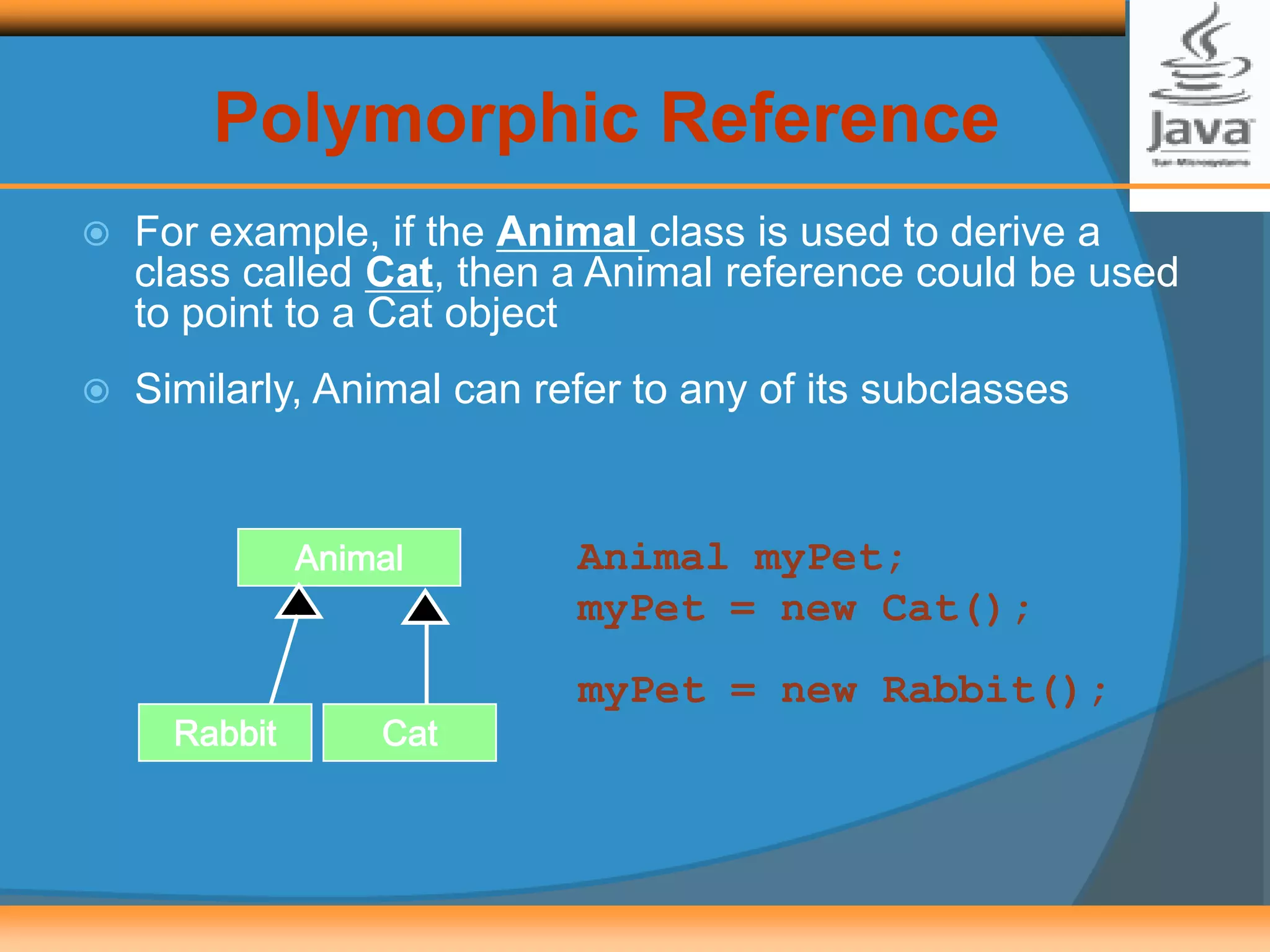
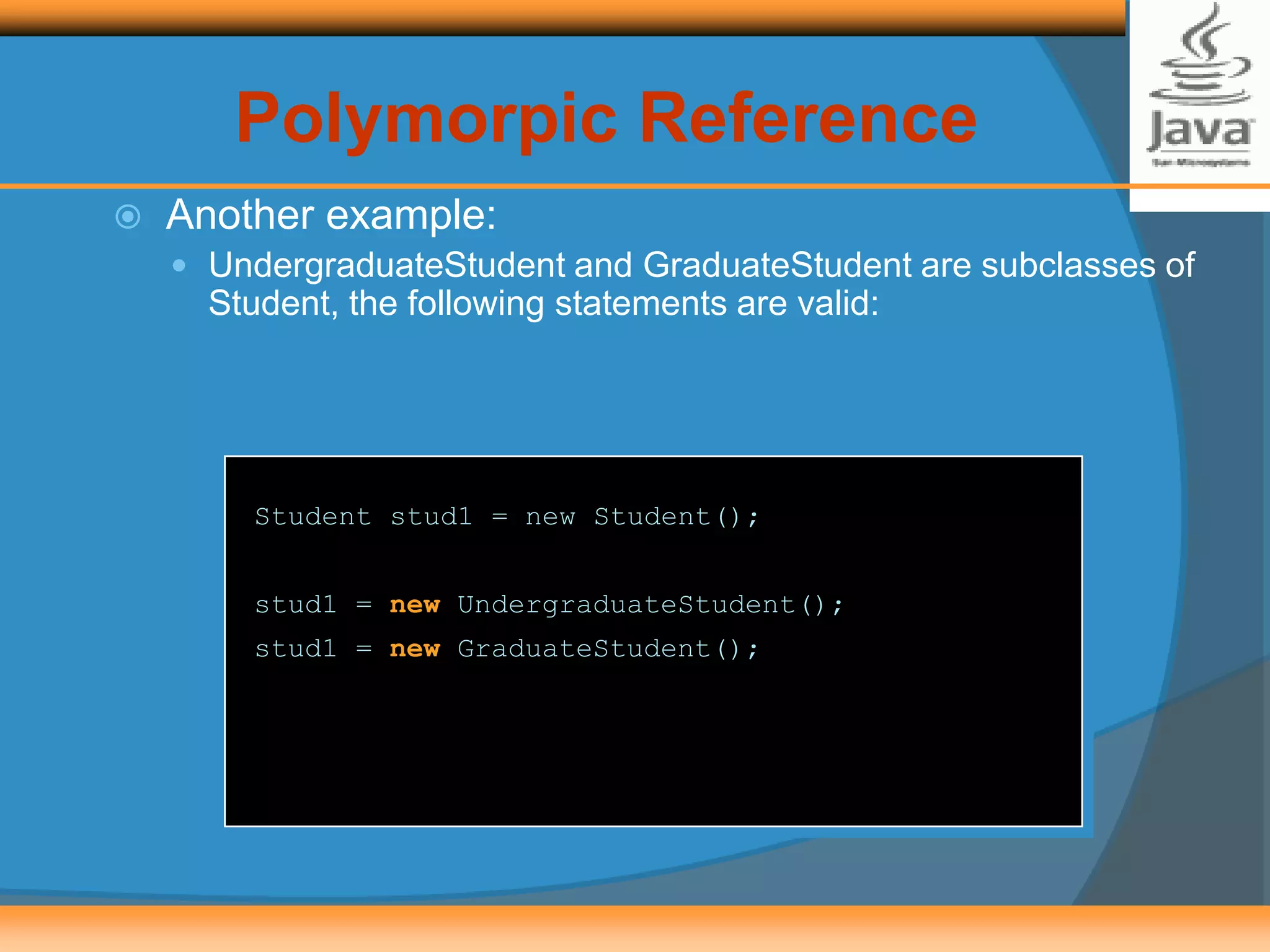
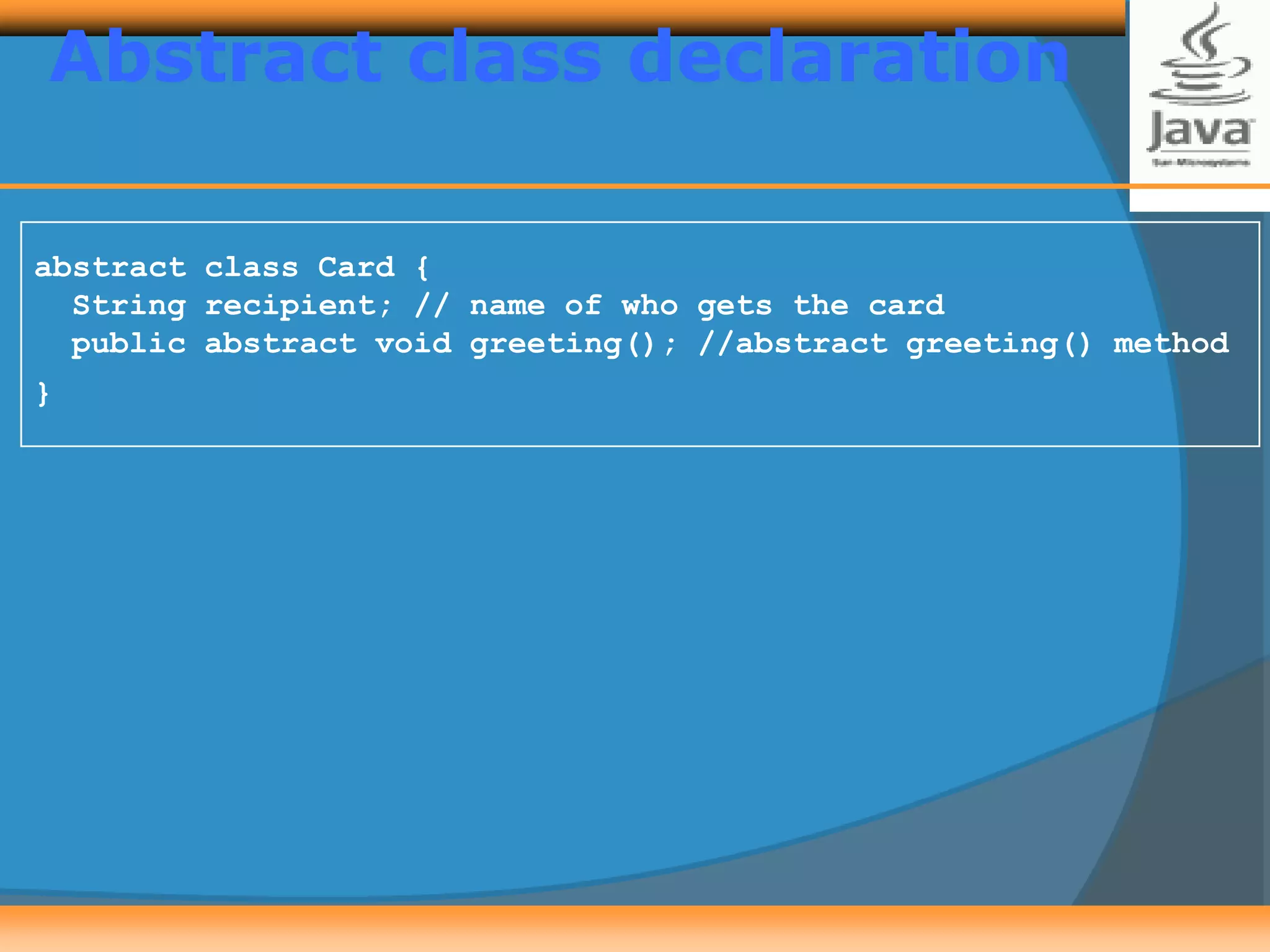
