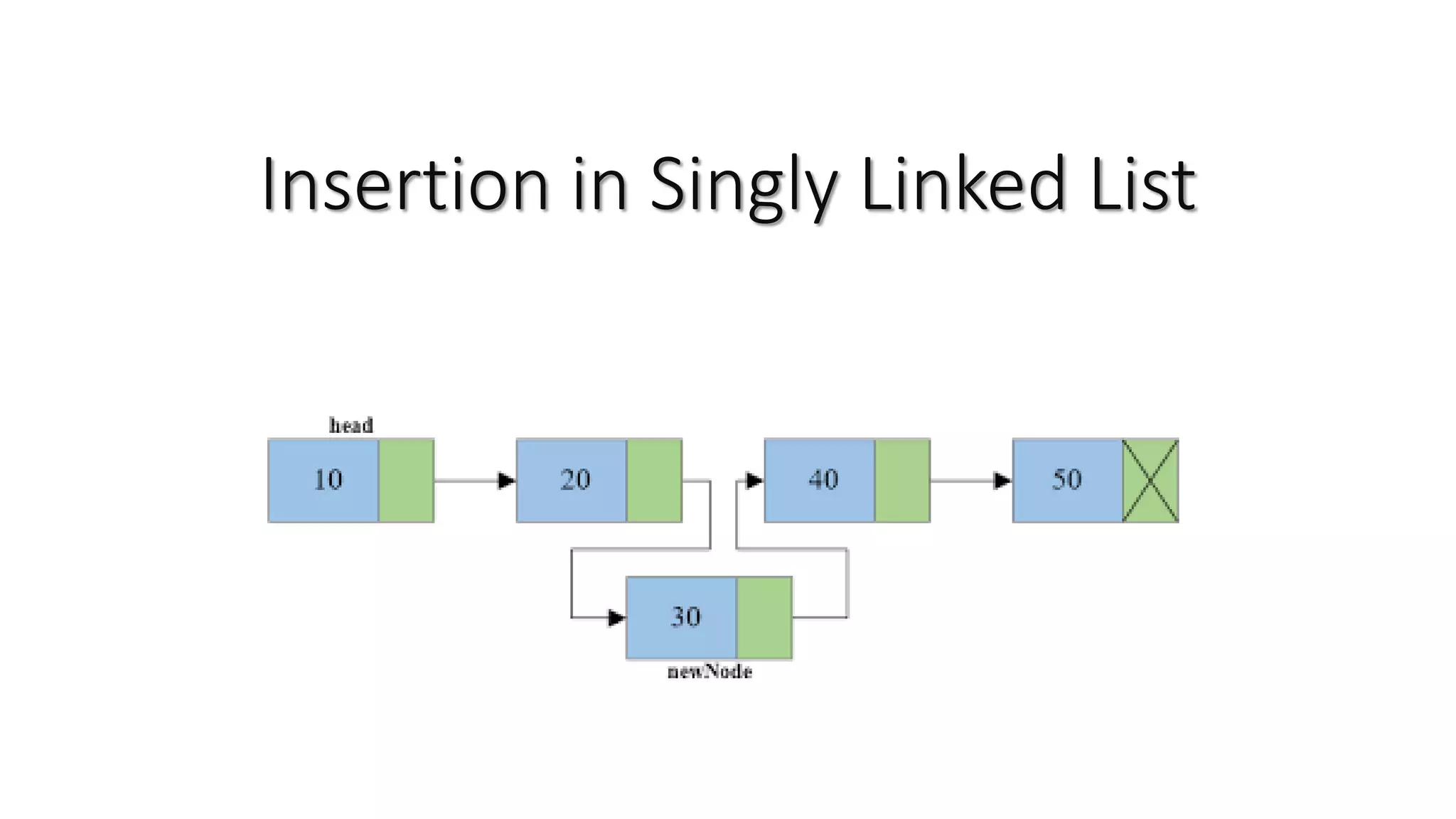
Insertion in a singly linked list can be done at the beginning, middle, or end of the list. To insert a node, a new node is first created and its data and link fields are initialized. For insertion at the beginning, the new node's link is set to the current head node and the head is updated to the new node. For middle insertion, the link of the new node is set to the link of the previous node and the previous node's link is updated to the new node. For end insertion, the link of the last existing node is updated to the new node and the new node's link is set to null. Traversal may be needed to reach the insertion point, with conditions to stop at









![Conditions
Condition to stop traversal at desired point
* Initialize Count with 1. # PTR =Pointer that is traversing.
Before given value (PTR -> Next) -> Data = ‘Value’ [#]
After given value PTR -> Data = ‘Value’ [#]
Before given position Count == ‘Position’ – 1 [*]
After given position Count == ‘Position’ [*]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/insertioninsinglylinkedlist-170509164604/75/Insertion-in-singly-linked-list-12-2048.jpg)
![Process Summary
(1) Create a New Node
(2) Apply values to the ‘Data’ and ‘Link’ part.
[Link part is NULL initially]
(3) Traverse in the linked list until we reach to the desired point.
(4) Insert Node using swaps of links.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/insertioninsinglylinkedlist-170509164604/75/Insertion-in-singly-linked-list-13-2048.jpg)
