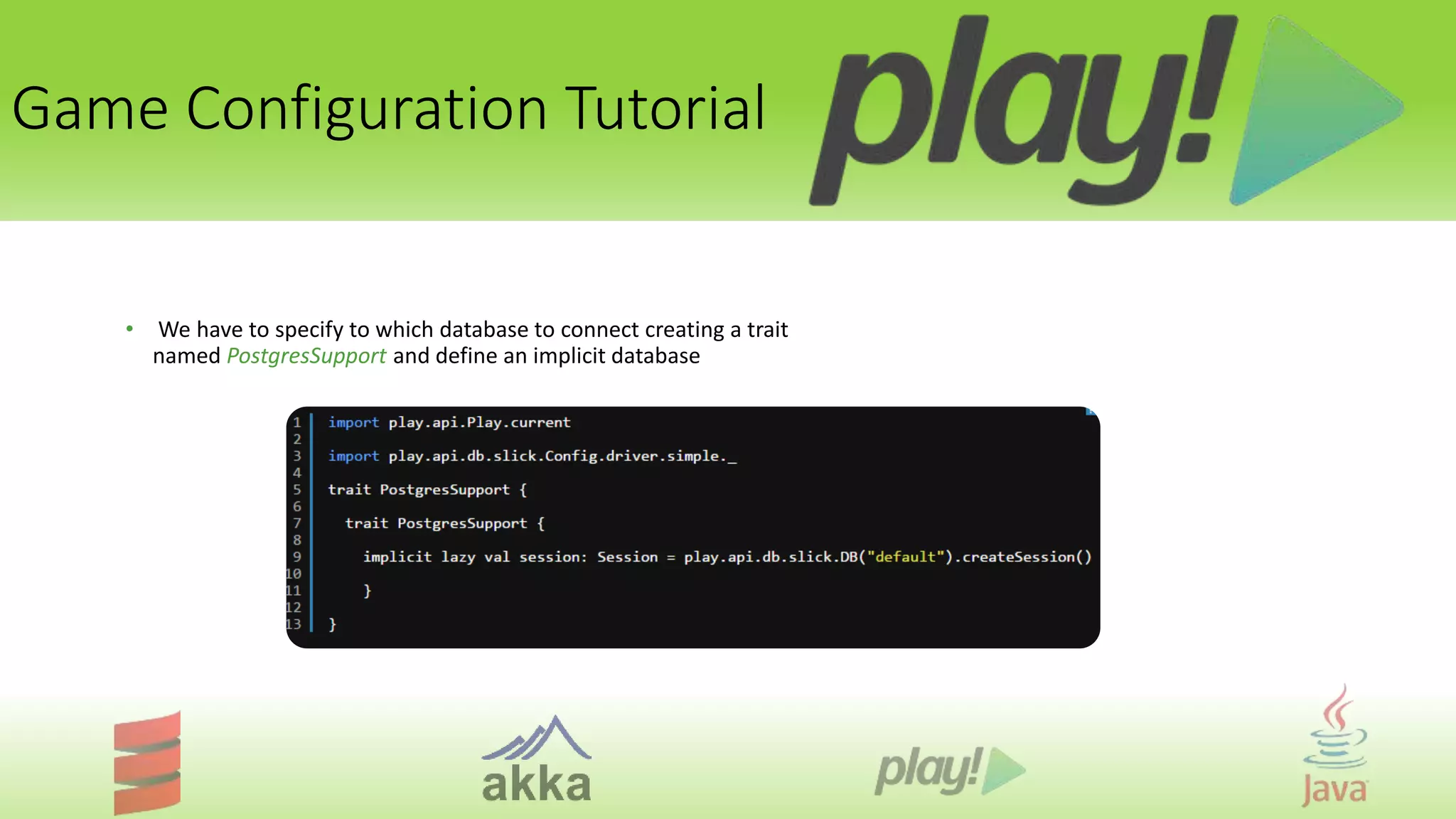
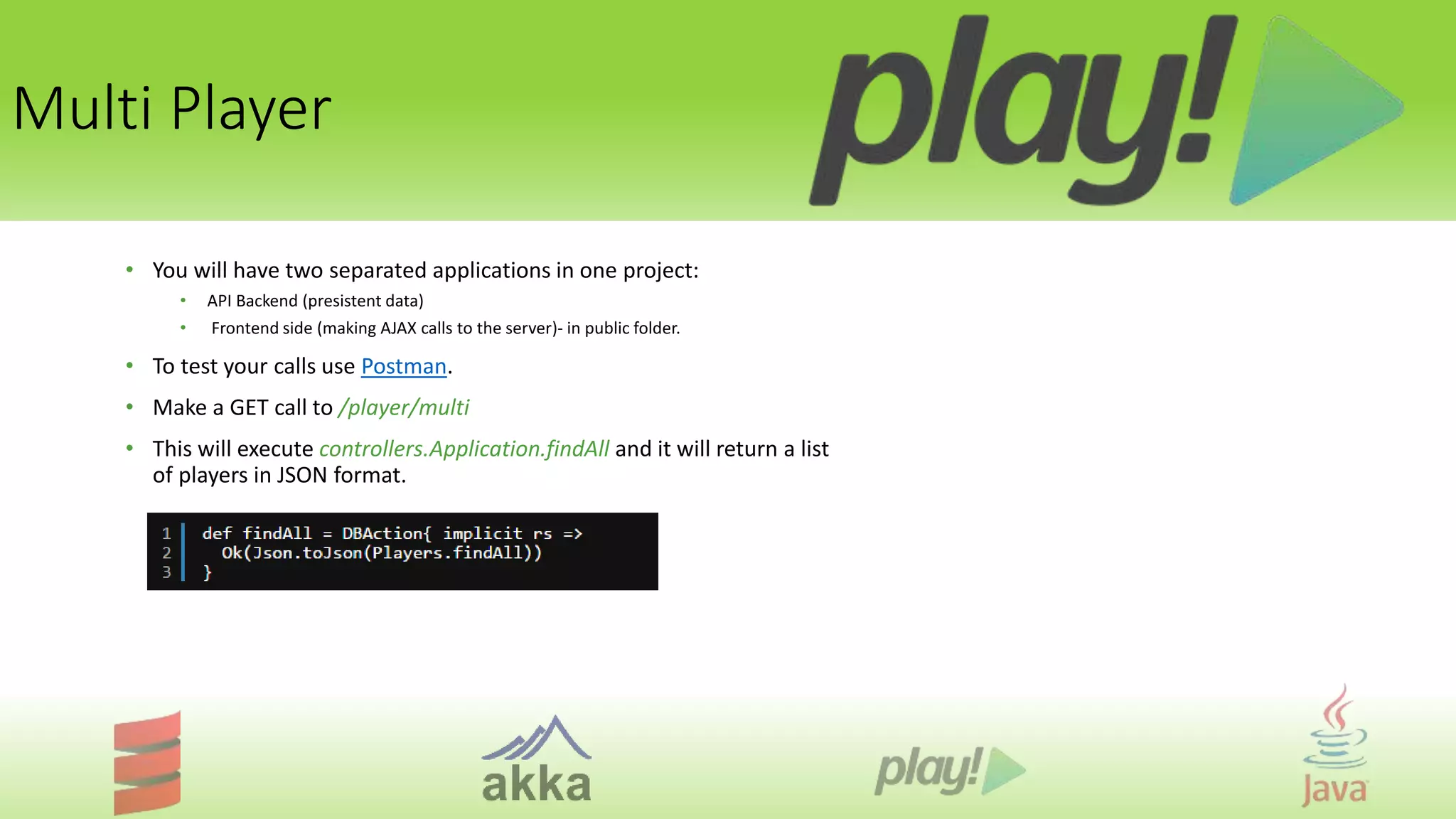
The document is a comprehensive tutorial on the Play Framework, an open-source web framework designed for building modern applications with a focus on simplicity and resource efficiency. It covers system requirements, game play tutorials, game configuration, and available features, detailing how to create and manage a Play application, including database interactions and multi-player functionalities. Additionally, it highlights essential plugins and modules for enhancing authentication, authorization, and performance within applications.