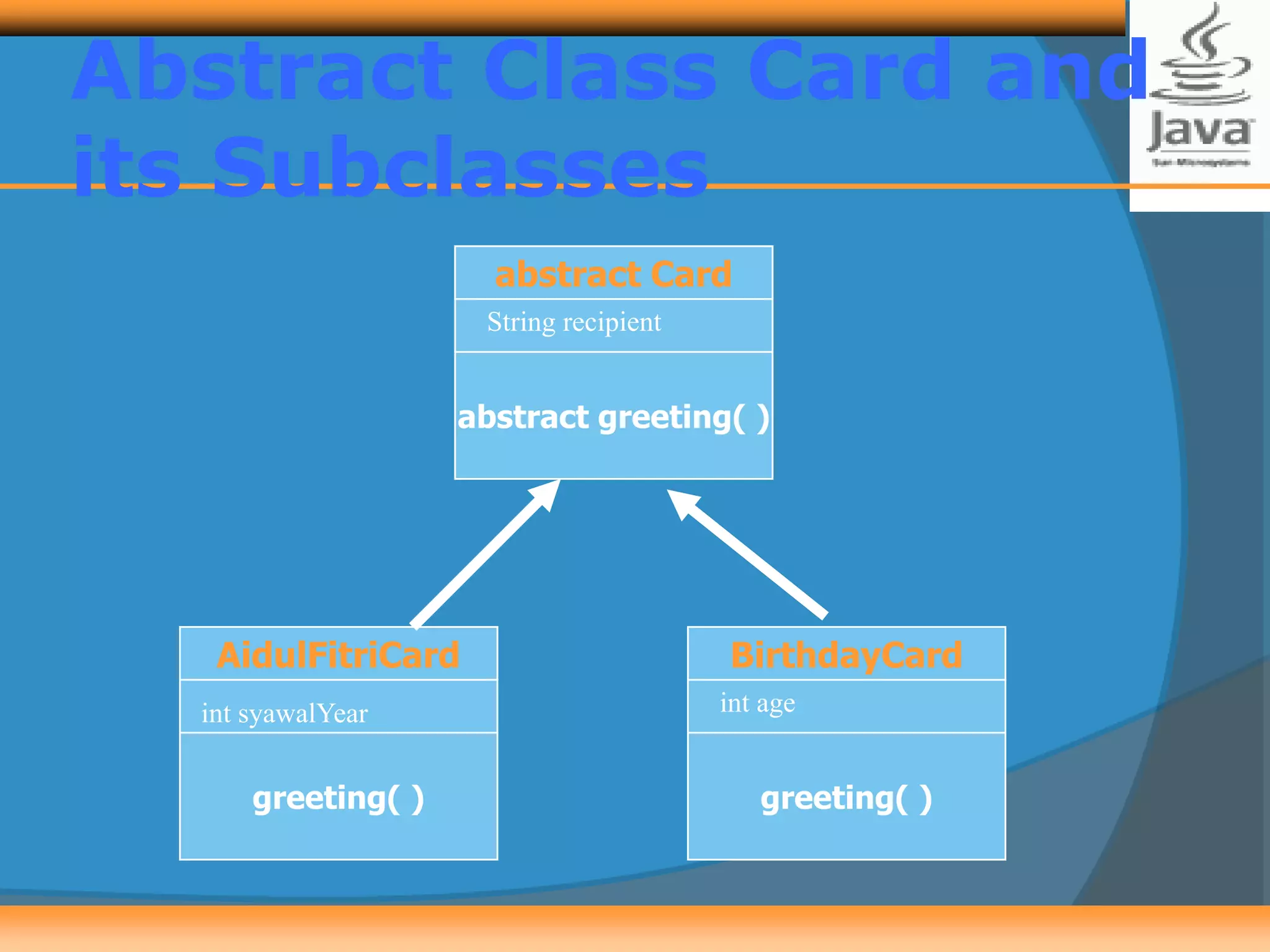
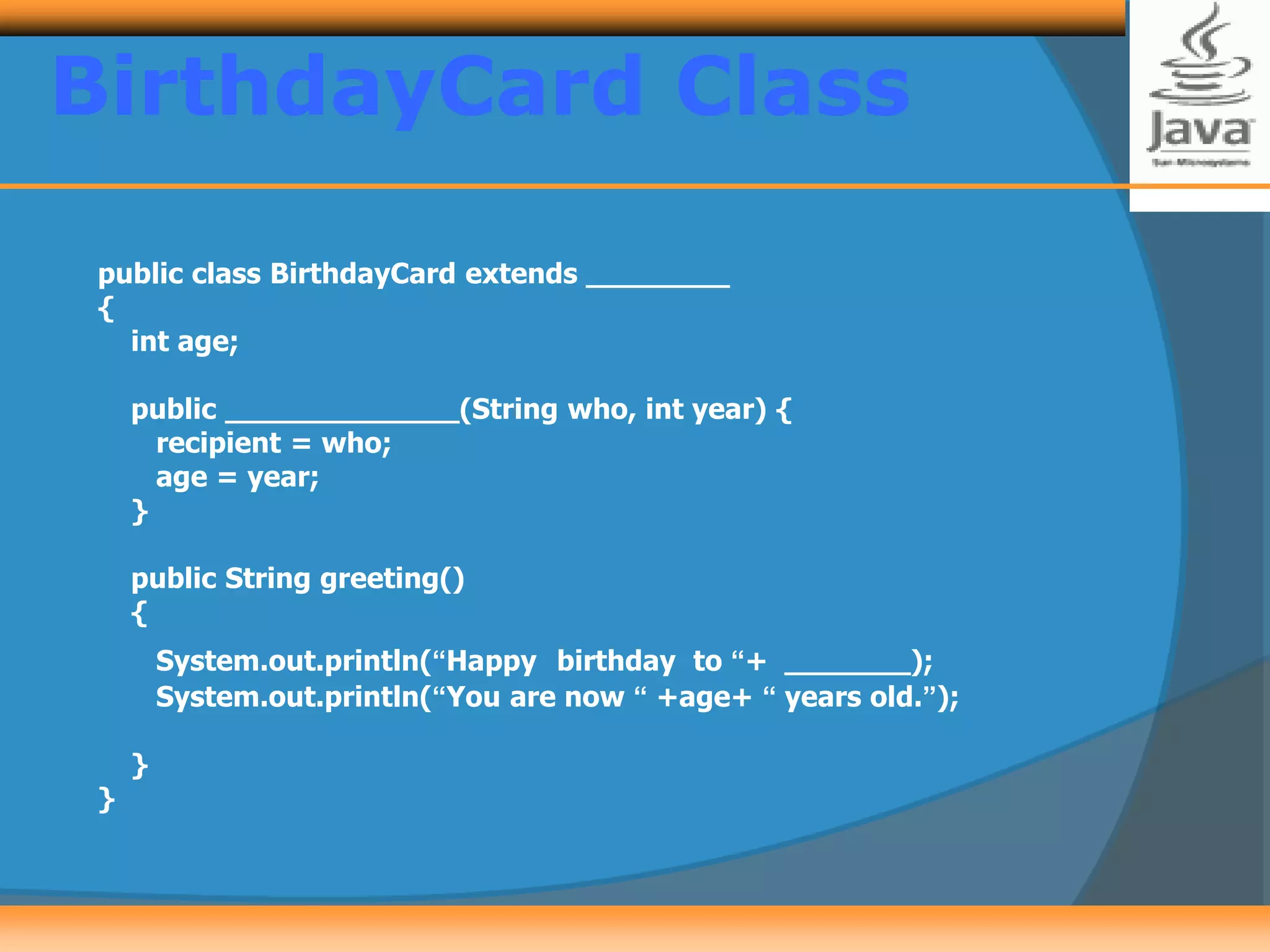
Polymorphism allows creating versatile software designs that can deal with multiple related objects. An abstract class cannot be instantiated but can be extended by subclasses, which must implement the abstract methods. The document provides examples of an Animal abstract class with a sound() abstract method, and a Card abstract class with a greeting() abstract method. Subclasses like AidulFitriCard and BirthdayCard extend Card and implement the greeting() method.

