The document provides a comprehensive guide on using Stormpath with Angular.js for user management, authentication, and authorization in single-page applications (SPAs). It details the implementation of JSON Web Tokens (JWTs) for secure authentication, the architecture setup for both server and client-side integration, and various strategies for securing cookies. Additionally, it emphasizes the advantages of Stormpath in handling user features and offers links to documentation and examples for developers.











![Client-Side: Add the SDK Dependencies
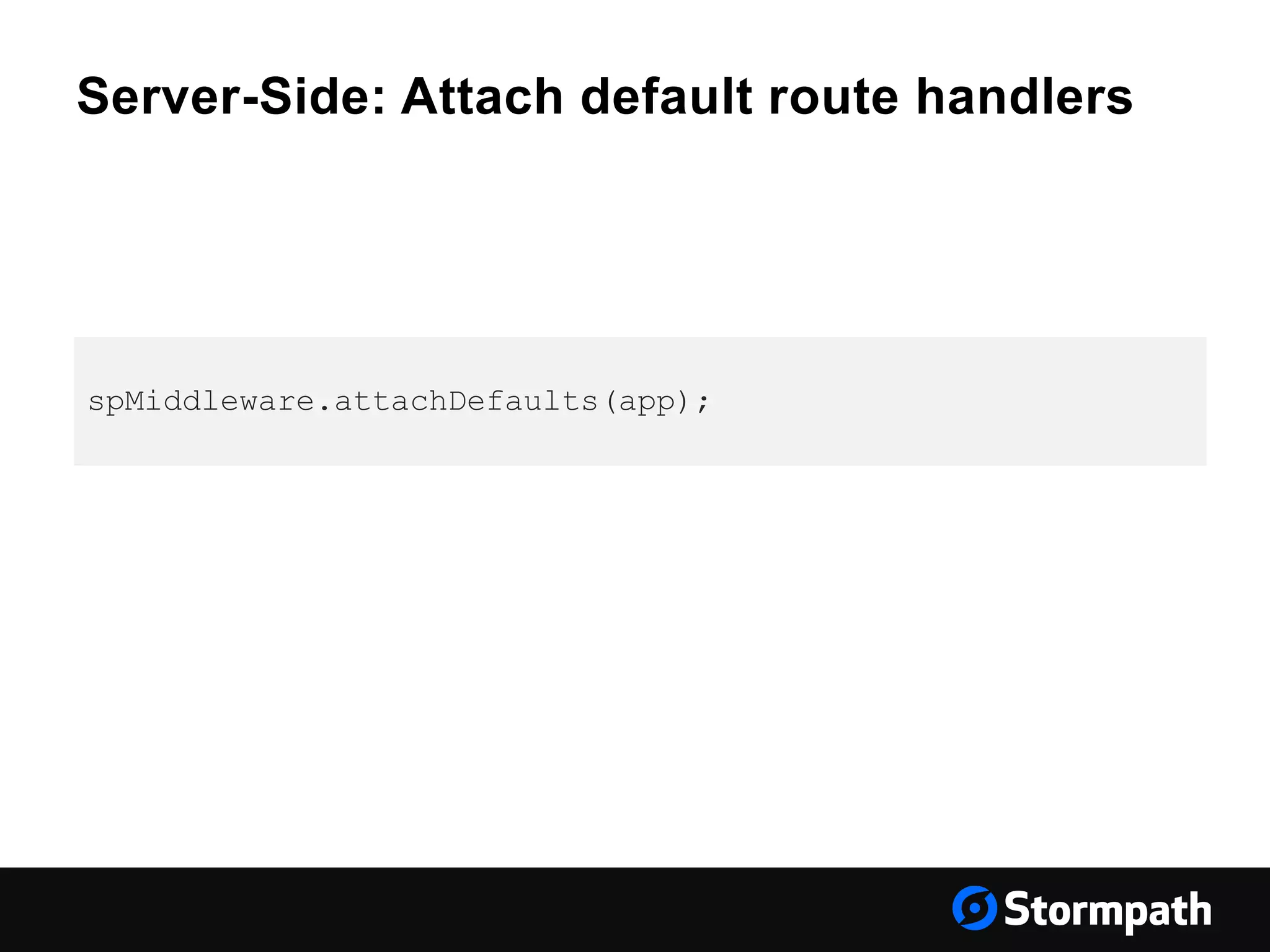
Stormpath, Angular & Your Architecture
angular.module('MyApplication', [
'ngCookies',
'ngResource',
'ngSanitize',
'ui.router',
'stormpath',
'stormpath.templates'
])](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/howtousestormpathinangularjs-150707185518-lva1-app6892/75/How-to-Use-Stormpath-in-angular-js-21-2048.jpg)