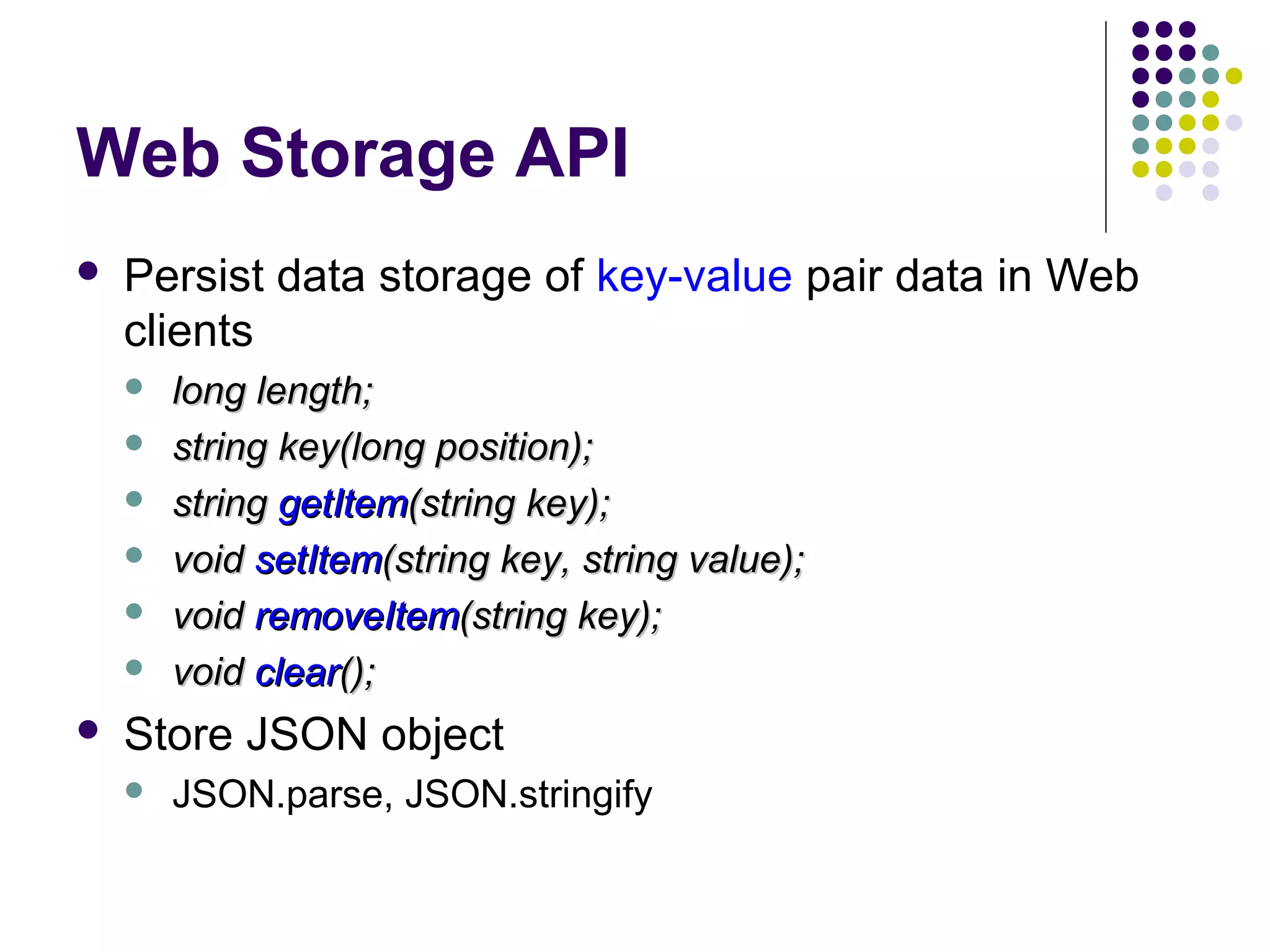
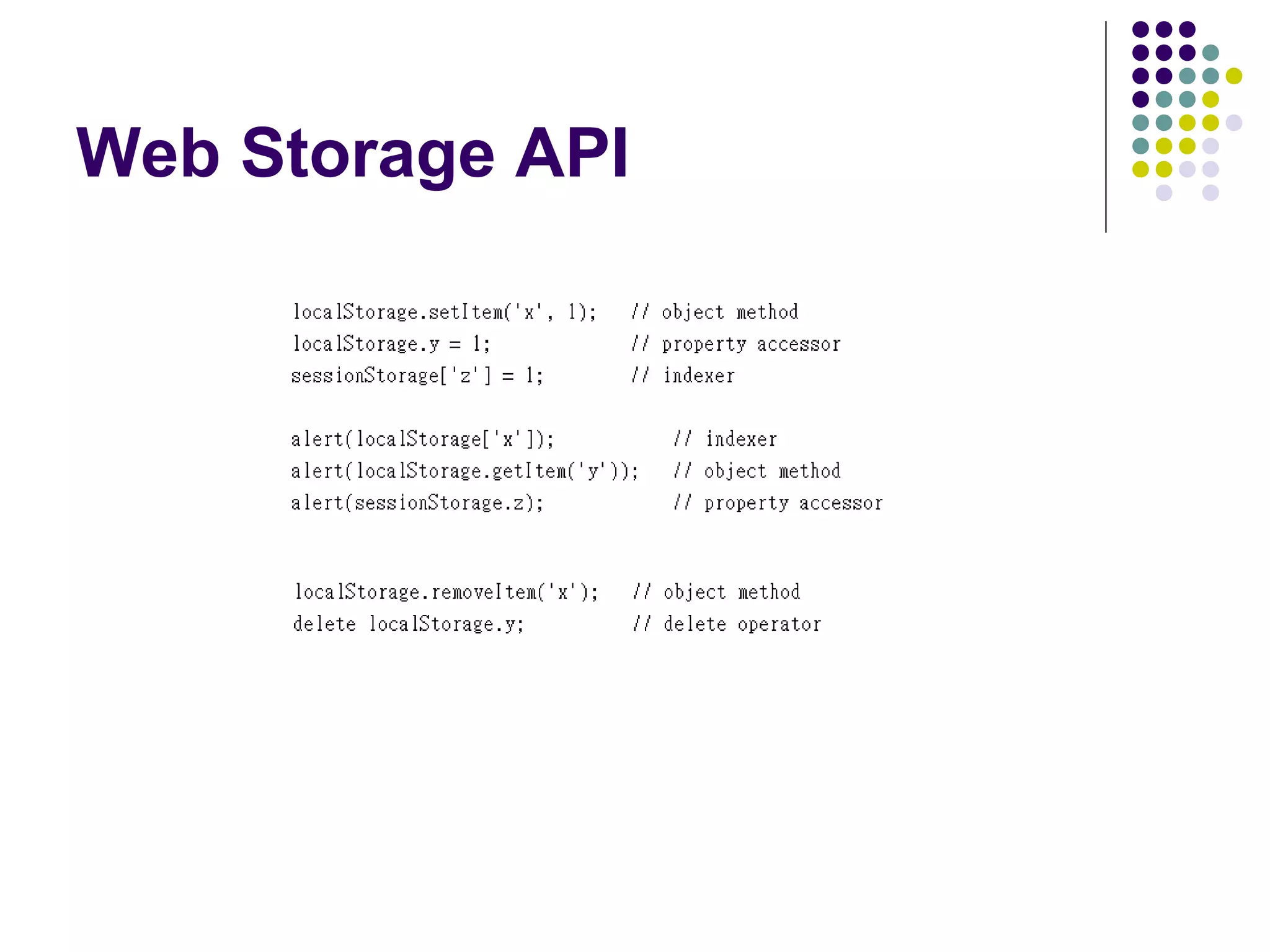
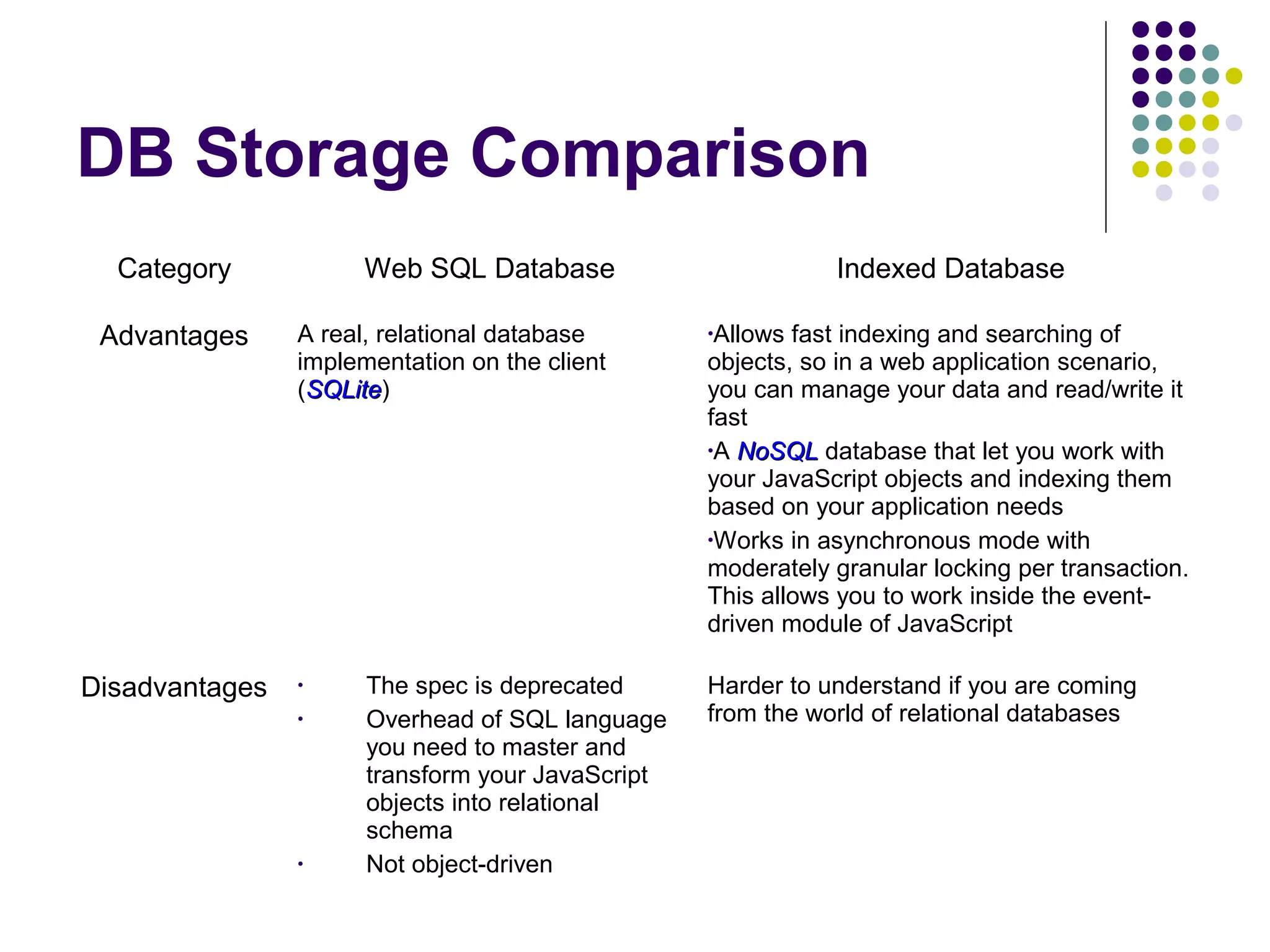
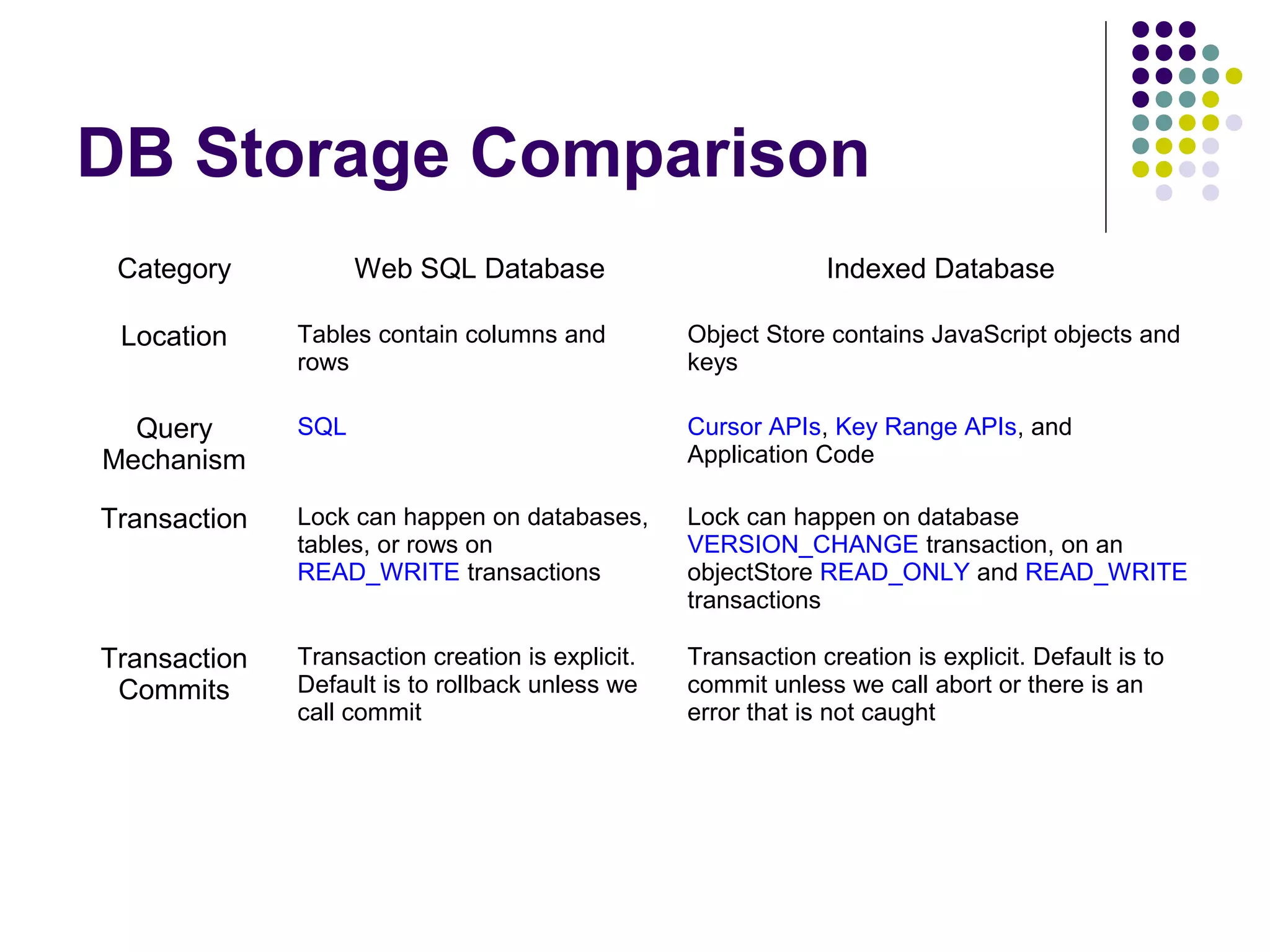
This document discusses various options for data storage in the browser. It begins by covering cookies, which have limitations in terms of size and speed. Web storage, including sessionStorage and localStorage, allows for more data to be stored client-side and accessed asynchronously without involving the server. The document then covers Web SQL Database and Indexed Database, which provide more robust storage and querying of data through SQL and NoSQL approaches, respectively. It analyzes the advantages and disadvantages of each approach and considers their browser support and performance characteristics for different use cases.