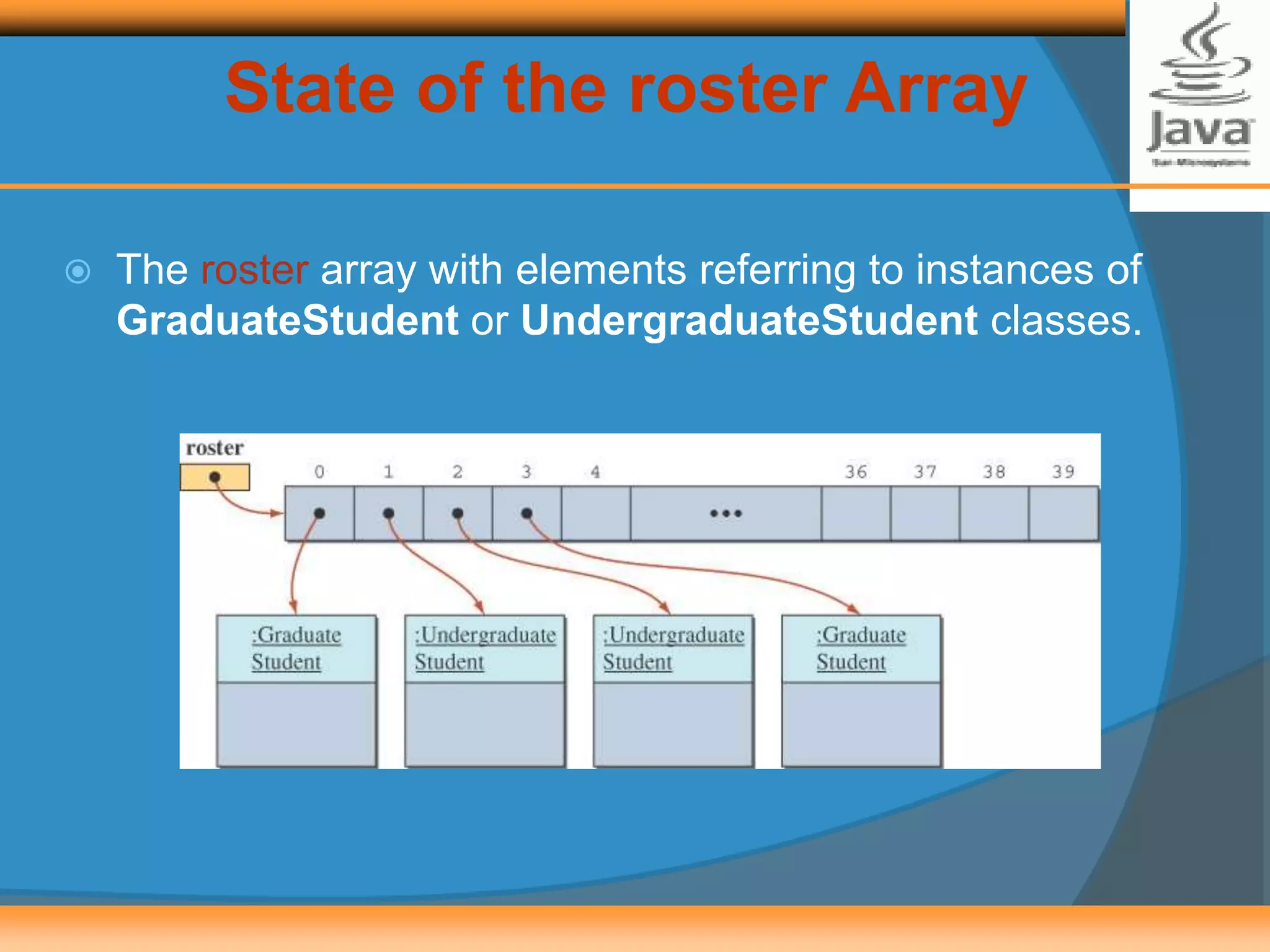
![Creating the roster Array
We can maintain our class roster using an array, combining
objects from the Student, UndergraduateStudent, and
GraduateStudent classes.
Student roster = new Student[40];
. . .
roster[0] = new GraduateStudent();
roster[1] = new UndergraduateStudent();
roster[2] = new UndergraduateStudent();
. . .](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter-8-2-140331204349-phpapp02/75/Inheritance-Polymorphism-2-7-2048.jpg)
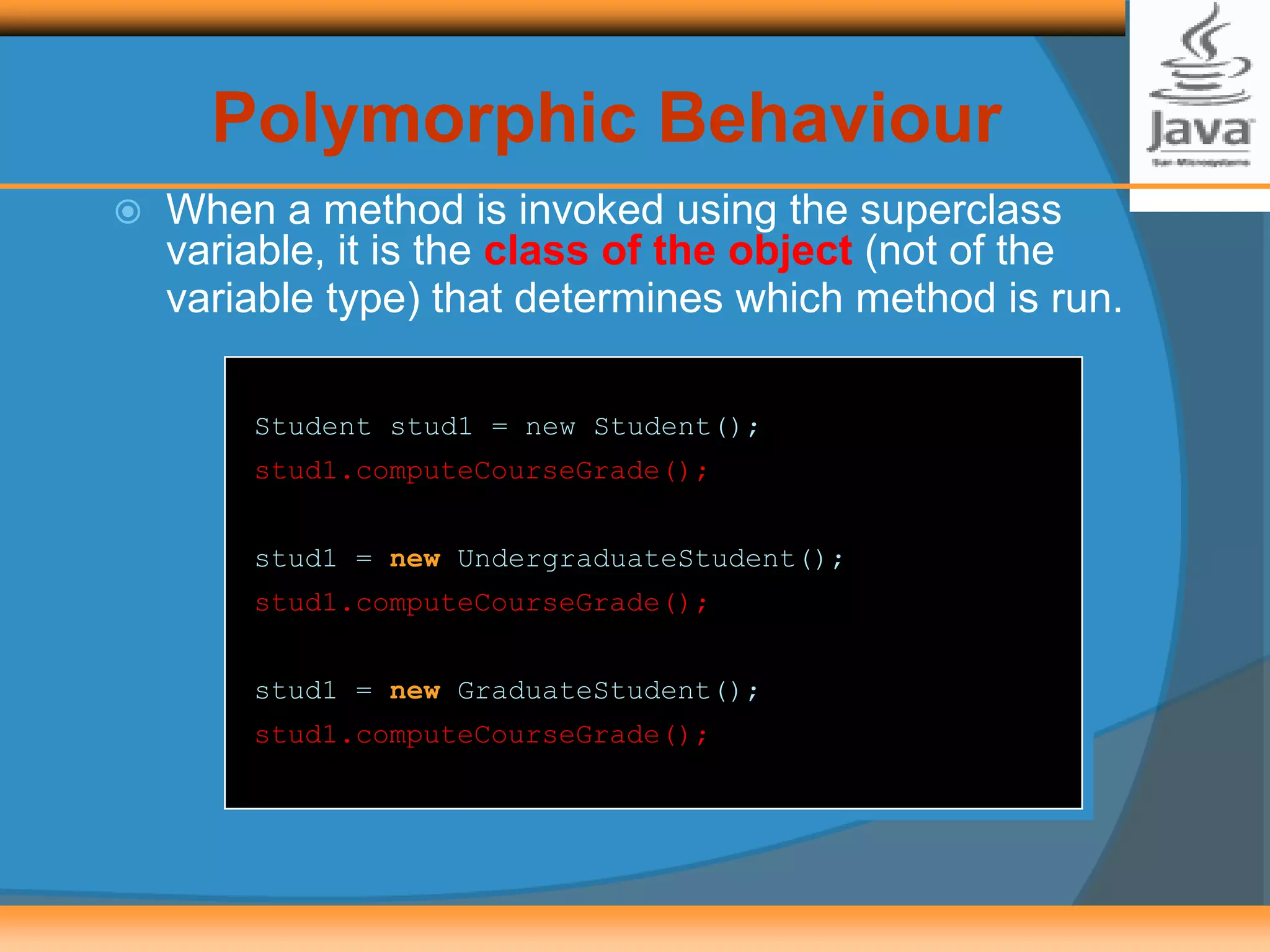
![Sample Polymorphic Message
To compute the course grade using the roster array, we execute
If roster[i] refers to a GraduateStudent, then the computeCourseGrade
method of the GraduateStudent class is executed.
If roster[i] refers to an UndergraduateStudent, then the
computeCourseGrade method of the UndergraduateStudent class is
executed.
for (int i = 0; i < numberOfStudents; i++) {
roster[i].computeCourseGrade();
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter-8-2-140331204349-phpapp02/75/Inheritance-Polymorphism-2-9-2048.jpg)
![The instanceof Operator
The instanceof operator can help us learn the class of
an object.
The following code counts the number of undergraduate
students.
int undergradCount = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < numberOfStudents; i++) {
if ( roster[i] instanceof UndergraduateStudent ) {
undergradCount++;
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter-8-2-140331204349-phpapp02/75/Inheritance-Polymorphism-2-10-2048.jpg)







![CardTester Program
public class CardTester {
public static void main ( String[] args ) {
String name;
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print(“Your name please>");
name = input.nextLine();
Card myCard = new AidulFitri( me, 1429 );
myCard.greeting();
myCard = new BirthdayCard( me, 35 );
myCard.greeting();
}
}
- Demonstrate abstract class and polymorphism](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter-8-2-140331204349-phpapp02/75/Inheritance-Polymorphism-2-22-2048.jpg)